Urethral Disorders
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
retrograde, ureterovesical, pressure, valve, UTI
Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR)
___________ passage of urine from the bladder into the upper urinary tract
Normal:
Urine enters the bladder but the _________________ junction prevents urine from regurgitating into the ureter
Protects the kidney from high ___________ in the bladder and from contaminated urine
Abnormal:
Incompetent ______ leads to reflux of urine into the ureter
Significantly increases the chance of ___ and kidney damage
ureterovesical, short, growth
Primary VUR
Most common
Incompetent or inadequate closure of the _______________ junction
Congenitally _____ intravesical ureter
Spontaneously resolves with patient _______
pressure, contraction, obstruction, >, >
VUR: Secondary and Epidemiology
Secondary
Abnormally high voiding __________ in the bladder which results in failure of the UVJ to close during bladder _____________
Associated with anatomic or functional bladder ____________
Epidemiology
Caucasian _ AA
Female _ Male
hydronephrosis, febrile UTI, females, bowel, bladder
VUR Clinical Presentation
Prenatal presentation
______________ on prenatal ultrasonography
Postnatal presentation
Postnatal diagnosis of VUR is usually made after a diagnosis of a ________ ___
Older toilet-trained children, especially __________, with VUR diagnosed after an initial UTI have a higher likelihood of having _______ and _________ dysfunction (BBD)
voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG)
What is the preferred diagnostic tool for VUR?
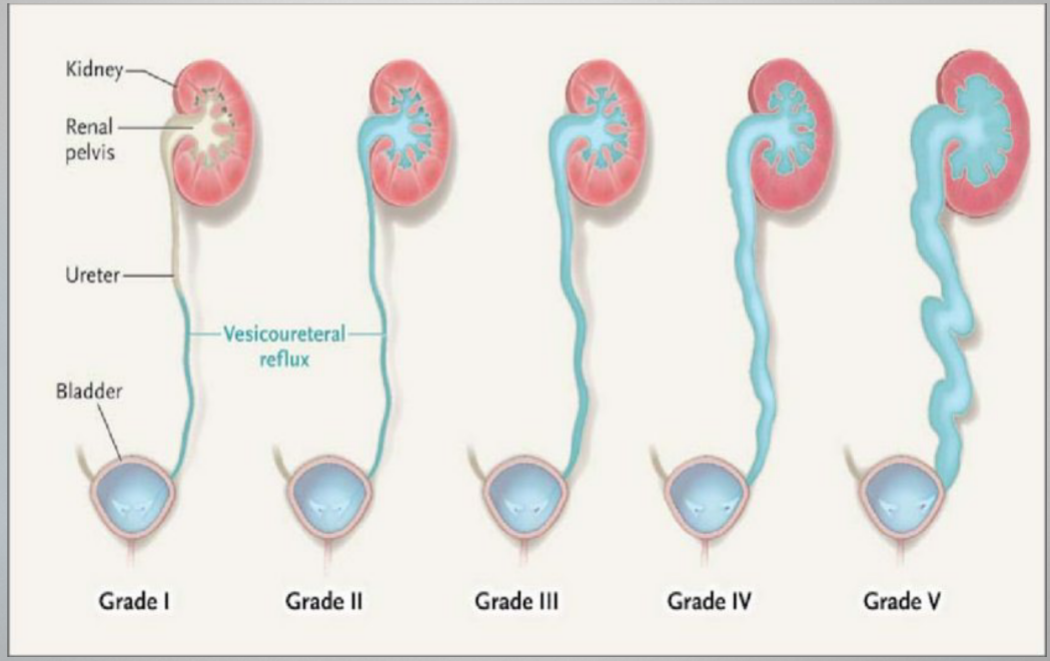
Grade I
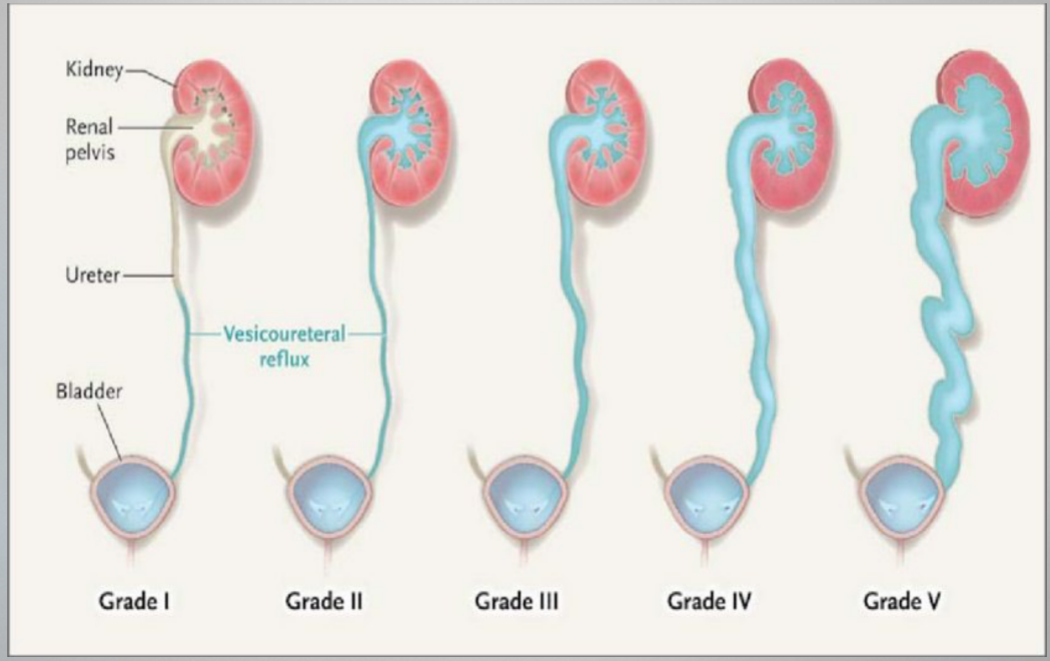
VUR Grades
reflux only fills the ureter w/o dilation
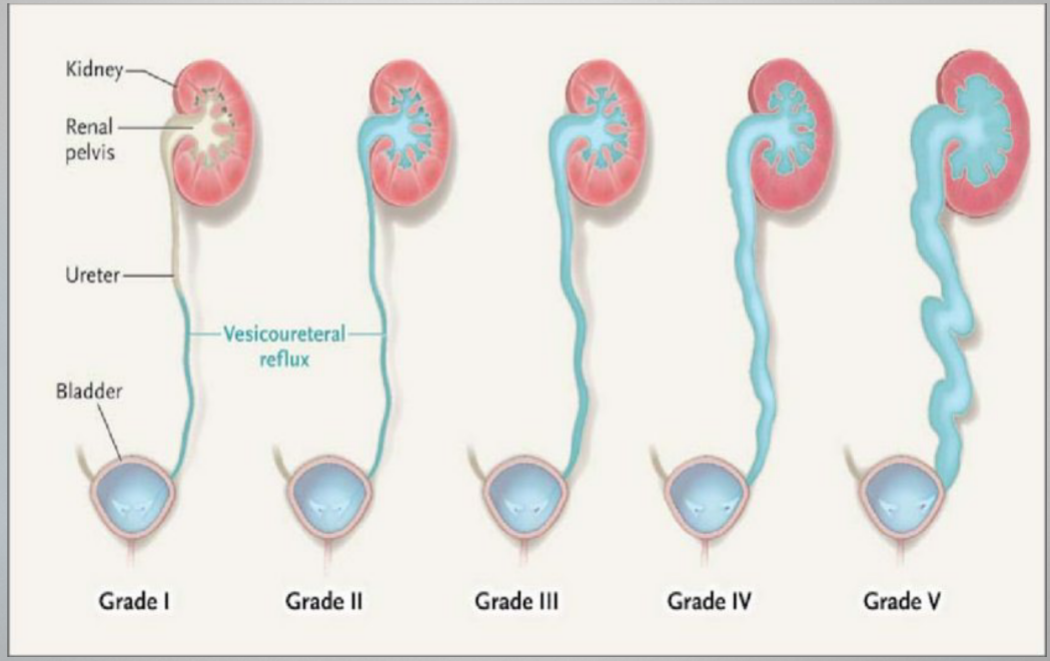
Grade II
VUR Grades
Reflux fills the ureter and the collecting system w/o dilation
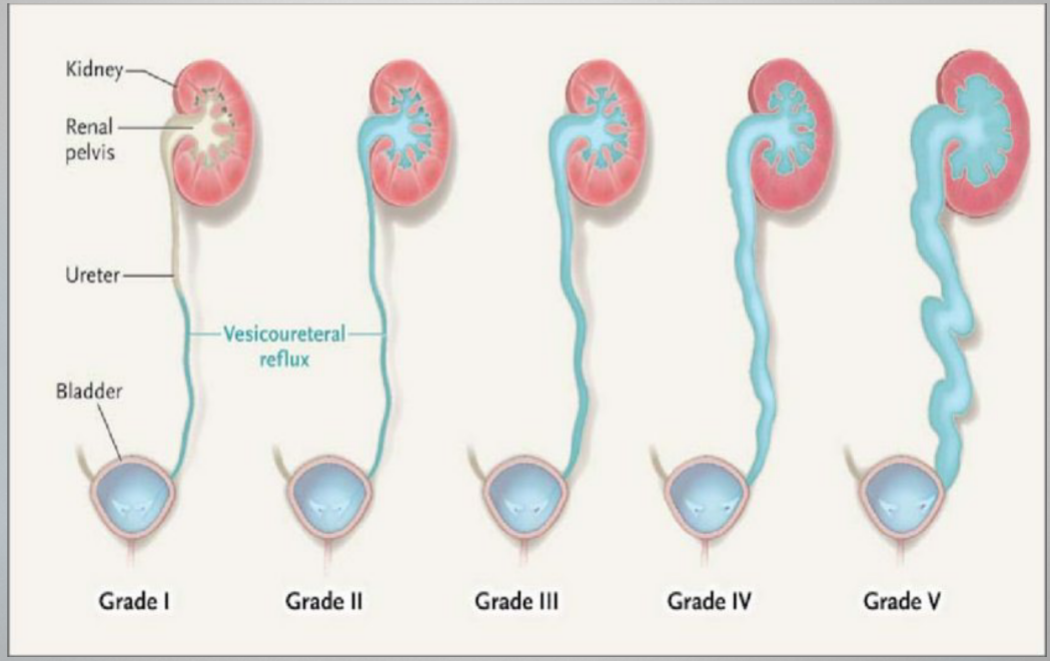
Grade III
VUR Grades
Reflux fills and mildly dilates the ureter and the collecting system with mild blunting of the calcyes
Grade IV
VUR Grades
Reflux fills and grossly dilates the ureter and the collecting system w/ blunting of the calcyes. Some tortuosity of the ureter is also present
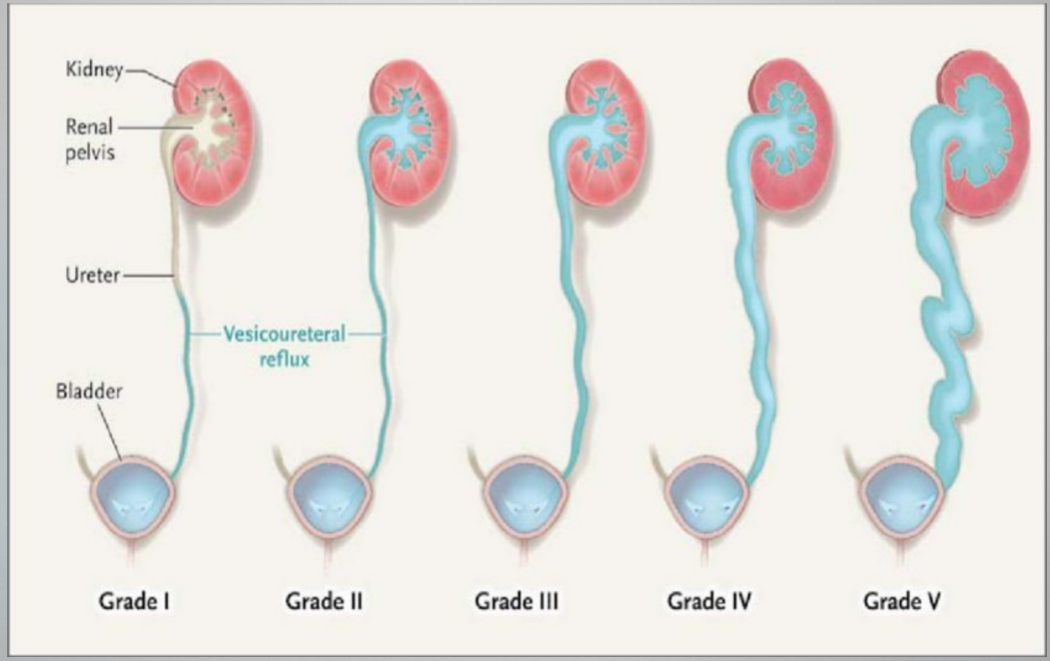
Grade V
VUR Grades
Massive reflux grossly dilates the collecting system. All the calices are blunted w/ a loss of papillary impression, and intrarenal reflux may be present. There is significant ureteral dilation and tortuosity.
pyelonephritis, renal, surveillance, prophylactic, bactrim, cephalexin, surgery
VUR Treatment
Goals
Prevent recurrent _____________ and UTIs
Prevent further ______ damage
Identify and treat children with bladder or bowel dysfunction
Grade I-II
Toilet Trained: ___________
Not toilet trained: _____________ antibiotics
Abx Prophylaxis
>2 months: ________ or nitrofurantoin
<2 months: _____________
Grade III-V
Abx prophylaxis
_________ indications
Continued grade IV/V beyond 2-3 y/o
Children who fail medical therapy
Children who have side effects from continuous abx
Those who are noncompliant with meds and f/u
congenital, ventral, ectopic, curvature, foreskin, prepuce, glans, scrotum
Hypospadias
_____________ anomaly resulting in abnormal __________ placement of the urethral opening
Defined as any or all:
_________ urethral meatus
Penile _____________ (chordee)
Ventral __________ deficiency with incomplete foreskin closure around the glans, leading to the appearance of a dorsal hooded ________
Location
Anywhere within the ______, the shaft of the penis, the _______, or perineum
androgenic, metabolism, estrogen, estrogenic, age, DM, pesticide
Hypospadias
Pathogenesis
Disruption of ___________ stimulation
Genetic
Gene mutations that affect androgen ____________ and __________ and androgen response
Environmental
Prenatal exposure to __________ compounds
Risk factors
Advanced maternal ___
Preexisting maternal __
Family hx
Smoke and ___________ exposure
Prematurity
Fetal growth restriction
Placental insufficiency
sexual, pelvic, karyotyping, electrolytes
Hypospadias
If severe hypospadias or hypospadias with cryptorchidism
Concern for a disorder of _______ development
_______ US
___________
Serum _________ w/ further eval for congenital adrenal hyperplasia
functional, deflection, standing, curvature, fertility
Hypospadias Referral and Correction
Reserved for pts with ____________ issues
Significant ___________ of the urinary stream
Inability to urinate from a ________ position
Erectile dysfunction d/t penile ____________
___________ issues
forme fruste, surgery, required
Hypospadias Classifications
_____ ______
NO surgical correction
Standard
Depends on urethral location and penile curvature
_________ may or may not be needed
Severe
Surgery ___________
tubularization, TIP, 2
Hypospadias Techniques
Standard Hypospadias
Primary _______________ (tubularized urethroplasty) with or w/o ___ (tubularized incised plate)
Severe Hypospadias
Onlay Island Flap
_ stage repair
dorsal, glans, incontinence, symphysis, sulcus, groove, penopubic, glans
Epispadias
_______ location of the urethra
Classification
Glandular
Urethra opens on the dorsal aspect of ______
Rarely have _____________
Penile
Urethral opening located between the pubic _________ and the coronal ______
Broad and gaping opening
Usually have a distal ______ from the meatus to glans
75% have incontinence
Penopubic
Urethral opening at the _________ junction
Dorsal distal groove through penis to ______
95% have incontinence
exstrophy, surgery, chordee, glans
Epispadias
Often associated with bladder _________
________ is required to correct the incontinence, remove _______, and extend the urethra out onto the _____
meatus, pendulous, bulbar
What are the parts of the anterior urethra?
Membranous, prostatic, bladder neck
What are the parts of the posterior urethra?
meatus
1
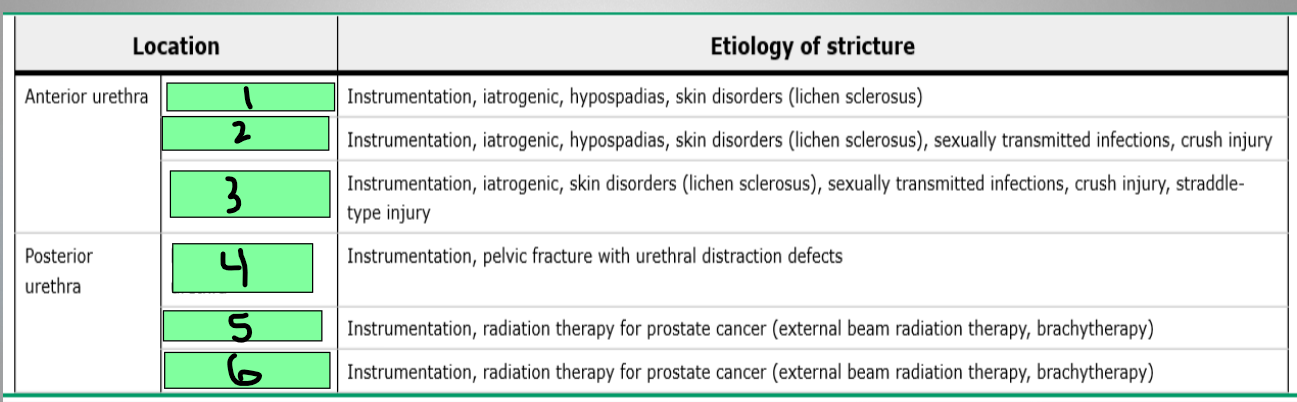
pendulous urethra
2
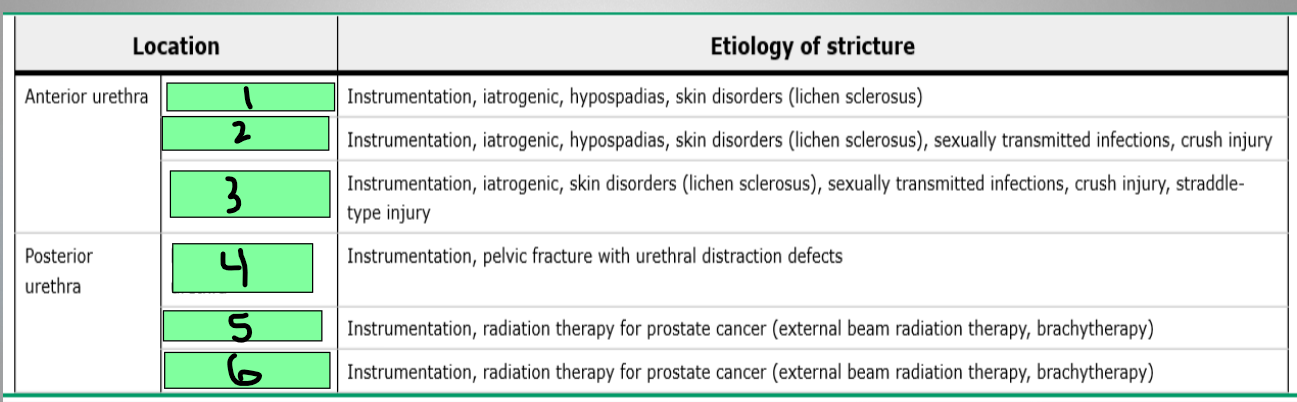
Bulbar urethra
3
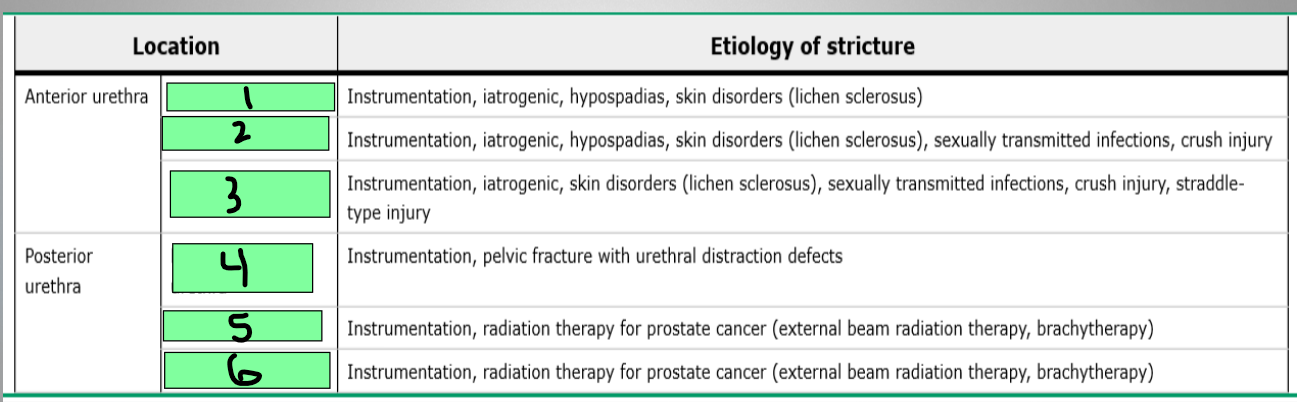
Membranous urethra
4
Prostatic urethra
5
Bladder neck
6
stream, incomplete, spraying, UTIs, postvoid, stones, hydronephrosis, fistula
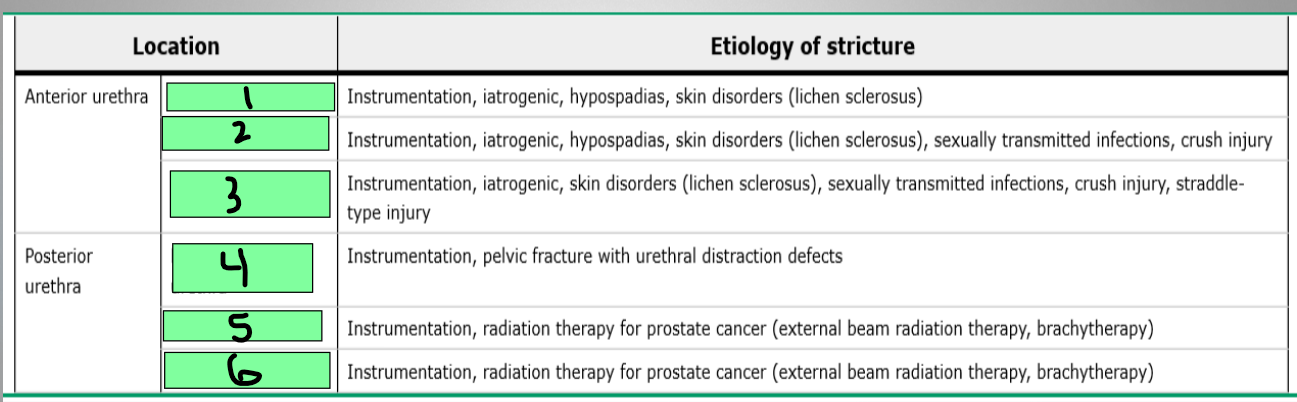
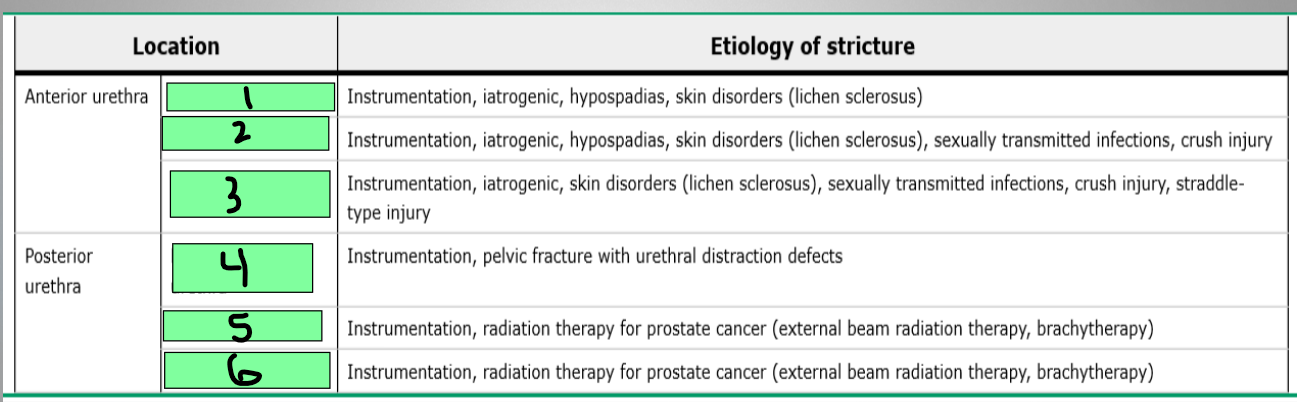
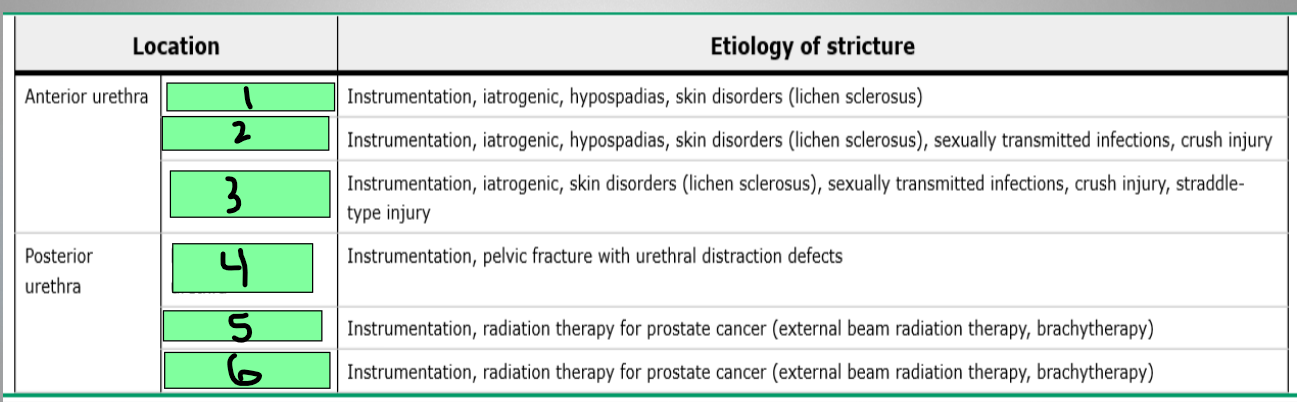
Urethral Stricture
Obstructive Voiding Symptoms (MC)
Decreased urinary _______
___________ bladder emptying
Other symptoms
_________ of urinary stream
Recurrent ____
Dysuria
Complications
Elevated _________ residual urine volumes
Bladder _______
UTIs
________________
Urethral _________
Abscess
low, high, cystourethroscopy, anterior, posterior
Urethral Stricture Diagnostics
Uroflowmetry
___ peak urine flow rate
Post void residual (PVR)
____ PVR
Postvoid volumes of 50-100 mL may indicate an abnormality
__________________
Used before treatment to further define stricture
Retrograde urethrogram (RUG)
Most useful at assessing the _________ urethra
Voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG)
Most useful at assessing the _____________ urethra
US urethrography
dilation, urethrotomy, high, reconstruction, diversion, suprapubic
Urethral Stricture Treatment
Minimally Invasive (most common initial Tx)
Urethral __________
Endoscopic _____________
***____ rate of recurrence
Invasive
Urethral ________________ (urethroplasty)
Other
Urinary ___________
____________ tube placement
Perineal urethrostomy
eversion, mucosa, postmenopausal, unknown, estrogen, valsalva
Urethral Prolapse
Circumferential _________ of the urethral ________ at the urethral meatus
Epidemiology
Prepubertal and ______________ females
Etiology
_________ mostly
Possibly from ___________ deficiency
Result of ________ voiding or constipation
Loose connections between muscle layers of urethra
painless, urinary, beefy red donut
Urethral Prolapse Signs/Symptoms
___________ bleeding
Can become painful or cause __________ symptoms
______ ___ _____ shaped protrusion
observation, estrogen, sitz, cauterization, foley, ureterocele
Urethral Prolapse Treatment
Conservative
____________, topical _________, and/or anti-inflammatory creams, and ____ baths
67% recurrence rate of non-operative treatment
Surgical
_______________, ligation around a ______ catheter, and complete circumferential excision
After reduction, cystoscopy should be done to r/o ____________