Honors Biology -Biochemistry Test Vocabulary & Terms
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:37 PM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
Condensation
The opposite of Hydrolysis, forms a new chemical bond rather than Hydrolysis breaking it down. Utilizes water!
2
New cards
Enzyme
Speed up reactions that would take very long on its own. Are proteins that occur in ONLY LIVING ORGANISMS.
3
New cards
Functional group(s)
Any types of molecules made up of carbon and another element other than Hydrogen that give out properties to organic molecules.
4
New cards
Hydrocarbon
Molecules made up of hydrogen and carbon.
5
New cards
Hydrolysis
Chemical breakdown of a polymer due to reaction with water, forms monomers.
6
New cards
Metabolism
A living organism that utilizes reactions to make energy.
7
New cards
Monomer
Molecule that can be bonded with other molecules to form a polymer. This is the base.
8
New cards
Organic
Anything containing living matter.
9
New cards
Polymer
Molecules composed of two or more monomers.
10
New cards
Reaction
Any sort of molecular change that occurs in living organisms.
11
New cards
Carbohydrate
Sugar polymers mainly consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. They contain short-term fuel for energy.
12
New cards
Cellulose
A polysaccharide (polymer) of carbohydrates.
13
New cards
Chitin
A polysaccharide with nitrogen found in fungal walls and bugs.
14
New cards
Disaccharide
Two or more monosaccharides bonded together.
15
New cards
Glycogen
The stored form of glucose/sugars.
16
New cards
Monosaccharide
A single sugar such as glucose or fructose, the simplest type of sugar.
17
New cards
Polysaccharide
A complex sugar made up of many chains of monosaccharides.
18
New cards
Starch
A type of carbohydrate found in only plants.
19
New cards
Fat
A lipid where energy is stored for long-term in the body.
20
New cards
Fatty Acid
The building blocks of lipids, are monomers.
21
New cards
Lipid
Fatty, waxy, or oily organic substances that store energy for long periods of time.
22
New cards
Lipid Bilayer
A phospholipid that creates good cell membranes.
23
New cards
Phospholipid
A lipid containing a phosphate group in its molecule.
24
New cards
Saturated fatty acid
Lipids that have a carboxyl head and a hydrocarbon chain.
25
New cards
Steroid
An example of a molecule that is made from cholesterol.
26
New cards
Triglyceride
A fat with three fatty acid chains and consists of a glycerol backbone. (Might need to work on this, don't rely on this definition)
27
New cards
Unsaturated fat acid
This is at least one double bond in the fatty acid chain.
28
New cards
Denaturization
Process of modifying the structure of a protein. (Primary, secondary, etc)
29
New cards
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
A nucleotide made up of an adenine base, ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups.
30
New cards
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
Molecule that contains the biological instructions that make each species unique.
31
New cards
Nucleic acid
A polymer of nucleotides
32
New cards
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
A single chain of nucleotides, which are composed of deoxyribose sugars.
33
New cards
Nucleotide
A nucleotide is a monomer of nucleic acids. Their job is to carry energy, help enzymes and send messages with chemicals.
34
New cards
Energy
The capacity to do work.
35
New cards
Entropy
A measure of how much the energy of a particular system has become dispersed.
36
New cards
Activation energy
The minimum amount of energy required to get a chemical reaction started.
37
New cards
Endergonic (endothermic)
Means "energy in", takes in energy. Usually cold to the touch.
38
New cards
Exergonic (exothermic)
Means "energy out", releases energy. Usually hot to the touch.
39
New cards
Product
Molecules that are produced by the reaction (after the activation energy/enzyme is used).
40
New cards
Reactant
Molecules that enter a reaction and become changed by it. They are the start in a chemical reaction.
41
New cards
Active Site
Pockets where catalysis occurs.
42
New cards
Catalase
An enzyme that makes a reaction run much faster than it would on its own.
43
New cards
Lock and Key Model
Where the key is a Substrate and the lock is an Enzyme.
44
New cards
Substrate
Molecule that an enzyme acts upon and converts to a product.
45
New cards
How can an Enzyme work?
The enzyme needs to have very specific conditions in order for it to properly work. Molecules have to fit perfectly and need to be complementary in shape, size, polarity, and charge.
46
New cards
What are the three main characteristics of enzymes?
Reusable, speeds up reactions, lowers activation energy.
47
New cards
What kind of Reaction is this?
Endothermic
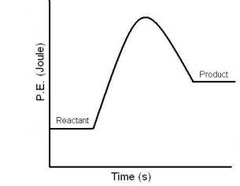
48
New cards
What kind of Reaction is this?
Exothermic
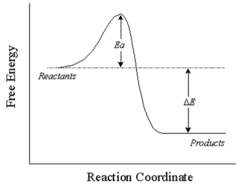
49
New cards
What elements make up Lipids?
Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen.
50
New cards
What elements make up Carbohydrates?
Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen.
51
New cards
What elements make up Proteins?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, and Oxygen.
52
New cards
What elements make up Nucleic Acids?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous.
53
New cards
What is the Key in the Lock and Key Model?
Substrate
54
New cards
What is the Lock in the Lock and Key Model?
Enzyme