Economics - Ujian Sekolah
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Correct me if Im wrong — Key answers= https://xtremepape.rs/threads/igcse-economics-coursebook-2nd-edtion-cambridge-textbook-answers.109496/ — Source= https://www.savemyexams.com/igcse/economics/cie/20/revision-notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is scarcity
A situation where there is not enough to satisfy everyone’s wants
What is the economic problem
Unlimited wants exceeding finite resources
Factors of production (4)
Land: gifts of nature available for production (most immobile)
Labour: Human effort used in producing goods and services
Capital: Human made goods used to produce other goods and services
Enterprise: The willingness and ability to bear uncertain risks and to make decisions in a business (most mobile)
What is Opportunity cost
The loss of the next best alternatve
What is a production possibility curve (PPC)
A curve that shows the maximum output of two types of products that a country can generate if it uses all of its factors of production.
A movement in the PPC occurs when
When there is any change in the allocation of existing resources within an economy
Microeconomics
The study of individual markets & sections of the economy. It examines the different choices individuals, households & firms make and what factors influence their choices.
Macroeconomics
The study of economic behaviour & decision making in the entire economy. It examines the role of the government in achieving economic growth & human development through the implementation of specific government policies
Questions that economies faces (3)
What to produce
How to produce
Who is the receive the products produced
Demand
The amount of a good/service that a consumer is willing & able to purchase at a given price in a given time period
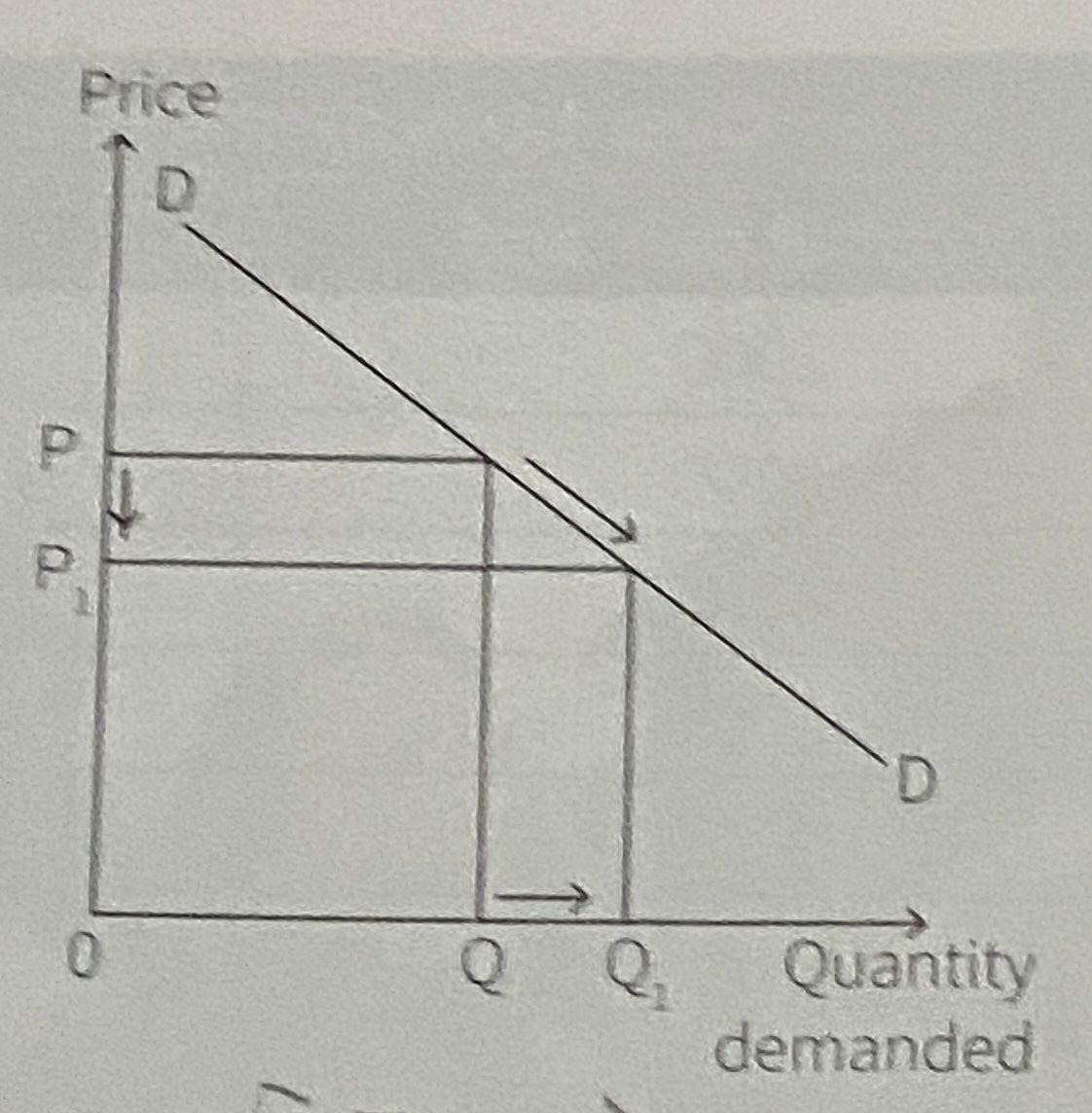
What is this?
Extension in demand
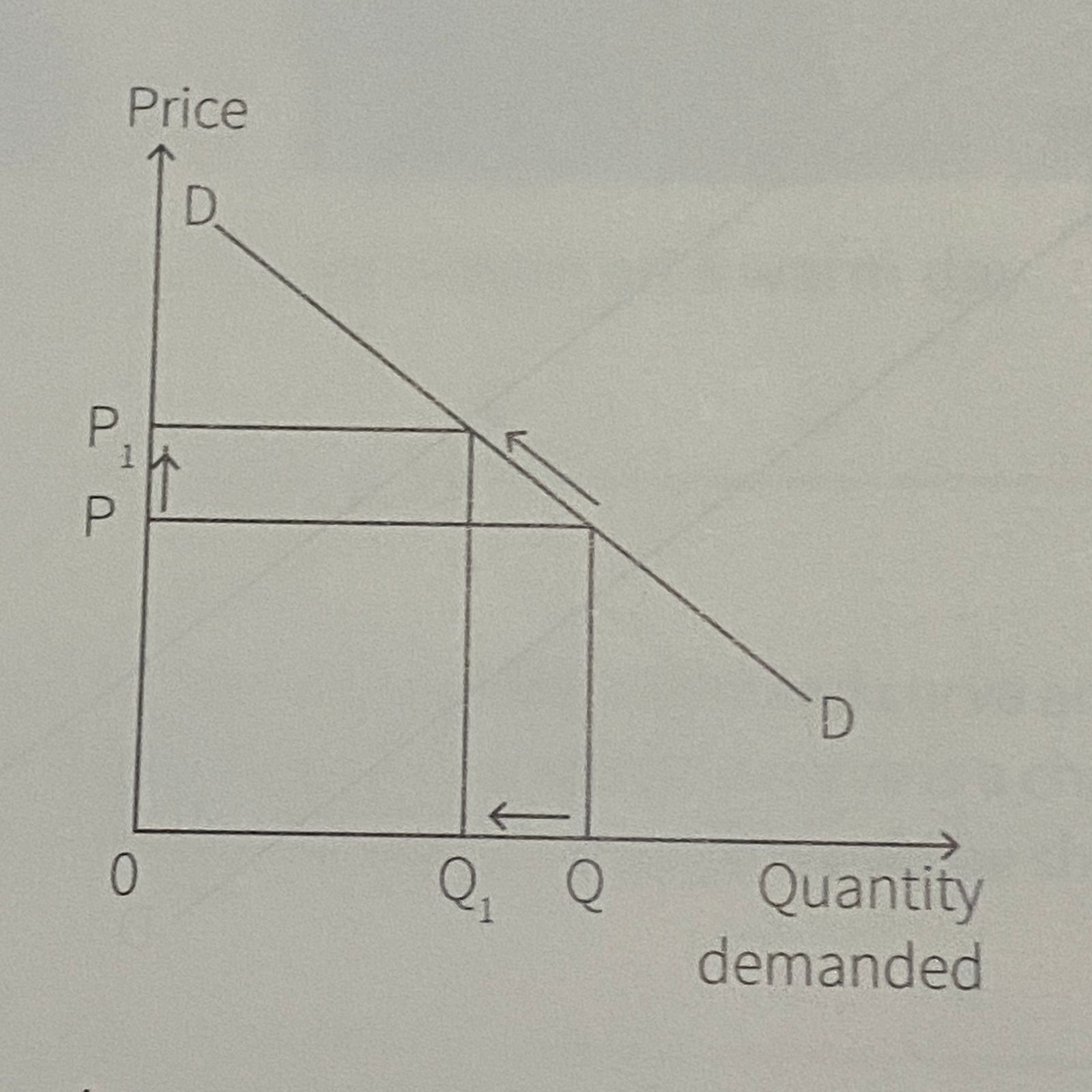
What is this?
Contraction in demand
What causes movement along the demand curve?
The price, which is the only factor that changes (this causes a change in quantity demanded)
Contraction = Increase in price, decrease in QD
Extension = Decrease in price, increase in QD
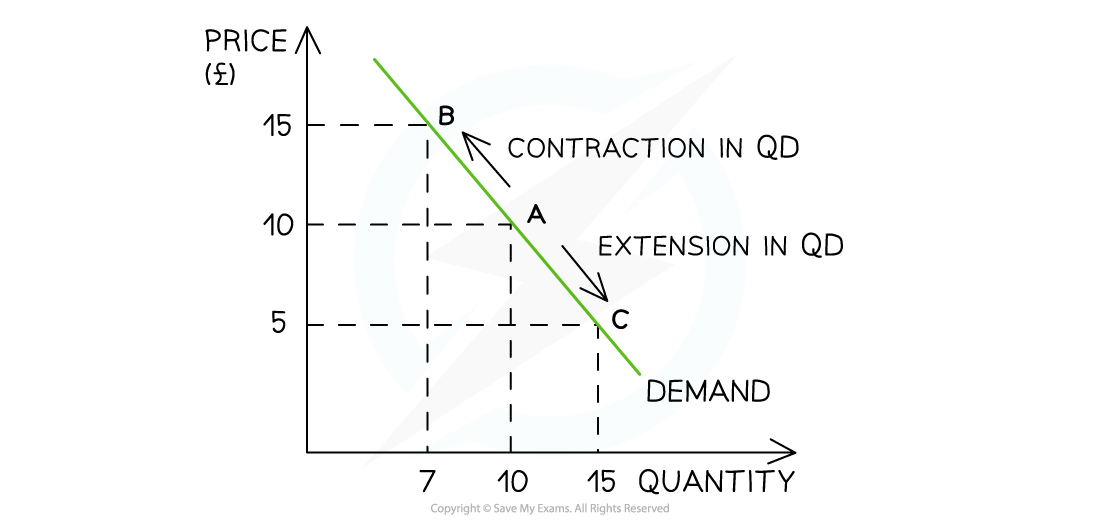
Example of movement along the demand curve
What is this?
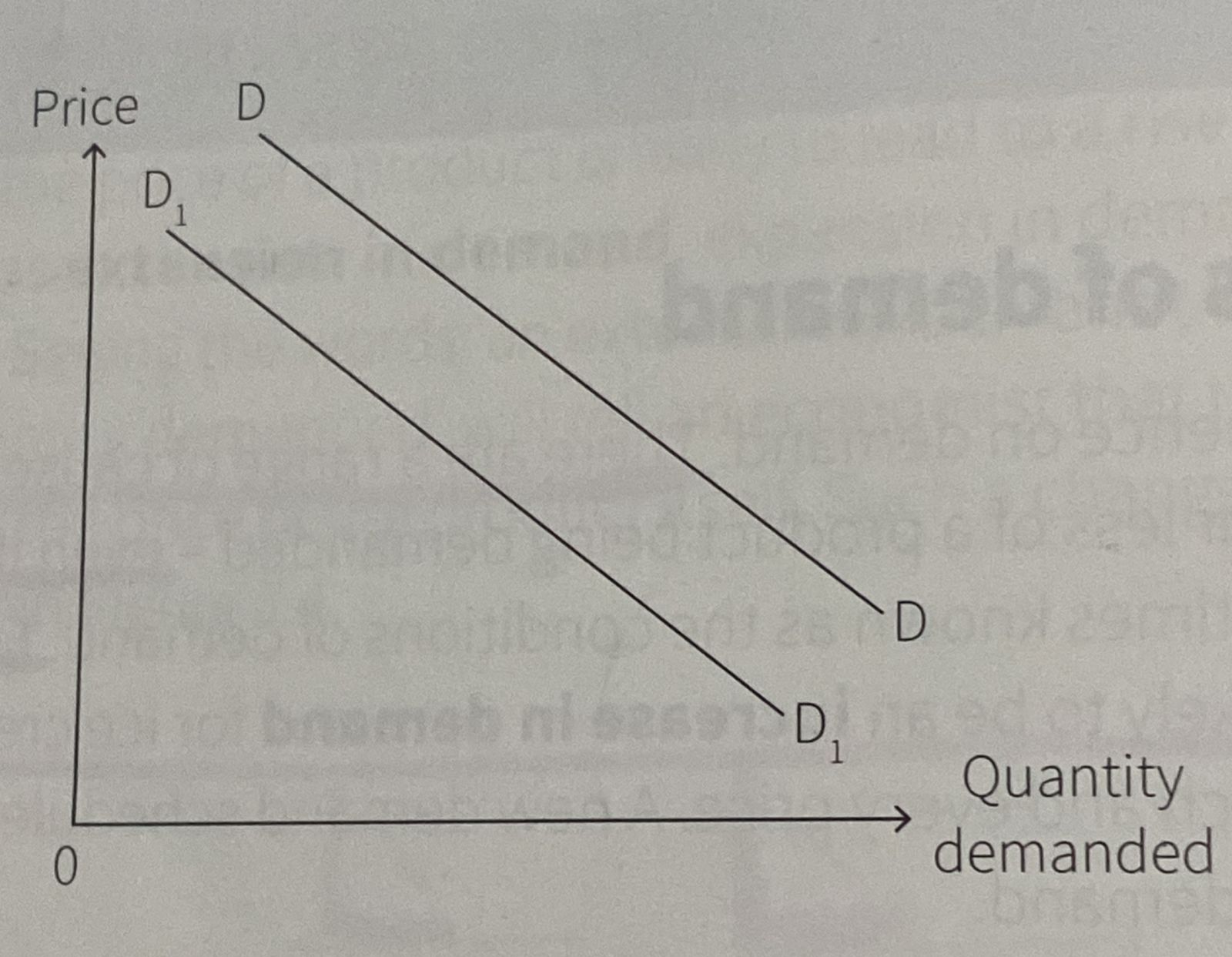
Decrease in demand
What causes the entire demand curve to shift?
Conditions of demand (irrespective of the price level)
Advertising campaigns
Changes in population
Changes in taste and fashion
Etc.
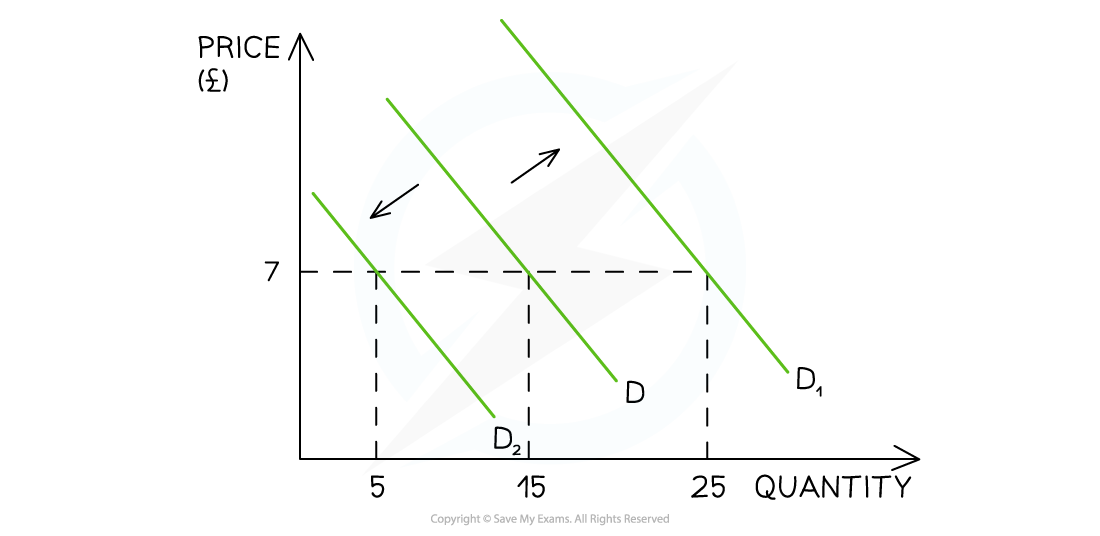
Example of shift of the demand curve
D1 → increase
D2 → decrease
Supply
The amount of a good/service that a producer is willing & able to supply at a given price in a given time period.
The supply curve is sloping upward as there is a positive relationship
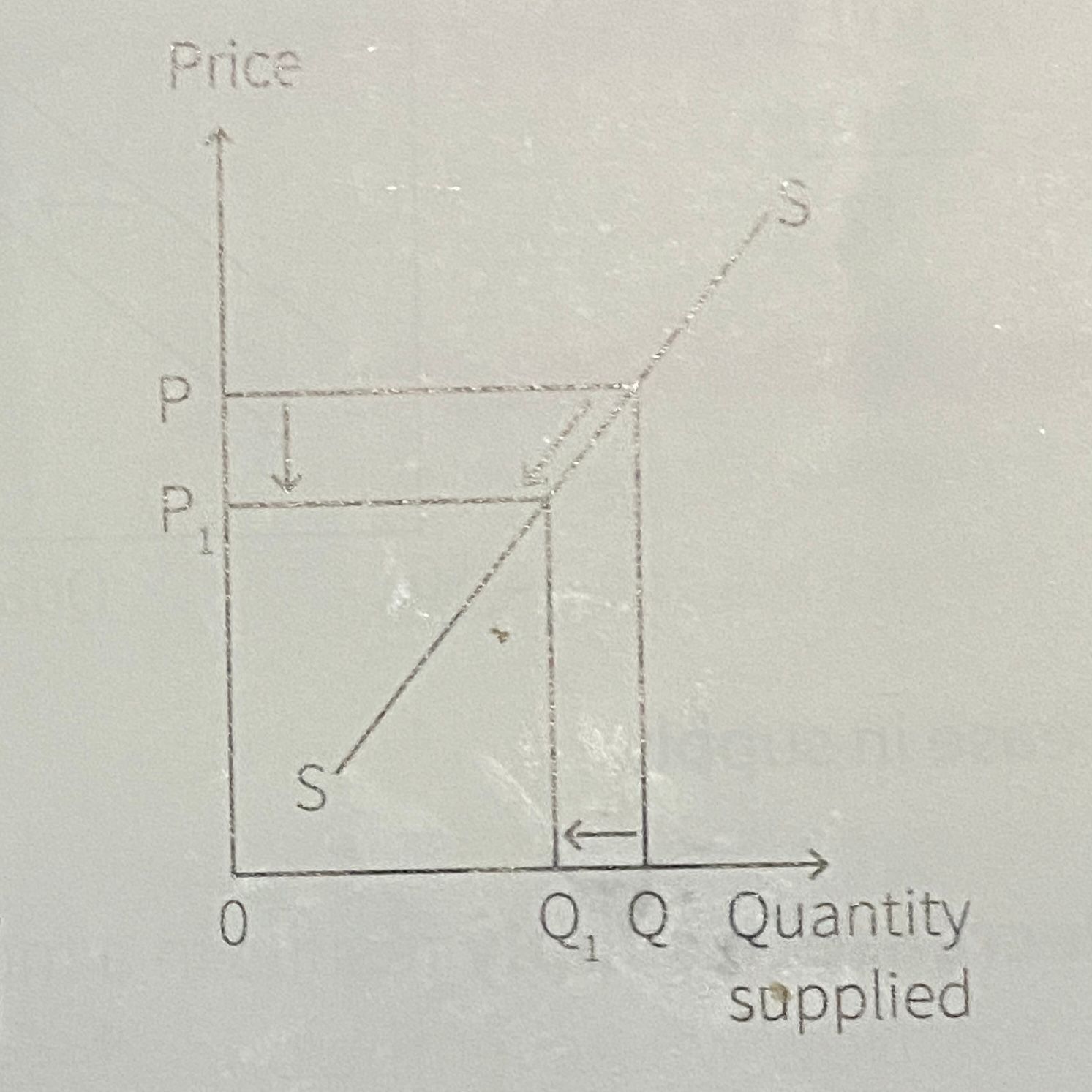
What is this?
Contraction in supply
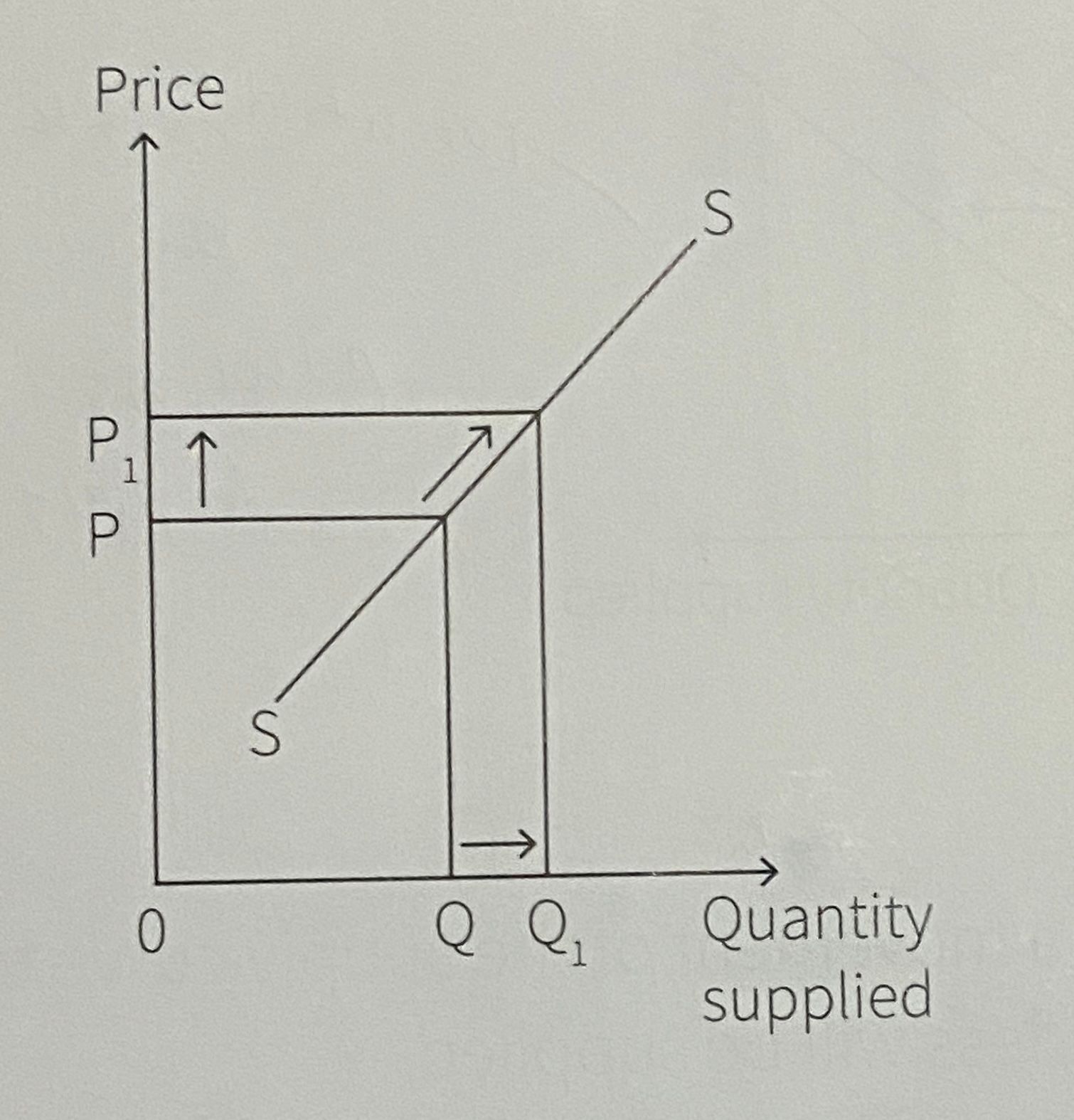
What is this?
Extension in supply
What causes movement along the supply curve?
Price (the only factor), there will be a change in QS (quantity supplied)
Extension = Increase in price, increase in QS
Contraction = Decrease in price, decrease in QS
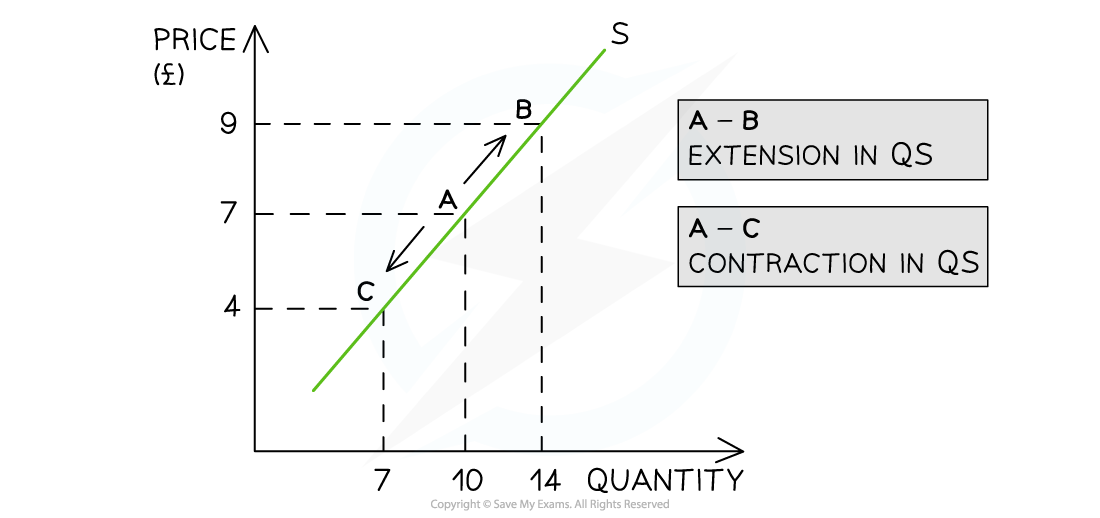
Example of movement along a supply curve
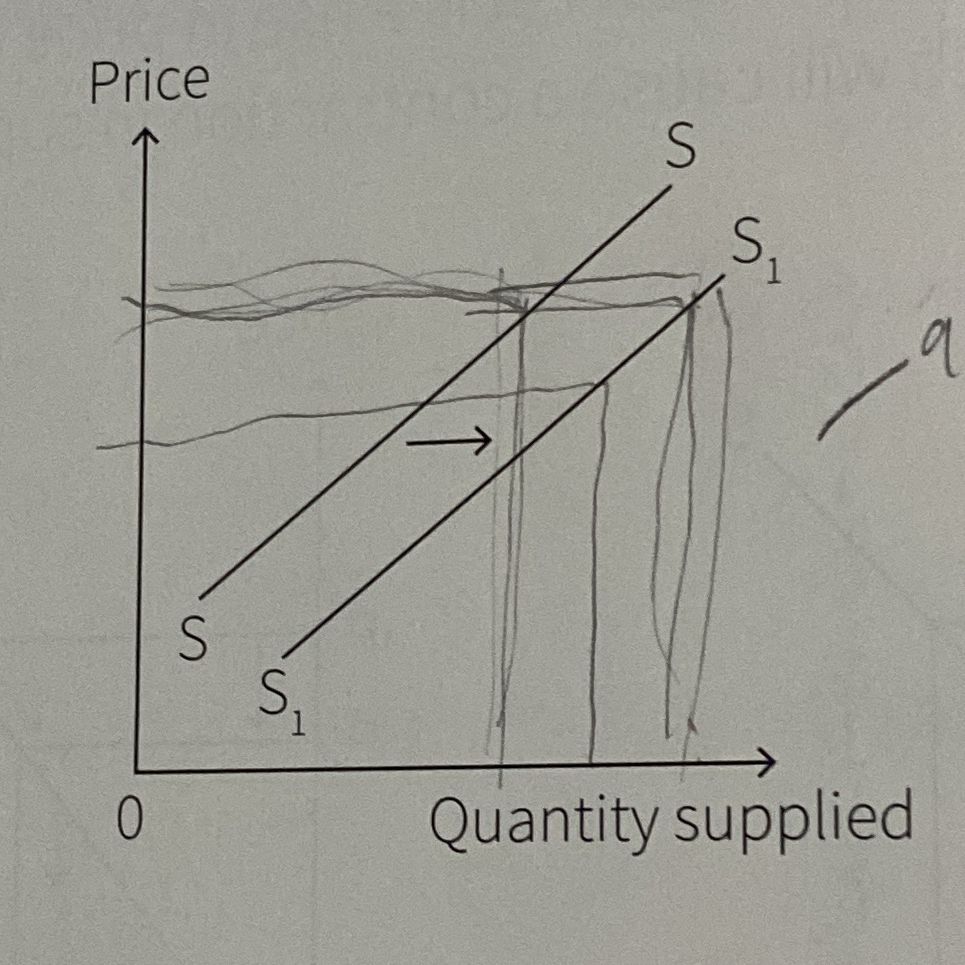
What is this?
Increase in supply
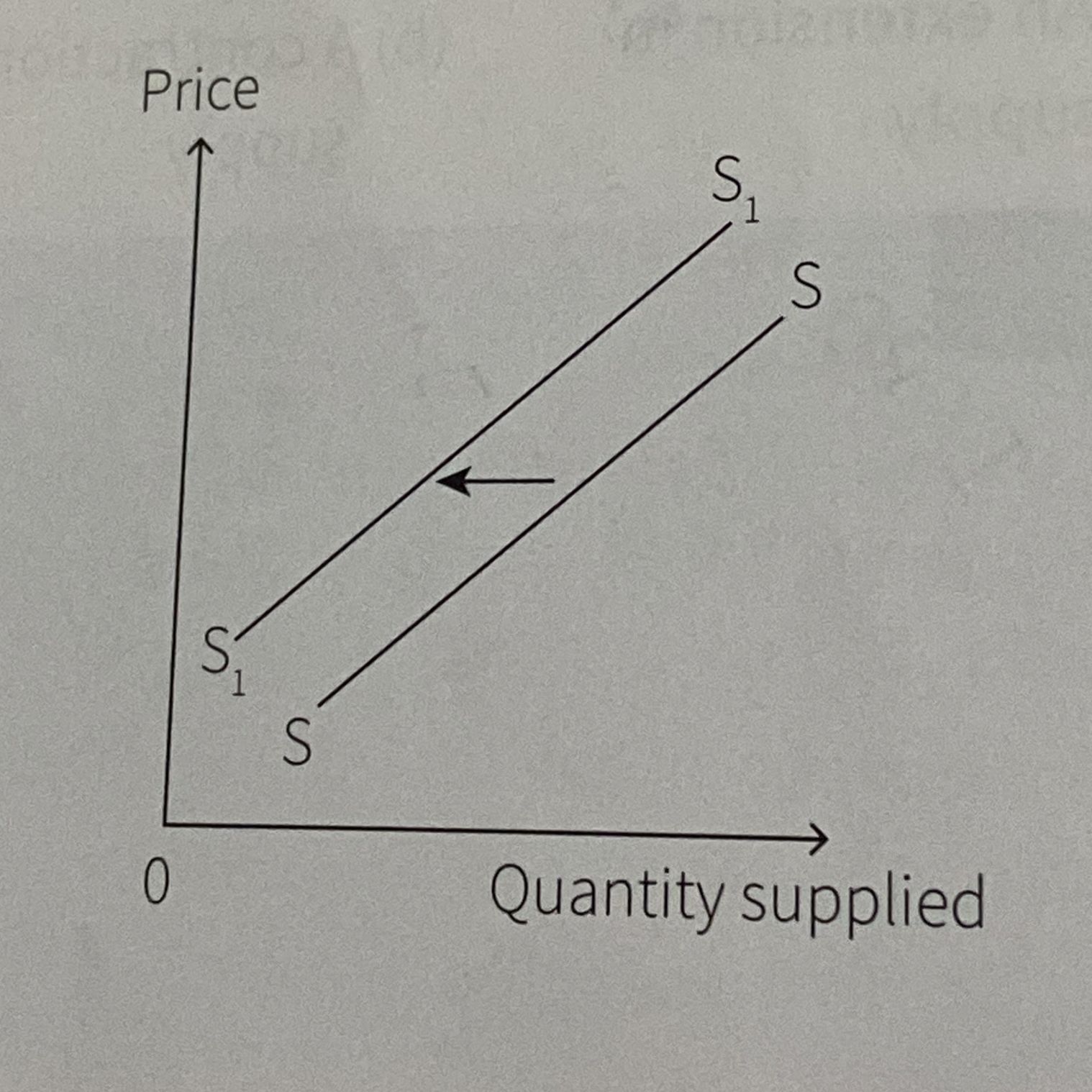
What is this?
Decrease in supply
What causes the entire supply curve to shift
Conditions of supply (irrespective of the price level)
Change in cost of production
Improvements in technology
Taxes
Subsidy
Conditions (health of livestock, crops, weather)
Prices of other products
Disasters and wars
Discoveries and depletions of commodities

Example of shift of the supply curve
S1 → Decrease
S2 → Increase
What is equilibrium
Demand = Supply
What is market disequilibrium?
Demand ≠ Supply
Shortage
Excess demand (supply cannot keep up)
Surplus
Excess supply (demand cannot keep up)
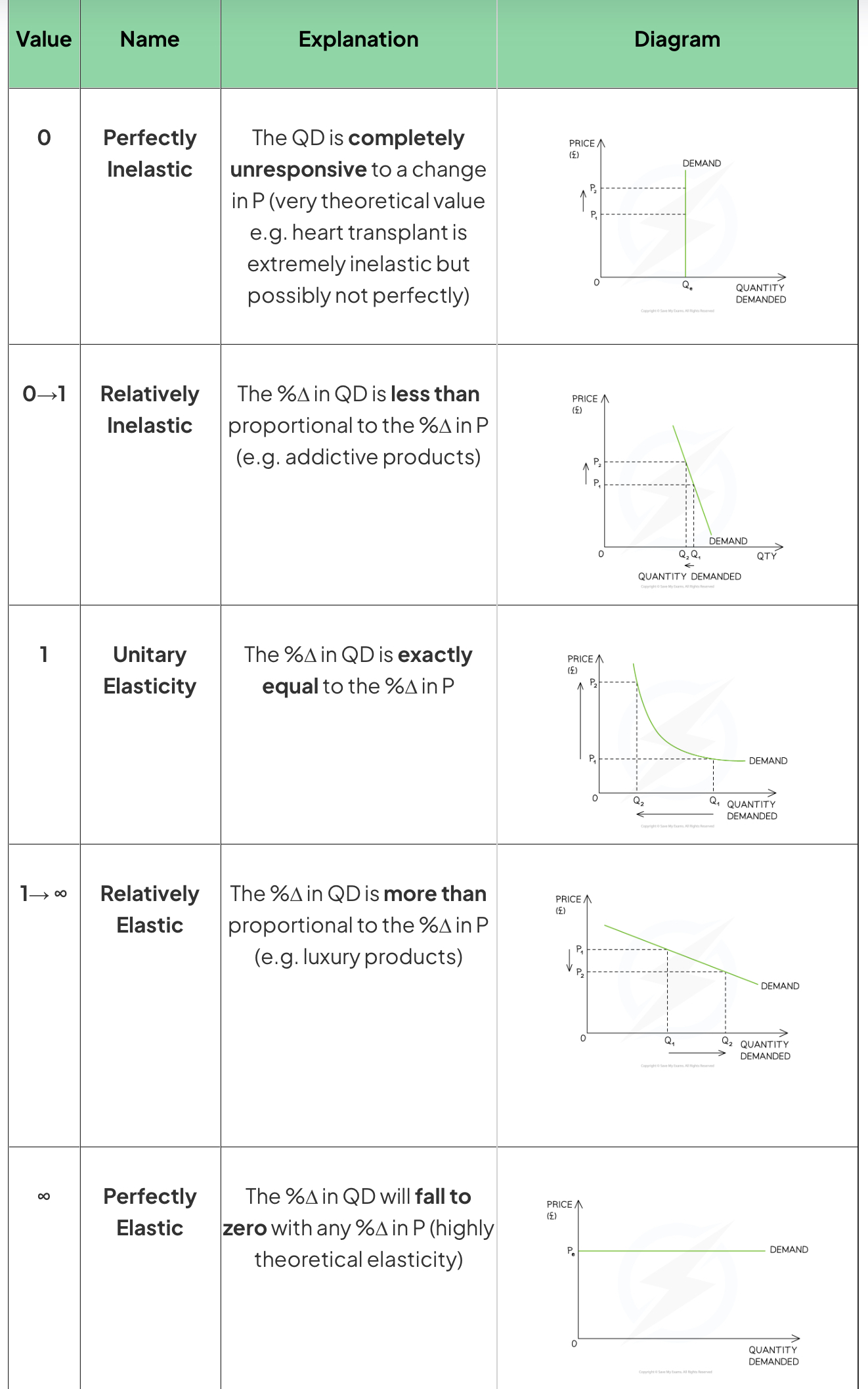
Price elasticity of demand (PED)
Price elasticity of demand measures how responsive the change in quantity demanded is to a change in price
The PED value will always be negative so economists ignore the sign and present the answer as positive.
PED formula
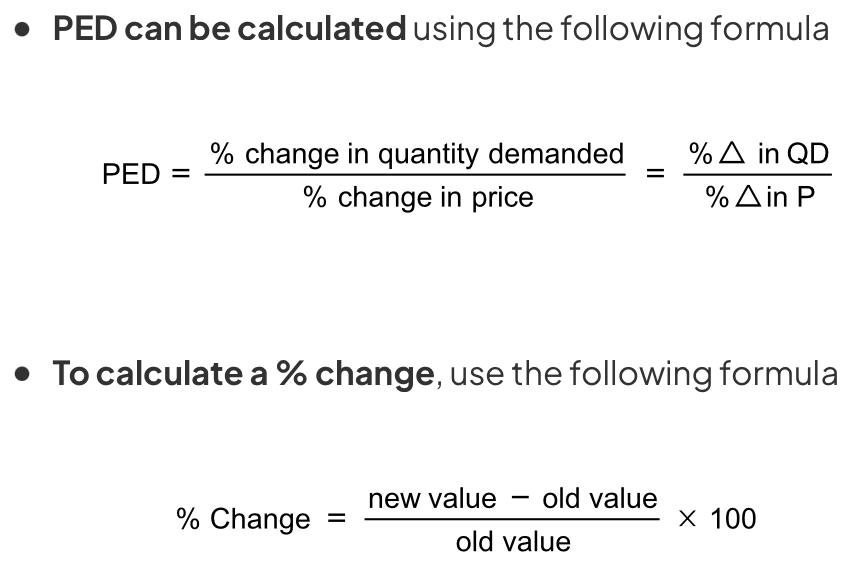
PED values (The PED value will always be negative so economists ignore the sign and present the answer as positive)
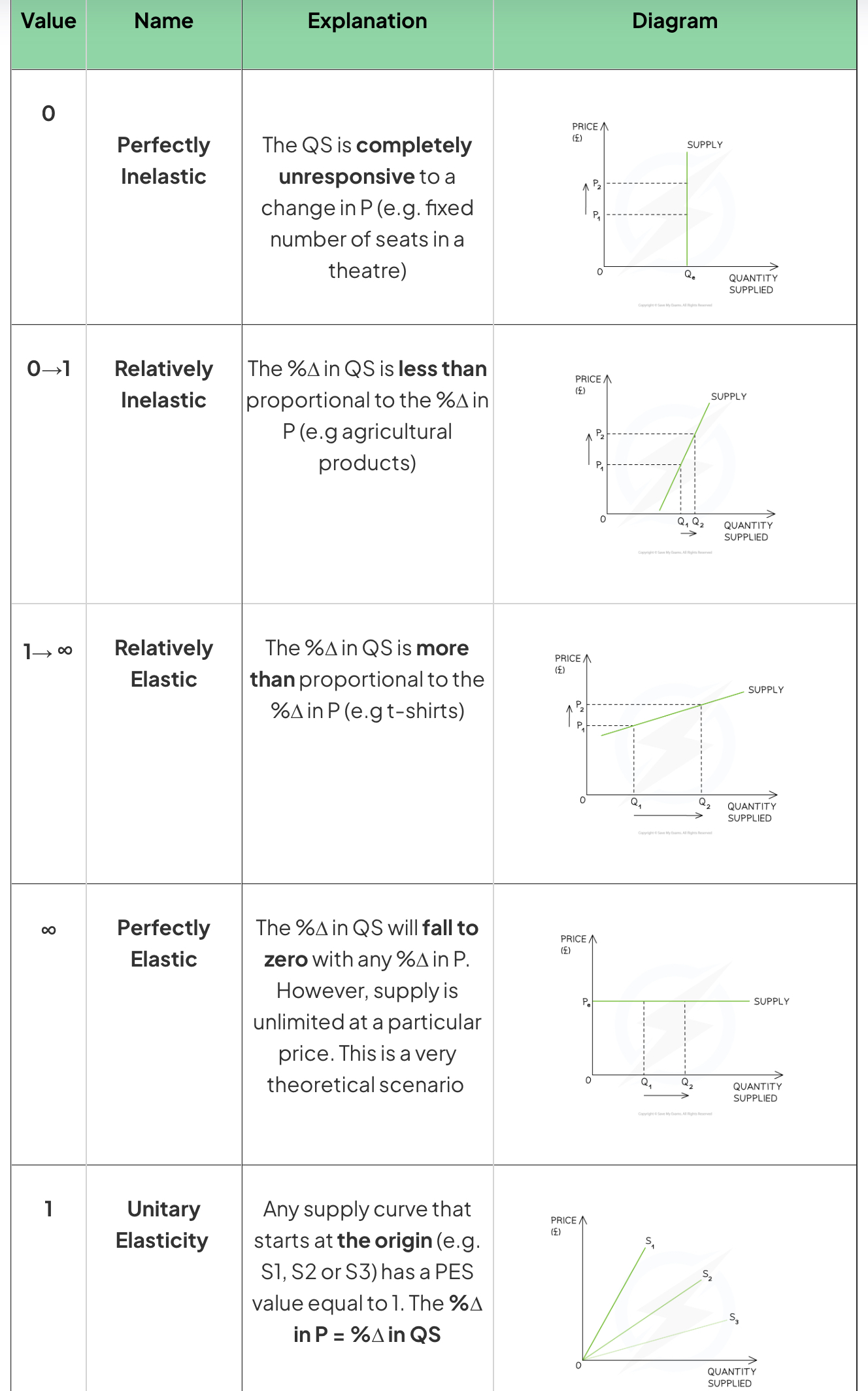
Price elasticity of supply (PES)
Price elasticity of supply (PES) measures how responsive the change in quantity supplied is to a change in price
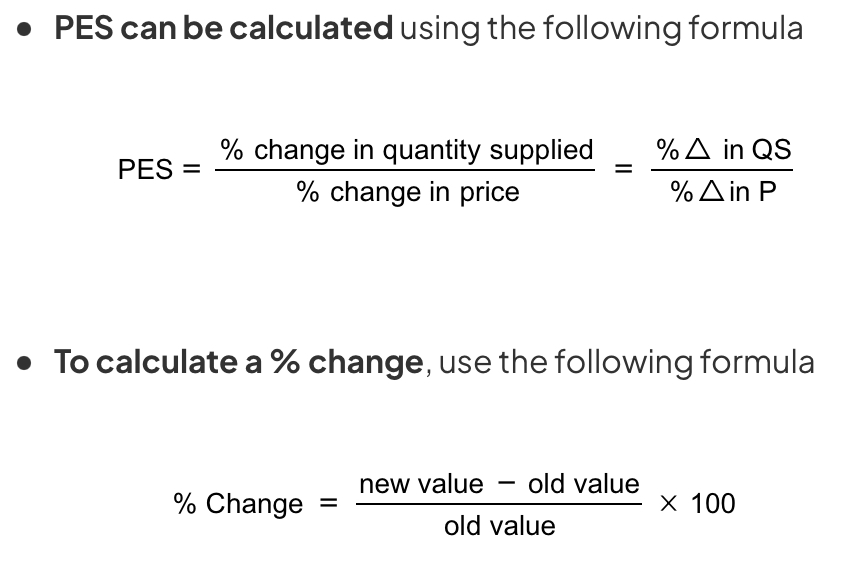
PES formula
PES value
What is a market economy
A market economy/free market economy is an economy that has no (little) government intervention in the allocation of resources & distribution of goods/services
Types of economy

Public sector
The part of the economy controlled by the goverment
Private sector
Covers business organisations which are owned by shareholders and individual
Advantage and disadvantages of market economy