OB lecture - basic ultrasound protocols
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What position is the patient in for a transvaginal exam?
Dorsal Lithotomy position
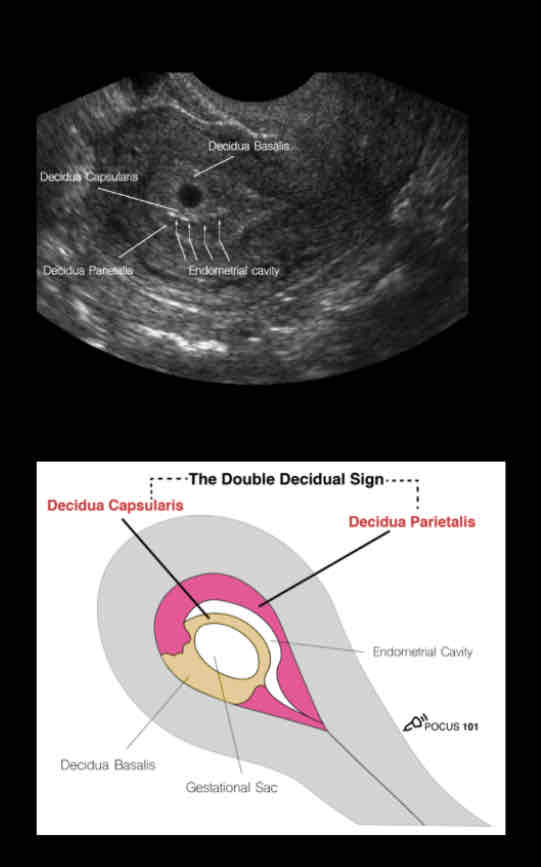
• Anechoic (dark)
• Round structure with an echogenic
(bright) border.
• Typically, it is in the upper 1/3 of the
uterine fundus.
• Make sure the sac is in the uterus by
tracking the vaginal stripe to the uterus.
true GS
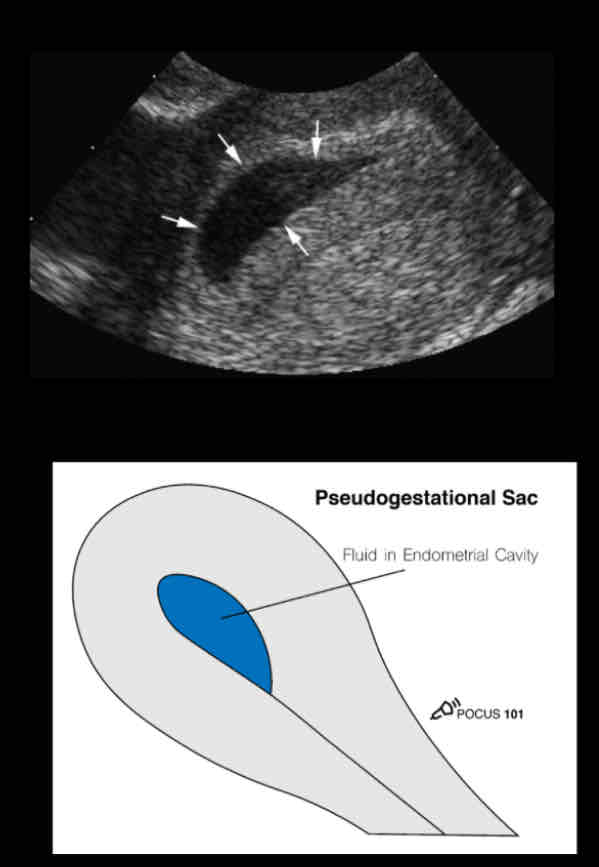
• more irregularly shaped
• Pointy-edged than a round gestational
sac.
• Border surrounding the sac is not as
echogenic
• The fluid is not completely anechoic,
there are some echoes seen in the fluid.
• A pseudo-gestational sac will not have
the contents of a maturing gestational
sac such as the yolk sac and embryo.
pseudo GS
What is the first trimester checklist?
• Look for signs of an IUP
• Gestational dating (Mean sac diameter, Crown rump length)
• Measure fetal heart rate
• Locate the fetal pole
• Optimize depth
• Turn on M-mode
• Place caliper over beating heart
• Measure and calculate heart rate
Prior to the appearance of a fetal pole, what can be used to estimate the gestational age?
the mean sac diameter
What are the equations for finding the mean sac diameter?
MSD (in mm) + 30 = Gestational age (in days)
MSD = (length + height + width) / 3
Once a fetal pole is present, what should be used to estimate the gestational age as it is the most accurate method of dating the pregnancy?
the crown-rump length
What is the crown-rump length?
the measurement between the top of the
head and the bottom of the torso
What is the equation for the crown-rump length?
CRL (in mm) + 42 = Gestational age (in days)
Fetal cardiac activity should be seen at a
crown rump length (CRL) of…
5-7mm
What is is the preferred way to measure fetal
cardiac activity over pulsed wave doppler
because it subjects the fetus to lower
ultrasound energy?
M-mode
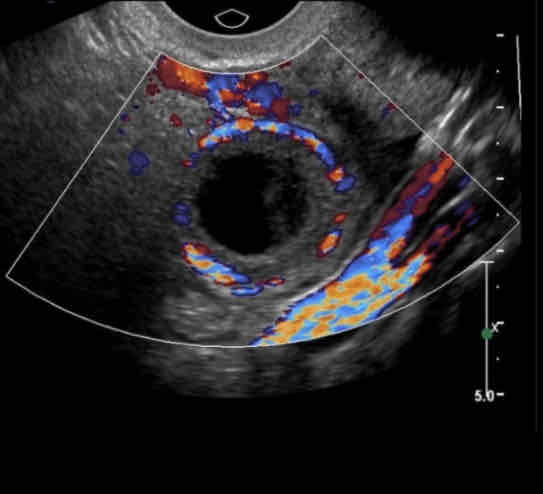
May find yolk sac or fetal pole. Will move independent of the ovary in response to transducer manipulation
Tubal ring is more echogenic
Tubal ring is thicker
Cystic fluid is more likely to be “clumpy” or have some echoes
May have ring of fire sign
Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy
Will move with the ovary in response to transducer manipulation
Tubal ring is less echogenic
Tubal ring is thinner
Cystic fluid is more likely to be clear and anechoic
May have ring of fire sign
Corpus Luteal Cyst
What does the picture show?
Corpus Luteal Cyst
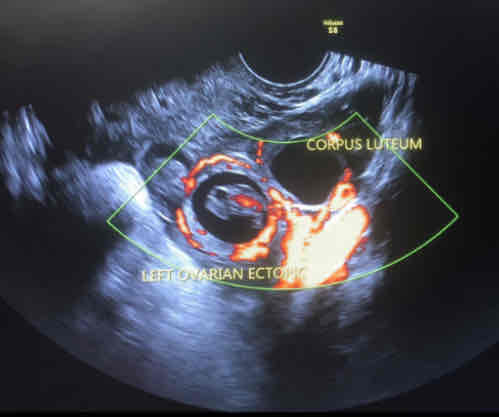
What does the picture show?
ectopic and corpus luteal
abnormal vaginal bleeding during a viable pregnancy
threaten miscarriage
vaginal bleeding with a dilated cervix while still retaining all products of conception
inevitable miscarriage
some products of conception have been retained
incomplete miscarriage
all products of conception have been expelled and bleeding has stopped
complete miscarriage
the fetus is non-viable but no products of conception has been passed
missed miscarriage
What encompasses disorders that begin at fertilization and involve abnormal proliferation of the trophoblasts that in a normal?
gestational trophoblastic disease
What is the most common forms of gestational trophoblastic disease known as?
molar pregnancies
• No fetal/embryonic tissue
• Abnormally elevated B-hCG levels: >100,000 mIU/mL
• abnormal oocyte with no nucleus, and therefore no maternal chromosomes
• paternal chromosomes are present
• trophoblasts proliferate and form swollen, “grape-like” villi or vesicles
Complete hydatidiform mole
• May contain fetal structures
• Normal B-hCG levels
• When an apparently normal oocyte is fertilized by sperm that
duplicates itself or, rarely, by two spermatozoa.
• triploid pregnancy with 69 chromosomes.
Partial hydatidiform mole
• Appear on ultrasound as a “snowstorm” inside the uterus
• The contents of the uterus are complex and heterogeneous and often contain many small cystic structures
• In addition, there may be theca-lutein cysts in the ovaries
molar pregnancy, aka hydatidiform mole
What are theca-lutein cysts?
thin-walled cystic structures (these are more common in 2nd-trimester complete moles)
What is the 2nd/3rd trimester checklist?
• Measure fetal heart rate
• Assess fetal lie and presentation
• Measure amniotic fluid volume (MVP)
• Fetal biometrics
• BPD, HC, AC, Femur length
• Evaluate placenta
We can still use M-mode to measure fetal heart rate. What steps described to calculate the fetal heart rate?
• Acquire a 4-chamber view of the fetal heart. This view can be found by scanning through the fetus in a transverse plane.
• Optimize the magnification and gain so that the fetal heart takes up the majority of the screen.
• The left atrium will be closest to the spine.
• The axis of the heart will be pointing to the left of the fetus.
• Use the calipers to measure the length of 1 (or 2 depending on the machine) cardiac cycle(s). The fetal heart rate should be calculated by the machine.
What is the fetal presentation in the picture?
Cephalic Presentation — Headfirst
What is the fetal presentation in the picture?
Shoulder Presentation — Shoulder/Arm first
This presentation will show a transverse (short axis) or oblique cross-section of the fetus in a mid- sagittal view of the uterus.
What is the fetal presentation in the picture?
Breech Presentation — Buttocks/Feet first
What refers to the relative orientation of the fetal and maternal spines and can either be longitudinal, oblique, or transverse?
Fetal lie
To determine the fetal lie, acquire a _____ view of the fetal spine and compare it to the maternal spine
mid-sagittal
The maternal and fetal spines are parallel (can be breech or cephalic presentations)
Longitudinal Lie
The fetal spine is at an oblique angle to the maternal spine
Oblique Lie
The maternal and fetal spines are perpendicular
Transverse Lie
What functions as a cushion for the fetus, helps protect it from infection, and promotes muscle, lung, and digestive system development?
Amniotic fluid
What refers to having too much amniotic fluid- associated with fetal malformations, developmental delay, and neurologic disorders
Polyhydramnios
What refers to having too little-associated with increased perinatal morbidity and mortality?
Oligohydramnios
Amniotic fluid volume can be assessed with ultrasound by measuring the
maximum vertical pocket of amniotic fluid MVP or SDP. What are the measurements?
• Oligohydramnios: <2 cm
• Normal: 2-8 cm
• Polyhydramnios: >8 cm
How to measure the MVP (maximum vertical pocket)?
• Scan the amniotic sac from left to right in a sagittal view.
• Estimate a location that has the deepest vertical pocket and measure it with the calipers.
• The caliper line must be in a vertical orientation.
• The caliper line must be free of any fetal parts or the umbilical cord.
In the 2nd and 3rd trimester, various measurements of the fetus, known as ___________, can be used to estimate the weight and gestational age.
fetal biometrics
What are measured in fetal biometrics?
• BPD - biparietal diameter
• AC
• HC - head circumference
• FL
The BPD can be measured routinely from when?
12 weeks’ gestation and occasionally earlier
What should you not see when you get a transverse view of the fetal head and at the level of the thalami?
You should not see the cerebral hemispheres
What is the arrow pointing to in this image?
cavum septi pellucidi (CSP)
What is the arrow pointing to in this image?
columns of fornix
What is the image of?
when you don’t see the calvarium
How to get head circumference?
• Use the same view that you acquired for the biparietal diameter measurement.
• Activate the head circumference (HC) measurement package on the OB/GYN preset.
• Trace the head circumference.
• If an ellipse tool is not available on your machine, measure the long axis diameter (OFD) of the head.
• The machine should calculate the head circumference from the BPD and OFD.
true/false: Head circumference is affected by head shape
false, head circumference is not affected by head shape
What is an index or ratio which is used to evaluate the shape of the head
cephalic index
how is cephalic index calculated?
It is calculated by measuring the maximum width (BPD) of the cranium
divided by its maximum length (occipital frontal diameter, OFD).
CI =BPD/OFD x 100
What is a normal cephalic index (CI)?
70%-86%
when the AP diameter is longer than the transverse diameter
Dolicocephaly
What does the following describe?
• CI is <70% (> 2 SD).
• may be seen in several conditions, including oligohydrmnios and multiple gestations.
dolichocephalic head
when the transverse diameter is greater than the AP (anterior posterior) diameter and the CI is > 86% (> 2 SD).
Brachycephaly
What may be seen in several conditions including synostosis, trisomy 21, and hydrocephalus?
brachycephalic head
What are the 3 views of the head?
transventricular view
transthalamic view
transcerebellar view
What view does the following describe?
• The lateral ventricles are paired C- shaped structures comprising a body and atrium
• 3 projections into the frontal, temporal, and occipital lobes, termed “horns.”
• The lateral ventricles communicate with the third ventricle through the
interventricular foramina of Monro.
• Each lateral ventricle has an estimated capacity of 7–10 mL
transventricular view
A fetal ultrasound can measure the widest part of the lateral ventricle to diagnose ventriculomegaly, which is when the ventricles are enlarged. What are the measurements?
• Mild: 10–12 mm
• Moderate: 13–15 mm
• Severe: Greater than 15 mm
The normal lateral ventricle size at 20 weeks of gestation is less than _____________ in width.
10 millimeters (mm)
What view allows visualization of the cerebellum and cisterna magna (posterior fossa)?
transcerebellar view
What is size in transcerebellar view?
Size is approx. age of the fetus up to 30 weeks
What does the following describe?
• fluid filled space
• 2-10 mm normal size
cisterna magna
What does the following describe?
• prenatal ultrasound measurement that assesses the risk of Down syndrome and other genetic problems in an unborn baby
• A normal measurement is less than 6 mm
nuchal fold thickness
what is abnormal cerebellar plane?
chiari 2 malformation
How should you take the abdominal circumference measurement?
The AC measurement should be taken at the skin line on a true transverse view at the level of the junction of the umbilical vein, portal sinus, and fetal stomach.
What should you see with abdominal circumference?
• At this location, the liver size is reflected.
• The visualized ribs should be symmetrical.
• The abdomen should not be compressed during image acquisition.
What is plane 11?
upper abdomen - stomach
What is plane 12?
umbilical cord insertion - ultrasound features
What is a valuable indicator of fetal growth because it reflects the development of abdominal organs such as the liver and spleen?
abdominal circumference (AC)
What describes the folllowing?
abnormal cord insertion
cord inters into apex of defect
contains liver +/- bowel etc
membrane covered
prenatal detection rate - 80%
abnormal karyotyoe - 50%
trisomy 18
abdominal wall defects - omphalocele
1-6:10,000 live births
young mothers
normal karyotype
majority isolated
oligohydramnios
10-15% late IUFD
normal cord insertion
defect below & to right of cord insertion
contains bowel only
free floating
“Cluster of grapes”
abdominal wall defects - gastroschisis
diahragmatic hernia
esophageal atresia
absent or persistently small
small bowel obstruction
pyloric stenosis
duodenal atresia
jejunal atresia
polyhydramnios gastrointestinal obstruction
When measuring the femur length what should not be included?
The cartilage at the ends of the femur should not be included in the measurement.
Only the __________ should be measured between the epiphysis, which represents the portion of the long bone formed by the primary ossification center.
diaphysis
Placenta previa: Placental edge _______, or covering, internal os from 16 weeks
<2.0 cm
What amniotic fluid assessment is used in twins?
use DVP not AFI