Heart Development
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What embryonic tissue forms the endocardial tubes?
Splanchnic mesoderm via angiogenic cell clusters in the cardiogenic plate.
What layers arise from the fused endocardial tube?
Endocardium (inner lining) and cardiac jelly.
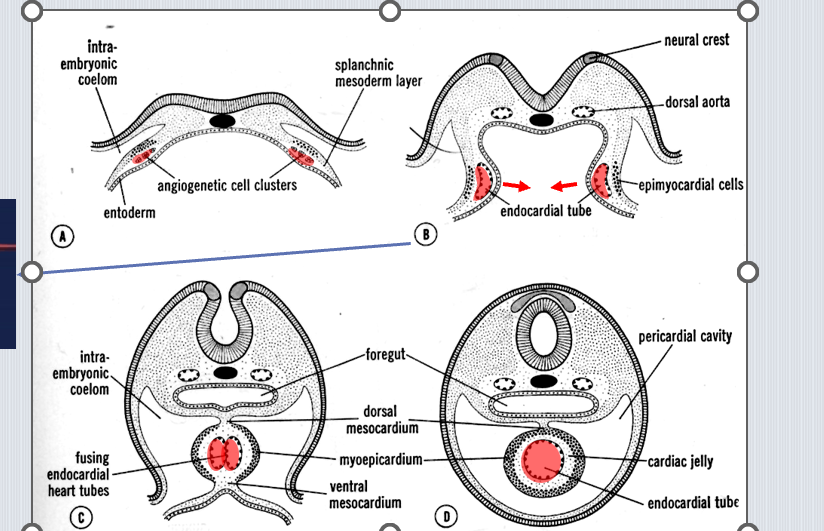

What is the embryonic origin of the myocardium?
Splanchnic mesoderm thickening around the endocardial tube.
What forms the epicardium?
Mesothelial cells from proepicardial organ (splanchnic mesoderm).
Name the five segments of the primitive heart tube (inflow to outflow).
Sinus venosus → primitive atrium → primitive ventricle → bulbus cordis → aortic sac.
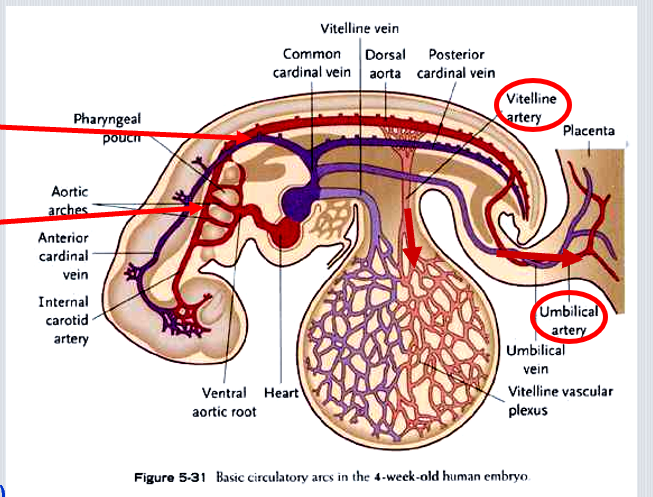
Which three paired veins drain into the sinus venosus?
Common cardinal veins, vitelline veins, and umbilical veins.

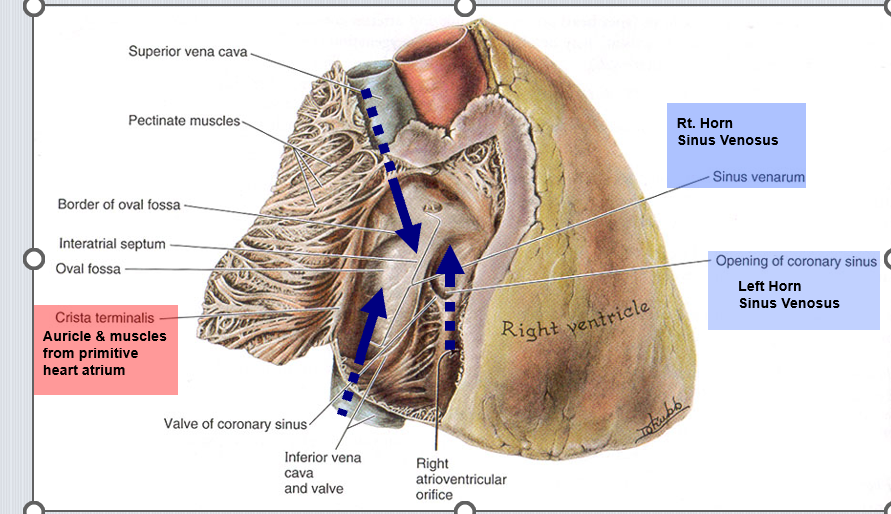
What adult structure derives from the left horn of the sinus venosus?
Coronary sinus.

What adult structure derives from the right horn of the sinus venosus?
Smooth sinus venarum of the right atrium.

What adult veins form from the anterior cardinal veins?
Brachiocephalic veins and SVC.
Which aortic arch gives rise to the common carotid arteries?
The third aortic arch.
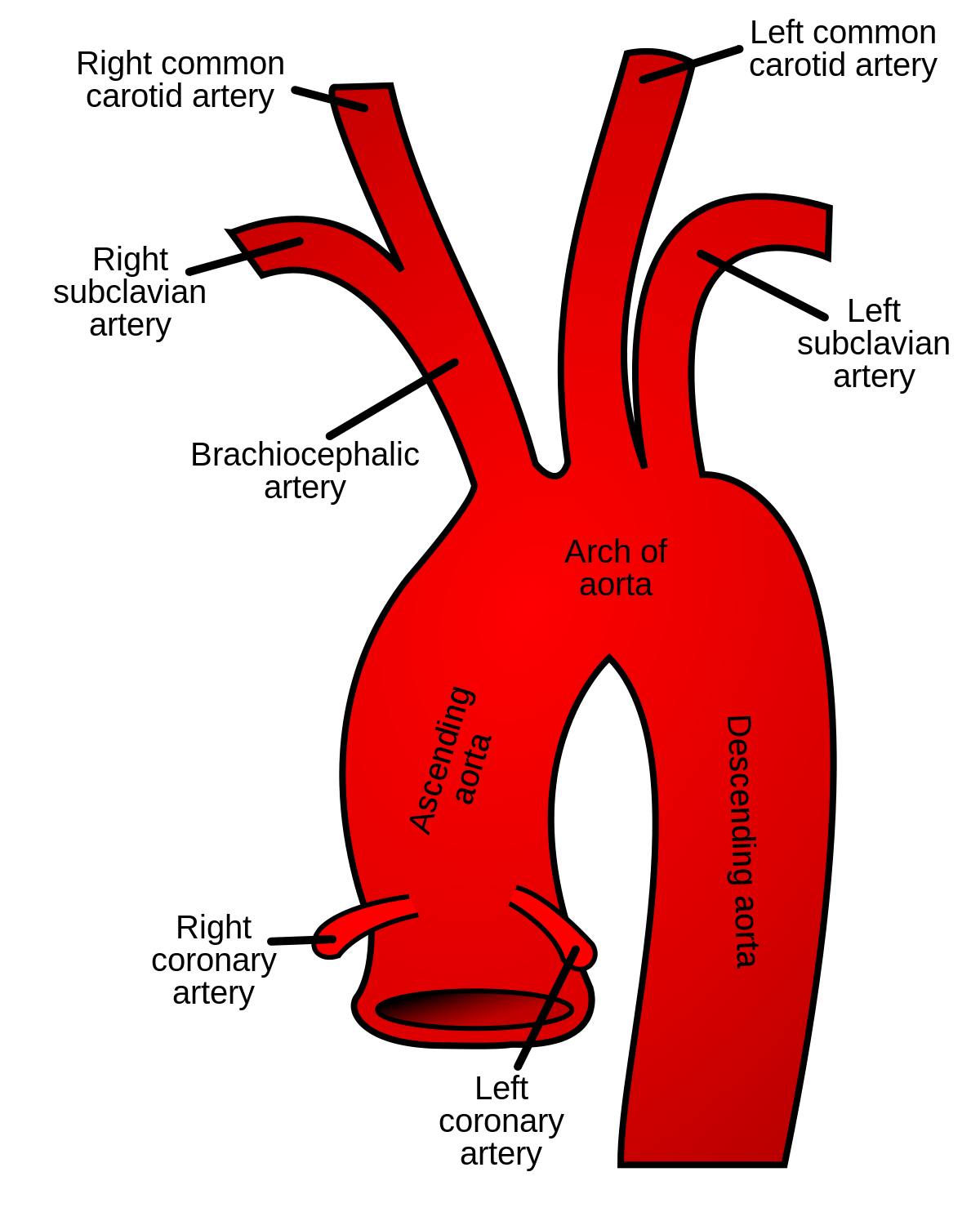

What do the left and right fourth aortic arches form?
Left → arch of aorta; Right → proximal right subclavian artery.
What do the sixth aortic arches form?
Proximal pulmonary arteries; distal left forms ductus arteriosus.
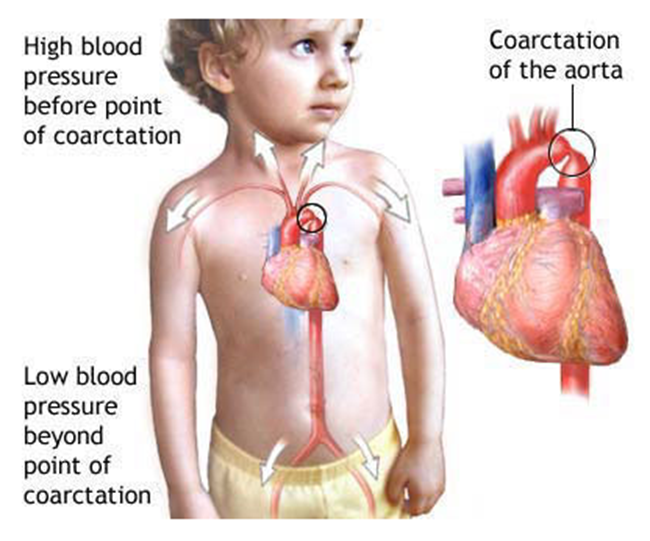
How does coarctation of the aorta affect circulation?
Narrowing near ductus arteriosus → collateral flow via intercostal arteries → rib notching.
What is cardiac looping?
S-shaped rightward (dextral) folding of the primitive tube positioning atria dorsally and ventricles anteriorly.
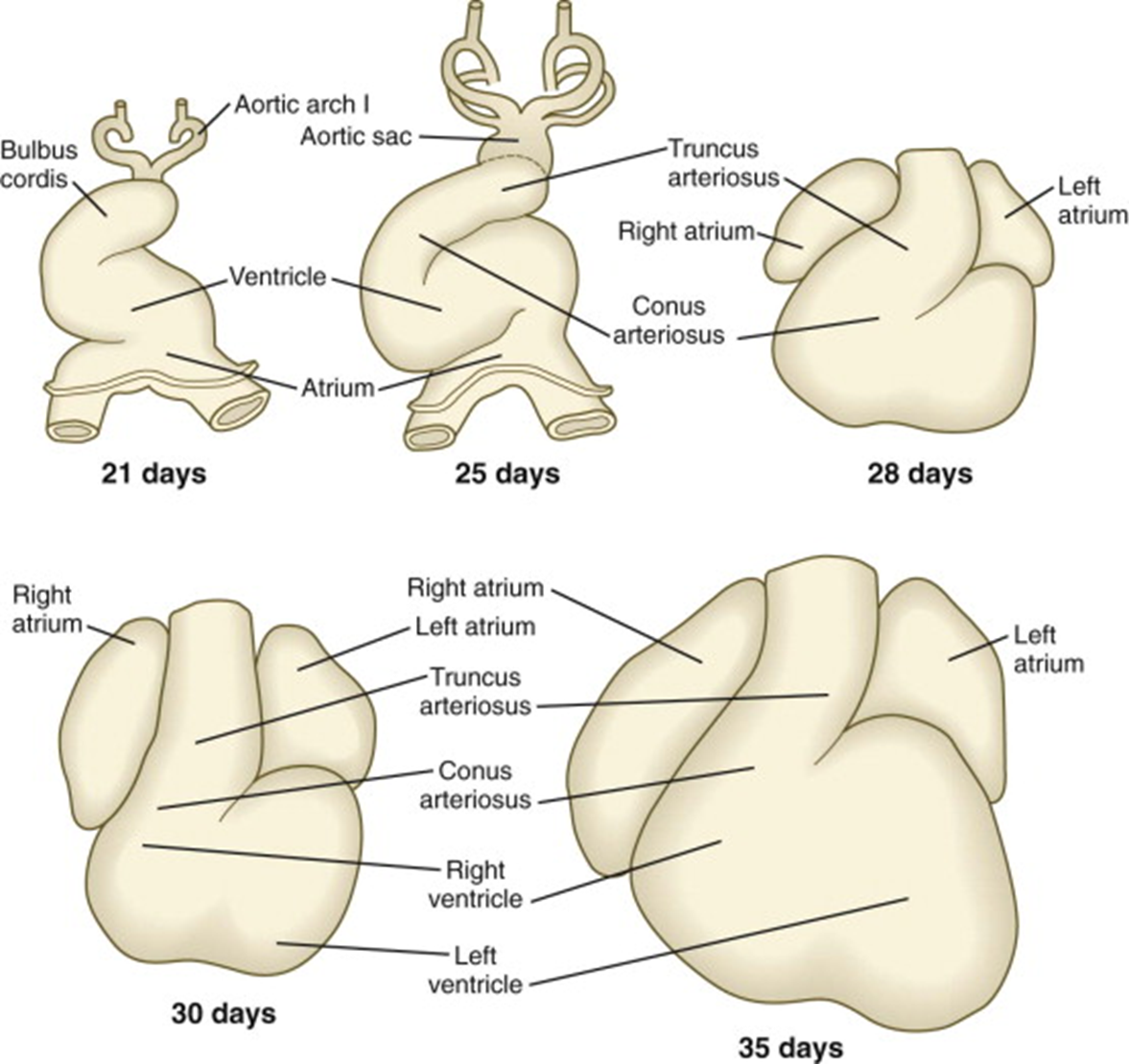
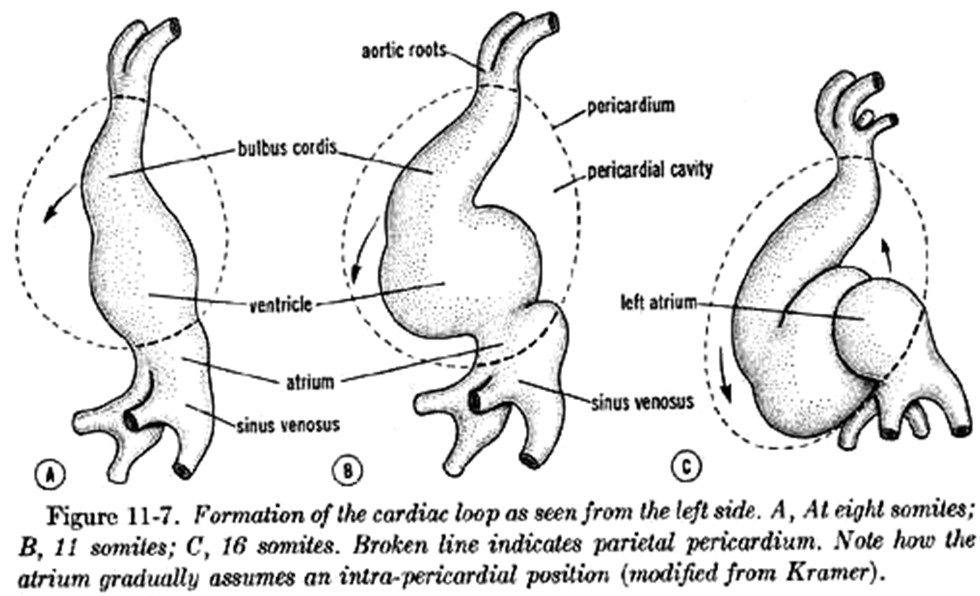
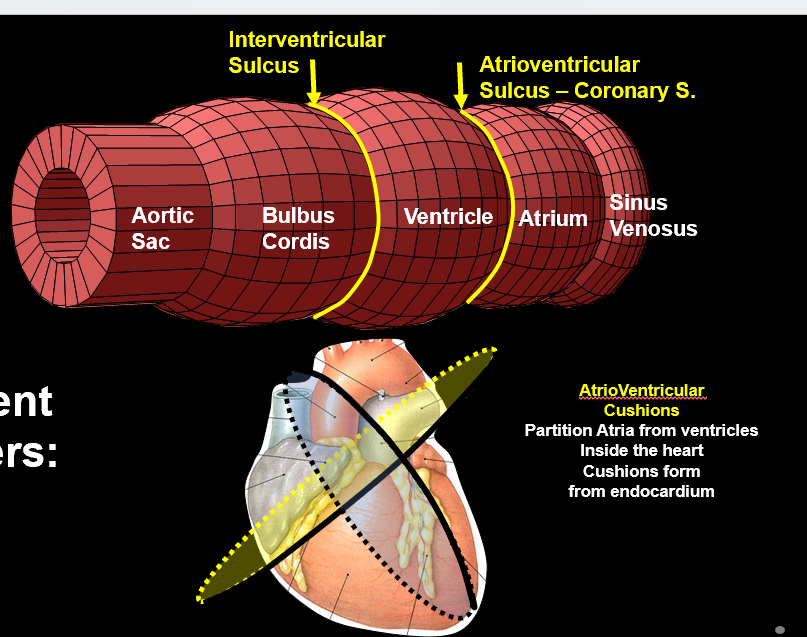
What sulci form on the looping heart?
Coronary (AV) sulcus between atria/ventricles and interventricular sulcus between ventricles.

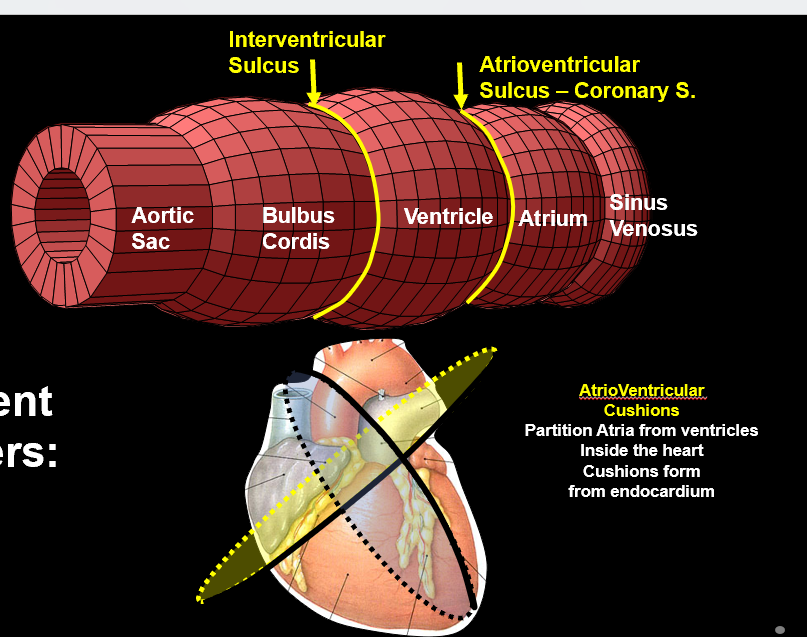
What do endocardial cushions become?
Atrioventricular septum, AV valves, and portions of membranous septa.

Name the steps of atrial septation.
Septum primum grows downward → ostium primum forms then closes → ostium secundum forms → septum secundum grows → foramen ovale remains.
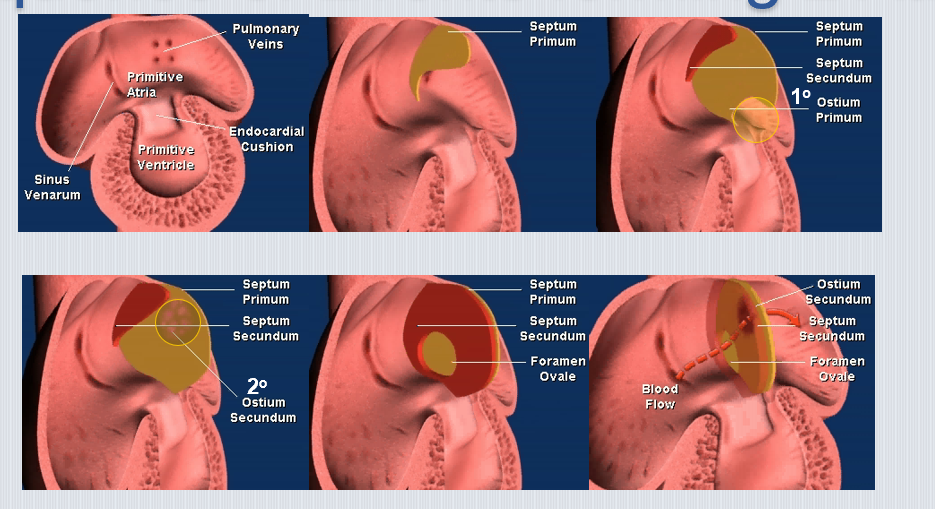

What becomes the foramen ovale after birth?
Fossa ovalis in the interatrial septum.
How is the muscular ventricular septum formed?
Growth of the ventricle floor upward toward endocardial cushions.
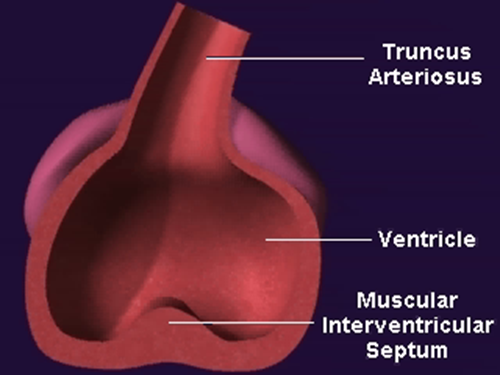
What creates the membranous septum?
Fusion of endocardial cushions with aorticopulmonary septum.
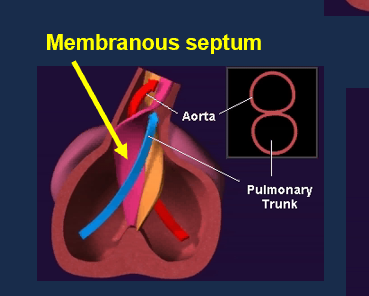

What is the heart’s fibrous skeleton?
Dense connective rings around AV and semilunar valves that anchor valves and insulate electrical conduction.
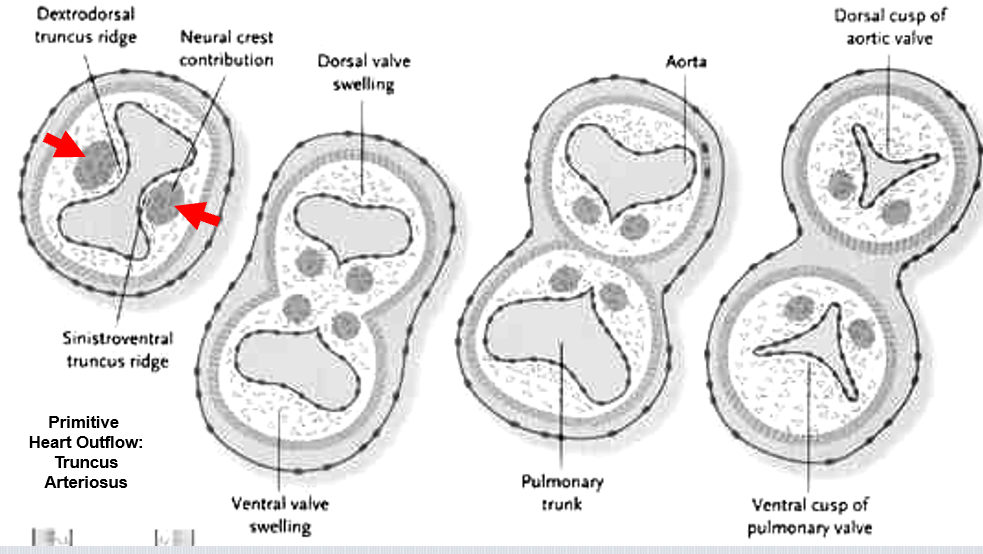
How does the truncus arteriosus divide?
Neural crest–derived aorticopulmonary septum spirals to separate aorta and pulmonary trunk.

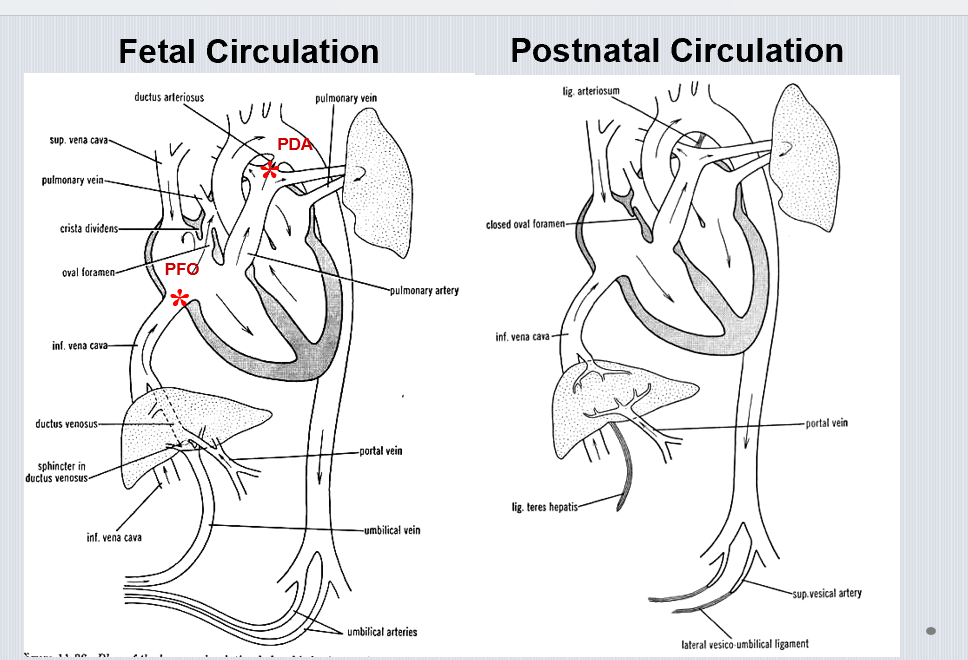
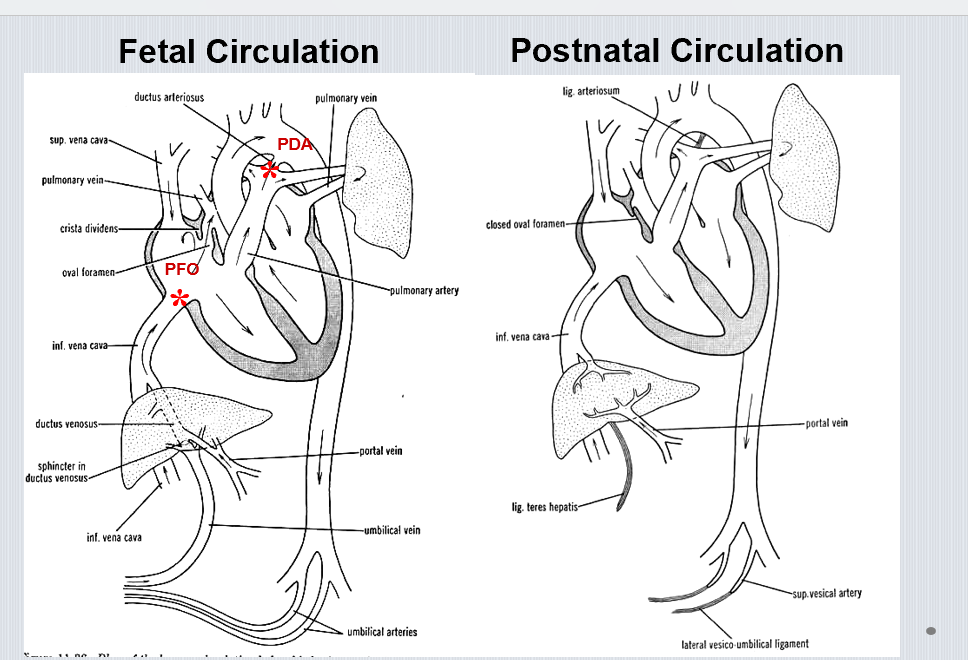
What shunts exist in fetal circulation?
Foramen ovale, ductus arteriosus, and ductus venosus.
What changes at birth close the foramen ovale?
Increased left atrial pressure pushes septum primum against septum secundum.
How does the ductus arteriosus close after birth?
Oxygenation and decreased prostaglandins cause muscular constriction to form ligamentum arteriosum.
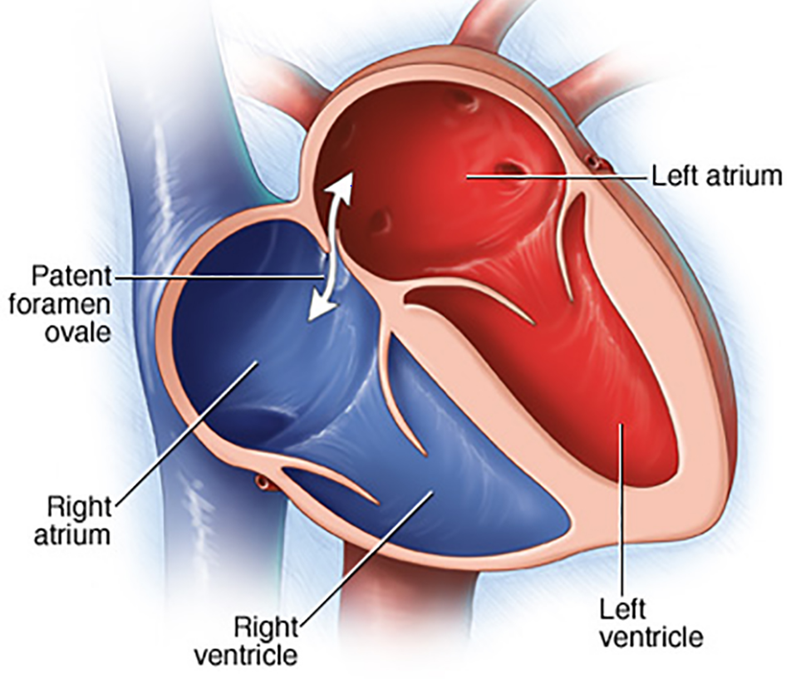
What is a patent foramen ovale (PFO)?
Incomplete closure of oval foramen → persistent atrial shunt.
What is a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)?
Failure of ductus arteriosus to close → continuous left-to-right shunt.

What is the most common congenital septal defect?
Ventricular septal defect (VSD) in membranous septum.
What four features define Tetralogy of Fallot?
VSD(ventricular septal defect), pulmonary stenosis, overriding aorta, right ventricular hypertrophy.
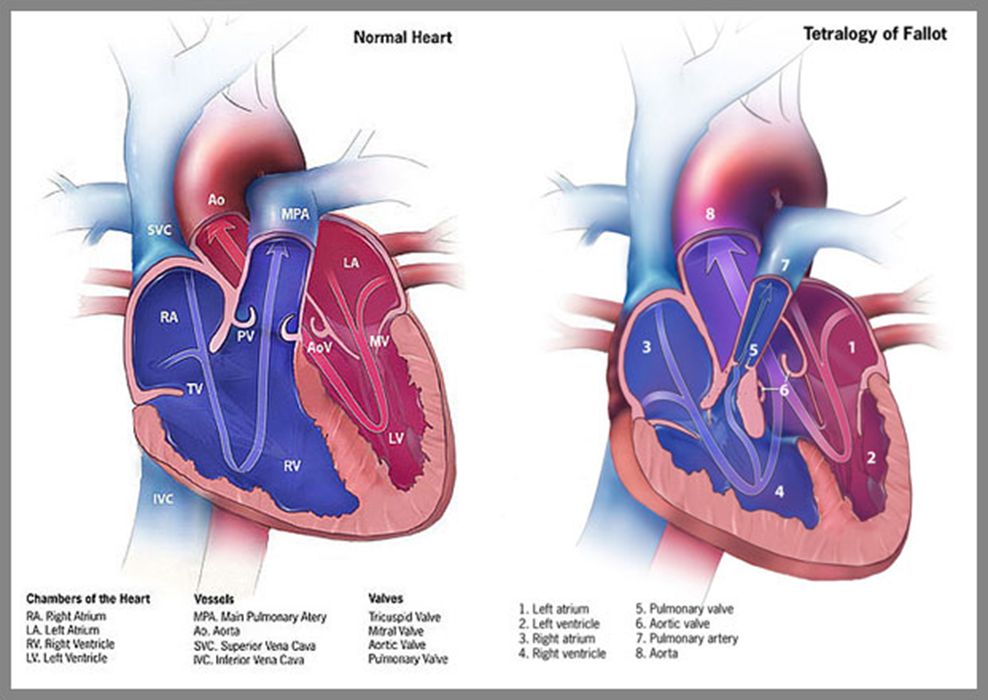
How does Tetralogy of Fallot cause cyanosis?
Pulmonary outflow obstruction + VSD → right-to-left shunt → deoxygenated blood enters aorta.
What embryonic origin underlies truncal septation defects?
Abnormal neural crest migration affecting aorticopulmonary septum.
Which adult vessel corresponds to the embryonic aortic sac?
Ascending aorta and root.
Where do the umbilical veins and ductus venosus drain in the fetus?
Into the sinus venosus via the IVC.
Why does the left ventricle have a thicker wall than the right?
Systemic resistance is higher than pulmonary resistance.
How do atrial and ventricular septation differ embryologically?
Atrial uses septal flaps (primum/secundum), ventricular uses muscular outgrowth + cushions.
What is the role of cardiac jelly?
Permits cushion formation and supports early myocardial expansion.
What is dextrocardia?
Heart positioned on the right due to abnormal looping.
How do atrioventricular valve leaflets derive from cushions?
Endocardial cushion tissue remodels into valve cusps and chordae.
What vessels form from the dorsal aorta’s vitelline arteries?
Celiac, superior and inferior mesenteric arteries.
How does Tetralogy of Fallot appear on a neonatal exam?
Cyanotic spells, clubbing, “boot-shaped” heart on X-ray.