Equipment (TCM 427) Midterm
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Tires
Simpler to operate, fuel efficiency, smoother operation, and could be more mobile
Tracks
Greater stability, more traction depending on surface, and better control on slopes or unstable ground
Excavators
Contains a long arm (boom) and a cab, can rotate up to 360 degrees, can be wheeled or tracked, and can be used for excavation, heavy lifting, demolition, removing sediments and debris from the bottom of water, and the cutting of trees
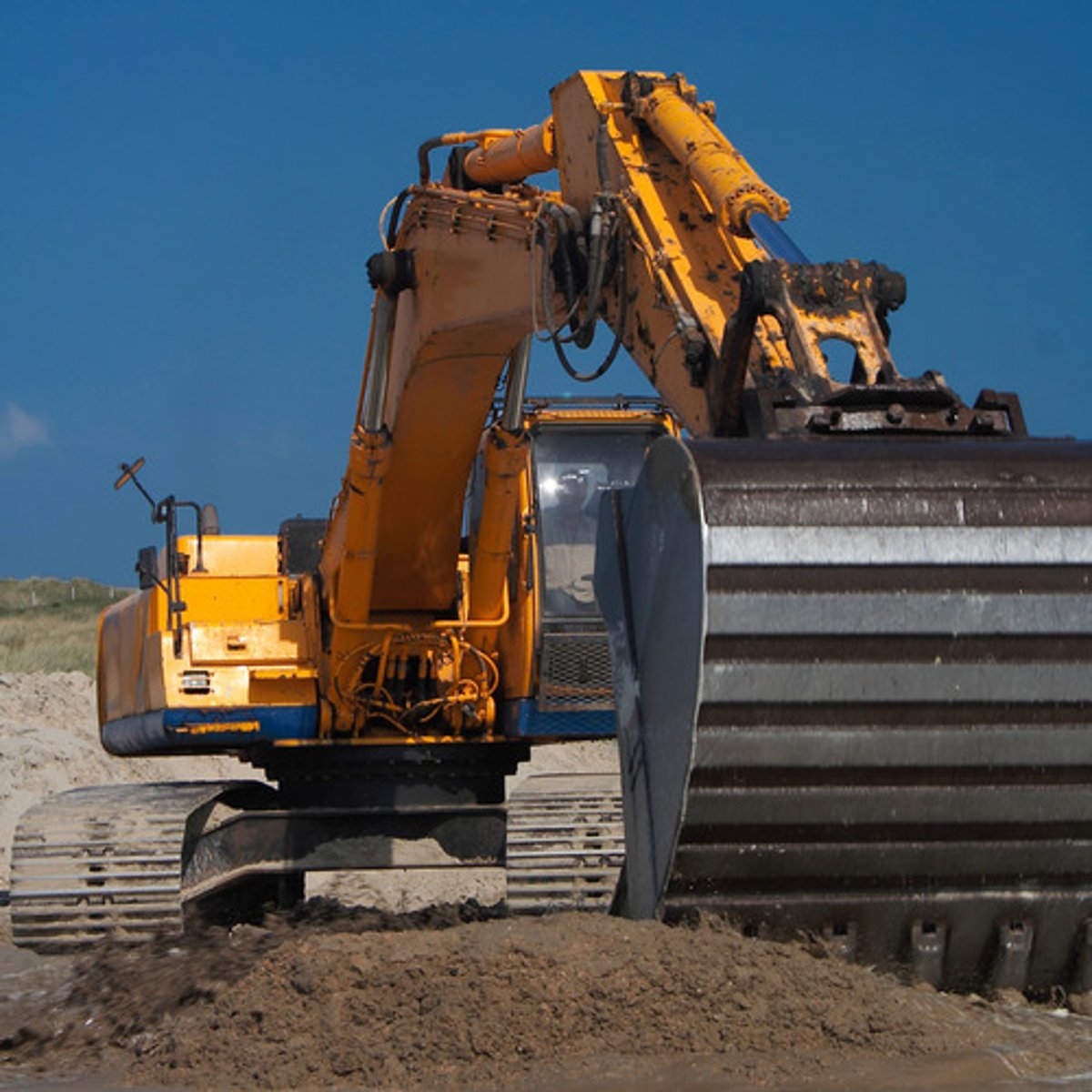

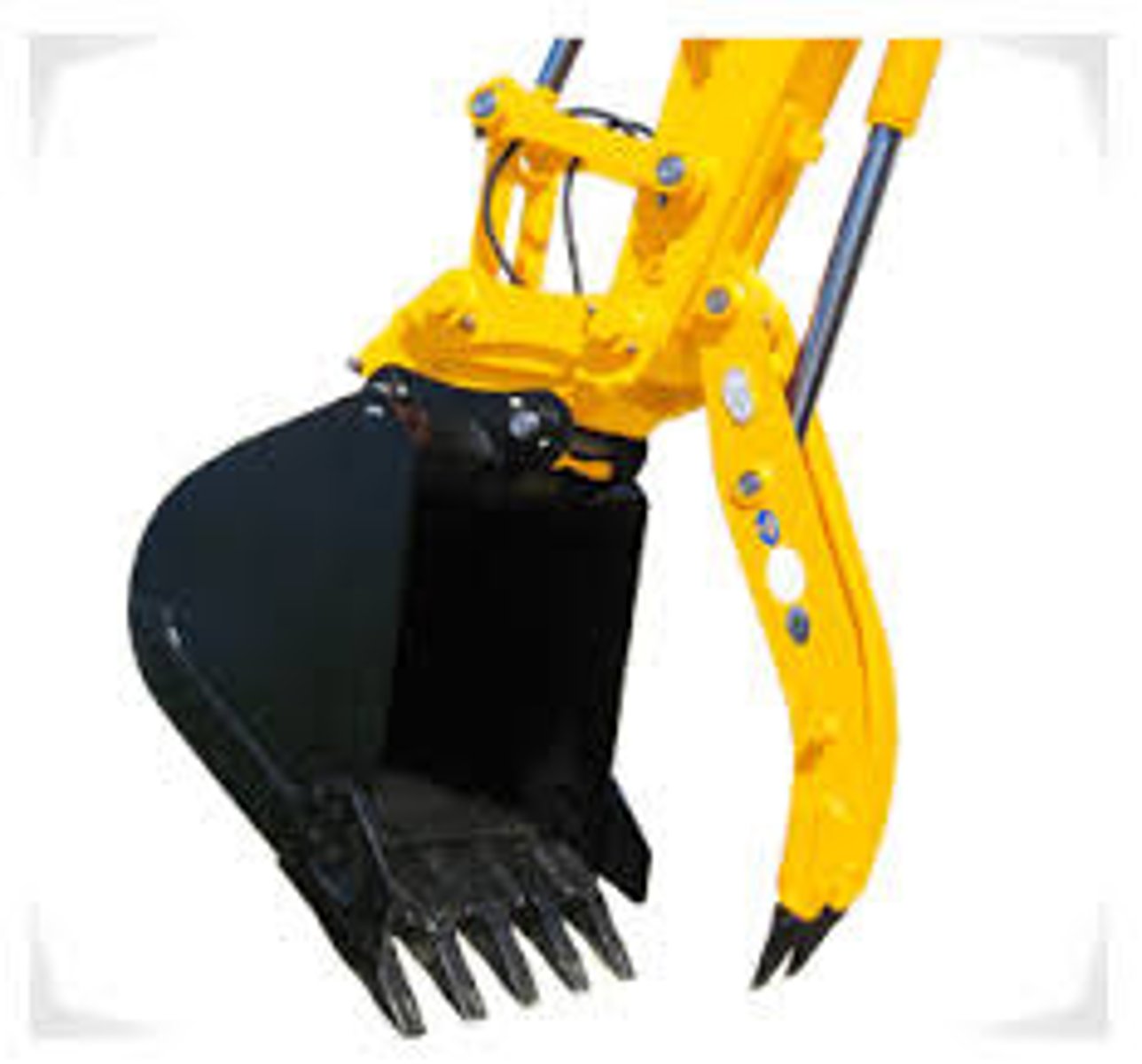
Bucket (Excavator)
What attachment is this for an excavator?

Hammer
What attachment is this for an excavator?
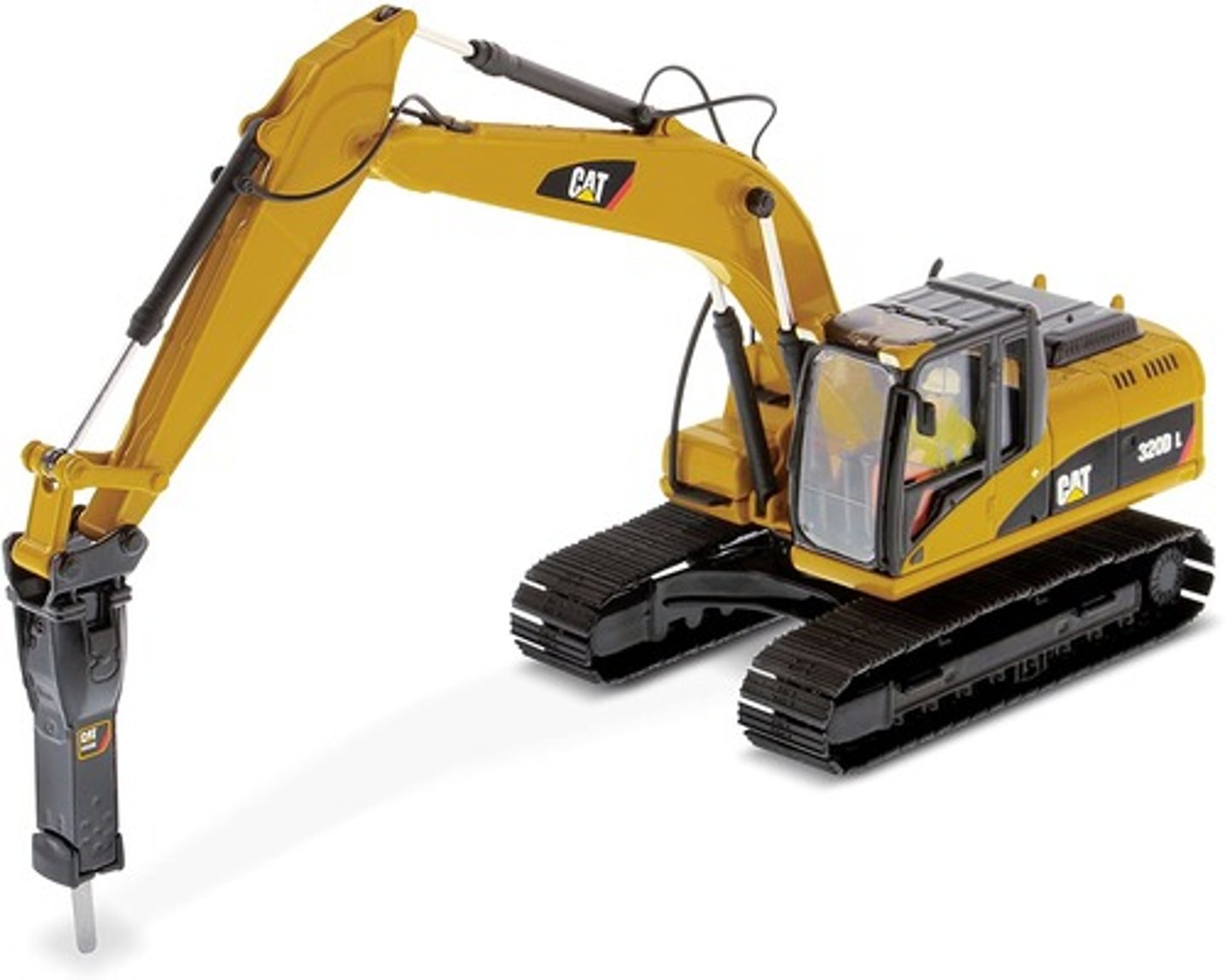

Coupler
What attachment is this for an excavator?
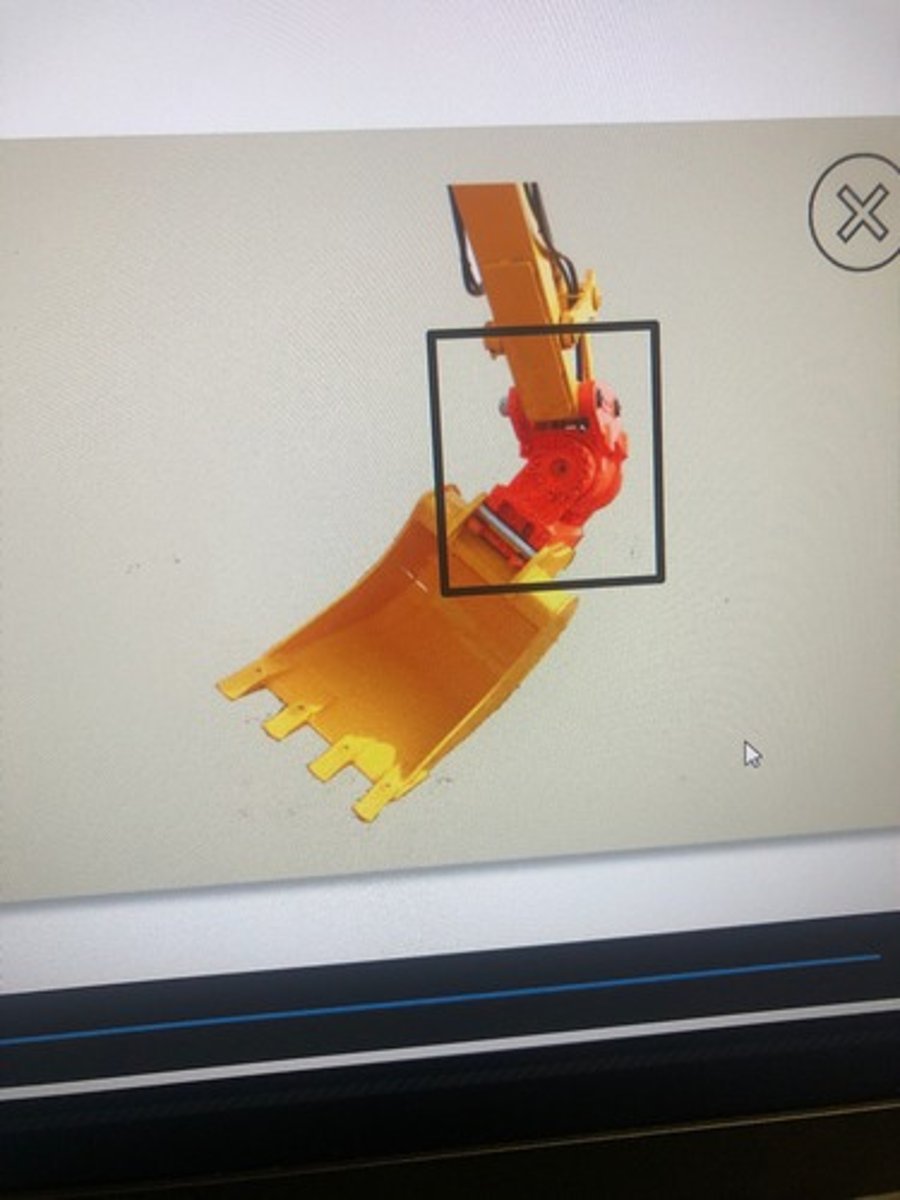
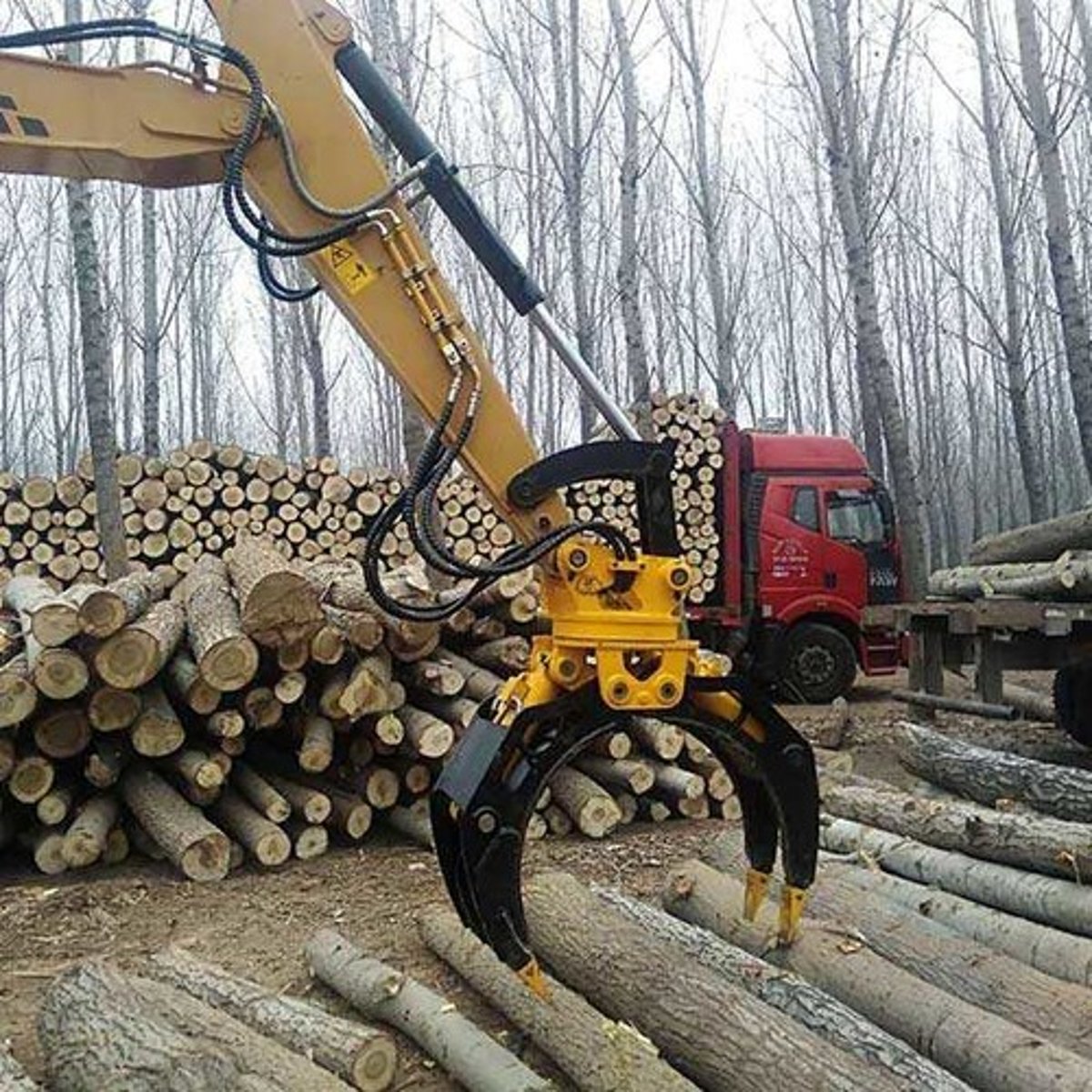
Grapples (Excavator)
What attachment is this for an excavator?

Thumbs
What attachment is this for an excavator?

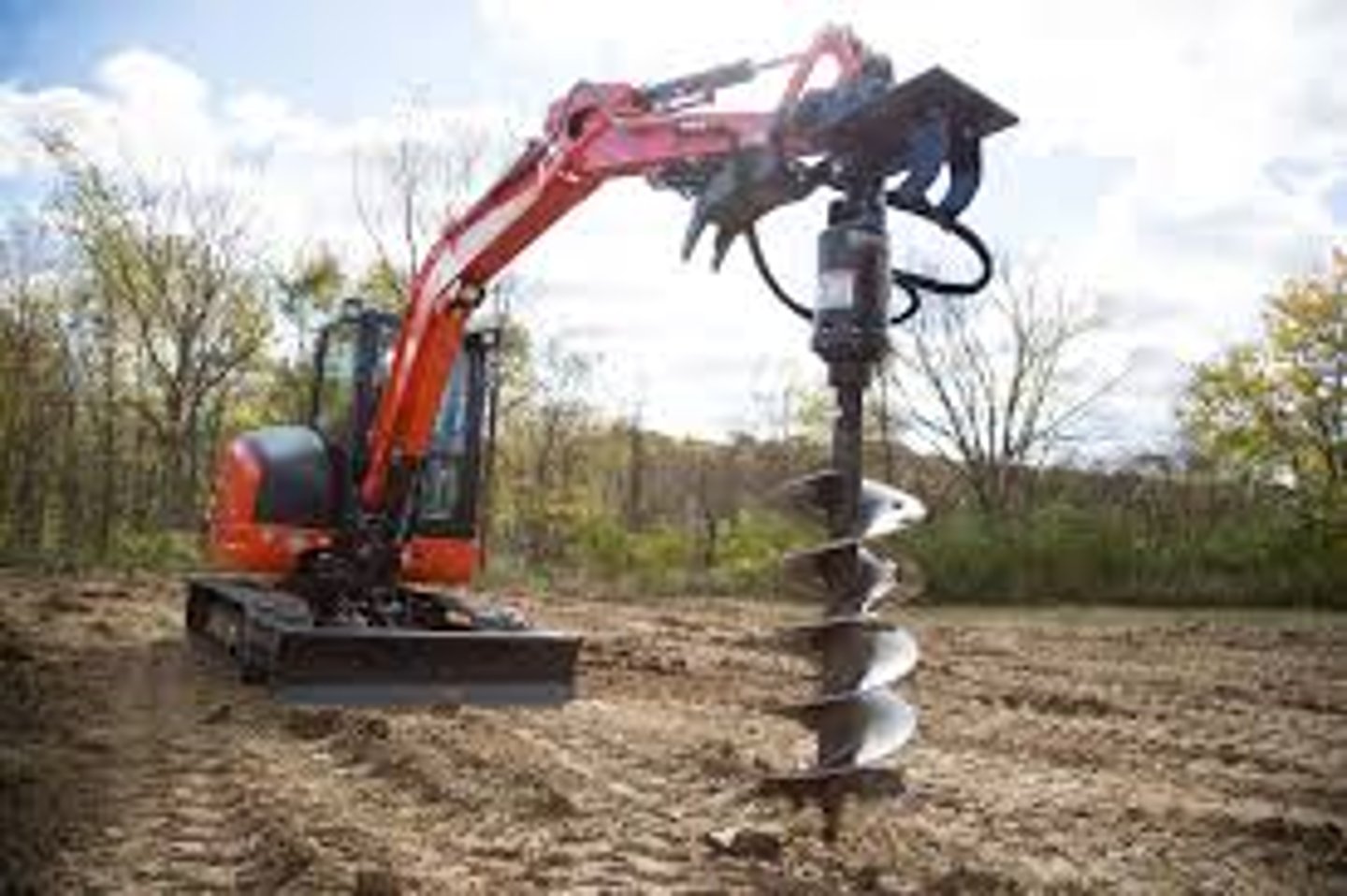
Auger
What attachment is this for an excavator?

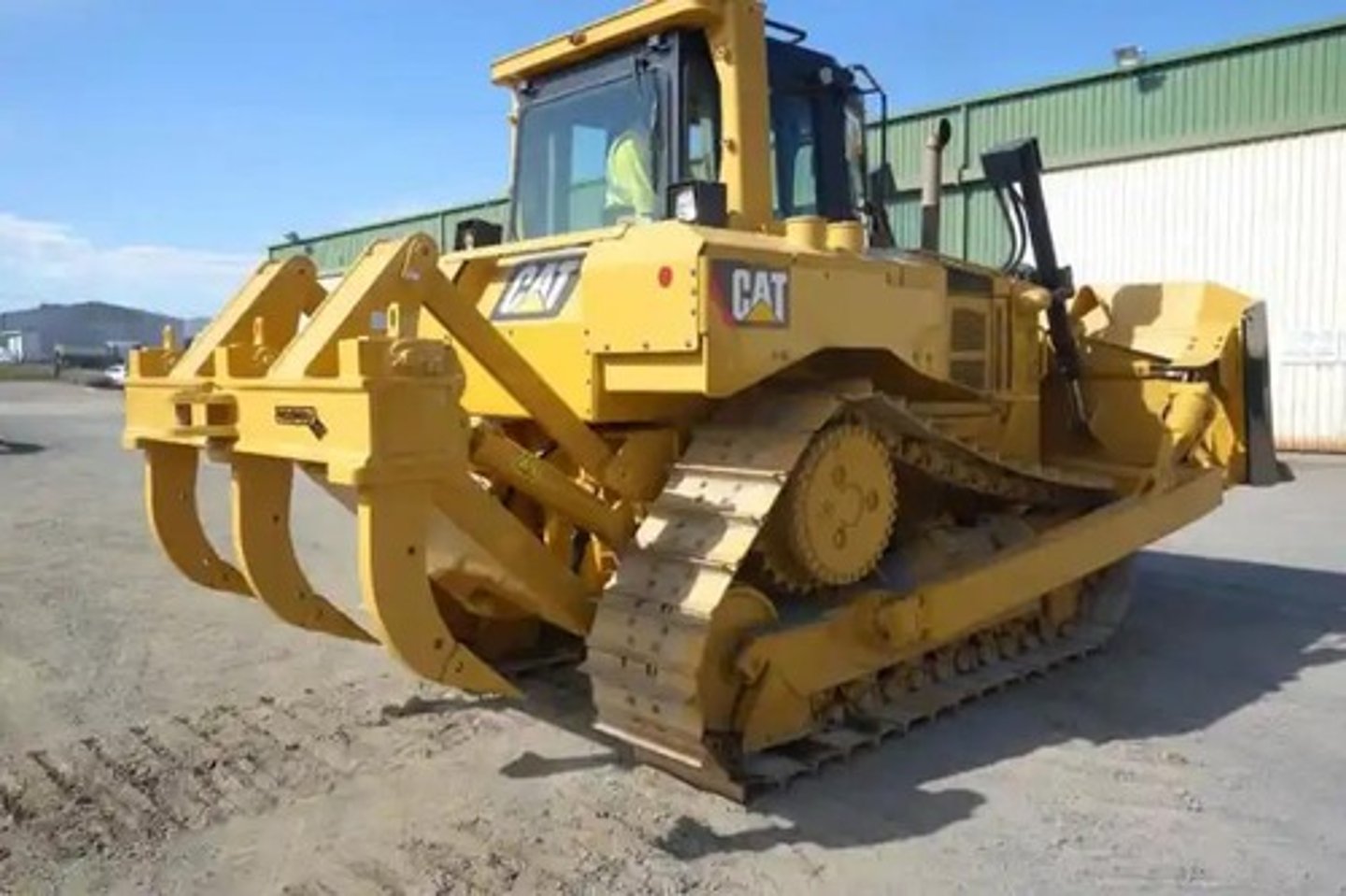
Rippers
What attachment is this for an excavator?

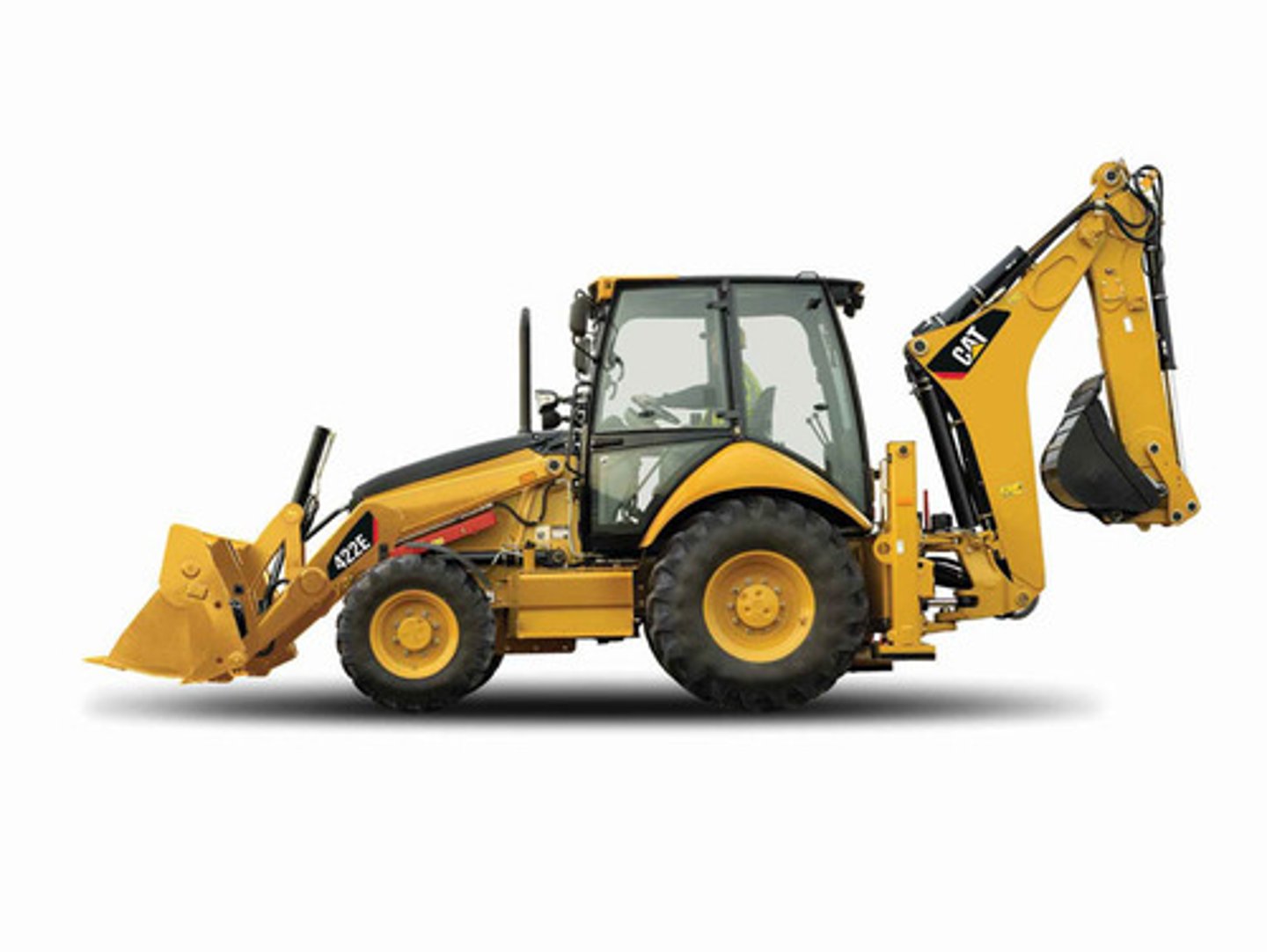
Backhoe
Used for multiple purposes where the hoe arrangement is provided on the back side of the cab while the loading bucket is provided on the front; most are wheeled tires.
Disadvantage: cannot lift much weight and cannot dig as deep

Bucket (Backhoe)
What attachment is this for a backhoe?

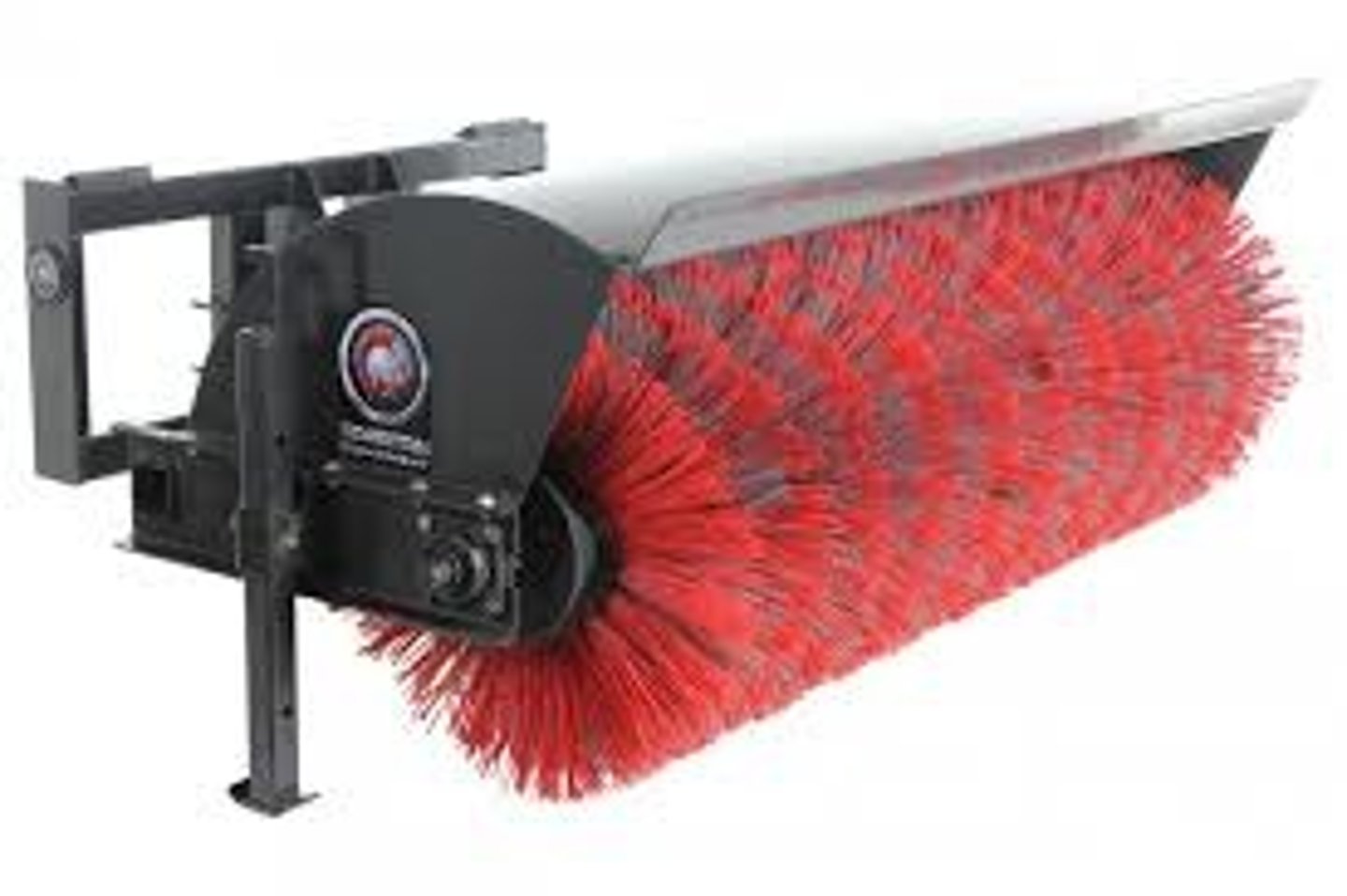
Broom
What attachment is this for a backhoe?

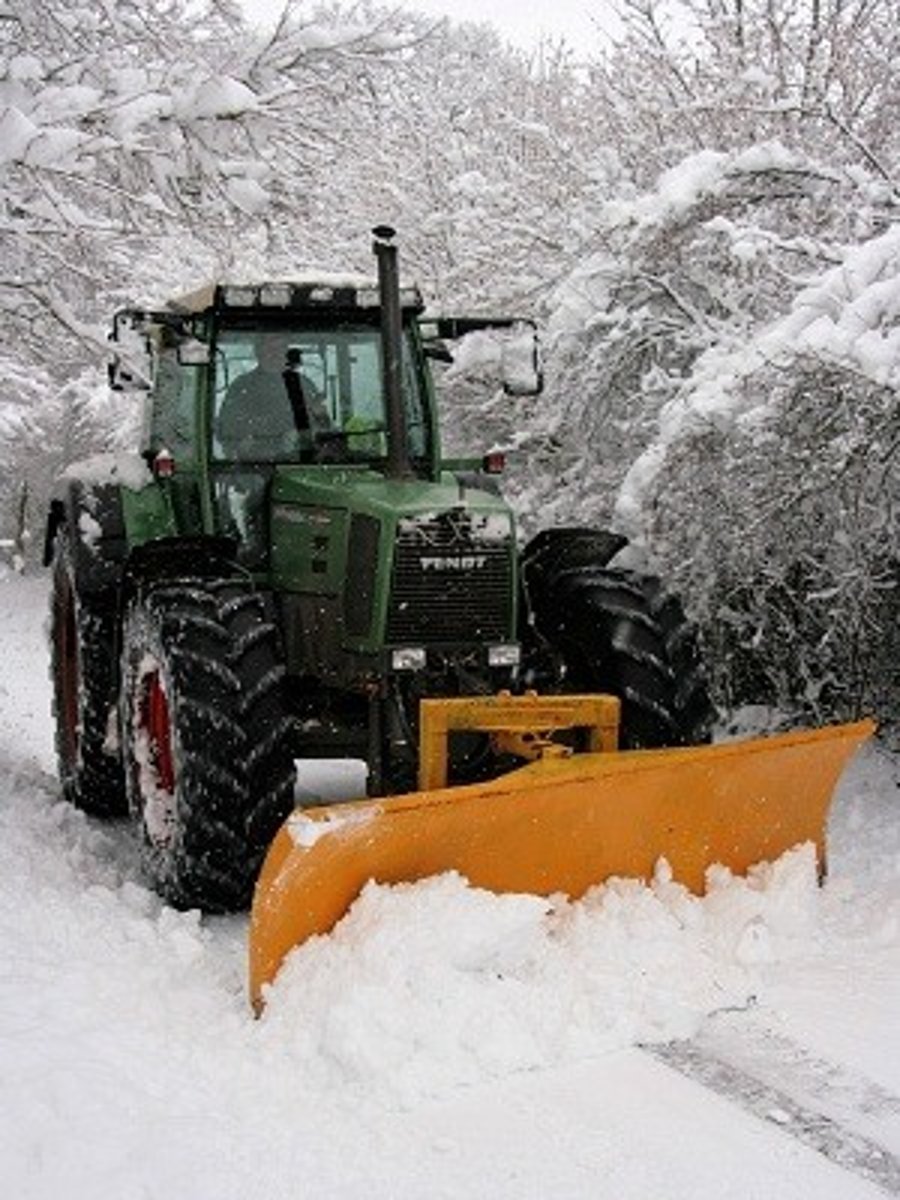
Snowplow
What attachment is this for a backhoe?

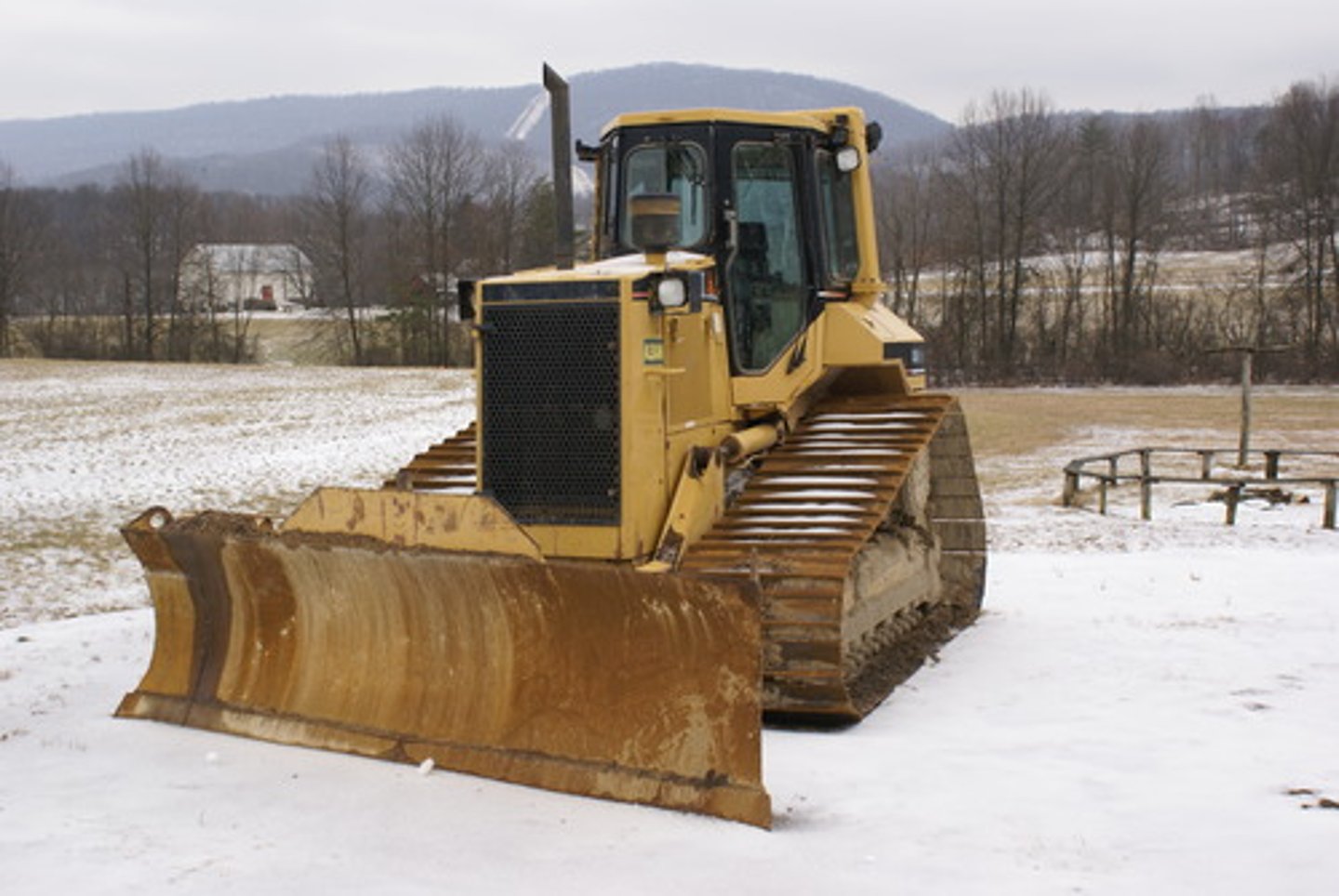
Bulldozer
The general purpose is to remove topsoil and push material, blades are the most common attachment, and they can be wheeled or tracked.
Disadvantage: the weight can compact soil which may lead to irrigation issues on shallow soil

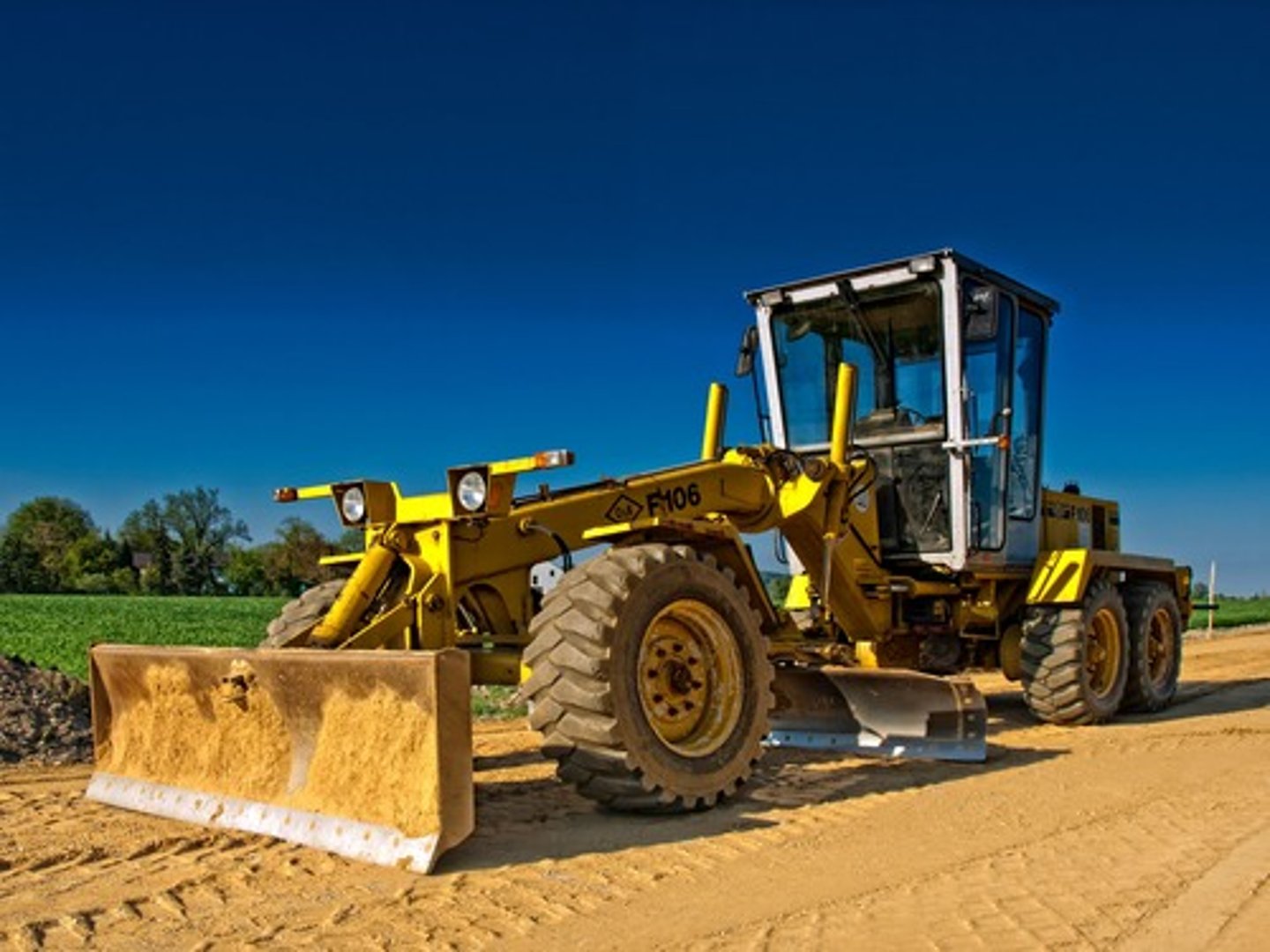
Graders
Most commonly used on road construction, road maintenance, parking lots, etc. to level or flatten the soil.
Disadvantage: limited traction because of rubber tires, not suitable for moving heavy loads, and too large for small projects.

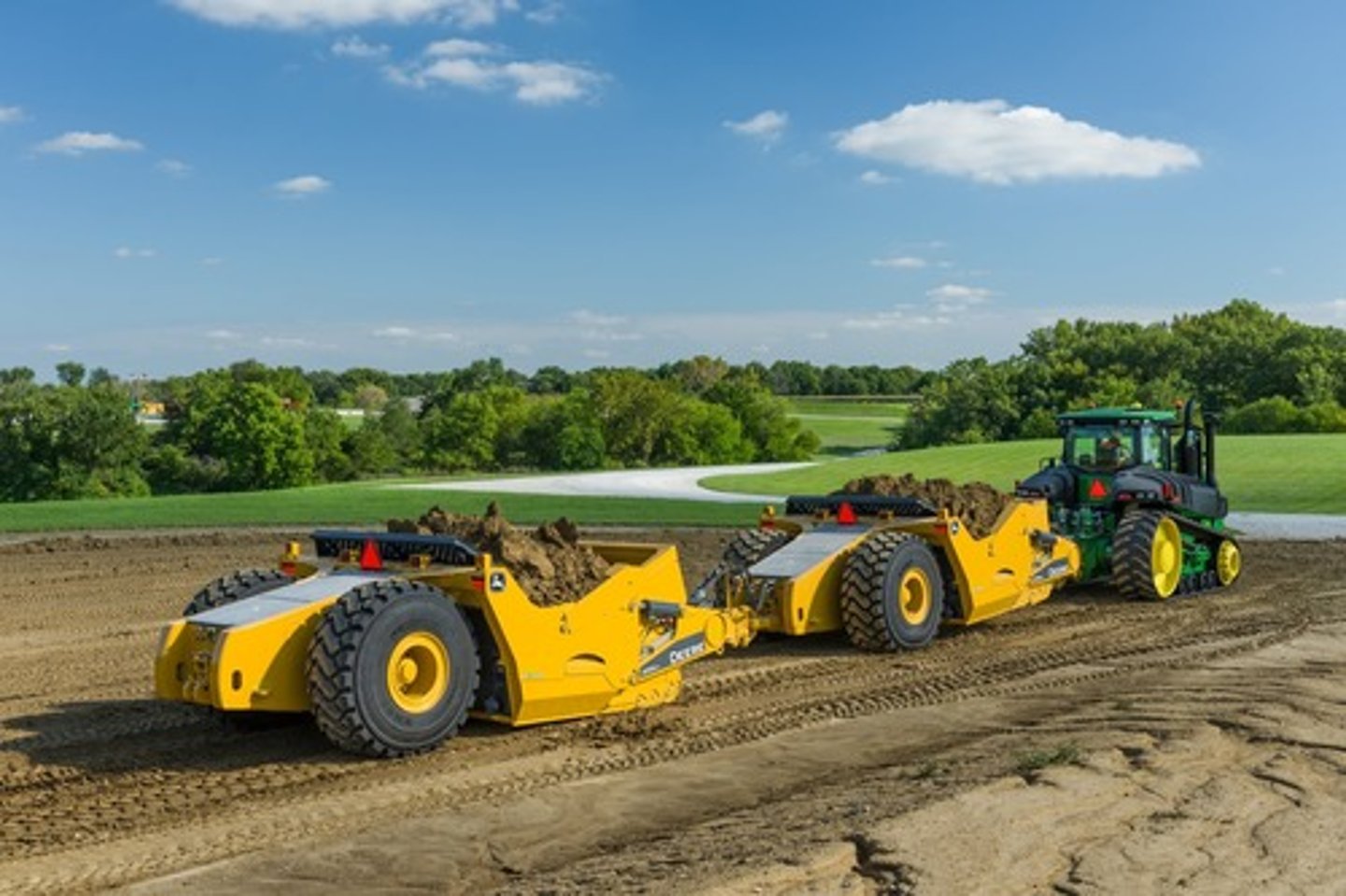
Scrapers
The general purpose is to scrape and level surfaces or material import/export (relocation). As the machine moves forward, dirt is collected into the bowl where it eventually becomes full.

Up to 300 ft
Economical haul distance for large dozers, pushing material
300 to 5,000 ft
Economical haul distance for push-loaded scrapers
More than 5,000 ft
Economical haul distance for trucks
William S. Otis in 1835 while working on the Boston and Providence Railroad
When and who invented the original shovel-excavating machine?
The second Industrial Revolution
What was the primary reason for the use of machines across the country?
Benjamin Holt in 1886 and 1890
Who created the first combine harvester and steam engine tractor?
John Froelich in 1892
Who invented the gas-powered tractor?
Ownership costs
Depreciation, insurance, taxes, salvage value, shop/storage expenses, major repairs and overhauls
Decrease
Does ownership cost increase or decrease with usage?
Operating costs
Consumables (fuel, oil, grease, and filters), repairs, maintenance, tires/tracks, and high wear items
Increase
Does operating costs increase or decrease with usage?
High wear items
Bucket teeth, cutting edges, truck body liners, and ripper tips
Dozer
A tractor with an attached blade to push material; can be used for backfilling, spreading, ripping rock, land clearing, and moving material. Can also be used for assisting scrapers to load.
Crawler bulldozer
Most ideal for traversing dense and irregular terrain due to the tracks giving greater traction. The heavy weight of the machine is great for moving heavy material from one area to another; also referred to as a track bulldozer.
Wheel bulldozer
Most ideal for soft/sensitive ground and operates on a smaller axis that allows for easier maneuvering. Sometimes called a tire bulldozer and is normally larger and faster than a crawler bulldozer.
Mini bulldozer
Most ideal for quickly working through jobs and traversing tight spaces. The small size allows for better speed, handling, and overall versatility; also known as a compact bulldozer.
Cushion ("C") Blade
Used for bulldozers when primarily pushing scrapers

Tilting
What is this blade adjustment?
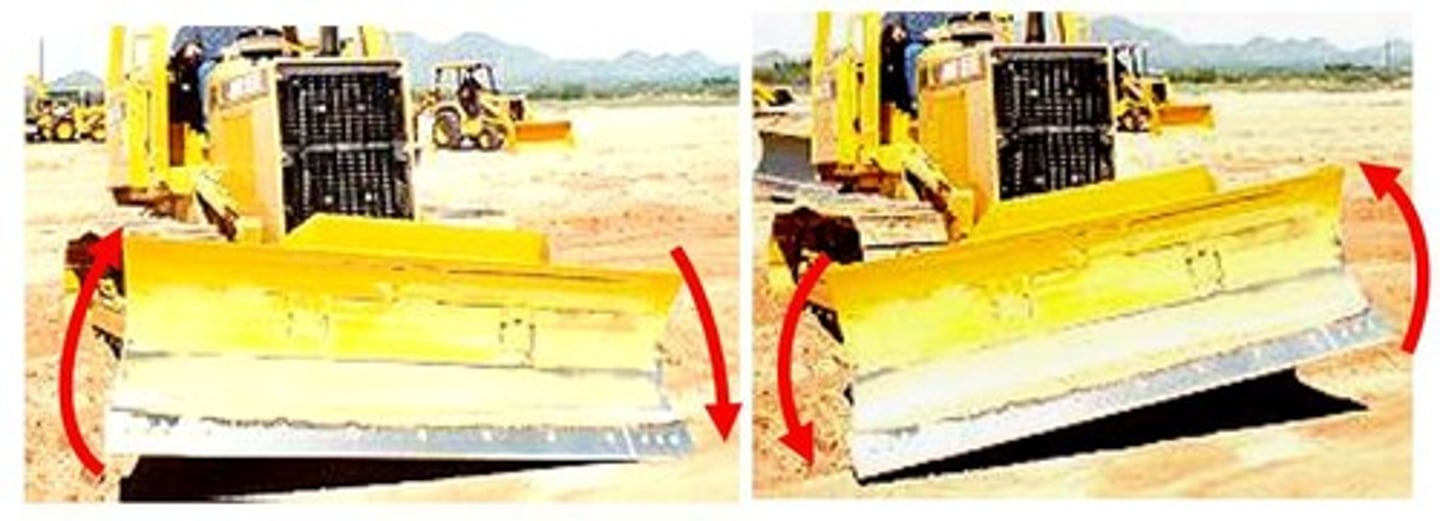

Angle
What is this blade adjustment?

Slot Dozing
A practice where an operator manipulates the blade to create walls of the material on each side of the machine to reduce the amount of spillage; increases production by 20%

Side-by-side Dozing
Requires coordination and extra maneuver time impacting productivity; increases production (15-20%) by minimizing spillage.
Dozer production rates
Type of blade, type and condition of material, and cycle time
Hoover Dam
A concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado River between Nevada and Arizona. Built during the Great Depression (1931-1936).
Conventional single engine scraper
Can reach speed as great as 35 mph, may not have the horsepower and tractive force to self load (need a pusher), and most ideal when haul grades are less than 5% and return grades are greater than 12%

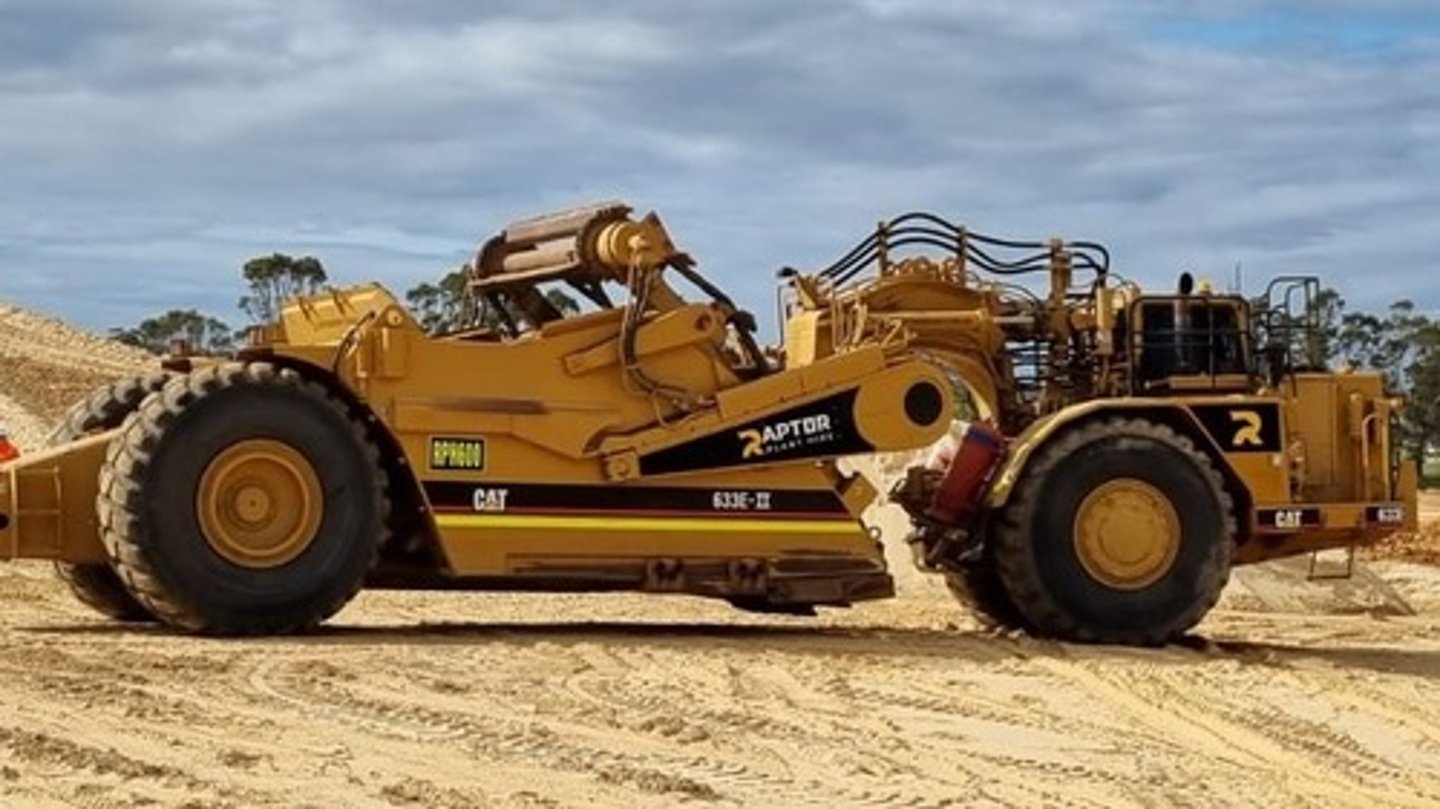
Self-loading "paddle wheel" scraper
Ideal for short hauls and can work alone, cost more initially and to operate, the elevator adds weight and takes horsepower.

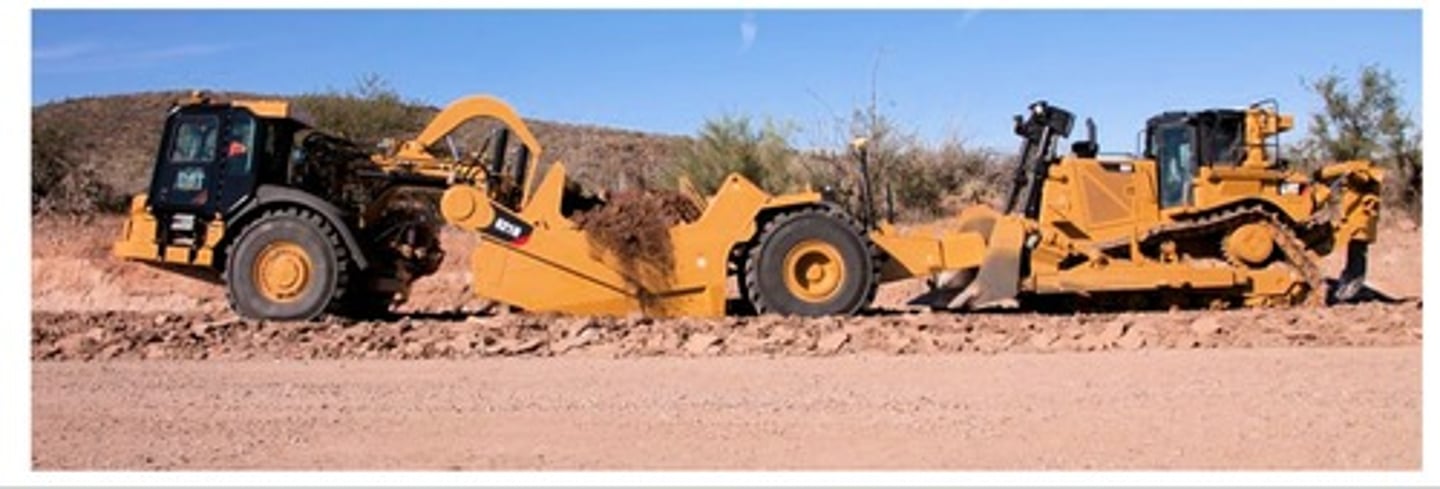
Self-loading "tandem" scraper
Twin engine scrapers are good for jobs that have adverse grades and poor foot, may need assistance loading, and owning and operating costs are about 25% higher.
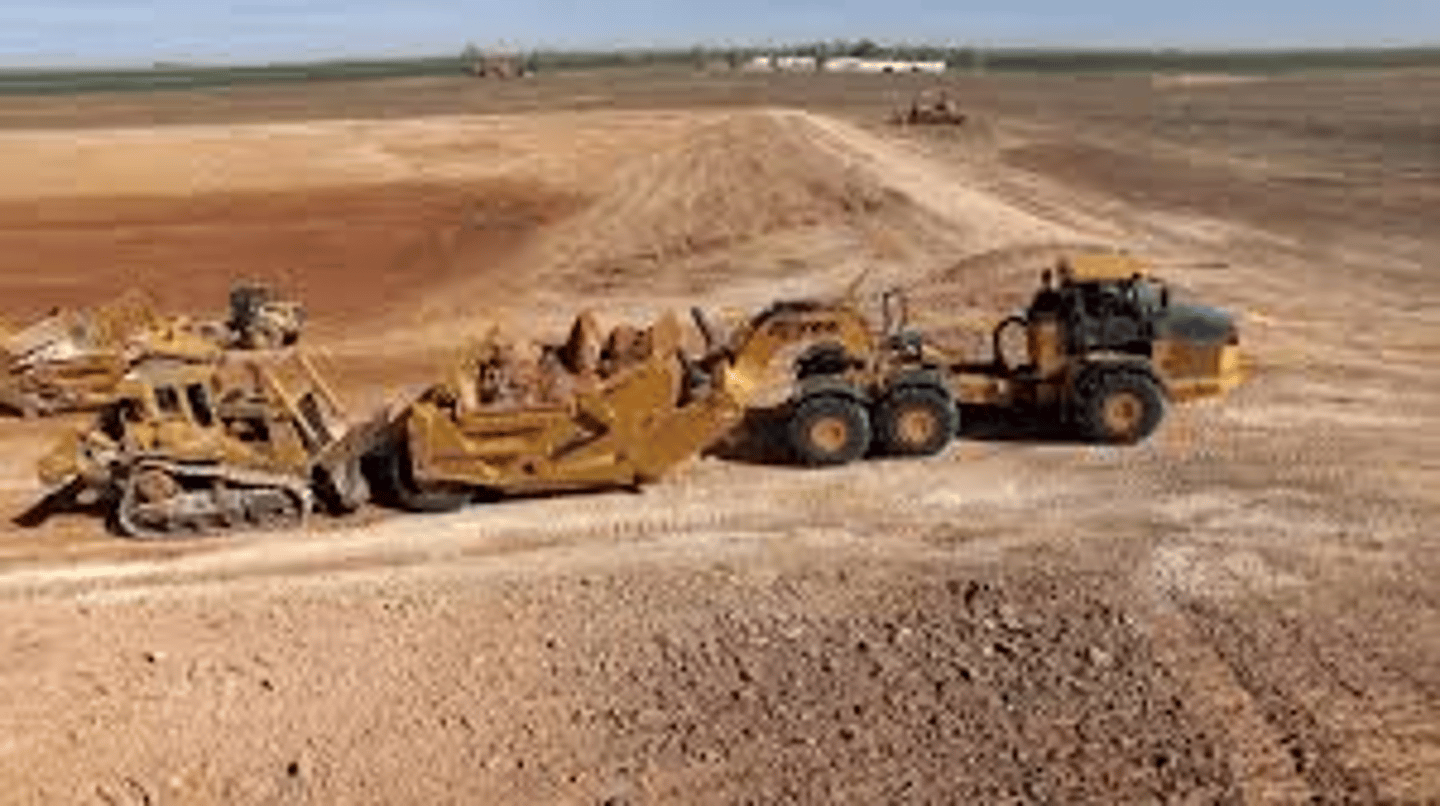

Push-pull scraper
Two or more scrapers that assist each other during loading by pushing and pulling each other. One is loading while one is assisting.

President Dwight Eisenhower in 1956
When and who created the Federal-Aid Highway Act?
Earthmoving
An operation where material is removed from high spots and deposited in low spots with the "making up" of any deficit with borrowing or the wasting of excess cut material
Density
The substances mass per unit of volume; typically improves structural performance
Cohesion
The quality of soil particles to be attracted to like particles, leads them to stick together
Coarse aggregate
Rock or gravel; generally greater than 1/4" in size
Fine aggregate
Sand or fine crushed stone; less than 1/4" but greater than a No. 200 sieve
Proctor compaction test
Used to find the optimal level of moisture for soil and the maximum dry density
Jaw crusher
Can crush hard rocks such as granite, basalt, ores, and concrete; produces coarse aggregate
Impact crusher
Can crush fine/medium rocks such as clay, limestone, coal, and dolomite; produces fine aggregate
Cranes
A primary machine used for the vertical movement of construction materials; used for hoisting and moving heavy loads
Static Cranes
Intended to be "installed" on the jobsite for long periods of time, designed to lift heavy loads along a certain path, and offer little flexibility
Mobile cranes
Intended to move things from one location to another, consists of a single lifting arm that can be raised or lowered, and frequently features a telescoping arm that can reach greater heights
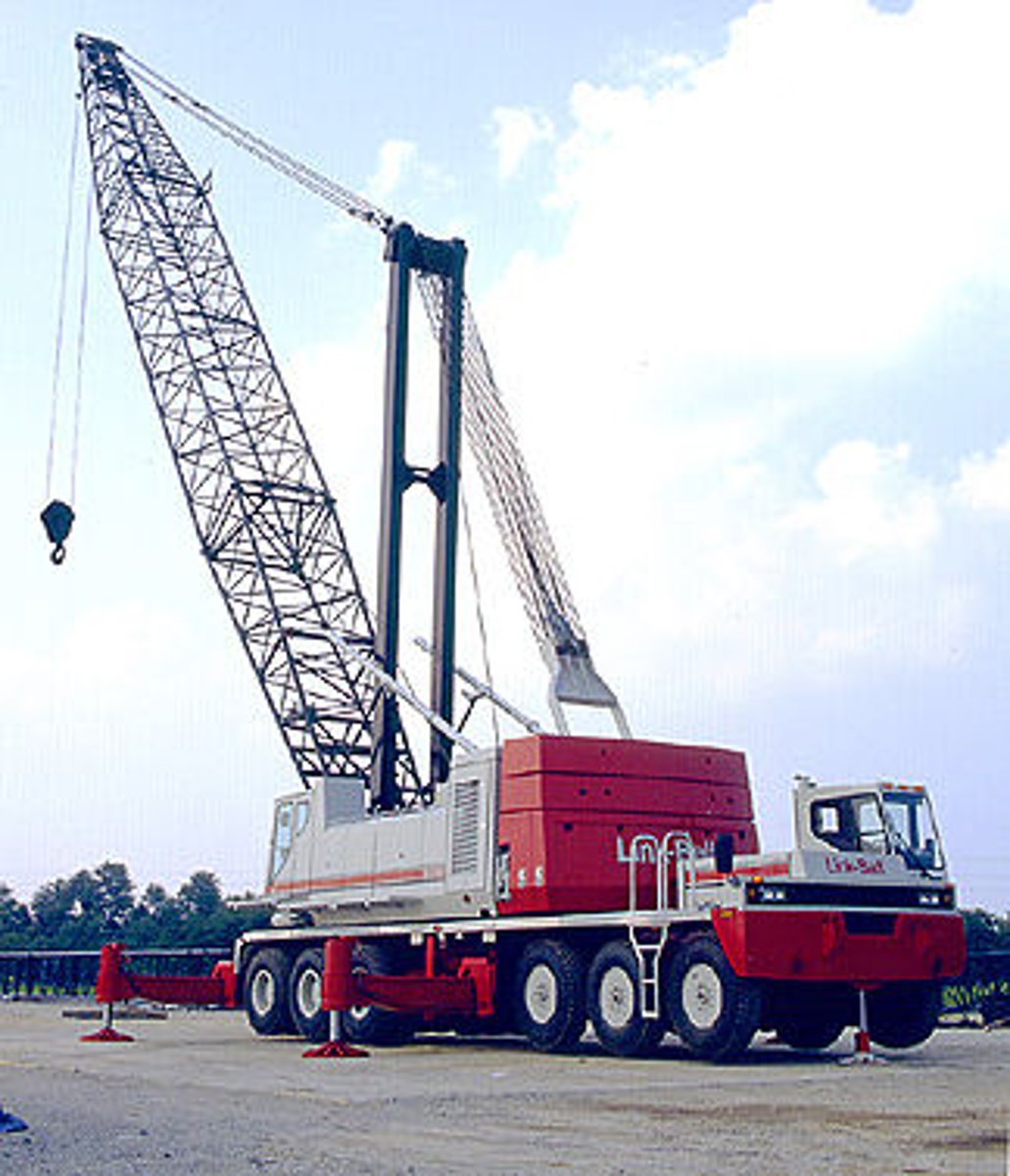
Crawler cranes
A tracked vehicle that "floats" on the soil and has a crane mechanism attached to it, can pick up and transfer a load, but hard to move between sites
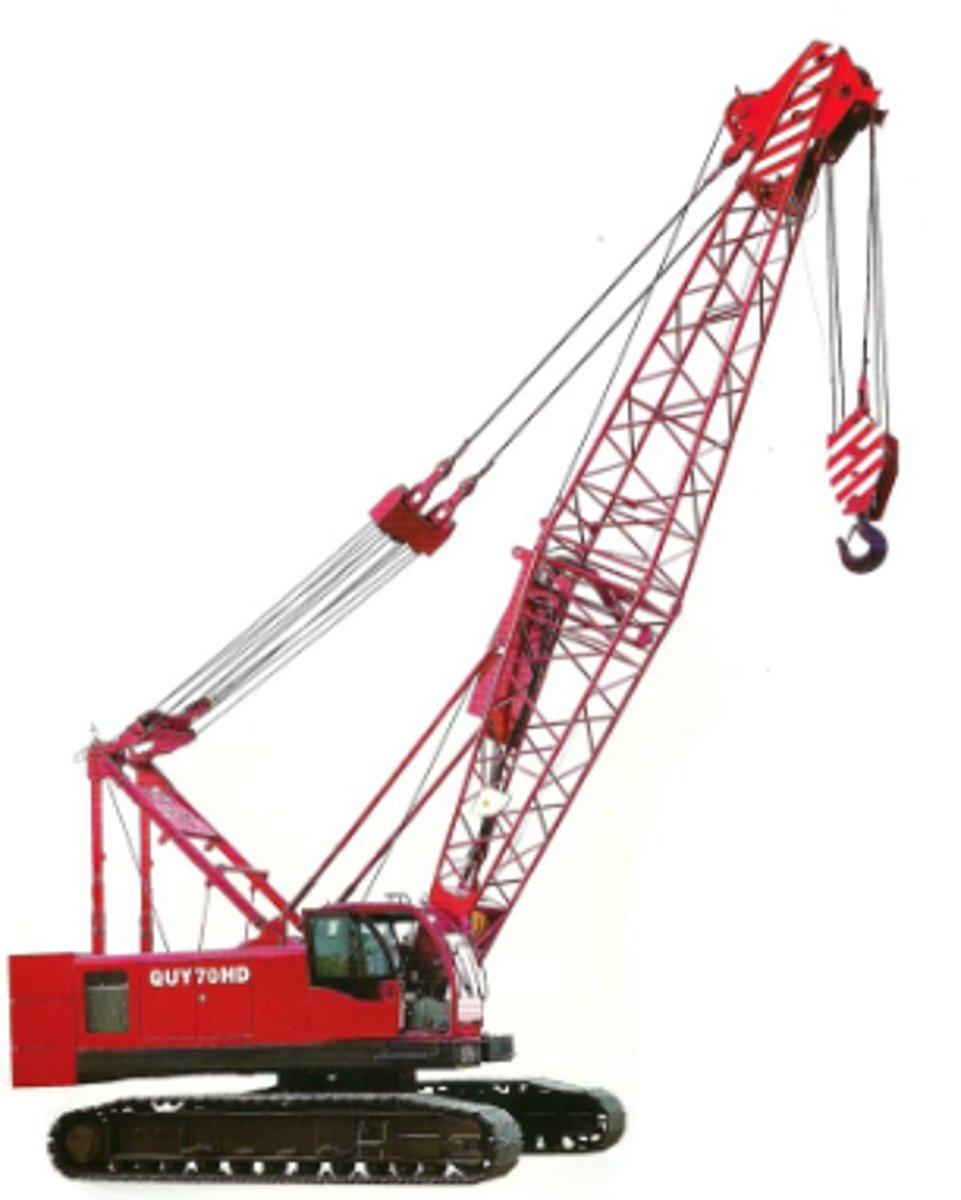

Lattice boom
Cable supported compression member
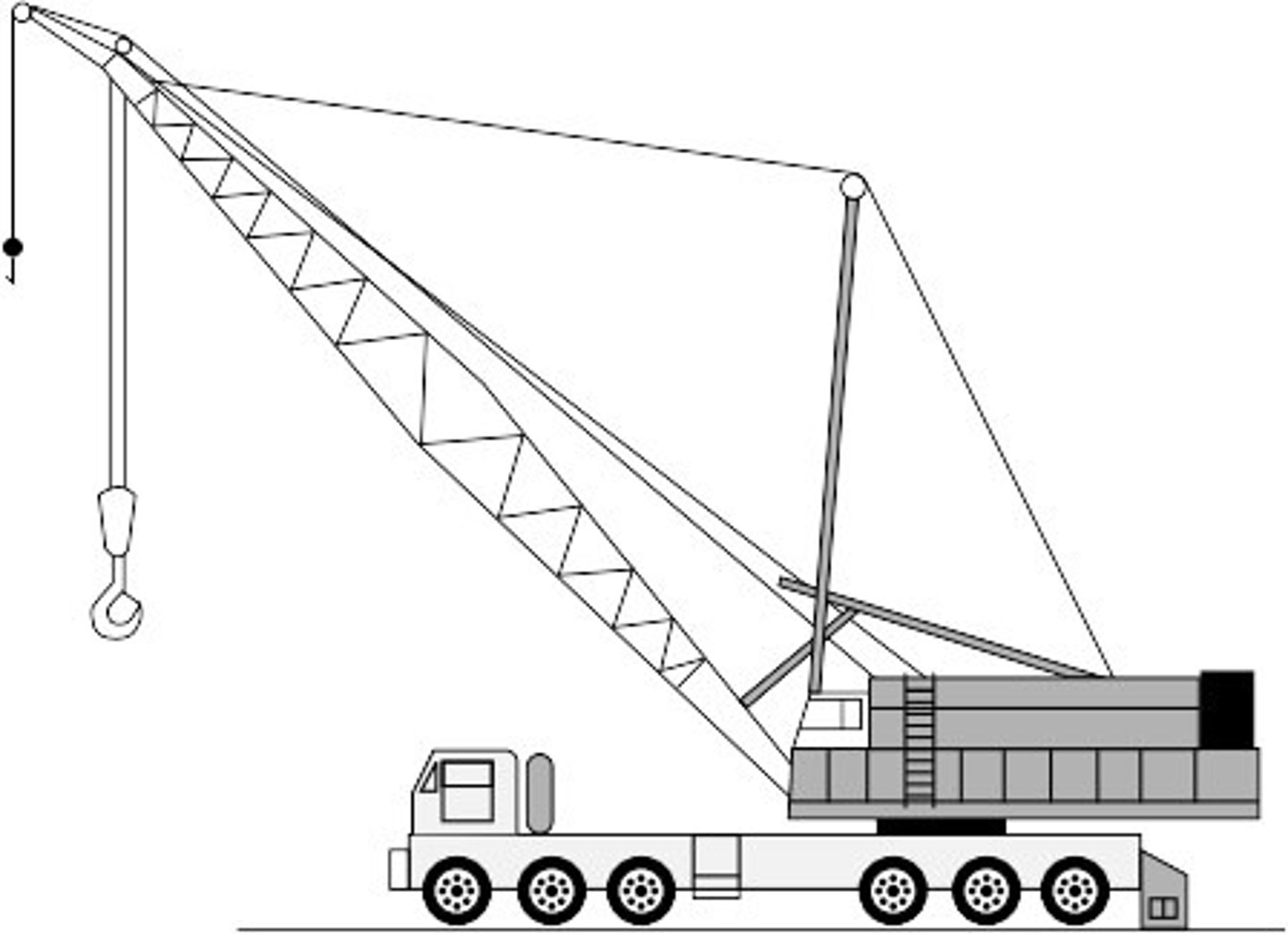
Telescoping boom
self supporting bending member
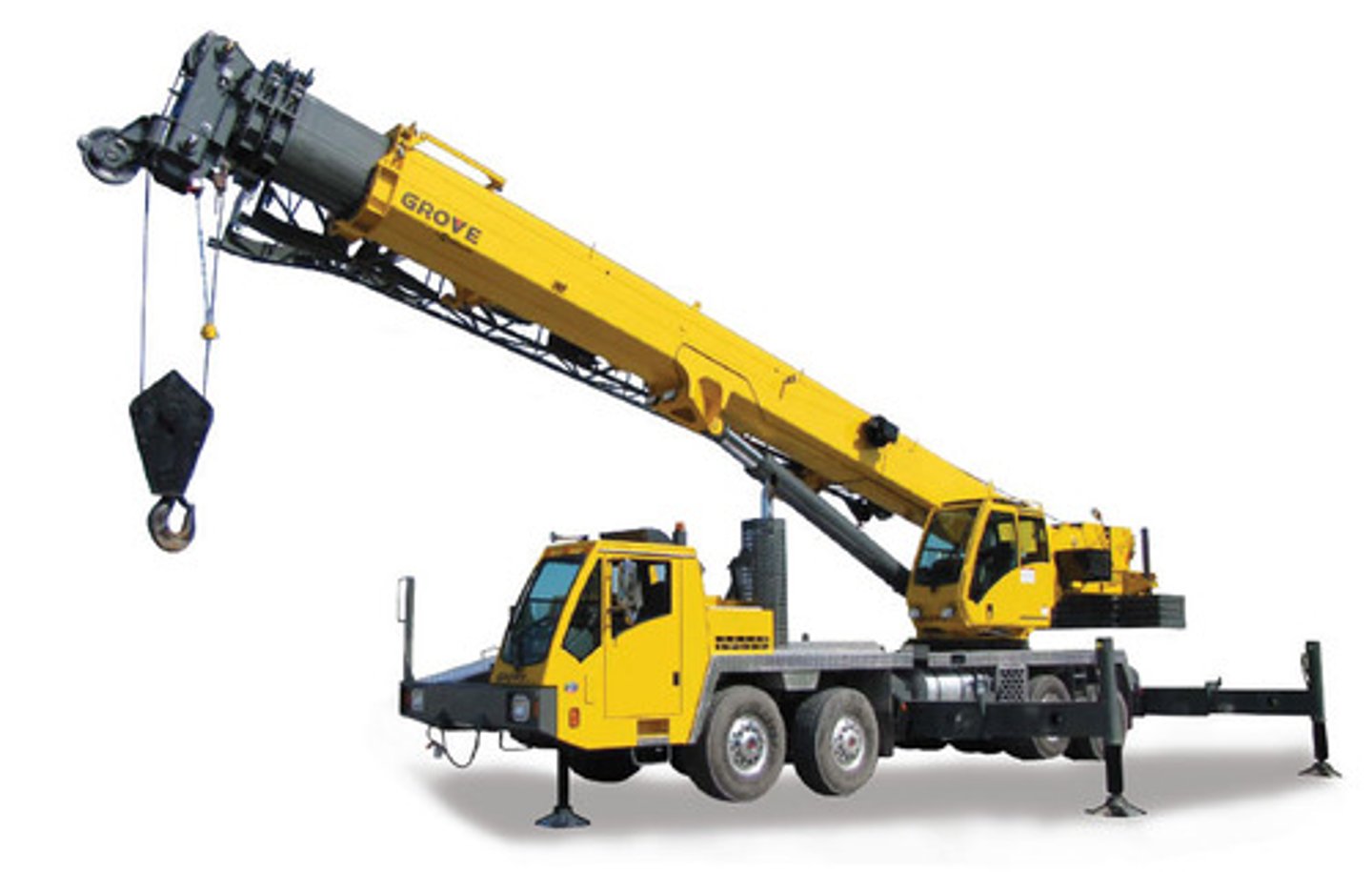

Lattice-boom truck-mounted crane
Made up of multiple steel bars welded together in a "W" or a "V" pattern. This increases the booms strength and minimizes its weight, which means additional lifting capacity.

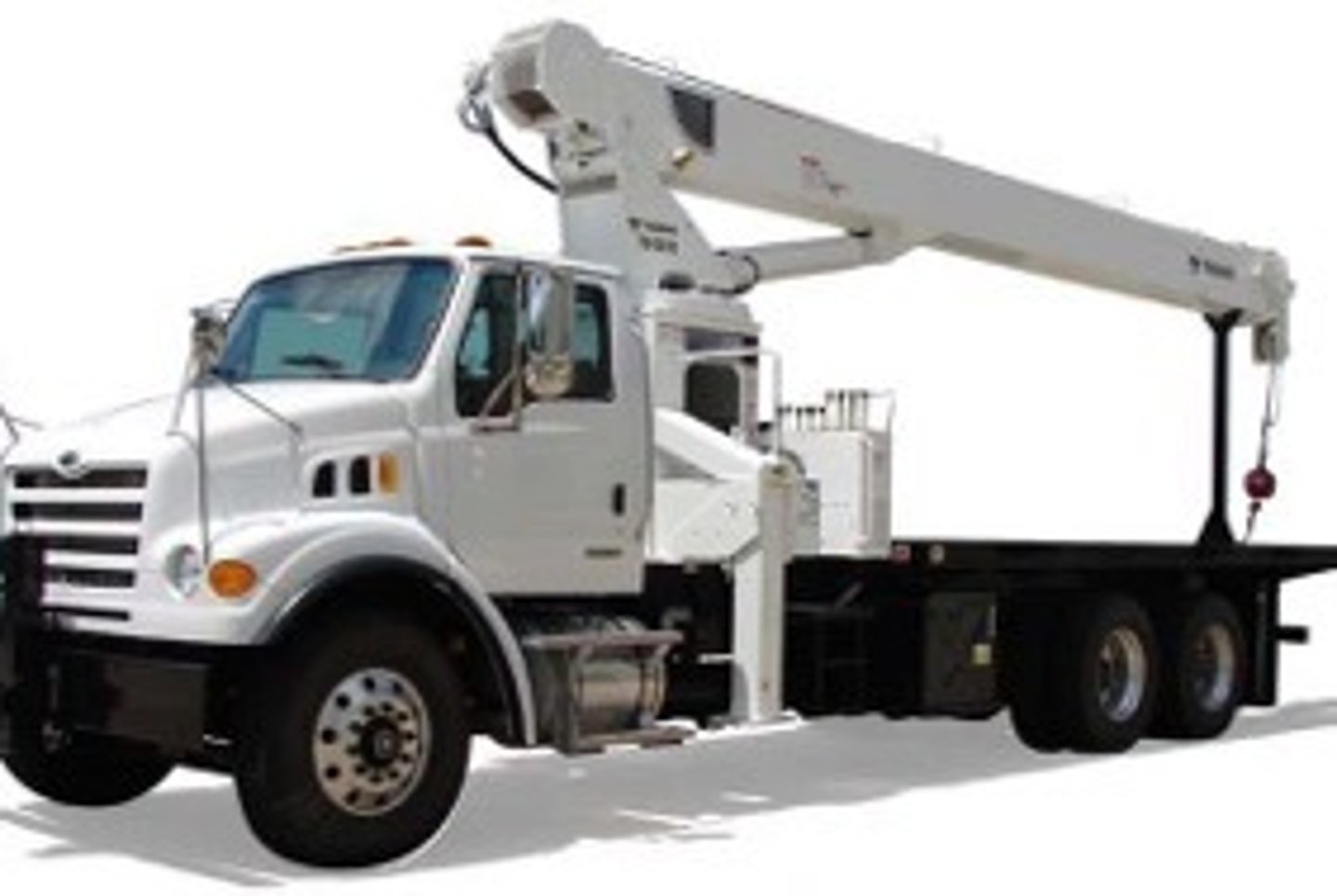
Telescopic-boom truck-mounted crane
Used to lift materials by use of a hydraulic winch and by raising and lowering the boom; operation is simple but cannot move a load. Can travel at highway speeds and move from project to project.

Outriggers
Stabilizing components for cranes
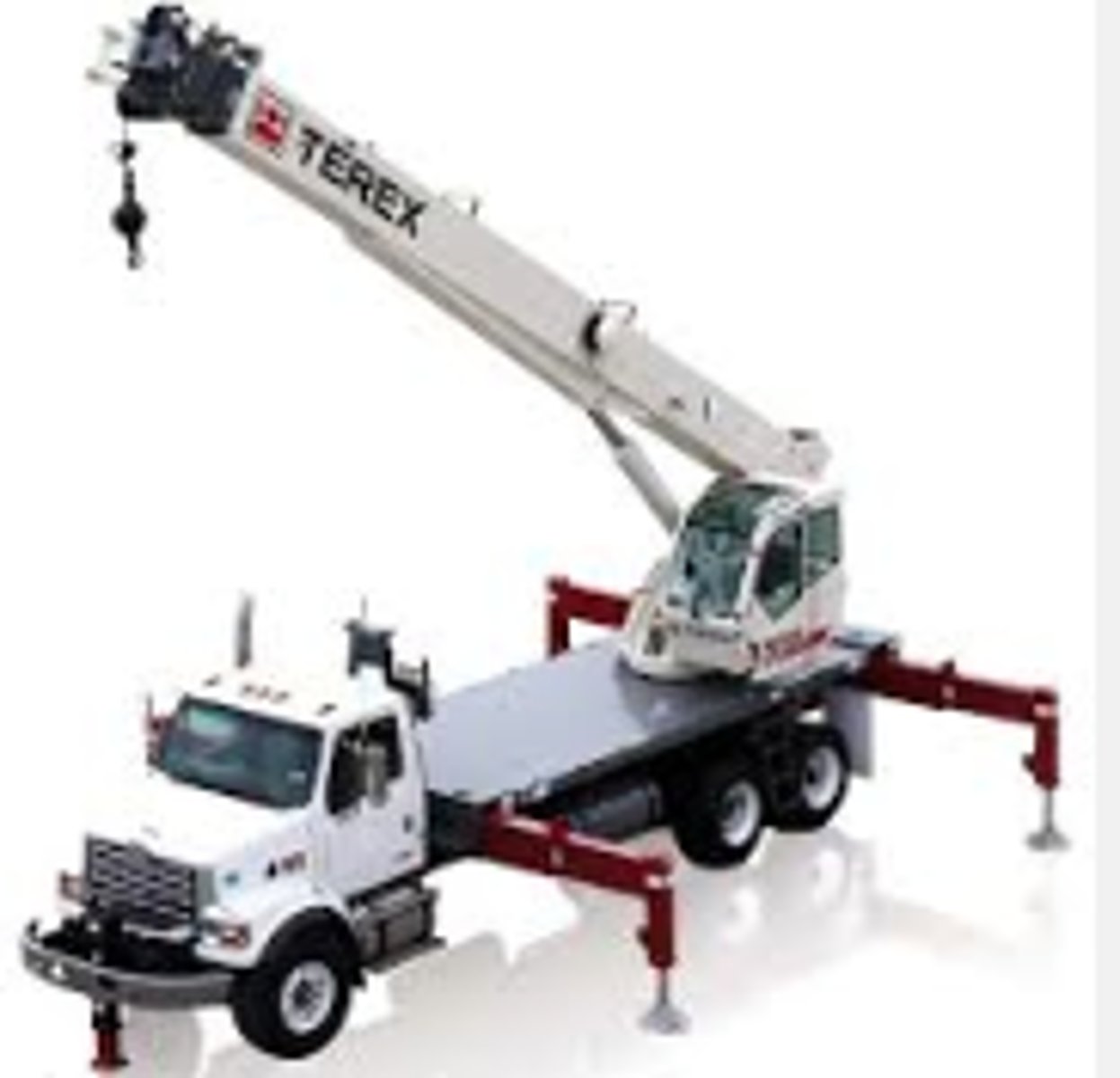

Counterweights
Balance the crane by offsetting the load

Main load line (cranes)
A cable that connects the hook block to the boom

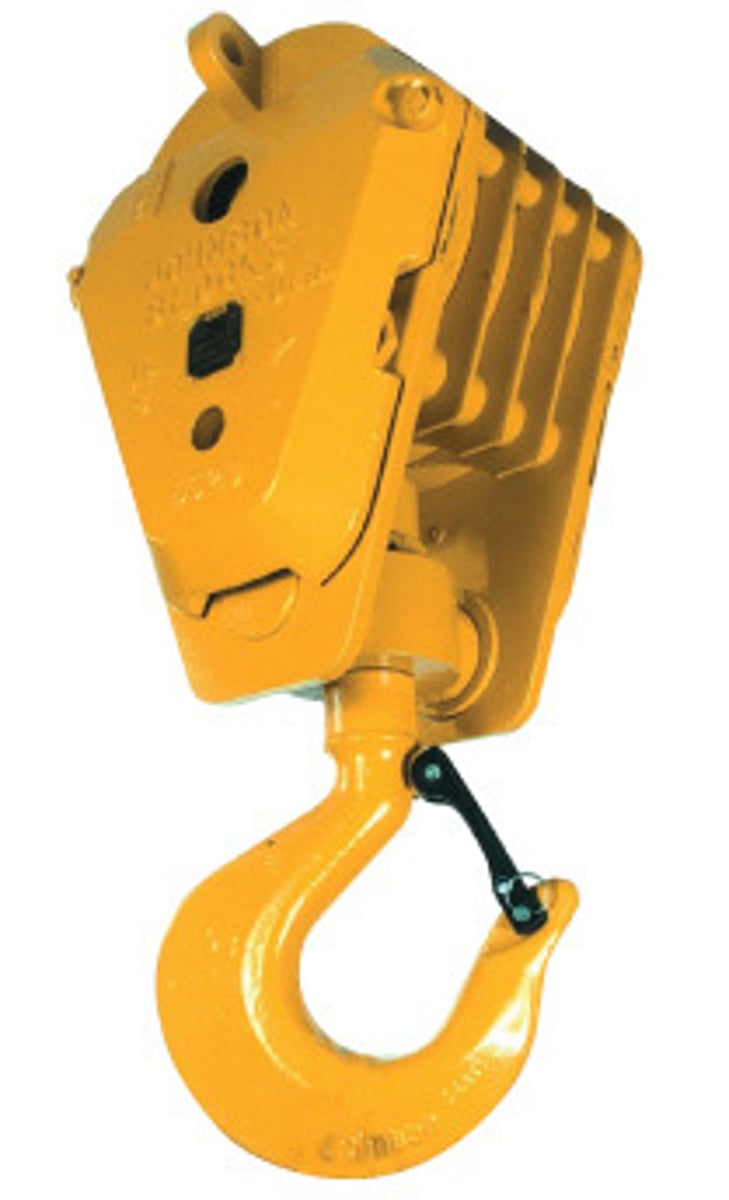
Hook block
The piece that connects the load to the crane

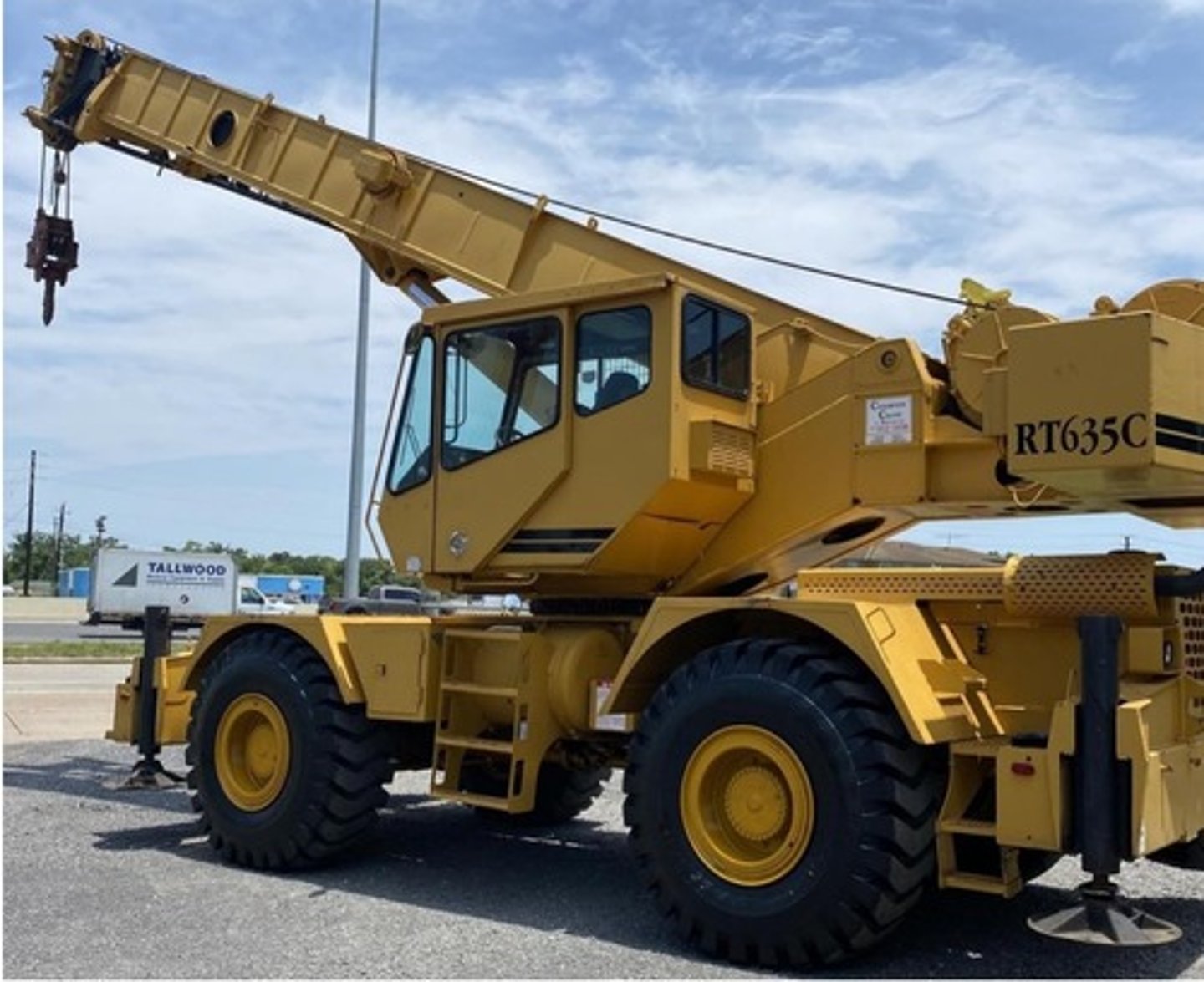
Rough terrain cranes
Used to pick and carry operations off-road and on rough terrains; outfitted with tires, outriggers, and telescopic booms. More manageable in tight areas; also known as "cherry pickers"

Reading load charts:
Above the line, loads are controlled by structural capacity. Below the line, loads are limited by machine stability.
Chain sling
The most popular due to its longevity, ease, and customizability. Getting replacement parts is easy.
Wire rope sling
Provides strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance
Fiber rope sling
Less likely to damage fragile loads; lightweight, extremely flexible, and easy to use. They are inexpensive but need replaced more often.
Spreader bar
Allows the user to attach the load at two points, evenly spreading the load throughout the bar.
Piling
Involves driving or drilling deep, vertical structural elements into the ground to support structures, especially in areas with weak soil, creating a stable foundation.
What to expect on a geotechnical report:
A general idea of subsurface conditions, a specific recommendation regarding foundation design and type, a general recommendation regarding site grading, floor slab and pavement support recommendations, and sometimes retaining wall and pavement section recommendations.
What not to expect on a geotechnical report:
Earthmoving assessment, earth moving quantities, or cost analysis.
Overloading
Takes a toll on equipment; premature aging and increased maintenance/repair
Required power
The power needed to overcome resisting forces and cause machine motion
Rolling resistance
The resistance of a level surface to constant-velocity motion across it; a measure of the force to be overcome to rotate a wheel over the surface on which it makes contact.
Rolling resistance is caused by:
Internal friction, tire flexing, and tire penetrating a surface
Grade resistance
The force-opposing movement of a machine up a frictionless slope; assists the machine when traveling down grade
Rolling resistance expressed in % grade
(Rolling resistance / 20 lb/ft) = G %
Total resistance equation
TR = Rolling resistance + Grade resistance
Power available
Engine horsepower and operating gear are the primary factors that determine the power available the the drive wheels (drawbar) of a machine.
Horsepower
A unit of measurement of power or the rate of which work is done
Rimpull
The tractive force between the tires of a machine’s driving wheels and the surface on which they travel; if you are on mud, you have less traction creating less power to be delivered from the wheel to the ground. (Changes based on speed)
Rimpull equation
(375 x hp x .85 eff) / speed (mph) = (lbs)
Usable power
Depends on project conditions such as the haul road surface conditions, altitude, and temperature. The coefficient of traction is the ratio between the maximum amount of pull a machine exerts before slippage and the total weight of drivers.
Altitude limits power
If equipment works at higher altitudes, where the air is less dense, the engine may produce at a reduced power output.
Travel time equation
TT Haul = (Haul distance (ft) / 88 x Speed (mph))
Compaction
Mechanically densifying materials by adding friction from the interlocking of particles; can improve load-bearing capacity, control shrinkage & swelling, and reduced permeability.
Permeability
The state or quality of a material or membrane that causes it to allow liquids or gases to pass through it.
Soil gradation, moisture content, and compaction effort
3 major factors that influence soil density
Subgrade
A surface of earth or rock leveled off to receive a foundation
Subbase
Underlying support placed below what is normally constructed as a base
Static weight, impact, vibration, and kneading
How can you increase density?
Pneumatic roller
Machine can feature one or two multiple rows of rollers at the front and/or rear; provides better paving by having better grip than other options, achieving a better density, and improves the look of the finished product.
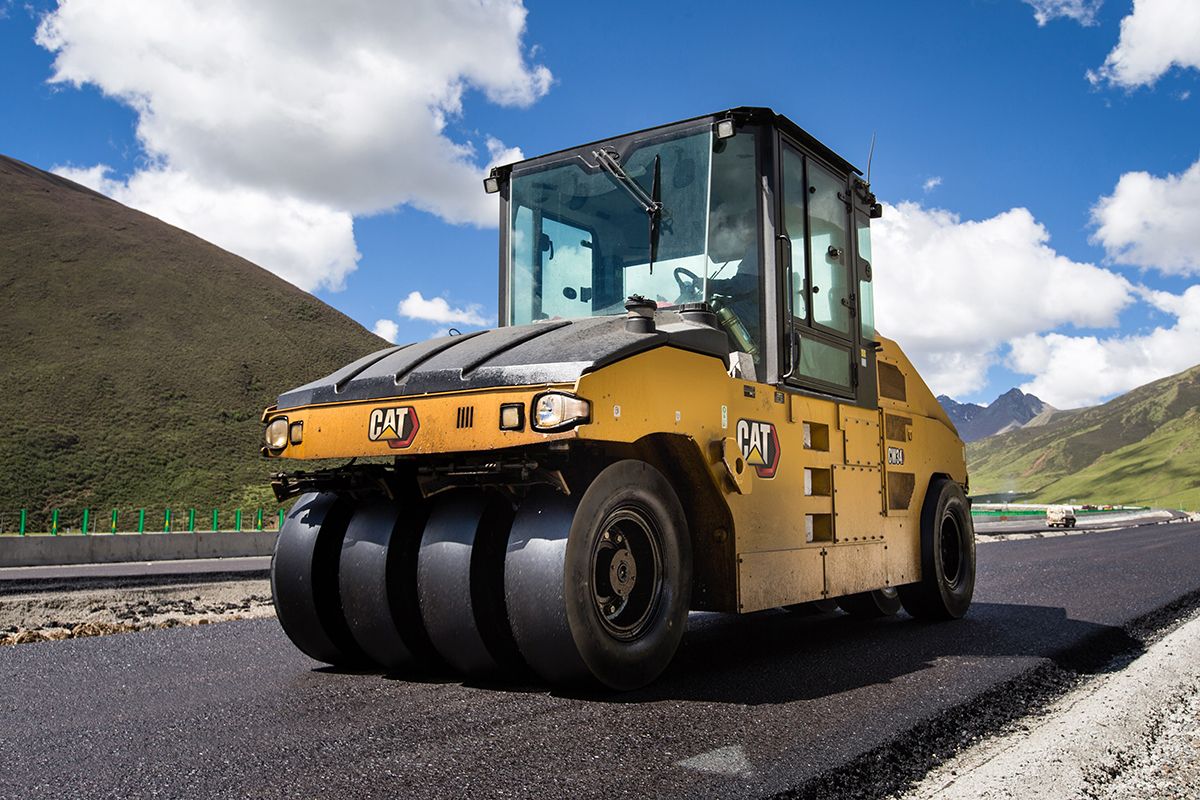

Vibratory roller
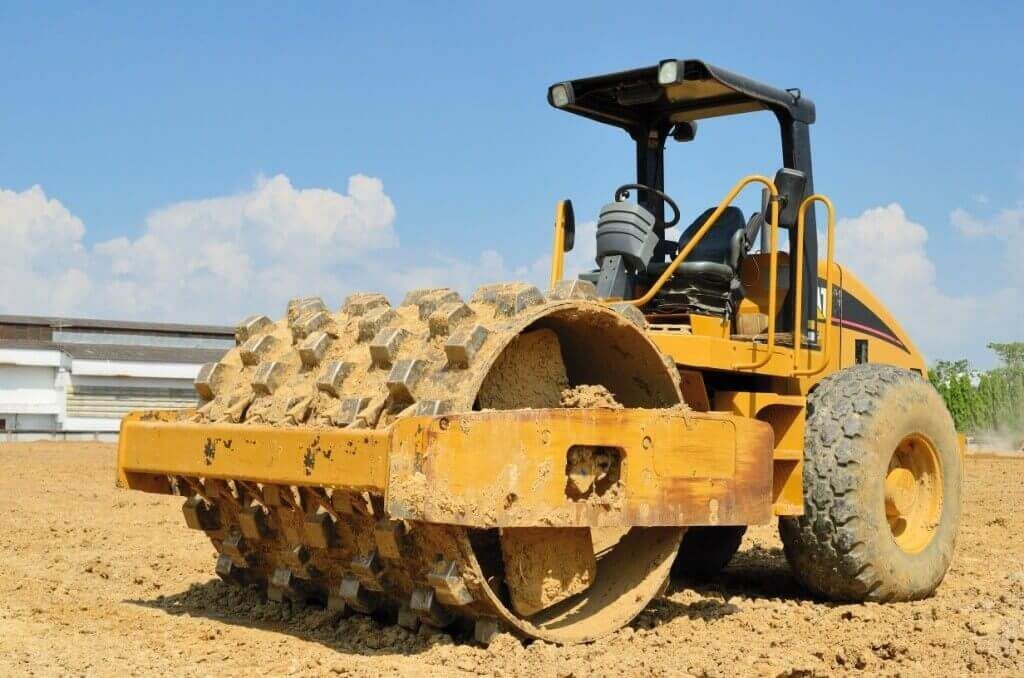
What machine is this?
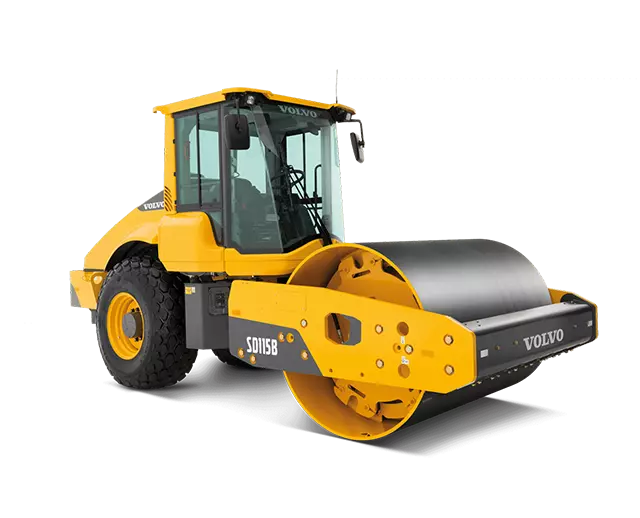

Tamping foot (Sheepsfoot) roller
Suitable for compacting all fine-grained soils, but generally not suitable for use on cohesionless granular soils.
