ECO 202 Chapter 13: Monopolistic Competition
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
monopolistic competition
many firms
no barriers to entry for new firms entering the industry
products are NOT identical to competitors
we expect MC to have zero long-run profit, but not face a horiztontal demand curve, face a downward-sloping demand curve
products sold by MC firms are differentiated from one another in some way
demand curve for MC
downward-sloping
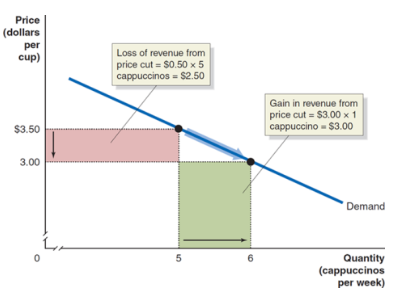
if a MCF raises their price, some but not all of its customers wills switch to buy the product elsewhere
total revenue increases initially and then decreases, so marginal revenue is initially positive, then negative
when a MCF reduces price, its revenue increases because the extra sales (output effect) BUT revenue also decreases because others were willing to pay the old price (price effect)
marginal revenue will always be lower than price (demand)
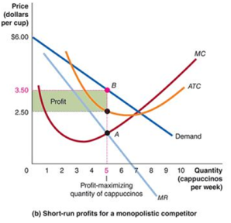
maximizing profit in the short run
produce until MC = MR
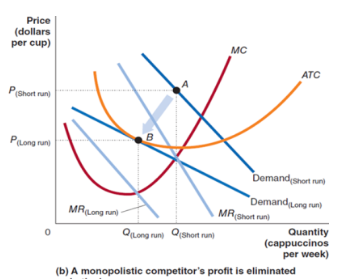
profits in the long run
when total revenue > total cost, firms make a profit, giving entrepreneurs incentive to enter the market
when new firms enter, demand decreases
demand becomes more elastic in the long run because cutomers have an easier time switching to competitors (so demand curve is flatter in the long run)
firm must break even, average total cost curve is tangent to demand curve
is zero economic profit inevitable
model predicts firms will earn no profit in the long run
BUT firms could innovate so their costs are lower or convince customers their product is better
demand will continue to fall to zero profit unless the firm is able to do something about it
efficiency in monopolistic competition
results in neither productive nor allocative efficiency
don’t produce at MC = MB (DC) so not allocatively efficient
average cost is above minimum point, so not productively efficient
has excess capacity: if it increased its output, the firm could produce at a lower average total cost
marketing
all the activities necessary for a firm to sell a product to a consumer
brand management
actions of a firm intended to maintain the differentiation of a product over time
effects of marketing on differentiation
effective advertising can increase demand and differentiate products, effectively making the demand curve more inelastic which allows firms to charge a higher price and earn more short run profit
it is critical to create a successful brand name to maintain differntiation and delay competition for profits
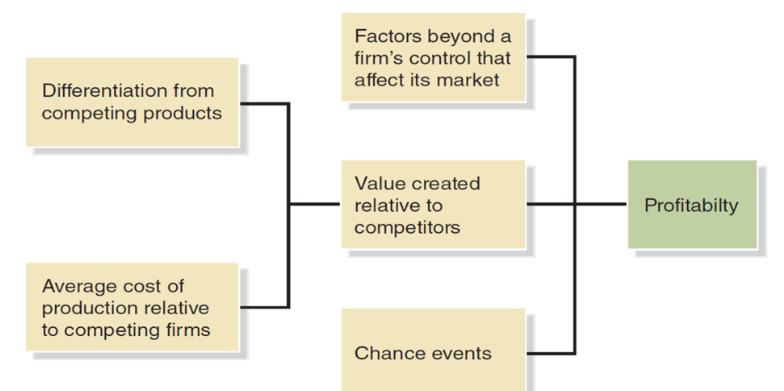
what makes a firm successful?
differentiation and production at lower costs creates value
value + chance events + factors affecting market beyond a firm’s control = profitability