Bacteriology Lab Final 2025
1/218
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
219 Terms
Why do Gram-positive organisms stain purple?
Thick, cross-linked peptidoglycan layer traps violet-iodine complexes, preventing decolorisation.
Why do Gram-negative organisms stain pink?
Thin peptidoglycan layer means violet-iodine complexes are washed out, which allows for recolorisation with safranin O.
What is the purpose of blood agar (BA)?
A non-specific medium made with sheep RBCs, useful for observing hemolytic and colony characteristics.
What are the three types of hemolysis?
Alpha (incomplete), appearing as a green halo; beta (complete), appearing as translucency around colonies; double-zone, with an incomplete outer zone and complete inner zone.
What do Staphylococcus colonies look like on BA?
Smooth, round, greyish to china white (S. hyicus).
Which Staphylococcus species are hemolytic?
S. aureus & S. pseudintermedius = double-zone hemolytic.
What is the purpose of the catalase test?
Detects catalase enzyme, which produces water and oxygen (bubbles) by breaking down H2O2.
What is the purpose of the oxidase test?
Detects cytochrome c oxidase enzyme, found in aerobic organisms, which oxidises the reagant to turn it purple.
What is the result of Staphylococcus on the following tests: catalase, oxidase?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative.
What is the purpose of the coagulase test?
Detects coagulase enzyme, which clots fibrinogen. Diagnostic for specific species in Staphylococcus.
Which Staphylococcus species are coagulase-positive?
S. aureus, S. hyicus, S. pseudintermedius.
What does Staphylococcus look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, cocci, clusters.
What kind of disease is caused by Staphylococcus aureus & pseudintermedius?
Pyodermatitis, mastitis; S. aureus (large animals), S. pseudintermedius (small animals).
What kind of disease is caused by Staphylococcus hyicus?
Swine exudative epidermitis (greasy pig disease), mastitis.
What kind of disease is caused by Staphylococcus chromogenes, epidermis, & felis?
Opportunistic mastitis; disease in cats (felis).
What do Streptococcus colonies look like on BA?
Grey to white, glossy round colonies.
Which Streptococcus species are beta-hemolytic?
S. agalactiae, S. equi ssp equi & zooepidemicus.
Which Streptococcus species are alpha-hemolytic?
S. dysgalactiae, S. uberis (also non-hemolytic), S. suis.
What is the result of Streptococcus on the following tests: catalase, oxidase?
Catalase negative, oxidase negative.
What does Streptococcus look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, cocci, chains.
What kind of disease is caused by Streptococcus agalactiae, dysgalactiae, & uberis?
Environmental mastitis, contagious & with a high SCC.
What kind of disease is caused by Streptococcus equi ssp. equi & zooepidemicus?
Strangles, mastitis, opportunistic wound infections.
What kind of disease is caused by Streptococcus suis?
Arthritis, valvular endocarditis.
What do Enterococcus colonies look like on BA?
Smooth, round, greyish-white colonies, alpha or non-hemolytic.
What is the result of Enterococcus on the following tests: catalase, oxidase?
Catalase negative, oxidase negative.
What does Enterococcus look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, cocci, chains.
What is the purpose of Edwards agar?
A BA base with crystal violet and esculin, selective for streptococci and enterococci. A positive result for esculin is hydrolysis (lack of fluorescence).
Which bacteria species are esculin positive on Edwards agar?
Streptococcus uberis, Enterococcus.
What do Trueperella pyogenes colonies look like on BA?
Round, irregular colonies with a rough surface, beta-hemolytic.
What is the result of Trueperella pyogenes on the following tests: catalase, oxidase?
Catalase negative, oxidase negative.
What does Trueperella pyogenes look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, pleomorphic coccobacilli.
What kind of disease is caused by Trueperella pyogenes ?
Opportunistic summer mastitis, purulent infections.
What do Corynebacterium colonies look like on BA?
Round, smooth, waxy and dry colonies, beta-hemolytic (pseudotuberculosis) or non-hemolytic (renale).
What is the purpose of the urease test?
Detects urease enzyme, which converts urea to ammonia. A positive result is pink (alkalinity).
What is the result of Corynebacterium on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative, urease positive.
What does Corynebacterium look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, pleomorphic (pseudotuberculosis) or palisading (renale) filaments.
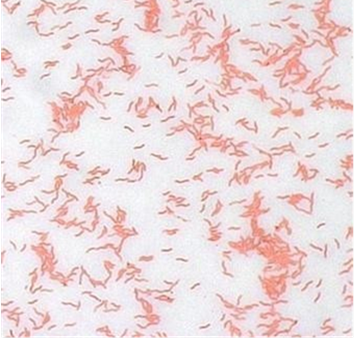
What kind of disease is caused by Corynebacterium renale?
Pyelonephritis, UTIs, cystitis, pizzle rot.
What kind of disease is caused by Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis?
Caseous lymphadenitis (biovar ovis), pigeon fever / lymphangitis (biovar equi, nitrite reducing).
What do Rhodococcus equi colonies look like on BA?
Mucoid pink colonies, non-hemolytic.
What is the result of Rhodococcus equi on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative, urease positive
What does Rhodococcus equi look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, intracellular coccobacilli, variable acid-fast reaction.
What kind of disease is caused by Rhodococcus equi?
Foal pneumonia and enteritis.
What do Listeria monocytogenes colonies look like on BA?
Smooth, round, translucent to grey colonies, beta-hemolytic.
What is the result of Listeria monocytogenes on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative, urease negative.
What is the purpose of the S.I.M. (sulfur, indole, motility) test?
Detects hydrogen sulphide production (black precipitate on stab line), indole production / deamination of tryptophan (pink layer on top of medium), and motility (growth away from stab line).
What is the result of Listeria monocytogenes on the S.I.M. test?
Sulphide negative, indole negative, motile positive (unique umbrella shape).
What does Listeria monocytogenes look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, short bacilli.
What kind of disease is caused by Listeria monocytogenes?
Circling disease, abortion, corneal edema.
What is the purpose of the CAMP test?
Detects CAMP factor, which is conducted by streaking a line of S. aureus perpendicular to a line of the test organism. A positive result is enhancement of the outer alpha-hemolytic zone of S. aureus.
Which organisms are positive on the CAMP test?
Streptococcus agalactiae (arrowhead), Trueperella pyogenes, Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis (reverse / inhibitory), Rhodococcus equi (shovel), Listeria monocytogenes.
What do Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae colonies look like on BA?
Small, smooth colonies, alpha-hemolytic.
What is the result of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase negative, oxidase negative, urease negative.
What is the result of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae on the S.I.M. test?
Sulfide positive, indole negative, motile negative.
What does Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, curved rods.
What kind of disease is caused by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae?
Swine diamond skin disease, polyarthritis, vegetative endocarditis.
What do Dermatophilus congolensis colonies look like on BA?
Small, dry colonies, beta-hemolytic.
What is the result of Dermatophilus congolensis on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative, urease negative.
What does Dermatophilus congolensis look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, small branching filaments arranged in a “railroad track” shape.
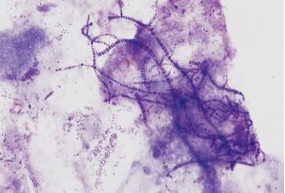
What kind of disease is caused by Dermatophilus congolensis?
Rain scald, lumpy wool.
What do Clostridium tetani colonies look like on BA?
Grey, irregularly spreading colonies, beta-hemolytic.
What is the result of Clostridium tetani on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative, urease negative.
What does Clostridium tetani look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, irregular rods with terminal endospores (matchstick).
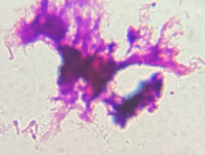
What kind of disease is caused by Clostridium tetani?
Rigid and spastic paralysis.
What do Clostridium perfringens colonies look like on BA?
Large grey, irregular shaped colonies, double-zone hemolytic.
What is the result of Clostridium perfringens on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative, urease negative.
What does Clostridium perfringens look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, bacilli, “boxcar” appearance.

What kind of disease is caused by Clostridium perfringens?
Gas gangrene, enterotoxemia, sudden death, pulpy kidney disease.
What do Clostridium septicum colonies look like on BA?
Swarming, irregular colonies, beta-hemolytic.
What is the result of Clostridium septicum on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase negative, oxidase negative, urease negative.
What does Clostridium septicum look like microscopically?
Gram-positive, large bacilli with spores.
What kind of disease is caused by Clostridium septicum?
Malignant edema, braxy.
What do Escherichia coli colonies look like on BA?
Large grey, moist, smooth colonies with variable hemolytic pattern.
What is the purpose of MacConkey (MAC) agar?
Selective medium for Gram-negatives, differentiating them based on lactose fermentation ability, which causes pink colonies to grow.
Does Escherichia coli grow on MAC?
Yes, is lactose-fermenting.
What is the result of Escherichia coli on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative, urease negative.
What does Escherichia coli look like microscopically?
Gram-negative, medium bacilli.
What kind of disease is caused by Escherichia coli?
Coliform mastitis, enteritis, UTI, neonatal scours, air sacculitis.
What do Klebsiella pneumoniae colonies look like on BA?
Pink, mucoid colonies, non-hemolytic.
Does Klebsiella pneumoniae grow on MAC?
Yes, is lactose-fermenting.
What is the result of Klebsiella pneumoniae on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative, urease positive.
What is the purpose of the citrate test?
Detects if an organism can use citrate as its source of carbon for growth, which turns the medium blue (alkaline). Diagnostic for Klebsiella.
What is the purpose of the T.S.I. (triple sugar iron) test?
Differentiation of Gram-negative, enteric bacteria according to their ability to ferment lactose, product H2S, or gas. Uses an aerobic slant and anaerobic butt. A positive for lactose-fermentation is yellow, H2S is black precipitate, and gas is cracks in the agar. Non lactose-fermenters will turn the slant red, due to running out of glucose and fermenting amino acids which are alkaline.
How can the results of the T.S.I. test be read?
A/A: acid over acid, lactose fermenter. K/A: alkaline over acid, glucose fermenter. K/K: alkaline over alkaline, non-fermenter.
What are the results of the following on T.S.I.? E. coli, Salmonella.
E. coli: A/A, G+, H2S-. Salmonella: K/A, G+, H2S+.
What does Klebsiella pneumoniae look like microscopically?
Gram-negative bacilli.
What kind of disease is caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae?
UTI, environmental mastitis, nosocomial infection.
What do Proteus mirabilis colonies look like on BA?
Large, grey, swarming colonies, non-hemolytic.
Does Proteus mirabilis grow on MAC?
Yes, is non lactose-fermenting.
What is the result of Proteus mirabilis on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative, urease positive.
What does Proteus mirabilis look like microscopically?
Gram-negative bacilli.
What kind of disease is caused by Proteus mirabilis?
UTI, environmental mastitis.
What do Salmonella colonies look like on BA?
Large, moist, grey colonies, non-hemolytic.
Does Salmonella grow on MAC?
Yes, is non lactose-fermenting.
What is the selective medium used for Salmonella?
Rappaport broth and MSRV agar, which select Salmonella due to its resistance to malachite green and osmotic pressure, and tolerance of low nutrition and pH. Appears as a pale halo formation on MSRV and blue colouring of Rappaport.
What is the result of Salmonella on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase negative, urease negative.
What does Salmonella look like microscopically?
Gram-negative bacilli.
What kind of disease is caused by Salmonella?
Enteric disease.
What do Pasteurella multocida colonies look like on BA?
Small, round grey colonies, non-hemolytic.
Does Pasteurella multocida grow on MAC?
No.
What is the result of Pasteurella multocida on the following tests: catalase, oxidase, urease?
Catalase positive, oxidase positive, urease negative.