Introduction to Arrays in Data Structures Cartes | Quizlet
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
Array
Organizes data in rows and columns.
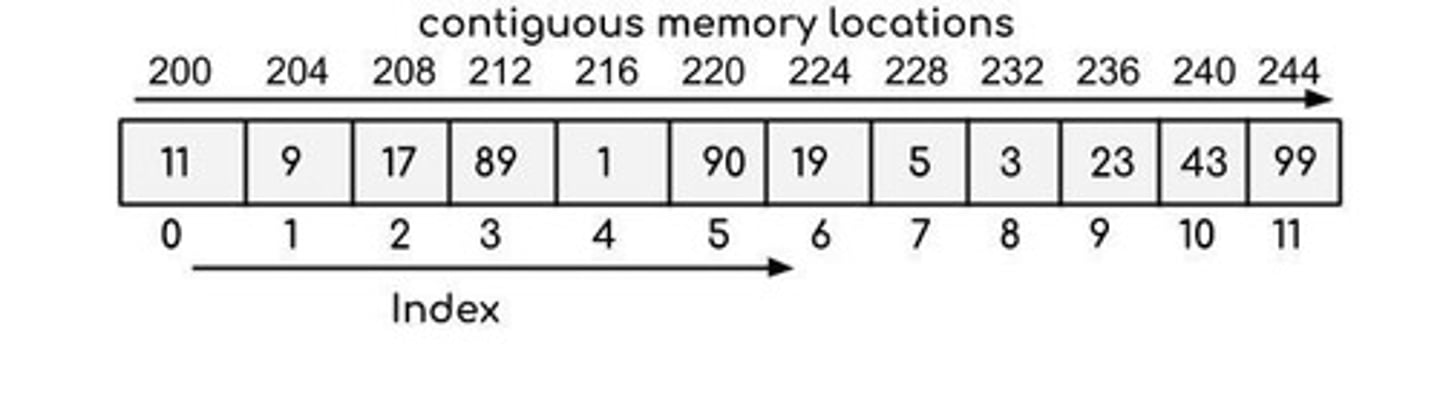
Contiguous Memory
Memory allocation in sequential, uninterrupted manner.
Declaration of Array
Syntax: dataType[] arrayName; Example: int[] numbers;
![<p>Syntax: dataType[] arrayName; Example: int[] numbers;</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4266be1b-357e-42e2-9e50-9bb5475e1e5f.jpg)
Initialization of Array
Assign values during declaration: dataType[] arrayName = {values};
Separate Declaration
Declare and initialize array in two steps.
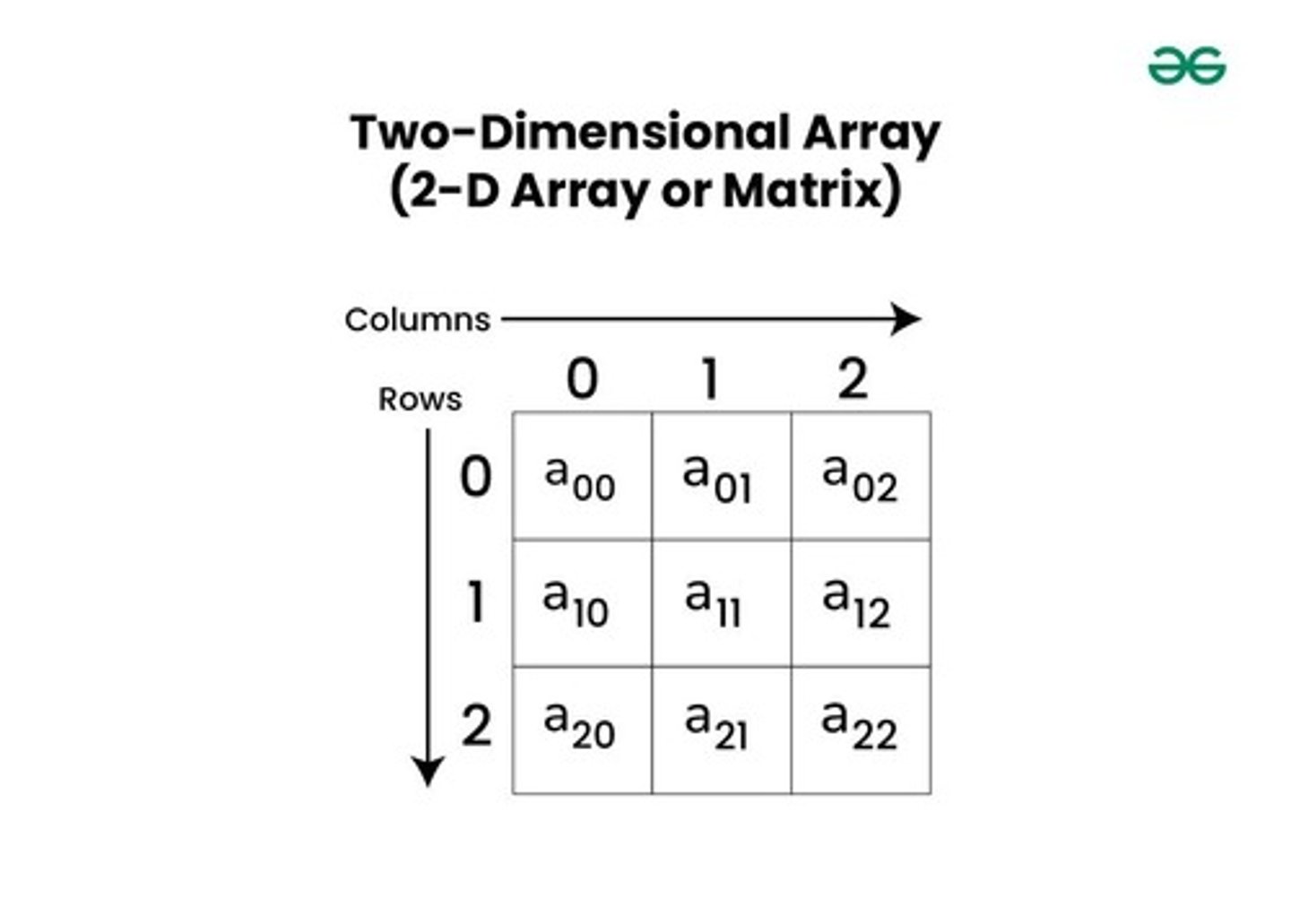
Multidimensional Array
Array with multiple dimensions; Example: int[][] arrayName.
![<p>Array with multiple dimensions; Example: int[][] arrayName.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7b2a62a9-62a5-4d48-885c-695fcc7d7173.jpg)
Array Memory Model
Visual representation of array elements and addresses.
Base Address
Starting memory address of an array.
Element Access Formula
Address of arr[i] = Base + (i × size).
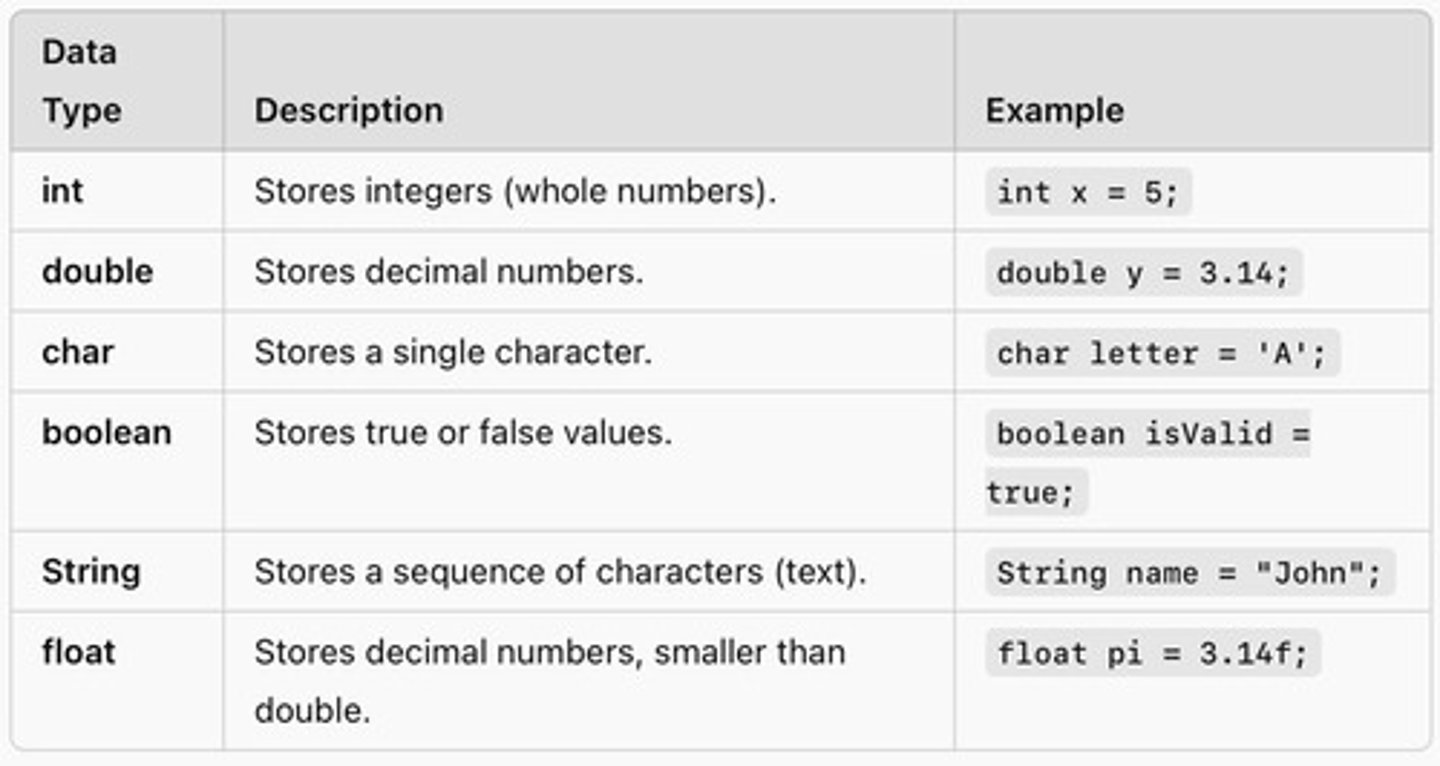
Data Type
Defines kind of data a variable can hold.
Dynamic Size
Array size can be determined at runtime.
Memory Allocation
Reserves memory for array in program's heap.
Traversal
Accessing each element in an array sequentially.
Search Operation
Finding a specific element within an array.
Manipulation
Modifying elements within an array.
IntelliJ IDEA
IDE used for writing and debugging Java programs.
One-Dimensional Array
Single row or column of data.
Two-Dimensional Array
Data organized in rows and columns.
Java Array Syntax
Defines how to declare and initialize arrays.
Array of Integers
Example: int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30};
Array Size
Number of elements an array can hold.
Element Size
Memory space occupied by each array element.
Array Operations
Manipulations performed on arrays in programming.
Searching for Elements
Finding a specific value in an array.
Sorting Arrays
Arranging elements in a specified order.
Accessing Elements
Retrieving values from an array using an index.
Updating Elements
Changing the value of an array element.
Array Traversal
Iterating through each element in an array.
Right-sized Array
Array with a fixed number of elements.
Variable-sized Array
Array that can change size dynamically.
For Loop Structure
Control flow statement for repeated execution.
Initialization
Setting up loop variable before iteration.
Condition
Expression evaluated to continue loop execution.
Update
Modification of loop variable after each iteration.
Passing Array as Parameter
Sending an array to a method for processing.
Returning Integer from Method
Method that calculates and returns an integer value.
Returning Void from Method
Method that performs actions without returning a value.
Returning an Array
Method that processes and returns an array.
String to Character Array
Conversion of a string into an array of characters.
Palindrome
Word or phrase that reads the same backward.
Reversing a Char Array
Changing the order of characters in an array.
Multidimensional Arrays
Arrays with multiple dimensions for grid-like data.
Example of Array Access
Accessing an element using its index in an array.
Example of Array Sorting
Using Arrays.sort() to arrange array elements.
reverse function
Reverses a string using character swapping.
char array
Array storing characters of a string.
2D Array
Array with two dimensions for grid data.
3D Array
Array with three dimensions for volumetric data.
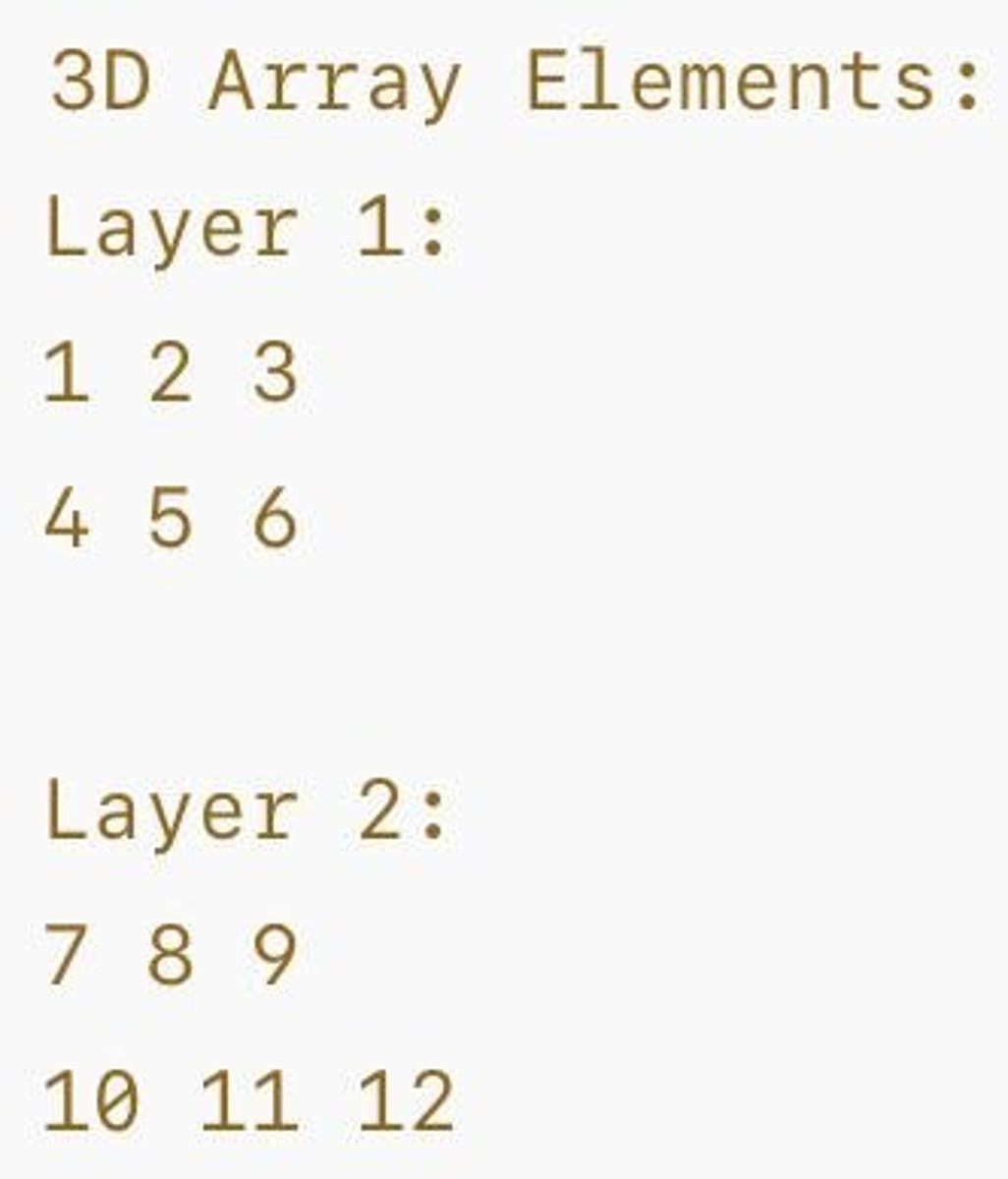
Array Declaration
Define array type and dimensions.
int[][] a
Declares a 2D integer array.
Accessing Elements
Retrieve value using row and column indices.
matrix[1][2]
Accesses element at 2nd row, 3rd column.
Modifying Elements
Change value at specified row and column.
Finding Length
Use array.length for rows, array[row].length for columns.
Traversing 2D Array
Iterate using nested loops for access.
Row-Major Order
Access elements row by row in loops.
Summing Elements
Use nested loops to calculate total.
Transposing Array
Switch rows with columns in a matrix.
Transpose Logic
Rows become columns and vice versa.
Arrays of Arrays
Array containing other arrays as elements.
Jagged Arrays
Rows of different lengths in an array.
Heap Memory
Dynamic memory allocation for array elements.
Example Matrix
int[][] matrix = {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9}}.
System.out.println()
Prints output to the console.
Nested Loops
Loops within loops for multi-dimensional access.
char c
Variable to temporarily store character during swap.
Inner Array
An array contained within another array.
Array of Arrays
A structure where arrays are nested within arrays.
Jagged Array
An array with inner arrays of different lengths.
Non-Uniform Row Sizes
Inner arrays can vary in length.
Array Initialization
Defining an array's structure and size.
Element Access
Retrieving specific elements using indices.
Array Traversal
Iterating through all elements in an array.
Row Slice
Extracting a specific row from a 2D array.
Immutable Original Array
Original array remains unchanged after slicing.
Subset of Elements
A selection of specific elements from an array.
Java Syntax for Jagged Array
int[][] jaggedArray = new int[3][];
Filling Jagged Array
Assigning values to different sized inner arrays.
Output of Jagged Array
Displays values from each inner array.
2D Array
An array with two dimensions, rows and columns.
Array Length
Number of elements in an array.
Java Arrays
Data structures for storing multiple values.
Nested Loop
Looping through each element of inner arrays.
Arrays.toString()
Method to convert array to string representation.
Memory Efficiency
Saves memory by using varying inner array sizes.
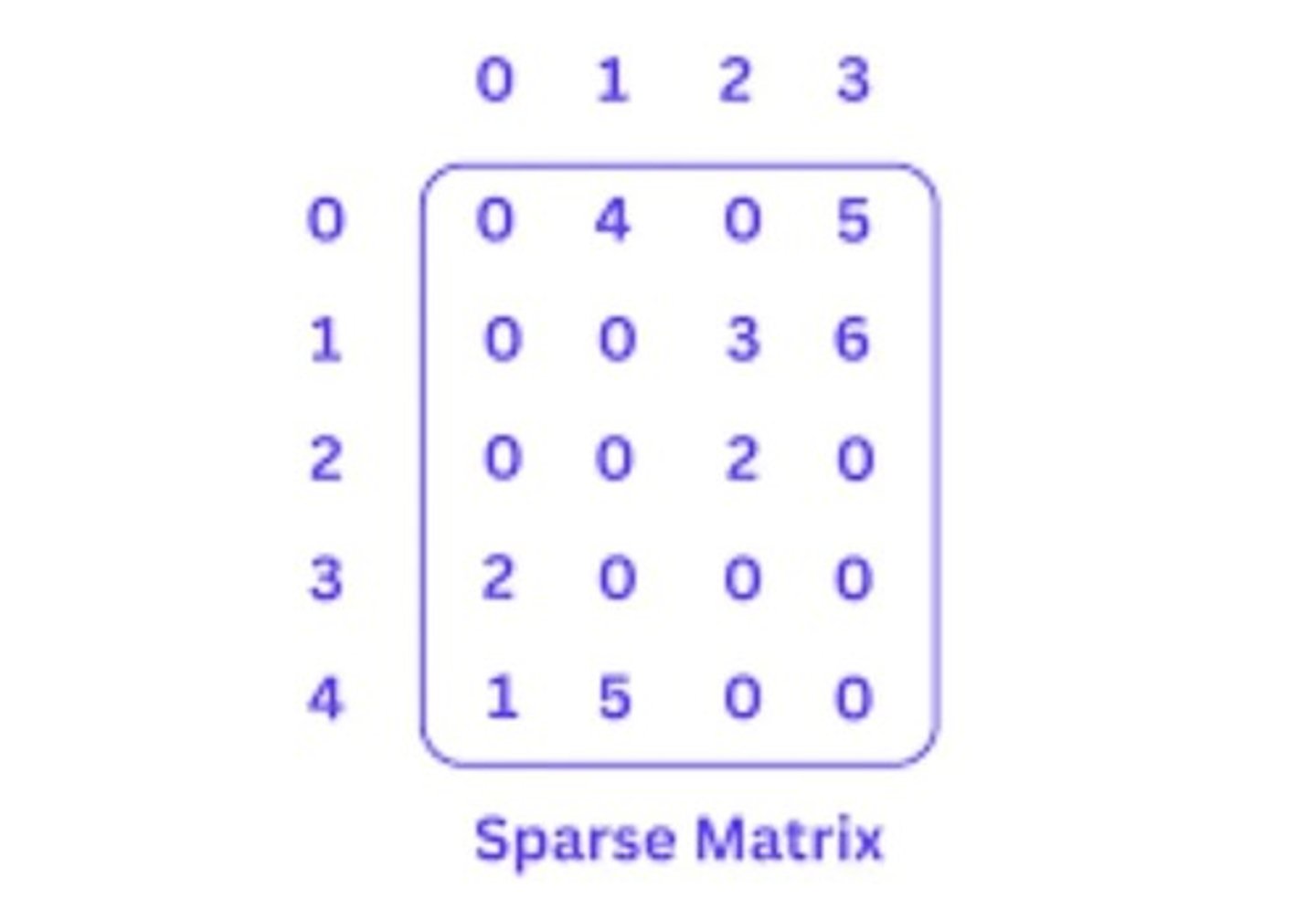
Code Example
Demonstrates array usage in Java programming.
Java Main Method
Entry point for Java applications.
Row Slice
Extracts specified row from a 2D array.
Column Slice
Extracts specified column from a 2D array.
Submatrix Extraction
Extracts a rectangular section from a matrix.
Enrollment Data
2D array representing student enrollments.
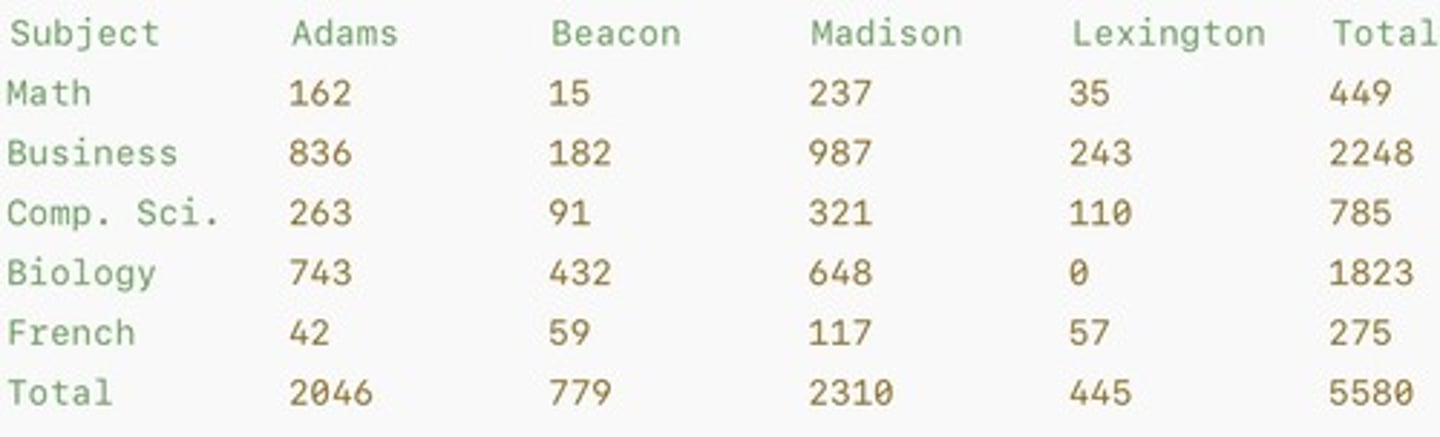
Row Totals
Sum of elements in each row.
Column Totals
Sum of elements in each column.
Grand Total
Sum of all elements in the array.
Matrix Initialization
Defining a 2D array with values.
Looping Through Rows
Iterating over rows of a 2D array.
Looping Through Columns
Iterating over columns of a 2D array.
Java Arrays
Data structure for storing fixed-size sequential collections.
Scanner Class
Used for obtaining input from the user.
Print Formatting
Control output layout in console.