6th cranial nerve
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
where is the 6th nerve nucleus located?
pons
describe the course of the 6th nerve
under 4th ventricle in caudal pons.
→ Fibers pass thru pons.
→ Pass thru corticospinal tract.
→ Exit midbrain & enter brainstem at pontomedullary junction.
→ Subarachnoid Space:
Runs upward between pons & clivus.
→ Pierces dura mater:
Runs between dura & skull in Dorello’s canal.
→ Enters cavernous sinus:
→ Enters orbit via Superior Orbital Fissure:
Supplies (LR).
nucleus in the pons, traverses brainstem and leaves to enter the subarachnoid space, makes a vertical ascent over the petrous apex bone over the clivus, enters cavernous sinus
what are 2 important anatomical features found on the 6th nerves journey?
cavernous sinus
subarachnoid space
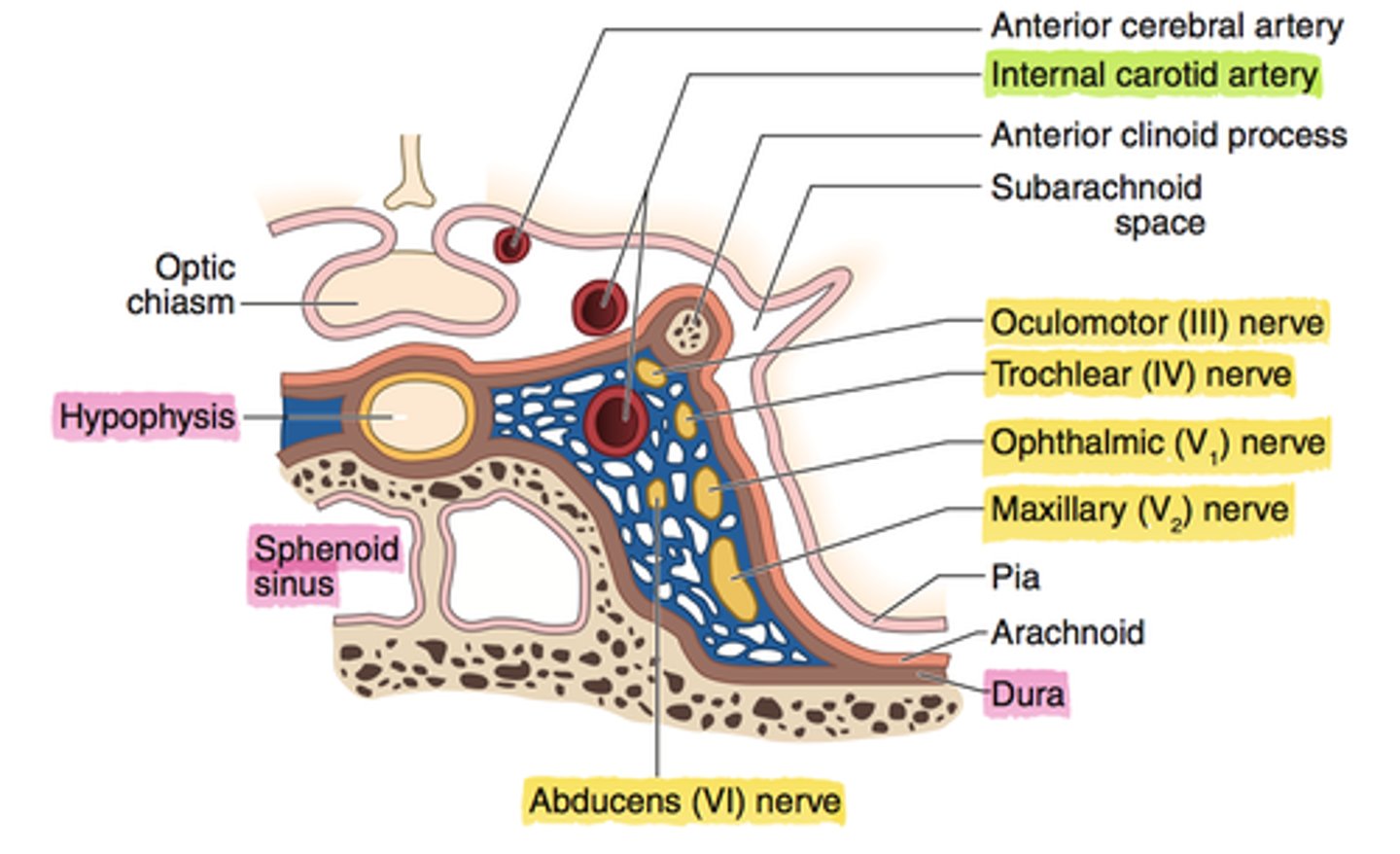
why is cavernous sinus an important anatomic feature for the 6th nerve?
it is adjacent to and wraps around the internal carotid artery - any issues affecting the ICA affect the 6th
briefly joined by oculosympathetic fibres responsible for pupil dilation, issues in this area can cause pupil abnormalities where pupil cant dilate
medial to 5th nerve (trigeminal) V1
possible aetiologies that can affect the 6th nerve?
aneurysm
tumour
trauma
increased intra cranial pressure
anrold-chiari malformation
what is an arnold-chiari malformation?
herniated cerebellum pushes down and pulls tissue along the spinal cord
causes displacement of structures in the brainstem
causing direct effect onto 6th nerve
how does increased intracranial pressure cause a 6th?
6th is stretched and tethered
could be due to mass
can cause a non-localising sign/false localising sign
what is a false localising sign
↑ICP - chiari malformation
6th presses down on sharp petrous apex- due to long course form brainstem & passage thru CS, affecting its function
= false localizing sign - presents as 6th but aetiology elsewhere in brain not along the course of 6th
↑ ICP stretch 6th nerve - tethered at Dorello’s canal = 6th NP horizontal diplopia &esotropia
The lesion causing raised ICP may be remote, such as:
Tumors in the posterior fossa.
Hydrocephalus.
Pseudotumor cerebri.
what is Gradenigo's syndrome?
can occur as a complication following middle ear infection
localised inflammation of petrous apex bone involves the 6th, causing pressure on it
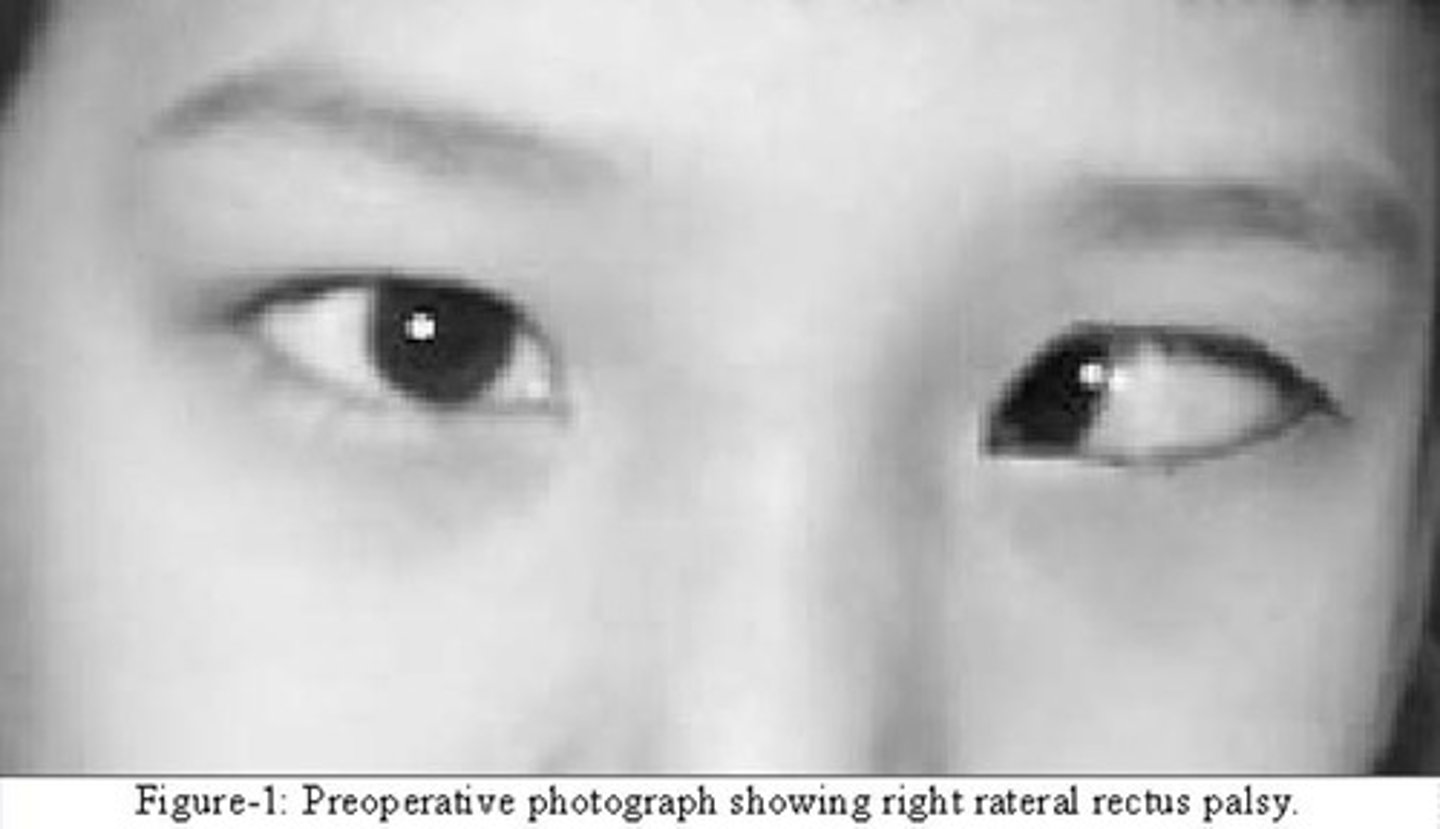
symptoms of Gradenigos syndrome?
reduced hearing, facial palsy
what is pseudo Gradenigo's
presents in a similr way to Gradenigos
nasopharyngeal carcinoma
how can a petrous bone fracture cause a 6th?
closed head injury damages the 6th
list aetiologies within the CAVENOUS SINUS causing a 6th
vascular lesion e.g. ICA aneurysm
thrombosis, tumour e.g. pituitary, meningioma, infection
Inflammation, ischaemia, trauma - skull fracture
Carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF)
where are the cranial nerves positioned in the cavernous sinus
which way will the diplopia be?
horizontal
would diplopia be worse at N or D
worse at D, may be phoric at near
which position of gaze would diplopia be worst at?
lateral gaze e.g. left LR 6th CNP, looks worse looking left
what is the general health like in someone with a 6th CNP?
vascular problems tend to occur in those 50+
what would the CHP be like in a 6th nerve palsy
face turn to the affected side e.g. right 6th CNP, turn to the right, eyes move to the left
what kind of deviation would they have for N and D?
D: esotropia
N: phoria
or bigger D>N
pathway
Origin: Beneath floor of 4th ventricle in caudal pons.
→ Fibers course ventrally and caudally through pons.
→ Pass through corticospinal tract.
→ Exit midbrain: Emerges on ventral surface of brainstem at pontomedullary junction.
→ Subarachnoid Space:
Runs upward between pons & clivus
→ Pierces dura mater:
Runs between dura & skull in Dorello’s canal.
→ Enters cavernous sinus:
Adjacent to internal carotid artery.
→ Enters orbit via Superior Orbital Fissure:
Supplies (LR).