Macro FRQ
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
AD/AS positive output gap
A positive output gap occurs when an economy's actual output is greater than its full-capacity output, which happens when demand is high. This can happen when factories and workers operate beyond their most efficient capacity to meet demand. A positive output gap is also known as an inflationary gap because increased demand also increases the price level.
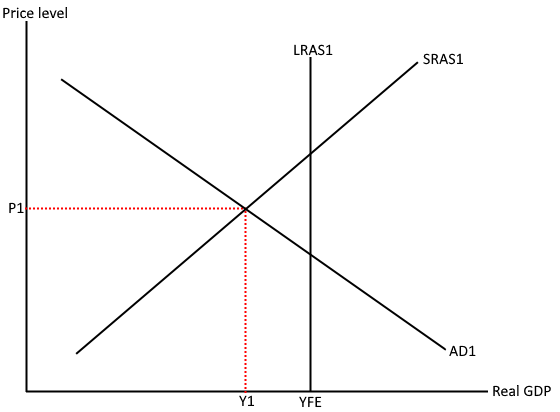
Effect of no policy
the term "no policy" typically refers to a scenario where policymakers do not actively intervene in the economy through fiscal policy (government spending and taxation) or monetary policy (central bank actions). In this scenario, the economy is left to operate according to market forces and without deliberate attempts to influence aggregate demand, employment, or inflation.
long run self adjustment
According to this view, markets are inherently stable and tend to move towards equilibrium over time. Key elements of the long-run self-adjustment process include:However, the speed and effectiveness of the adjustment process can vary depending on factors such as the flexibility of prices and wages, the degree of market competition, and the presence of frictions or rigidities in the economy.
monetary policy
the actions taken by a country's central bank (or monetary authority) to influence the economy by controlling the money supply, interest rates, and credit conditions.
draw money market graph
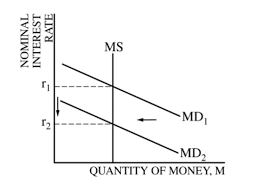
policy assuming limited reserves
When a central bank operates with limited reserves, it may face constraints in its ability to conduct monetary policy effectively, particularly through traditional means such as open market operations and setting reserve requirements. In such a scenario, the central bank may need to employ alternative strategies to achieve its policy objectives such as interest rate targeting
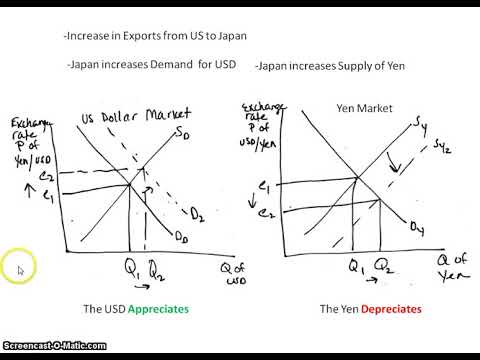
foreign exchange graph
effect of change in a real interest rate
A decrease in the real interest rate makes borrowing cheaper for businesses and individuals, leading to an increase in investment spending.
Changes in real interest rates can influence saving behavior. A decrease in real interest rates may reduce the incentive to save and vice versa
Lower real interest rates can stimulate aggregate demand through increased borrowing and spending, potentially leading to higher inflationary pressures if production capacity is constrained. Conversely, higher real interest rates can help moderate inflationary pressures by reducing demand and spending.
Balance of payment CFA surplus
A surplus in the Current Account means that the value of exports of goods and services, net income from abroad, and net transfers received from abroad exceeds the value of imports of goods and services, net income paid abroad, and net transfers sent abroad.
increased foreign reserves, strengthens the currency, potential for investment abroad
net exports effects
Overall, net exports play a crucial role in shaping economic performance, employment, exchange rates, and international trade relations. Policymakers often monitor net exports closely and may implement measures to promote export growth, reduce trade imbalances, and support overall economic stability and growth.
fiscal policy
Overall, fiscal policy plays a crucial role in shaping economic activity and GDP growth. By adjusting government spending and taxation, policymakers can influence aggregate demand, consumption, investment, and overall economic performance. However, the effectiveness of fiscal policy depends on various factors, including the size and timing of policy measures, the responsiveness of households and businesses to policy changes, and the overall state of the economy.