Serious Mental illnesses Ch 32
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is serious mental illness
uDefined: Group of psychiatric conditions, most of which are primarily biological in origin, that can significantly affect functioning and one's quality of life, especially if they go untreated
This can be mood disorders, perosnality disorders, psyhotic, diff types of schizophrenia.
uU.S. organizations use the abbreviation SMI
u4.6% of all adults in United States have SMI
Bipolar- very high,- no impulse control- nothing stops them, very low.
Deoression- keep going down.
Know basics to meds-
Schizoprenia- they have paranioa- delusions, hallucination
We want to evaluate the adherence to plan-
Suicide is 12x more likely in a pt w a serious mental illness- always assess that risk. Answer= safety option
30% of theses clients abuse drugs- when they smoke with their meds it makes them not work as well.
Priaprism- when they have an erection and it wont go down.
What are examples of serious mentall illness?
uMood disorders
uPersonality disorders
uPsychotic disorders
Subtypes of schizophrenia
These can be lifelong disorders that have early onset during late teenage years. Many pts expereince sucessful recovery and function at high levels withi minimal to no symptoms of their disorder. Other times there may cycles of recover and decompensation.
Marcus, 23, has been stigmatized all his young adult life ever since, at the age of 16, he began displaying early schizoid symptoms. Teased and bullied in high school and one (disastrous) semester at college, he has tried a long string of fast-food jobs, only to be fired because of a crippling social anxiety in such a fast-paced setting. He is currently homeless after becoming physically aggressive and frightening his aging parents.
What should you consider w older adults who have mentall illness?
Treatment for SMi has changed over the past decades, trainsitioning from institutonalization to more out patient community based services and promoting independence. Older adults. are more accostomed to the institutionizalion with extended hospitilzation. - Usually they have experienced their care within mental state hospitals.
Before deinstitutionalization, psychiatric hospitals were long-term residences
Even though the number of people who suffered from SMI was small- they created a burden on the community and social policy in regard to placement and demand for care.
uPatients became dependent on services and structure and were unable to function independently- Tx was strictly regimed and quality of care was not the best- so basic human rights were violated. These pts had little to not input on their tx.
u
Because of this- trainsiitoning to indepence in the community was difficult after all the years of institutionalization. DT years of poor health maintenance , bad diet, and housing, and substance yse took a toll on older adults physically. ow, current challenges are inadequate housing, diet, and more physical toll and medication-dt induced medical conditions like diabetes or metabolic syndrome. Dt theire complex needs- they tend to live in assisted living or nursing homes rather than being in the community w support and resources.
Some antipsychotics- can throw pts into diabetes, meds have to have labs drawn every few months
A word- in the book
Know in the textbook-

What should you consider about younger adults with serious mental illness?
uLimited experience with formal treatment- People who haven’t lived in an institution (like a hospital or long-term care facility) are usually less likely to become overly passive (not taking initiative) or dependent (relying too much on others).
uExperience series of disjointed short-term hospitalizations- They experience hospitalizations that are shorter in length and then get reffered to an uptpatient .
uHospitals often fail to recognize need for treatment- when they stay at the hospital it can stabilize the illness but then not recognize the need for tx. Because of this it creates poor tx adherence- they have Cycles of quick treatment, brief recovery, nonadherence,and relapse
intermittent tx puts young adults at risk for more problems-
uAdditional problems, such as increased frequency of relapse and hospitalizations, legal difficulties like getting areested and going to hjail, homelessness, substance use, unemployment, and poorer long-term prognosis. Poorer long-term prognosis” means that, over time, the expected outlook or predicted outcome for someone’s health or condition is less favorable compared to others. Patient B delays treatment, has repeated episodes of severe depression, and struggles with other health issues. Their long-term prognosis is poorer, meaning they are more likely to have ongoing depressive episodes, difficulty functioning in daily life, or higher risk of complications (like substance use or suicide).
“Prognosis” = the likely course or outcome of a disease or condition.
Decompensation- withdrawn,
Relapse-
See what it looks like in each disorder
How does serious mentall illness develop?
uSimilarity to Chronic Physical Illness
uOriginal problem develops
uOriginal problem increases
uCoping erodes- the original problem overhwlems and erodes the ability to cope which leads to new problems
uNew problems develop (e.g., loss of social skills)
Ex. a person with schixophrenia may exprenience paranioa and a loss of social skills- making Social interactions produce more anxiety
ex. girl is very afraid of dogs- and now is afraid of other people - this makes it hard for her to have other interactions and build connections
uWithdrawal leads to isolation & lack of support- as a result Coping and functioning continue to deteriorate
What is the difference between rehabilition and recovery
Rehabilitation—focuses on
uManaging patients’ deficits
uHelping them learn to live with their illness
Help pt to function their daily rles and goal to stabilize the disability with little focus on the idea of recovery . focused on living witht the diablity rather than improving quality of life achieveing recovery
Recovery—focuses on
uClient empowerment and strengths
Patient centered- emphasizes the person and the future rather than the illness and the present
Involves active partnership between provider and pt
Focuses on strengths and abilities rather than dysfunction and disability
Encourages independence and self determination
uAchieving goals of clients’ choosing- not the staff
emhapsizes that the staff works together to help the pt build on their strengths and achieve the highest quality of life
uLeading increasingly productive and meaningful lives
Supported by NAMI- national alliance on mental illness
After an anxious outburst outside a popular restaurant, Marcus is taken by police for a mandatory 3-day psych hospitalization for the third time in 6 weeks.
Fortunately for Marcus, due to a rise in the tourist industry in his city, the city council has developed a “three-strikes” program for its mentally ill homeless population. After three mandatory hospitalizations, patients are given a case worker who works to help patients find more long-term rehabilitation options to help keep them off the streets.
What are some issues confronting those with SMI
Establishing a meaningful life- they find it difficult with the possibility that they will never be the people they once were. Things that can help them are to help others, volunteer or manage their illness. If they have a lot of free time- rent books/movies, going to walks, joining. a club house or day program where they can counter social withdraw, increase social skills, and build support systems
uPhysical disorders-
omorbid conditions- greater risk of also have physical illnesses- Ex. hypertnesion, obsesity, doabetets, cardiovascular disease. They have a short lifespan 10-20 yrs and at more risk of premature death. Dt poor understanding of medical conditions, medication nonadherance, missed appointments and followups, limitied fianical and community resources. They may feel unwelcomed n clincis dt apperance Ex. pt had priaprims- erection and said demons were sticking needs down there- physcian didnt assess for priaprism.
Suicide- 12x more freqently with SMI,
Substance use- 20% abuse drugs/ acholol, ciggaretes they account for 40% of people who buy yhem. nicotine can reduce the efefctiveness of pscych meds. it riases bp and hr which can cause anxiety
Social problems
Stigma- perception that an individual is flawed- that they may be violent
This causes Isolation and lonliness, shame, and anger and can lead to discrimination getting healthcare, housing, and emplyment.
The stigma of poor self image- impaired hygeience can reduce social interaction and interfere witht hem developing relationships- even gf/bf, support groups and clubhouse programs can help w this.
Victimization- they are more likely to be vitims of violence then to be violent. victims of sexual assult. drug use and poor living condition in high crime neighborhoods increase this and can worsen psych conditions.
Economic challenges
Unemployment and poverty- more than 60% unempolyed and disbaility beenfits dont provide enough to live off. cant afford meds
Housing instability- affordable housing may be in unsafe neighborhoods, might not want to live w parents. nonadherance w tx, impaired self care, household distruption result in them beinf asked to leave shared housing. Ngeative reputuation w landlords , arrested- which could lead to decrease in housing, there are options like no reject eject if yiu stay in a hospital for a long time
Caregiver burden- resources are vocational housing support. helps people not only with housing needs (like finding or keeping a safe place to live) but also with vocational needs (like getting and keeping a job, job training, or career development).plan for trasnition of family caregiver to another caregiver or independence beofre a crisis happends and plan for finanical support like living trusts to avoid relapse and promote stability
What are some treatment issues with those confronting SMI
uTreatment issues
uAnosognosia: inability to recognize one’s own illness, need to be able to apply. mental illness affects brain- which is the one thing got make good decisions- thats why its hard and takes months/yrs for someone to recognize and accept a mental illness.
uNonadherence- never shame pt or blame. = more chance of relapse. Cause of nonadherance: anosognosia, med side effects, costs, lack of trust in providers, poor access to healthcare, stigma of mental illness
uMedication side effects- involuntary movmeents- dystonias- treatable. Diabetes, drowsiness-take night.
uTreatment inadequacy- barriers to finding a provider- not accepting new pts, insurance plans, not being close to work or home.
uResidual symptoms- symptoms that do not improve completely with consisent tx. For ex- a pt with schizophrenia being treated for strange beleifies, social withdraw, low energy even after pshyosis has occured. This can cause the pt to discontinue tx and leads to worsen illness. this happens more in older adults.
Relapse chronicity, and loss- relapse causes hoplessesnes. each relapse cause loss of frienships, housing, employment- makes it hard for discharge planning. = decompensation and longer hospital stays.
What can you do to help w Anosognosia:

Ex. Im cured,
Focus on helping pt get it right.
What can you do to help w non adherance
establish a trusting theraputic relationship

What interventions do you do for residual symptoms.
Once ohsyical symptoms are ruled out- do non pharmac tx for things like lack of energy, or social interest. individual therapy or group therapy can help, adress social isolation by expanding social oultets anf increase physical acitivty
Marcus’s case worker finds him a bed in a halfway house for men with SMI. During intake, the admissions nurse learns from Marcus that he initially did well on his medications when he was first diagnosed.
“But then,” Marcus says, “I started doing good and I figured out that I was cured. I didn’t need those drugs and their side effects anymore. I don’t need them now either. I’m not ill. I’m just pissed off. People are just out to get me, like in high school. This society never changes.”
Part of Marcus’s illness, then, is an inability to recognize that he is ill. This is called
A.relapse.
B.anosognosia.
C.nonadherence.
residual symptom.
ANS: B
Anosognosia is a symptomatic inability to recognize the illness as an illness. Relapse is the cycle of getting better only to fall into the cycle of severe SMI symptoms and behaviors again. Sometimes this is due in part to nonadherence: noncooperation with one’s treatment regimen. While this is certainly true of Marcus, the nonbelief in his own illness is in itself called anosognosia.
What are some SMI resources
uResearch & educational support, docuemntaries- good for providers
uComprehensive community treatment- Those who receive tx have diffiiculty acheiveing finanical independence- so now they can do the medicaid buy in program- allows coverage. the goal of community tx is to improve pts ability to function and quality of life. They can get outpatient care
uCommunity services and programs- the public healthcare system uses tax to provide services even to those without insurance.

What are some community services and programs
•Case management- helps pts w day to day needs- tx coordination and access to services. they can work in the pts house, school, and workplace. - give them access to services while also providing education, guidance, and support. they can also monitor meds to promote adherance. ACT
•Day programs- provide structure and therapeutic activities for clients who attend the program one or more days a week. Teach about social skills, adls, prevocational skills- needed before getting a job, provide social interaction and peer support. staff monior the pts status - and there may be peer support specialtisis.
•Group and individual psychotherapy
uFamily therapy- providing knowledge and skills to help families to support their loved ones
uPsychoeducation- educate about mental health topics like psychotropic drugs and skills- conflict resolution,
uSupport groups-
Crisis intervention services- help the pt cope when face stress and trauma or relapse . stressors like changes in routines, annvieraries of traumatic events, financial problems, victimization, may cause crisis. This hells to manage the stressors in a less restrictve setting anf avoid more inpatient care. Ex on call 24 hrs, hotlines- high crisis, warmlines/ supportlines, crisis residental- few days or 2 weeks - in between community residence and hospitalization.
What are some community services and programs
•Emergency psychiatric services- emergency meds, assessments, criris intervention, emergency adjustments. 24hr psych eval program that can start emergency inpatient admission on involuntary basisis. Mobile crisis team- professions who go to residences, jails, street corners. police officers can start involuntary emergency evals.
•Housing services- help living indipendently, mantaining stability and avoid homeless. room and board homes, they also have places that group them into forensic history. ex. think housing clincial.
•Partial hospitalization programs (PHPs)- impatient programs. go monday- friday most of the day. provide stabilization before beign release to other community services. or control symptoms to avoid inpatient care.
•Intensive outpatient programs (IOPs)- similar to PHP but less time
•Community outreach programs- focus on homeless or people who dont seek care on their own. conitnous outreach is needed to make a difference
•Multiservice centers- collab w outreach programs to supply hot meals, laundry, showers, clothes, transportation, phones, lailing adress, good when seeking work or benefits
Substance use treatment- clinics: provide theraputic and rehab services and med assited tx such as detox, methadone- opiod withdraw, psyhcotherapy
What is ACT
uAssertive community treatment (ACT)- Consumer works with multidisciplinary team to receive range of services as opposed to going to multiple agencies. improves the quality of life, reduced inpatient admissions, incareation, and homelessness. at least one memeber of the team is avaialable 24hrs a day for crisis care. emphasis on treating pts withtin their own enviornment.
WHat is Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)-
uCognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)- Focus on patterns of thinking and “self-talk”- (what one says to self internally)it uses natural consequences and positive reinforcers to shape a persons behaior more positive.
Helps them reduce and cope w symptoms like delusions and impaired social functioning.
What is Cognitive enhancement therapy (CET)
Cognitive enhancement therapy (CET)-
Neuroplasticity.- One part of the brain can assume functions for the compromised part of the brain. Computer-based drills and exercises to strengthen brain function. Brain exercise therapy, ex diff movements w hands which turns on different areas in brain and makes connections in brain. - it increases mental challenge and strenghtens fucntions like focusing attention and processessing and recalling information. it can helpw interpreting social and emotional info, like judging a persons mood from expression or tone of voice. it leads to improvement in cognition and improves social and vocational funcitoning.
what is family support and partneership tx for SMI
uFamily support and partnership- Includes NAMI’s Family-to-Family program. : understanding SMI, coping skills, and recovery process
familu support is one of the strongest predictors of recovery. when providers work as empathetic partners it enhances tx and reduces conflict.
Standing too close, resolving conflict, role play
uVocational rehabilitation and related services- Clubhouse model (consumers run programming), Supported employment model (on-the-job coach), The Village is an example of this
•NAMI’s Family-to-Family program focuses on understanding SMI, coping skills, and the recovery process.
•NAMI meetings and support groups are specific to various SMIs, for example, the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance, serve as excellent sources of support and practical guidance for primary consumers (patients) and secondary consumers (their significant others).
WHat is social skills training
uSocial skills training: Teaching wide variety of social and ADL skills. focuses on making progress in small increments. people have social deficitis that cause functional impairment. for ex. someone may not know person space- this can lead to rejection and poor job evaluation. care providers break down interpersonal skills like how to resolve conflict, teach how to manage the problem step by step, and use role play and group interaction to practice skills.
what is Vocational rehabilitation and related services
uVocational rehabilitation and related services
training skills to enhance employment and finanical support to keep that employment.
uClubhouse model- Clients run programming for peers. coffee shops, housekeeping services, teach all memebers to perform a job in the business and how to run it.
uSupported employment model- helps to get them employed-
Financial incentives to employers
Rapid placement in job preferred by the patient
Continuing individualized support on the job
Integration of mental health and employment services
What are other treatment approaches?
uCourt-Involved Intervention
Psychiatric advance directives- legal documents that allows a person to choose/set their care in case they become impaired (judgement, hospitalized), this allows them to maintain control over their treatment or be court ordered
Guardianship- appointment of a guardian to make decision for the patient during times of impairment or disability; agonsinia . guardians can be anyone, but are appointed prior to and usually in a court process. pt cant authorize their own tx- it requires the guardians approval. Payee- someone like a volunteer or staff member who can manage the finances- bc the pt is responsible for using the clients funds.
What are consumer run programs
a lot like vocational rehabilitation services. informed clubhouses that offer socialization, recreation, group classes. even snack bars or janitorial survices that provide client employment while also encourgaing independence and building vocational skills. EX.helping run a resturant,
how does peer suport help ppl with SMI
uPeer Support- – peer advocate (who has usually experience the same thing); (give example of sexual assault advocate)
they are more likely to upon up to someone who has been through the same things.
How does technologoy and exercise help SMI
uTechnology- mainly used by the healthcare providers in tracking patients progress in making appointments, medication compliance, and ordering needed services,
can reduce healthcare costs, imrpove tx access and client outcomes. helps them remember appointment, tx, helps manage their stress, prevent weight gain through exercise and diet.
Exercise- Don’t underestimate the power of exercise!!! - helps cope w their symptoms , reduces anxiety, depression, self esteem, weight conrrol for ppl w diabetets or hypertension. motivation and group interventions can help w participation. communitry recreational centers can provide discounts passes for pts w SMI. day centers or clubhouses can offer diff classes.
j
Marcus’s new therapist helps him learn to focus on identifying his own distorted thinking and using “self-talk” to get control of a situation and turn his thinking around. This treatment is popularly referred to as
A.ACT.
B.CET.
C.CBT.
NAMI.
ANS: C
CBT (cognitive behavioral therapy) involves helping the patient focus on (a) identifying distorted thinking and (b) using “self-talk” to come to a more realistic frame of mind. In ACT (assertive community treatment), the consumer works with multidisciplinary team to receive range of services as opposed to going to multiple agencies. CET (cognitive enhancement therapy) uses computer-based drills and exercises to strengthen brain function. Finally, NAMI (National Alliance on Mental Illness) is not a treatment so much as it is a family and caregivers’ support agency. It is the leading mental health consumer support and advocacy organization in the United States.
What are the assessment strategies for SMI patients
Assessment strategies
uIntentional risk- to self or others- suicide/ homocide
uUnintentional risk- inadequate nutrtion, clothing not suitable for weather, neglect of medicial needs, carelessness while driving, smoling, or cooking
uDepression or hopelessness
uAnxiety
uSigns of impending relapse- decrease sleep, increased impulsivness or parionia, diminished reality testing- trouble telling the difference between what is real and what is not. increased delusional thinking, or command hallucinations- for exampe hearing voices that tell them to do something.
uPhysical health problems can cause psych symptoms and be mistaken for mentall illness or relapse. ex. brain tumors or drug toxicity.
uComorbid illnesses- what meds are they on, how many, when do you take it.
uTreatment nonadherence- not using meds, missing appointments, illicit drug use, not wnating to talk about these issues.
Note their mood, hygiene, serious mental illness- weigh them. Subsatnce abuse- decompensating
AIMS,
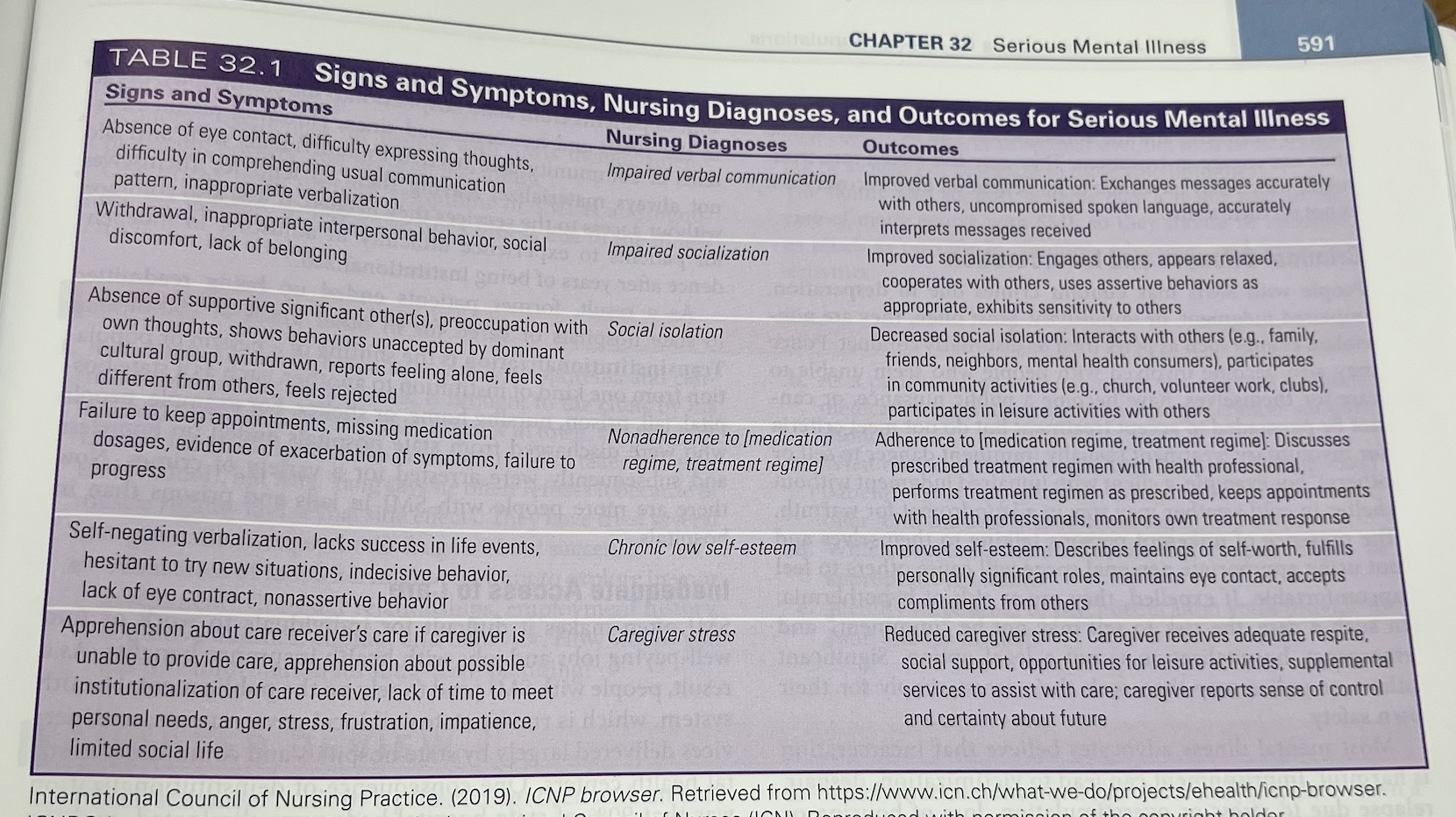
Nursing Diagnoses
uImpaired verbal communication
uImpaired socialization
uSocial isolation
uNonadherence
uChronic low self-esteem
Caregiver stress
What are the S/S of someone with SMI
Table 32.1 lists selected signs and symptoms of problems associated with SMI, potential nursing diagnoses that apply to the patient with SMI, and examples of specific nursing outcomes.

What interventions can you do.

Plan nursing care based on evidence-based practice in caring for individuals with complex mental health needs, prioritizing safety, therapeutic communication, and multidisciplinary communication
. Recognize signs and symptoms of acute and chronic mental illness (e.g., schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depression, anxiety disorders).
Implement individualized teaching plans to educate clients and families about mental health conditions, treatment adherence, symptoms management, and available support services.
Evaluate the client’s adherence to the treatment plan and the effectiveness of their support system in promoting recovery and continuity of care.