BIO LEC EXAM 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/162
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:32 AM on 2/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
1
New cards
Anatomy
the study of body structures
2
New cards
Physiology
the study of function of anatomical structures
3
New cards
Gross anatomy/macroscopic anatomy
examines large, visible structures
4
New cards
Surface anatomy
exterior features
5
New cards
Regional anatomy
body areas
6
New cards
Systemic anatomy
organ systems
7
New cards
Clinical anatomy
medical specialties
8
New cards
developmental anatomy
from conception of death
9
New cards
microscopic anatomy
examines cells and molecules
10
New cards
cytology
study of cells and their structures
11
New cards
cyt
cells
12
New cards
histology
study of tissues and their structures
13
New cards
cell physiology
process within and between the cells
14
New cards
organ physiology
function of specific organ
15
New cards
systemic physiology
function of an organ system
16
New cards
pathological physiology
effects of disease
17
New cards
embryology
is the discipline concerned with developmental changes occurring from conception to birth
18
New cards
coronal plane
also called a frontal plane, is a vertical plane that divides the body or organ into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts
19
New cards
transverse plane
also called a horizontal plane or *cross-sectional plane,*divides the body or organ into superior (top) and inferior (bottom) parts
20
New cards
midsagittal plane
median plane, is a vertical plane and divides the body or organ into equal left and right halves
21
New cards
anterior
in front of ; toward the the front surface
22
New cards
posterior
In back of; towards the back surface
23
New cards
dorsal
towards the back side of human body
24
New cards
ventral
toward the belly side of the human body
25
New cards
superior
close to the head
26
New cards
inferior
closer to the feet
27
New cards
caudal
toward the rear or tail end
28
New cards
rostral
toward the nose or mouth
29
New cards
medial
towards the mid-line of the body
30
New cards
lateral
away from the mid-line of the body
31
New cards
Ipsilateral
on the same side
32
New cards
contralateral
on the opposite side
33
New cards
deep
closer to the inside, internal to another structure
34
New cards
superficial
closer to the outside, external to another structure
35
New cards
proximal
closer to the point of attachment to trunk
36
New cards
distal
farther away from point of attachment to trunk
37
New cards
Cephalic
head region
38
New cards
Pectoral
chest
39
New cards
Abdominal
abdomen
40
New cards
Femoral
thigh
41
New cards
Patellar
front of the knee
42
New cards
Crural
leg
43
New cards
Tarsal
ankle
44
New cards
first quadrant
right upper quadrant
45
New cards
second quadrant
left upper quadrant
46
New cards
third quadrant
right lower quadrant
47
New cards
fourth quadrant
left lower quadrant
48
New cards
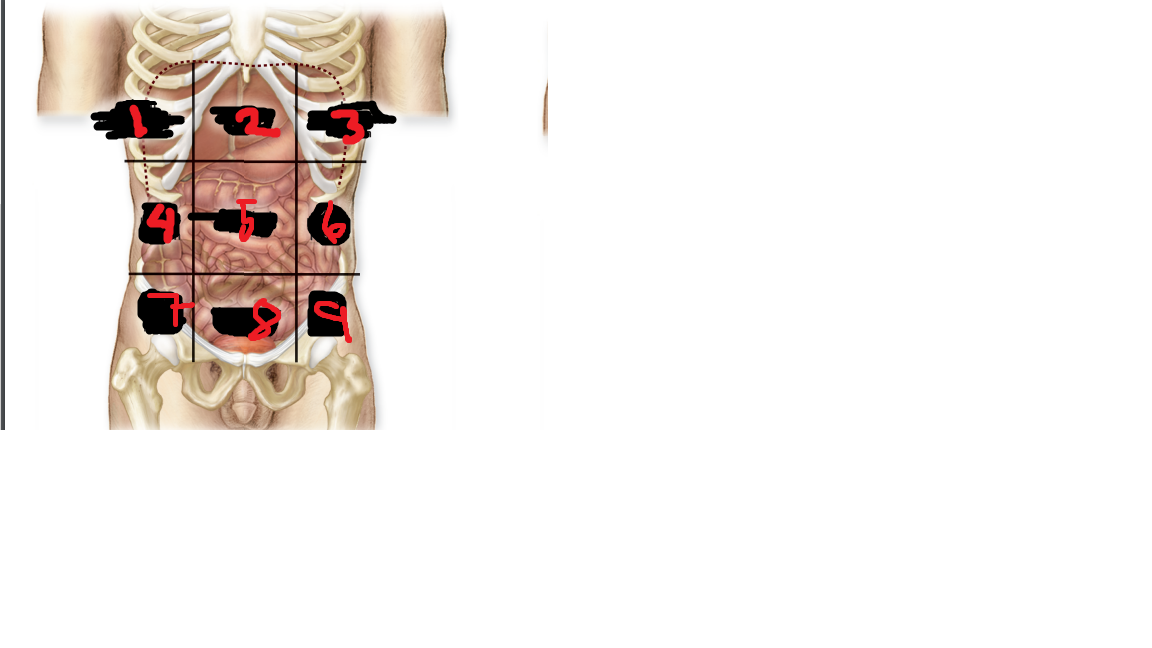
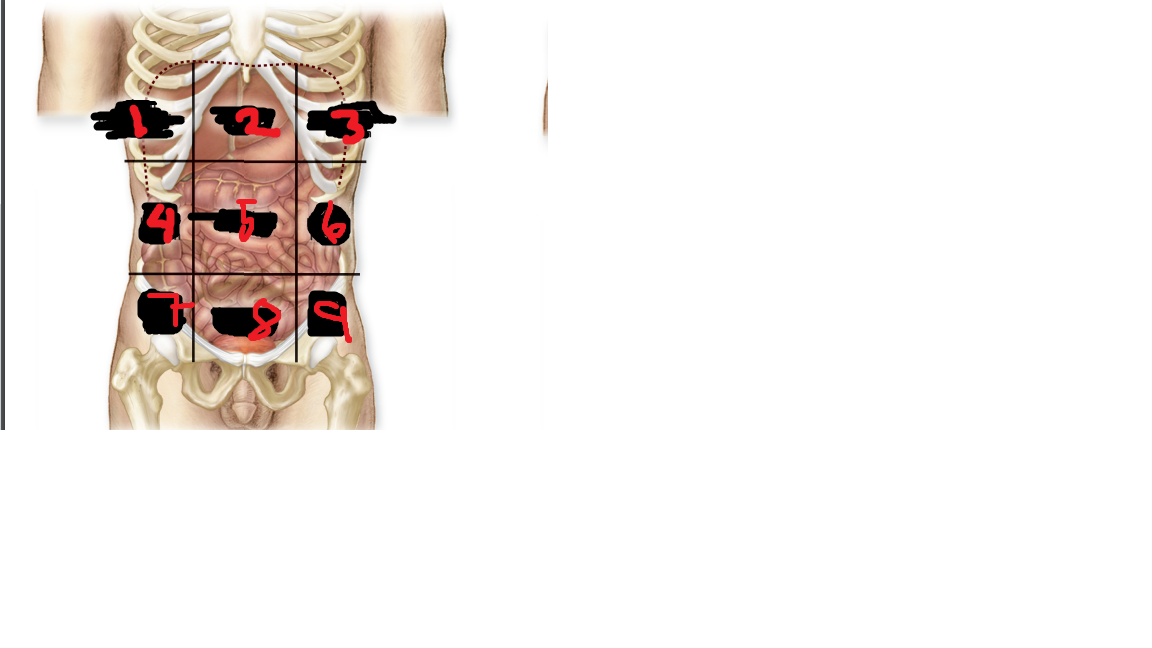
right hypochondriac region
what is 1
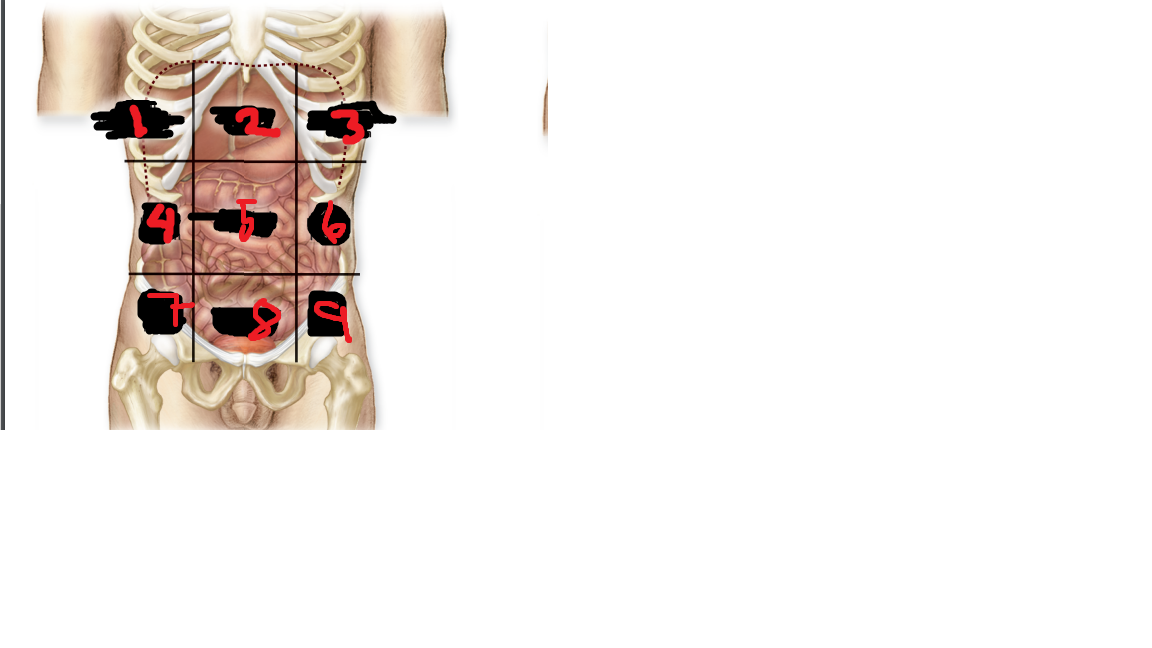
49
New cards
epigastric region
what is 2
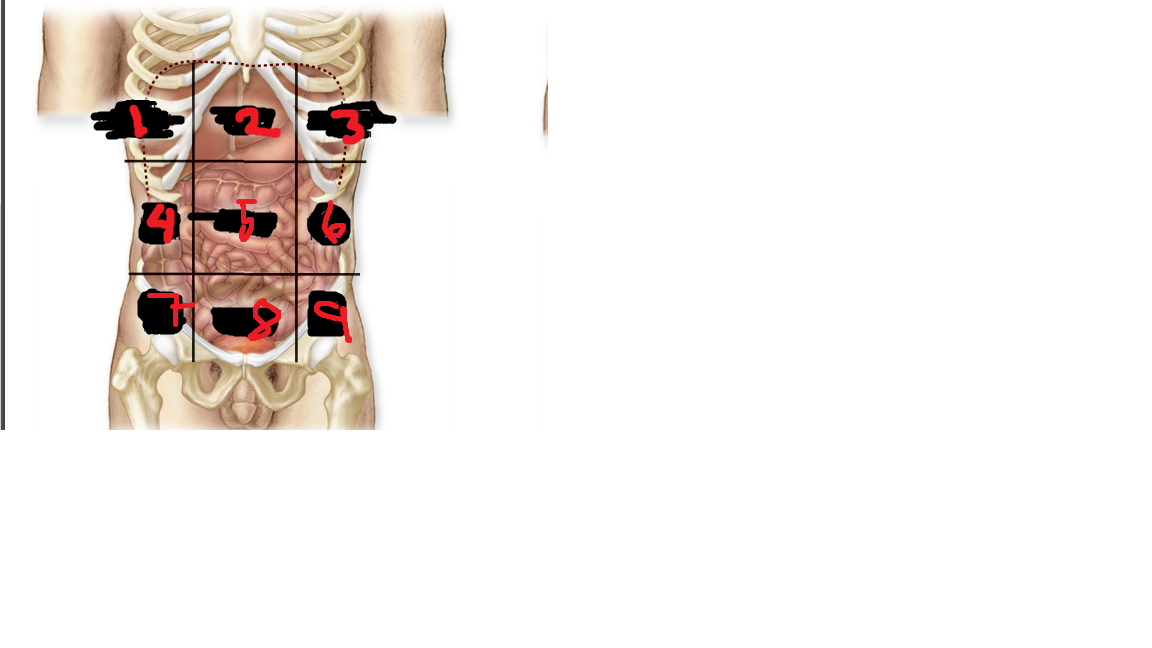
50
New cards
left hypochondriac region
what is 3
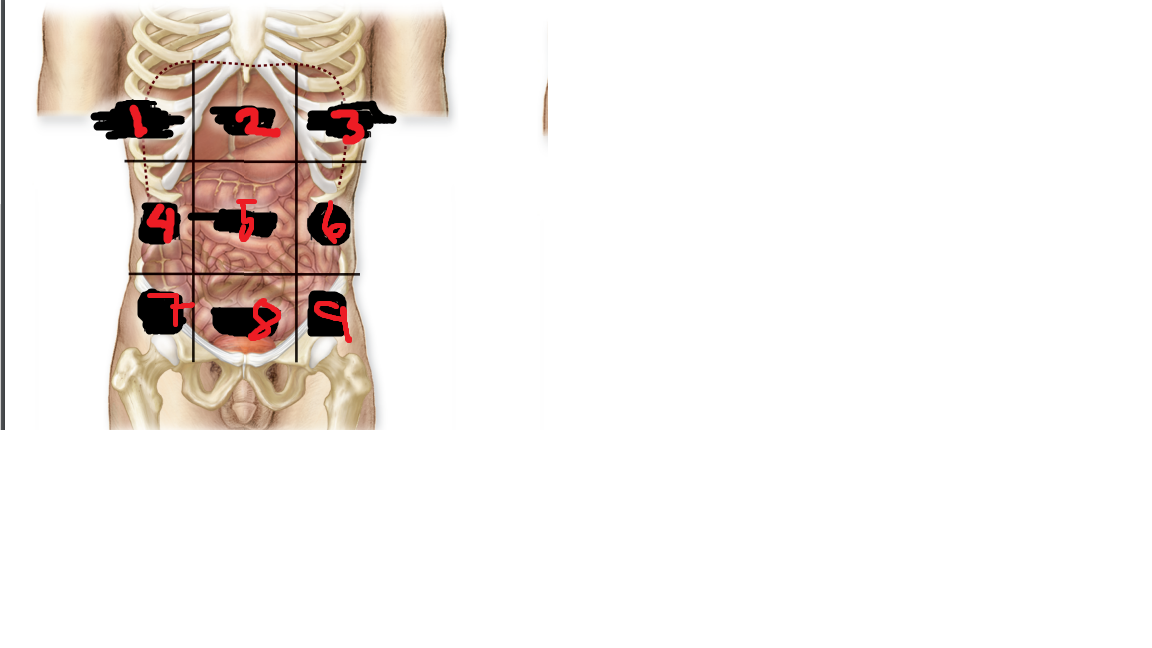
51
New cards
right lumbar region
what is 4
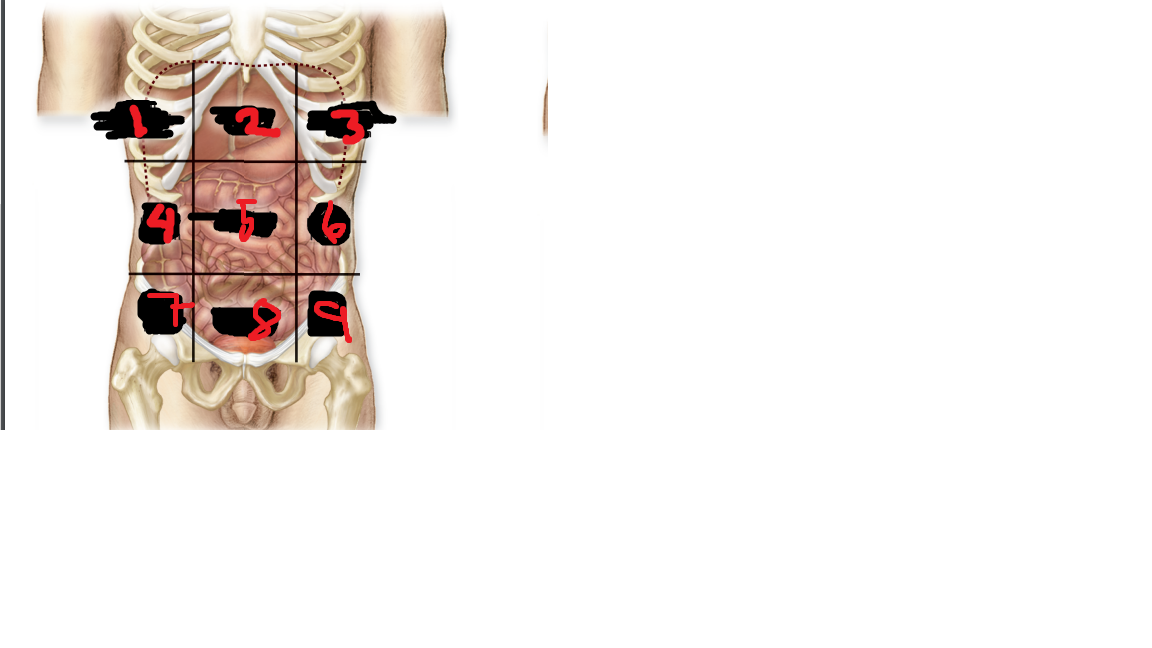
52
New cards
umbilical region
what is 5
53
New cards
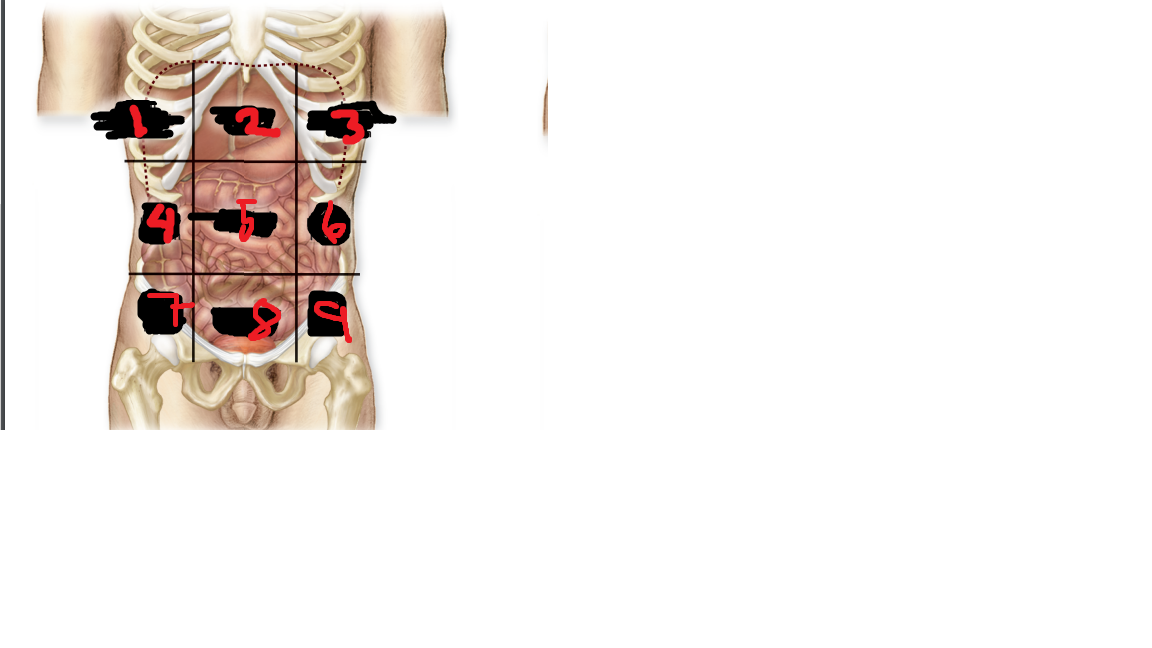
left lumbar region
what is 6
54
New cards
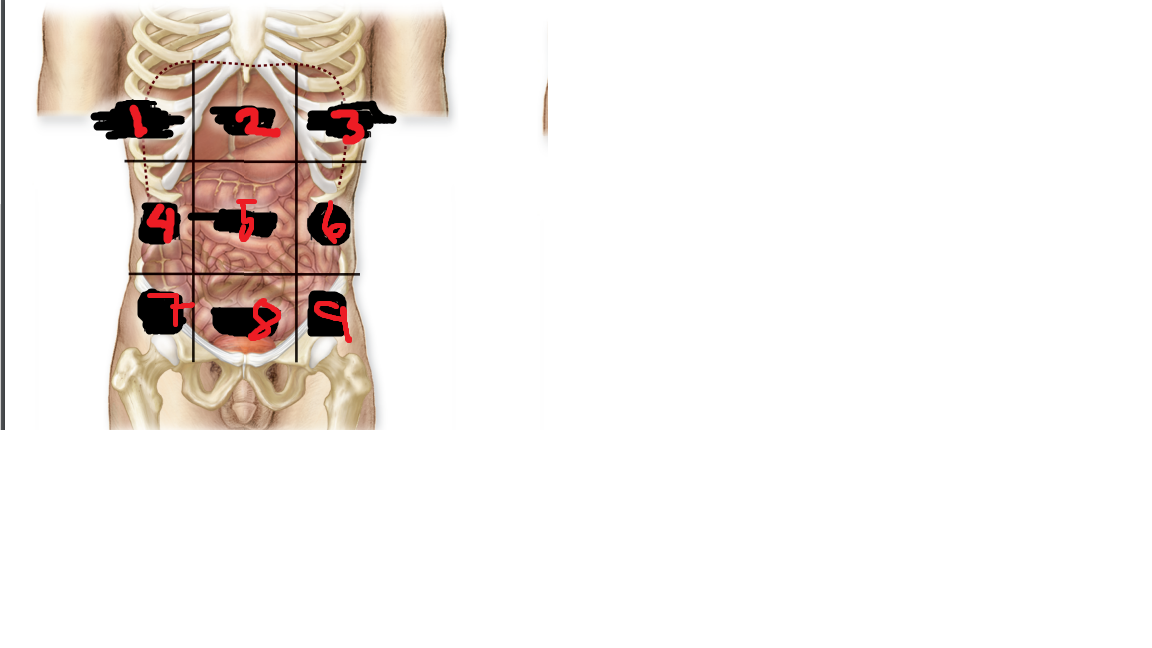
right iliac region
what is 7
55
New cards
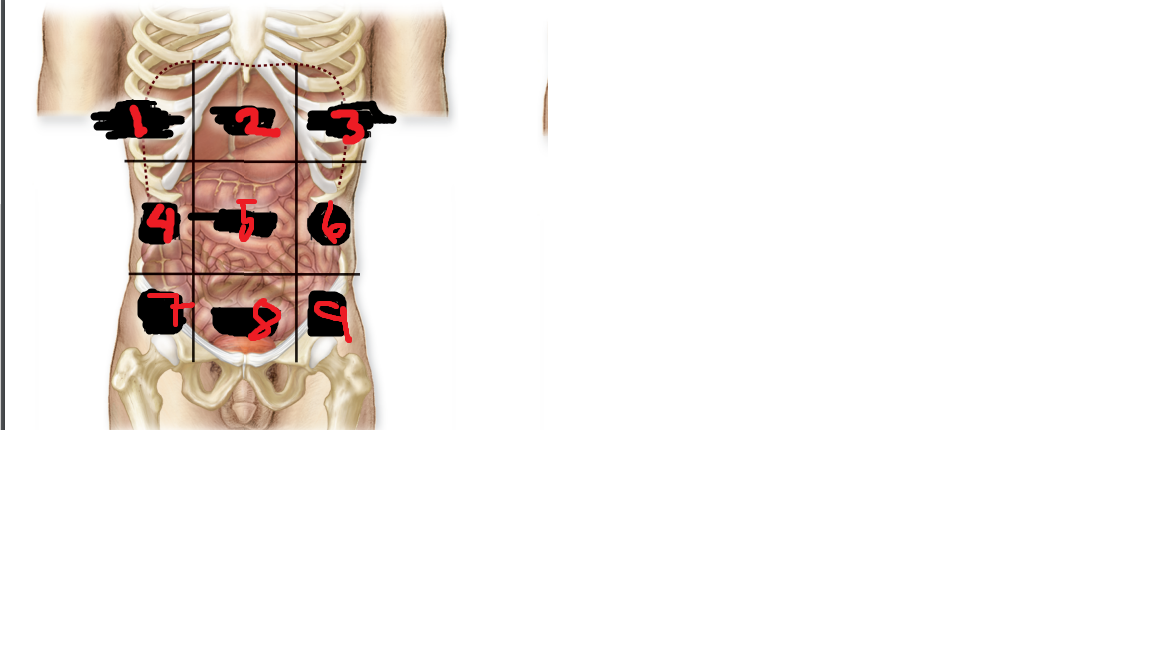
hypogastric region
what is 8
56
New cards
left iliac region
what is 9
57
New cards
forms the external body covering, protect deeper tissues, synthesize vitamin D
Functions of Integumentary system
58
New cards
Functions of Skeletal system
protects and supports the body organs
59
New cards
Functions of Muscular system
allows locomotion, facial expression, maintain posture, produces heat
60
New cards
Functions of Nervous system
controls muscles and glands, responding to internal and external changes
61
New cards
Functions of Endocrine system
composed of glands that regulate processes such as, growth, reproduction, metabolism, etc.
62
New cards
Functions of Cardiovascular system
transport blood, oxygen, nutrient and waste throughout the body
63
New cards
Functions of Lymphatic System/Immunity
picks up interstitial fluid and returns back to the blood, provide protection against bacteria and viruses
64
New cards
Functions of Respiratory system
keeps the blood constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
65
New cards
Functions of Digestive system
breaks down food, absorbs nutrients and eliminates feces
66
New cards
Functions of Urinary system
eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body.
67
New cards
Functions of Reproductive system
its overall function is to produce offspring.
68
New cards
parts of Integumentary system
skin and connective tissues
69
New cards
parts of Skeletal system
skeleton
70
New cards
parts of Muscular system
muscles
71
New cards
parts of Nervous system
brain, spinal cord, neurons
72
New cards
parts of Endocrine system
hypothalamus, pituitary gland
73
New cards
parts of Cardiovascular system
heart and blood vessels
74
New cards
parts of Lymphatic System/Immunity
lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes
75
New cards
parts of Respiratory system
trachea, bronchi, lungs
76
New cards
parts of Digestive system
mouth, esophagus, stomach
77
New cards
parts of Urinary system
kidneys, ureters
78
New cards
parts of Reproductive system
testes, vagina
79
New cards
what is the the order of organization
subatomic particles to atom to molecule to macromolecule to organelle to cell to tissue to organ to organ-system to organism.
80
New cards
biochemistry
the study of cell chemistry
81
New cards
Chemistry
the study of property, structure, and composition of matter
82
New cards
Serous membranes
line body and cover organs
83
New cards
parts of Serous membrane
pleural, pericardial, peritonea
84
New cards
Homeostasis
Body’s maintenance of a stable internal environment
85
New cards
homeostatic mechanism
monitor aspects of the internal environment and corrects any changes
86
New cards
receptor
provide information about stimuli
87
New cards
Control center
tells what a particular value should be (includes a set point)
88
New cards
effectors
elicit responses that change conditions in the internal environment
89
New cards
Negative feedback
The response of the effector negates the stimulus and the Body is brought back into homeostasis.
90
New cards
Positive feedback
The response of the effector increases change of the stimulus, body is moved away from homeostasis and is also use to speed up the process.
91
New cards
Negative feedback example
regulating blood sugar and temperature
92
New cards
positive feedback example
blood clot
93
New cards
Requirements of Organism
Water, food, oxygen, heart and pressure
94
New cards
Peritoneal cavity
chamber within abdominopelvic
cavity
cavity
95
New cards
Parietal peritoneum
lines the internal body wall
96
New cards
Visceral peritoneum
covers the organs
97
New cards
normal body temperature in fahrenheit
98\.6 degrees Fahrenheit
98
New cards
normal body temperature in celsius
37 degrees Celsius
99
New cards
physiological pH
Neutral
100
New cards
atomic number
number of protons in the nucleus of one atom