03.10 BIO Cells, Bacteria, & Viruses (ALL)
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Cells

Anton van Leeuwenhoek
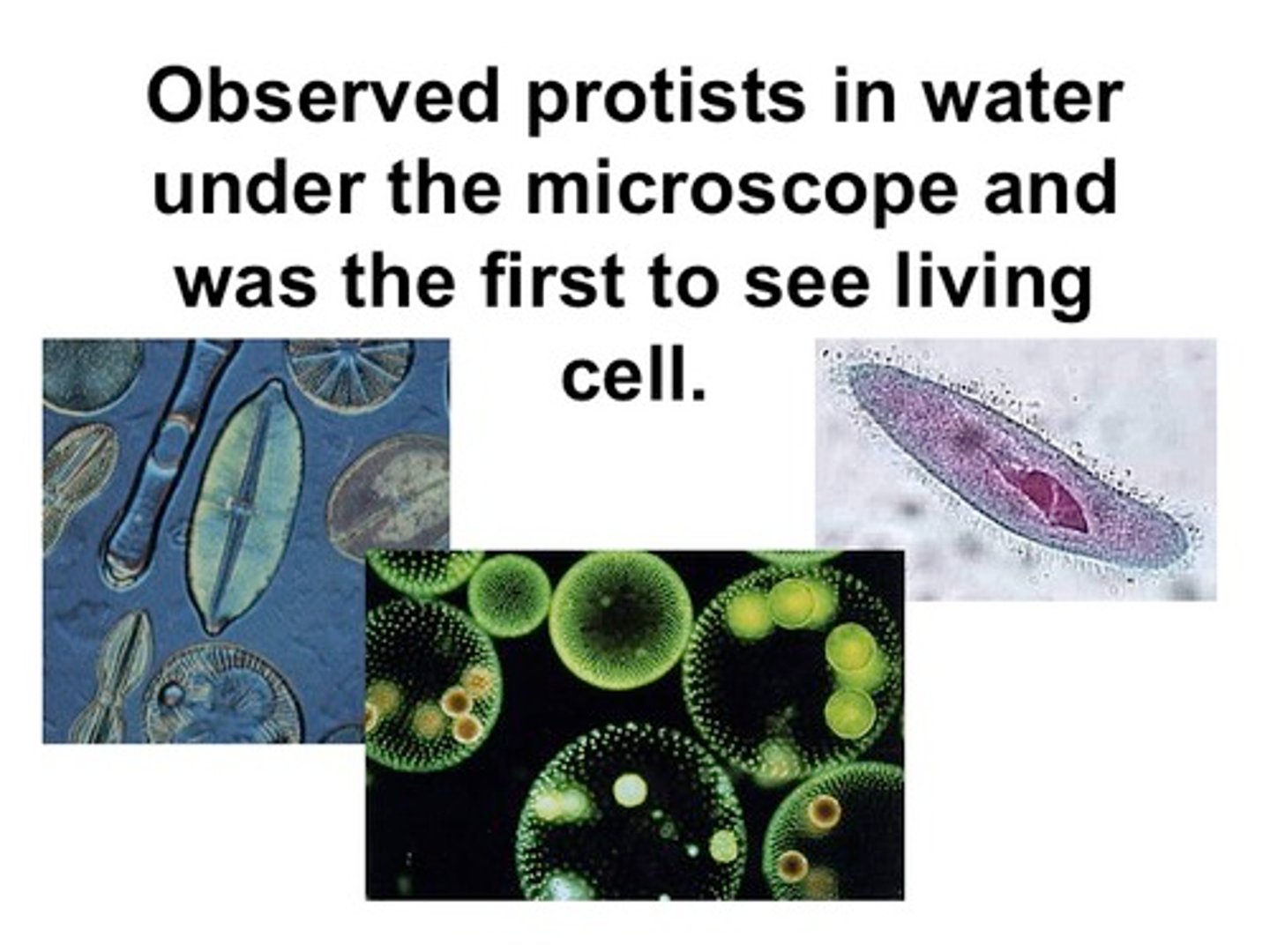
Robert Hooke

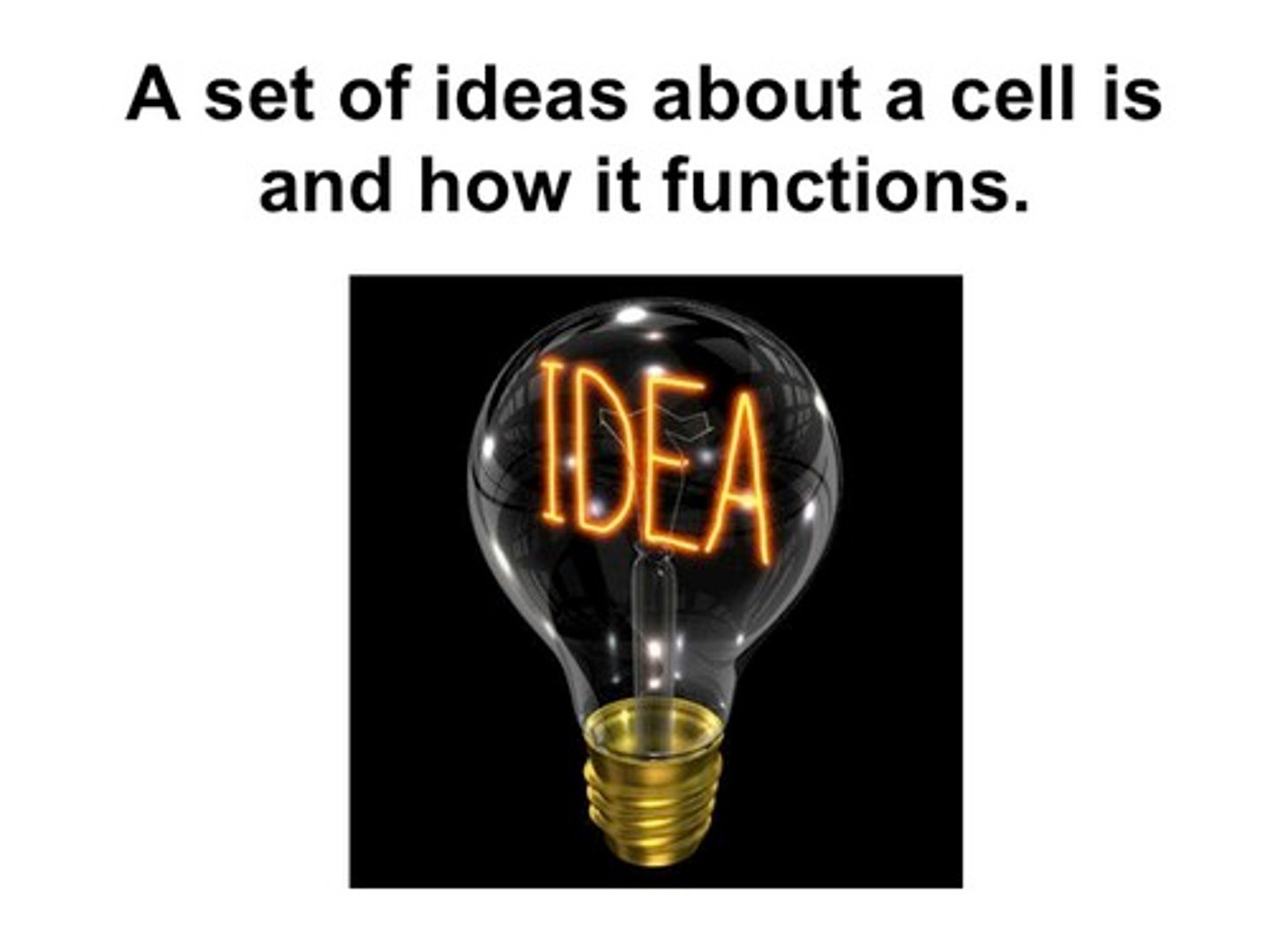
The Cell Theory is . . .
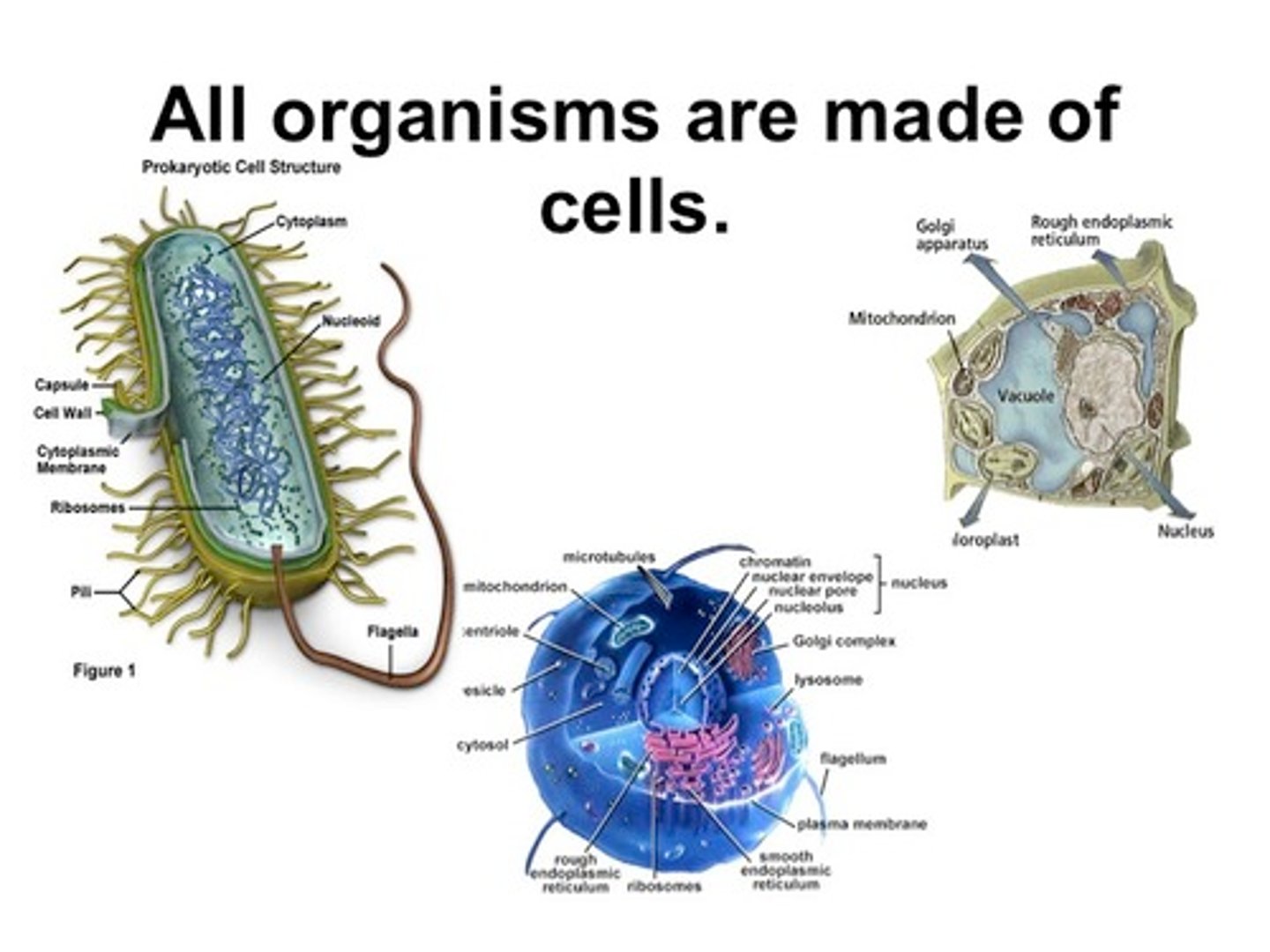
Part I of the cell theory states that . . .
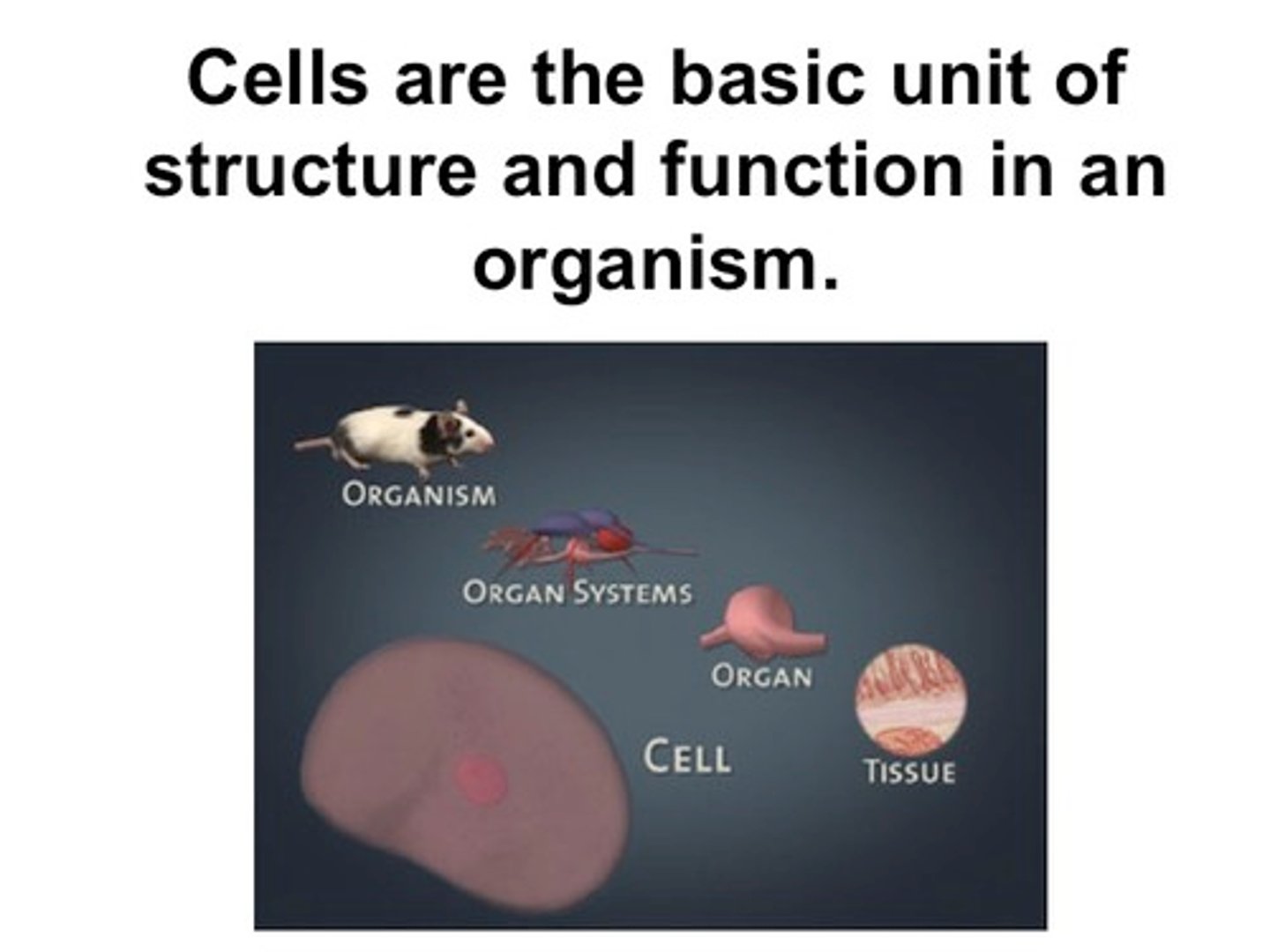
Part II of the cell theory states that . . .
Part III of the cell theory states that . . .
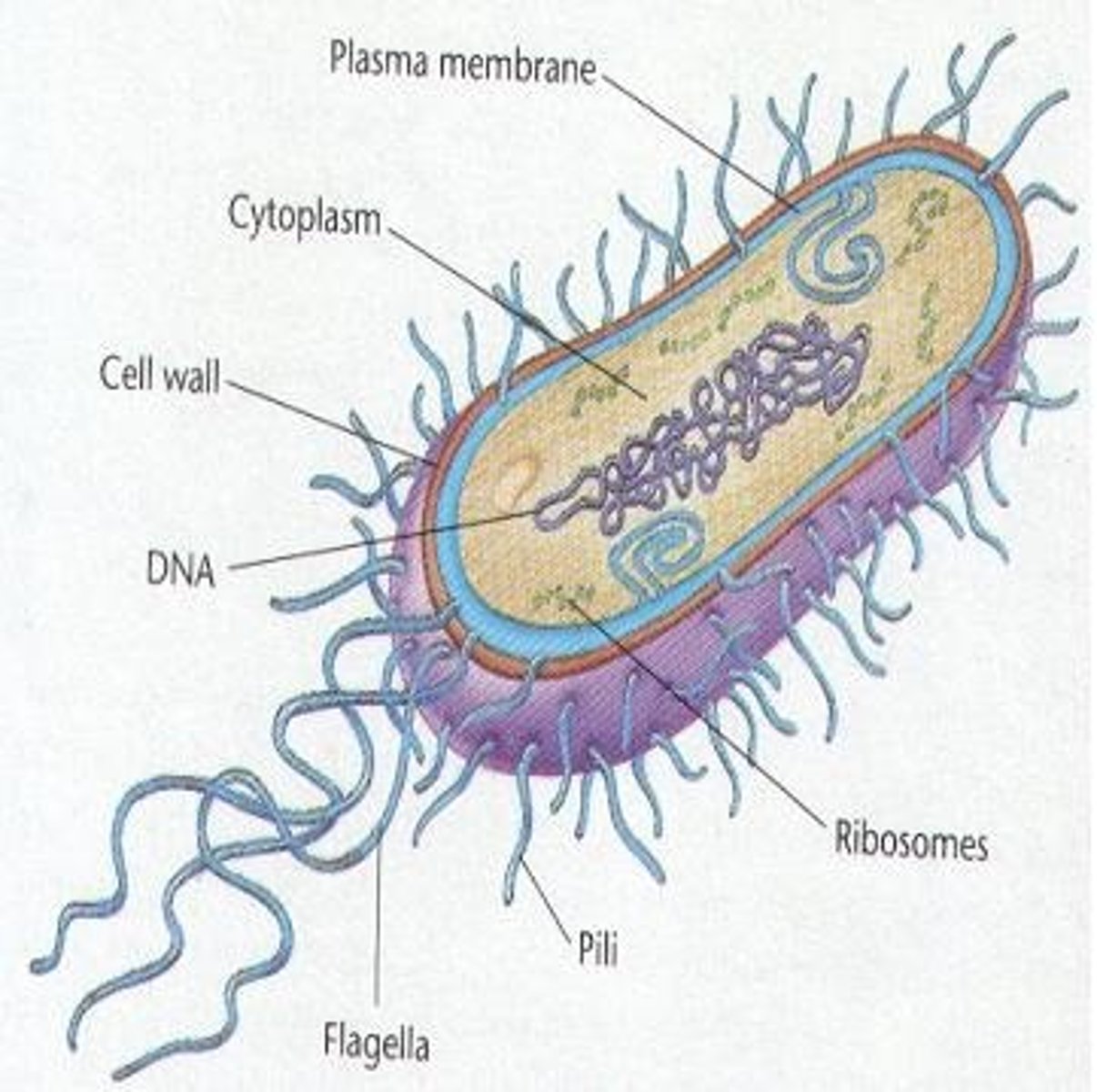
Prokaryote
Cells that have no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
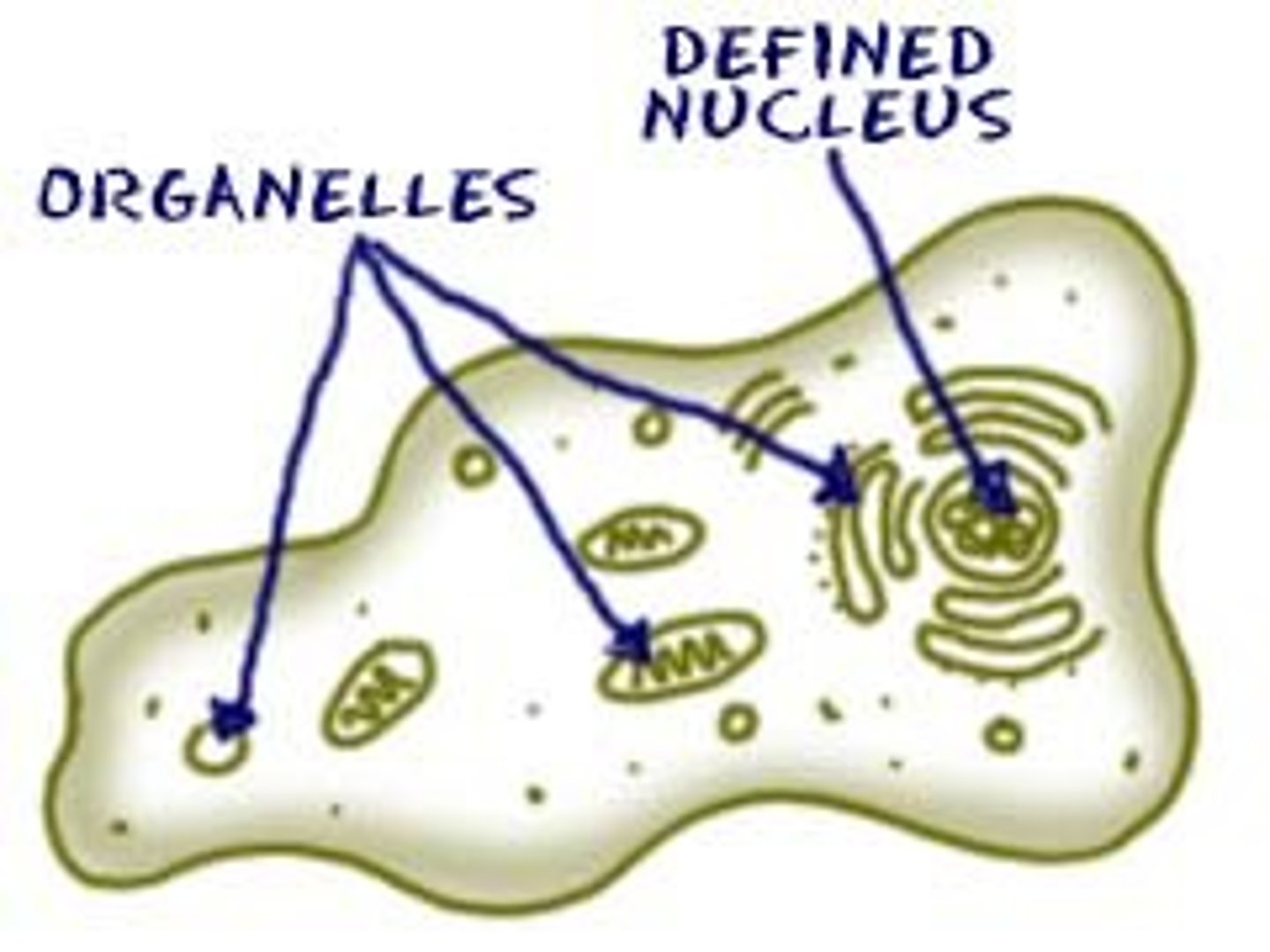
Eukaryote
Cells that contain an nucleus and membrane-bound organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplasts, mitochondria and Golgi apparatus
Kingdoms that include prokaryotic cells
Eubacteria and Archaebacteria
Kingdoms that include eukaryotic cells
Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia
DNA
Genetic material found in all cells that carries the instructions for life
Nucleus
is a large membrane-enclosed structure found in eukaryotic cells that contains the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA
Cell membrane
Structure that surrounds both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and helps to control what enters and leaves the cell
Ribosomes
Structures found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that is the site of protein synthesis
Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance in which cell structures are found
Flagella
Structure found in some prokaryotic and some eukaryotic cells that aids in movement
Cell Wall
Structure found in prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic plant cells that provides support and protection for the cell
Scientific Theory
Explains how or why something happens in the natural world; relies on inferences; widely accepted as true but can be disproven or change over time.
Scientific Law
Explains what happens in the natural world; based on observations and facts; that holds true every time it is tested.
Fact
Something known as true
Hypothesis
A prediction or educated guess that can be tested by a scientific investigation; Follows the If...then...because format.
Archaebacteria & Eubacteria
Two kingdoms that are made up solely of prokaryotes
Eubacteria
This kingdom consists of bacteria that live everywhere on Earth and have peptidoglycan in cell walls
Archaebacteria
This kingdom consists of bacteria that typically live in extreme environments, do NOT have peptidoglycan in their cell walls
Peptidoglycan
A protein carbohydrate compound found in the cell walls of eubacteria
Bacterial Cell Wall
A structure that protects and gives shape to the bacterial cell that may or may not include peptidoglycan
Bacterial Cell Membrane
A structure that controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell; also contains enzymes important to cellular respiration
Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance that contains DNA, ribosomes, essential compounds
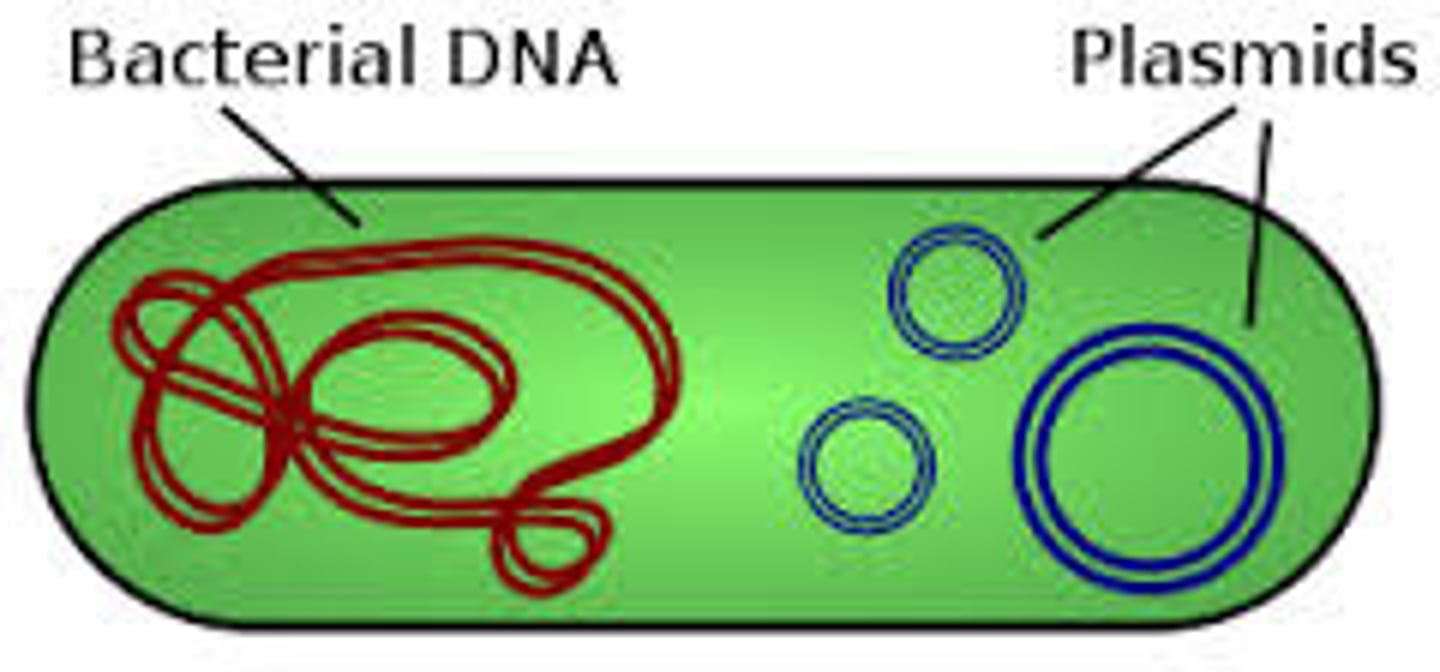
Bacterial Chromosome
circular thread of DNA that contains the cell's genetic information
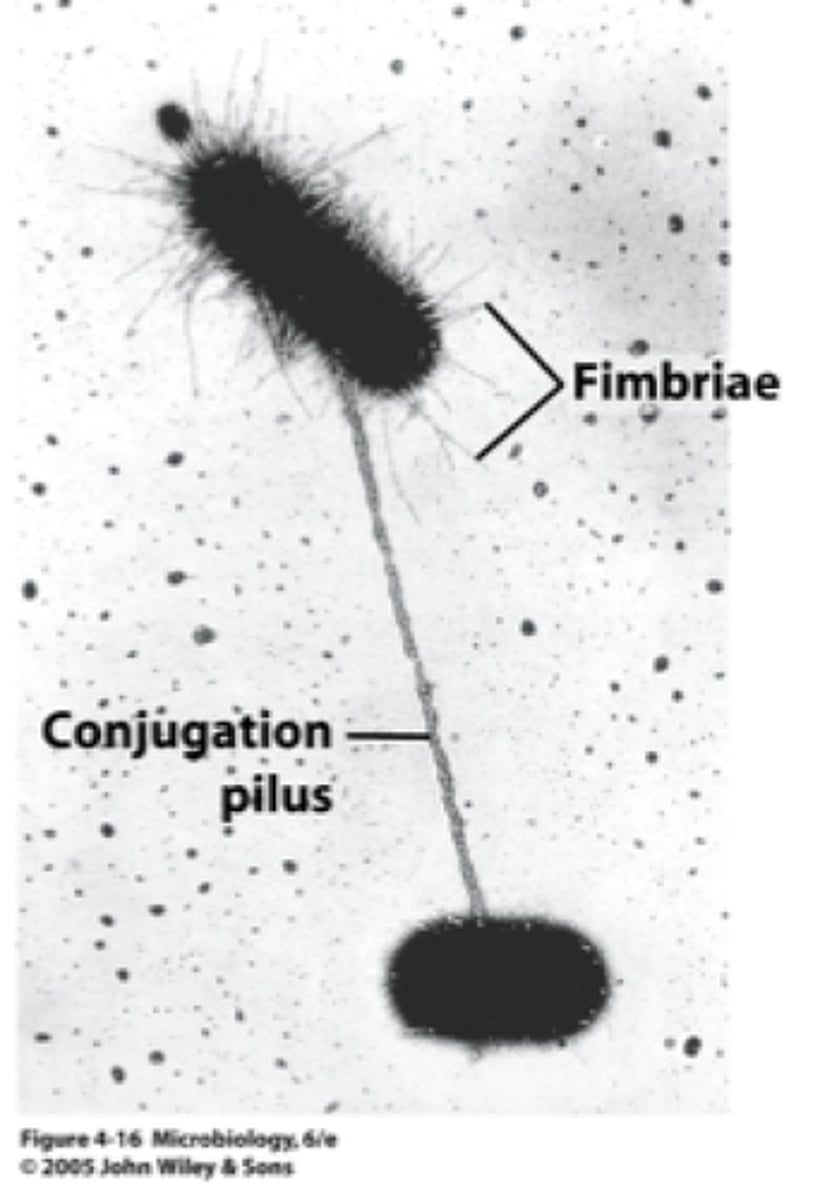
Pilus
A short. thick hair-like protein structure that allows a bacterium to attach to other bacteria and surfaces.
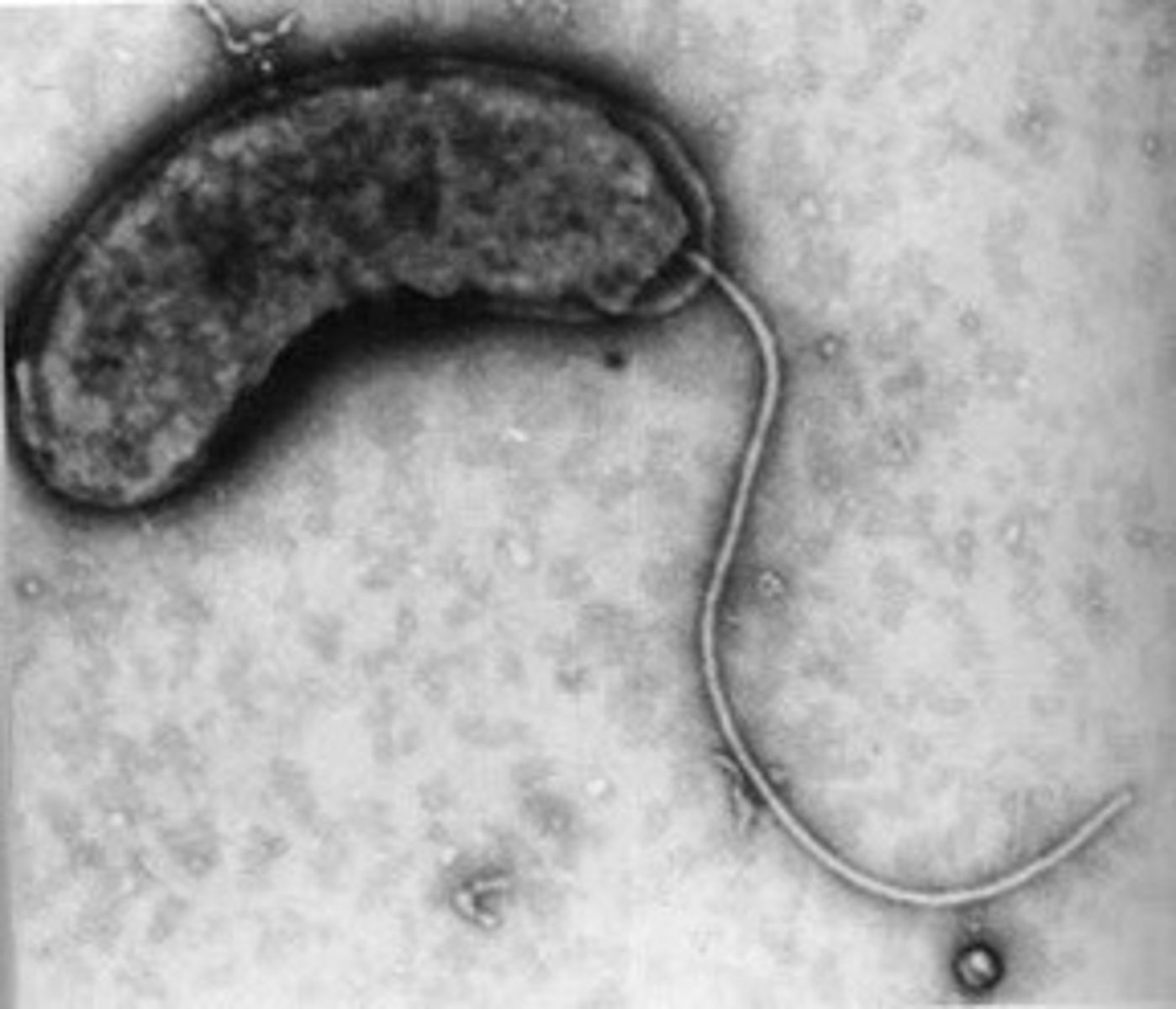
Flagellum
Long whip-like structure that allows the cell to move
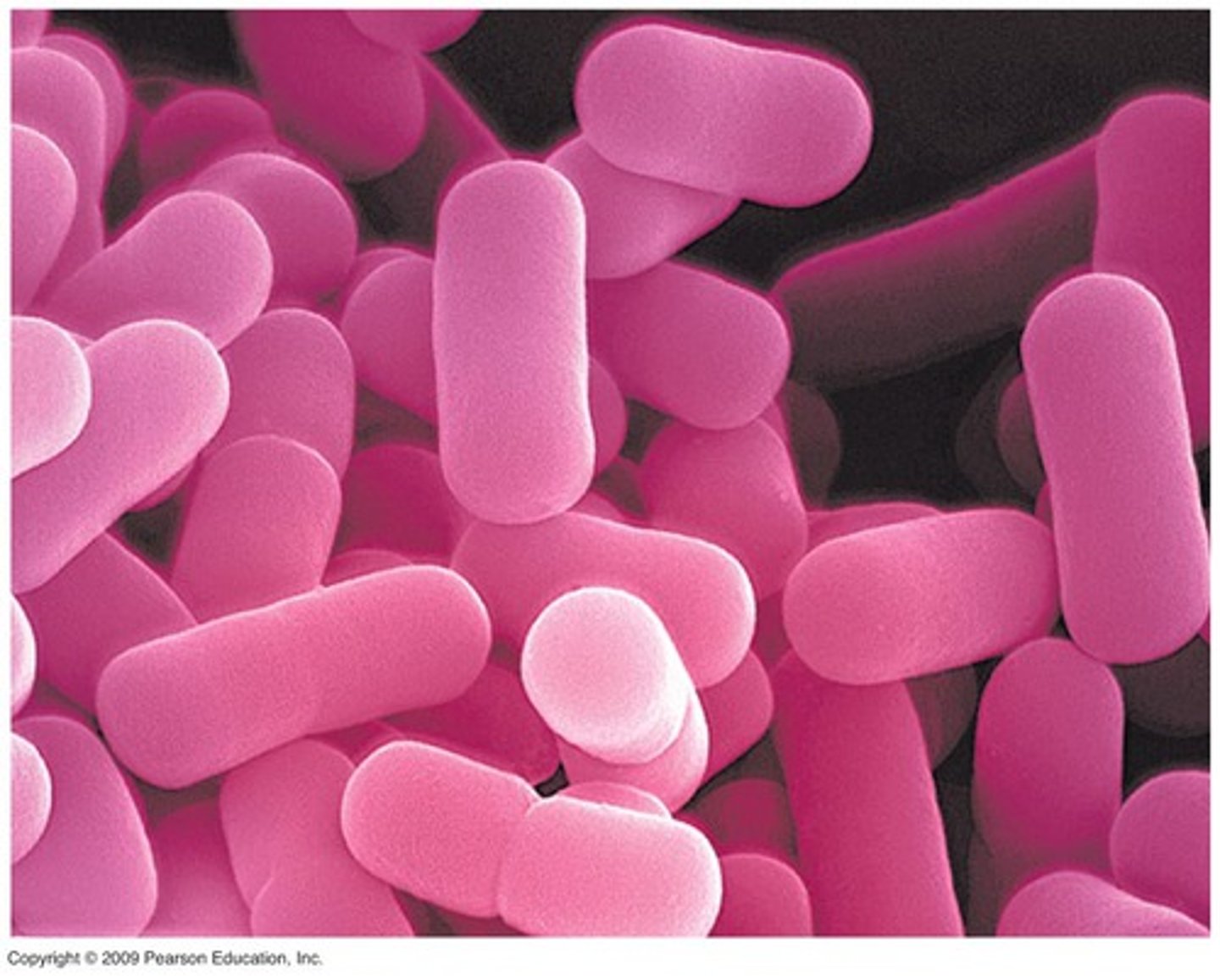
Bacilli (rod-shaped)
Bacteria that are rod-shaped; example includes Bacillus anthracis that causes anthrax
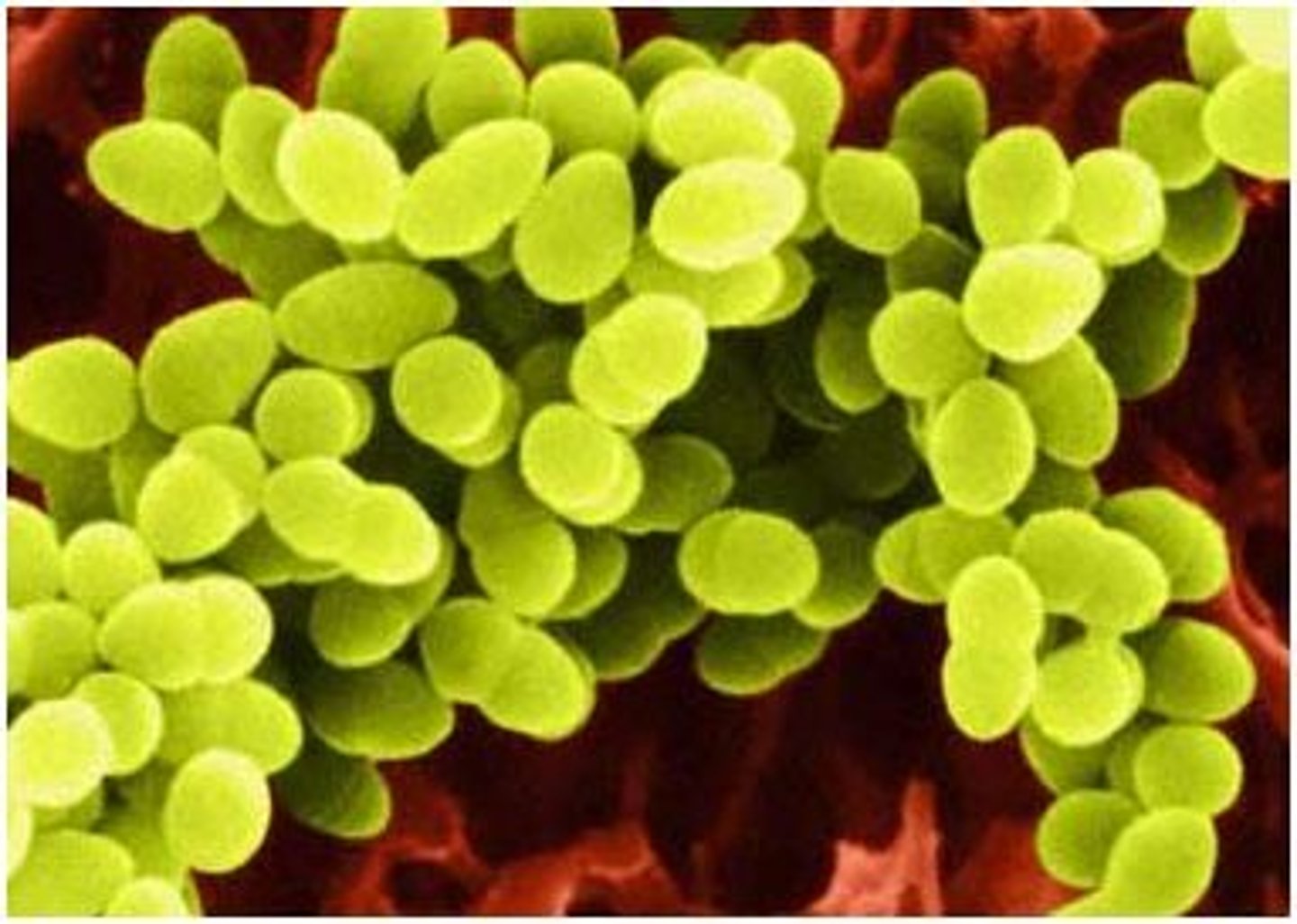
Cocci
Bacteria that are round; examples include staph infections and Gonherrea
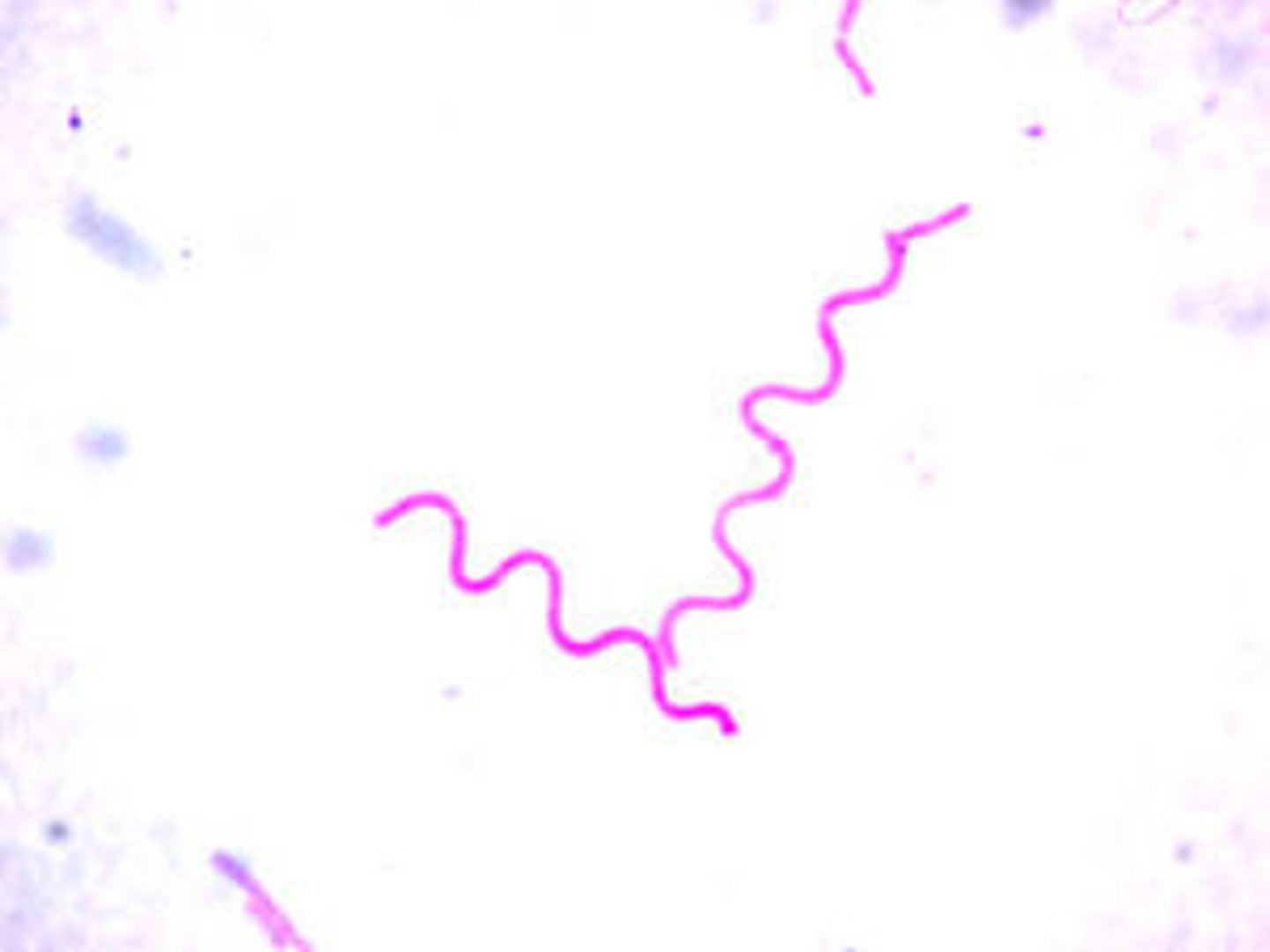
Spirillum
Bacteria that have one or more twists; examples include
Syphillis and Lyme Disease
Bacterial modes of nutrition
Phototrophs, chemotrophs and heterotrophs
Bacterial Photoautotrophs
Bacteria that use light to make their own food; example includes cyanobacteria
Bacterial Chemoautotrophs
Bacteria that use high energy molecules to make their own food; example include some archaebacteria that live in ocean vents
Bacterial Heterotrophs
Bacteria that rely on other organisms for their energy and food supply; examples include decomposers
Binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size; most common form of reproduction
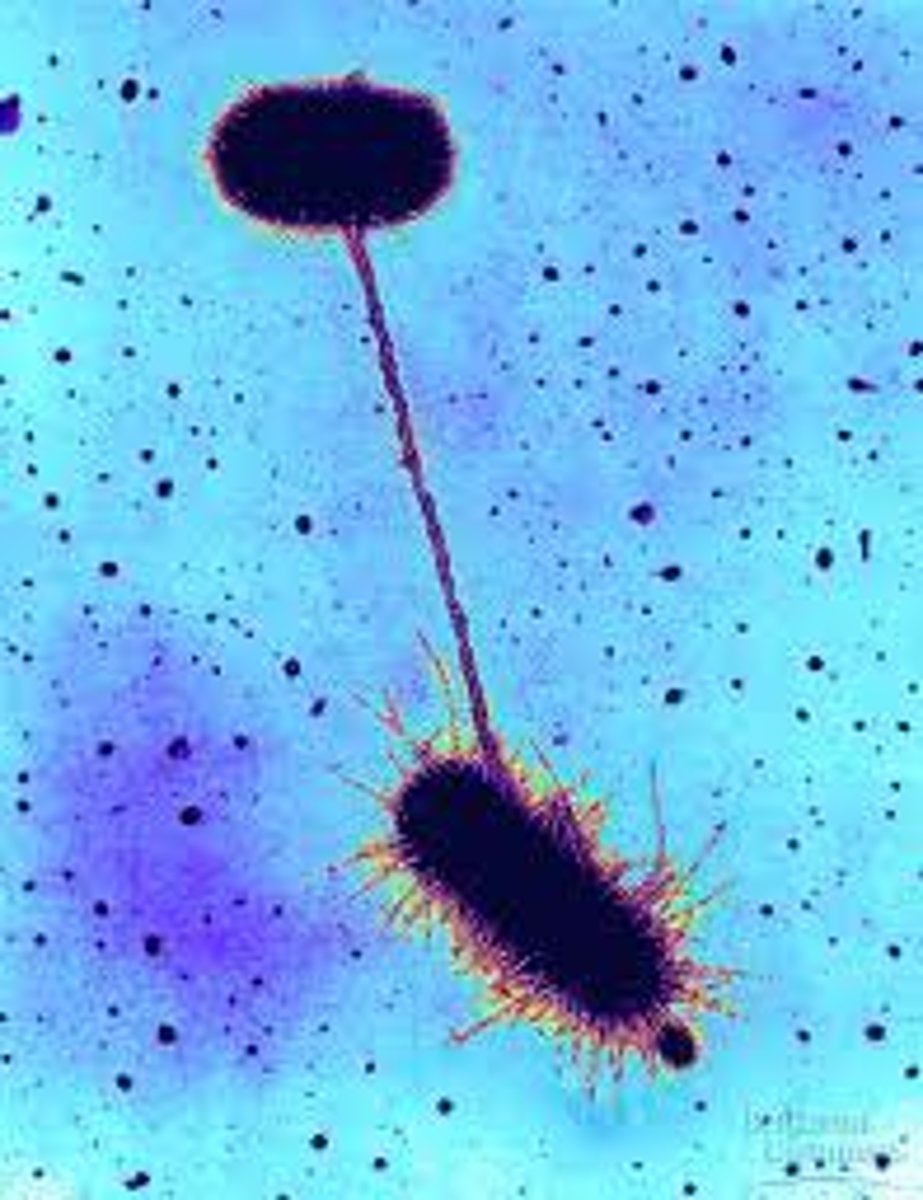
Conjugation
In bacteria, a type of sexual reproduction in which two bacteria exchange pieces of DNA through the pili.
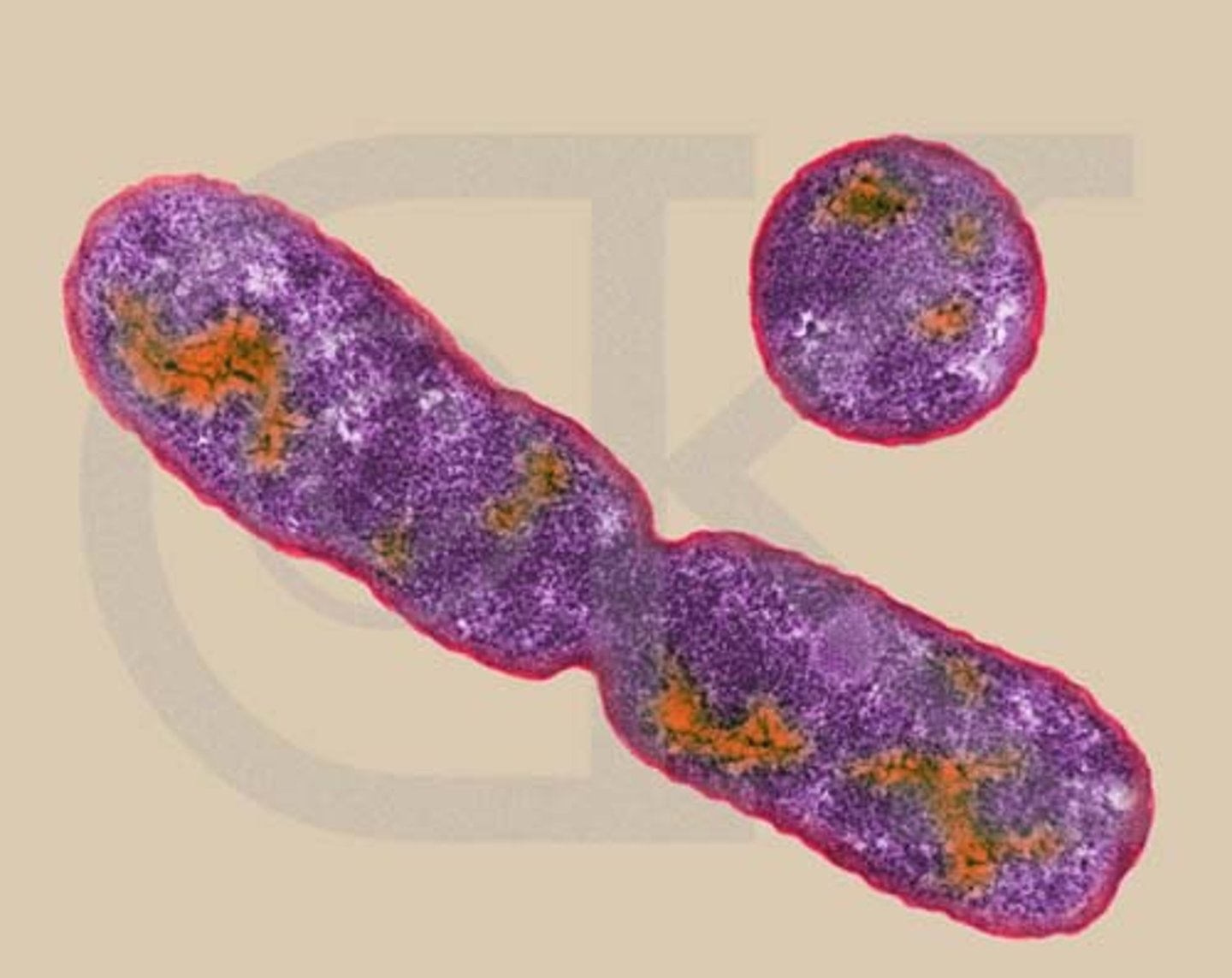
Bacerial endopore
A structure that can be formed by many species of bacteria that allow them to survive harsh conditions
Ideal conditions for bacterial growth
Temperature between 80˚F to 100˚F
Moist
Dark
lenty of food
Role of Bacteria in the Environment
Producers in many ecosystems that capture energy by photosynthesis.
Decomposers in many ecosystems that break down the nutrients in dead matter.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria help to convert nitrogen in the atmosphere into a form that plants can use.
Bacteria as Decomposers
Bacteria help recycle nutrients and remove wastes from water
Nitrogen Fixers
Some bacteria help to convert nitrogen in the atmosphere (N2) into a form that can be used by plants
Human uses of bacteria
- Make foods and beverages such as butter, cheese, yogurt, sauerkraut, and vinegar
- Tan leather, make linen, cure tobacco
- Remove wastes and poisons from water
- Mine minerals from the ground
- Synthesize drugs and chemicals via genetic engineering
- Produce vitamins in human intestines
Bacterial Infections (Examples)
Lyme Disease
Tetanus
Tuberculosis
Bacterial meningitis
Staphylococcus infection
Strep throat
Bacterial Infections (Treatment)
Antibiotics
Antibiotics
Drugs used to treat bacterial infections; examples include penicillin, ampicillin, sulfa drugs, etc.
Antibiotic resistance
Bacteria either evolve by mutation or acquire from another bacterium the ability to survive and not respond to treatment by antibiotics
Two ways bacteria cause disease
Damage the cells and tissues of the infected organism by breaking down the cells for food.
Release toxins (poisons) that travel throughout the body interfering with the normal activity of the host.
Methods used to control bacterial growth
Sterilization, disinfectants, food processing, pasteurization
Pasteurization
A process of heating food to a temperature that is high enough to kill most harmful bacteria without changing the taste of the food.
Sterilization
The process of destroying all microbes
Disinfectants
Chemical products that destroy all bacteria, fungi, and viruses (but not spores) on surfaces.
Food processing
Bacteria can cause food to spoil.
Refrigerated food stays fresh longer because the bacteria will take longer to multiply.
Boiling, frying, or steaming can sterilize certain foods.
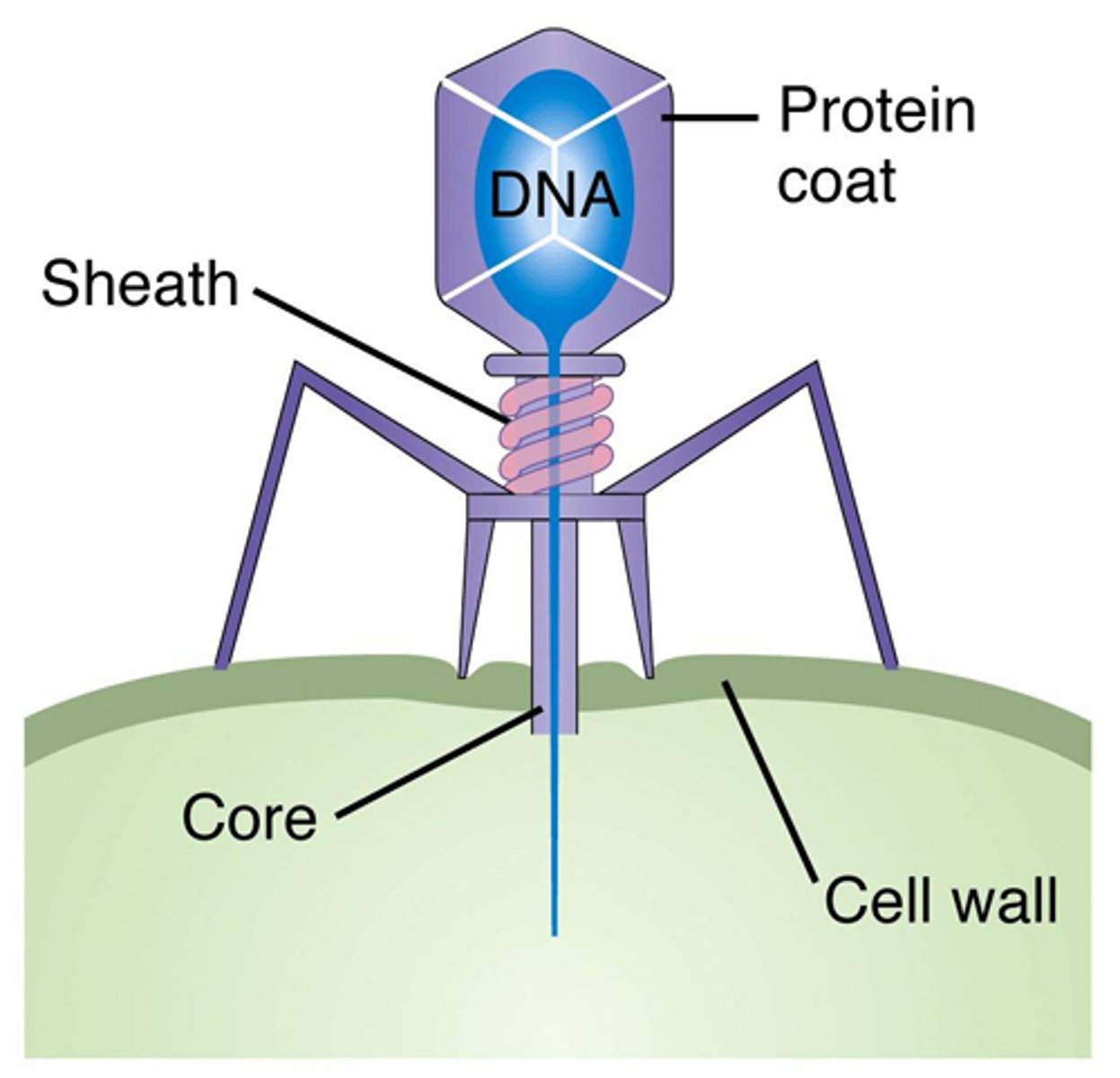
Virus
A nonliving particle composed of a protein coat and a nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA), which is dependent on a host organism for replication
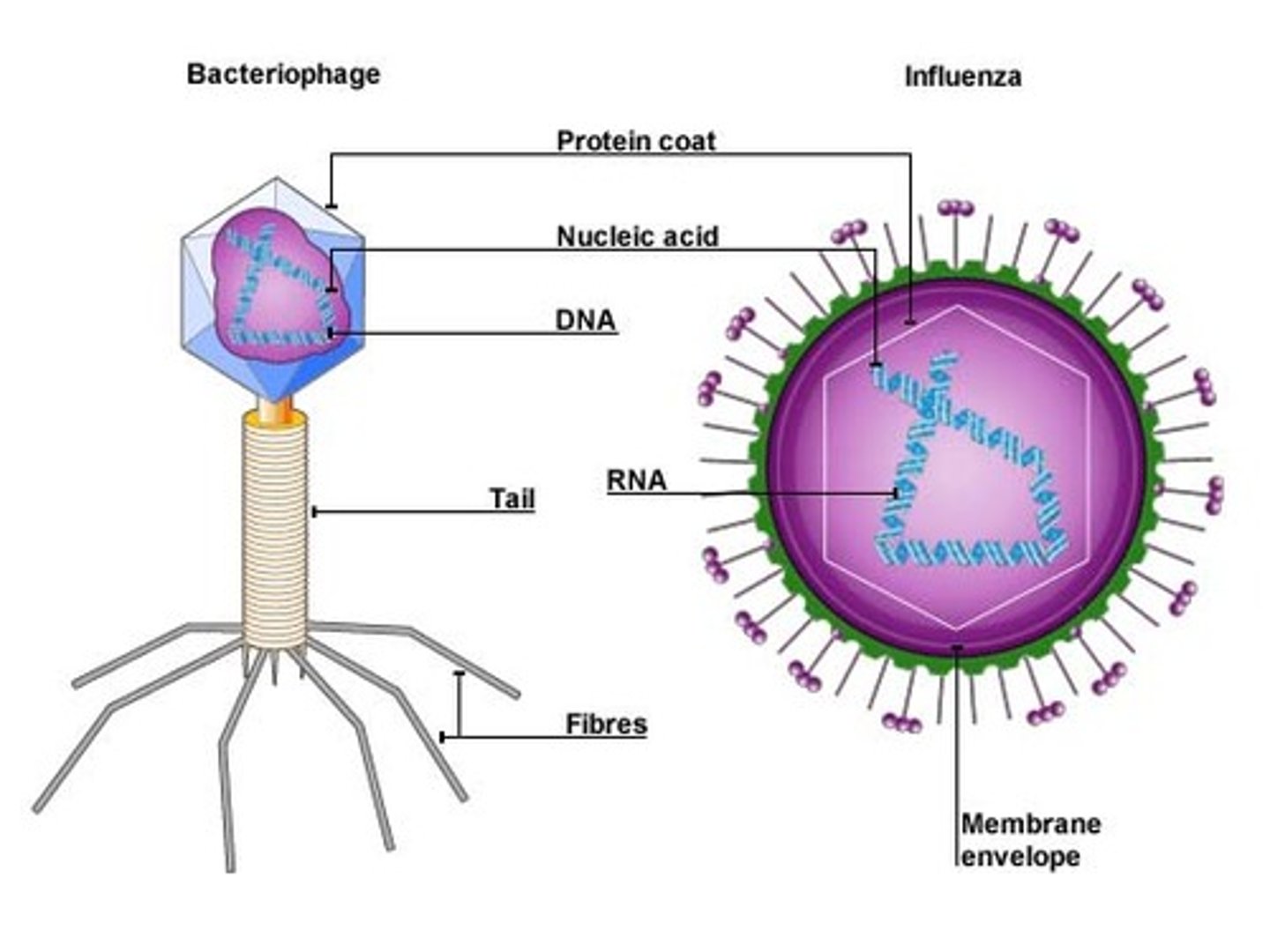
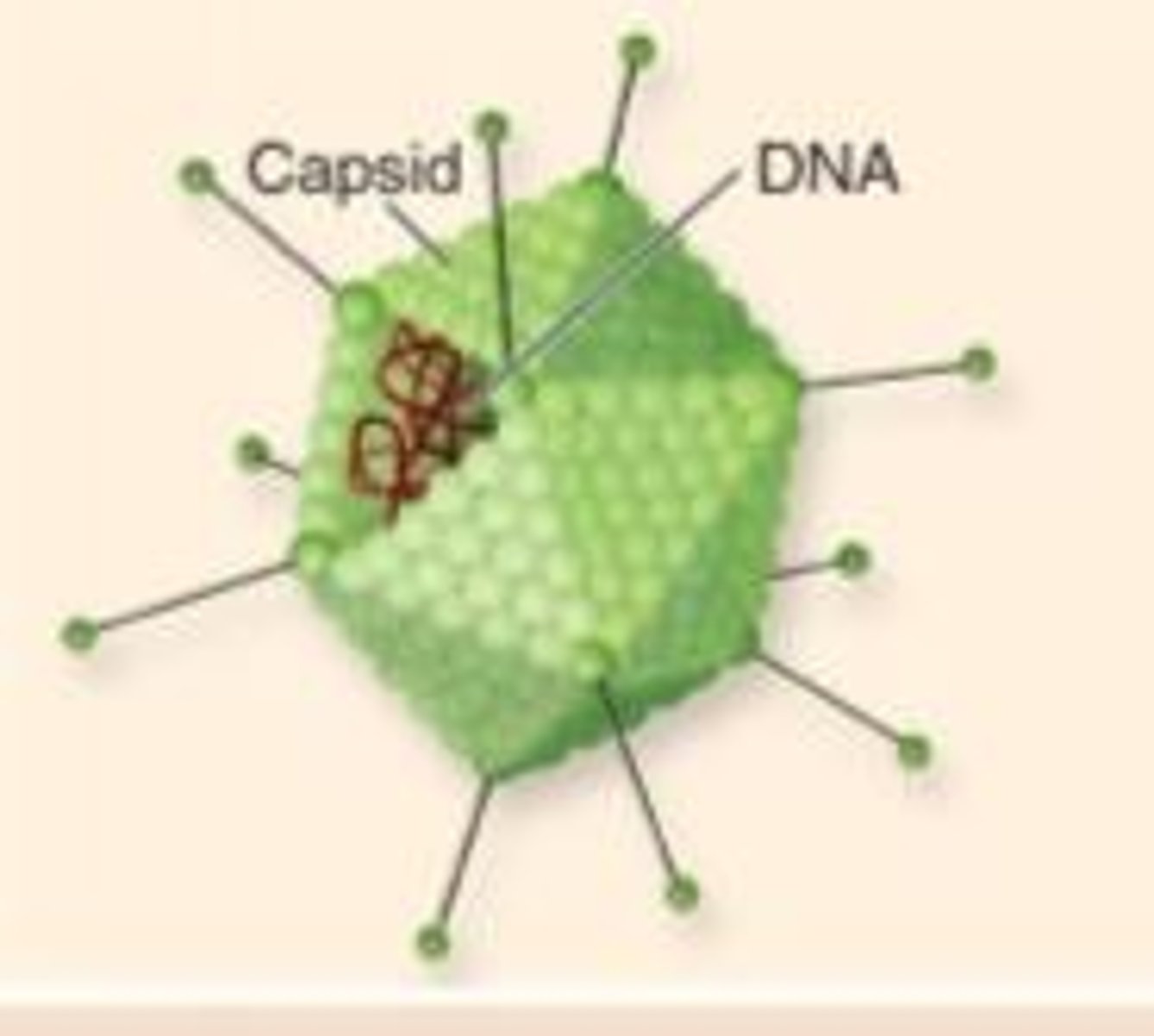
Capsid
The outer protein coat of a virus
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria
Viral shapes
Icosahedron
Helical
Spherical
Round
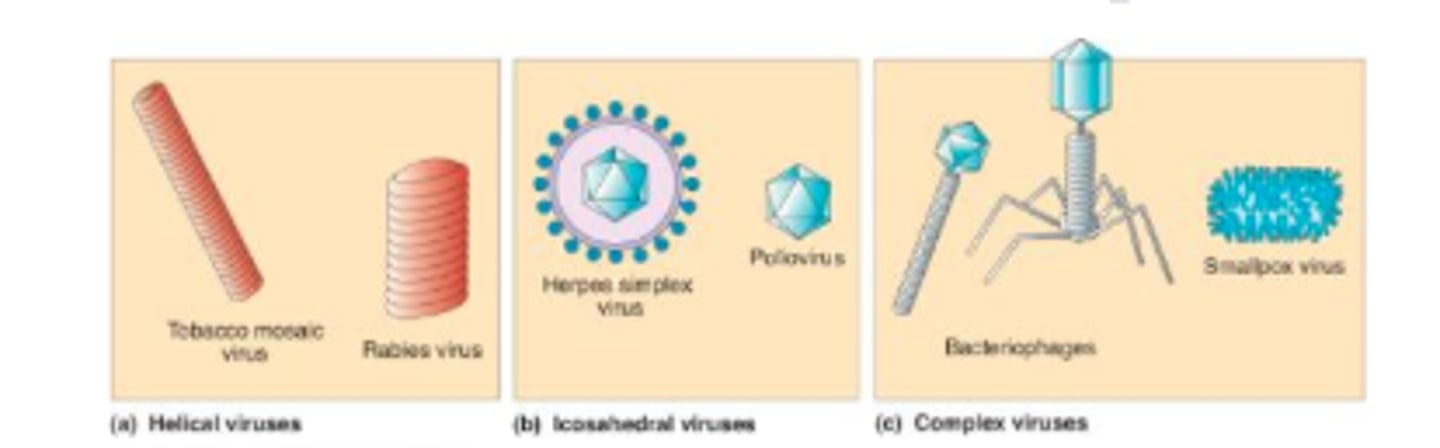
Icosahedron
A virus that consists of 20 trianguar faces
Examples: chicken pox, polio
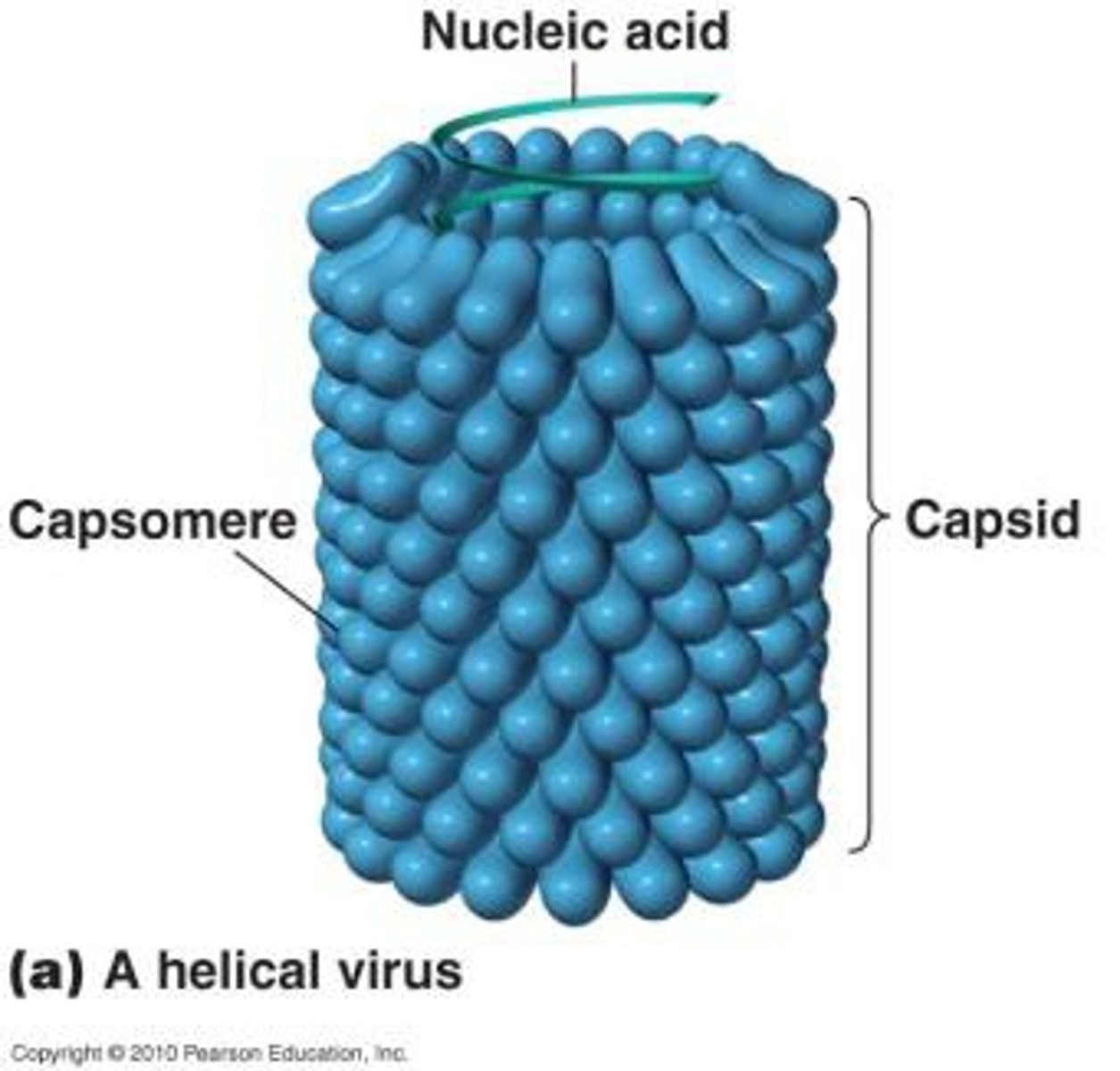
Helical
A virus that looks like a coiled spring
Examples: rabies, measles, tobacco mosaic
Spherical
A virus that is round
Example: Influenza
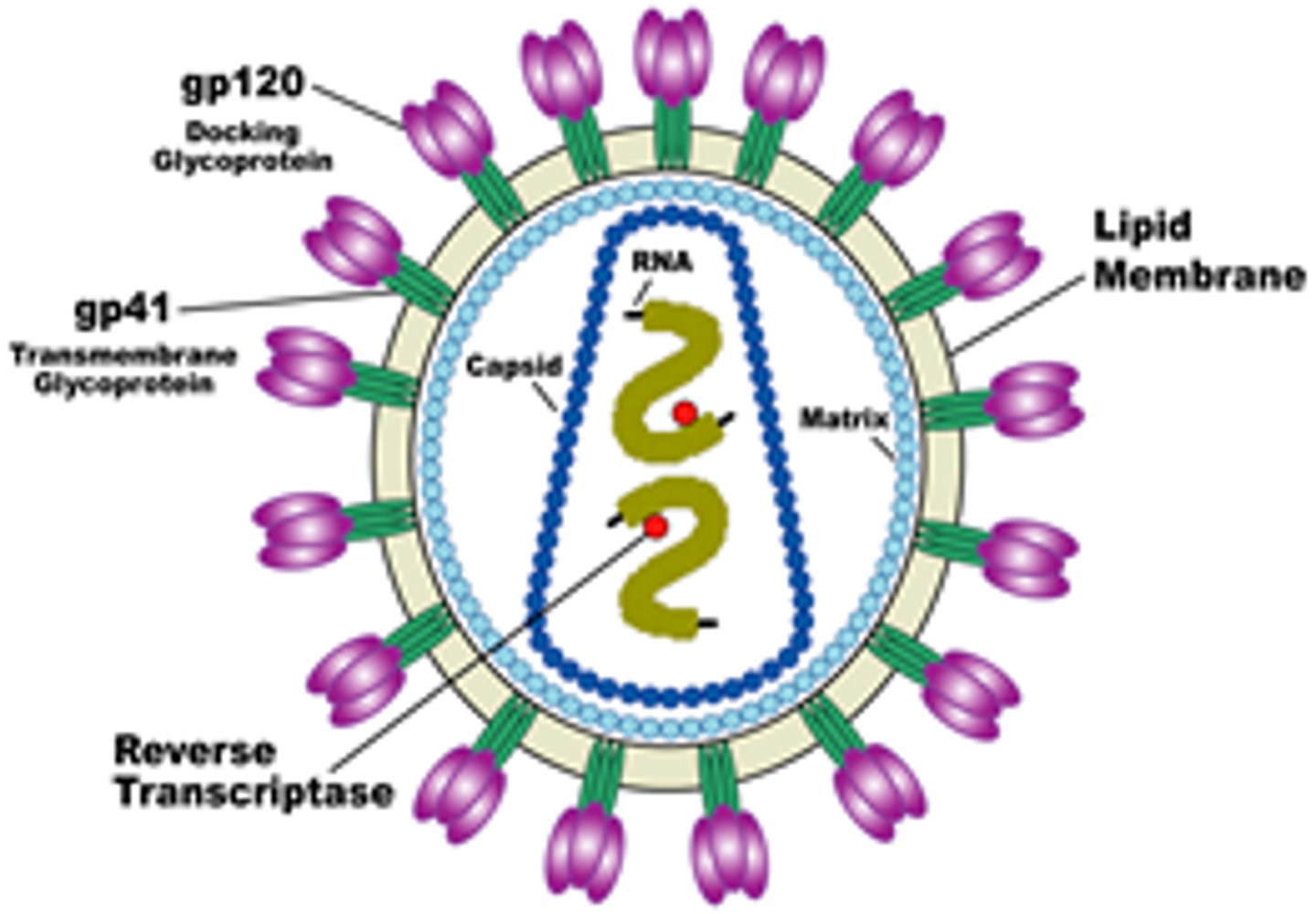
Retrovirus
Viruses that contain RNA as their genetic material
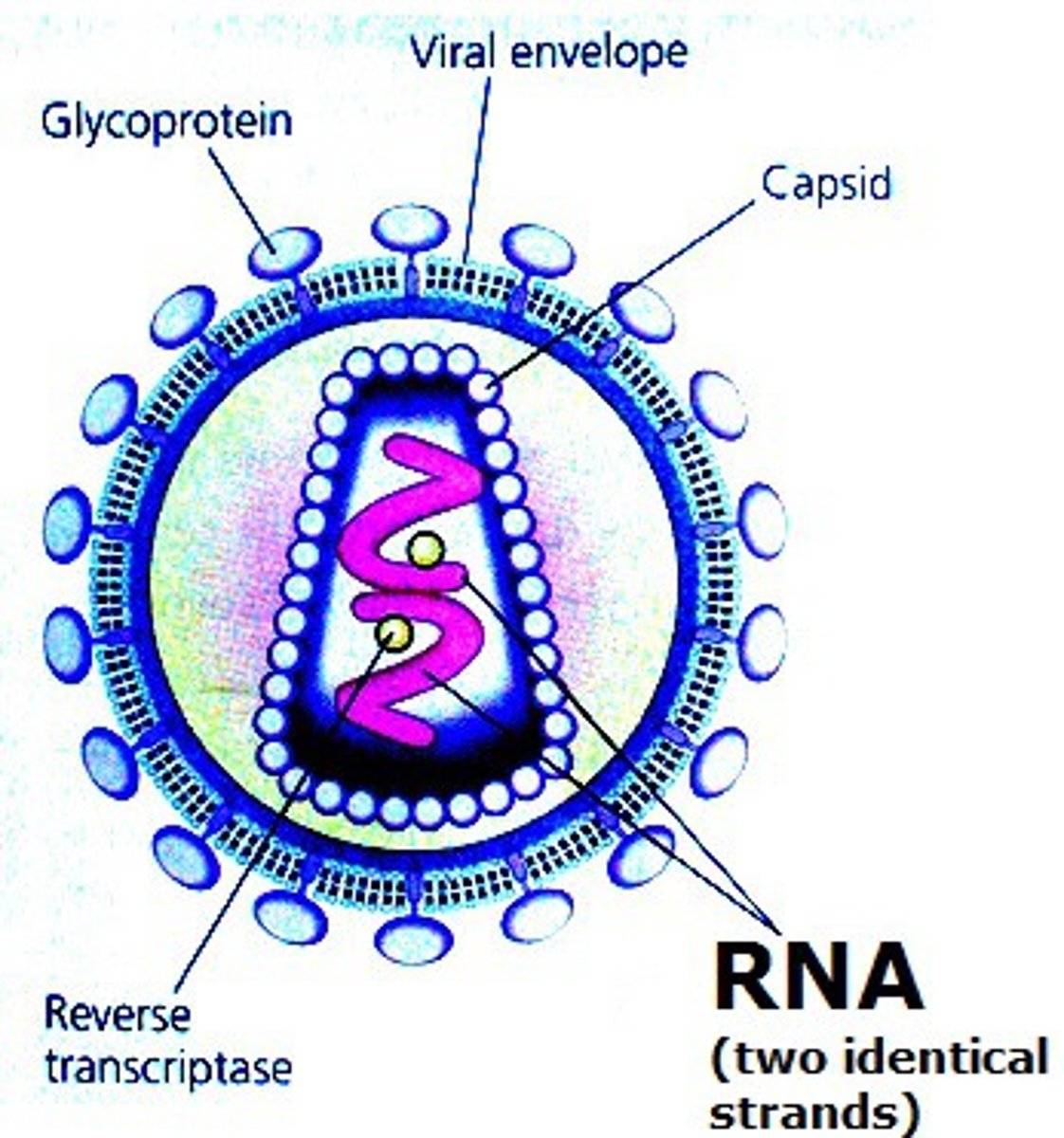
Viral infection (Description)
Caused when a virus invades a host cell and takes over the cell to make copies of itself.
Viral Infections (Examples)
AIDS
Chicken Pox
Common Cold
Influenza (the flu)
Measles
Polio
Rabies
AIDS
A retrovirus which over a period of years weakens the capacity of the immune system to fight off infection so that weight loss and weakness set in and other afflictions such as cancer or pneumonia and may result in death
Chicken pox
An airborne viral infection that that grows in the respiratory tract results in a skin condition characterized by a rash that develops in pushils & vesicles lasting 5-7 days
Influenza (Flu)
A highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory passages causing fever, severe aching, and catarrh, and often occurring in epidemics
Measles
An acute, highly contagious infection caused by the rubeola virus and transmitted by respiratory droplets
Polio
A highly infectious viral disease that causes inflammation of the nerve cells of the brain stem and spinal cord, leading to paralysis
Rabies
A viral infection of the brain and spinal cord that is transmitted by the saliva, urine, or feces of an infected animal
Viral reproduction
The viral DNA or RNA takes over the host cell's machinery and forces it to create new viruses
Two ways viruses cause disease
Invade and destroy certain cells in the body.
Change patterns of growth and development of infected cells.
Human uses of viruses
Gene therapy
Production of drugs
Pathogens
A bacterium, virus, or other organism that can cause disease
Two ways that bacteria cause disease
Damage the cells and tissues of the infected organism by breaking down the cells for food.
Release toxins (poisons) that travel throughout the body interfering with the normal activity of the host.
Diseases Caused By Bacteria
Lyme Disease
Tetanus
Tuberculosis
Bacterial meningitis
Staphylococcus infection
Strep throat
Vaccine
A weakened or inactive version of a pathogen that stimulates the body's production of antibodies which can aid in preventing an infection.
Antibiotics
Drugs used to treat bacterial infections; examples include penicillin, ampicillin, sulfa drugs, etc.

Penicillin
An antibiotic produced by a fungus that kills bacteria by interfering with cell wall production
Two ways viruses cause disease
Invade and destroy certain cells in the body.
Change patterns of growth and development of infected cells.
Diseases Caused By Viruses (Examples)
Common cold
Influenza (flu)
AIDS
Chicken pox
Hepatitis B
West Nile
Ebola
Zika
Retrovirus
A virus that contains RNA as its genetic material
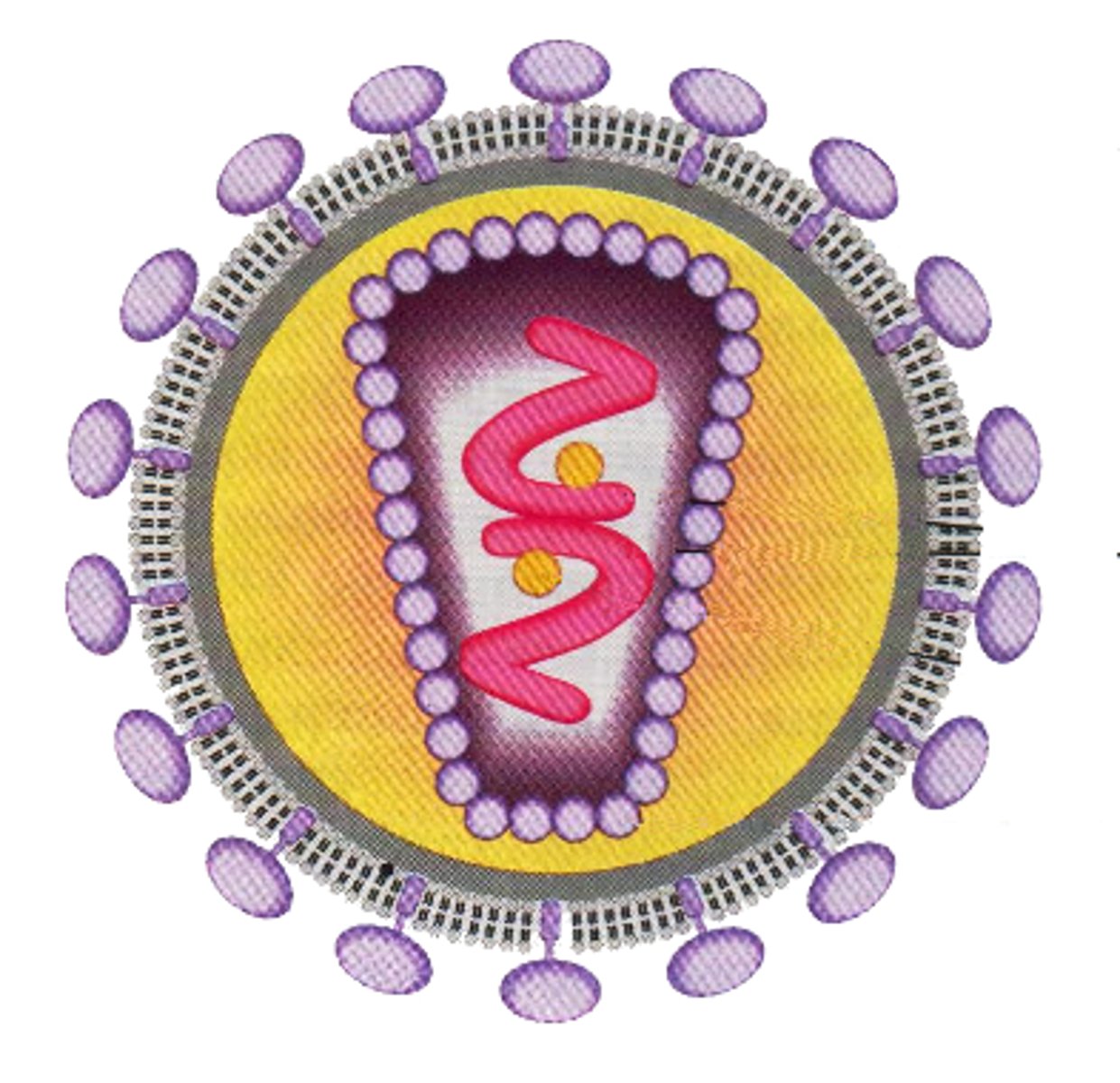
Common Cold
A retrovirus usually associated with swollen nasal mucous membranes and the production of fluid from the sinuses and nose.

Chicken pox
An airborne viral infection that that grows in the respiratory tract results in a skin condition characterized by a rash
Measles
An acute, highly contagious infection caused by the rubella virus and transmitted by respiratory droplets
Rabies
A viral infection of the brain and spinal cord that is transmitted by the saliva, urine, or feces of an infected animal
Polio
A highly infectious viral disease that causes inflammation of the nerve cells of the brain stem and spinal cord, leading to paralysis
HIV
A retrovirus which over a period of years weakens the capacity of the immune system to fight off infection so that weight loss and weakness set in and other afflictions such as cancer or pneumonia and may result in death
Influenza (Flu)
A highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory passages causing fever, severe aching, and often occurring in epidemics
Ebola
A contagious viral disease originating in Africa. It is transmitted by blood and body fluids and causes body organs and vessels to leak blood, usually resulting in death
Zika
A viral infection transmitted primarily by mosquitoes. An infection during pregnancy can cause the brain to not fully develop.
Oncogenic Viruses
Viruses capable of causing cancer; examples include Epstein-Barr, human pappiloma virus (HPV), hepatitis B, and herpes
Diseases Caused By Bacteria (Examples)
Cholera
Lyme Disease
Tetanus
Tuberculosis (TB)
Bacterial Meningitis
Strep Throat
Cholera
A bacterial infection caused from drinking contaminated water that causes extreme dehydration and diarrhea. Can cause death very fast if left untreated
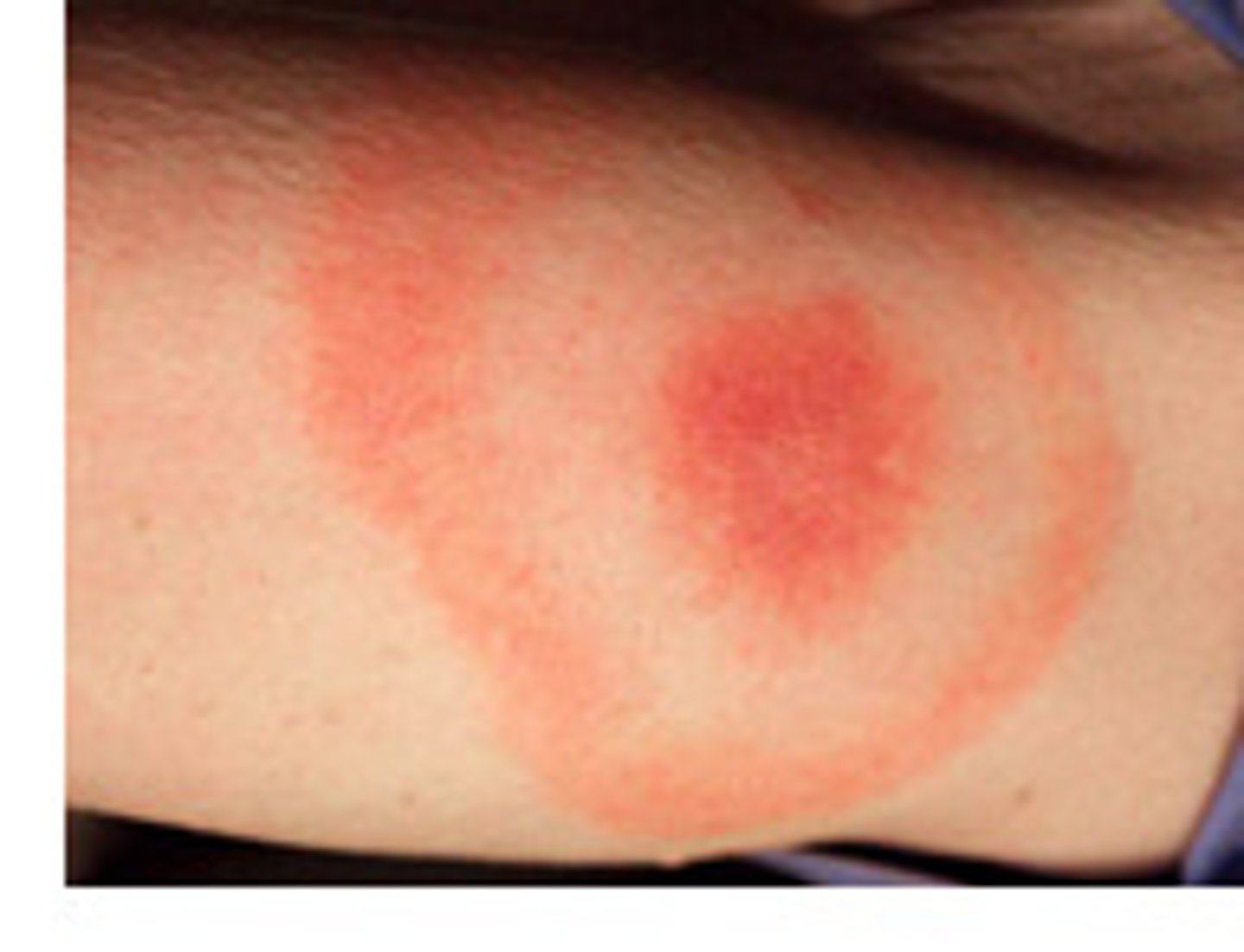
Lyme Disease
A tick-borne bacterial infection that causes a rash, often in a bull's-eye pattern, and flu-like symptoms. Joint pain and weakness in the limbs also can occur
Tetanus
A bacterial infection spread through contact that causes painful muscle spasms, particularly in the jaw and neck; can lead to death but can be prevented with a vaccine
Tuberculosis (TB)
A bacterial infection that may affect almost all tissues of the body, especially the lungs