TFN: MAAM PALICPIC
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
Betty Neuman
made the Neuman Systems Model
Betty Neuman
Born in 1924 on a farm near Lowell, Ohio.
Betty Neuman
In 1947, she completed her nursing education with double honors at People’s Hospital School of Nursing (now General Hospital) in Akron, Ohio.
Betty Neuman
As a young nurse, she moved to California and worked in a variety of nursing roles including hospital staff, head nurse, school nurse.
Betty Neuman
She was also involved in clinical teaching in University of Southern California Medical Center, Los Angeles in the areas of medical surgical, communicable disease and critical care.
Betty Neuman
She had always been interested in human behavior. She attended the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) with a double major in Public Health and Psychology.
Betty Neuman
In 1957, she completed her Baccalaureate Degree with Honors in Nursing
Betty Neuman
In 1966, she received her Master’s Degree in Mental Health and Public Health Consultation from the University of California at Los Angeles.
Betty Neuman
In 1985, she completed her Doctor’s Degree in Clinical Psychology from Pacific Western University.
Betty Neuman
A strong/good advocate of Mental Health
Neuman Systems of Model
Neuman first published this model in 1972. Further development and revisions of the model are illustrated in the second (1989) and third (1995) editions. In the fourth edition, it will offer an integrative review of use of the model with guidelines for application of the model in practice, research, education and administration.
General System Theory
Gestalt Theory
Philosophical Views of de Chardin and Marx (One part - three of a whole)
Concept of Stressors
Levels of Prevention from Caplan’s Conceptual Model
Several Theoretical Sources Neuman took in in her Model
General System Theory
Reflects the nature of living organisms as an open system in interaction with each other and with the environment.
Open system
the interaction with each other, interpersonal, and the interaction with the environment.
Gestalt Theory
Describes homeostasis as the process by which an organism maintains its equilibrium and health under varying conditions.
Gestalt Theory
Focuses on the equilibrium or balance that needs to be maintained, disruption of the balance, illness would come in.
Philosophical Views of de Chardin and Marx (One part - three of a whole)
Anything that happens to the one part affects the whole, if one factor affects the totality of a person other parts of the whole will also not function as well.
Deductive
top-down (paubos)
Inductive
bottom-up (paigbaw)
Concept of Stressors
stress increases the demand for readjustment. This demand is non-specific; it requires adaptation to a problem, irrespective of the nature of the problem.
internal
external
Stressors can be classified into two
External Stressors
stressors that pertains to the environment
Internal Stressors
stressors that pertains to the problems within the person
Levels of Prevention from Caplan’s Conceptual Model
These stressors can be prevented from occurring and from disrupting the balance or the equilibrium of the open system which is us by the levels of prevention; primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention.
Primary prevention
is used to protect the organism before it encounters a harmful stressor.
Secondary and Tertiary Prevention
are used after the client’s encounter with a harmful stressor.
Primary Level
health promotion and disease prevention
Secondary Level
early detection of disease and treatment
Tertiary Level
health restoration and prevention of the reoccurrence of the disease and prevention of complications.
Client System
composed of variables that function to achieve stability in relation to the environmental stressors experienced by the client, and can be one or a combination of physiological, psychological, sociocultural, developmental, and spiritual variables.
physiological
psychological
sociocultural
developmental
spiritual
Variables in the Client System
Physiological
a variable that tackles the body structure and function
Psychological
a variable that tackles mental processes in interaction with the environment
Sociocultural
a variable that tackles effects and influences of social and cultural conditions
Developmental
a variable that tackles age-related processes and activities
Spiritual
a variable that tackles beliefs and influences
Neuman Systems Model
Neuman Systems Model
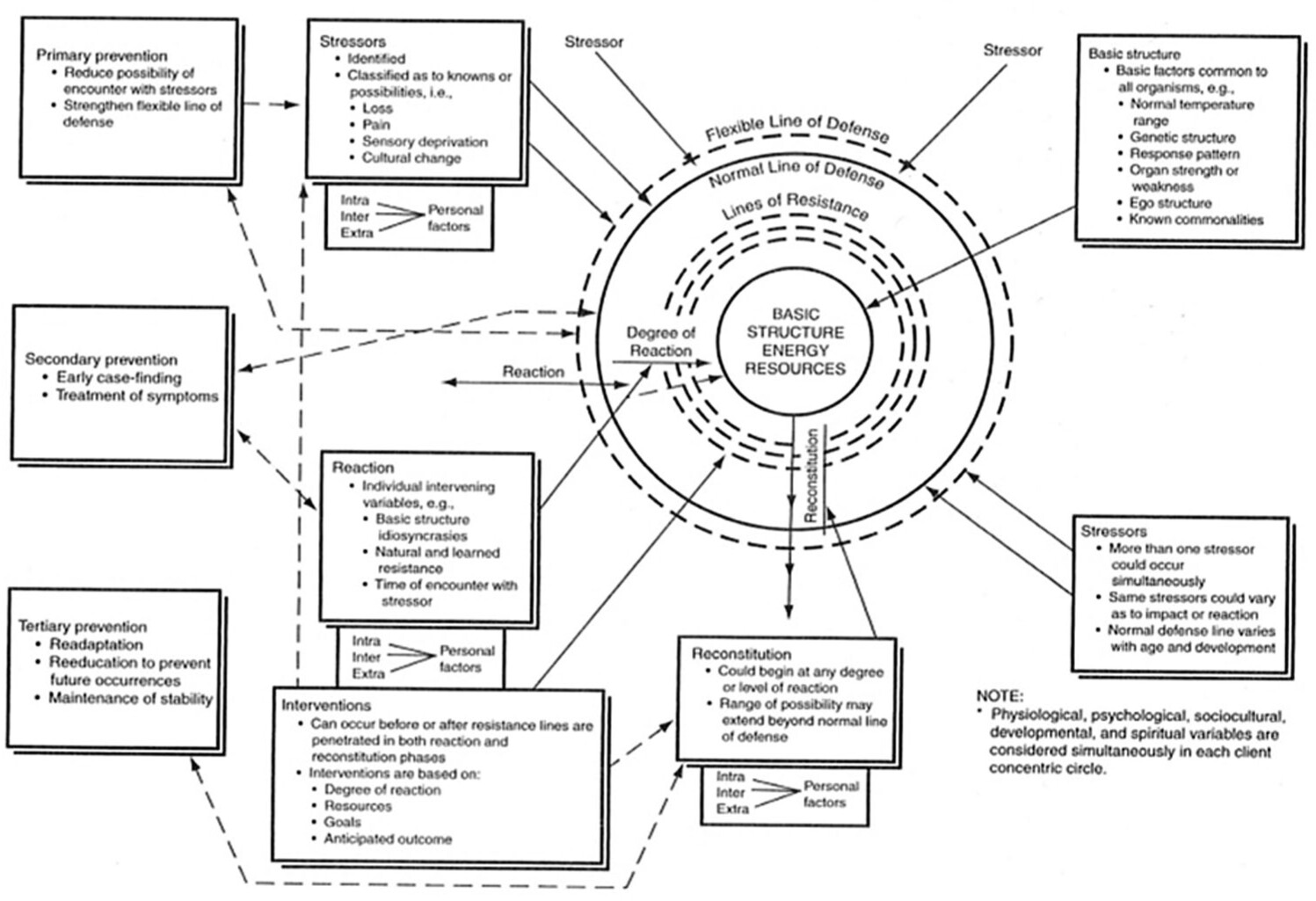
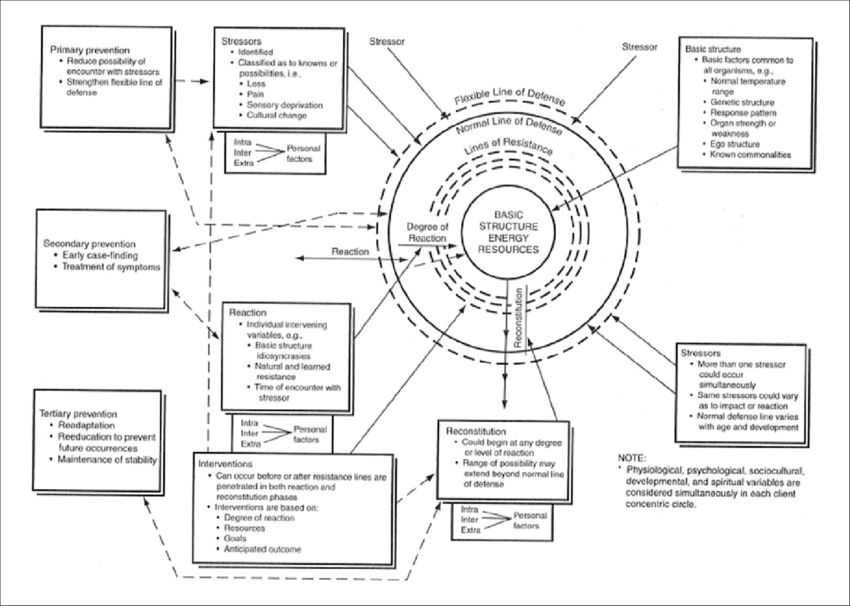
Consists of the basic structure, lines of resistance, normal line of defense, flexible line of defense, the concept of health, stressors, and degree and reaction.
Basic Structure
referred to as the central core which is made up of the basic survival factors common to human beings. These factors include system variables, genetic features, and strengths and weaknesses of the system parts.
Lines of Resistance
act when a Normal Line of Defense is invaded by too many stressors, producing alterations in the clients’ health.
Lines of Resistance
It acts to facilitate coping to overcome the stressors that are present within the individual.
Normal Line of Defense
to achieve the stability of the system, it must act in coordination with the normal wellness state. It must reflect the actual range of responses that is normally acted by clients in response to any stressor.
Normal Line of Defense
It is the baseline in determining the level of wellness of the client within the continuum of health.
Flexible Line of Defense
serves as a boundary for the Normal line of Defense to adjust to situations that threaten the imbalance within the clients’ stability.
Flexible Line of Defense
It expanded the range of normal defense from becoming invaded by the stressors thus increasing its protection.
Health
a continuum of wellness to illness that is dynamic in nature (constantly subject to change).
Optimal wellness
can only exist when the needs of the total system are completely met.
Wellness
exists when all system subparts interact in harmony with the whole system and all system needs are being met.
Illness
occurs at the opposite end of the continuum from wellness and represents a state of instability and energy depletion.
Stressors
external factors/forces that produce tensions, alterations or potential problems causing instability within the client’s system, including intrapersonal, interpersonal, and extrapersonal forces.
intrapersonal forces
interpersonal forces
extrapersonal forces
Stressors may come from the following
Intrapersonal forces
self. It occurs within the individual and correlates with the internal environment.
Example: conditioned responses
Interpersonal forces
person to person. It occur between one or more individuals and outside the client system though at a proximal range.
Example: role expectations
Extrapersonal forces
person to environment. It occur outside the individual or outside the client system at a distal range.
Example: social policy and financial circumstances
Degree of Reaction
The degree of system instability resulting from stressor invasion, which can be positive (negentropy) or negative (egentropy).
Reactions
are the outcomes/produced results of certain stressors and actions of the lines resistance of a client.
Reactions
It can be positive or negative depending on the degree of reaction the client produces to adjust and adapt with the situation.
negentropy
egentropy
Neuman specified reactions as:
Negentropy
set towards stability or wellness.
Egentropy
set towards disorganization of the system producing illness.
Intervention
purposeful action to help the client, retain, attain, and maintain system stability.
Prevention
used to attain balance within the continuum of health. These are actions that generate good results or are aimed towards hindering negative outcomes.
Primary Prevention
Secondary Prevention
Tertiary Prevention
Three Levels of Prevention
Primary prevention
focuses on foreseeing the result of an act or situation and preventing its unnecessary effects as possible.
Primary prevention
It also aims to strengthen the capacity of a person to maintain an optimum level of functioning while being interactive with the environment.
Primary prevention
Example: health promotion and disease prevention
Secondary prevention
focuses on helping alleviate the actual existing effects of an action that altered that balance of health of a person.
Secondary prevention
It aims to reduce environmental influences that lead to the decline of the level of functioning of a person and strengthening or restoring a person's resistance after the illness exposure.
Secondary prevention
Involves the treatment of symptoms following a reaction to stressors.
Secondary prevention
Example: early detection of disease and prompt treatment
Tertiary prevention
focuses on actual treatments or adjustments to facilitate the strengthening of a person after being exposed to a certain disease or illness.
Tertiary prevention
It aims to prevent the regression or reoccurrence of the illness in the manner of rehabilitation.
Tertiary prevention
involves the maintenance of optimal wellness following treatment.
Tertiary prevention
Example: disability avoidance and physical therapy.
Reconstitution
the adjustment state from the degree of reaction.
Reconstitution
It is the state of going back to the actual state of health before illness occurred.
Nursing
person
health
environment
Metaparadigm or the key concepts in Neuman's model.
Nursing
Neuman believes that it is concerned with the whole person.
Nursing
She views it as “a unique profession in that it is concerned with all the variables affecting the individual’s response to stress.”
Person
Neuman regarded the concept of it as an individual, family, community, or the society.
Person
She sees it as an ‘open system’ that works together with other parts of its body as it interacts with the environment.
open system
is characterized by the presence of an exchange of information and reaction with other factors surrounding a person.
Health
Neuman views it as a continuum from wellness to illness that is dynamic in nature.
Environment
Neuman defines it as the “internal and external forces surrounding the client, influencing and being influenced by the client.” It can alter or improve the systems in which the person exists
Practice (The Neuman Systems Model)
unified and holistic approach
multidisciplinary as nurses use the nursing process format and prevention as an intervention to collaborate with the healthcare team
Addressing the problem of an individual, family, community, or society in a different practice setting is really helpful.
it is very much applicable to the hospital, clinic, nursing home, rehab, and even in birthing centers.
It is also applicable for clients experiencing complex stressors.
Help nurses to formulate an approach that can prevent and alleviate the client's condition.
Applicable in organizing a framework to plan care
Education (The Neuman Systems Model)
Been widely used both by nursing students and educators
the model demonstrated effectiveness and conceptual transition among levels of nursing education
it has formed a basis for continuing study after graduation
This model provides a direction to validate nursing roles and activities setting its applicability beyond nursing practice.
Research (The Neuman Systems Model)
Incorporated the use of testing the efficacy and usefulness of the model in different areas and scope of the nursing practice
the model has been most widely used frameworks used in nursing research as it guides the enhancement of nursing care
Clarity (The Neuman Systems Model)
Neuman's model is initially clear as to its conceptual description wherein its structure shows itself as a central nucleus wrapped by normal and defensive lines.
It presented information congruent with traditional nursing values
It's consistent with other non-nursing theories
Simplicity (The Neuman Systems Model)
Neuman's Systems Model is viewed to have contradicting reactions. Others say that her model was not simple enough but others believe that it can be easily understood and used.
Simple because:
Used to understand the help of a person
Identify the related stressors and possible reactions
Have prevention and restoration activities
Generality (The Neuman Systems Model)
Her theory was comprehensive and adaptable for the nurse to use in the different practice settings.
Its applicability is congruent with the social, physical, physiological, psychological, spiritual aspects of a person which is very holistic.
Accessibility (The Neuman Systems Model)
Some critics believe that the use of Neman's model increases the collection of empiricism within the scope of nursing practice.
Therefore, it is predicted that the enhancement of the theory has an increasing chance.
Importance (The Neuman Systems Model)
Neuman's theory provides guidelines for a professional nurse to have an accurate assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation of the planned care for their clients.
This model also serves as a guide for them that can be useful for further research.
Sister Callista Roy
Born on October 14, 1939 in Los Angeles, California
Sister Callista Roy
A sister or a member of St. Joseph of Carondelet
Sister Callista Roy
A nurse theorist and a professor at the William F. Connell School of Nursing at Boston College, Massachusetts
Sister Callista Roy
Earned her Bachelor of Science in Nursing in1963, from Mount Saint Mary College, LA
Sister Callista Roy
Finished her Masters degree in Pediatric Nursing in 1966
Sister Callista Roy
Doctorate in Sociology was conferred to her in 1977 from the University of California, LA
Sister Callista Roy
She was Post-Doctoral Fellow and Robert Wood Johnson clinical nurse scholar at University of California, LA
Roy's Adaption Model
Focuses on the concept of adaptation of the person and is both deductive and inductive in nature.