Organic Chemistry II - Exam 1
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is the most important question in chemistry?
Where are the electrons?
MRI Paragraph
The popular medical diagnostic technique of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is based on the same principles as NMR, namely the flipping (i.e. resonance) of nuclear spins of H atoms by radio frequency irradiation when a patient is placed in a strong magnetic field. Magnetic field gradients are used to gain imaging information, and rotation of the gradient around the center of the object gives imaging in an entire plane (i.e. slice inside patient). In an MRI image, you are looking at individual slices that when stacked make up the three-dimensional image of relative amounts of H atoms, especially the H atoms from water and fat, in the different tissues
The popular medical diagnostic technique of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is based on the same principles as NMR,.....
namely the flipping (i.e. resonance) of nuclear spins of H atoms by radio frequency irradiation when a patient is placed in a strong magnetic field
Which reagents that can carry out the following reaction:
Reaction with an epoxide at the less-hindered site followed by a second step with a mild acid (HCl/H2O) to give an alcohol with a new carbon-carbon bond.
Grignard reagent
Organolithium reagent
Gilman reagent
When carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones react with nucleophiles, the nucleophile will make a new bond with
The carbonyl carbon atom
In this class, we classify the four most common carbonyl mechanisms as Mechanisms A - D. When Grignard Reagents react with aldehydes and ketones, the reaction mechanism is
Mechanism A
When carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones react with nucleophiles, what type of intermediate is always created?
A tetrahedral intermediate
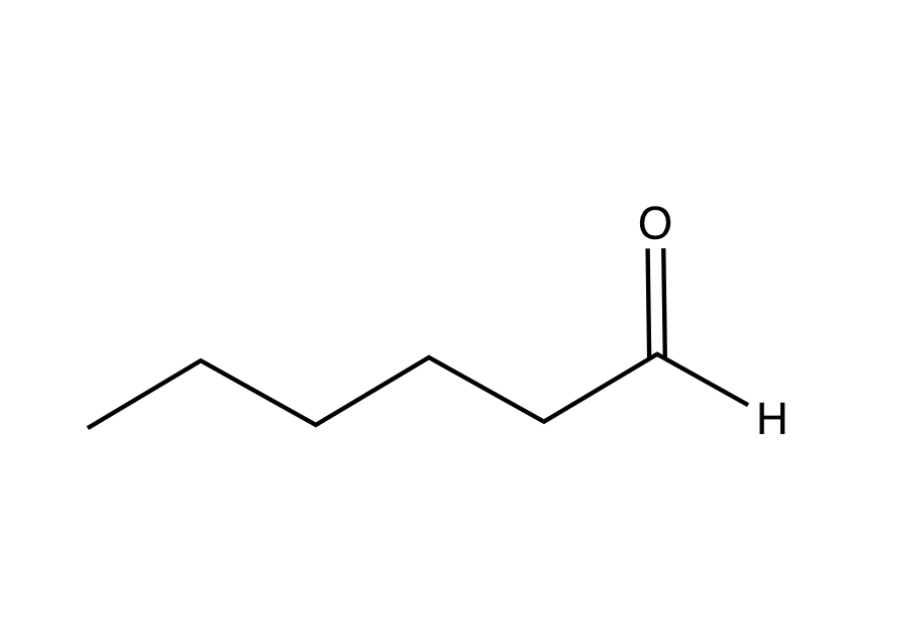
Name this molecule
Hexanal
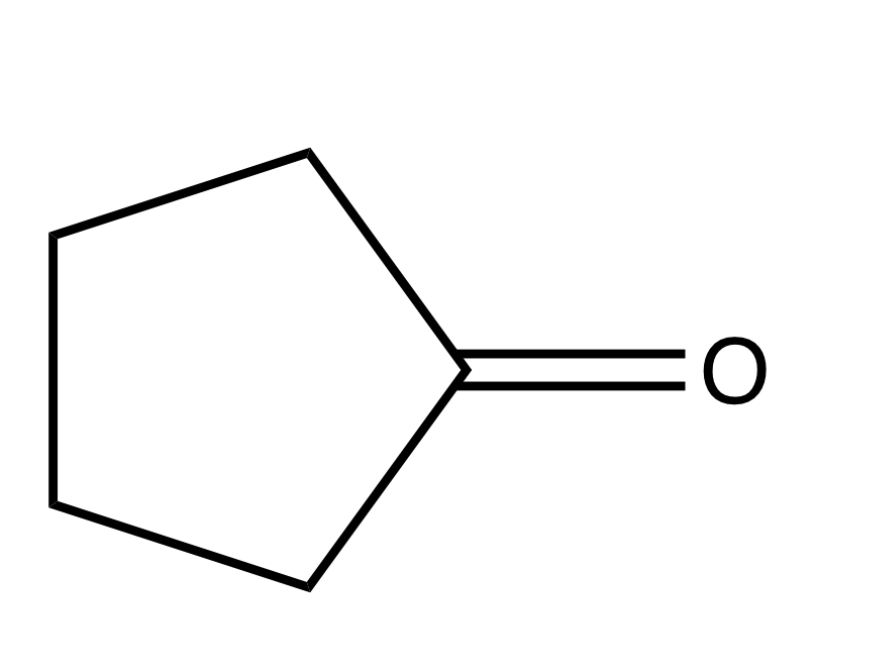
Name this molecule
Cyclopentanone
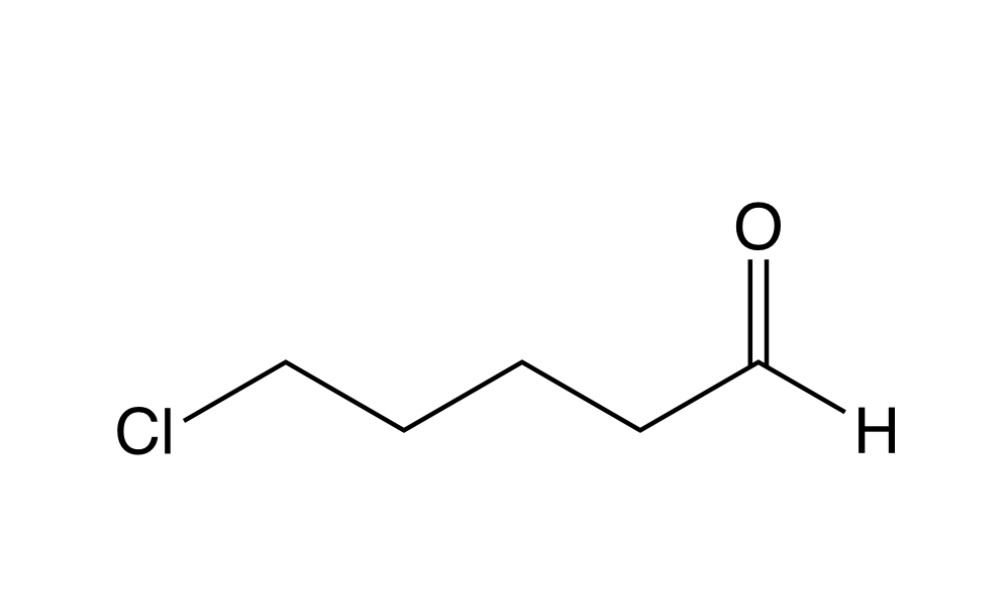
Name the molecule
5-chloropentanal
2,3-dimethyloctanal
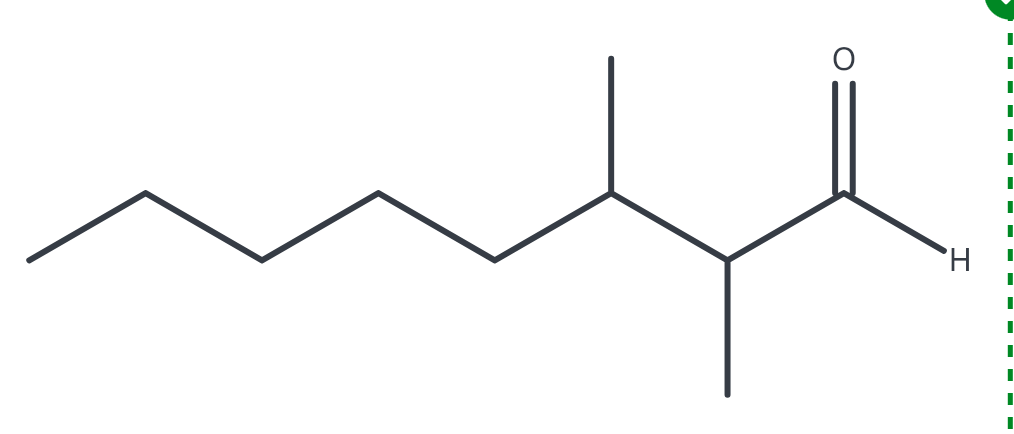
(R)-2-methyoxypentanal
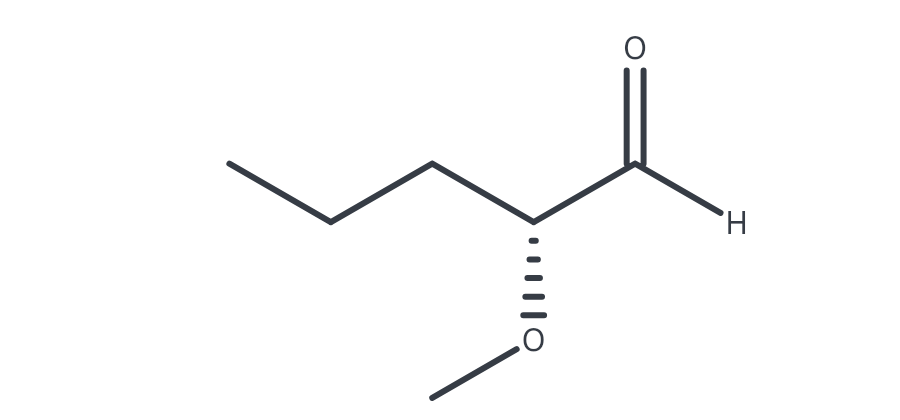
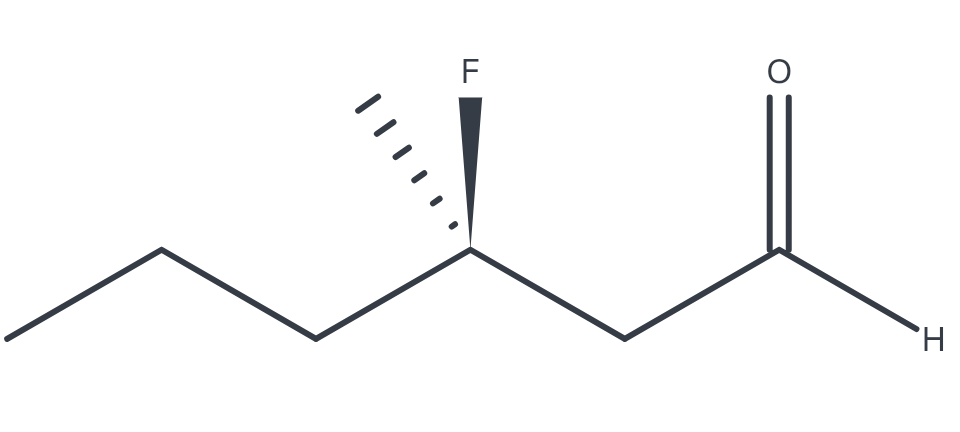
(R)-3-fluoro-3-methylhexanal
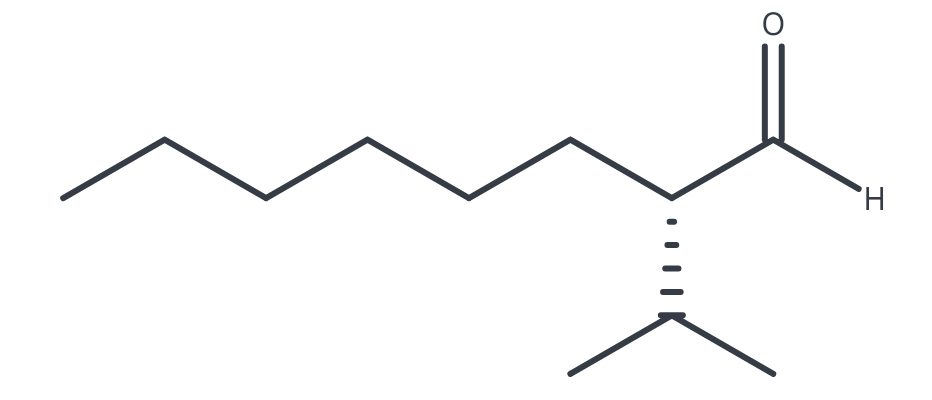
(S)-2-isopropyloctanal
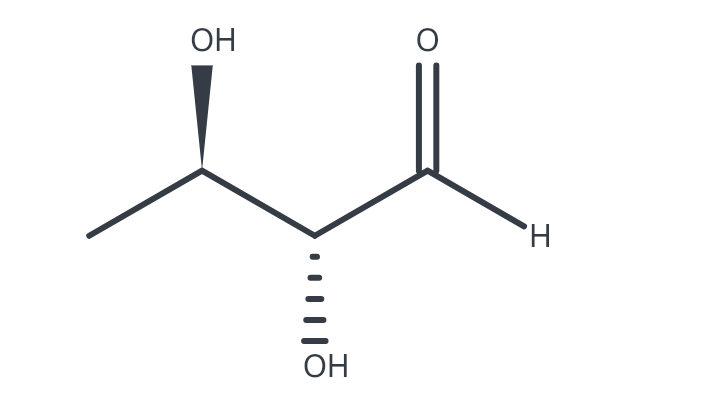
(2R, 3R)-2,3-dihydroxybutanal
The Wittig reaction uses a special reagent called a phosphonium
ylide
An important thing to remember about the Wittig reaction is that the mechanism
Has a four-membered ring intermediate
Grignard Reagent Reacting with Epoxide
1) Make a bond
2) Add a Proton
Metal attached to a carbon - carbon is partially negative
4 total arrows:
1) Arrow tail from nucleophile metal-carbon to the less hindered site of the epoxide
2) Arrow from the bond being attacked to the O on the epoxide
3) Arrow tail starting at the O to the arrow head pointed to the H atom on the HCl
4) H bond to Cl
KRE: There is a new C-C bond that is two carbons away from the -OH group
Grignard Mechanism reacting with an Aldehyde or Ketone
1) Make a bond
2) Add a proton
Metal attached to a carbon - carbon is partial negative
4 total arrows:
1) Arrow tail from nucleophile metal-carbon to carbon on the aldehyde or ketone
2) Double bond O arrow to oxygen
3) Arrow tail from O to arrow head on the H of the HCl
4) Arrow tail from H bond to arrow head on the Cl
KRE: -OH group attached to the same C atom as the new C-C bond
When an aldehyde or ketone reacts with 1) NaBH4 followed 2) H2O, the reaction follows
Mechanism A
Weak nucleophiles such as alcohols
are not strong enough to react with carbonyls directly so we add acid to make the carbonyl into a much stronger electrophile.