VIDEO NOTES (Class 8 & 9) Chapter 7
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is expense recognition?
Expenses should be recorded when you receive the product or good, not when you pay for them
What are the three approaches to expense recognition?
Direct Association
Immediate Recognition
Systematic Allocation
What’s Direct Association?
If an expense is directly tired to earning a specific revenue, you should record the expenses at the same time
ex: if you sell a good for 100, and the inventory cost of that good is directly tied, you should record sales revenue at the same time as COG
Immediate Recognition
some sales aren’t tied directly to a sale, but help support it overall
it should be recorded right away, at the same period
ex: advertisement made in march, sales boost in April. Record it in march, as soon as they are made
What’s systematic allocation?
some costs don’t relate to a single sale/period, like equipment, so instead we record them as assets and spread the cost overtime
ex: depreciation
Where do you report inventories?
On income statement, in Cost of Sales
How does inventory work in accounting?
Spoiler: it helps you determine Gross Profit
it appears on the balance sheet under current assets until its sold
then it becomes COG in expense on income statement
Sales Revenue - COG = Gross profit

Inventory Purchasing
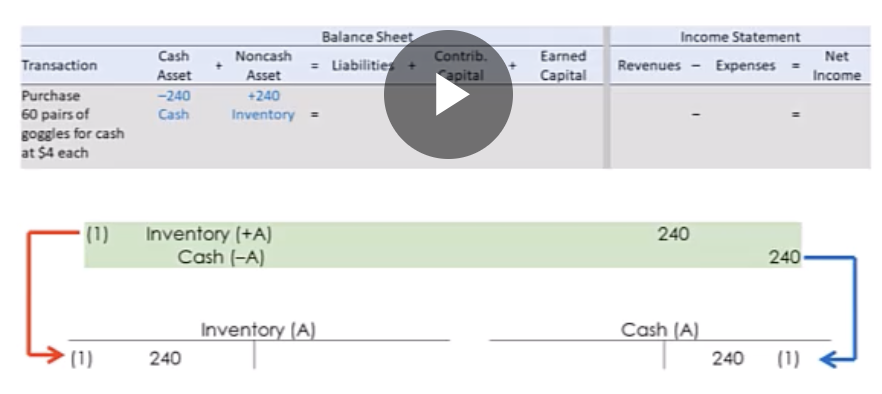

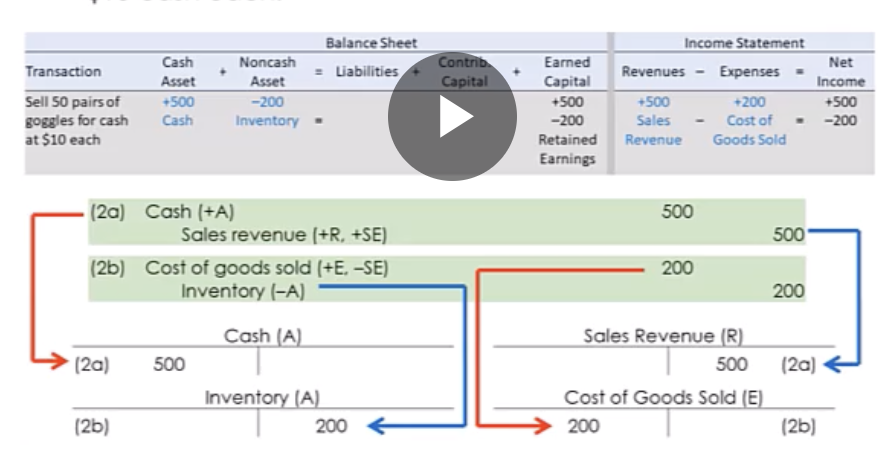
What are “costs” for inventory?
Cost to acquire
Cost of transportation
Cost for preparing goods for sale
Cost with consideration to incentives
When should a company report inventory?
Only when it is legally owned, not just physically on site
Reported inventory = legal ownership
Buyer recognizes inventory at the time of shipment
What are the 3 inventory categories for manufactures?
Raw materials
Work in Progress, partially completed goods
Finished goods

What’s the formula for COGAFS, Cost of Goods Available For Service?
Beg Inv + Purchase = COGAFS
What’s COGS?
Cost of Goods Sold
Which statements do COGS and Ending inventory end up on
COGS = Income Statement
Ending Inventory = Balance Sheet Assets
What’s COGS formula?
COGS = Beginning Inventory + Purchases − Ending Inventory
COGS = Beginning Inventory (on original) + (cost of goods purchased) Purchases - Ending Inventory (on balance sheet for next period)
What’s inventory ending formula?
Inventory ending balance = Inventory Beginning + Purchases - COGS
What are the 3 main inventory costing methods?
FIFO
LIFO
Weighted Average Cost
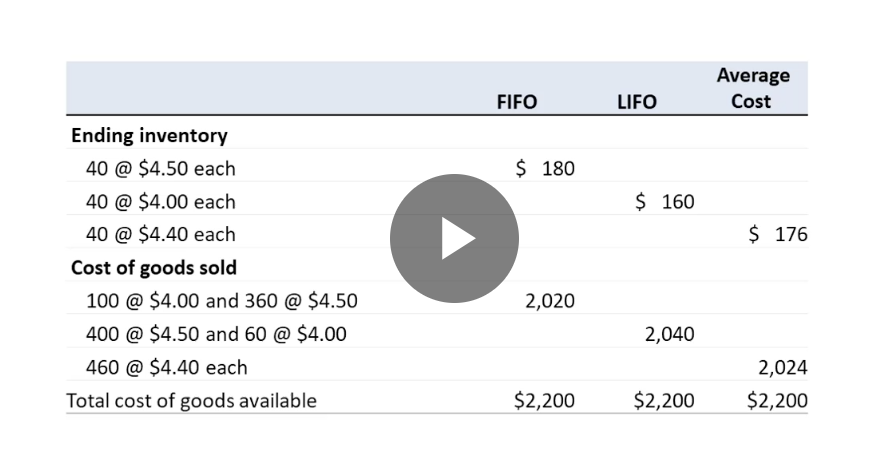
What’s FIFO?
First in, First out
First costs recorded are the first to be transfered from balance sheet assets (inventory) to income statement (costs of goods sold)
What’s LIFO?
Last in, First Out: Last costs recorded are first to be moved from balance sheet (as inventory) to income statement (as COG)
What’s AC?
Average Cost: An average of all cost of goods sold is transferred from inventory to COGS

w/ FIFO method First Inventory in, First Out


With LIFO method, Last Inventory In, First Out

Which one produces a higher COGS?
LIFO
Which one producers a lower COGS?
FIFO
use Average Cost Method

Comparing Costing Methods
Who has to report the LIFO reserve?
The difference between LIFO and FIFO costs & current value of inventory
It is required to be reported by companies that use the LIFO method
What is the LIFO reserve formula?
LIFO reserve = FIFO ending inventory cost - LIFO ending inventory cost
What’s Estimating FIFo cost of goods sold formula?
FIFO cost of goods sold = LIFO cost of goods sold - Change in LIFO reserve
When is LIFO reserves used?
comparing gross profits of a company using FIFo with another company using LIFO
Why doesn’t LIFO not completely accurate?
LIFO doesn’t accurately represent the cost that a company would incur, it is older (cheaper), which may not reflects todays actual costs
FIFO reflects current market conditions , because it uses newer inventory costs for ending inventory
What’s the balance sheet effects of FIFO?
FIFo uses current value on balance sheet, if prices fall, that means the cost and market adjustments will lower
What’s the balance sheet effects of LIFO?
When prices are rising, LIFO ending inventory is undervalued compared to FIFO (as it doesn’t represent the current cost a company would have to pay today if they repurchased the same inventory items)
Why is LIFO reserve viewed as an “unrealized holding gain”
a gain that comes from holding inventory as prices are rising
How does FIFO affect cash flow in rising prices?
higher pretax income → higher income taxes → less cash available
How does LIFO affect cash flow in rising prices?
Lower income → lower taxes → more cash available.
Why does management adopt LIFO?
save more from taxes
So what happens when you use LIFO?
it increases gross profit, results in higher pretax income, leads to higher taxes
So what happens when you use FIFO?
gross profits look less, less tax, more cash flow
How do you adjust LIFO to FIFO on balance sheet?
LIFO reserve + LIFO inventory - FIFO inventory
How do you adjust LIFO to FIFO on income statement?
LIFO cogs - Change in LIFO reserve = FIFO cogs
How does the IFRS allow reporting to be done?
NOT with LIFO, only with FIFO or AC
Reminder, how do you calculate Gross Profit Margins?
GPM = Sales revenue - cogs/ sales revenue
What’s inventory turnover?
says how quickly inventory is being sold
Whats inventory turnover formula?
INVT = cogs / average inventory
What’s average inventory days outstanding?
how long inventories are held/on the shelf b4 being sold
What’s Average inventory days outstanding formula?
AIDO: average inventory / average daly cost of goods sold = sold entire inventory x times in that year
What does higher inventory turnover imply?
favorable, strong sales, efficient inventory management, selling inventory quickly
improvement in manufacturing efficient
higher profit margins
excessive purchases
What does lower inventory turnover imply?
excessive production
lower margins
missed trends/tech advances
increased competition
Changes in promotion policies
Why is it important to optimize inventory
too much inventory is expensive
too little inventory leads to lost sales
what are some operational strategies to reduce inventory levels?
improve manufacturing process, eliminate bottle necks and work in process build up, less inventory pilling
Just in time JIT delivers, suppliers deliver materials only when needed, to reduce the storage of raw materials
demand pull production: raw materials are used only when theres customer demand to prevent overproduction and excess inventory
What’s adjusting turnover ratios?
a different version of inventory turnover that helps provide a more accurate measure, when a company uses LIFO
What’s adjusting turnover formula?
LIFO cogs / Average FIFO inventory ( FIFo - based) = Adjusted inventory turnover
Why do we adjust?
LIFO inflates COGS, and udnerstates the inventory, this makes the incorrect turnover ratio, so this adjustment makes it more accurte
How do we fix this issue?
change the beg and ending inventory values to use LIFO reserve information
What’s the Net realizable value rule?
rule to make sure inventory is not overstated
What’s the Net realizable value formula?
NRV = Selling Price − Costs of Completion − Selling Costs
What’s the Lower of Cost
Prevents overstating inventory value on financial statements
What’s the Lower of Cost formula?
LCNRV Inventory Value=min(Cost,NRV)
What’s the formula for FIFO gross profit when given LIFO info
FIFO cogs = LIFO cogs - change in reserve LIFO
FIFO gross profit = revenue - FIFO cogs