Advanced Sports Medicine - The Knee
1/55
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
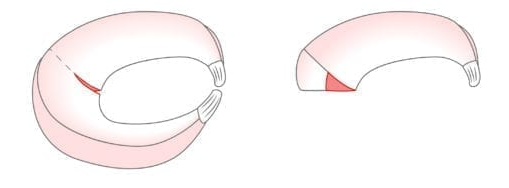
Radial meniscus tear
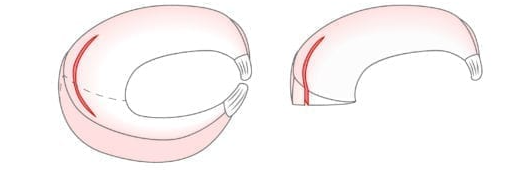
Longitudinal meniscus tear
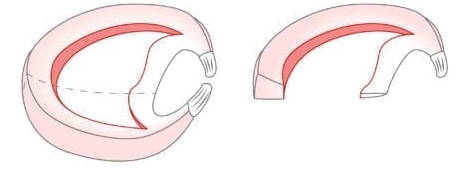
Bucket handle meniscus tear
Valgus Stressor
Medial force on knee
Varus Stressors
Lateral forces on knee
Hamstring muscle group
Biceps femoris, semi membranous, semi tendinous
Pes Anserine muscle group
Sartorius, semi tendinous, gracilis
Muscles responsible for internal rotation
Sartorius, semi tendinous, gracilis (Pes anserine), popliteus, semi membranous
Muscles responsible for external rotation
Biceps Femoris
Muscles responsible for extension
Quadriceps (vatus lateralis, rectus femoris, vastus medialis)
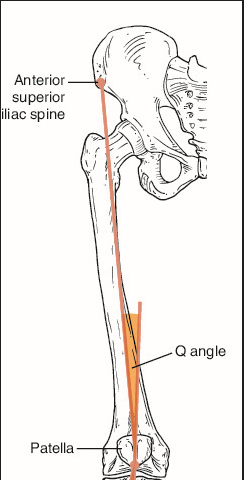
Q-angle standards (Measured from anterior superior iliac spine to patella to tibial tuberosity)
Male: 10 degrees Female: 15 degrees
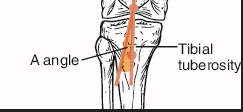
A-angle standards (Measured from patellar apex to tibial tuberosity)
>35 degrees is a bad sign
Genu valgum or “Knock knees”
knees move inwards towards each other, compresses lateral meniscus, stresses MCL
Genu varum or “Bow legged”
Hyperextended knees, internal rotation of tibia, can cause rickets (soft bones), stresses LCL, compresses medial meniscus and IT band
Genu recurvatum
Hyperextended knees, lordosis (excessive curve of lumbar spine), stresses ACL and PCL + gastrocnemius, popliteus, plantaris
Patella Alta
Patella rests superiorly, tendon ratio is greater than 1:1
Patella Baja
Patella rests inferiorly, tendon ration less than 1:1
Tibial torsion (measures rotation of tibia)
< or > 15 degrees is a BAD sign
Femoral anteversion “pigeon toed”
Internal rotation of femur, caused by internal rotation of >70 degrees
Femoral retroversion “Duck footed”
External rotation of femur, caused by external rotation of >45 degrees
MCL Sprain causation
Involves medial meniscus occasionally, caused by varus (lateral) force
LCL Sprains causation
Caused by valgus (medial) force, complete tears involve PCL and occasionally ACL
ACL Sprains causation
Sprained by non contact situations the most out of ligaments, caused by twisting and hyperextension of knee, caused by valgus (lateral) force
Unhappy Triad
Injury of MCL, medial meniscus, and ACL
PCL Sprains causation
Usually injured among other ligaments, caused by forced hyperflexion (movement is likely to also tear ACL), falling on a bent knee
Allograft
ACL repair from a dead person
Autograft
ACL repair from own body (patellar tendon, semi tendinous, gracilis)
Meniscectomy
Either partial (inner 1/3) or full removal of meniscus
Meniscal injuries causation
Forceful internal rotation/external rotation while flexing or extending knee (courtesy lunges)
Meniscal Repair
Outer 2/3 of meniscus repaired
Patellar dislocation/ subluxations causation - conditional
Genu valgum
Genu recurvatum
Patella alta
Weak vastus medialis
Probated feet (waking on inner portion of feet)
Patellar dislocation/ subluxations causation - action
Planting foot, decelerating, changing directions + hit on medial side of knee while planted
IT Band friction syndrome causation
Leg length discrepancy
Tight quads/hams
Genu varum
Excessive foot pronation
Tight heel cord
Running on uneven surfaces such as running down hills
IT Band friction syndrome
Friction with lateral femoral epicondyle, tenderness, crepitus, swelling
Osgood-Schlatters
Avulsion fracture of tibial tuberosity
Osgood-Schlatters causation
Growing too fast, tight quads, repetitive jumping
Screw home mechanism
The mechanism in which the tibia rotates in order to lock the knee
Two tendons that support the patella
Quadricep & patellar tendon
Medial meniscus tear
forceful internal/external while locked at 10-30 degrees
Lateral meniscus tear
forceful internal/external while locked at 70 degrees
Structures concerned with genu valgum
Compressed lateral meniscus, stressed MCL
Structures concerned with genu varum
Stressed LCL, compressed medial meniscus and IT band
Structures concerned with genu recurvatum
Stressed ACL + PCL, gastrocnemius, popliteus, plantaris
Bones the make up the knee
Femur, tibia, patella, femur
Muscles that perform knee flexion
Biceps femoris, planatris, popliteus, semi membranosous, semi tendonosous, sartorious, gracilis, gastronemius
Quadriceps muscle group
Vastus lateralis, rectus femoris, vastus medialis
Another name for patellar tendinitis
Jumper’s knee
Structure that connects each menisci
Transverse ligament
Attachment site on tibia for quad muscles
Tibial tuberosity
Patellar tendinitis
Inflammation of patellar or quadricep tendon, caused by overuse (repetitive jumping)
Purpose of medial collateral ligament
Protects against valgus (medial) stressors
Purpose of lateral collateral ligament
Protects against varus (lateral) stressors
Purpose of anterior cruciate ligament
Stabilizes against internal rotation, prevents tibia from moving anteriorly
Purpose of posterior cruciate ligament
Prevents hyperextension, posterior movement of tibia, and internal rotation