Atmospheres test
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
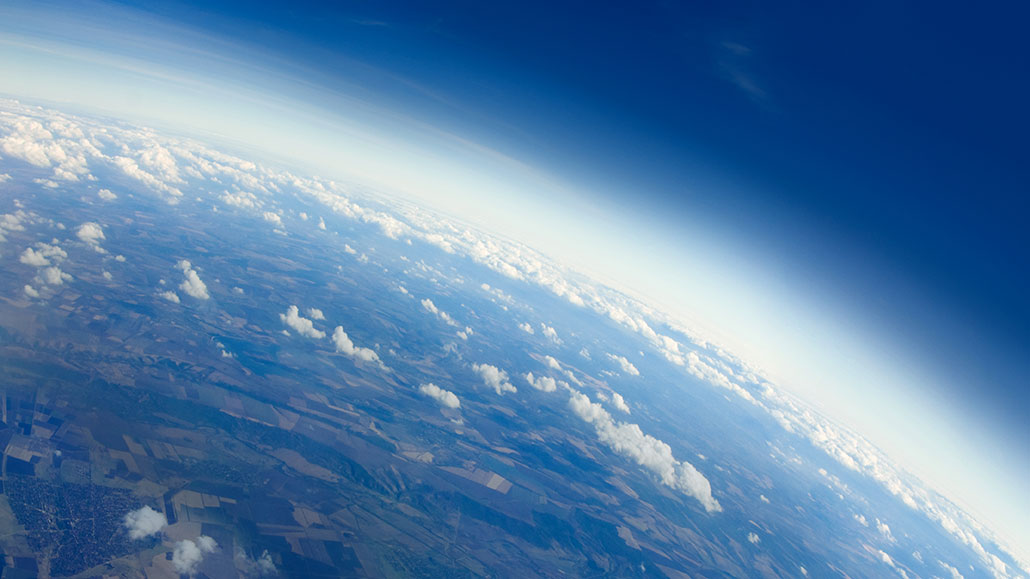

Define the atmosphere:
The atmosphere is a layer of gases that surrounds Earth. It consists mostly of nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. It also has a variable amount of water vapour, usually around 2 - 3%. Methane can also be found.
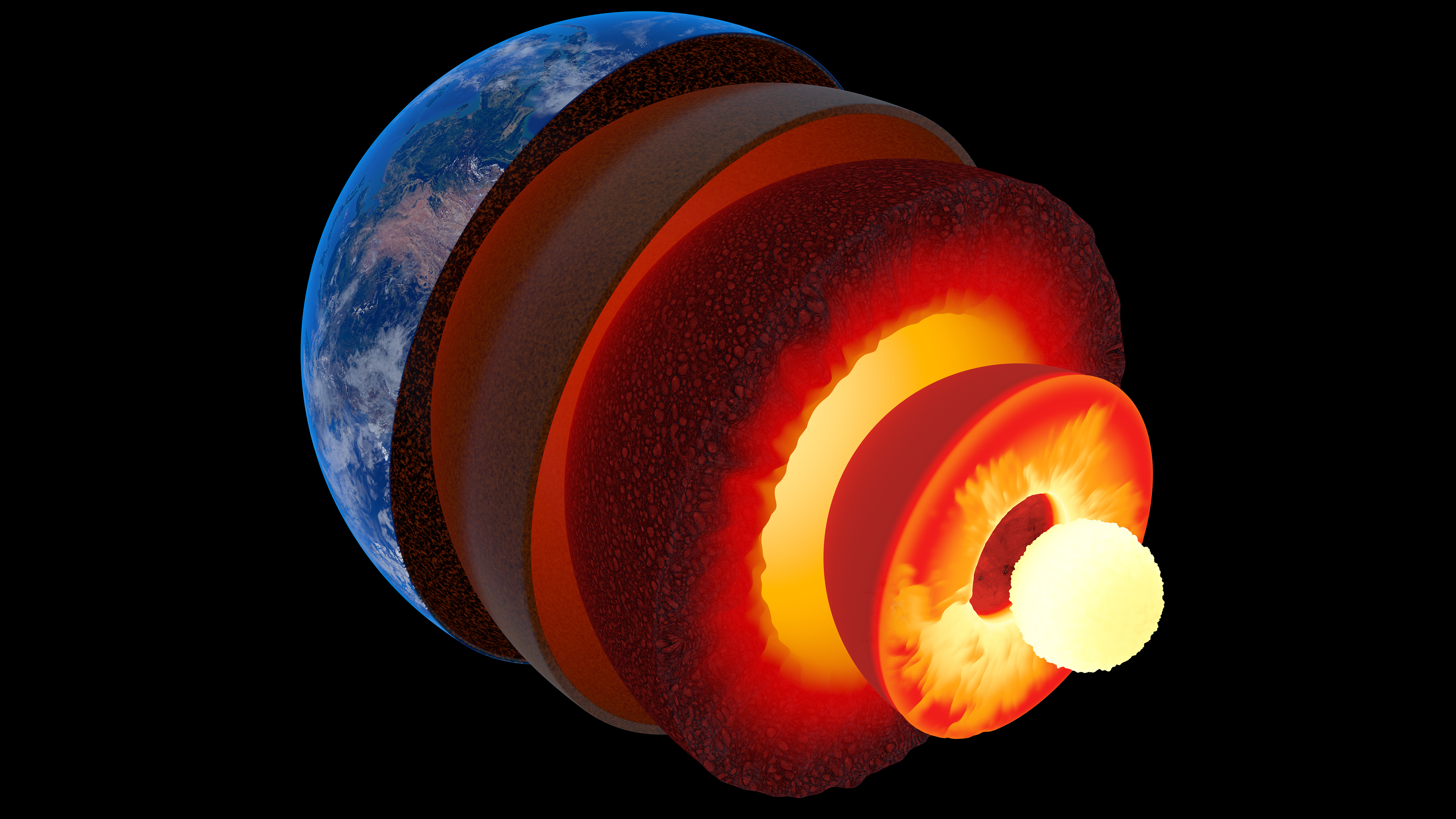

Define the lithospere:
The lithosphere is the outermost rocky layer of the Earth, consisting of the mantle and crust. It contains the continents and is made up of basalt and granite. Fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas can also be found.
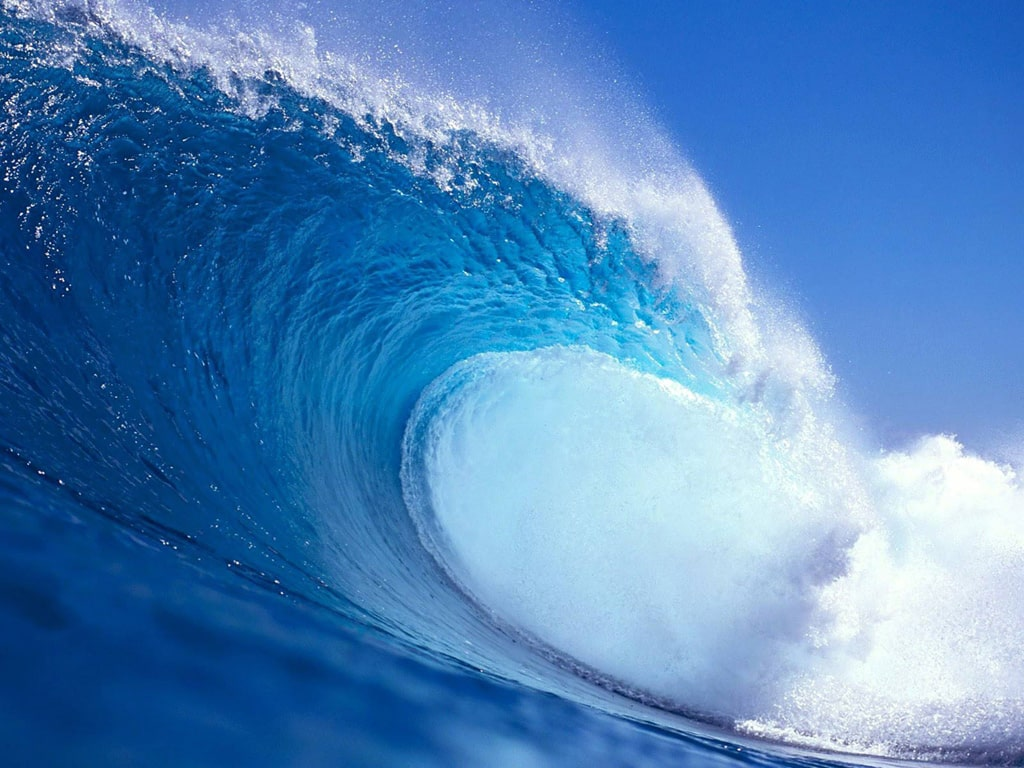

Define the Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere is all the liquid and frozen water on Earth. This including oceans, lakes, rivers. Dissolved CO2 can be found in water.
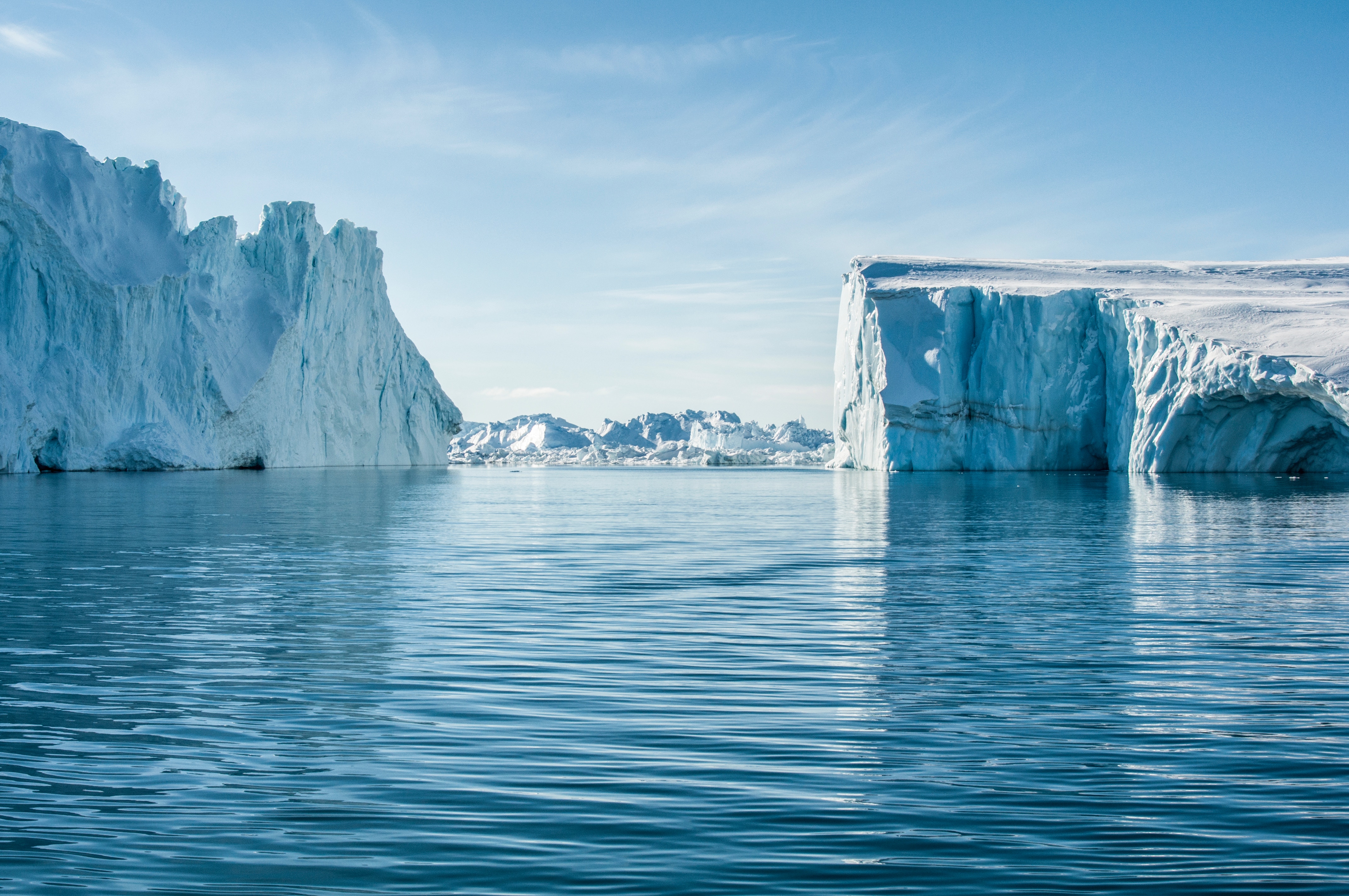

Define the cryosphere
The cryosphere is the frozen part of the hydrosphere. includes sea ice, glaciers and ice caps.

Define the biosphere
The biosphere is made up of all living things on Earth, including plants, animals and bacteria. There is a great interdependence between different parts of the living world.

Why are the earth’s spheres balanced?
The Earth's spheres stay balanced because they constantly exchange materials like gases, water, minerals, and nutrients.

What would happen if the Earth’s spheres were unbalanced?
If Earth's spheres were unbalanced, materials like gases, water, minerals & nutrients would fall out of sync. That could trigger pollution, ecosystem collapse, or sudden climate shifts.
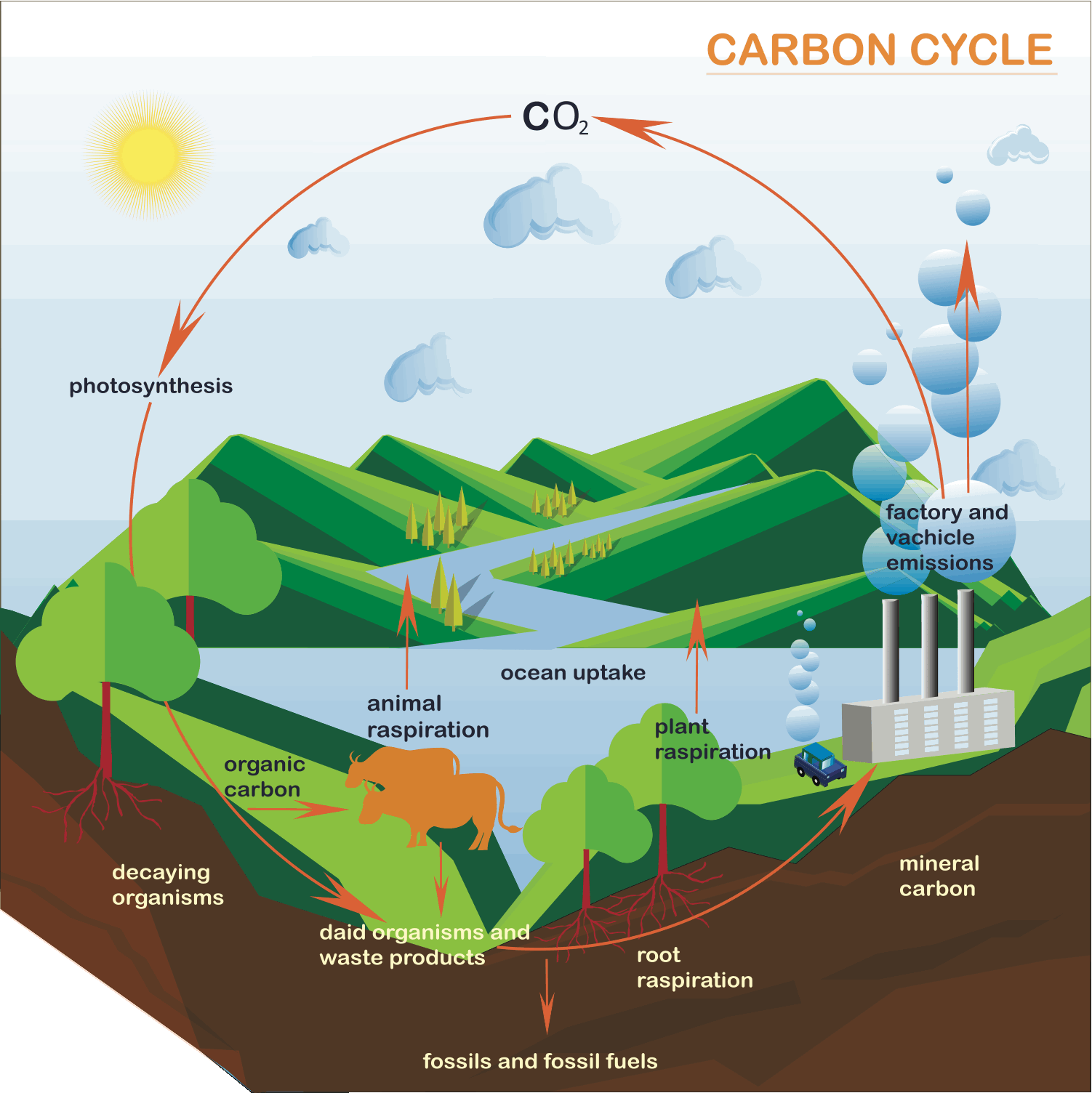

Define the carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the process where carbon circulates through Earth's spheres; the biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and and atmosphere.

Describe the two types of carbon.
Organic carbon: found in plants, animals and soil
Inorganic carbon: e.g. CO2 found in water and atmosphere, or carbon in minerals and rocks.
Provide an example of carbon stored in each of Earth's spheres.
Lithosphere – Carbon stored in fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
Atmosphere – Carbon stored as carbon dioxide gas.
Hydrosphere – Carbon dissolved in oceans as carbon dioxide or carbonate.
Biosphere – Carbon stored in trees and plants as biomass.
List and briefly describe the 5 processes that cycle carbon.
Combustion
Combustion is the process where a fuel reacts with oxygen, releasing energy whilst producing carbon dioxide and water.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process in which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugars (like glucose).
Respiration
Respiration is the process where living organisms convert organic carbon compounds into carbon dioxide, releasing energy for their life processes.
Decomposition
Decomposition is the process where dead organic matter is broken down into simpler substances, releasing carbon back into the atmosphere.
Carbon Ocean exchange
Carbon ocean exchange is the process where carbon dioxide moves between the atmosphere and the ocean’s surface. Warm water releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere whilst cool water absorbs it.
Which processes add carbon into the atmosphere?
Respiration
Decomposition
Combustion
Warm ocean surfaces
Which processes remove carbon from the atmosphere?
Photosynthesis
Cool ocean surface
*practice carbon cycle model
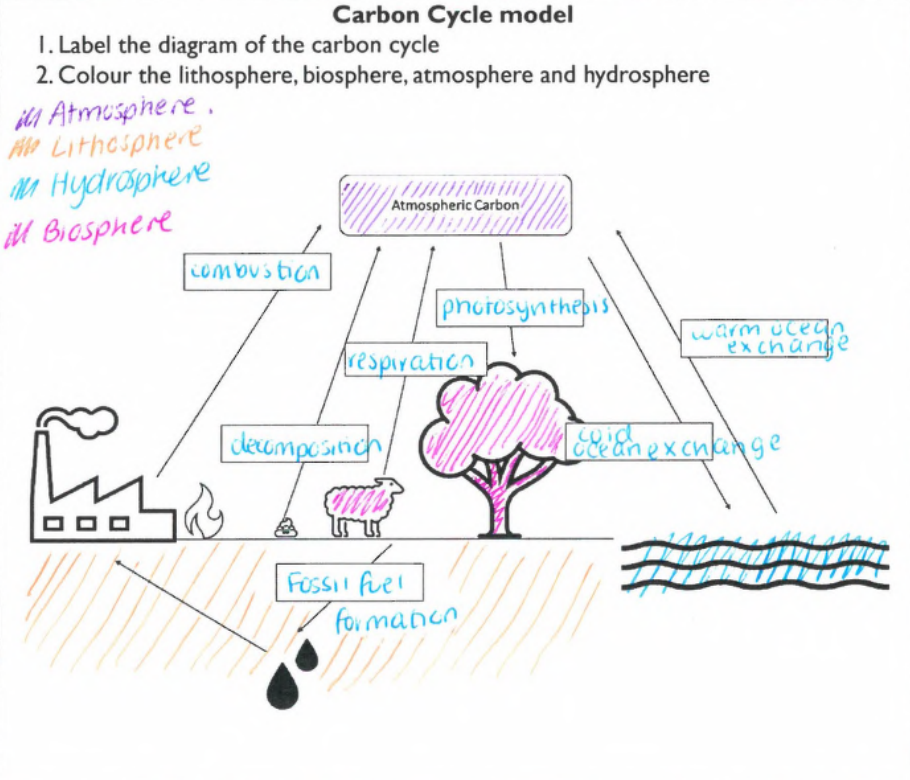
Explain what will happen to each sphere when the carbon cycle becomes unbalanced.
Atmosphere - increased carbon dioxide which traps more heat, leading to climate change and extreme weather
Biosphere - The temperature will increase, harming ecosystems and food chains eventually leading to extinction events
Hydrosphere - Acidification, warming and rising sea levels
Lithosphere - less carbon stored in sinks, acceleration soil degradation, erosion and nutrient loss.
Define the term carbon sink
A long term store of carbon dioxide form the atmosphere. includes forests, ocean, fossil fuels.
Describe the greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse effect is natural process in which the sun emits short wave radiation that passes straight through the atmosphere and trap heat, warming the earths surface while some of that heat is radiated back out as infrared radiation.
Identify three examples of the greenhouse gases.
Examples of greenhouse gasses include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide.
What are some positive effects of the greenhouse effect on Earth?
Supporting life: The moderate temperatures created by the greenhouse effect allows for the existence of liquid water which is crucial for all know life forms.
Agricultural benefits: in some regions, a longer growing season due to a slightly warmer climate can be beneficial for agriculture, allowing for more crop production
Reduced winter morality: in regions with harsh winters, a slightly warmer climate can lead to fewer deaths from extreme cold.
What is the enhanced greenhouse effect?
The enhanced greenhouse effect refers to the intensification of the natural greenhouse effect due to increased levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, primarily caused by human activities.
How are humans causing an enhanced greenhouse effect?
Humans are causing an enhanced greenhouse effect primarily through the emission of greenhouse gases, largely from burning fossil fuels, industrial processes, deforestation, leading to increased amounts of CO2 in the atmosphere.
What are the consequences of an enhanced greenhouse effect on Earth.
The consequences of an enhanced greenhouse effect include, rising global temperatures, extreme weather evens, sea level rise and ocean acidification,
*understand diagram of water cycle
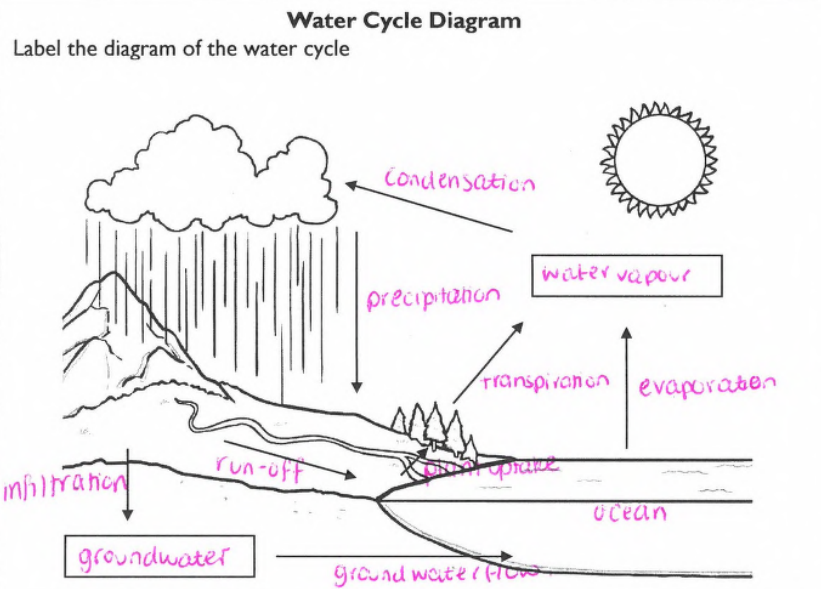
What are the water cycle processes:
Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, runoff, transpiration and infiltration.
Summarise Evaporation
Evaporation, in the water cycle, is where liquid water turns into gas or water vapour and rises into the atmosphere.
Define condensation.
In the water cycle, condensation is the process where water vapor in the atmosphere cools and changes back into liquid water, forming tiny water droplets or ice crystals.
Define precipitation
In the water cycle, precipitation is the process where water falls from the atmosphere to the Earth's surface. This includes rain, snow, sleet, and hail.
Define Run off
In the water cycle, runoff is the flow of water across the land surface. This excess water moves over the land, eventually entering streams, rivers, and other bodies of water.
Define transpiration.
Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapour into the air through small openings in their leaves.
Define Infiltration
Infiltration is the process where water on the ground surface soaks into soil.
Define plant uptake
The process by which plants absorb water and nutrients from the soil through their roots.
Describe how the water cycle is balanced
The water cycle is balanced through a dynamic exchange of water among the atmosphere, land, and oceans, where processes like evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff continuously redistribute water to maintain long-term stability across Earth's systems.
Describe 1 way that humans affect the water cycle and cause it to become unbalanced. What effect is had on each sphere.
One way humans affect the water cycle is deforestation.
How it impacts each sphere:
Atmosphere: With fewer trees, less water is released into the air through transpiration, reducing humidity and potentially changing local rainfall patterns.
Biosphere: Animals and plants lose their habitats, and some species may die off or migrate.
Hydrosphere: Reduced transpiration and changes in rainfall can lower river and lake levels, and increase surface runoff, leading to erosion and flooding.
Lithosphere: Increased runoff causes soil erosion, depleting nutrients and degrading land quality.
Describe how indigenous knowledge is being reaffirmed and contributing to western science
Indigenous knowledge is reaffirmed as Western science confirms Aboriginal oral histories, like the 37,000-year-old Budj Bim eruption. These stories accurately describe geological events such as lava flows and coastal formation. Archaeological and DNA evidence confirm the tribe’s long presence, showing oral traditions preserve reliable environmental records that contribute to modern science.
Define the relationship between indigenous fire burning practices and the use of carbon credits in Australia.
Indigenous cultural burning—early dry-season fires based on traditional knowledge—reduces the severity of late-season wildfires and cuts greenhouse gas emissions. The emissions saved are measured and turned into carbon credits under Australia’s ACCU Scheme. These credits, totaling about 1.2 million tonnes a year since 2012, provide income for Indigenous ranger programs, cultural renewal, and caring for the land. This links traditional practices with modern carbon markets, helping the environment and supporting Indigenous communities.
Define climate chagne
Climate change is a long-term change in the Earth’s temperature with massive and permanent ramifications
Describe one solution for the impacts of climate change.
One solution for climate change is planting more trees and increasing greenery across Australia. Trees absorb carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas, helping to reduce its levels in the atmosphere. Adding green spaces, rooftop gardens, and vertical gardens around urban areas can also cool cities, improve air quality, and support biodiversity. This natural approach helps fight climate change while making cities healthier and more resilient.