CH: 9 Extended Review
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Regions of the Vertebral Column
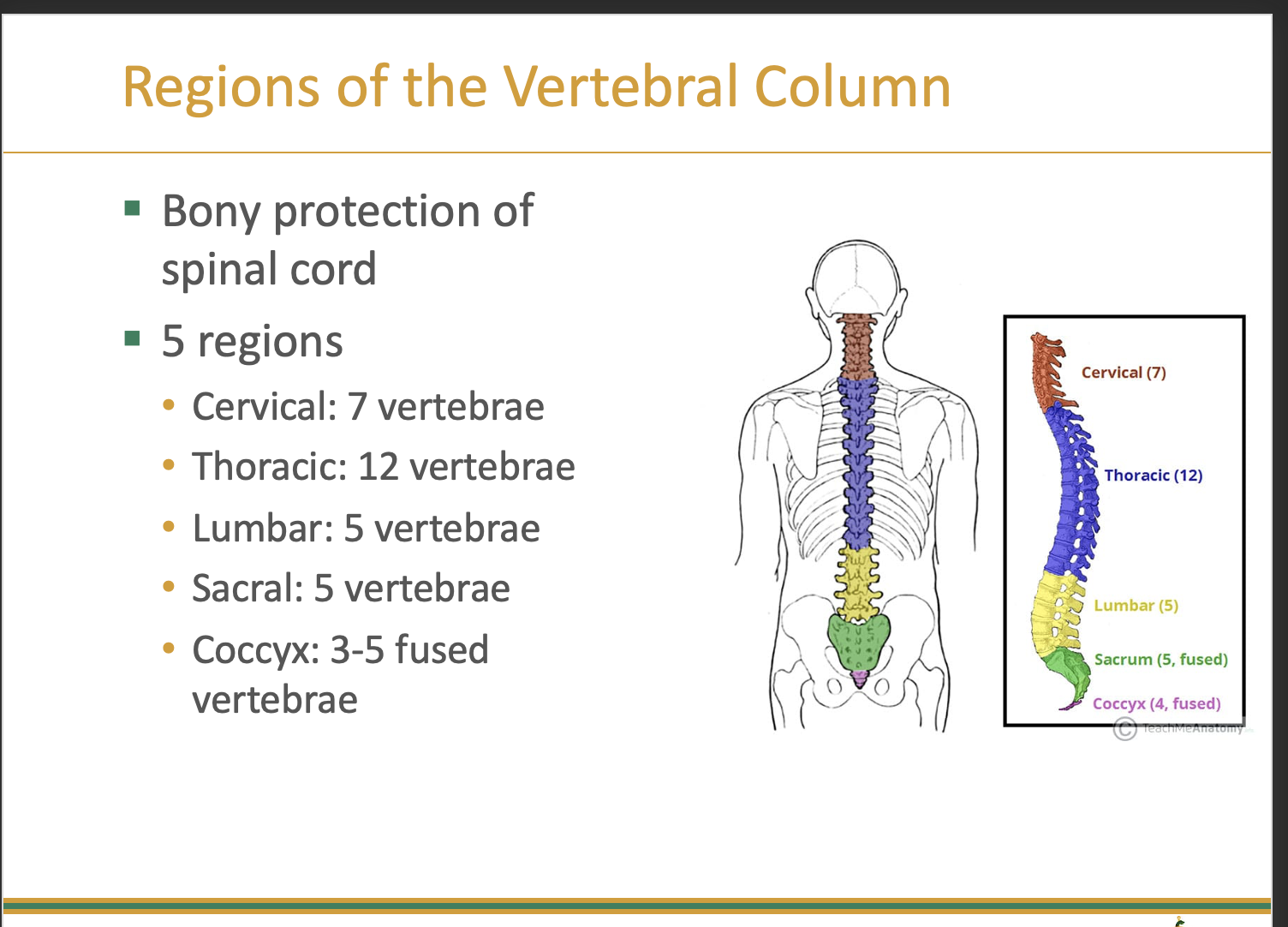
Vertebral Curves: Cervical and lumbar regions
•Convex anteriorly
•Lordotic
Lordosis
Excessive inward curvature of the spine, particularly in the lumbar region.
Vertebral Curves: Thoracic and sacral regions
•Concave anteriorly
•Kyphotic
Kyphosis
excessive posterior curvature of the spine, typically in the thoracic region.
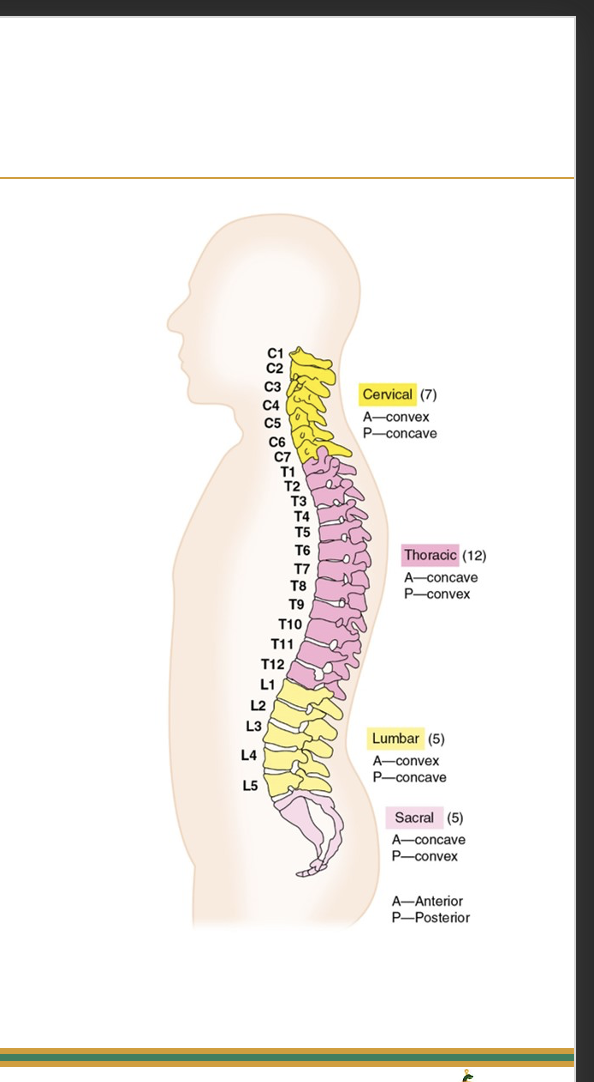
Motions of the Vertebral Column
Vertebral column is triaxial and includes motions of the neck and trunk
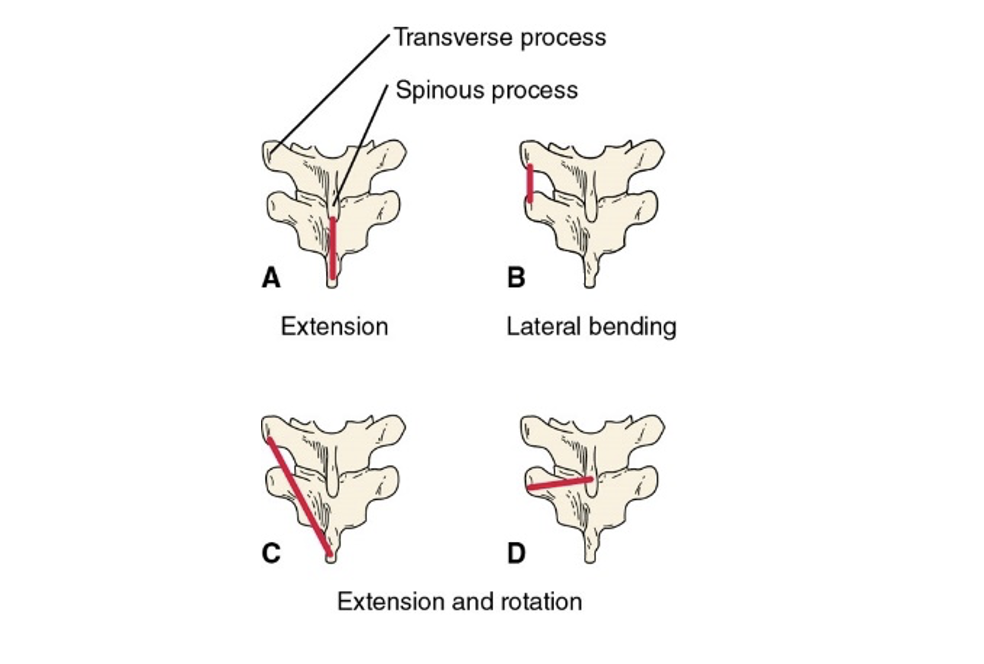
Vertebral Column Motions: Flexion and Extension
occur within the sagittal plane about a frontal axis
Vertebral Column Motions: Lateral bending
occurs within the frontal plane about a sagittal axis
Vertebral Column Motions: Rotation
occurs within the transverse plane about a vertical axis.
Articulating Facets Orientation: Cervical spine
is within the frontal plane with lateral portion anterior to medial portion of facet. Motion in all three planes and axes
Articulating Facets Orientation: Thoracic spine
•Orientation of facets is within the frontal plane
•Motion limited by ribs
•Lateral bending
Articulating Facets Orientation: Lumbar spine
is within the sagittal plane with facets facing medial to lateral. Motion primarily allows flexion and extension.
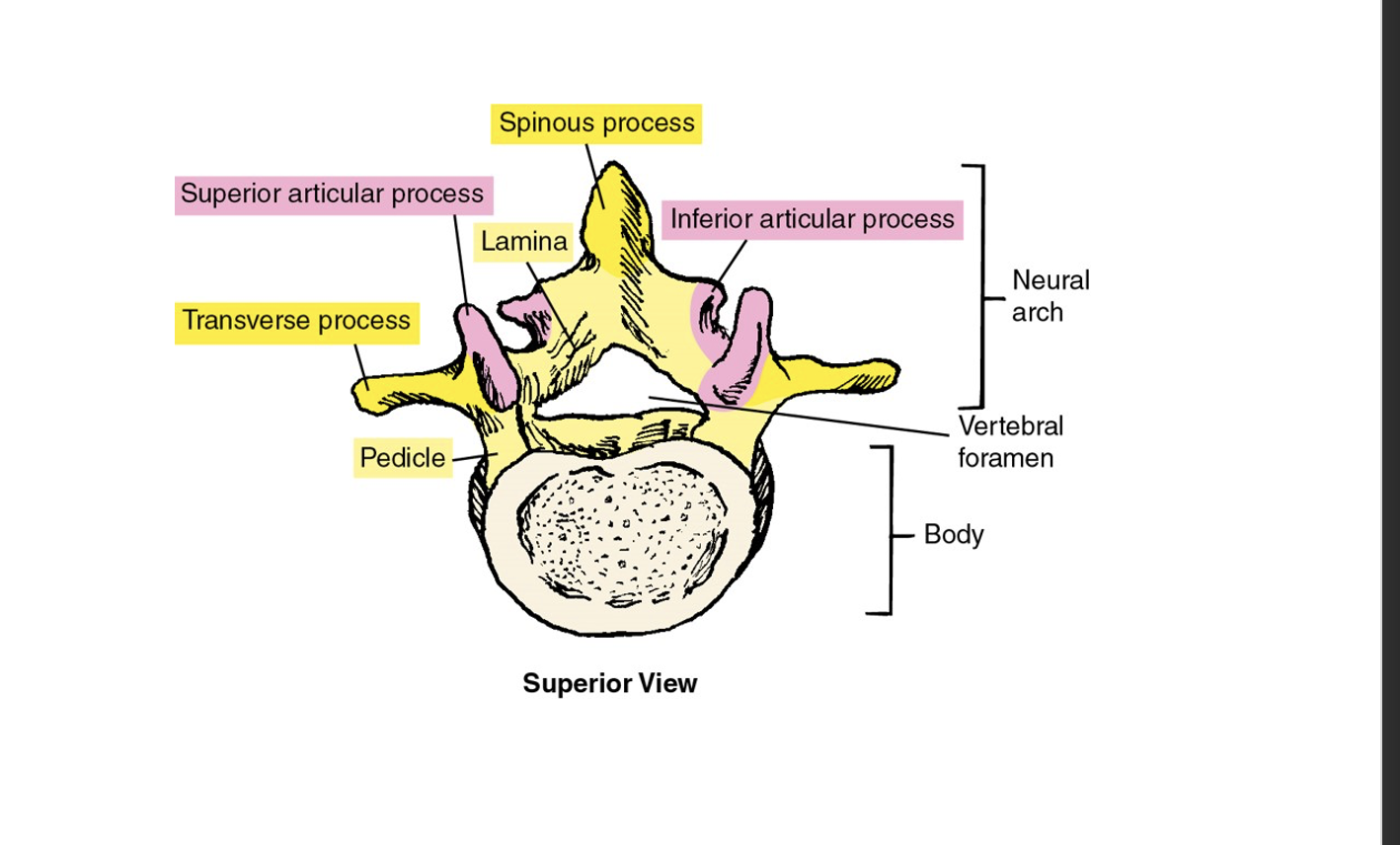
Bony landmarks of Vertebrae
include the spinous process, transverse process, and vertebral body that provide attachment points for muscles and ligaments.
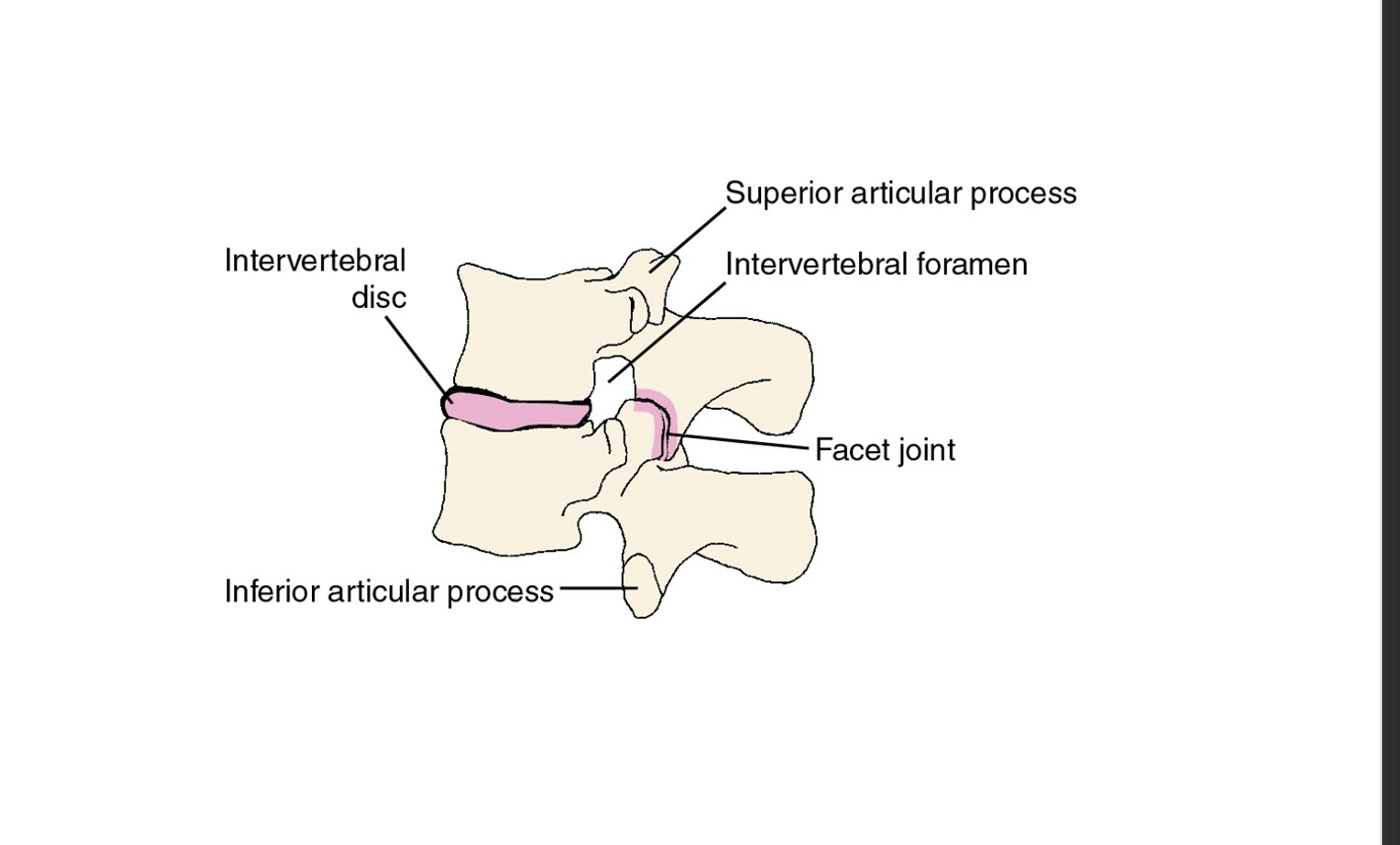
Intervertebral Foramen and Facet Joint
are openings between adjacent vertebrae allowing for the passage of spinal nerves and blood vessels, while facet joints provide articulation between vertebrae for movement and stability.
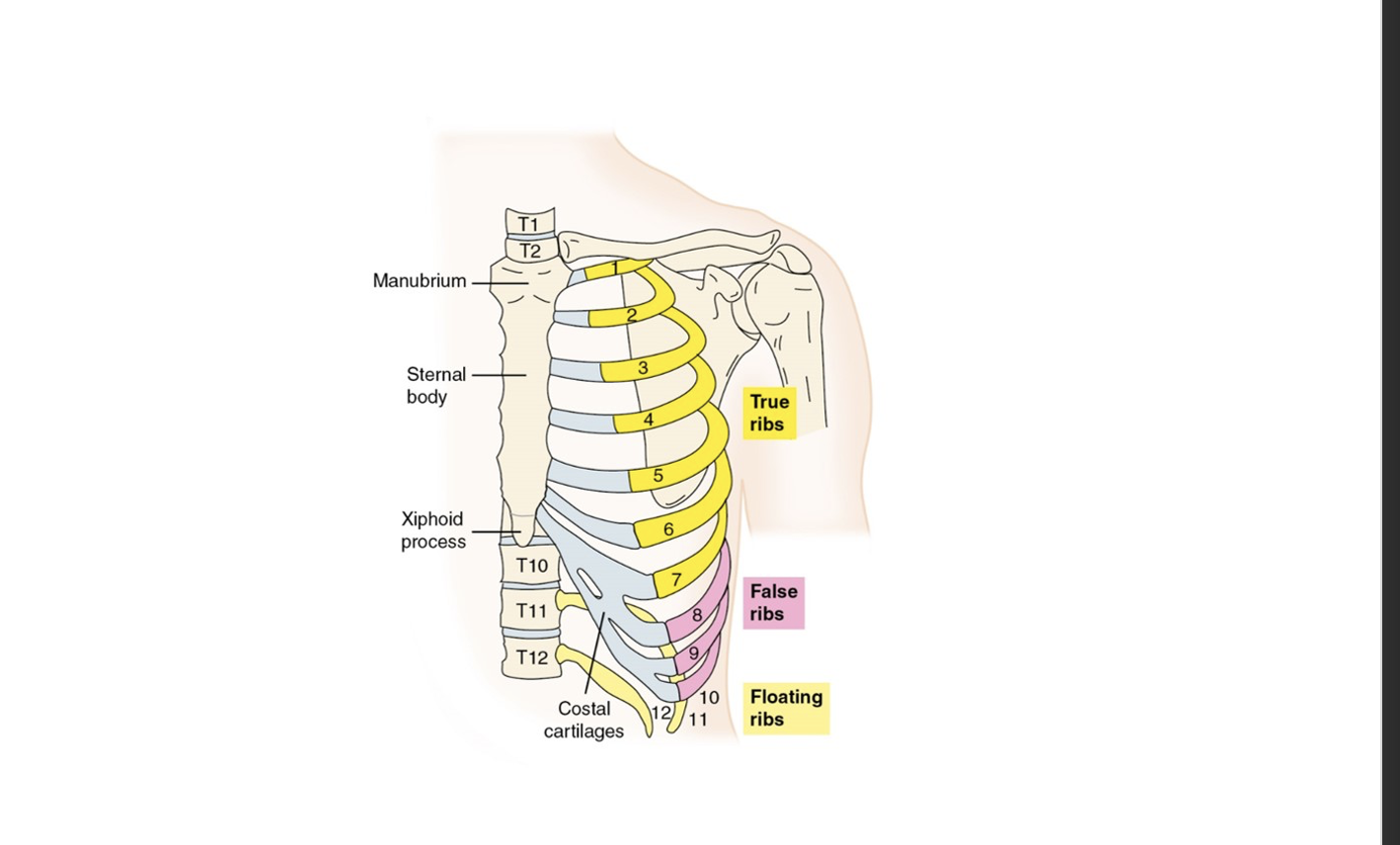
Thoracic Cage
is a structure formed by the ribs, sternum, and thoracic vertebrae that protects the thoracic organs and supports the upper body. It also plays a role in respiration.
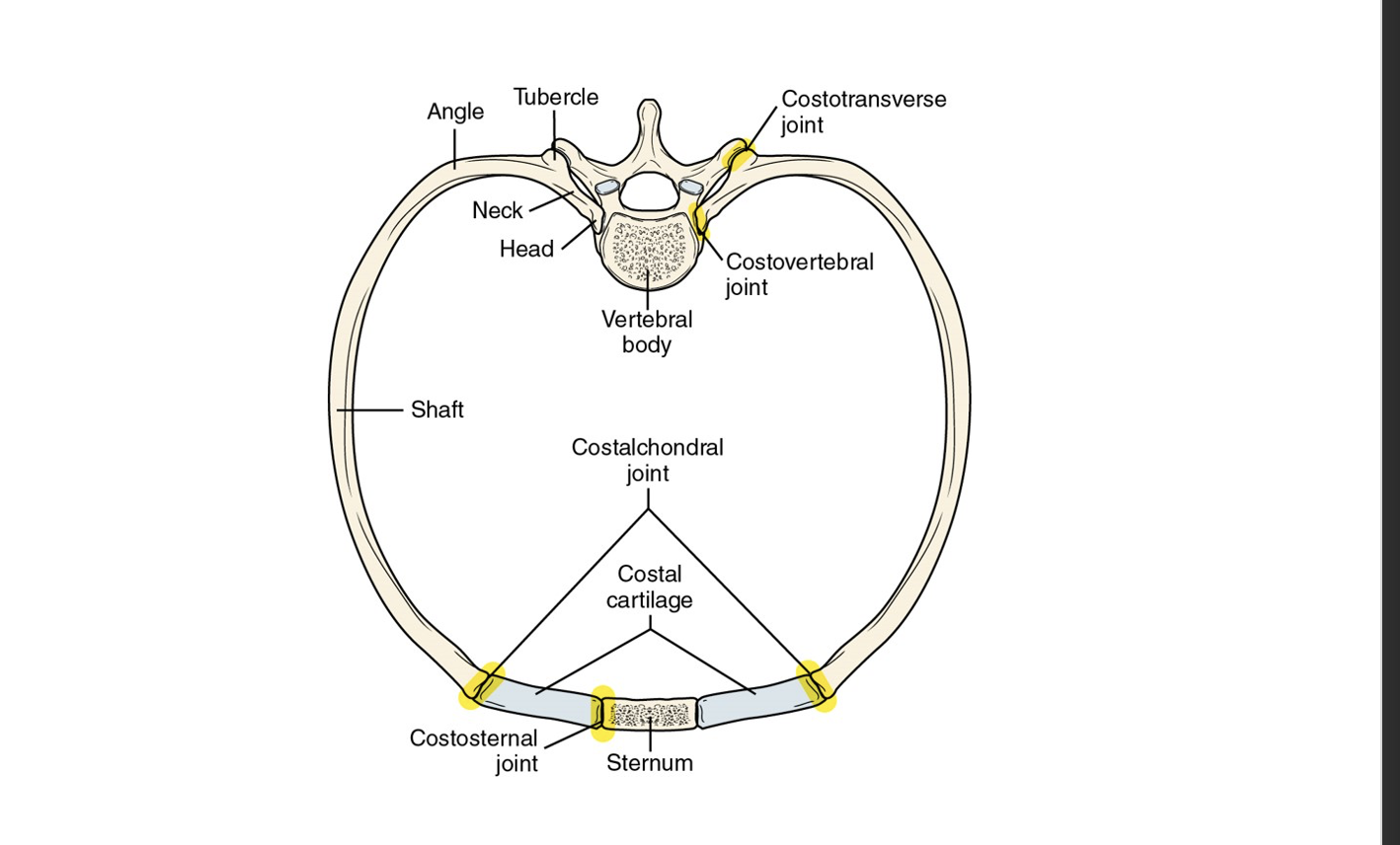
Costovertebral and Costotransverse Joints
are joints formed between the ribs and the vertebrae, allowing for movement during breathing and providing stability to the thoracic cage.
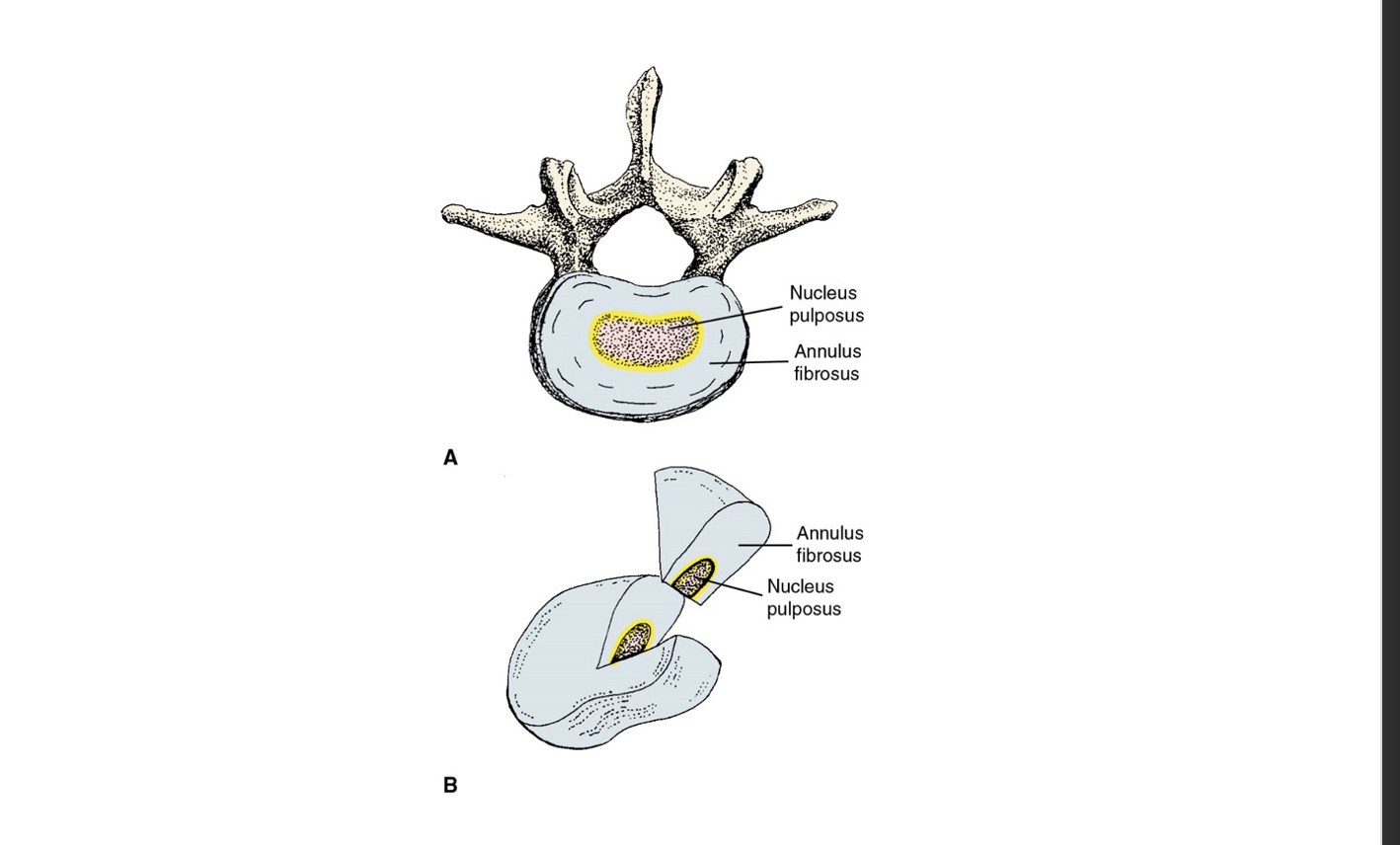
Parts of a Vertebral Disk
consist of the annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus, which provide cushioning and absorb shock between vertebrae.
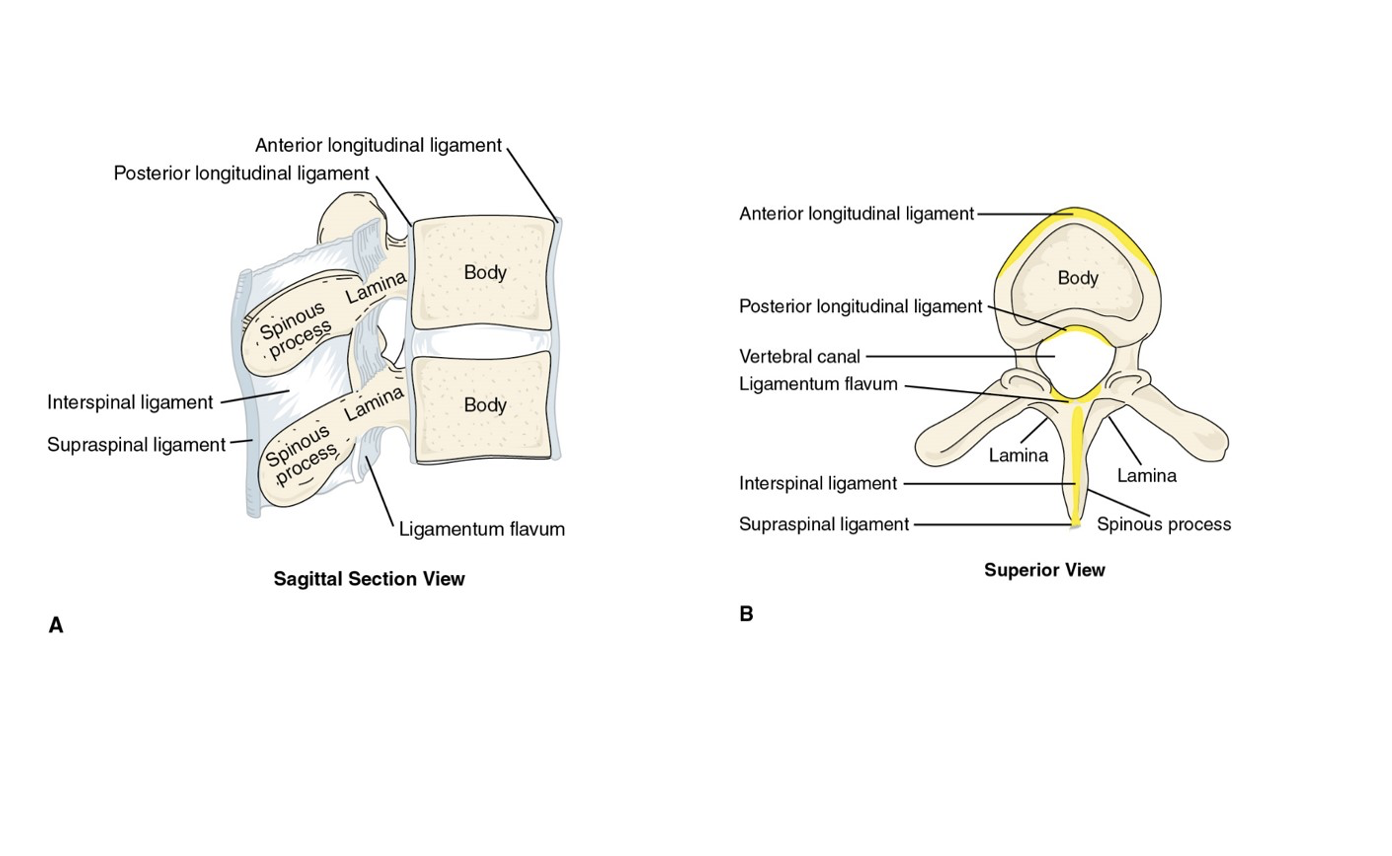
Vertebral Ligaments
are strong connective tissues that bind the vertebrae together, providing stability and support to the spine while allowing for a limited range of motion.
Vertebral muscles: Anterior: Trunk
Rectus abdominis
External oblique
Internal oblique
Transverse abdominis
Vertebral muscles: Lateral: Trunk
Quadratus lumborum
Vertebral muscles: Posterior: Trunk
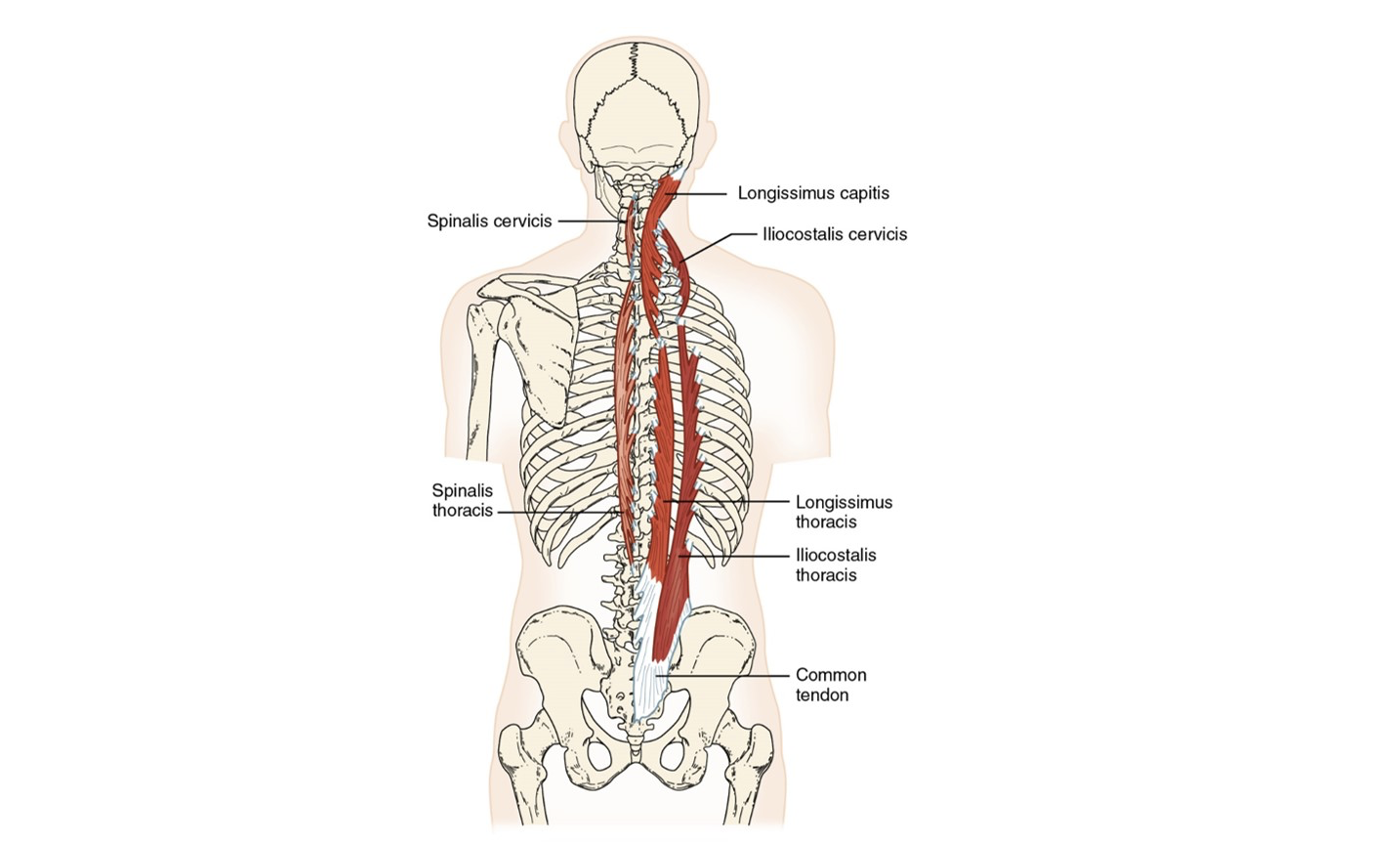
Erector spinae group (3)
Transversospinalis group (3)
Interspinales
Intertransversarii
Posterior Trunk Muscles: Extension
Spinalis (ES)
Interspinales
Posterior Trunk Muscles: Extension and lateral flexion
Longissimus (ES)
Intertransversarii
Iliocostalis (ES)
Posterior Trunk Muscles: Extension and rotation to same side
Splenius cervicis
Posterior Trunk Muscles: Extension and rotation to opposite side
Semispinalis (T)
Multifidus (T)
Rotatores (T)
Erector spinae group (3)
Spinalis, Longissimus, Iliocostalis
Iliocostalis
lateral, will have attachment to rib
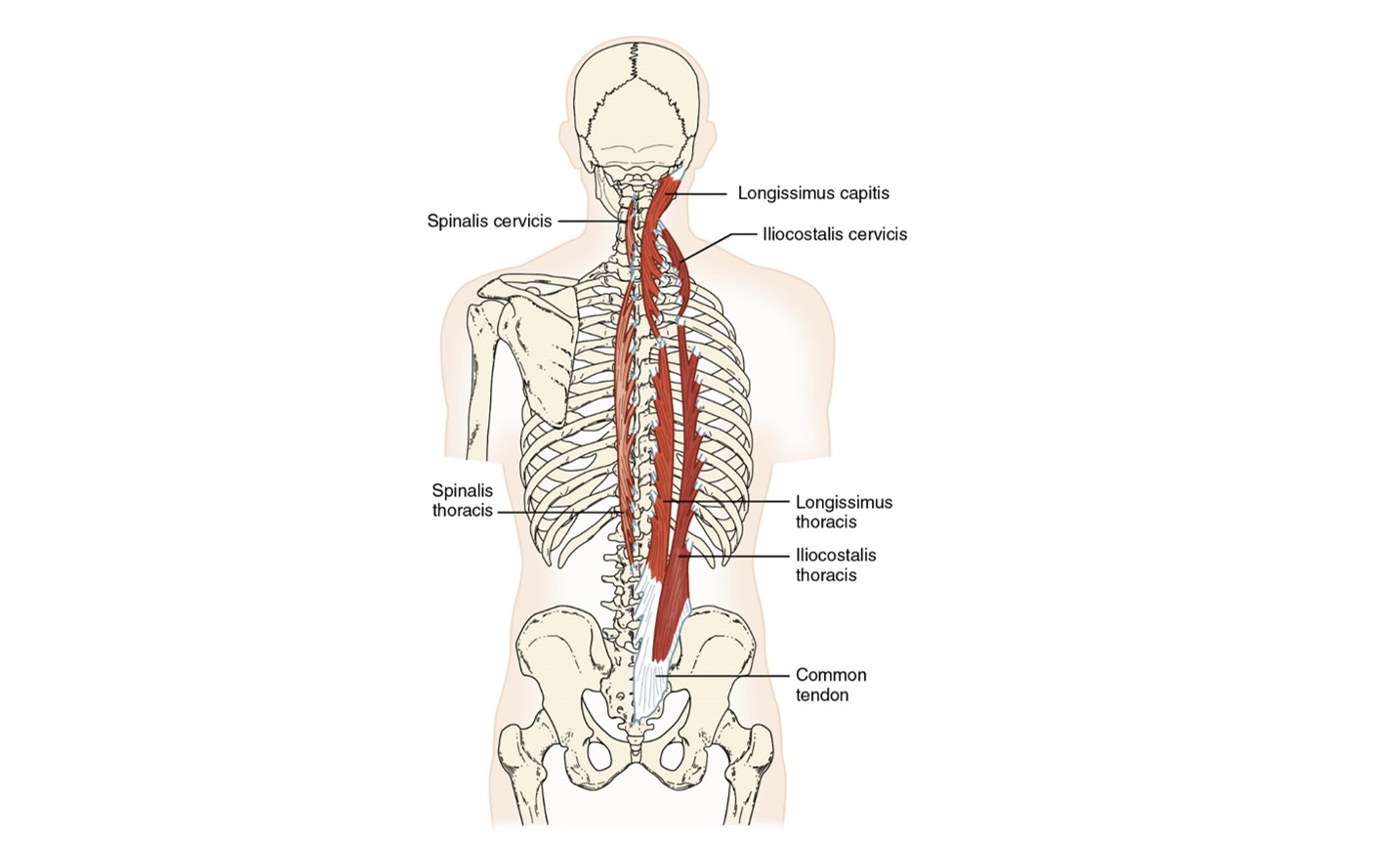
Longissimus
the intermediate muscle of the erector spinae group
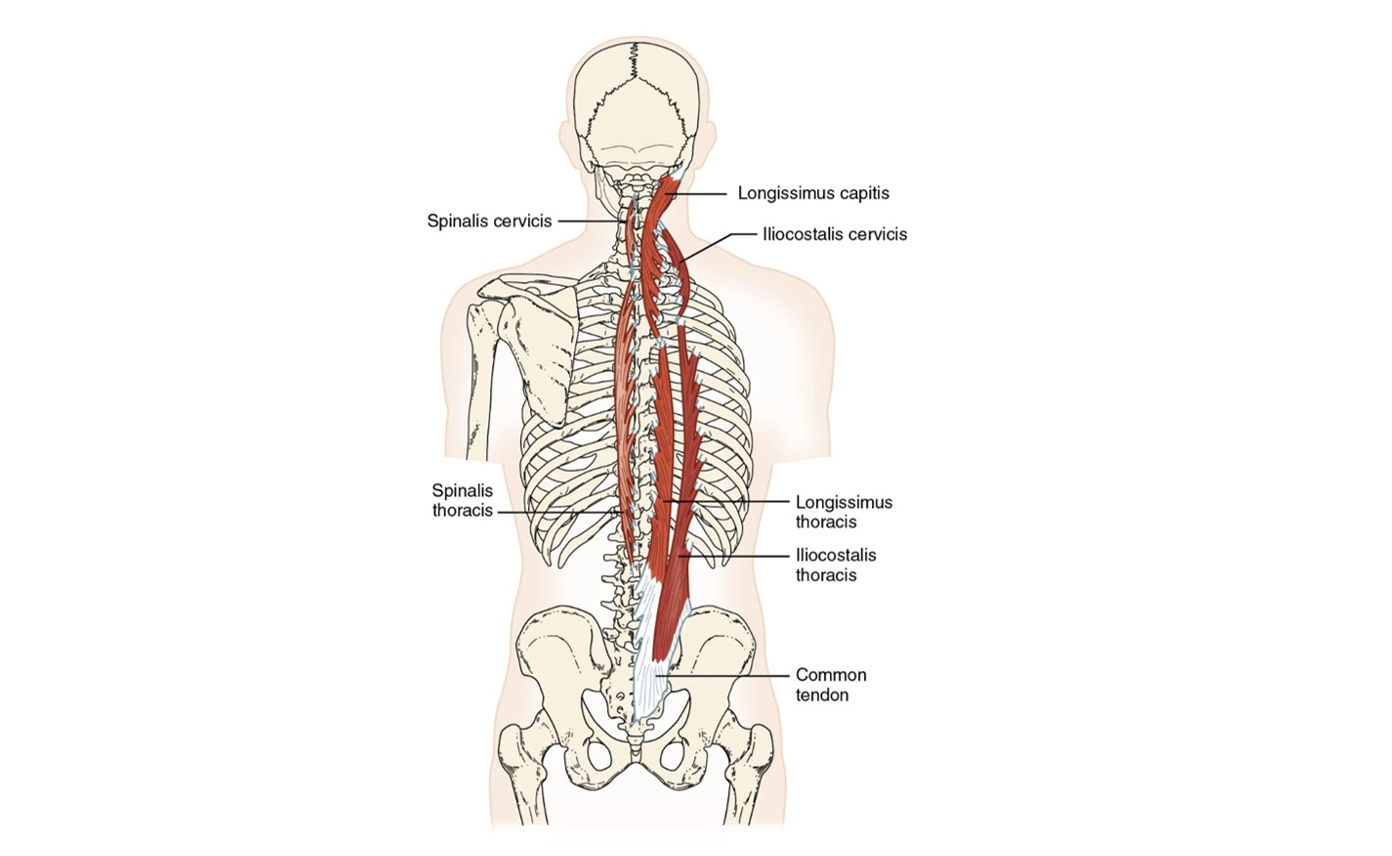
Spinalis
medial, closest to the spine
Transversospinalis Muscle Group
a deeper set of muscles that lie beneath the erector spinae group, responsible for stabilizing and rotating the spine. Include multifidus, rotatores, and semispinalis.
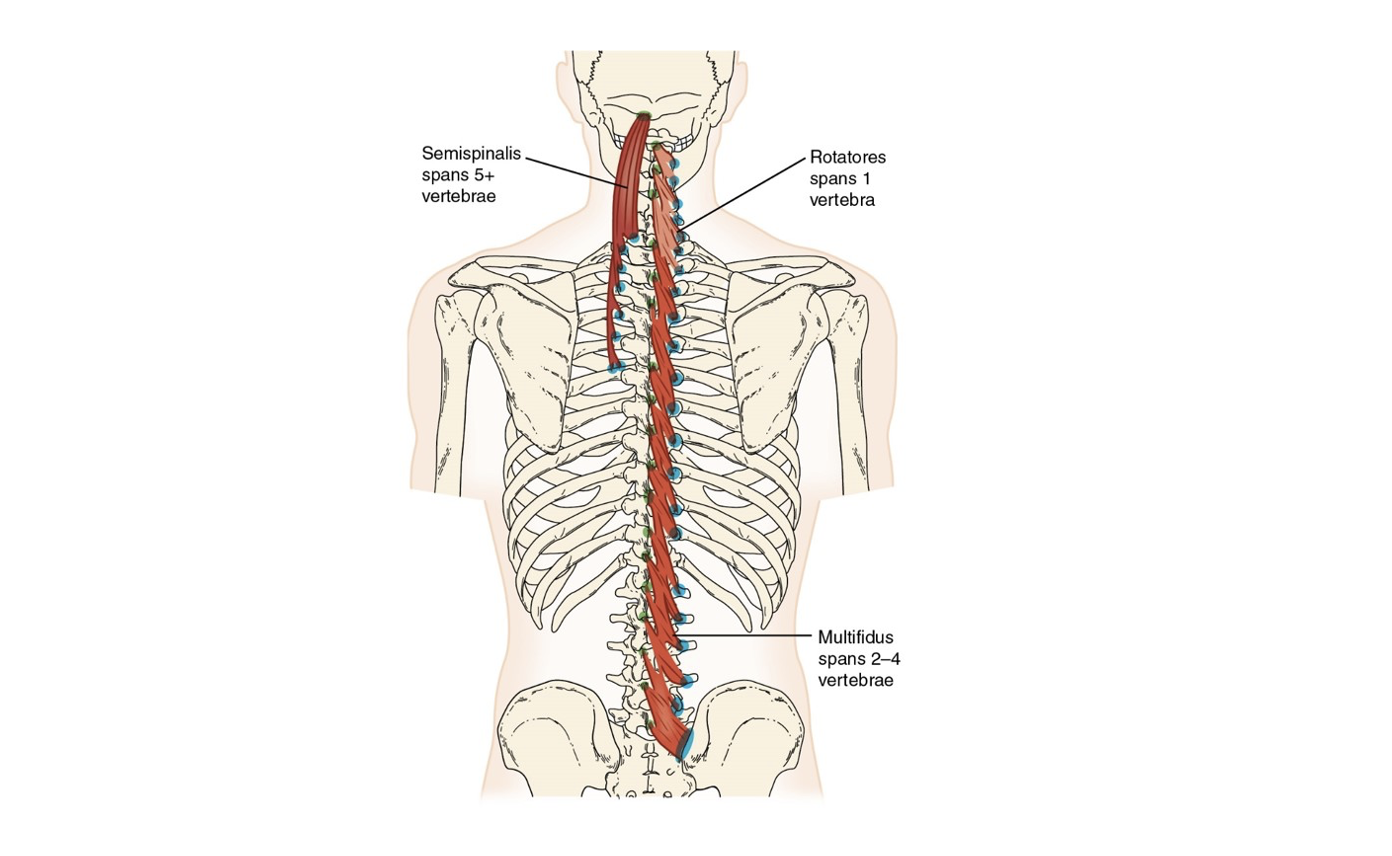
Semispinalis
most superficial, only one that attaches to occiput
Multifidus
deep to semispinalis, sacrum to C4-C7, span 2-4 vertebrae
Rotatores
shortest and deepest, aid in stabilization of the spine along with multifidi, span only 1 vertebra
Interspinales Muscles
small muscles located between adjacent spinous processes, assisting in spinal extension.
Interspinales: origin
Spinous process of vertebra below
Interspinales: insertion
Spinous process of vertebra above
Interspinales: Action
Neck and trunk extension
Interspinales: innervation
Spinal nerves
Intertransversarii Muscles
Muscles located between the transverse processes of adjacent vertebrae, assisting in lateral flexion of the spine.
Intertransversarii: Origin
Transverse process of vertebra below
Intertransversarii: Insertion
Transverse process of vertebra above
Intertransversarii: Action
Neck and trunk lateral flexion to same side
Intertransversarii: innervation
Spinal nerves
Line of Pull
Determines muscle action for posterior trunk muscles
Rectus Abdominis Muscle
A long, flat muscle that extends vertically along the front of the abdomen, responsible for flexing the spine and stabilizing the pelvis.
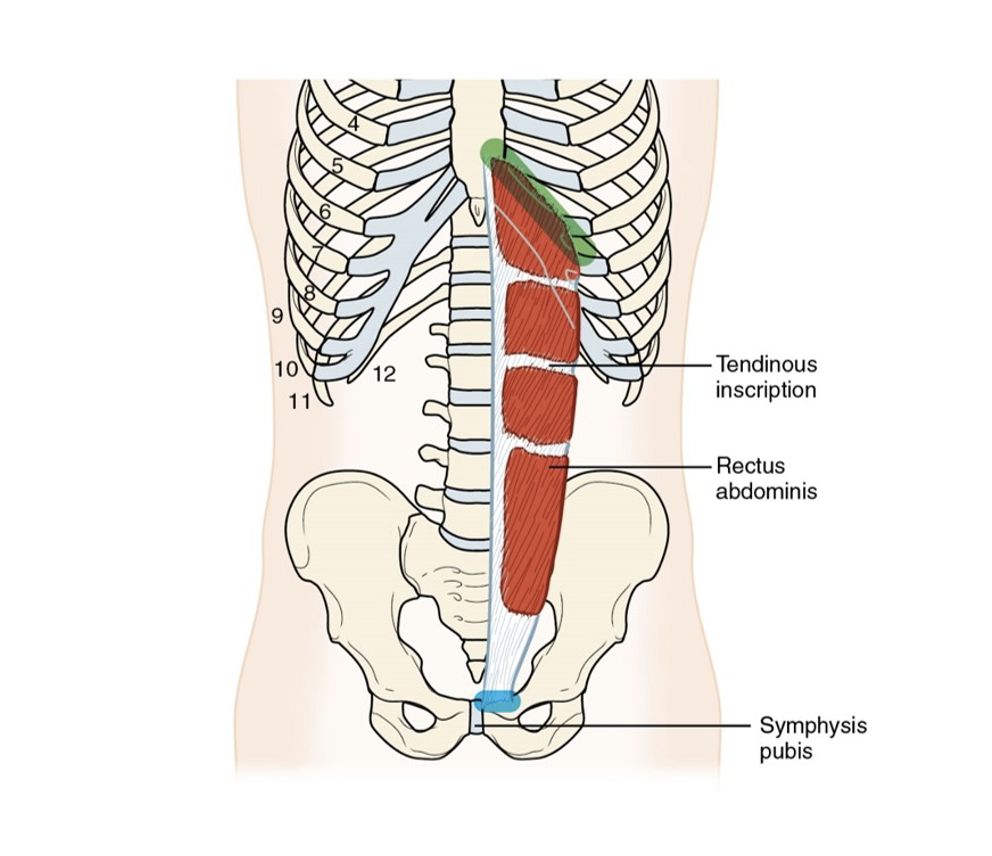
Rectus Abdominis Muscle: Origin
Pubic crest
Rectus Abdominis Muscle: Insertion
Xiphoid process and costal cartilages of 5th through 7th seventh rib
Rectus Abdominis Muscle: Action
Trunk flexion: compression of abdomen
When pelvis stabilized: depresses ribs
Accessory muscle of respiration
Rectus Abdominis Muscle: Innervation
7th through 12th thoracic nerves
External Oblique Muscle
A muscle located on the lateral sides of the abdomen that aids in trunk rotation, flexion, and supports abdominal compression.
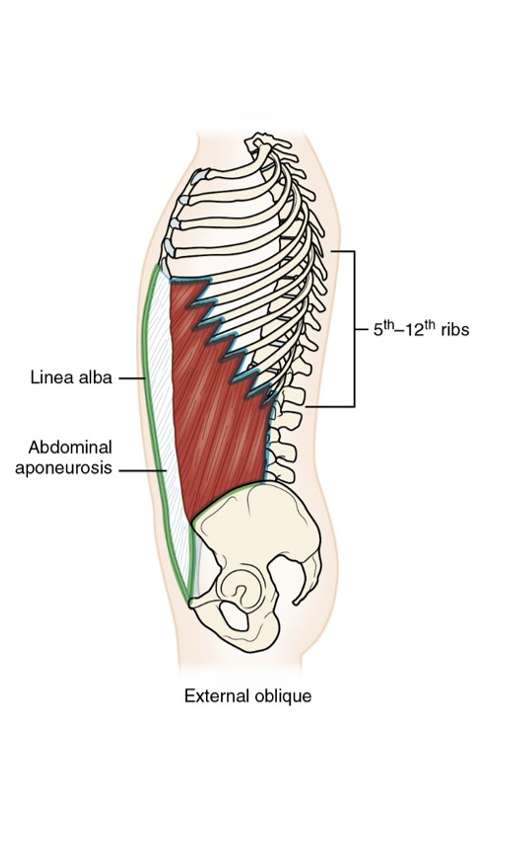
External Oblique Muscle: Origin
Lateral surface of lower eight (8) ribs
External Oblique Muscle: Insertion
Iliac crest, pubic tubercle, and linea alba via abdominal aponeurosis
External Oblique Muscle: Action
Bilaterally: trunk flexion; compression of abdomen
Unilaterally: trunk lateral flexion and rotation to opposite side
When pelvis stabilized: depresses ribs
Accessory muscle of respiration
External Oblique Muscle: Innervation
8th through 12th intercostal, iliohypogastric, and ilioinguinal nerves
Internal Oblique Muscle
Located beneath the external oblique, the internal oblique muscle functions in trunk rotation, lateral flexion, and also aids in compressing the abdomen.
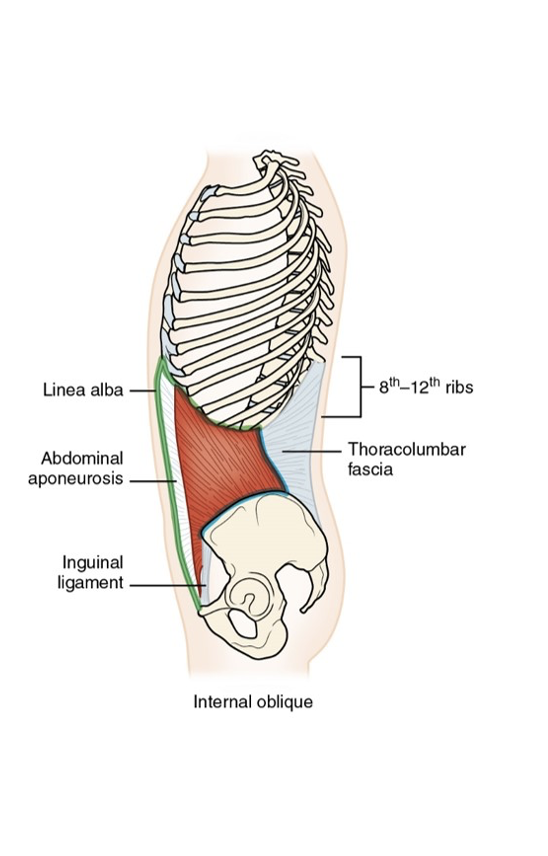
Internal Oblique Muscle: Origin
Inguinal ligament, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia
Internal Oblique Muscle: Insertion
8th through 12th ribs, linea alba via abdominal aponeurosis
Internal Oblique Muscle: Action
Bilaterally: trunk flexion; compression of abdomen
Unilaterally: lateral trunk flexion and rotation to same side (as the internal oblique)
When pelvis stabilized: depresses ribs
Accessory muscle of respiration
Internal Oblique Muscle: Innervation
8th through 12th intercostal, iliohypogastric, and ilioinguinal nerves
Transverse Abdominis Muscle
Deepest abdominal muscle, vital for core stability, with functions in compressing the abdomen.
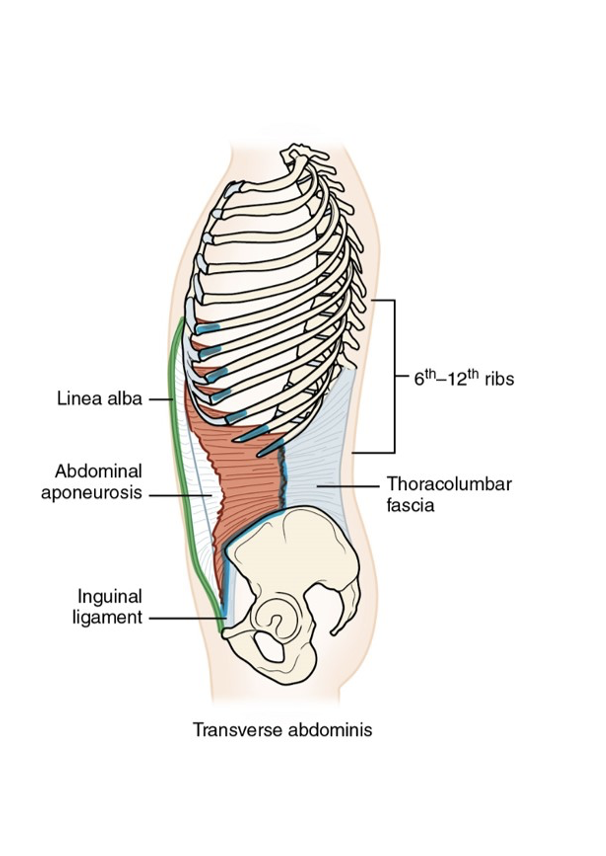
Transverse Abdominis Muscle: Origin
Inguinal ligament, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia; costal cartilages of the lower seven (7) ribs
Transverse Abdominis Muscle: insertion
Pubic crest, linea alba via abdominal aponeurosis
Transverse Abdominis Muscle: Action
Compression of abdomen
Accessory muscle of respiration
Transverse Abdominis Muscle: Innervation
7th through 12th intercostal, iliohypogastric, and ilioinguinal nerves
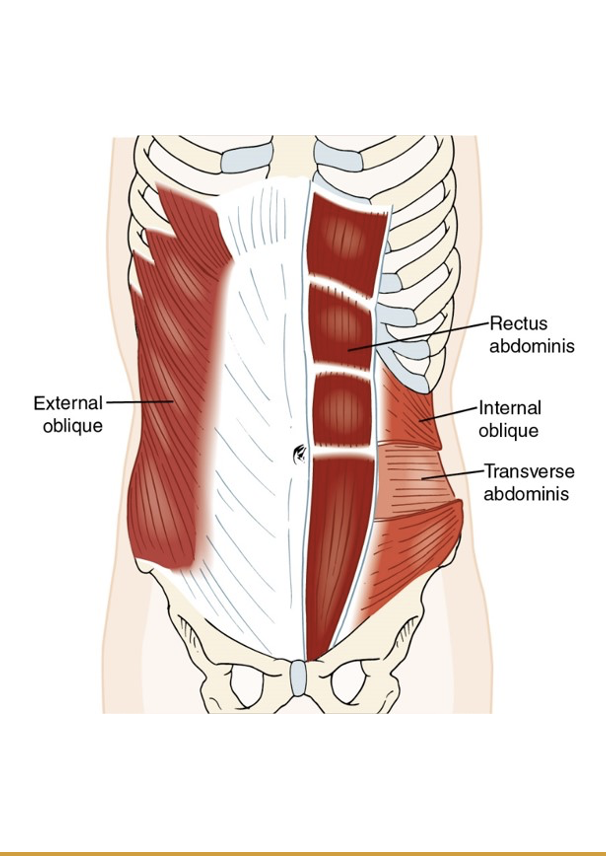
Relationships of Abdominal Muscles
Quadratus Lumborum Muscle
Stabilizes the pelvis and lumbar spine, assists in lateral flexion of the vertebral column.
Quadratus Lumborum Muscle: Origin
Iliac crest
Quadratus Lumborum Muscle: Insertion
Twelfth rib; transverse processes of all five (5) lumbar vertebrae
Quadratus Lumborum Muscle: Action
Trunk lateral flexion to same side. Pelvic elevation on same side.
Quadratus Lumborum Muscle: Innervation
12th thoracic and 1st lumbar nerves
Diaphragm Muscle
Main muscle of respiration, separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
Diaphragm Muscle: origin
Xiphoid process, ribs, lumbar vertebrae
Diaphragm Muscle: Insertion
Central tendon
Diaphragm Muscle: Action
Inspiration
Diaphragm Muscle: Innervation
Phrenic nerve (C3, C4, C5)