Topic 9 - forces and their effects
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
examples of interactions objects at a distance without contact
gravitational attraction
there is an attraction between two objects with mass, the larger mass gives greater attraction
electrostatic attraction/repulsion
a large charge gives greater force
like charges repel, opposite charges attract
magnetic attraction/repulsion
a stronger magnet gives stronger field, having a greater force
like poles repel, opposite poles attract
examples of interaction of objects with contact
normal contact force
the force is perpendicular to the place of contact
friction
surfaces that are rough cause friction when moved
what is a vector
a vector has size and direction - eg. a force of 10N directed downwards
weight, velocity, force, displacement etc
what is scalar
scalar has just size - so direction plays no part in describing the value
mass, distance, speed etc
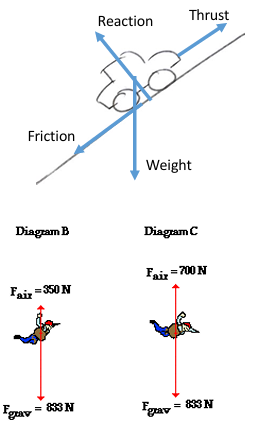
vector diagrams
free body diagrams
shows the direction of forces that are present in a situation
points to note:
the reaction force always acts at the normal to the line of contact, from the point of contace
friction acts in the opposite direction to movement, along line of contact
weight always acts downwards, acting from Centre of Mass
scale drawings
the length of each arrow represents its size (in relation to the other forces acting on the object)
so direction with larger arrows shows the resultant force
if arrows are in opposite directions with equal length
(equal in magnitude but opposite in direction)
the forces cancel out
so the object is in equilibrium
so travels at a constant velocity
diagram:
at B, the drag is a lot less than the weight, as shown by the arrows, so the resultant force causes him to accelerate
at C, the difference in arrow lengths is less, so the resultant force is smaller, so smaller acceleration
what is an isolated solid system
isolated solid systems means no forces are present that come from a source outside the system
eg. a magnetic ball just rolling down a hill, an external force would be a magnet at the top of the hill
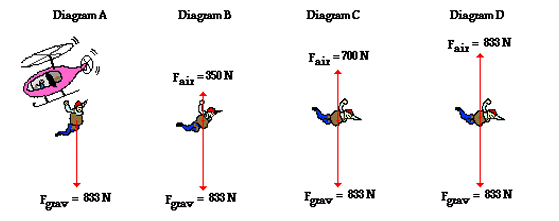
explain forces when skydiving
forces that act are air resistance and weight
initially, the skydiver has no air resistance and the only force acting on him is weight
as he falls, he accelerates, increasing his speed
this makes air resistance increase
therefore, the resultant force decreases
therefore, acceleration decreases as F=ma, so he is not speeding up as quickly
eventually weight and air resistance are equal and balanced, so there is no resultant force
so there is no acceleration and terminal velocity is reached
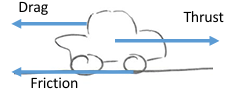
explain forces on a vehicle
initially, low air resistance and thrust is only hindered by friction
air resistance increases, decreasing resultant force
eventually the car is travelling at terminal velocity, where the thrust is balanced by drag and friction, so no resultant force acts
(this is immediately changed when more thrust is added, as it now becomes the resultant force until the drag increases to balance it again)
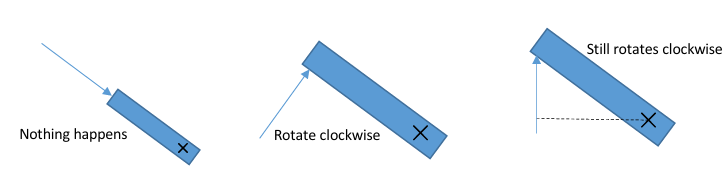
describe situations where forces can cause rotation
rotation occurs….
if an object is attached to a pivot point
a point which it can rotate about, but it cannot move away from
and a force is applied not towards the point (see diagram)
the object will not rotate, and will just be held still, as there is no resultant force
if the force is applied perpendicular to the object
it will move about the pivot in this direction
if the force applied not perpendicular to object
need to find perpendicular distance from pivot to line of force
see which direction it will turn
moment of a force (newton metre, N m) = force (newton, N) x distance perpendicular to the direction of the force (metre, m)
bike riding - pressing your foot down on the pedal, causes a moment about the pivot, turning the pedal arm
equilibrium occurs when: sum of anticlockwise moments = sum of clockwise moments
explain how levers and gears transmit the rotational effects of forces
gears can change speed force or direction by rotation
for an example when the first gear is supplying the force
if connected to a gear with fewer teeth (ie. smaller gear)
the second gear will turn faster
but with less force
in an opposite direction to the first gear
if connected to a gear with more teeth (ie. larger gear)
turns slower
more force
in opposite direction
the second gear will always turn in the opposite direction
the blue gear is supplying the power
to increase the power, a larger gear is used for the secondary (red)
as the force on the red gear is a further distance from its pivot, the momentum of the larger gear is greater
way to reduce unwanted energy transfer
lubrication - reduces friction, so reduces unwanted energy transfer (less heat loss etc) and increases efficiency