Benign Epithelial Pathology
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
HPV
• Double stranded DNA virus
• Tropism for squamous epithelium (likes to infect skin and mucosa)
• Most individuals are asymptomatic
• Transmission through sexual and nonsexual person-to-person
contact, salivary transfer, contaminated objects, autoinoculation,
breast-feeding, perinatal transmission, and, possibly, prenatal
transmission
yes
is squamous papilloma associated with HPV
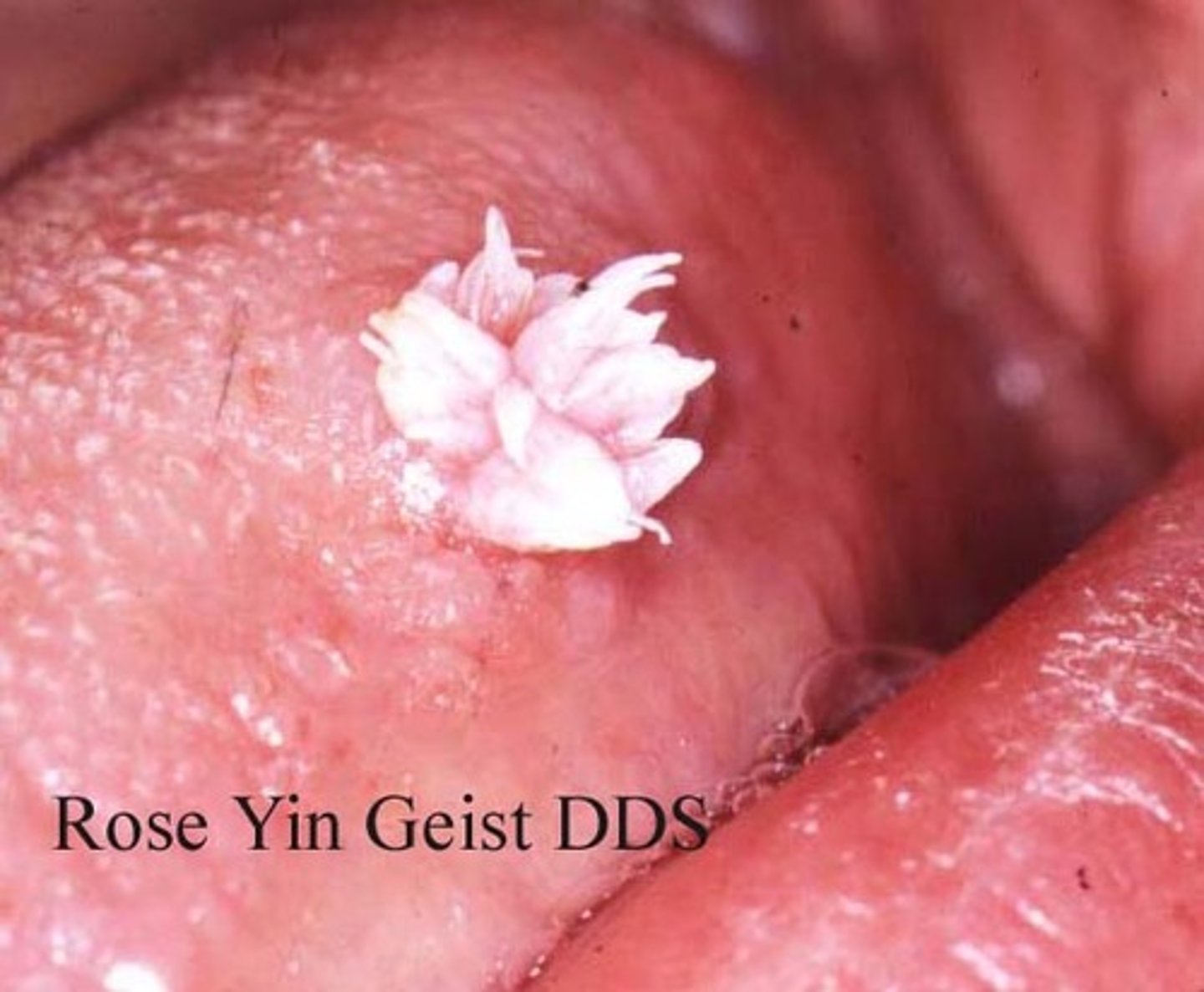
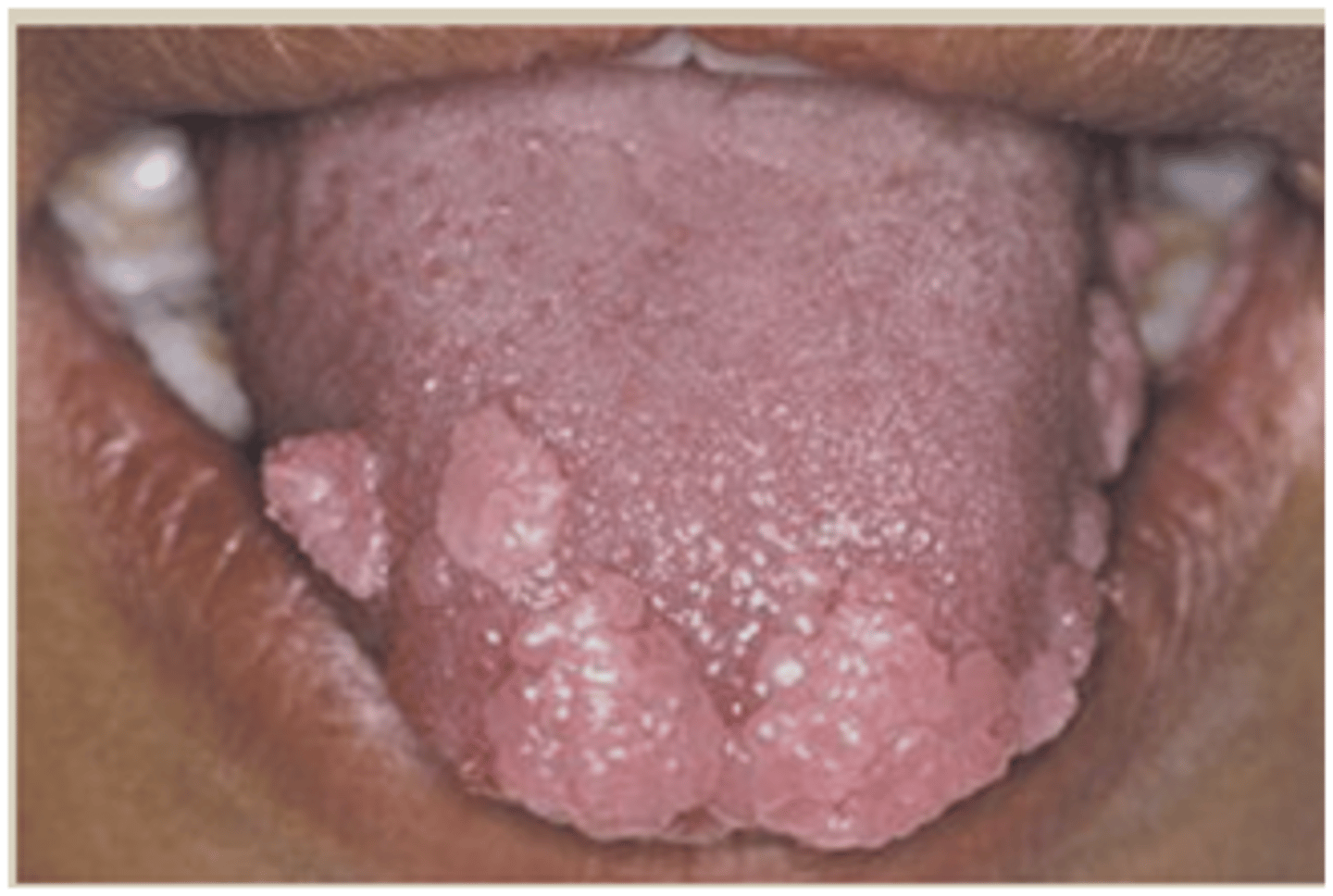
squamous papilloma
Which benign epithelial lesion:
• Benign papillary or verruciform
lesion
• HPV types: 6 and 11 (low-risk)
• Very common
• Tongue, lip, soft palate
• Can occur at any age
• Asymptomatic
• 0.5 cm to 3.0 cm
• Soft, painless, exophytic nodule
• Finger-like projections
• Cauliflower or wart-like
• May be pink or white
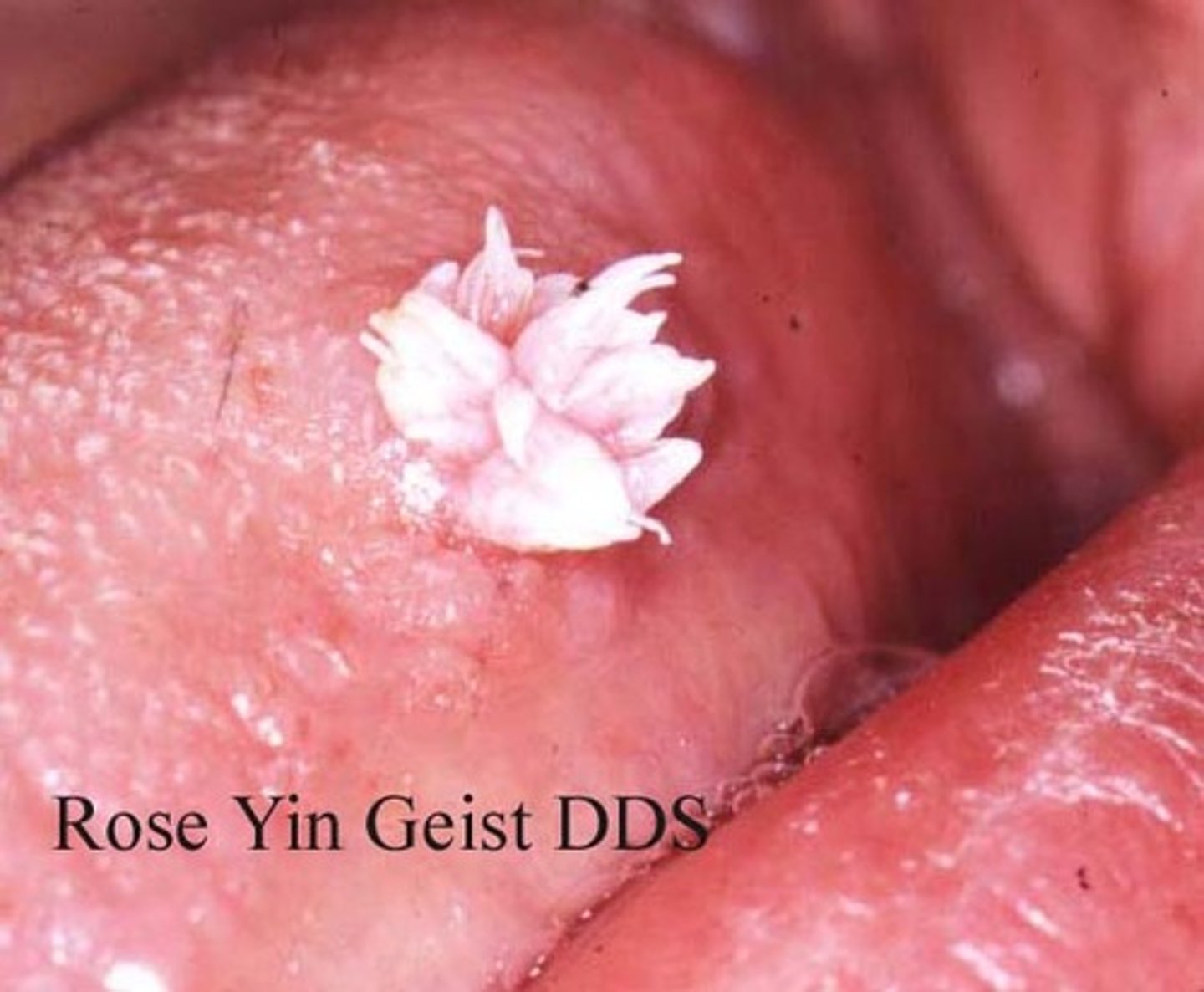
squamous papilloma
histology of which benign epithelial lesion:
• Finger-like projections
• Fibrovascular cores
• Koilocytes (virally-altered
epithelial cells)
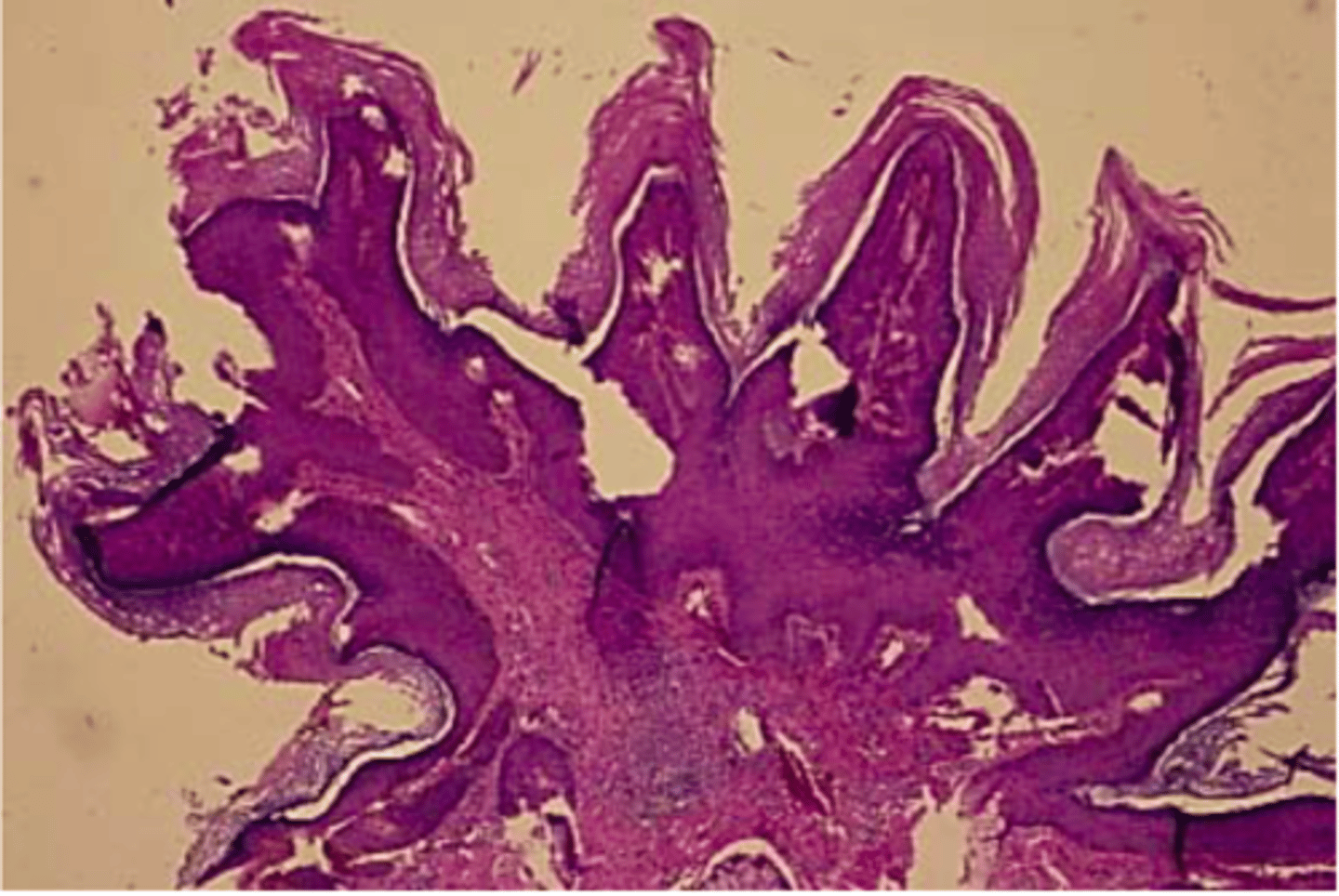
squamous papilloma
squamous papilloma
treatment for which benign epithelial lesion:
• Conservative surgical excision
• No malignant transformation
yes
is verruca vulgaris associated with HPV
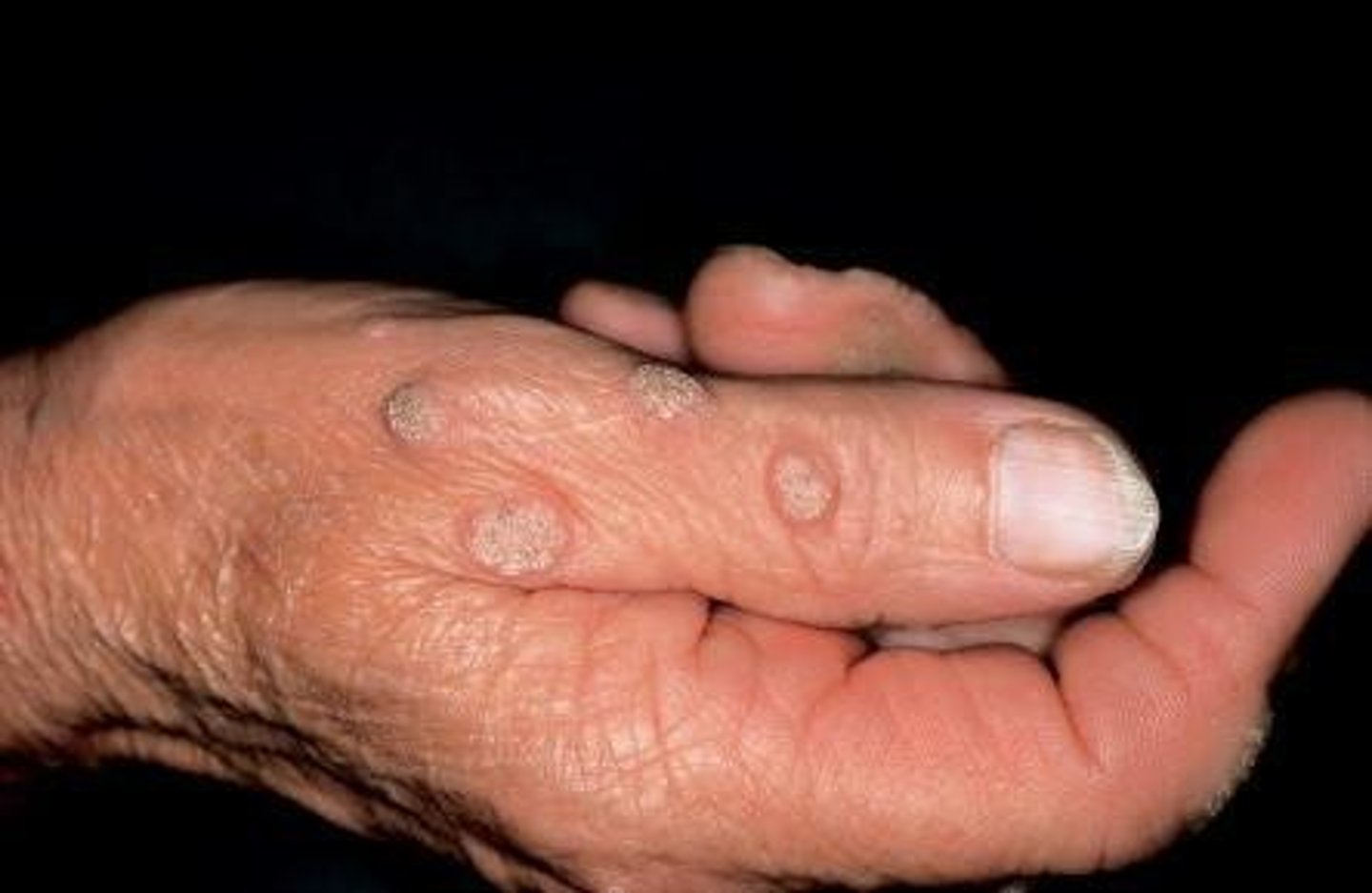
verruca vulgaris
Which benign epithelial lesion:
• HPV Type: 2 (low-risk)
• Occur on the skin much more
commonly than the oral mucosa
• Most common in kids
• May be multiple
• Painless papule or nodule
• Papillary projections
• Rough, pebbly surface
• Usually white when in the oral
cavity
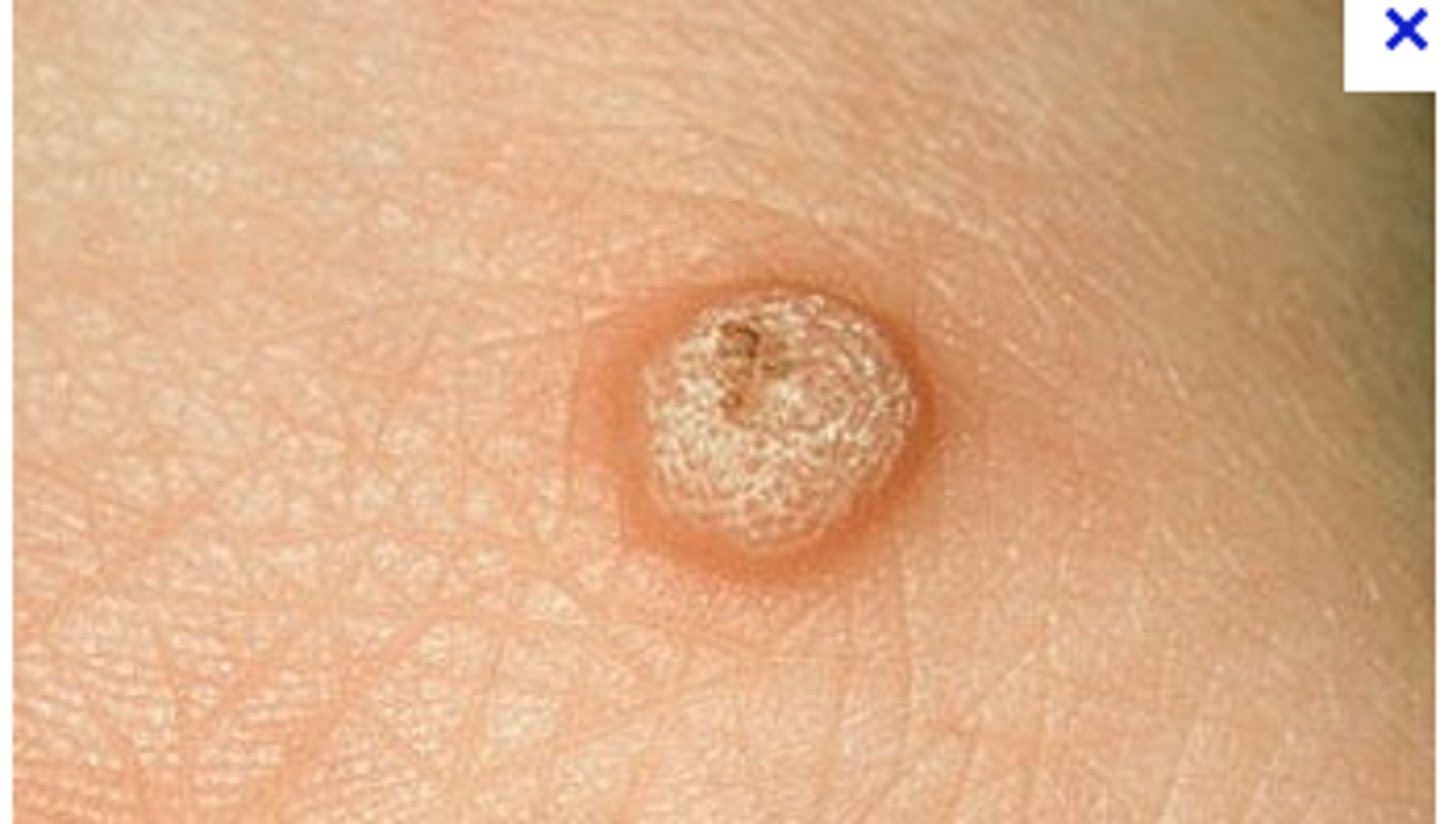
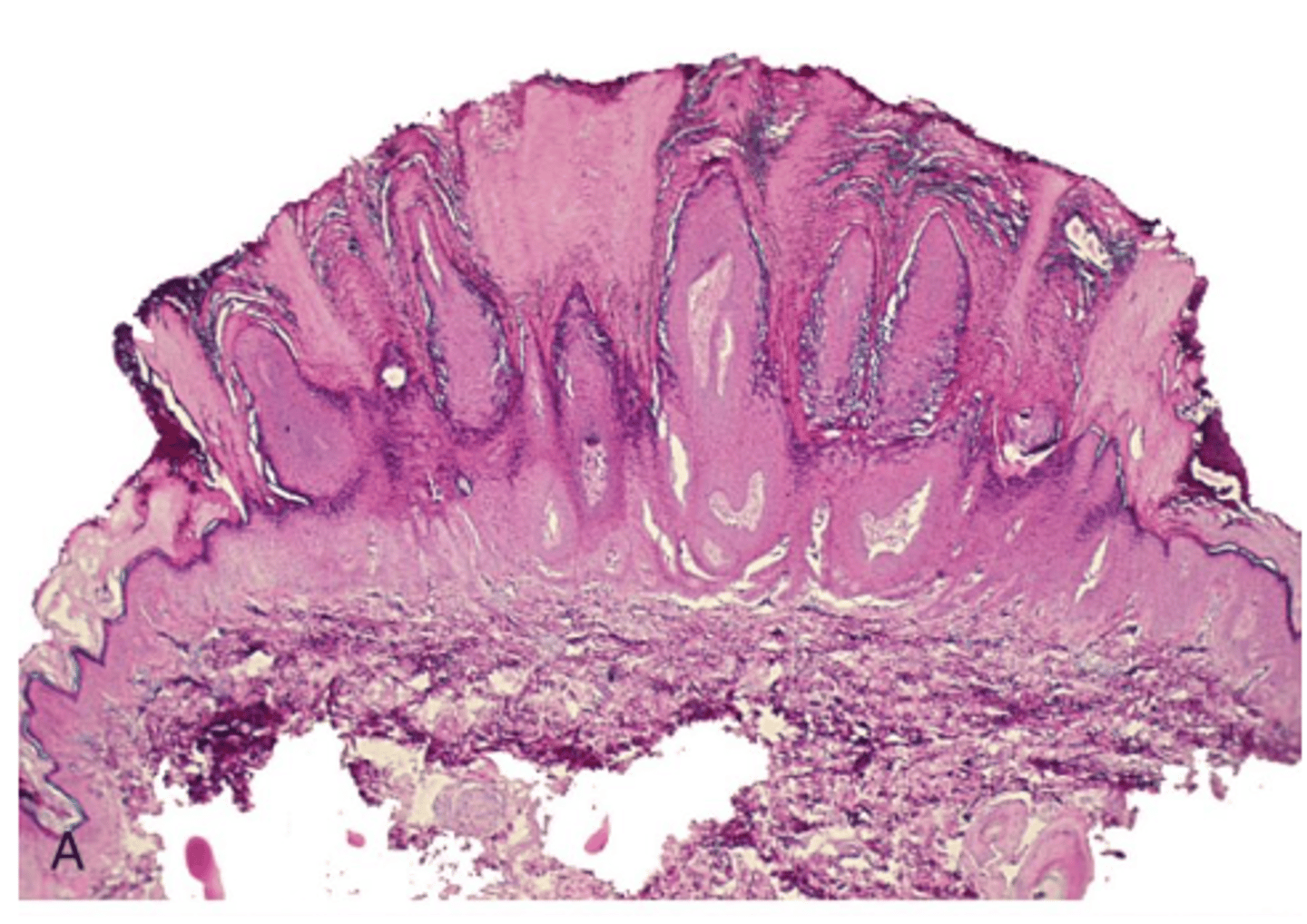
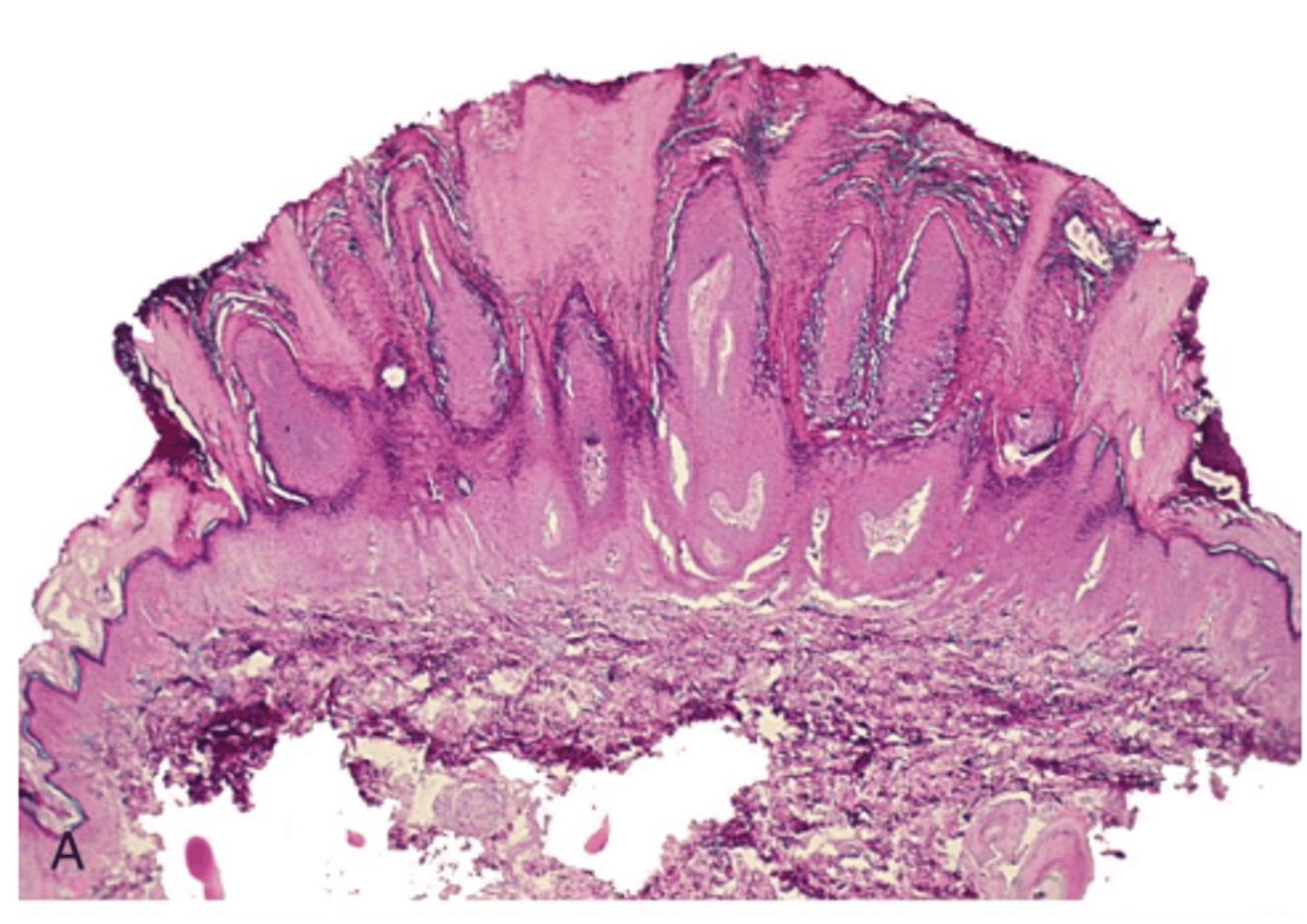
verruca vulgaris
histology of which benign epithelial lesion:
• Very, very similar to squamous
papilloma
• Hyperkeratotic
• Finger-like, pointed projections
• Cupping effect
• Koilocytes
verruca vulgaris
treatment for which benign epithelial lesion:
• Surgical excision
• 2/3 disappear spontaneously
with no treatment
• No malignant transformation
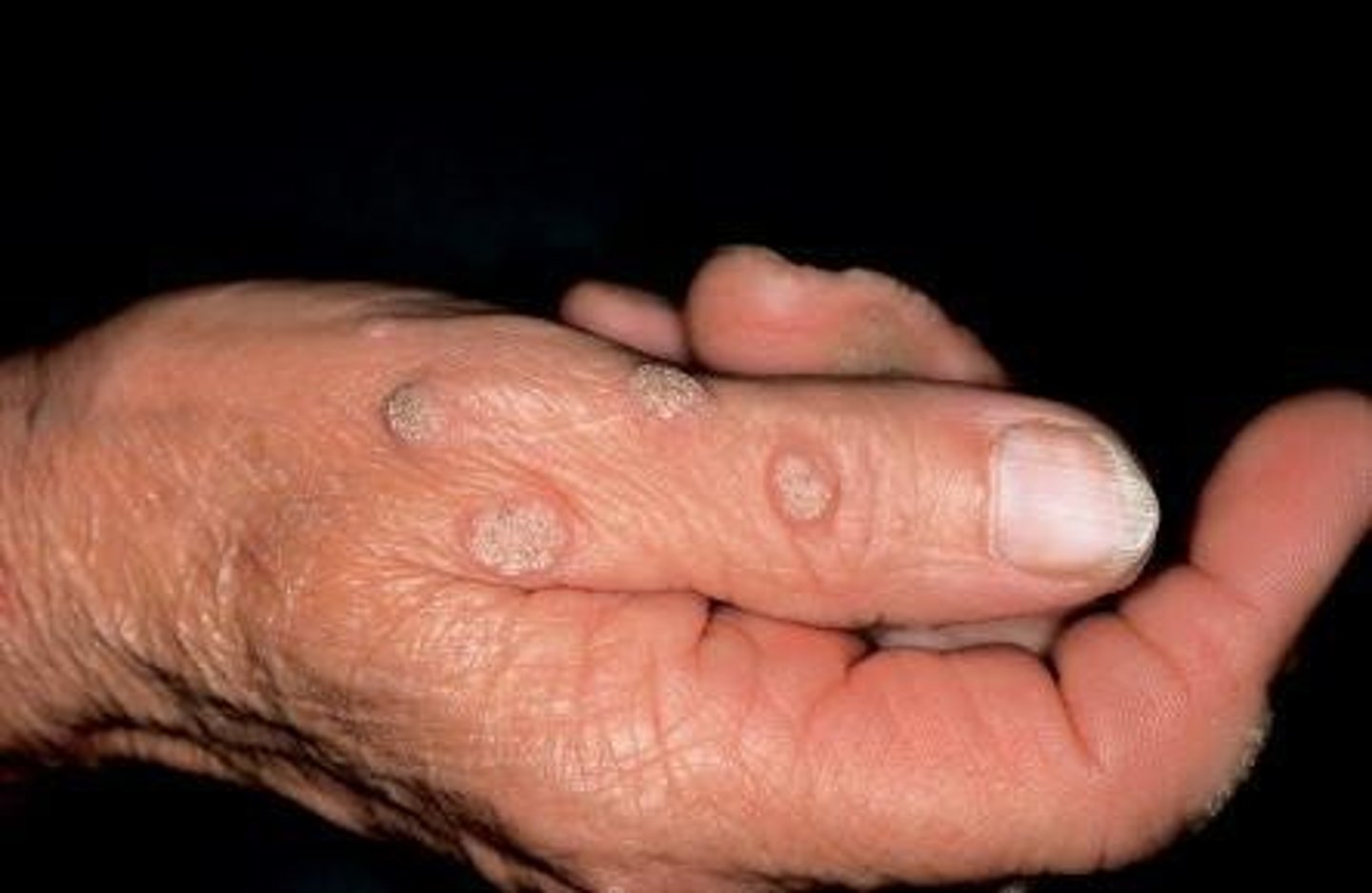
verruca vulgaris
verruca vulgaris histology
yes
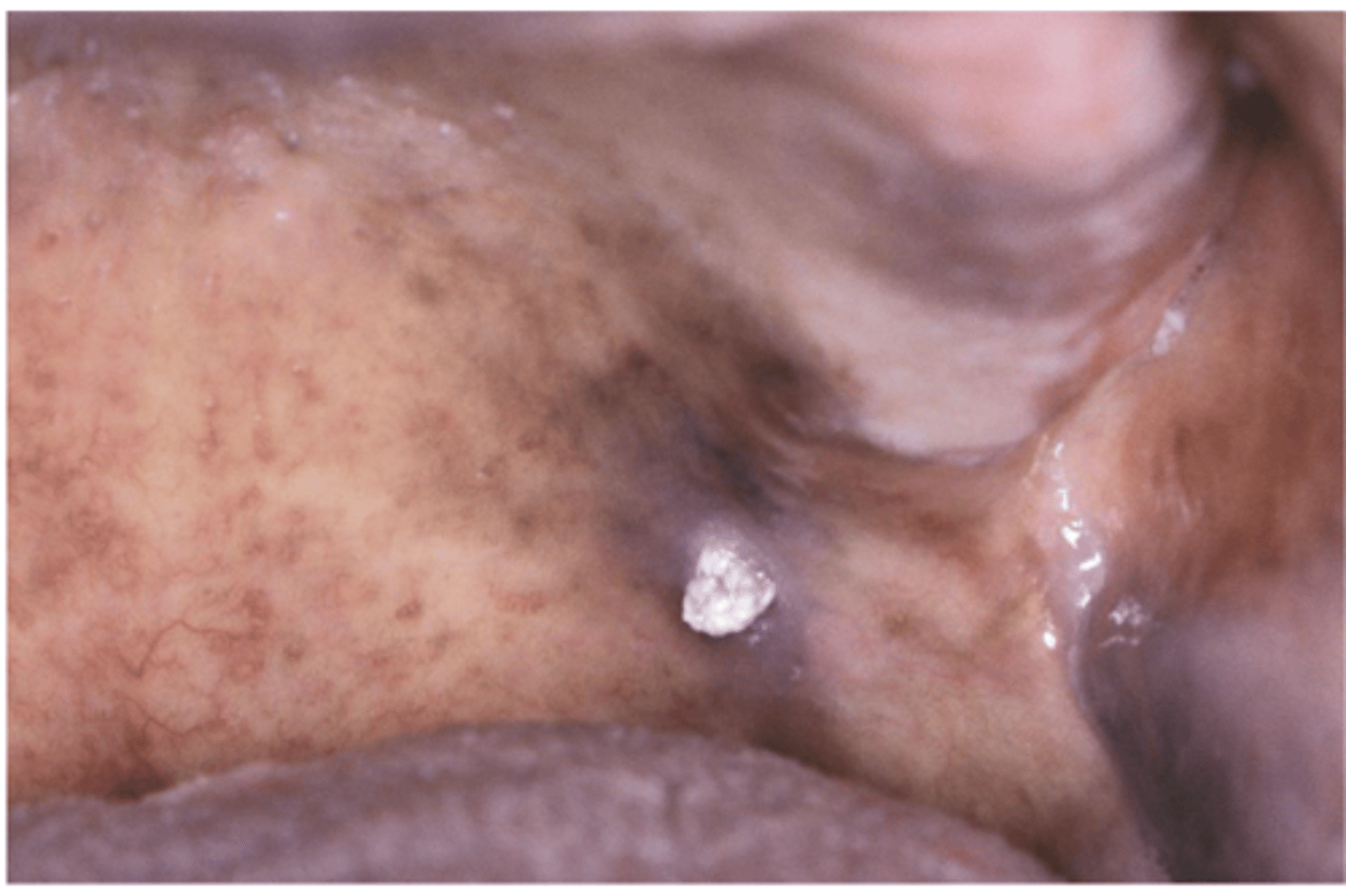
are condyloma acuminatum associated with HPV
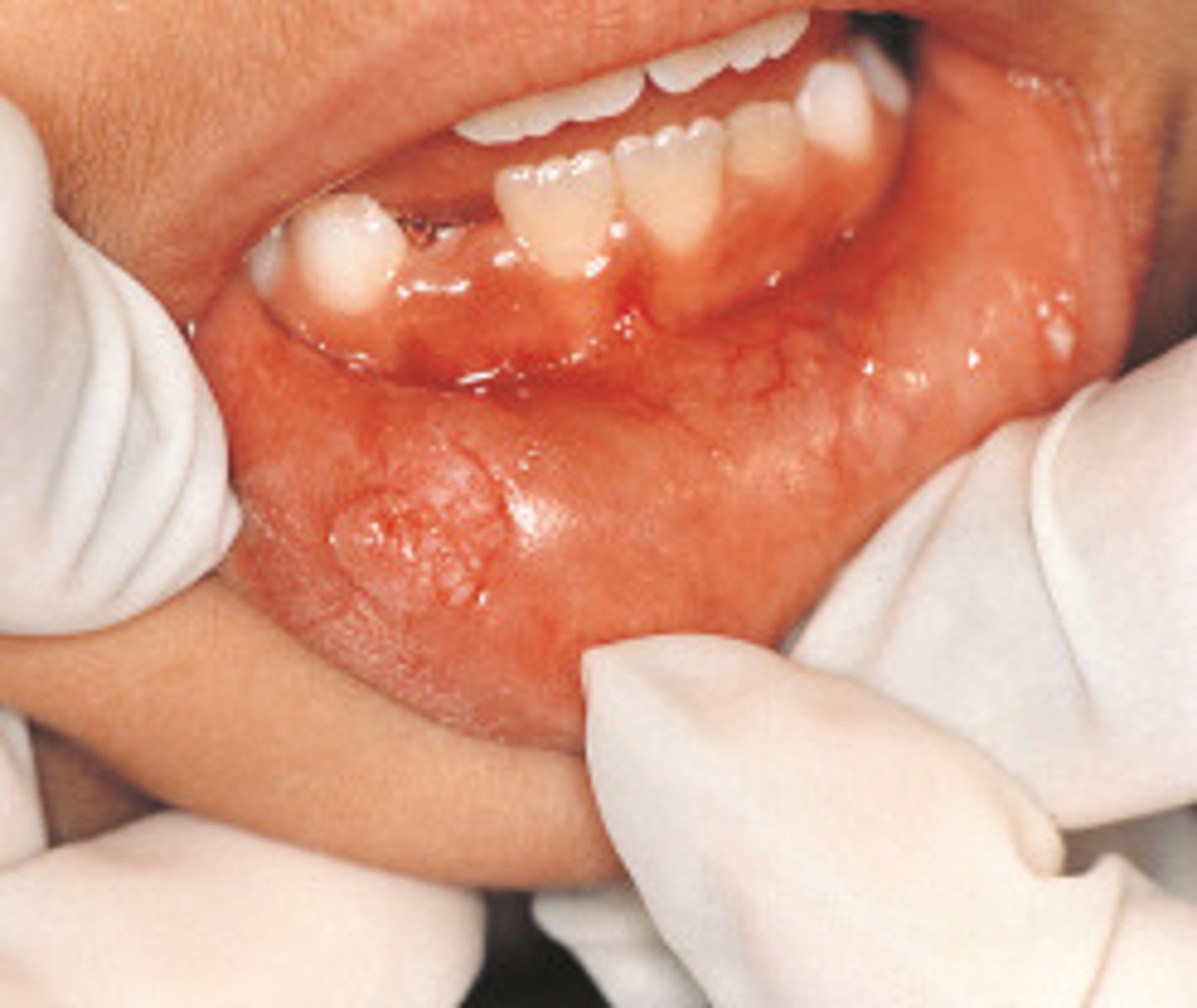
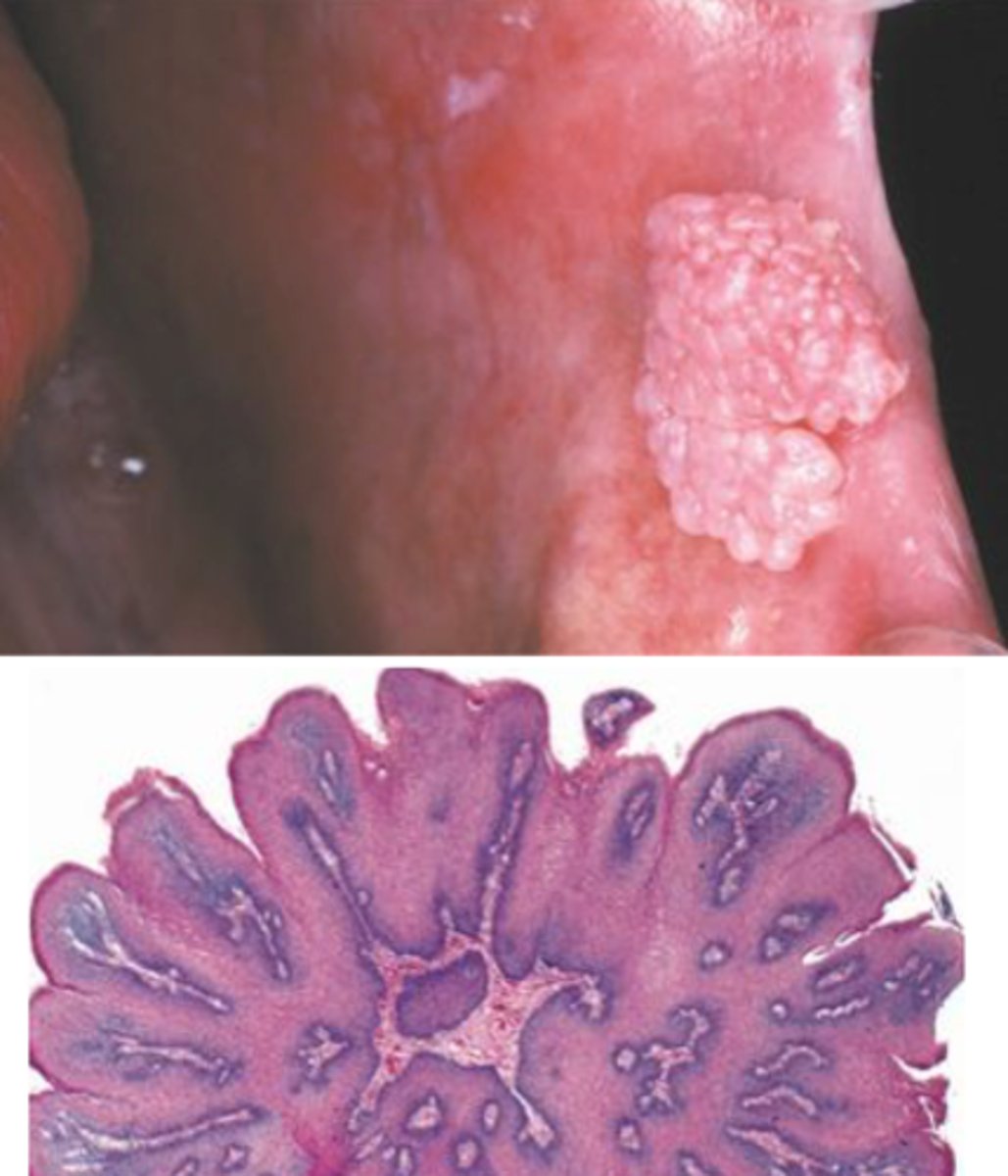
condyloma acuminatum
Which benign epithelial lesion:
• Can involve any mucosal
surfaces
• Usually attributed to HPV 6, 11
(low-risk)
• Autoinoculation is possible
• Sessile
• Pink
• Non-tender
• Exophytic mass
• Short, blunted projections
• Multiple/clustered
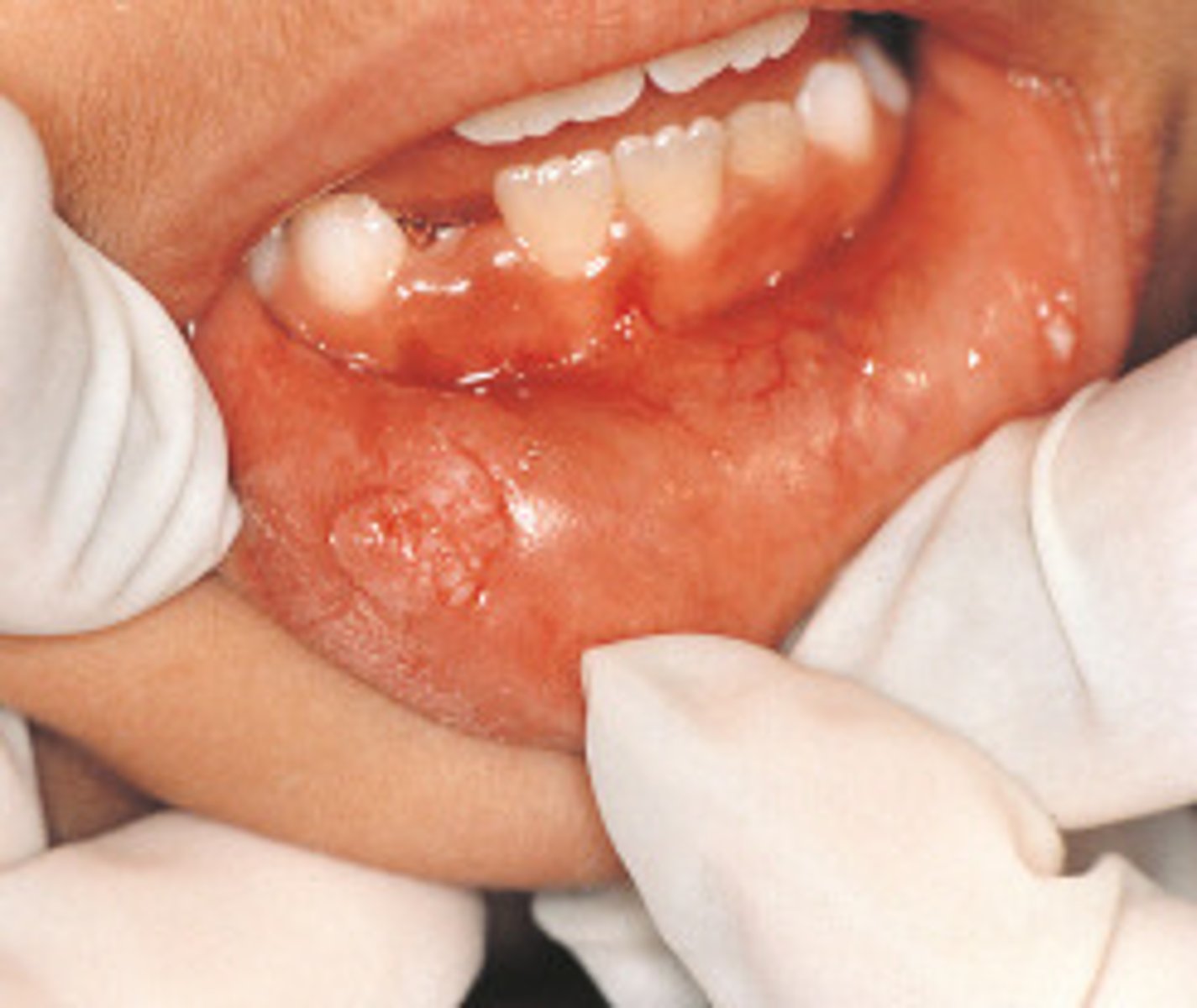
condyloma acuminatum
treatment for which benign epithelial lesion:
• Conservative surgical excision
• Vaccine for prevention
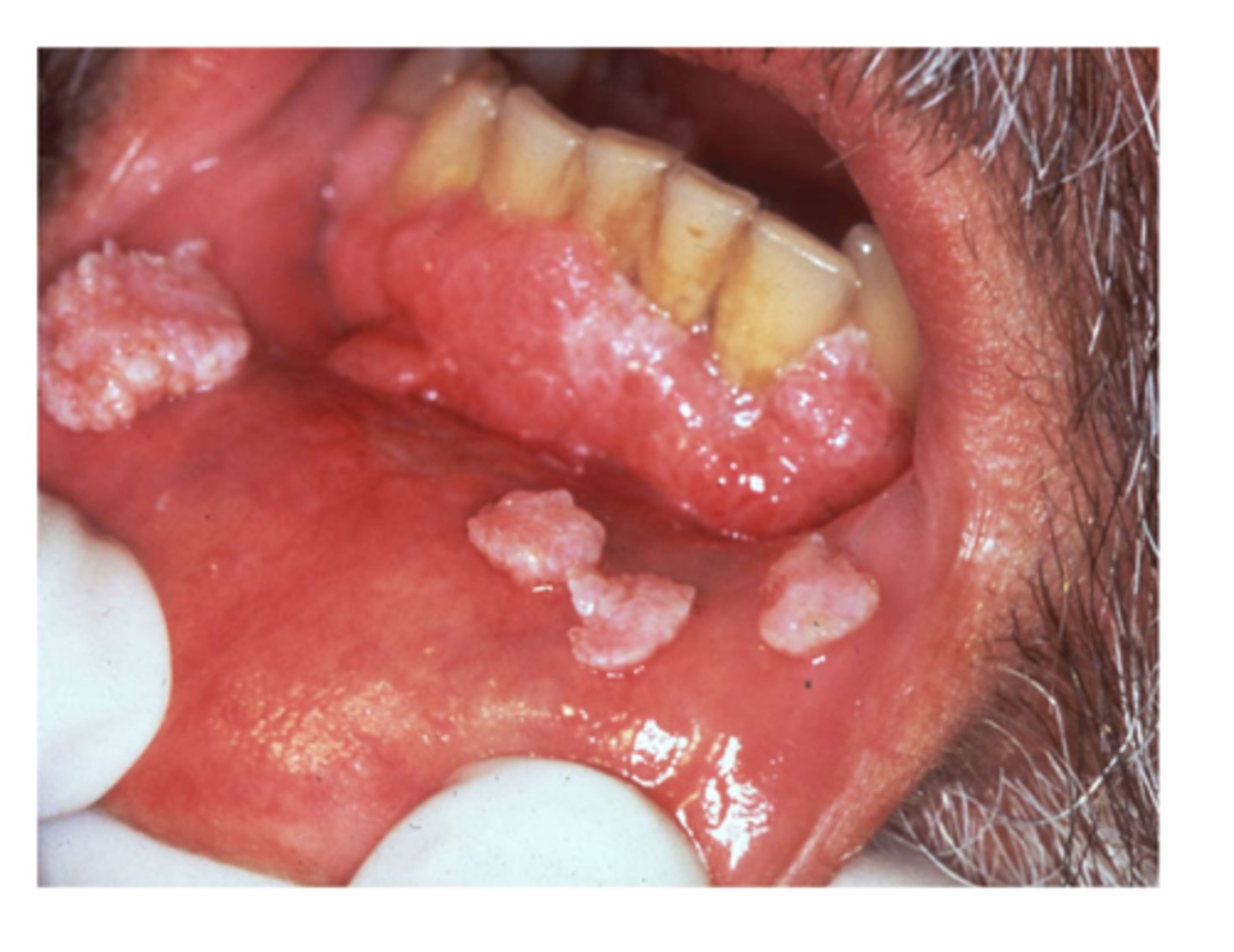
condyloma acuminatum
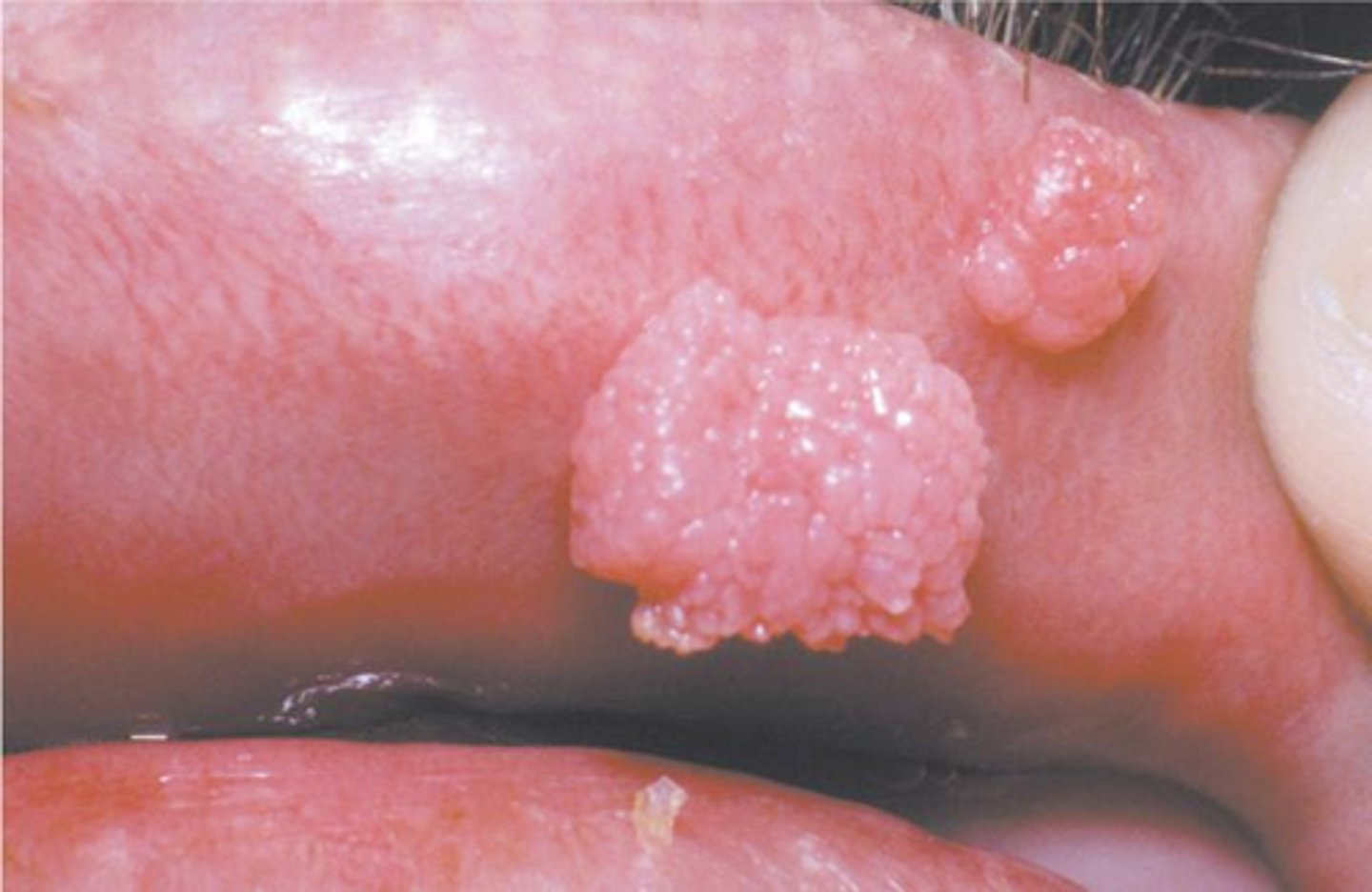
yes
is multifocal epithelial hyperplasia associated with HPV
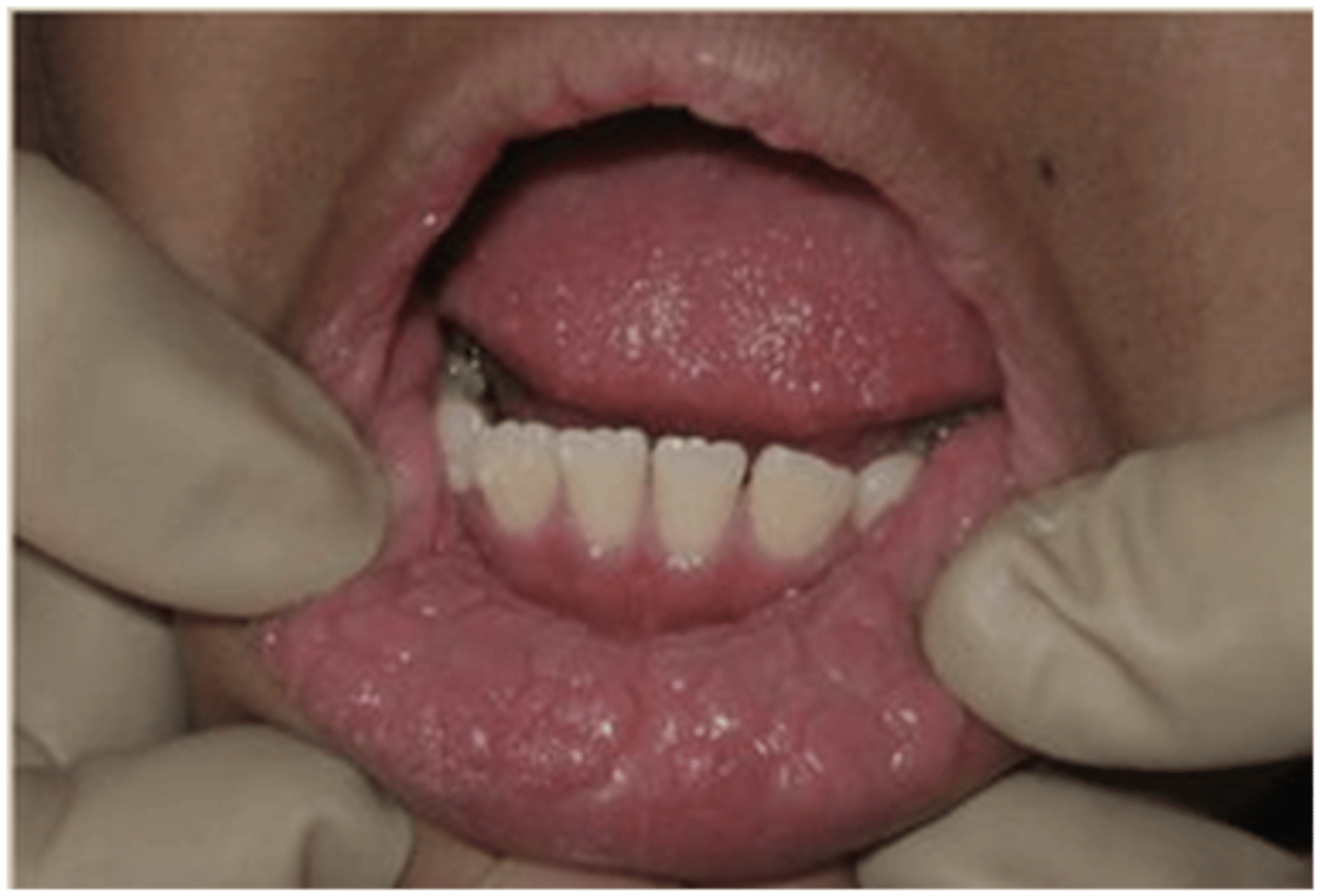
Multifocal Epithelial Hyperplasia
Which benign epithelial lesion:
• HPV types 13 and 32 (low-risk)
• Usually affects children and
household transmission is
common
• Multiple
• Small (0.1-1.0cm)
• Pink
• Well-demarcated
• Flat-topped or round
papules/nodules
• "Cobblestone"
• Pebbly
Risk factors:
• Genetic susceptibility
• Lower socioeconomic status
• Crowded living conditions
• Poor hygiene
• Malnutrition
• HIV infection/immunodeficiencyMultifocal Epithelial Hyperplasia
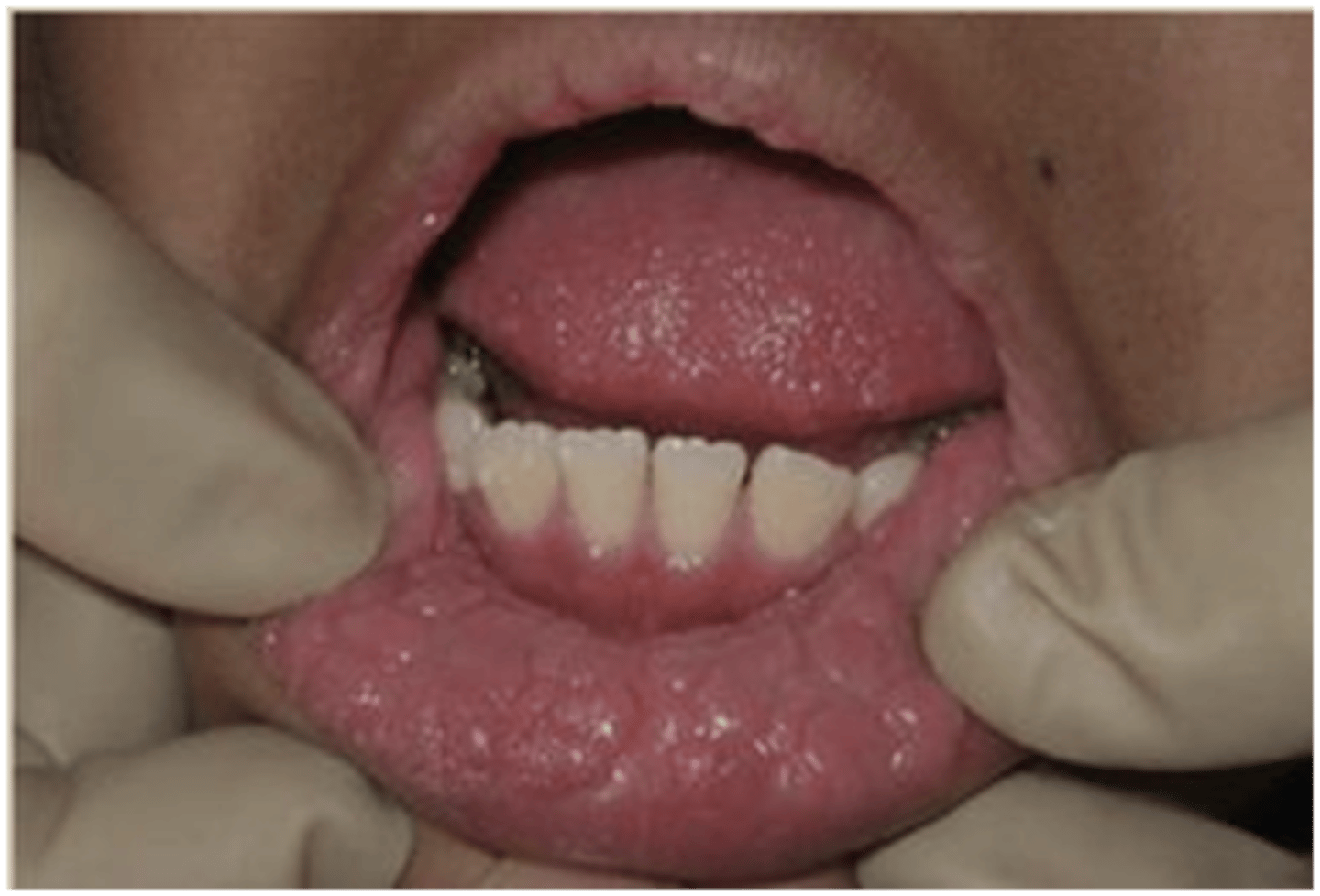
Multifocal Epithelial Hyperplasia
treatment for which benign epithelial lesion:
• Spontaneous regression
• Recurrence is possible
• No malignant potential
• Excision for diagnosis or
esthetics
Multifocal Epithelial Hyperplasia
no
is molluscum contagiosum associated with HPV
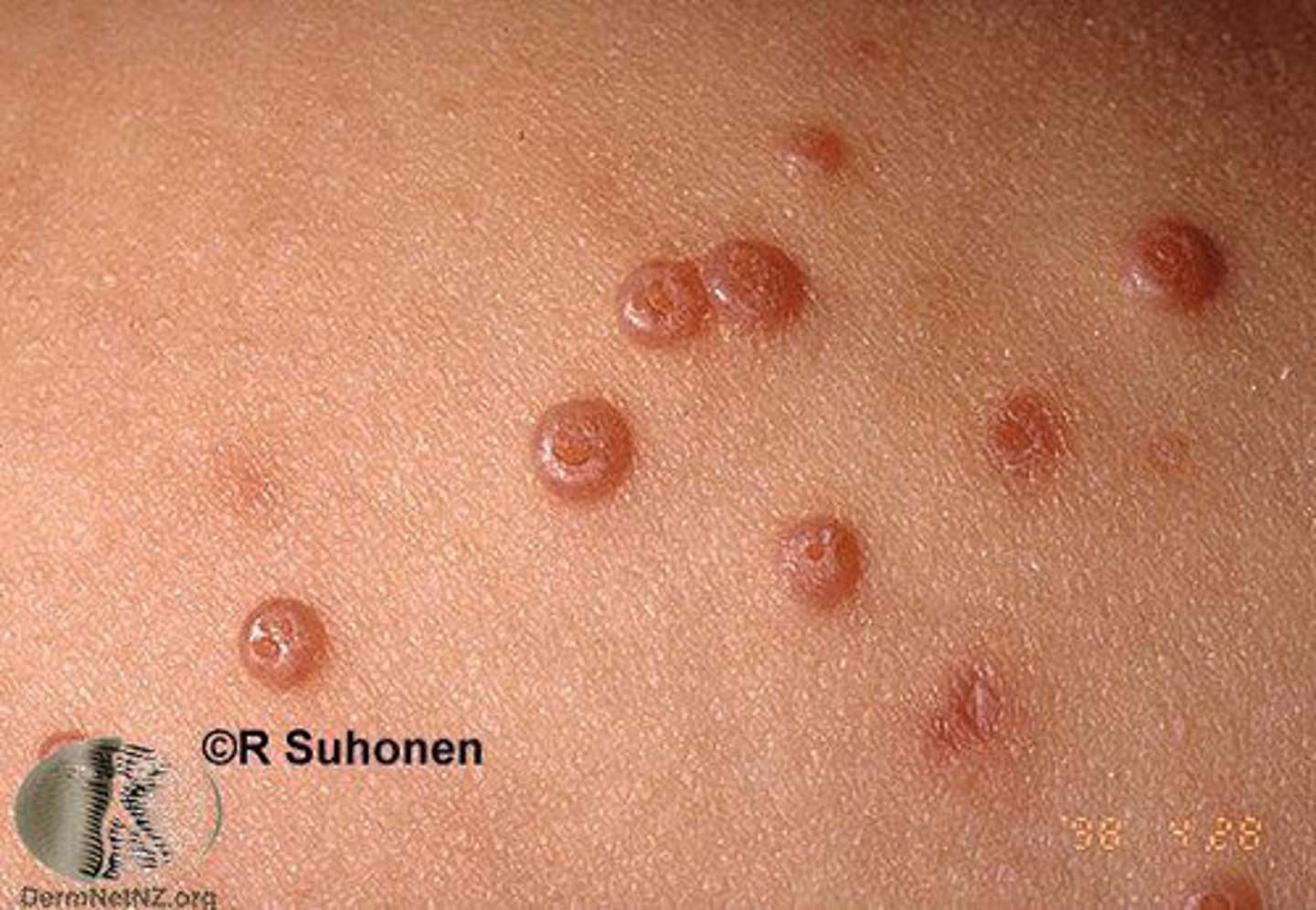
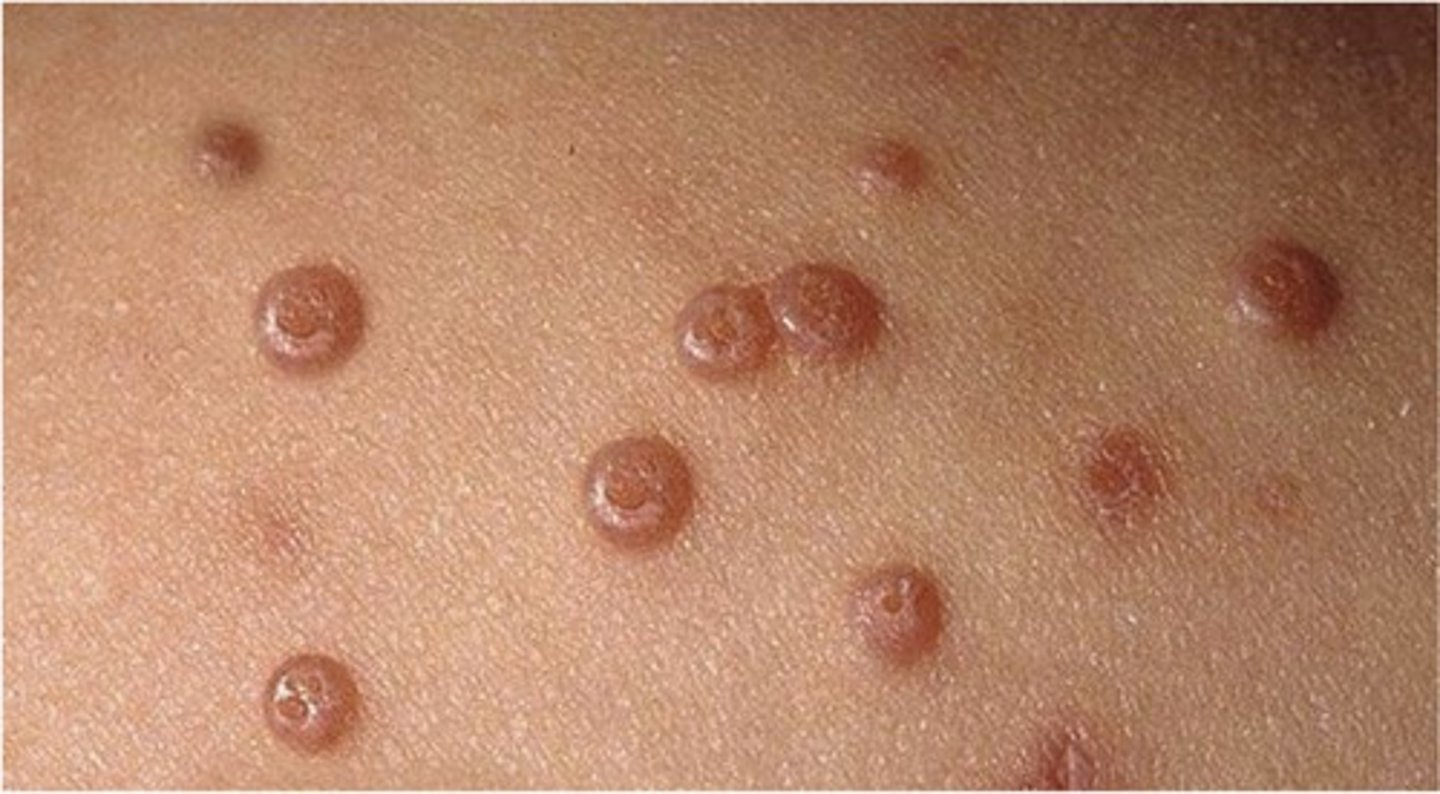
molluscum contagiosum
Which benign epithelial lesion:
• Molluscum contagiosum virus
• Children and young adults
• Skin of the neck, face, trunk,
genitalia
• Oral involvement is rare
• Contagious
• Most are asymptomatic
• Multiple, clustered, white or
pink, smooth-surfaced sessile
papules (2-4mm)
• Central indentation/plug
• Umbilication
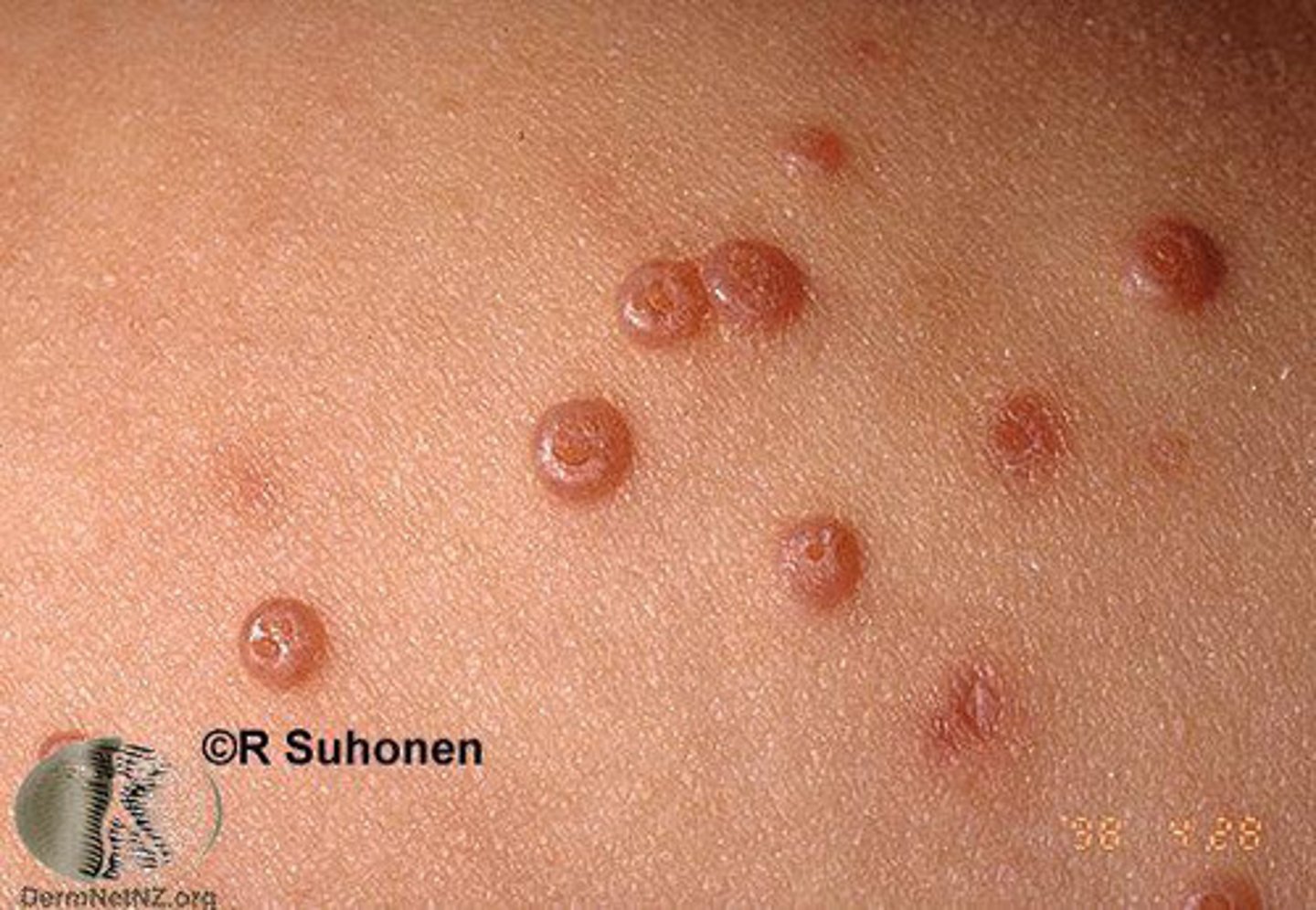
molluscum contagiosum
treatment for which benign epithelial lesion:
• Spontaneous remission in 6-9
months
• Recurrence in ⅓
• Curettage or cryotherapy
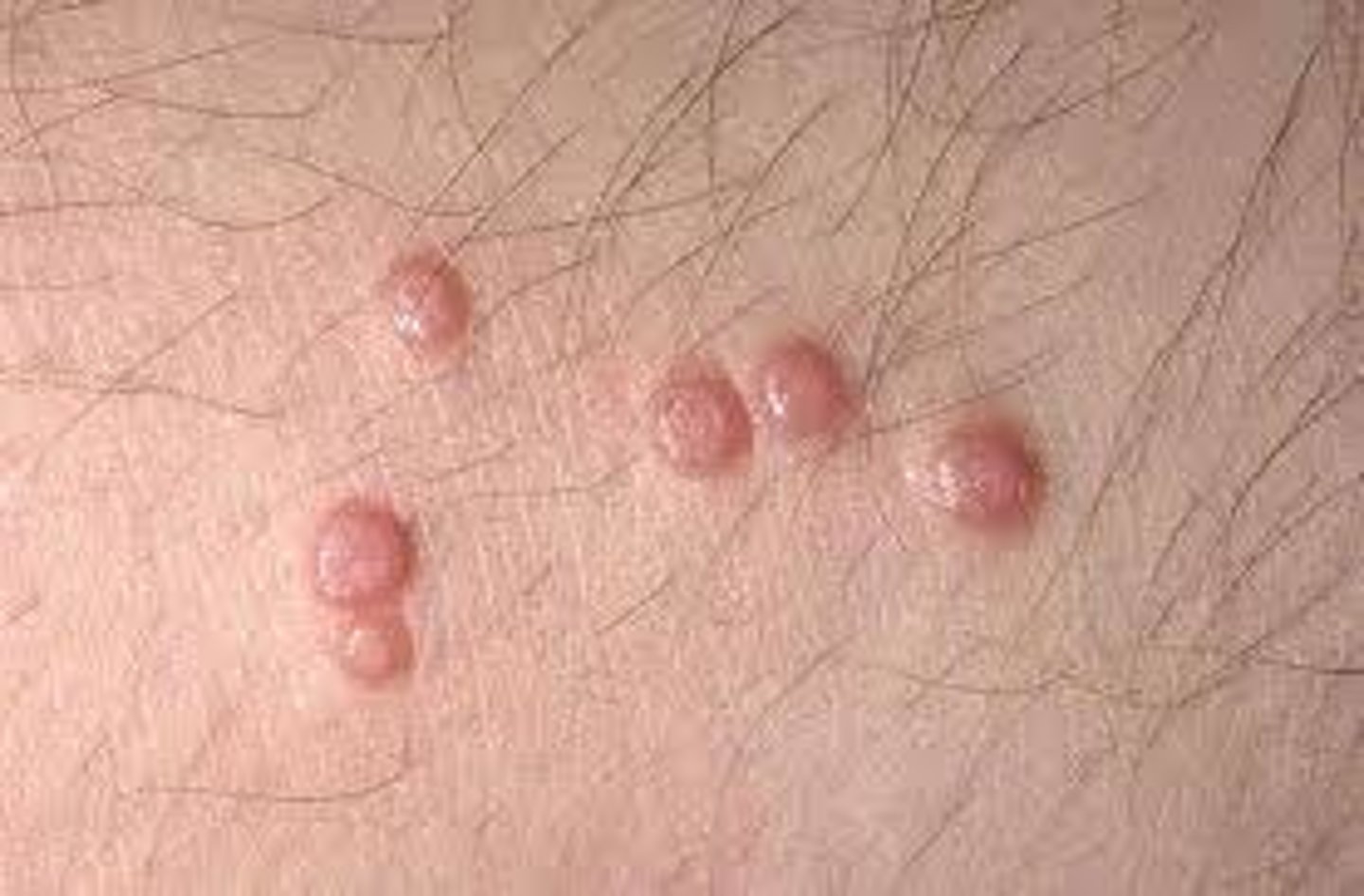
molluscum contagiosum
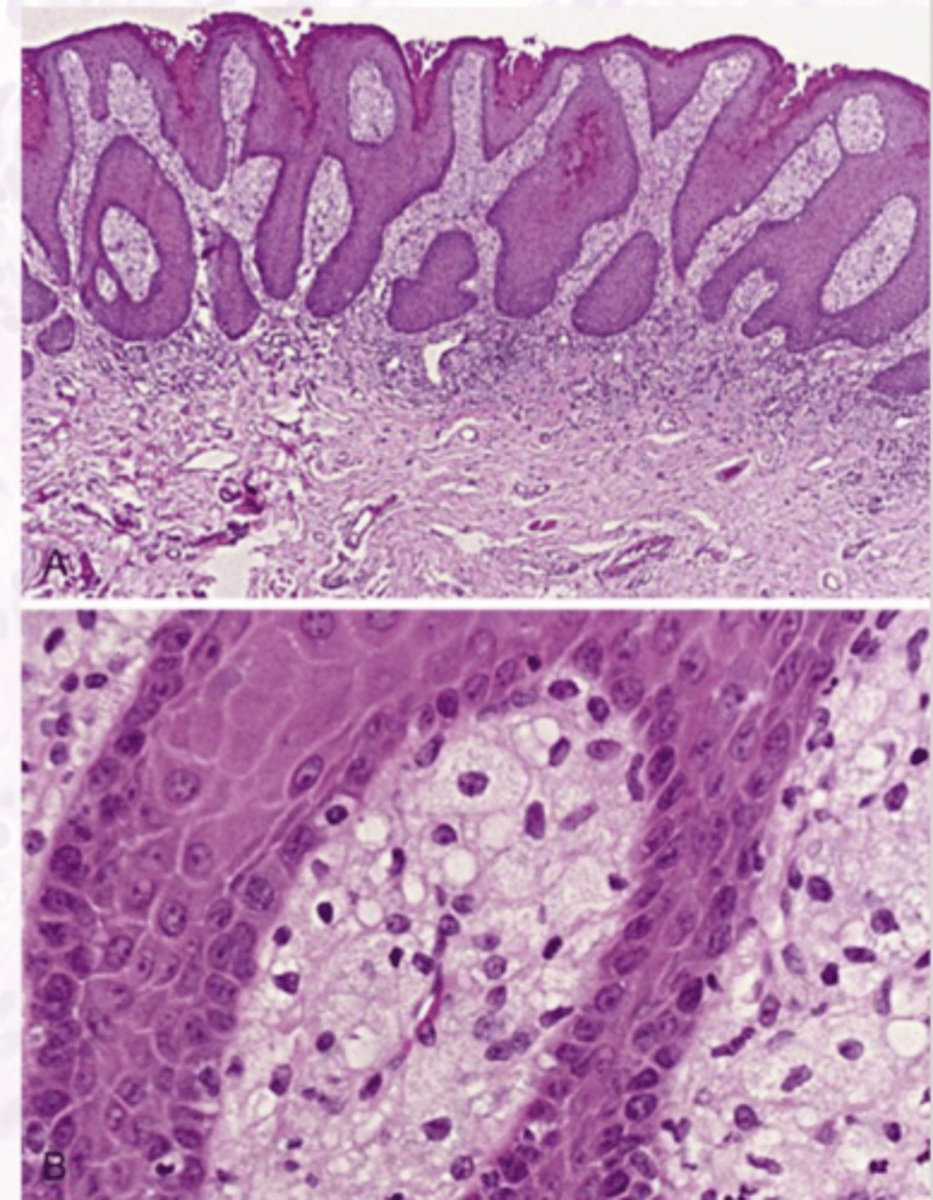
Verruciform xanthoma
Which benign epithelial lesion:
• Accumulation of lipid-laden
histiocytes called xanthoma cells
• Not associated with viruses, or
metabolic conditions
• Cause is unknown but likely a
reaction to trauma
• Asymptomatic
• Well-demarcated
• Sessile
• Slightly elevated mass
• Yellow, white, or red
• Papillary/roughened (verruciform) surface
• 50% on the gingiva or alveolar
mucosa
• Can mimic squamous cell
carcinoma
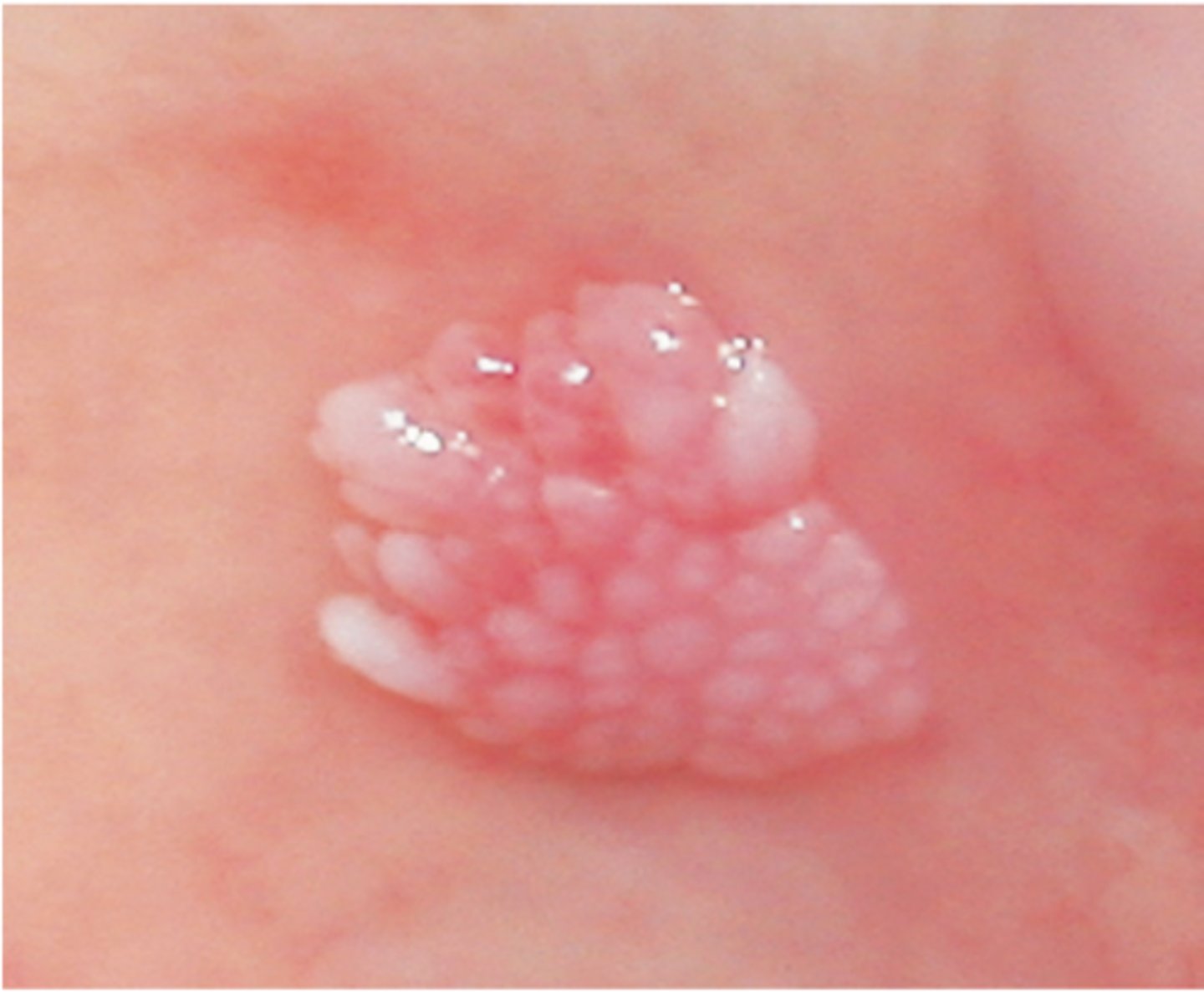
Verruciform xanthoma
treatment for which benign epithelial lesion:
• Excision is the treatment of choice
• Tend not to recur even if incompletely excised
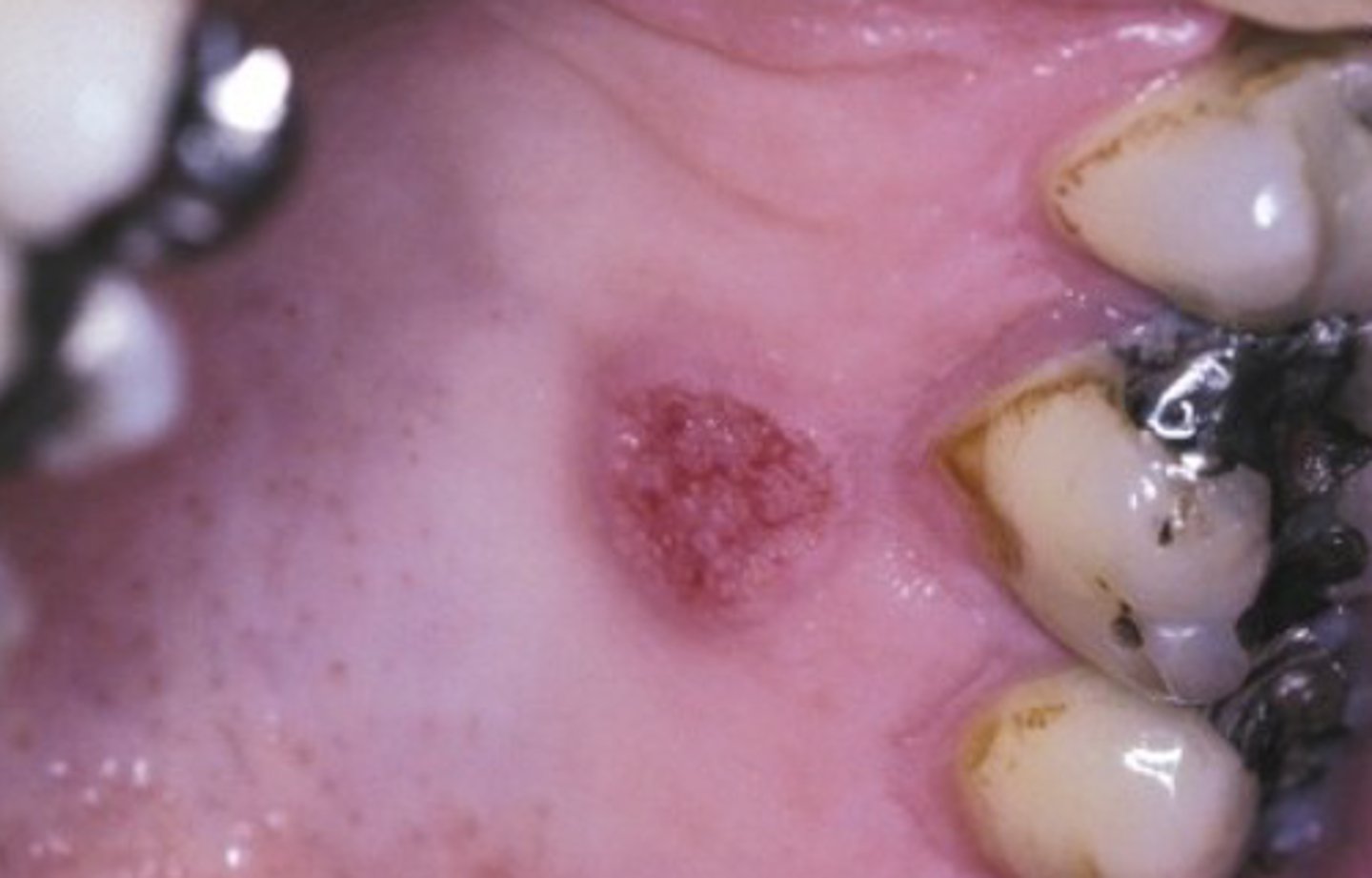
Verruciform xanthoma
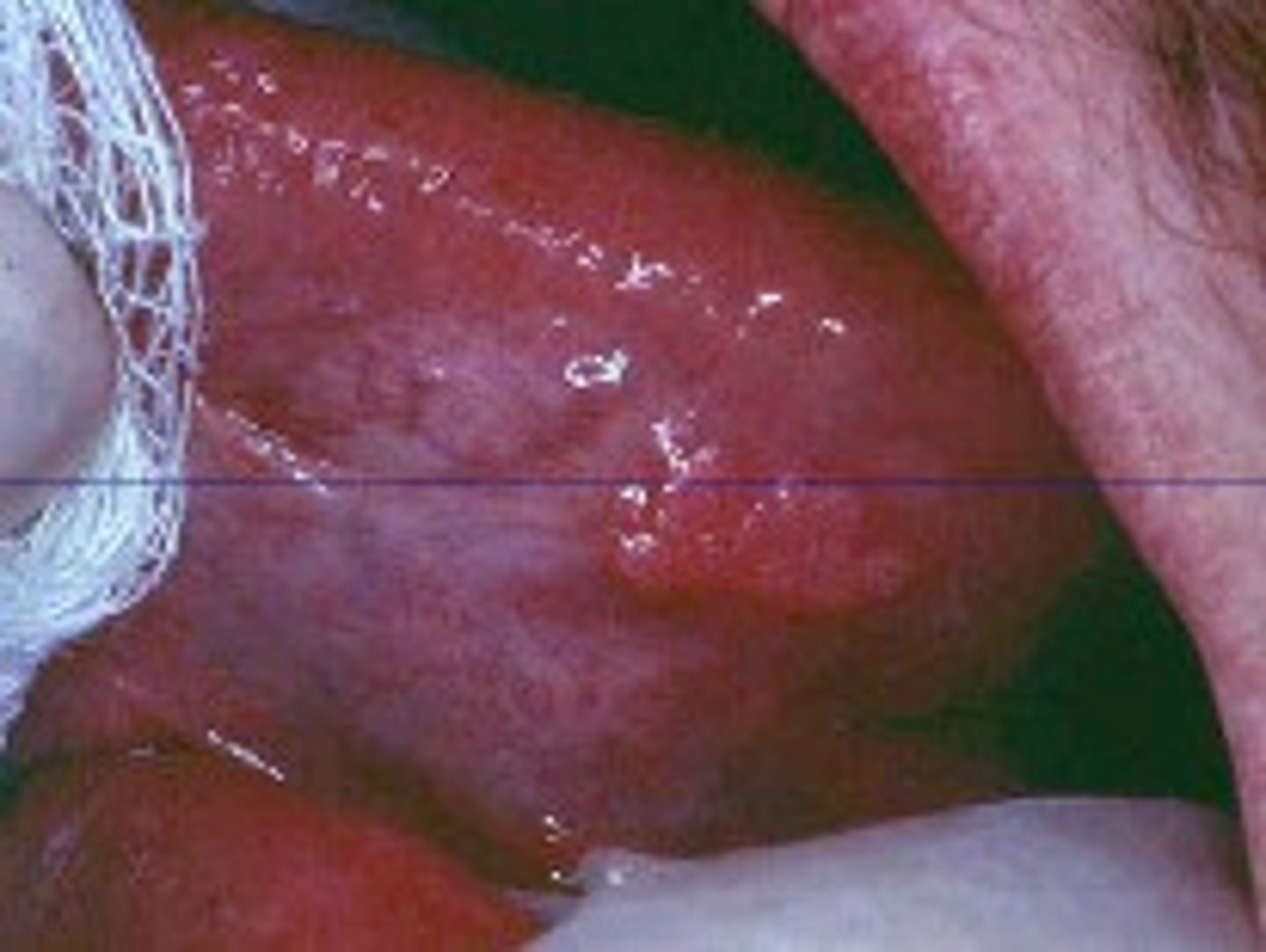
Verruciform xanthoma histology
no
is sebaceous hyperplasia associated with HPV
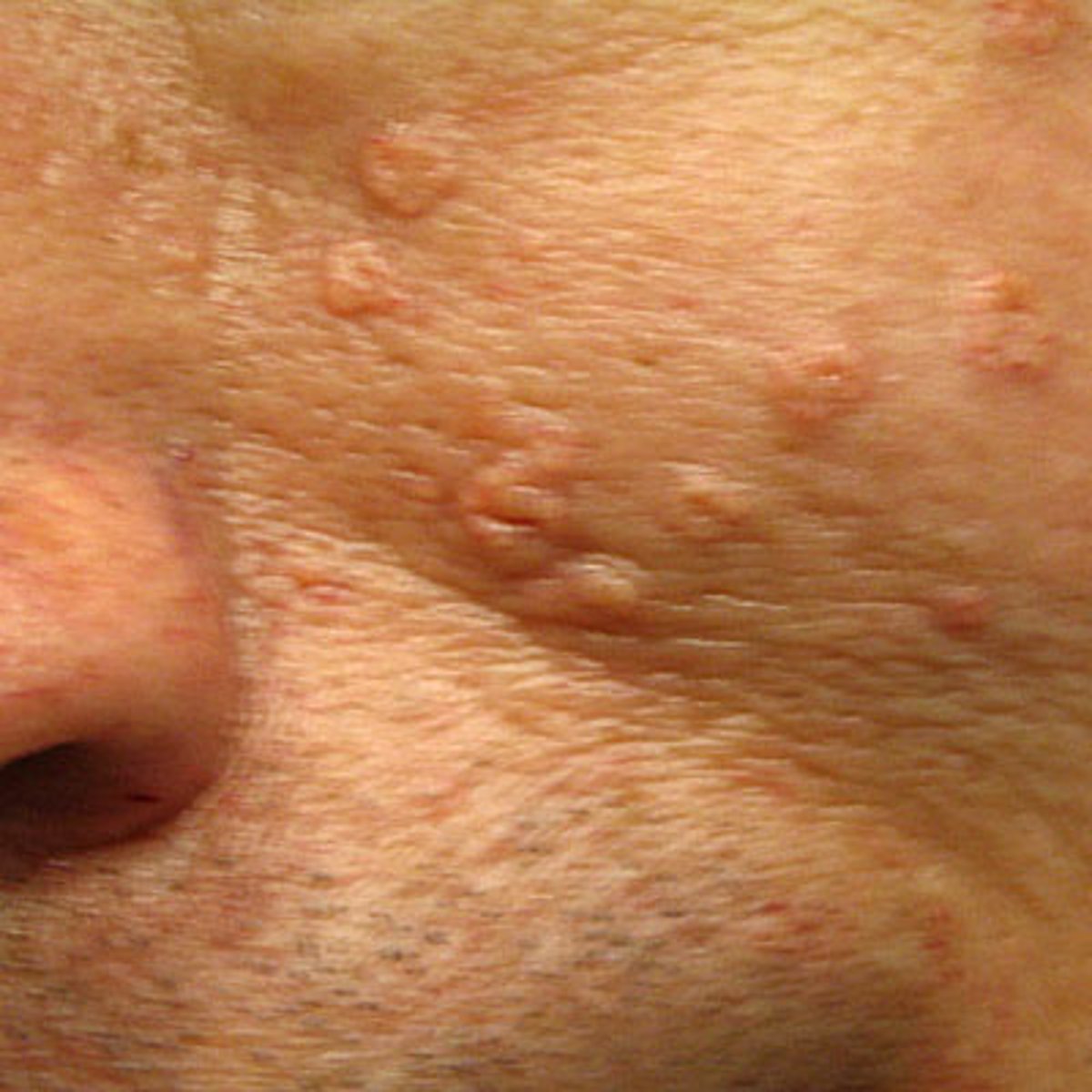
sebaceous hyperplasia
Which benign epithelial lesion:
• Non-tender papules
• Yellow, white or skin-colored
• Slow growing
• Central umbilication
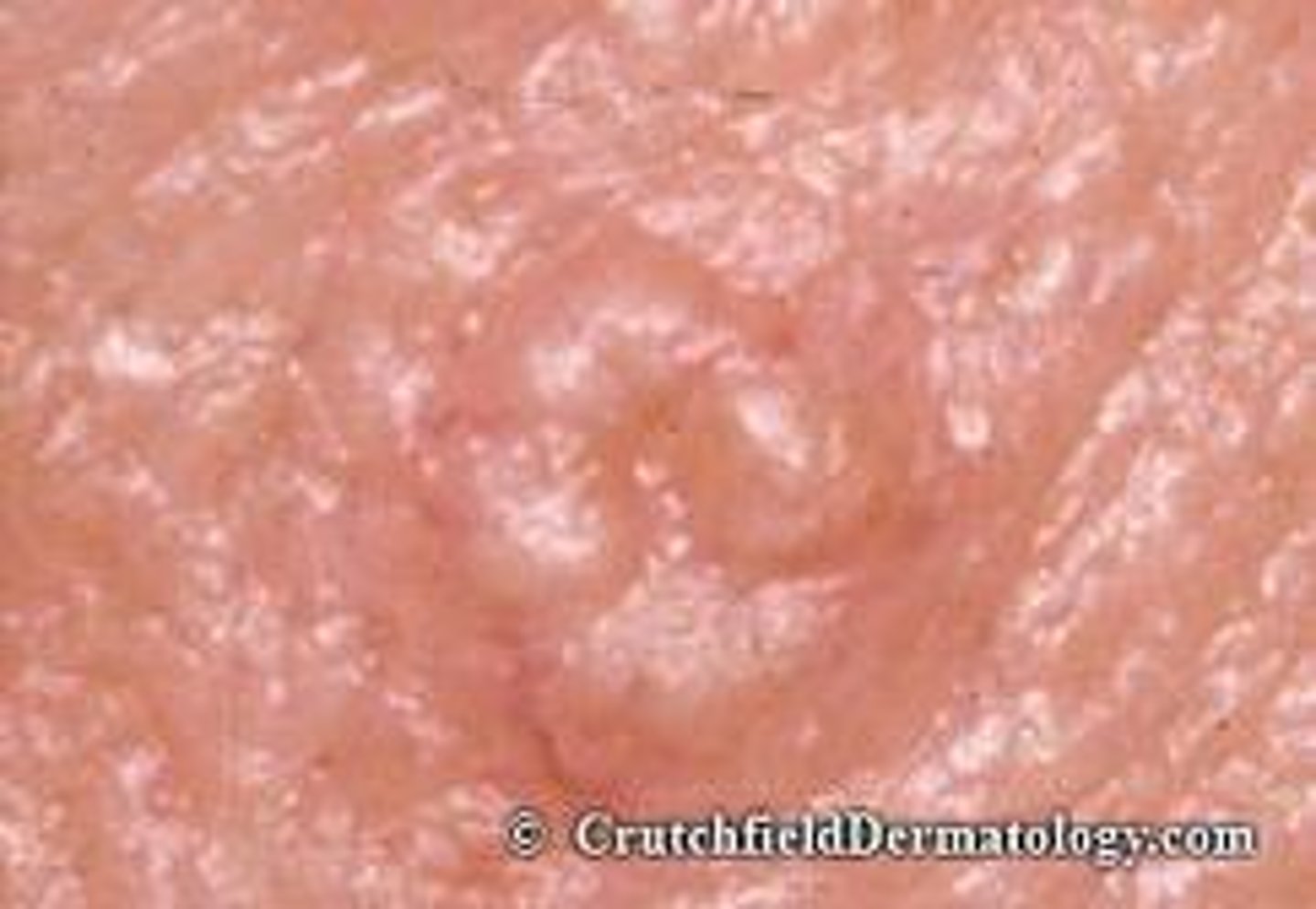
sebaceous hyperplasia
treatment for which benign epithelial lesion:
• No treatment is necessary
• Except for cosmetic reasons or if basal cell carcinoma cannot be eliminated
from the clinical differential diagnosis
sebaceous hyperplasia
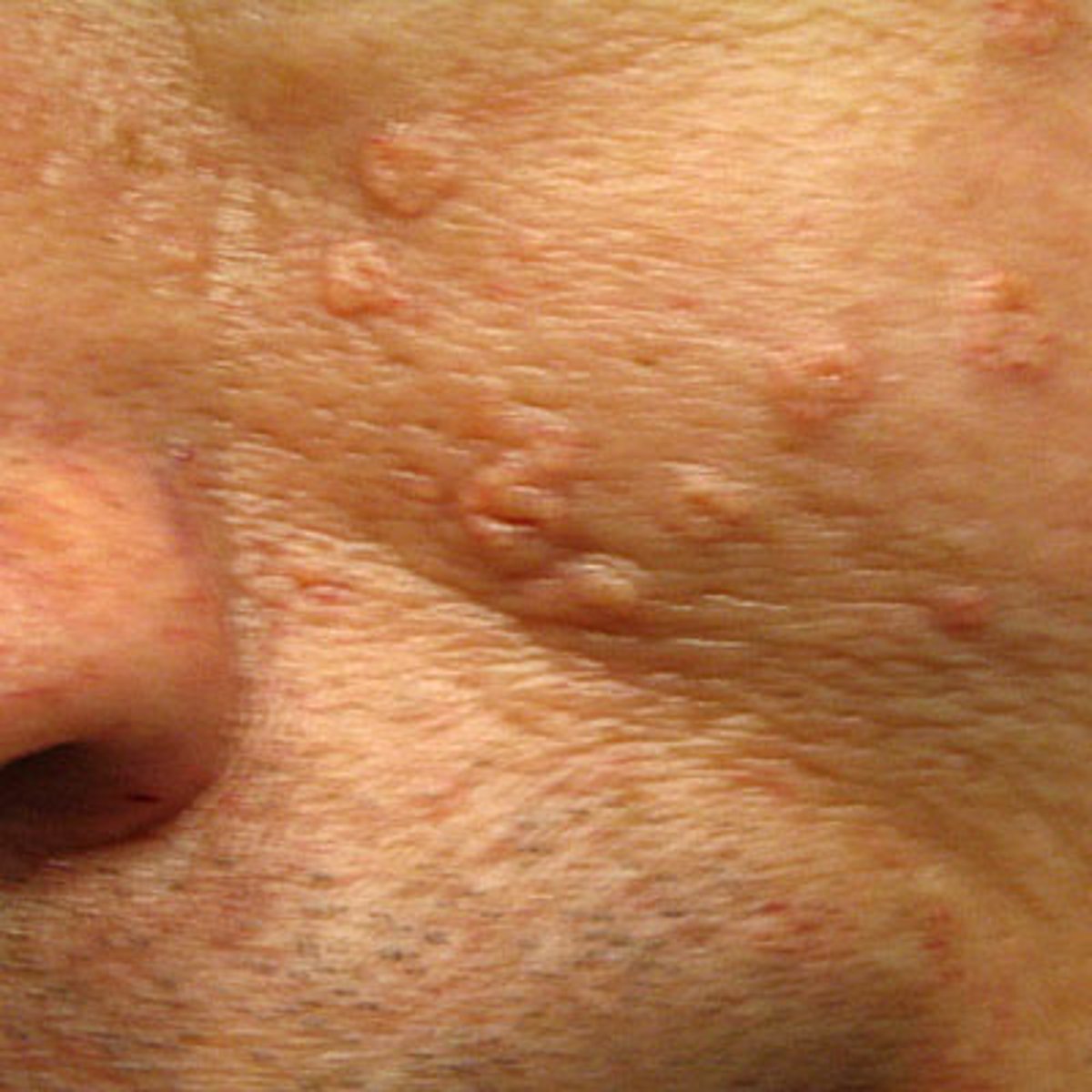
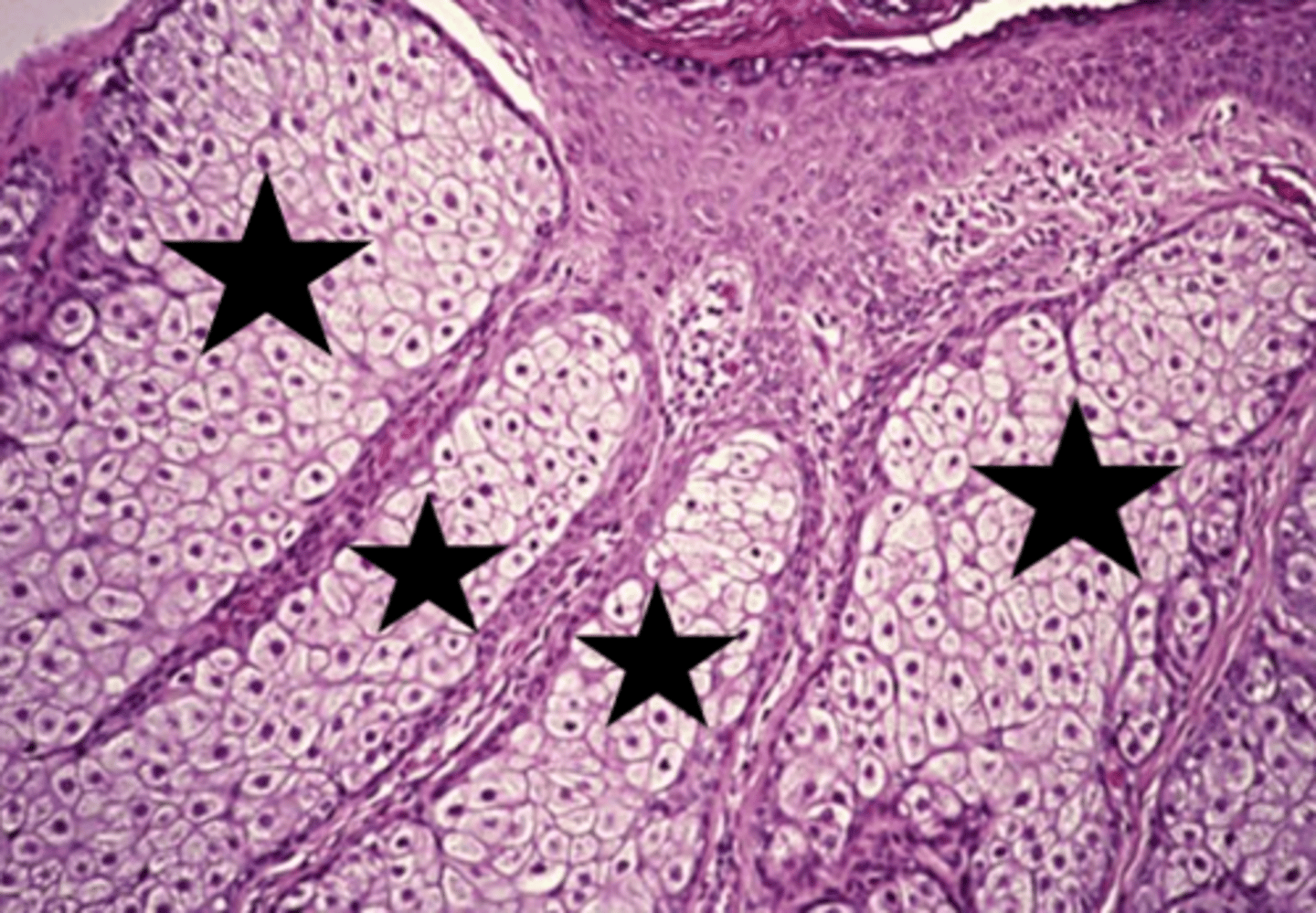
sebaceous hyperplasia histology
seborrheic keratosis
which type of pigmented lesion:
• Extremely common lesion in
older patients
• Unknown cause
• Does not occur in the mouth
• Brown-tan macules that over
time become sharply
demarcated plaques
• Can be rough, fissured,
verrucous
• "Stuck on" appearance
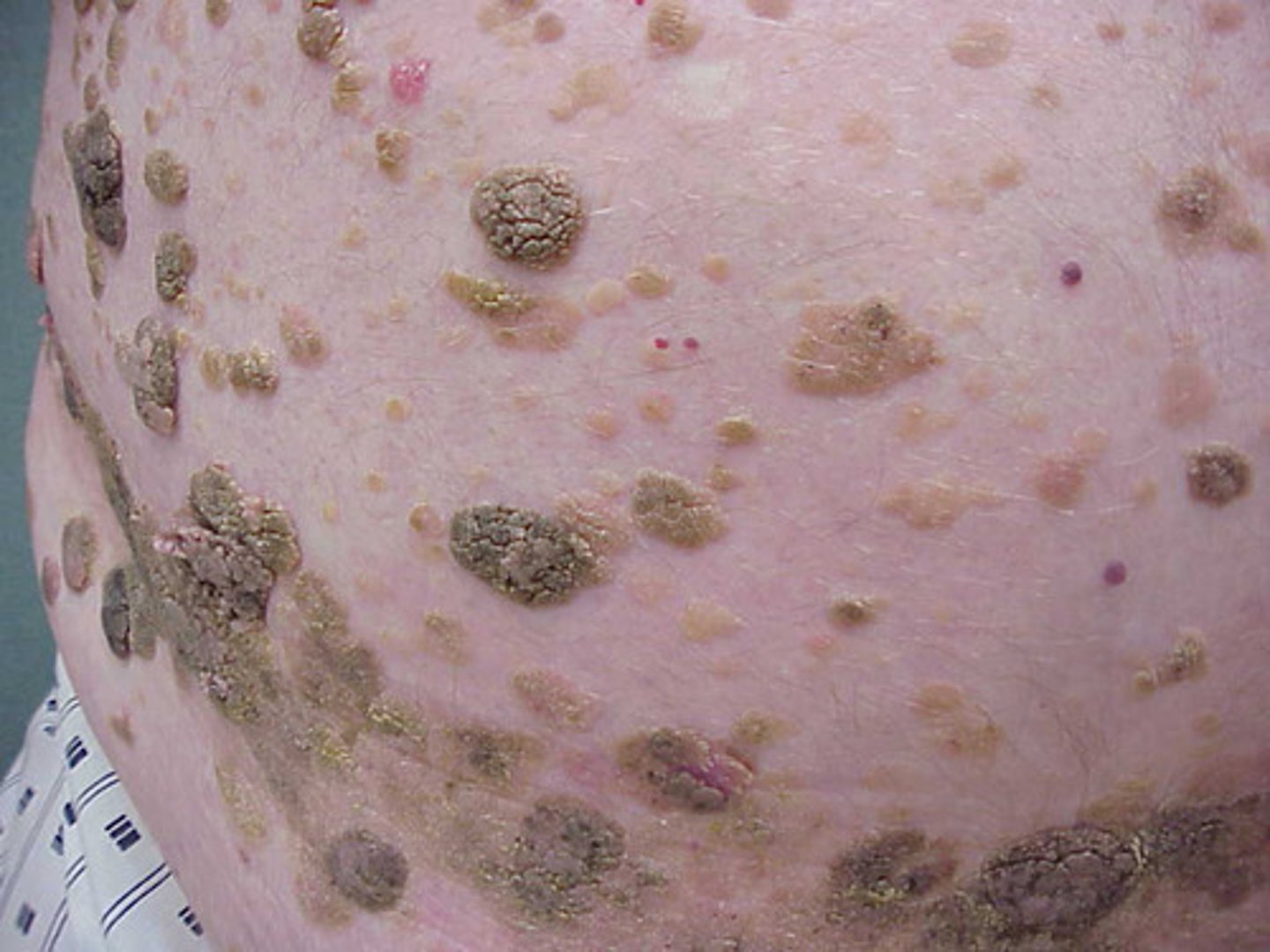
seborrheic keratosis
treatment for which type of pigmented lesion:
• Rarely removed unless there are
esthetic concerns or they are
becoming irritated
• No malignant potential
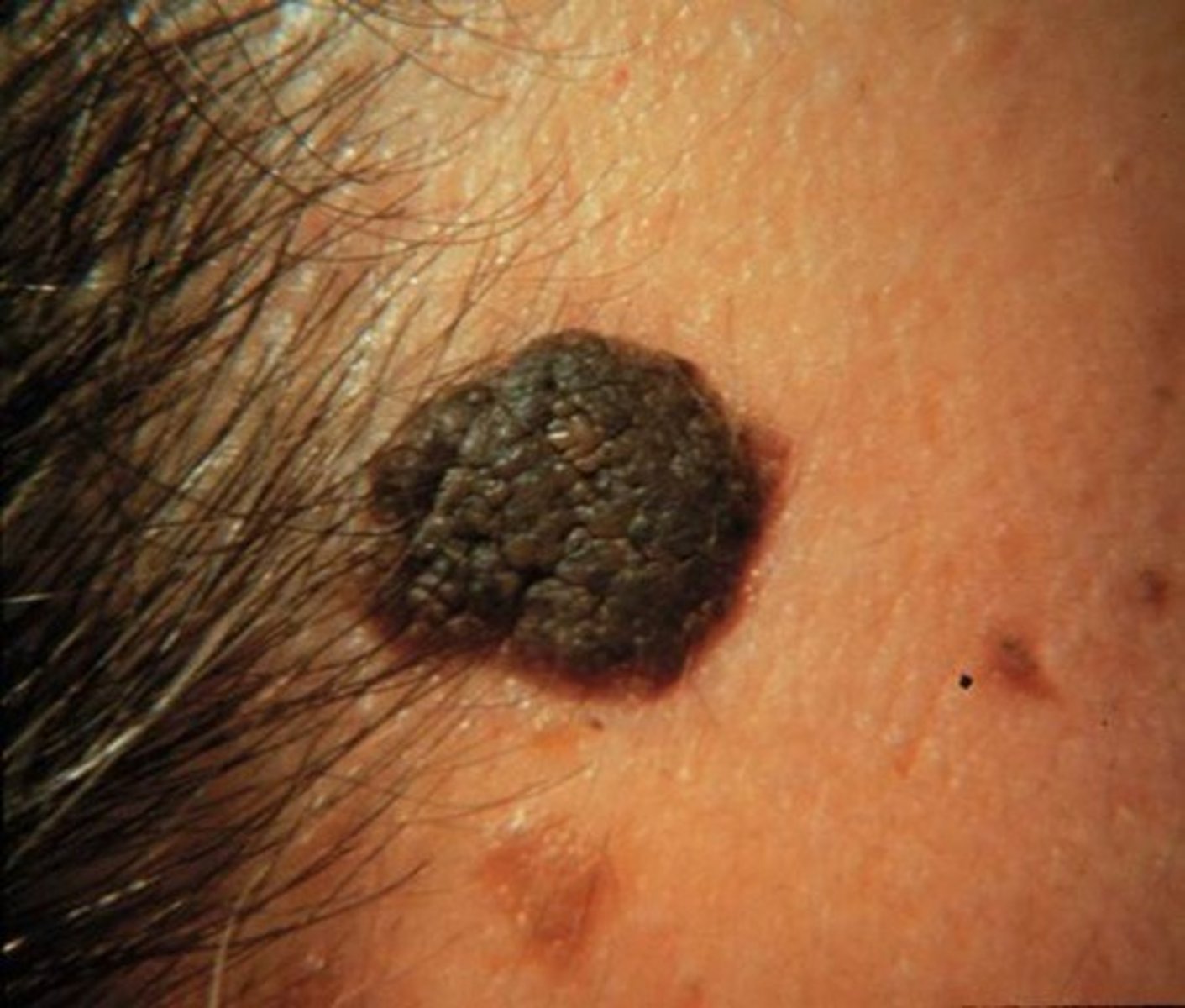
seborrheic keratosis
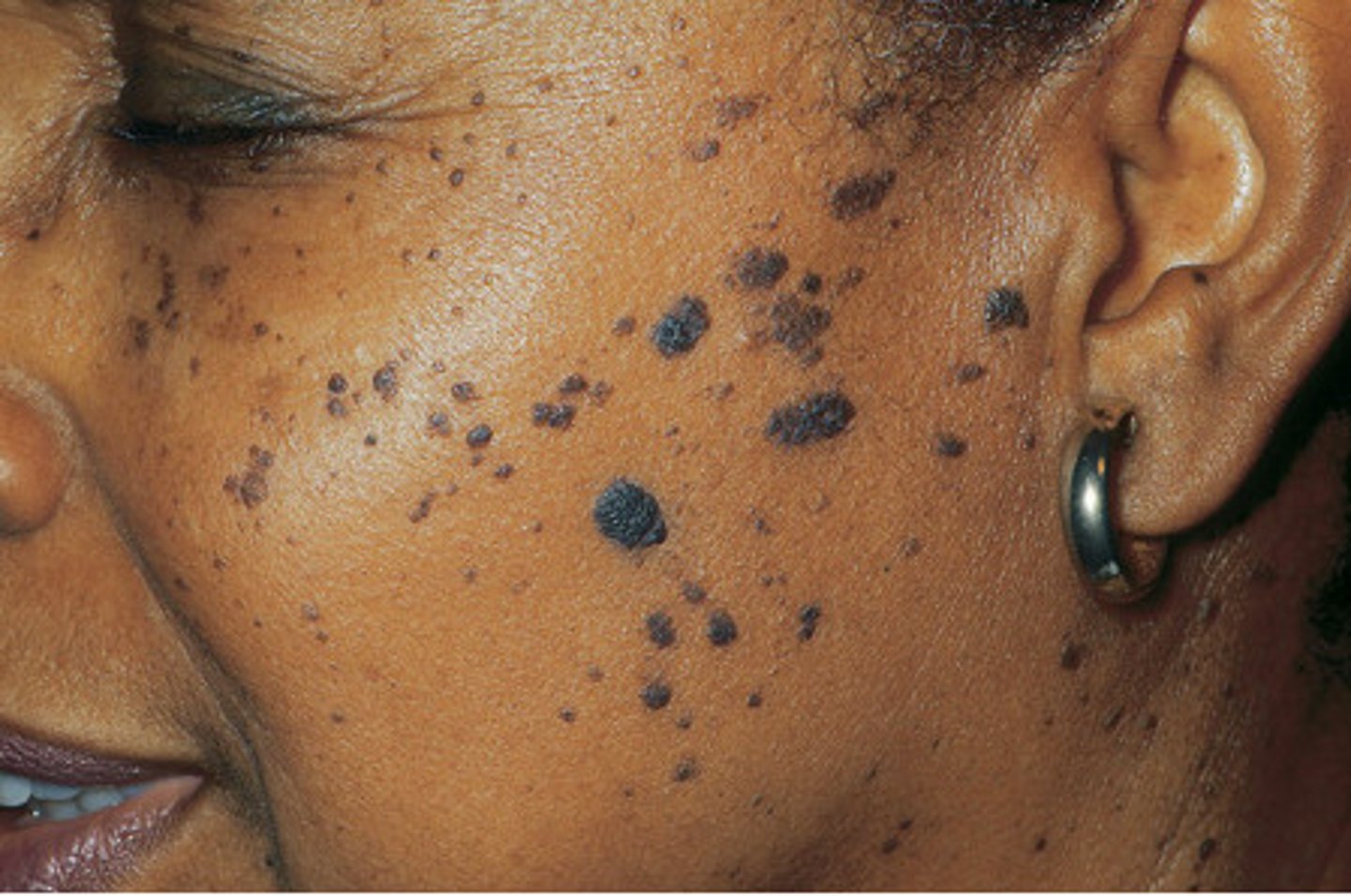
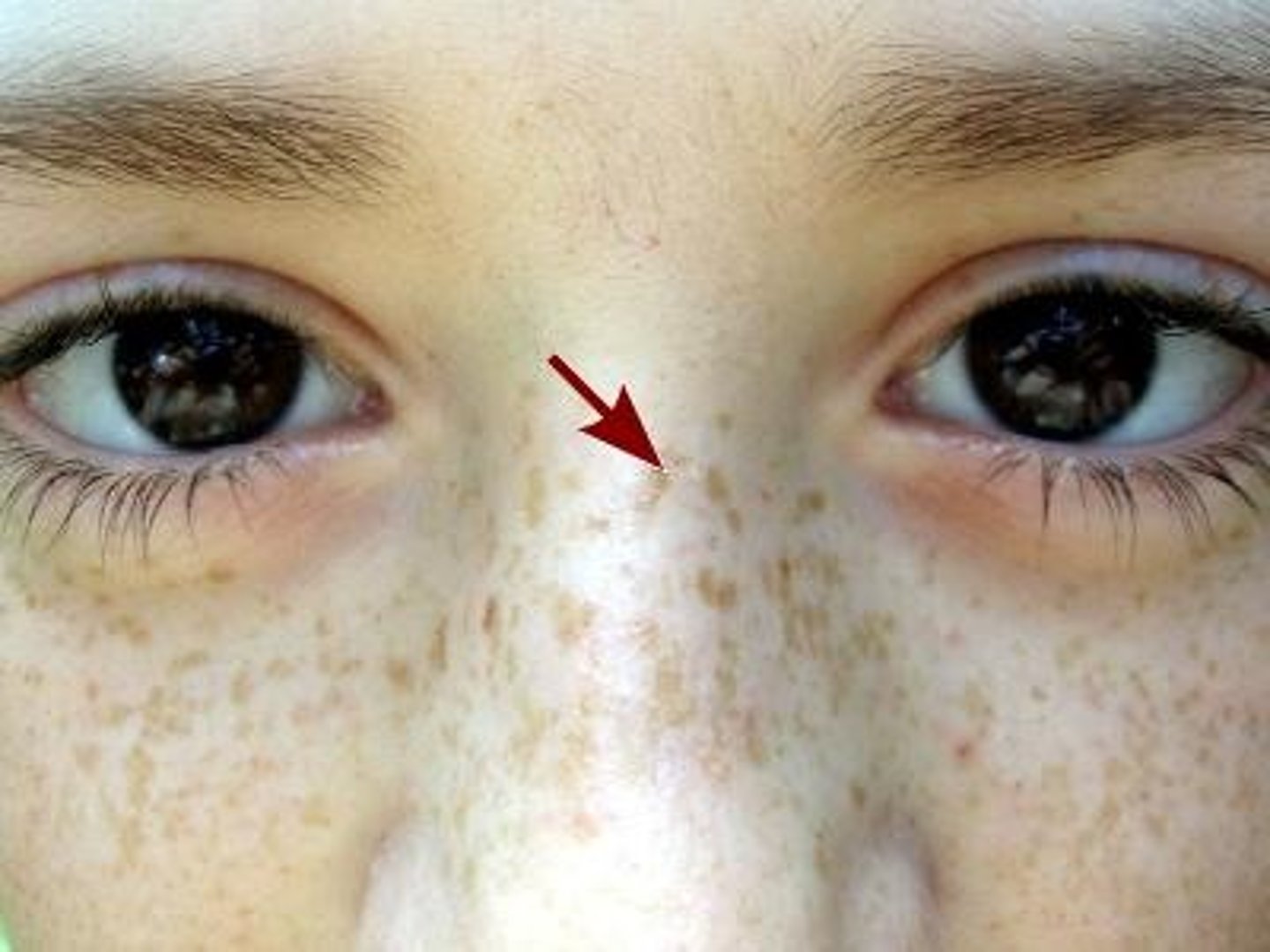
ephelis
which type of pigmented lesion:
• Focal area of increased melanin
• NOT an increase in number of
melanocytes
• More pronounced after sun
exposure
• Common
• Become less prominent over
time
• Does not occur in the mouth
• <0.3 cm
• Sharply demarcated
• Round/oval
• Uniformly light brown macule
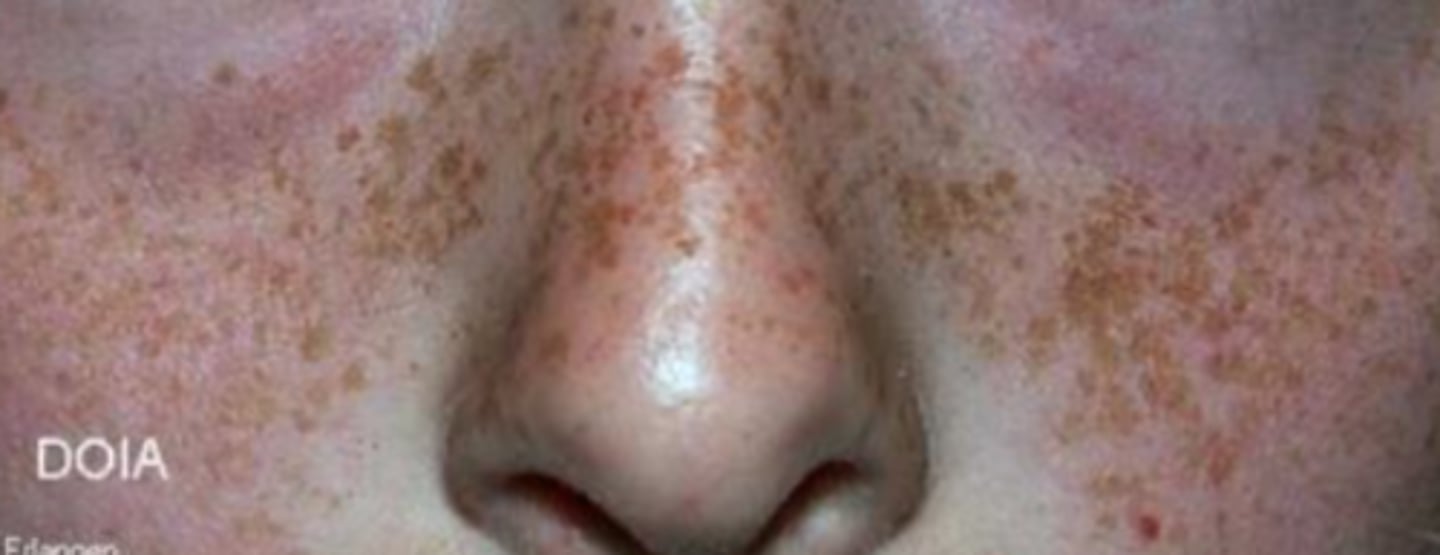
ephelis
treatment for which type of pigmented lesion:
• No treatment is necessary
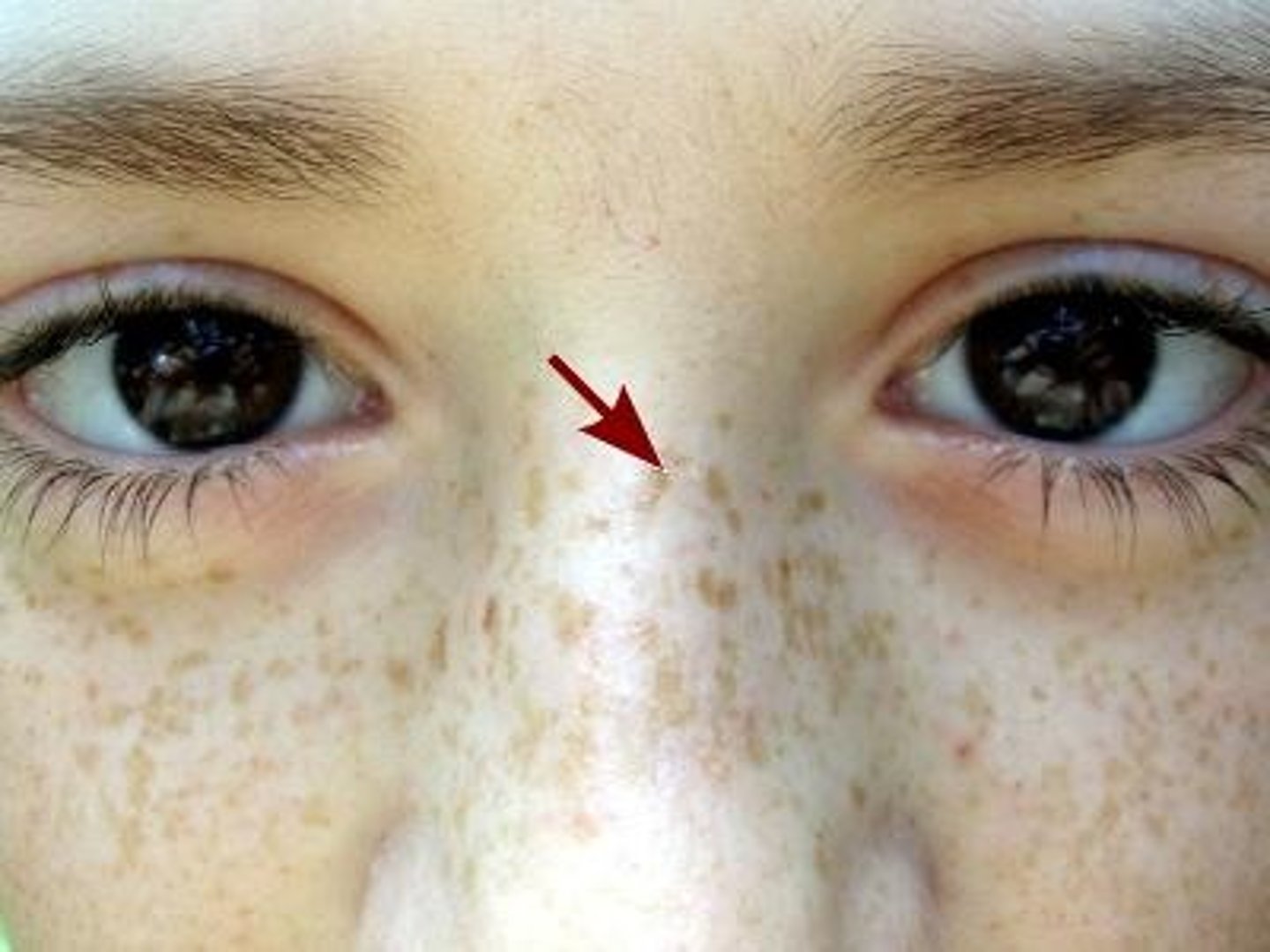
ephelis
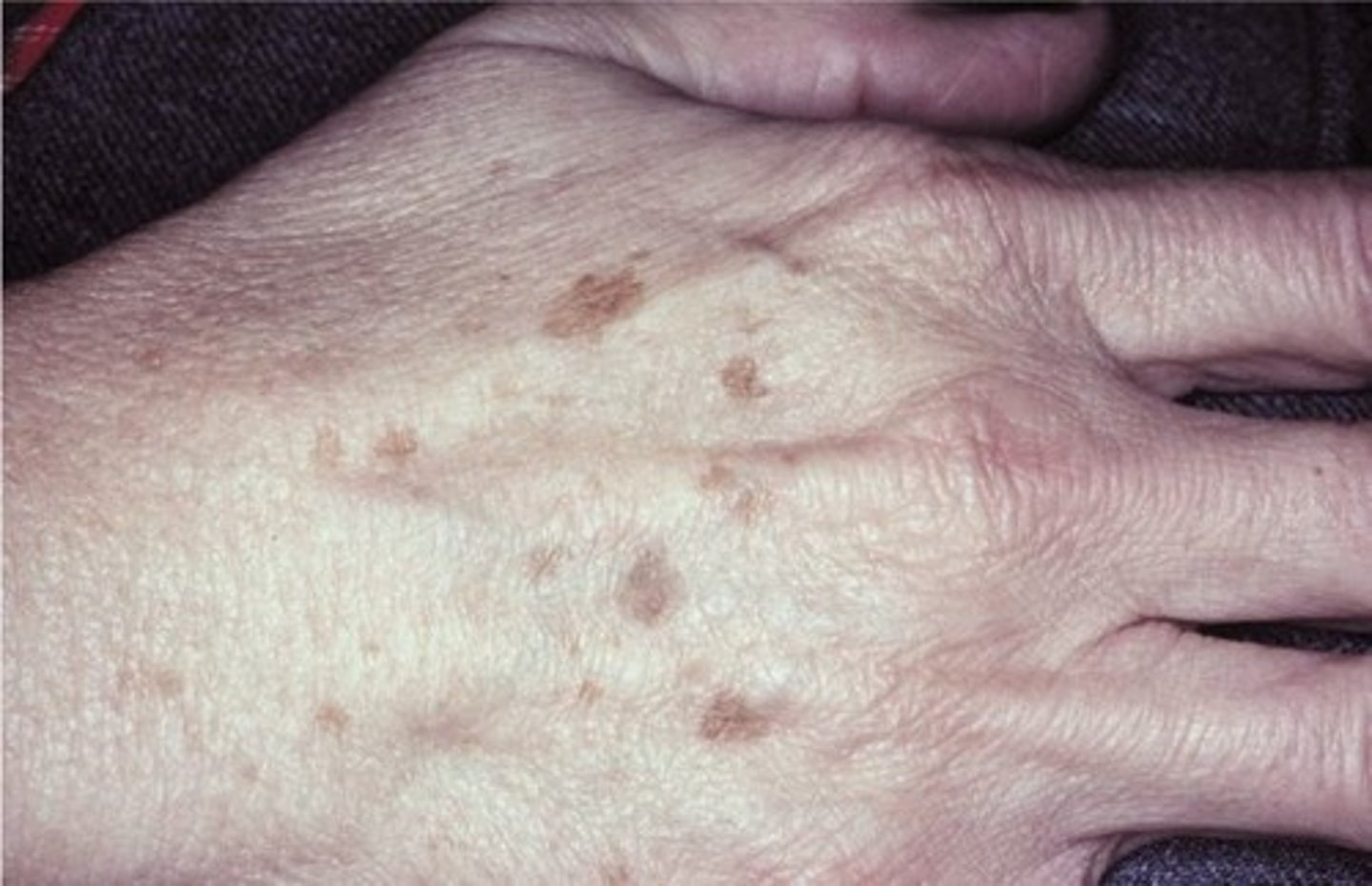
actinic lentigo
which type of pigmented lesion:
• Benign
• Found on photo damaged skin
• 90% of elderly Caucasians
• Does not occur in the mouth
• <0.5cm
• Uniformly pigmented
• Brown to tan macules
• Well-demarcated but irregular
borders
• Lesions may coalesce
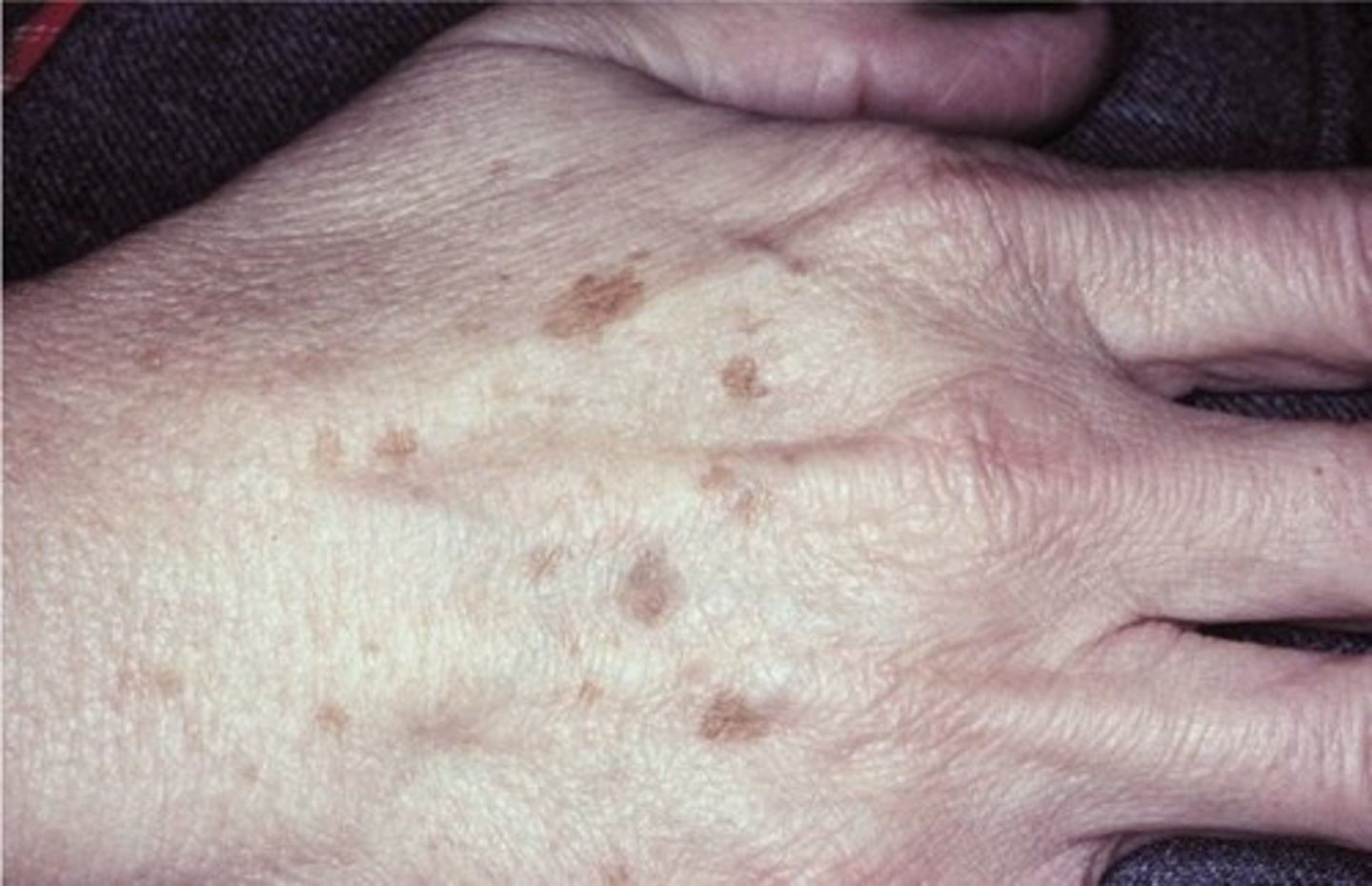
actinic lentigo
treatment for which type of pigmented lesion:
• No treatment except for
cosmetic reasons
• Sunscreen = Prevention
• Does NOT undergo malignant
transformation
• Photo damaged skin indicates a
risk for developing other skin
cancers
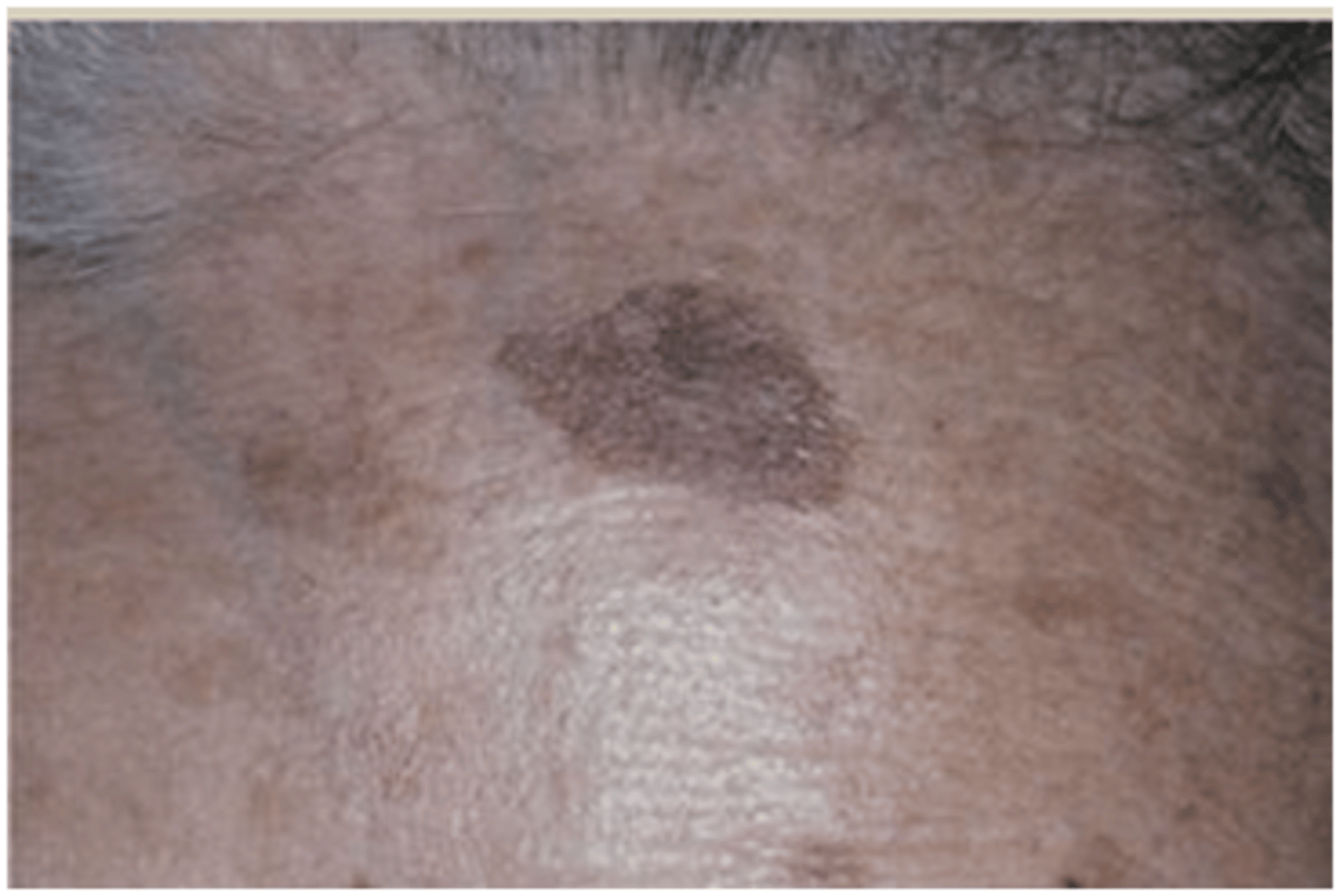
actinic lentigo
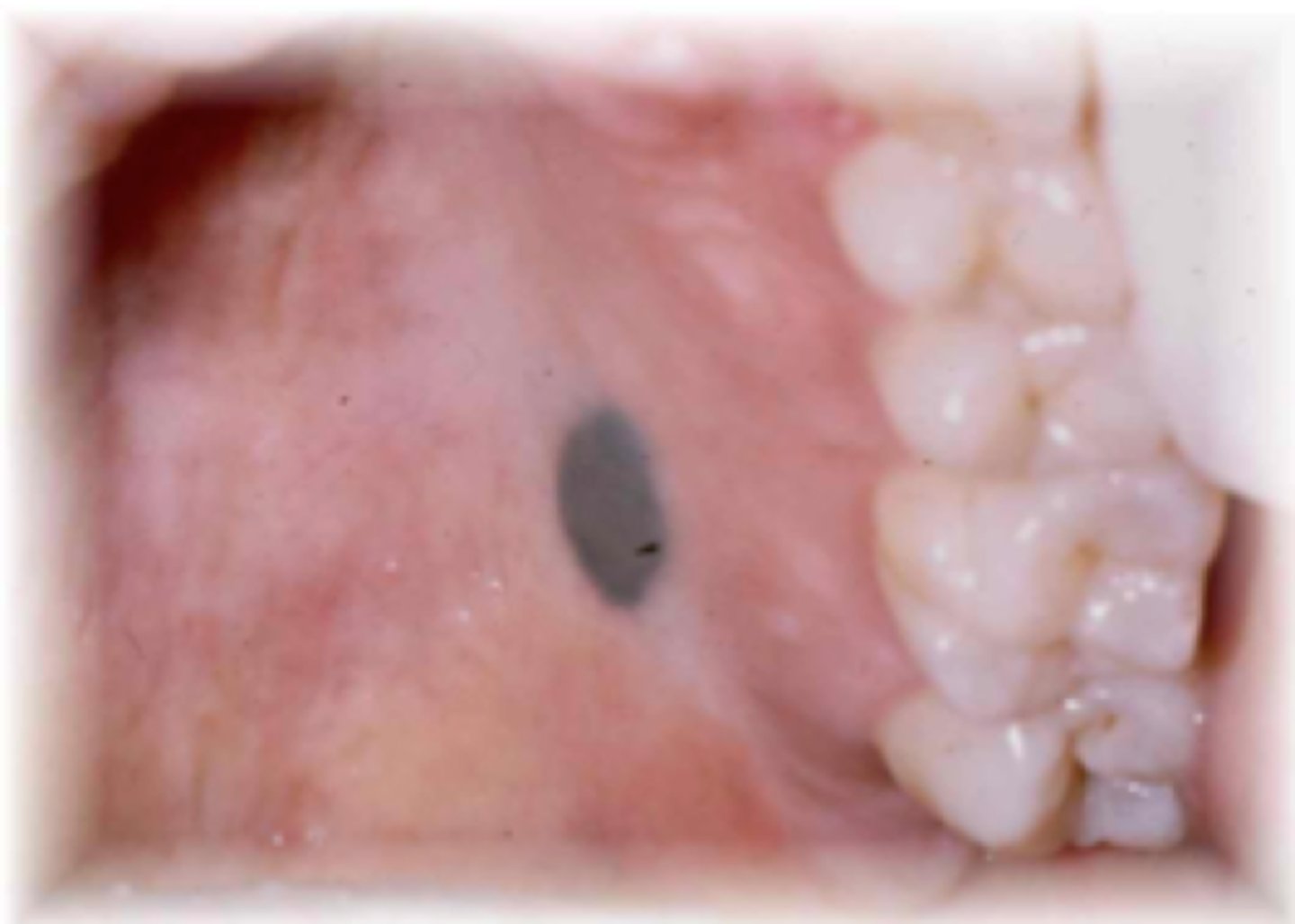
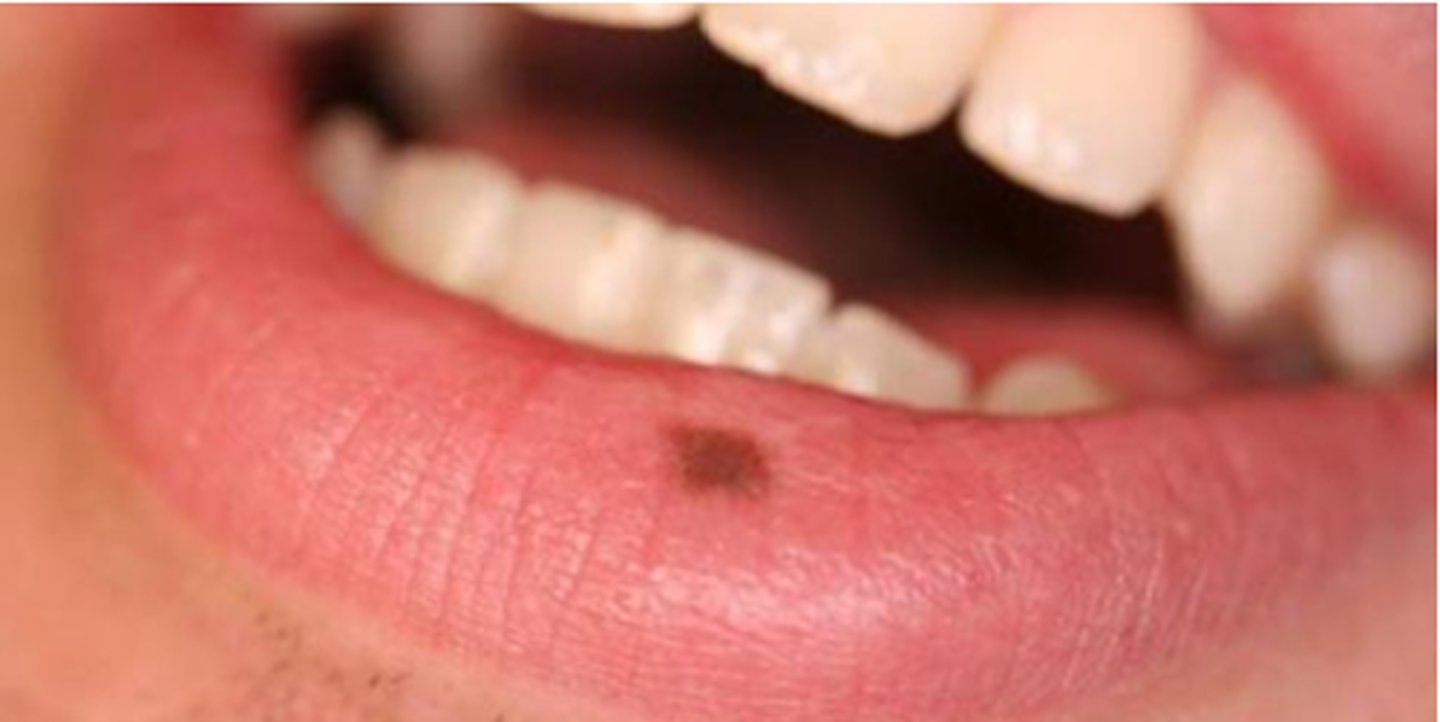
oral melanotic macule
which type of pigmented lesion:
• Solitary mucosal discoloration
• Increase in melanin deposition
and increase in melanocytes
• Cause is unknown
• Not dependent on sun exposure
• Most common oral melanocytic
lesions submitted to oral
pathology laboratories
• Discrete, usually solitary, tan-to-
brown-to-black, painless
macules
• Evenly pigmented
• Less than 1 cm
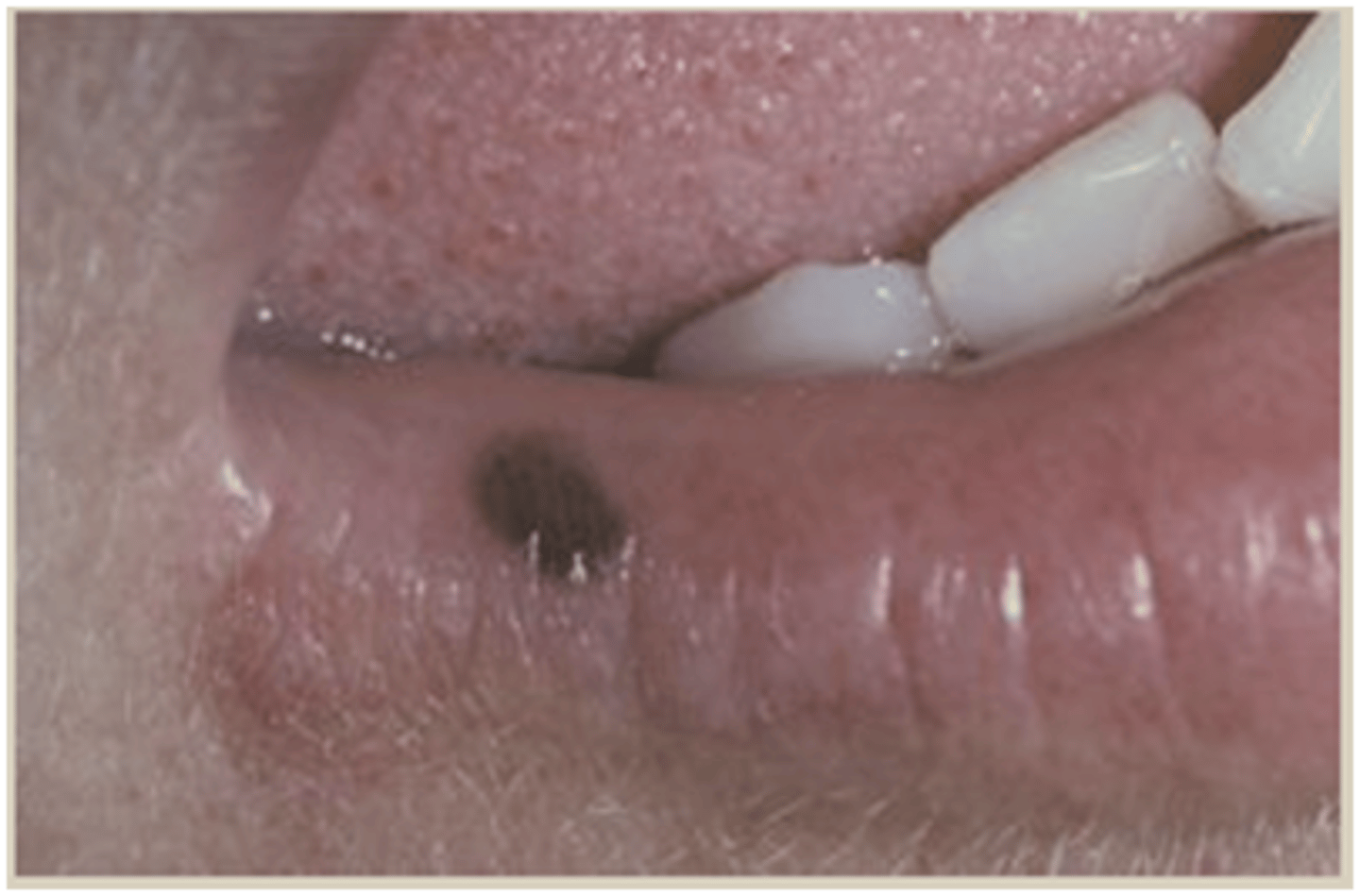
oral melanotic macule
treatment for which type of pigmented lesion:
• No treatment is necessary, but I
recommend biopsy of all oral
pigmented lesions
• Has no malignant potential, but
it is necessary to rule out the
possibility that it could be
melanoma
oral melanotic macule
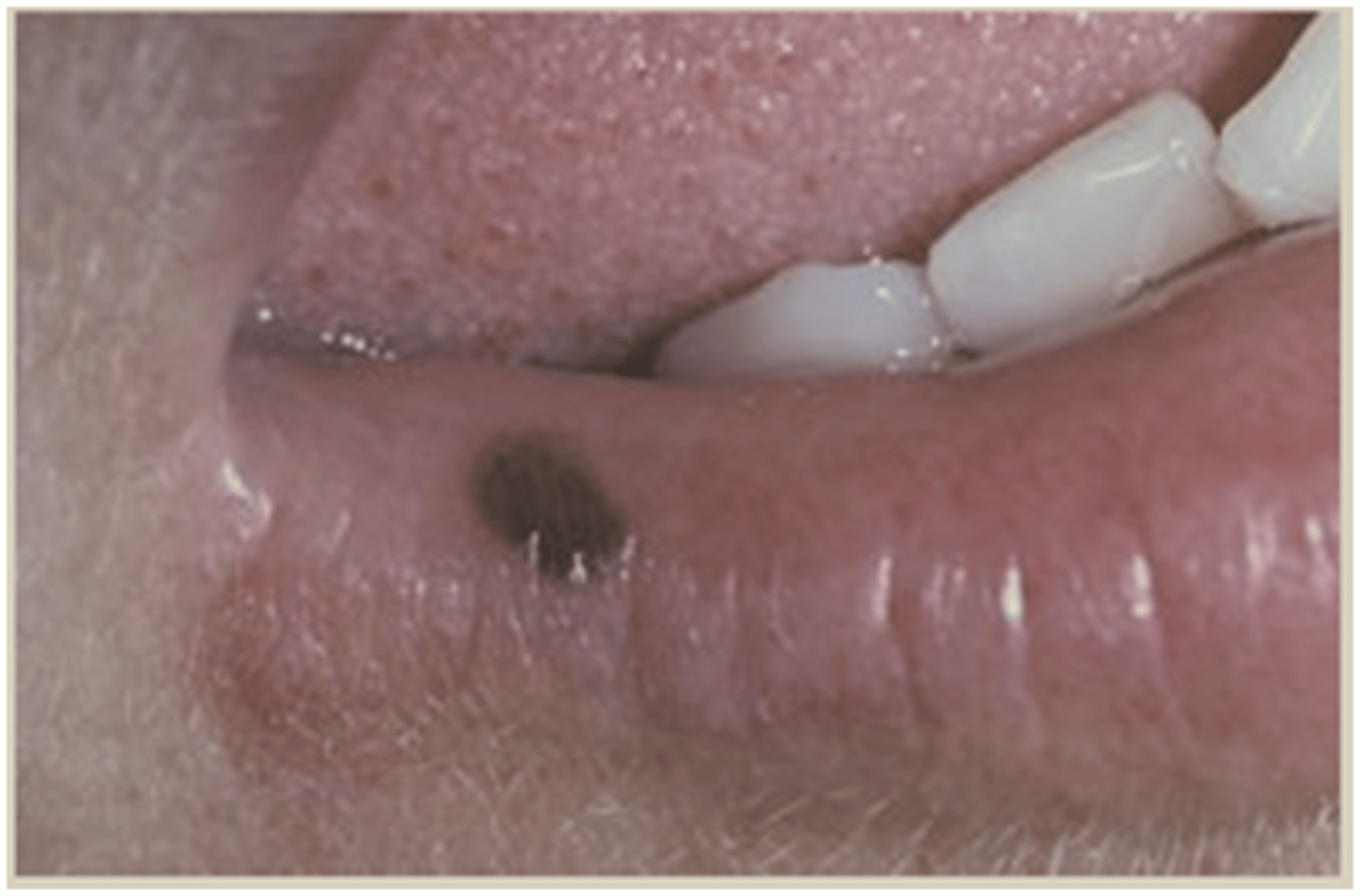
oral melanoacanthoma
which type of pigmented lesion:
• Benign
• Acquired pigmentation
• Reactive
• Female predilection
• More common in those of
African descent
• Lesions rapidly increase in size
• Flat, brown to black
• Irregular borders
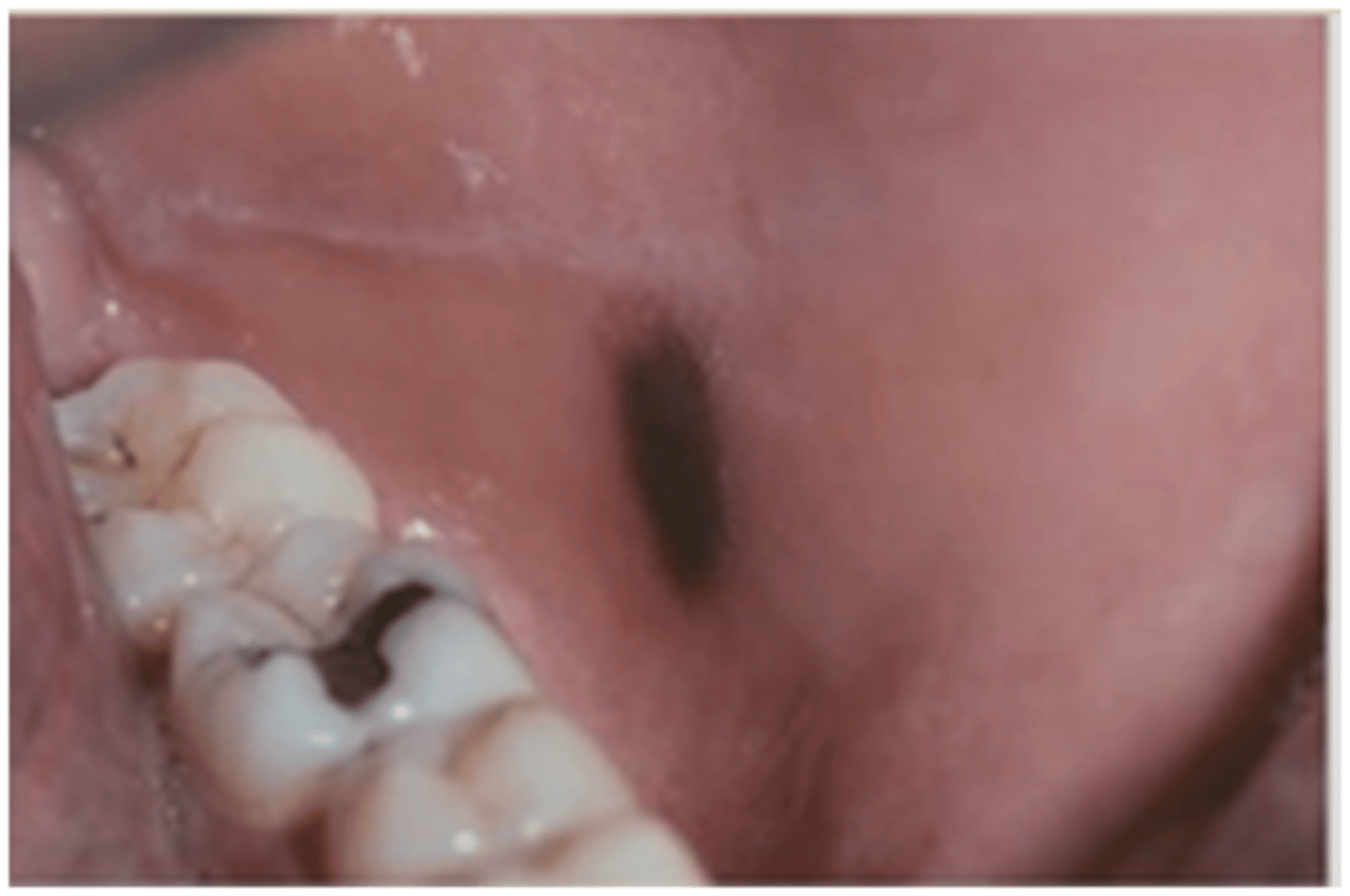
oral melanoacanthoma
treatment for which type of pigmented lesion:
• Biopsy to rule out melanoma
• Once diagnosis is established, no
treatment is necessary
• Lesions fade over time
• No malignant potential
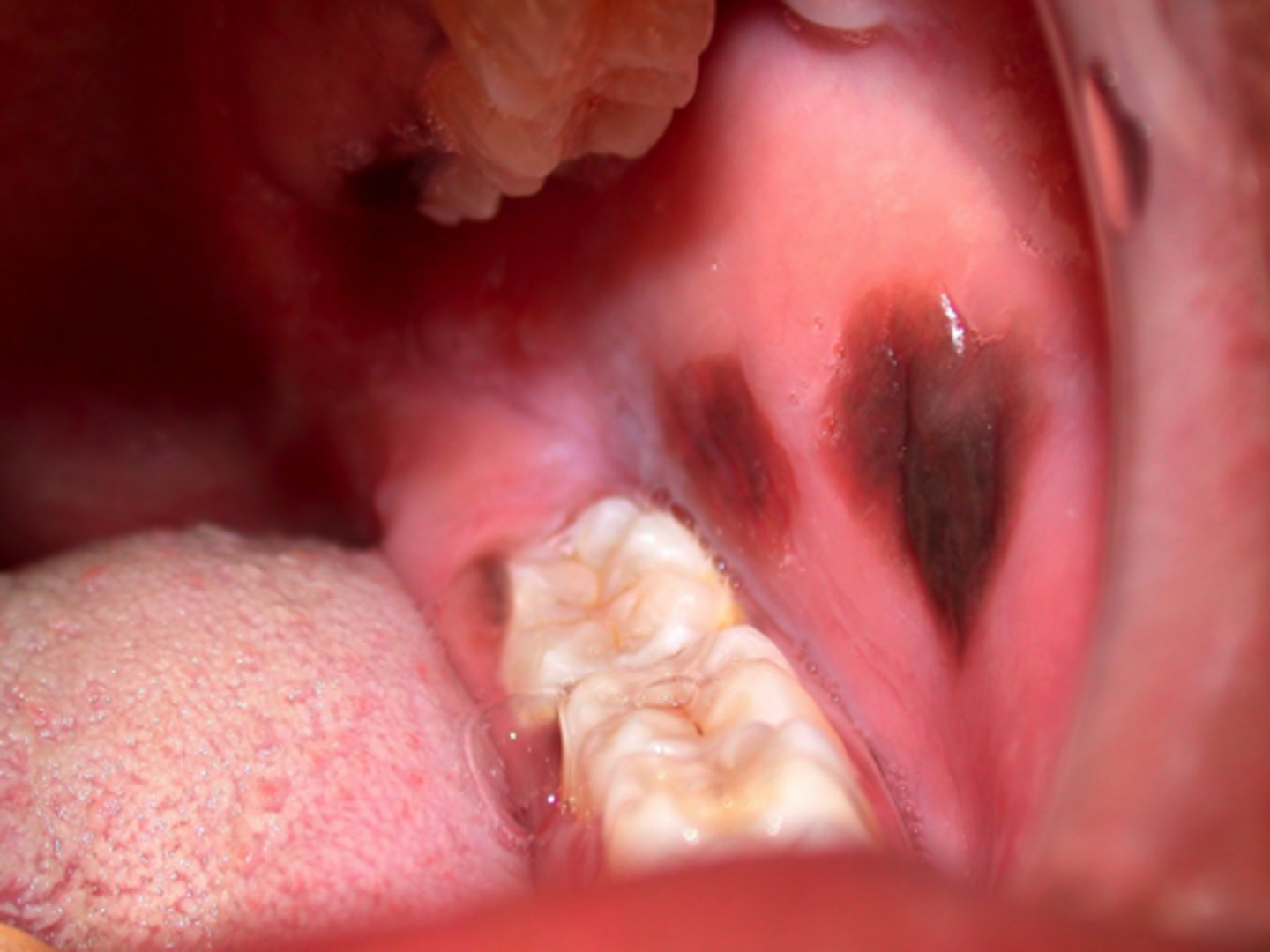
oral melanoacanthoma
Acquired melanocytic nevus
which type of pigmented lesion:
• Common mole
• Benign proliferation of nevus
cells
• "Most common of all human
tumors"
extraoral:
• Asymptomatic
• Round
• Slightly raised
• Brown to black
• Uniformly pigmented
intraoral:
• Uncommon
• More than one in five intraoral
nevi lack pigmentation
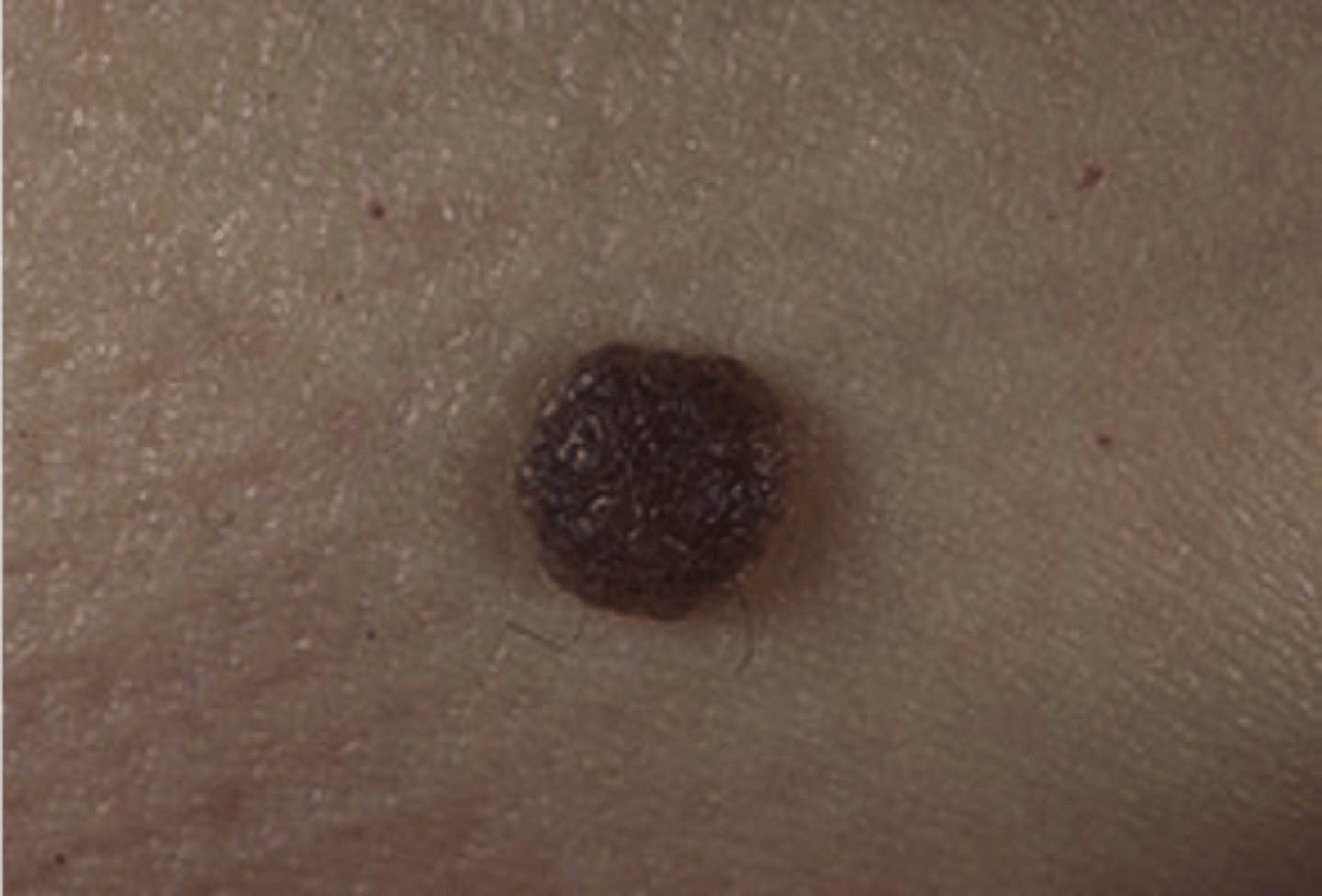
Acquired melanocytic nevus
treatment for which type of pigmented lesion:
• It's a pigmented lesion so you
know I want you to biopsy it
• Once the diagnosis is
established, no treatment is
necessary
• Recurrence is unlikely
• Current evidence does not
suggest that oral melanocytic
nevi are a marker of increased
risk for developing oral mucosal
melanoma
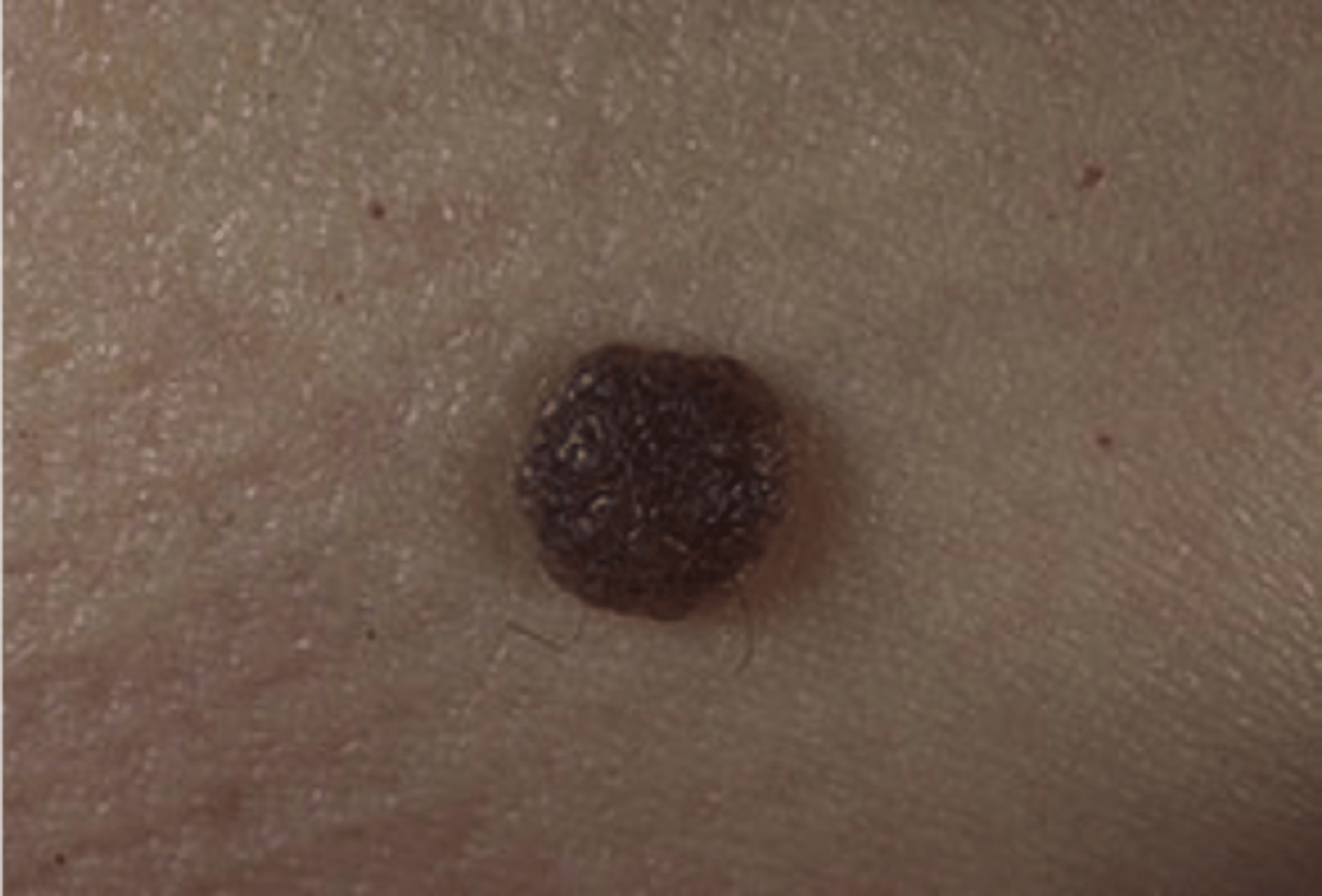
Acquired melanocytic nevus
blue nevus
which type of pigmented lesion:
• Uncommon
• Benign proliferation of
melanocytes deep in the
connective tissue
• Children/YA
• Blue in color→ Tyndall Effect
• Usually found on the palate
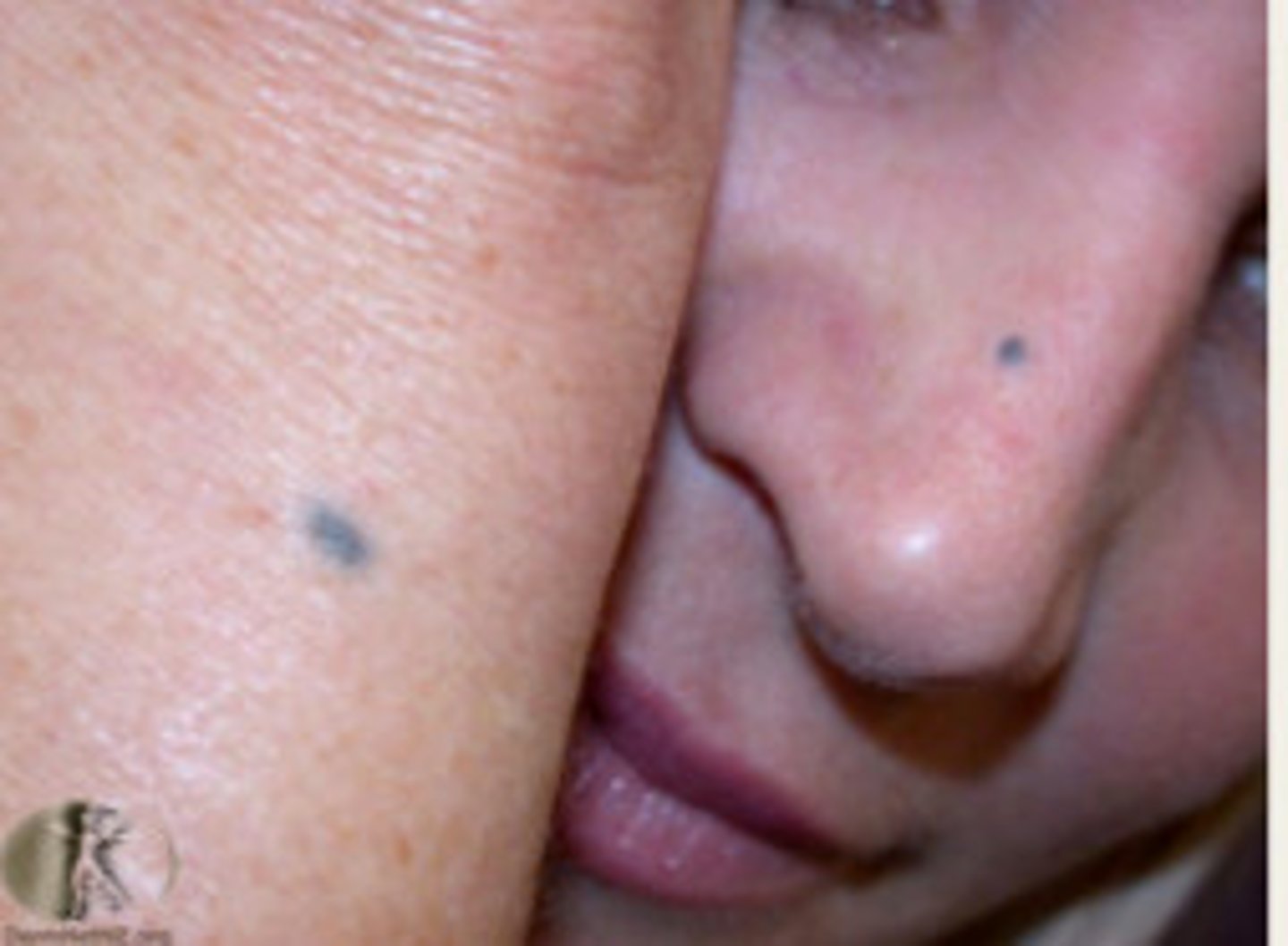
blue nevus
treatment for which type of pigmented lesion:
• It's pigmented so I want you to
biopsy it
• Conservative excision is curative
• Transformation to melanoma
has been reported
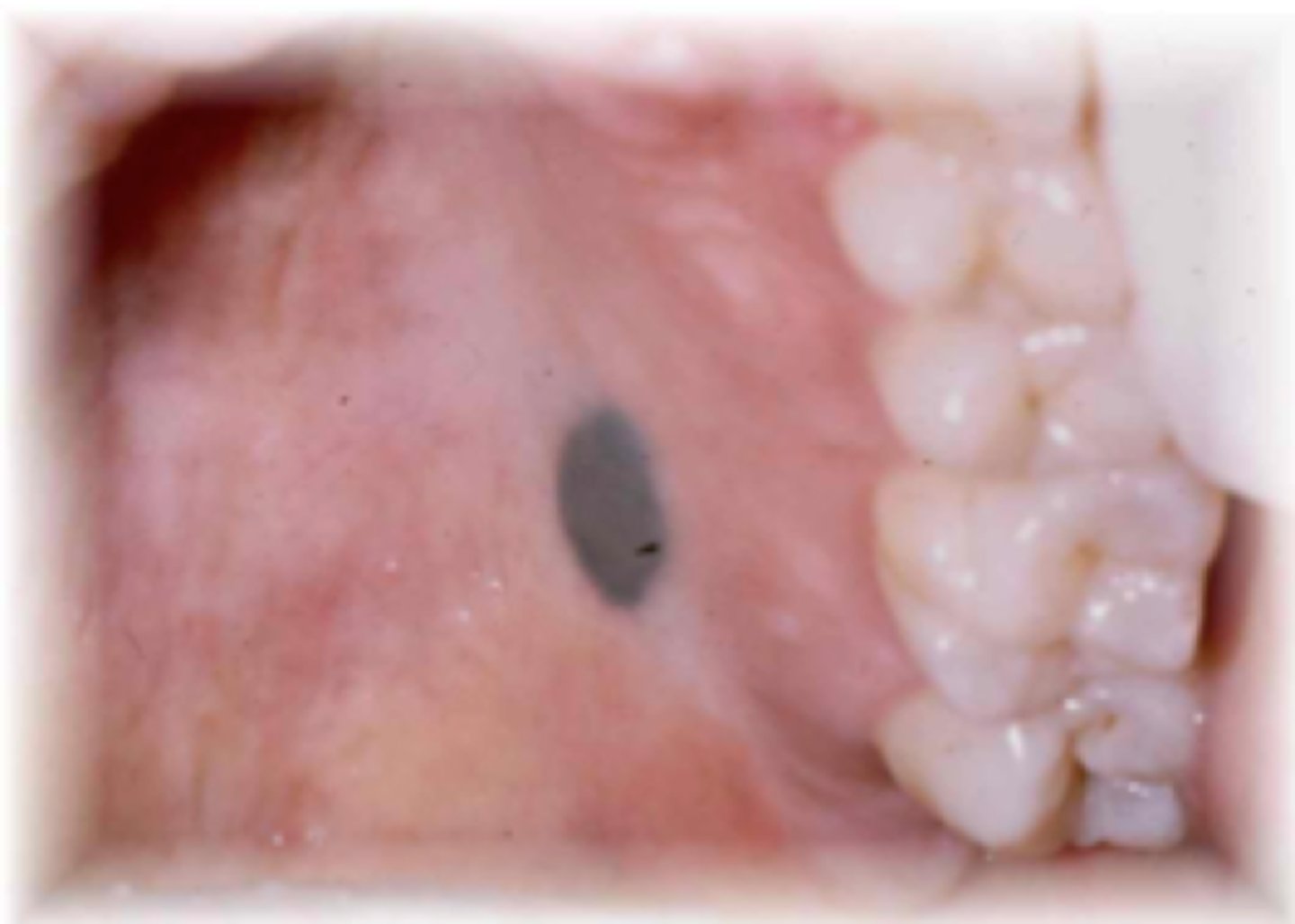
blue nevus