Exercises 14-22
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Blood Agar
What media type tests for the presence of exoenzymes?
Gelatin
Polymer of collagen that makes up connective tissues
Liquefies above 25ºC
Gelatinases
Break down collagen
Nutrient acquisition, virulence
Embden-Meyerhof Pathway (Glycolysis)
Converts 1mol glucose to 2mol pyruvate
Aerobic Respiration
Molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor (more ATP generated)
Anaerobic Respiration
Inorganic ions other than oxygen are final electron acceptor
Fermentation
Doesn’t require oxygen and organic substrate is final electron acceptor
Phenol Red
Indicator of acid production (yellow color = acidic)
Durham Tube
Indicator of presence of air bubble
Indole Test
Measures ability of bacteria to break down tryptophan to indole via tryptophanase
Methyl Red Test
Determines ability to oxidize glucose to make acid end products
Voges Proskauer Test
After enough time, K. aerogenes converts acids to acetoin
Barritt’s Reagent
Turns pink with acetylmethylcarbinol
Citrate Test
Determines the ability of an organism to use the enzyme citrase to use citrate as a sole carbon source
Bromothymol Blue
Used in the Citrate Test
Indicator → turns from green to blue at a pH above 7.6+
Citrate Carbon Source
If there is growth present on the slant, and if the color has changed from green to blue
Hydrogen Sulfide
Has the same medium as Indole test
Gas produced by certain Enterobacteriaceae by two pathways
Cysteine Desulfurase
Reduction of amino acids that contain sulfur lie cysteine (found in peptone) using this in pathway 1 of H2S gas production
Thiosulfate Reductase
Reduction of inorganic sulfur compounds using this in pathway 2 of H2S gas production
Urease Test
Designed principally to distinguish Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella from other members of Enterobacteriaceae
This test can yield ammonia and carbon dioxide
Ammonia production indicated by magenta color
Complete Proteolysis
Indicating elevated pH due to deamination
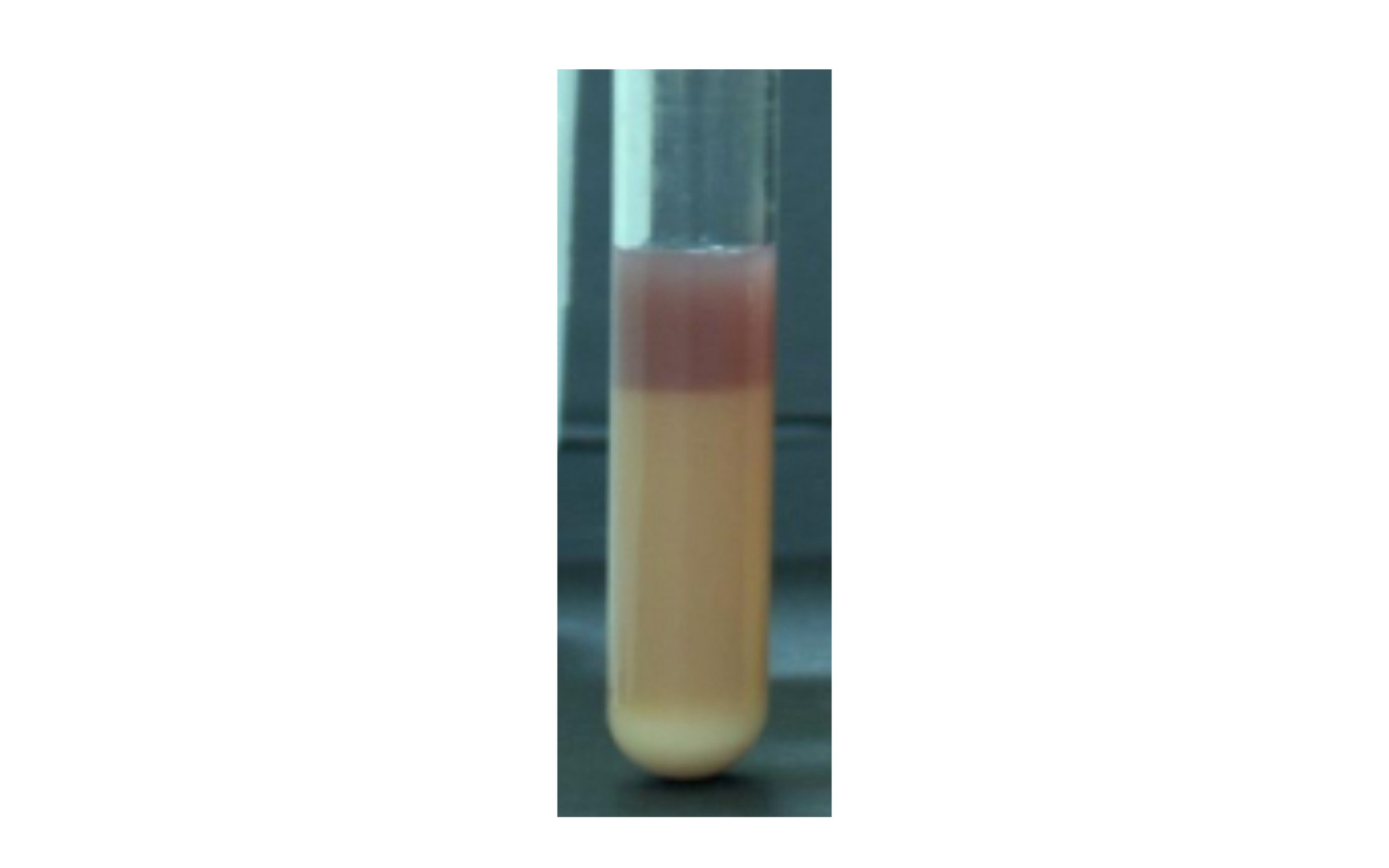
Acid Clot
Indicated by solidified medium with pink acid top and reduced acid bottom
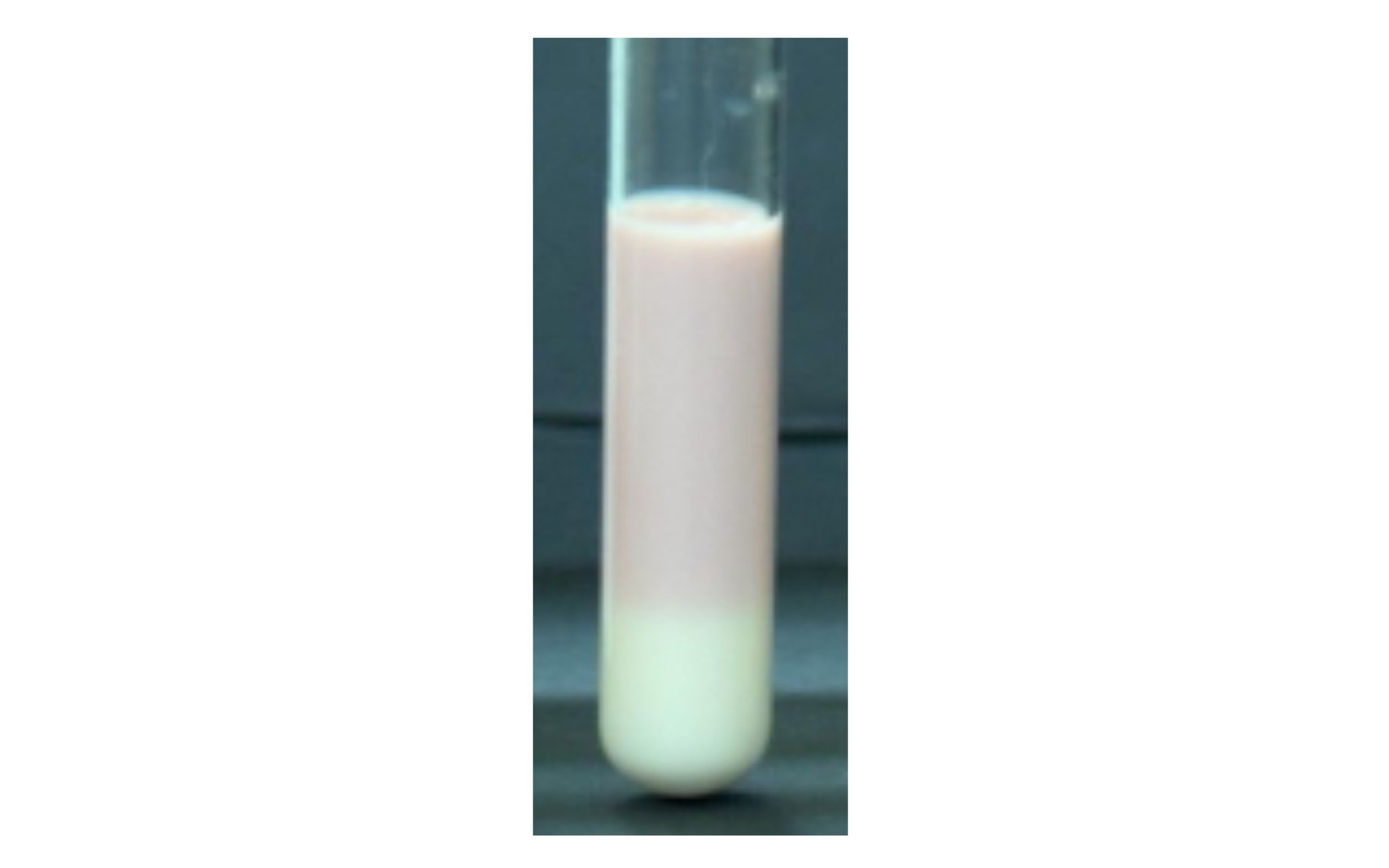

Curd Formation, Alkaline Reaction
Yellowish semisolid bottom with a blue top
Partial degradation of casein into shorter polypeptide chains
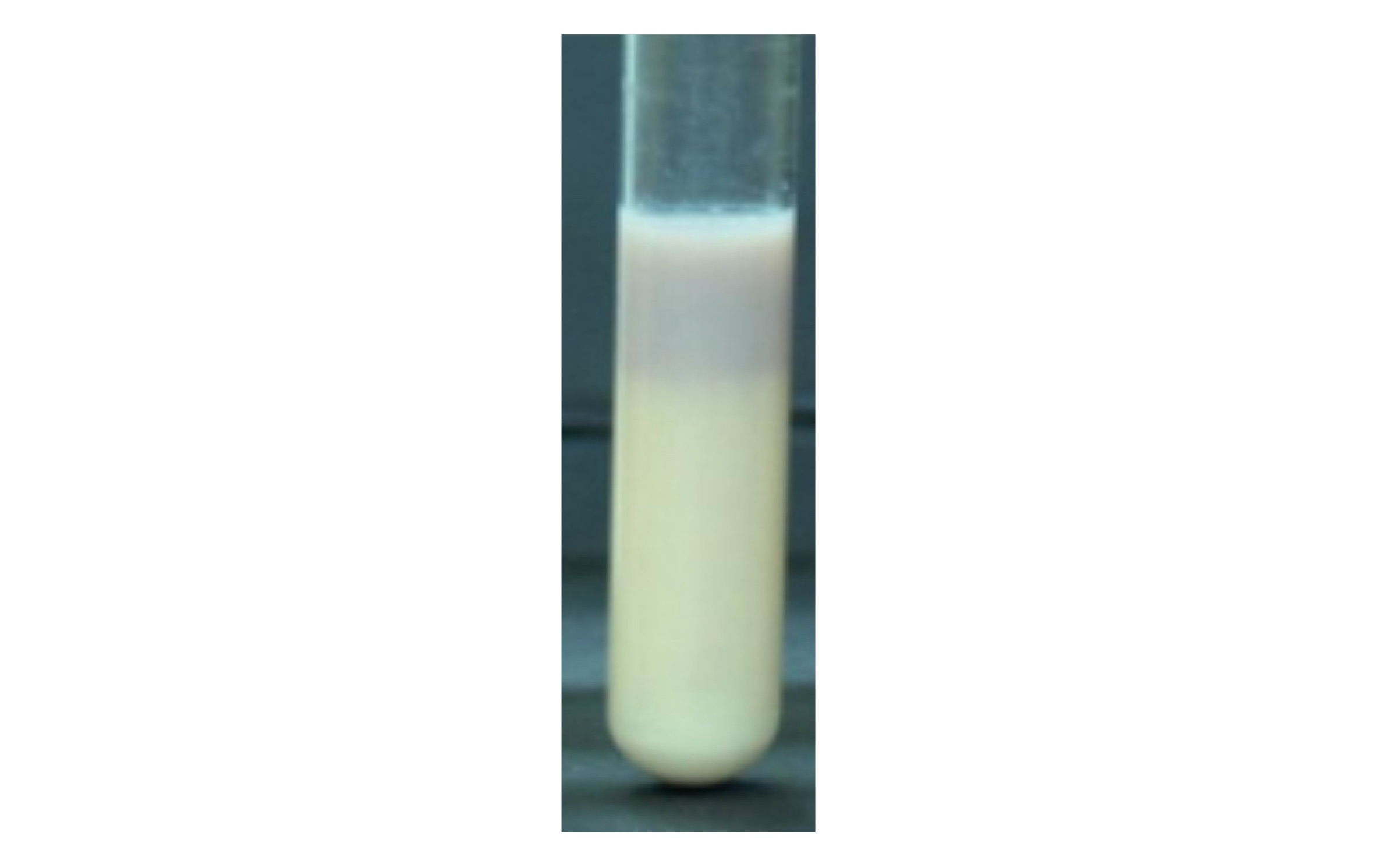

Alkaline Conditions
Purple litmus reaction with reduced litmus at the bottom
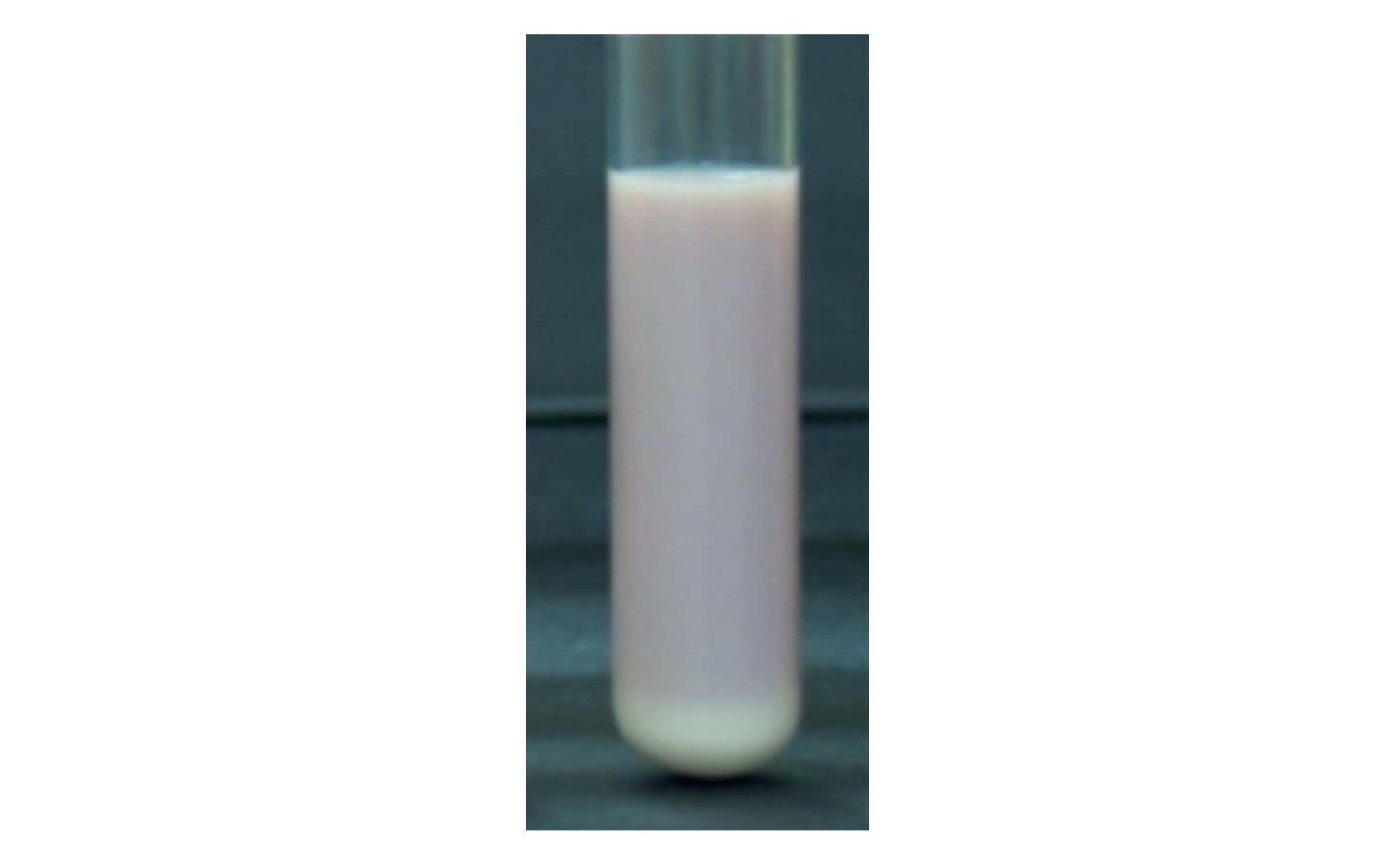

Acid Production
Pink tube without acid clot formation or proteolysis
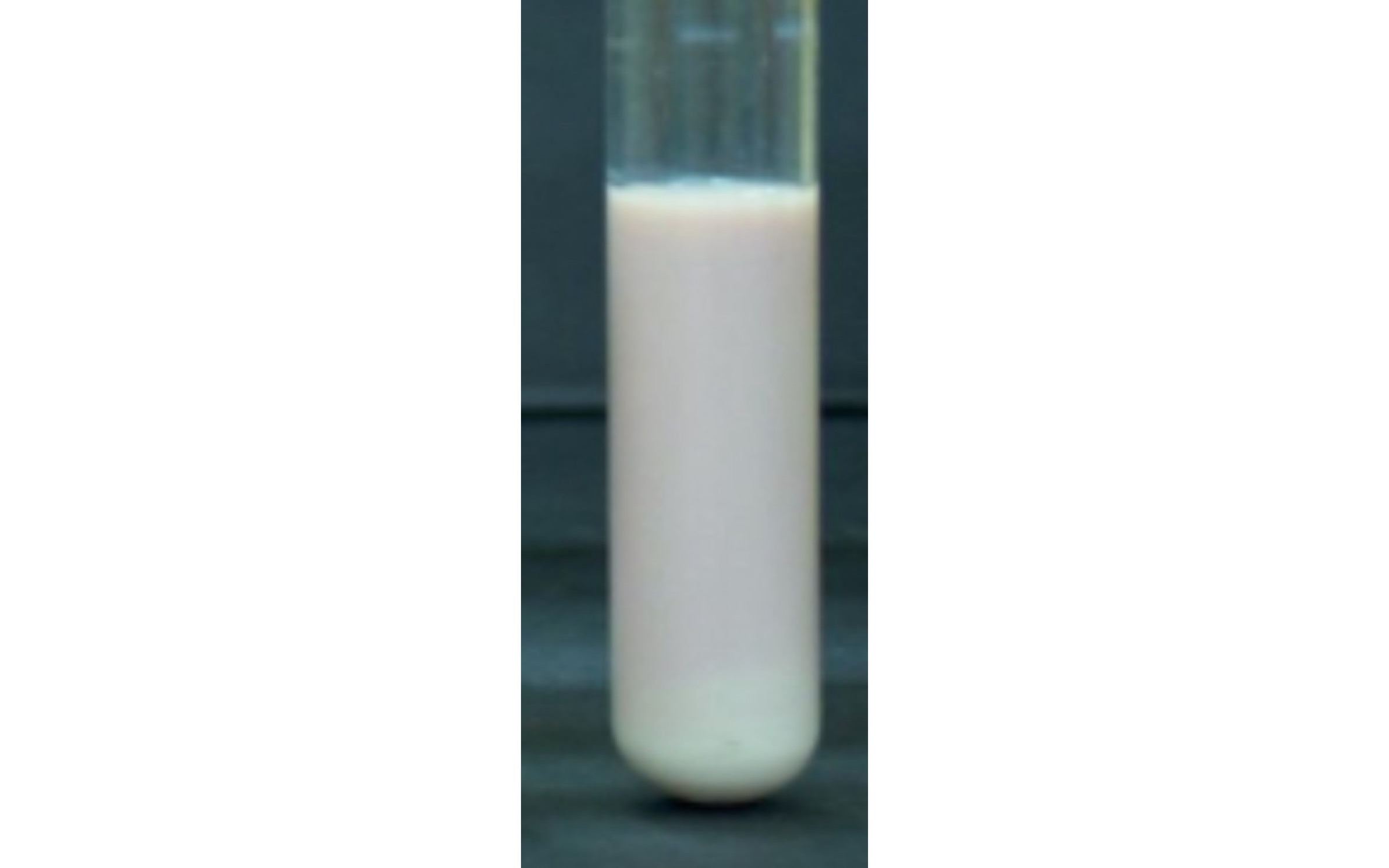

Anaerobic Respiration
Where nitrate can serve as a terminal electron acceptor, and ther eduction of nitrate is catalyzed by nitrate reductase
Catalase Test
Performed to distinguish members of the Staphylococcaceae and Micrococcaceae species from Streptococcaceae
Bacillus
Gram-positive rods that are positive for the catalase test
Clostridium
Negative for the catalase test
Oxidase Test
Used to differentiate strict aerobic respiratory microorganisms from facultative or fermentative microorganisms
More commonly, used to differentiate Enterobacteriaceae (negative) from Pseudomonadaceae (positive)
Can be used for identification of Neisseria (positive)
Cytochrome Oxidase
Heme-containing enzyme that is the terminal redox protein used in the ETC of microorganisms that use oxygen as their terminal electron acceptor
Responsible for transferring electrons directly to oxygen to form water as one of the products of aerobic respiration
Chromogenic Reducing Agent
This is used in the cytochrome oxidase test as an indicator to detect bacteria that produce cytochrome oxidase
Chemical that changes or produces color as it become oxidized
p-aminodimethylaniline oxalate
Donates electrons to cytochrome oxidase and becomes oxidized itself, changing colors from light pink to a dark maroon (almost black)
Indicator used in lab for the Oxidase Test
Mixed Acid Fermentation
The methyl red test indicates whether or not the bacteria utilizes what
Hydrolytic Enzymes
Exoenzymes are mainly this → reduce high-molecular-weight materials into their building blocks by introducing water into the molecule, liberating smaller molecules, which may then be transported into the cell
Endoenzymes
Function inside the cell and are mainly responsible for synthesis of new protopalsmic requirements and production of cellular energy from assimilated materials
Amylase
Enzyme involved for the hydrolysis of starch → results in maltose molecules
Lipases
Hydrolyze triglycerides
Cleave the ester bonds in triglycerides by the addition of water to form the building blocks glycerol and fatty acids
Kovak’s Reagent
p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, HCl, and butanol combined form this
Litmus Milk
Differential medium in which microorganisms can metabolize milk substrates depending on their enzymatic complement
Casein
Milk protein
Acid Curd
Lactic acid (or other organic acid) cause the precipitation of casein as calcium casinate to form an insoluble clot
Hard clot, will not move
Rennet Curd
Paracasein converts to calcium paracaseinate (in the presence of calcium) and forms an insoluble clot
Soft semisolid clot
Rennin
Enzyme that acts on casein to form paracasein
Zinc
Will catalyze the spontaneous reduction of nitrate to form nitrite
Will only cause the medium to turn red if in the presence of UNCONVERTED NITRATE
SIM Media
Differential medium used to detect three bacterial characteristics:
Sulfide production
Indole production
Motility
Commonly used to differentiate members of the Enterobacteriaceae family
IMViC Tests
Special tests for the separation of enteric microorganisms
Indole, Methyl Red, Voges-Proskauer, and Citrate
Gelatin Agar
Agar that is primarily used as a growth medium to identify bacteria that produces gelatinase enzymes
Also used for general microbial growth and for identifying Vibrio species
Tributyrin Agar
Agar that is primarily used to detect and identify bacteria capable of producing lipase
Needs a substrate to determine results
Starch Agar
Agar that is primarily used to detect and identify microorganisms that can hydrolyze starch—in specific, those that can produce α-amylase
Gelatinase Test
Test that involves inoculating a nutrient gelatin medium with a bacterial culture, incubating it, and then checking for liquefaction
Starch Hydrolysis
Test that involves flooding an inoculated starch agar plate with Gram’s iodine solution
Exoenzymes
Enzymes that act on substances outside of the cell—most high-molecular-weight substances are not able to pass through cell membranes and use be degrades into low-molecular weight materials before being transported into cell