CP: Module 1.2
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
To measure lung volumes like total lung capacity (TLC) and residual volume (RV)
What is a plethysmograph used for in PFT?
The volume and rate of air exhaled.
What does a spirometer measure?
Standing, unless the patient can't do so.
When performing spirometry, what position is preferred?
Age,
height,
sex,
and race/ethnicity.
What factors are normative spirometry values based on?
Recent surgeries,
eye issues,
aneurysms,
TB exposure,
collapsed lung,
stroke,
or coughing blood.
What are some safety screening questions before spirometry?
• Maximal volume air contained in lung at end of max inspiration, 5-7L
What is Total Lung Capacity (TLC)?
Max air forcibly exhaled after max inhalation.
What is Forced Vital Capacity (FVC)?
Normal breath out, 0.4-0.7L.
What is Tidal Volume (TV)?
Air exhaled per minute (TV x RR), ~4L/min.
What is Minute Ventilation (VE)?
Air left in lungs after max exhale, ~1L.
What is Residual Volume (RV)?
Extra air you can inhale after normal breath in.
What is Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)?
Extra air you can exhale after normal breath out.
What is Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)?
Air left after normal breath out (ERV + RV).
What is Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)?
Max air breathed in 12 sec; normal = FEV1 x 40.
What is Maximum Voluntary Ventilation (MVV)?
Diffusion capacity; normal is >80% predicted.
What is DLCO and what's a normal value?
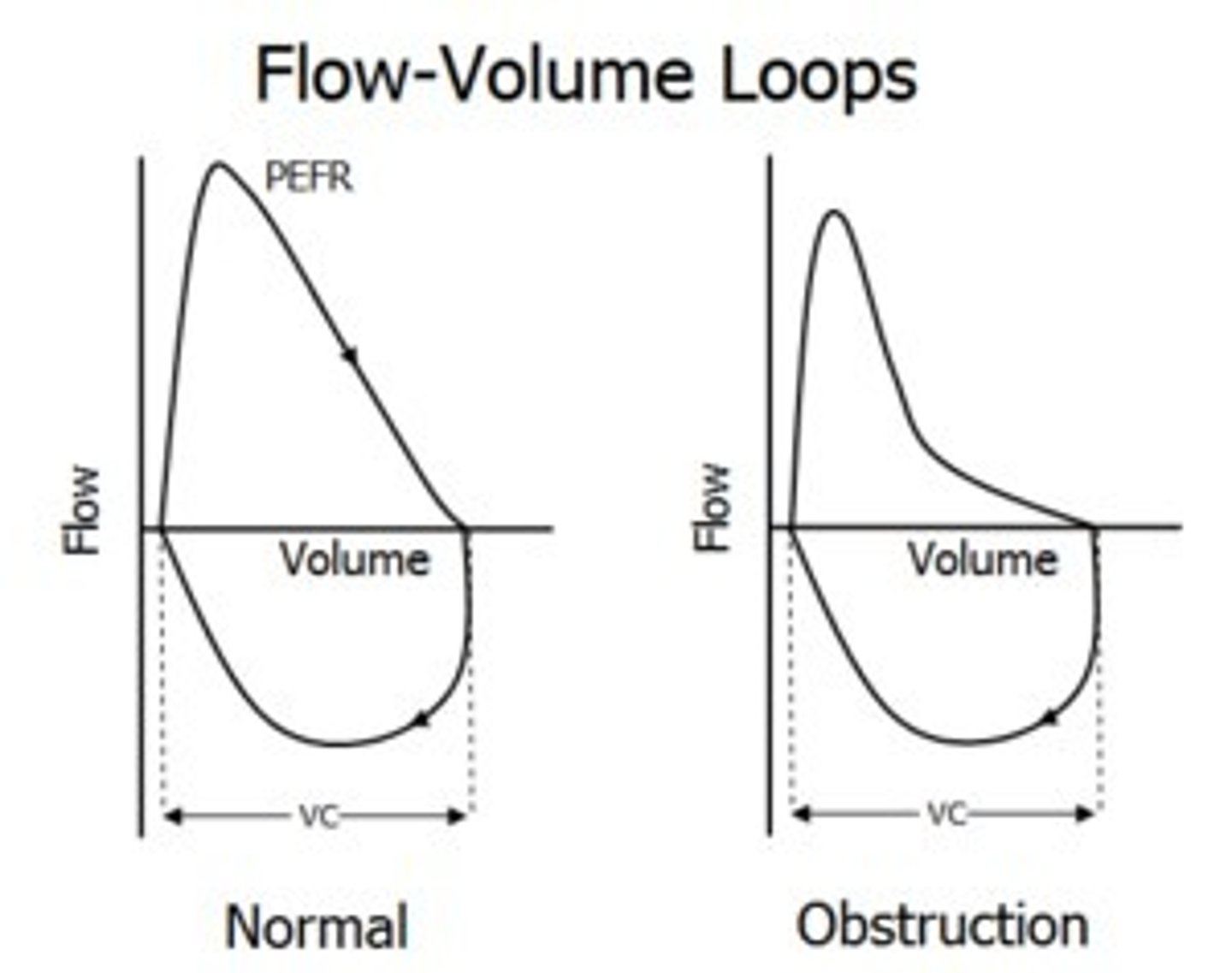
Relationship between airflow and lung volume during forced breathing.
What does the flow-volume loop show?
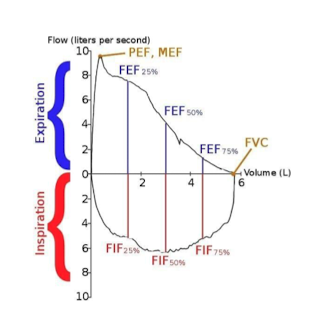
Fastest airflow during FVC maneuver; reflects effort.
What is Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF)?
Flow between 25-75% of exhaled FVC; reflects mid-airway flow.
What is FEF25-75%?
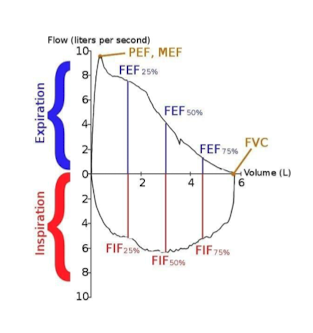
% of air exhaled in first second; normal ≈ 80%.
What does FEV1/FVC ratio represent?
Obstructive: ↓ FEV1/FVC;
Restrictive: ↓ FVC, TLC, with normal or ↑ FEV1/FVC.
How do obstructive and restrictive patterns differ in PFT?