AP BIO Unit 2 Review
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
cell theory?
all living things are composed of cells
the cell is the basic unit of life
all cells come from preexisting cells
cell types?
prokaryotes & eukaryotes
prokaryotes characteristics?
plasma membrane
cytosol
ribosomes
circular chromosomes of DNA in a nucleoid
also contain plasmids
1-10 micrometer diameter
eukaryotes characteristics?
plasma membrane
cytosol
ribosomes
chromosomes of DNA in a nucleus
typically don’t contain plasmids
membrane bound organelles
10-100 micrometer diameter
what happens to cell size as a cell gets bigger?
SA:V decreases
what happens when SA:V decreases?
there is less SA to bring in needed materials for the greater volume; waste cannot get out fast enough to prevent the cell from dying
what is the endomembrane system composed of?
nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough)
golgi apparatus
vesicles
lysosomes
plasma membrane
what does the endomembrane system do?
it optimizes reactions by minimizing competitive reactions and localizing needed molecules and conditions
can increase SA in organelles where reactions occur
creates a transport system for materials exiting or entering the cell
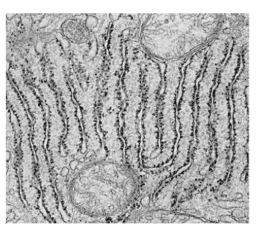
rough endoplasmic reticulum characteristics?
rough bc of ribosomes attached to the outside surface
proteins made here are released from the cell
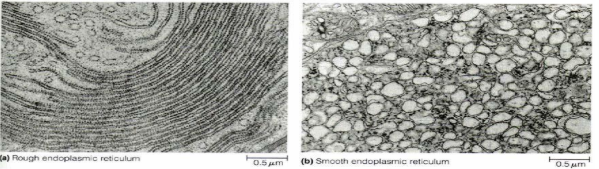
smooth endoplasmic reticulum characteristics?
doesn’t have any attached ribosomes; also has a different shape
it makes lipids
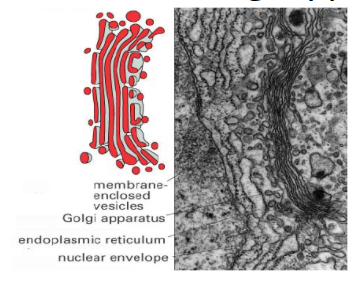
golgi apparatus characteristics?
modifies, sorts, and packages up proteins before sending them out
vesicle characteristics?
can form in various locations in the cell
RER, SER, golgi, lysosomes, cell membrane
they store or transport things
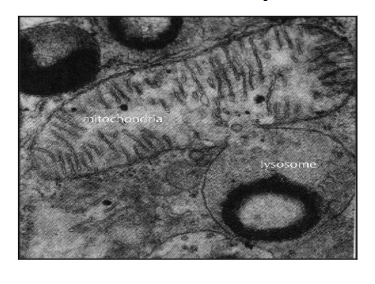
lysosome characteristics?
contain digestive enzymes that break down macromolecules
can also be used to digest food in single-celled organisms
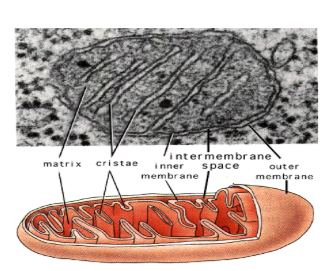
mitochondria characteristics?
organelle w/ double membrane
the inner membrane has folds into the interior called cristae
this is the site of cellular respiration which generates energy for the cell
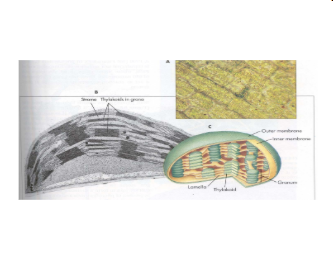
chloroplasts characteristics?
organelle with the least 2 membranes
this is the site of photosynthesis where carbon dioxide and water are used to create glucose
found only in plants
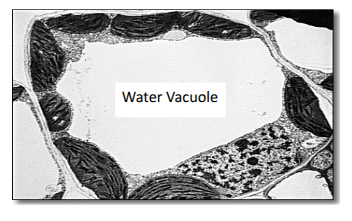
water vacuole characteristics?
stores water and nutrients for later use
generates turgor pressure for the plant
found only in plants
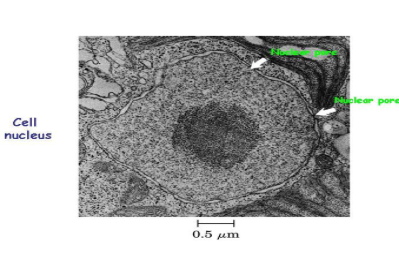
nucleus characteristics?
stores genetic information in DNA (chromatin)
made of the nuclear membrane, DNA and the nucleus
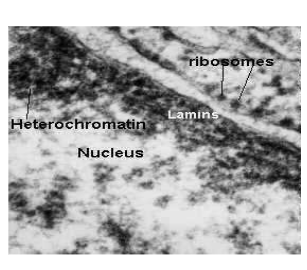
nuclear membrane characteristics?
separates the inside of the nucleus from the outside
made of the same kind of membrane as the cell membrane
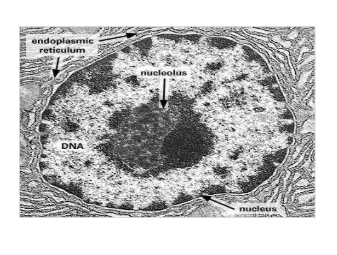
nucleolus characteristics?
makes ribosomes
usually 1 or 2 found in eukaryotic cells
ribosomes characteristics?
read copies of genes which gives them instructions to make proteins
non membrane-bound
cytoskeleton characteristicsmicrotubules ?
involved in structure of the cell and movement of things inside the cell
microtubules characteristics?
hollow tubes made of repeating dual protein complexes
structural support inside the cell
serve as highway system for chromosomes and vesicles
microfilaments characteristics?
composed of 2 twinning acting protein filaments
involved in changing cell shape
along with motor proteins and myosin filaments, they can cause movement such as cell contraction during mitosis
intermediate filaments characteristics?
made of twisted, string protein filaments
involved in stabilizing cell shape
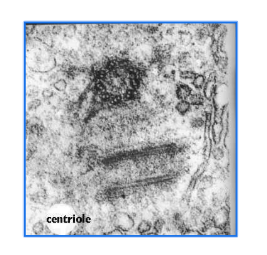
centrioles characteristics?
made of microtubules
used during mitosis when a cell reproduces itself
not found in plant cells
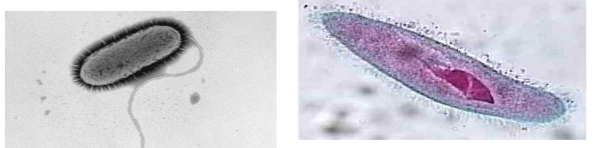
cilia and flagella characteristics
made of microtubules
involved in movement of materials near a cell
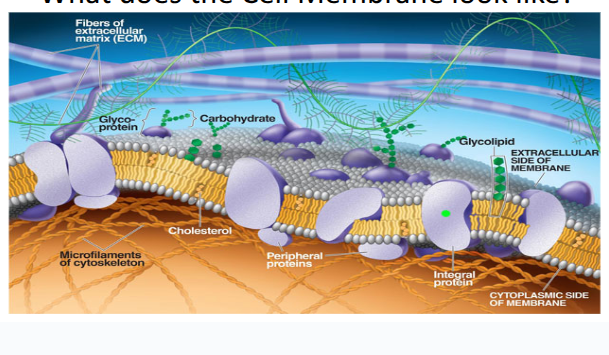
what does the cell membrane look like?
made of a phosphoipid bilayer
contains protein molecules
carbohydrates attached to protein molecules called glycoproteins
carbohydrates attached to lipids called glycoplipids
cholesterol
inside layered with cytoskeleton
outside layered with extracellular matrix
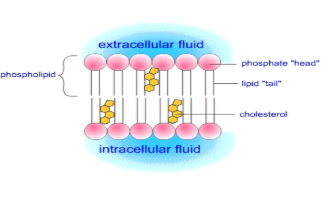
phsopholipid billayer characteristics?
double layer of phospholipid molecules
interspersed with cholesterol molecules and proteins
it is a selectively permeable membrane
what happens with selective permiability?
what gets through the phospholipid bilayer depends on 3 things:
size: larger molecules can’t get through
charge: charged molecules can’t get through
solubility: water soluble molecules can’t get through
membrane proteins characteristics?
proteins can be integral or peripheral
can play active roles in cell functioning or play a structural role
characteristics of glycolipids and glycoproteins?
consists of a carbohydrate chain attached to a membrane proteins or a phospholipid
involved in recognition by other cells and other chemical messengers
functions of the cell membrane?
regulates what enters and leaves the cell
provides protection and support
structure/function of cell walls?
provide support and protection
barrier to some substances
protection from osmotic lysis (explosion due to overfilling w/ water
cell walls of plants, fungi and bacteria are made of different substances.
what do all cells exist in to survive?
liquids; meaning there’s water inside and outside of the cell
how do cells cross the membrane?
particles come in and out of cell changing the concentration both inside and outside the cell; particles moving though the phospholipid bilayer do this by simple diffusion
what is diffusion?
in a solution, particles move from areas with more particles (high conc) to areas with less particles (low conc)
this occurs with no added energy to make molecules move
passive diffusion
how does diffusion in liquids work?
particles will appear to continue to move until there is an equal concentration of them everywhere
this is equilibrium
particles will still continue to move but equally in all direction
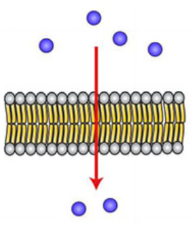
how does simple diffusion work?
allows molecules to pass straight through the phospholipid bilayer
these molecules can’t break any of the 3 rules of selective permeability
these molecules will move from the side with a high concentration of that molecule to the side with a low concentration
no energy Is used to make it move
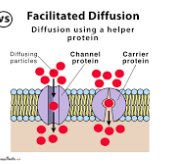
how does facilitated diffusion work?
molecules will randomly move through the pores in Channel Proteins
these molecules break 1 or more rules of simple diffusion
similar to simple diffusion, movement occurs down the concentration gradient with no added energy
channel proteins allow free movement and acts like a tunnel (ex. aquaporin)
special ion channels move specific ions
carrier proteins change the shape and the shape changes causes the solute to move
what is osmosis?
diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membranes
types of osmosis?
isotonic
hypotonic
hypertonic
isotonic solution characteristics?
“same strength”
the concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside the cell
water moves into and out of the cell in equal amounts
healthy animal cell/ok plant cell
hypertonic solution characteristics?
“above strength”
solution outside has a higher solute concentration than the inside of the cell
more water move out of the ell than in
dehydrated animal or plant cell
hypotonic solution characteristics?
“below strength”
solution outside cell has a lower solute concentration than inside the cellmore water enters the cell than out
animal cell experiences lysis (cell destruction)/ healthy plant cell
how does water move in plants?
water potential
what goes on in roots?
active transport moves nutrients from solid to roots
root hairs create a large SA to uptake water because of the water potential
water travels into the vascular tissue of the root by 1 of the 3 different types of movement
characteristics of root hairs?
the epidermis of root tips is more permeable to water than other cells
root hairs greatly increases the SA of the root tip
root hairs can then pass water and nutrients on to other cells
cell compartments?
travel routes depend on several compartments of plant cells
the apoplast consists of all the interconnected cell walls
the symplast consists of all the cytoplasm, connected by plasmodesmata
routes of transport in plants?
the transmembrane route
the symplastic route
the apoplastic route
what happens in the symplastic route?
involves crossing 1 plasma membrane and then remaining within the symplast
what happens in the apoplastic route?
it does not cross a plasma membrane and remains within the apoplast
what happens in the transmembrane route?
it involves repeated moves across plasma membranes
how does transport from epidermis to vascular tissue work?
water and nutrients soak into the cell walls of the root hairs; the solution can then travel via the apoplastic route
some of the solution crosses the plasma membrane and travels via the symplastic route
the solution may switch from apoplastic to symplastic along the way
the endodermis cell walls contain a waxy material called the Casparian strip; all materials must cross the plasma membrane into endodermal cells to cross the strip
endodermal cells release water into their cell walls which is taken up by the xylem cells
xylem characteristics?
dead hollow cells used to transport water
made of tracheids which are connected by pits
some plants have vessel elements which are shorter, fatter and have perforations rather than pits
stomata characteristics?
the rate of transpiration is controlled by stomata as the surrounding guard cel
role of potassium pumps?
when it is pumped into guard cells, water flows in. Why? - this bows the shape of the guard cells
when potassium is pumped out, the water flow is reversed and the guard cells flatten
phloem characteristics
live cells called sieve tube members
connected by sieve plate
lack of a nucleus, ribosomes, and vacuole
work with companion cells that provide materials to the sieve tube member
what is movement from sugar?
from source to sink
what is a source?
a location that makes sugar or stores sugar as starch
what is a sink?
a location that uses sugar
what is short distance movement similar to?
water movement
how does sugar in a solution move?
from cell to cell via the symplastic or apoplastic route
why Is cotransport needed?
it is required to move sugar across a plasma membrane
what is cotransport?
a type of active transport where a cell membrane proteins simultaneously moves 2 substances across the membrane
what happens in vertical transport?
active transport moves sugar from a source into the phloem this reduces water potential
osmosis causes water to enter the phloem which increases the pressure and causes movement towards lower pressure areas
active transport causes sugar to move into sink cells which owners the pressure
this causes water to return to xylem cells
since sink cells are always using or storing sugar, concentration there is always lower than the surrounding cells