Ch 9 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Asexual Reproduction
One parent organism replicates its DNA and splits the contents of one cell into two. This creates two genetically identical offspring.
What organisms generally reproduce asexually
Unicellular Organisms
Sexual Reproduction
The DNA of the offspring comes from two parents. An egg fuses with a sperm, yielding the first cell of the offspring.
What organisms generally reproduce sexually
Multicellular Organisms
Why is Sexual Reproduction beneficial
Sexual reproduction produces genetic diversity among offspring, which increases the chance that some offspring survive in changing environments.
Homologous Chromosomes
Matching pairs of chromosomes that carry the same genes in the same order.
Diploid Cells
Cells with two sets of Chromosomes (Chromosomes from Mom and Dad)
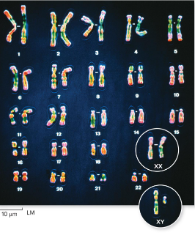
Karyotype
All of the chromosomes from a diploid human cell.
Human cells contain how many homologous sets of chromosomes
23
Human cells contain how many homologous sets of autosomes
22
Autosomes
The numbered chromosomes. These chromosomes are the same for both biological males and females
Human cells contain how many sets of sex chromosomes
1
Alleles
Which are alternative versions of the same gene.
Chromatids
When members of a homologous pair are replicated, identical alleles are on sister chromosomes.
Haploid
Cell has only one set of chromosomes.
Zygote
The first cell of a new organism.
Zygotes grow and develop by
Mitosis
In adults, specialized diploid cells called
germ cells
Independent assortment
Chromosome pairs align randomly, scrambling the combination of chromosomes for each gamete
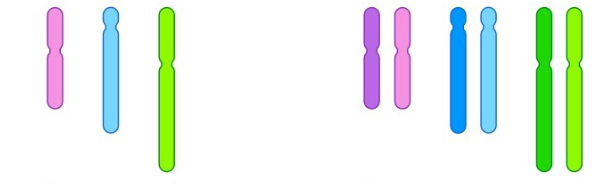
Whats the difference between Diploid and Haploid cells
Haploid cells have one copy of each chromosome while Diploid have two copies of each chromosome
Nondisjunction
If chromosomes fail to separate properly, abnormal gametes form.
Triple-X syndrome
Tall stature, menstrual irregularities, increased risk of giving birth to triplo-X daughters or XXY sons
Klinefelter, or XXY, syndrome
Variable, but often include sexual underdevelopment, long limbs, large hands and feet, development of breast tissue
Jacobs, or XYY, syndrome
Often few noticeable symptoms; tall stature, acne, problems with speech and reading
Turner syndrome
Short stature, sexual underdevelopment, infertility
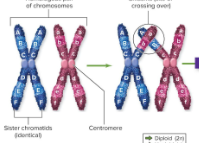
crossing over
two homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange pieces, scrambling the genetic material.
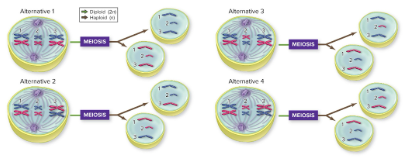
independent assortment,
chromosome pairs align randomly, scrambling the combination of chromosomes for each gamete.
How many chromosome combinations are possible in metaphase I arrangement?
223 = 8,388,608
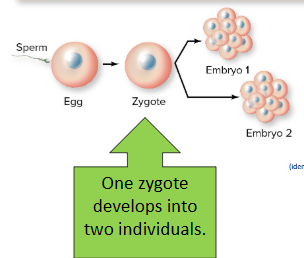
Monozygotic twins are genetically
Identical. An embryo splits in two. Each embryo then develops independently.
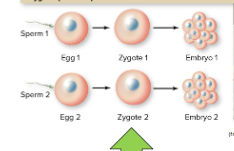
Fraternal twins
two sperm cells fertilize two separate egg cells, and the offspring might look very different.
nondisjunction.
If chromosomes fail to separate properly, abnormal gametes form.
Spermatogenesis produces _______ sperm cells for each germ cell
four
Oogenesis produces ____ egg cell for each germ cell
one