4U BIOLOGY: HOMEOSTASIS
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Process by which a constant internal environment is maintained, despite a fluctuating external environment
Homeostasis
An alternate term for homeostasis.
Dynamic equilibrium
What is a threshold level?
Tolerable range at which homeostasis can be maintained
3 main components of homeostatic control mechanisms
Sensor (Monitor)
Coordinating Centre (Integrator)
Effector (Regulator)
What is negative feedback?
Balancing action occurs in response to a change in environment
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK: Order the following. Sensor, effector, stimulus, integrator, response
Stimulus, sensor, integrator, effector, response
What type of homeostatic response amplifies conditions away from the baseline state?
Positive feedback
ECTOTHERM: Definition, Examples
An organism whose activity is regulated by/fluctuates based on the environment
Invertebrates, (most) fish, amphibians
ENDOTHERM: Definition, Examples
An organism that maintains its own constant body temperature
Part of brain responsible for nerve and hormone function
Hypothalamus
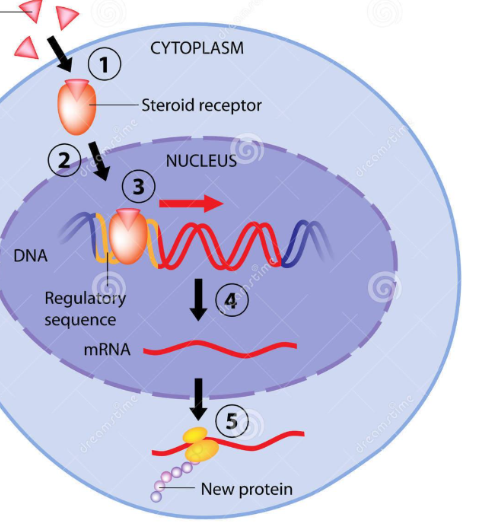
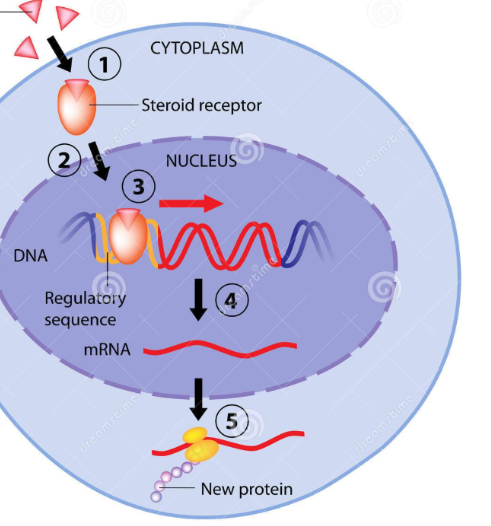
STEROID HORMONES: Makeup, Function, Examples
Cholesterol (Fat-soluble)
Binds to receptor INSIDE TARGET CELL to cause changes
Sex hormones, cortisol
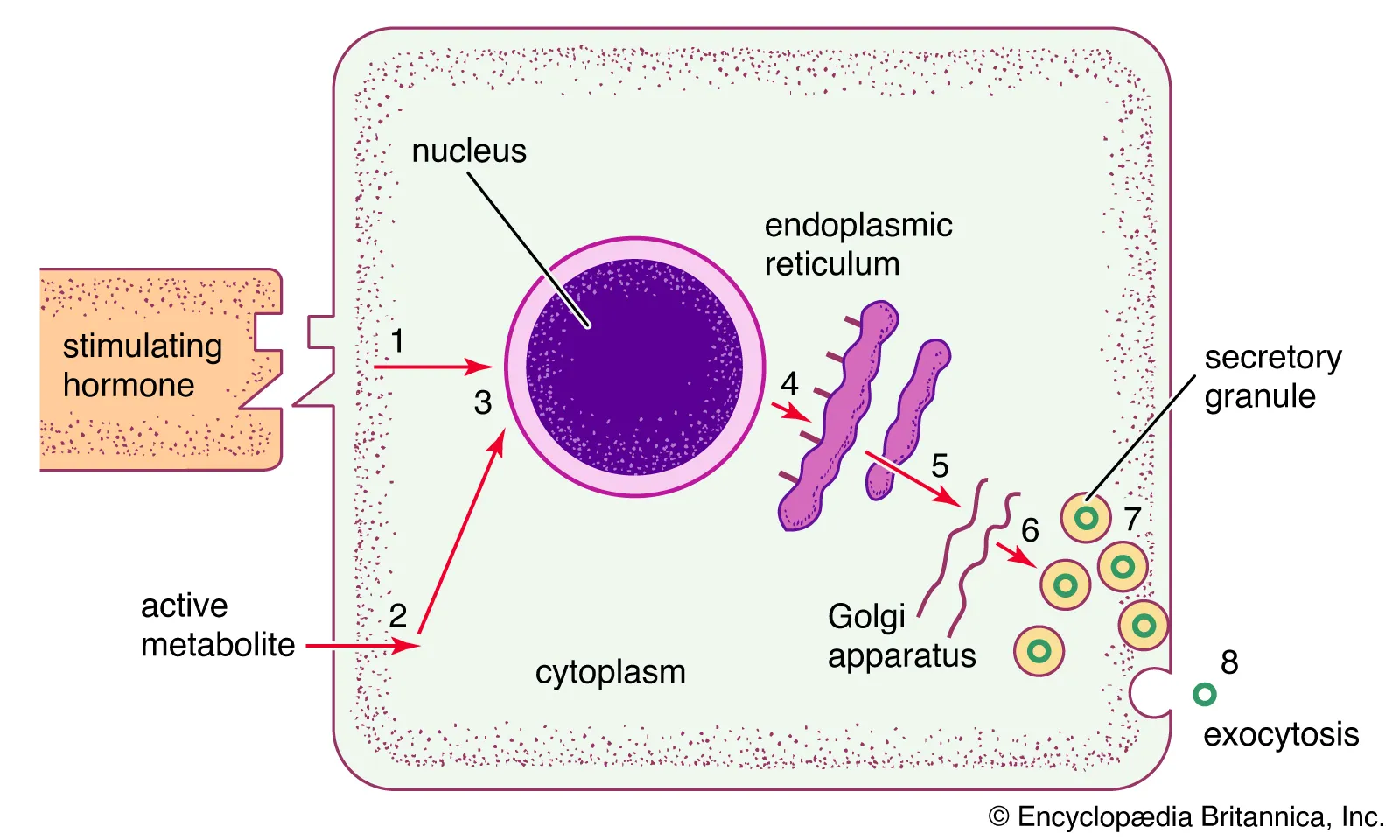
PROTEIN HORMONES: Makeup, Function, Examples
Amino acid chains (Water-soluble)
Binds to receptors on CELL SURFACE
E.g insulin, growth hormones
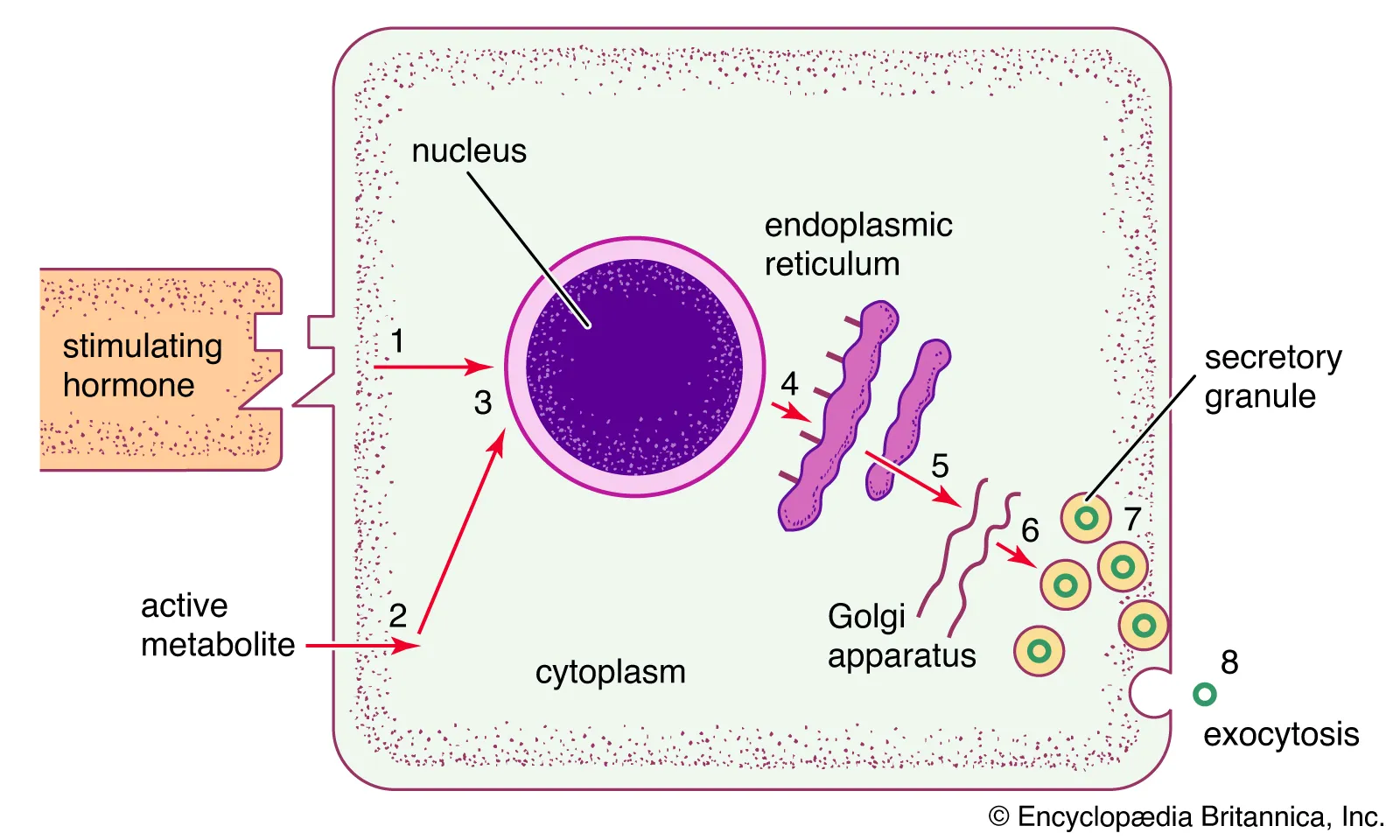
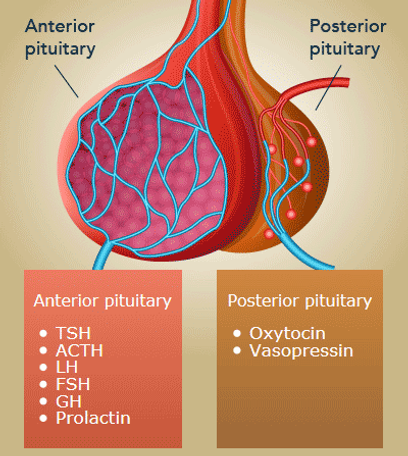
Which pituitary lobe STORES hormones produced by the hypothalamus? Which ones?
Posterior Pituitary Gland
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH), Oxytocin

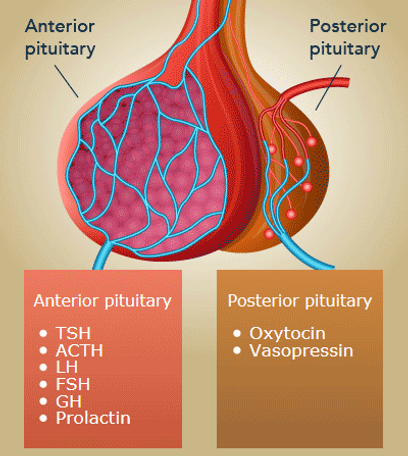
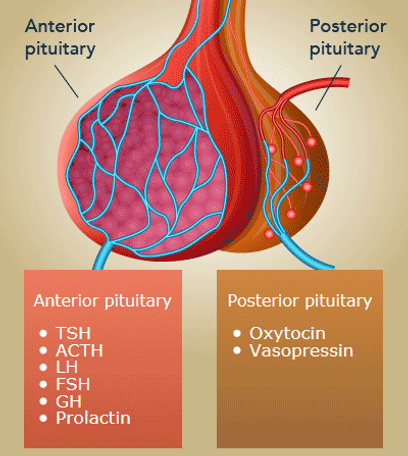
Which pituitary gland produces and releases ITS OWN HORMONES?
Anterior pituitary gland
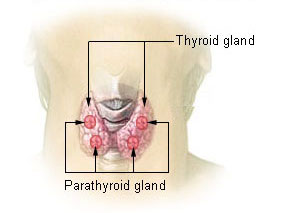
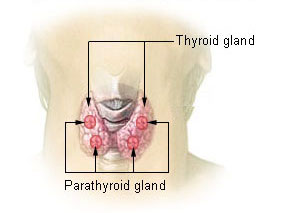
3 Glands that affect metabolism:
Thyroid Gland
Parathyroid Gland
Anterior Pituitary Gland
Ratio of T3 to T4 secreted by the thyroid gland.
35:65
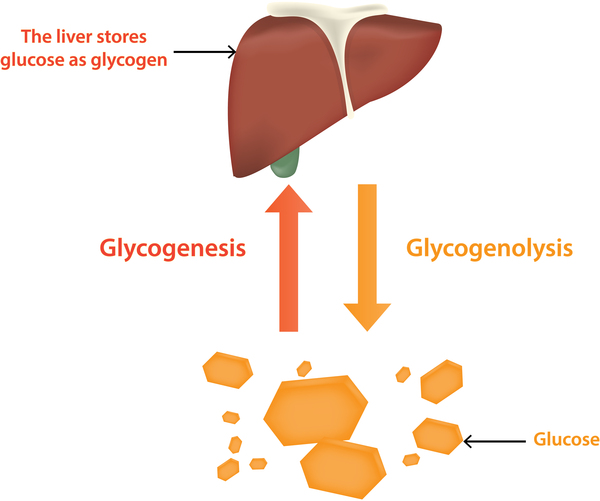
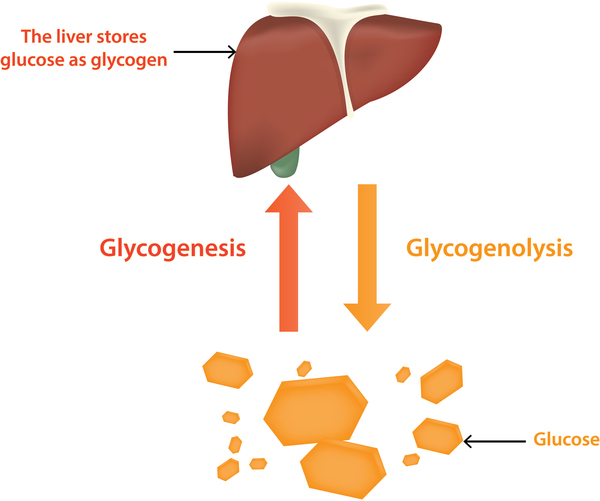
Glucose is stored as ______ in the liver/muscle cells ?
Glycogen
What are Islets of Langerhans?
Cells in the pancreas that produce hormones.
(T/F) Beta islet cells produce glucagon.
False. Beta islet cells produce insulin.
What is the human body’s ‘metabolic bank’?
Liver
What is the relationship between insulin and glucagon?
They are antagonistic hormones
What causes Type I Diabetes? Type II?
Early degeneration of beta cells (Typically childhood)
Decreased production/use of insulin
Why does diabetes cause excess urination?
High concentration of glucose in kidneys draws water out of blood
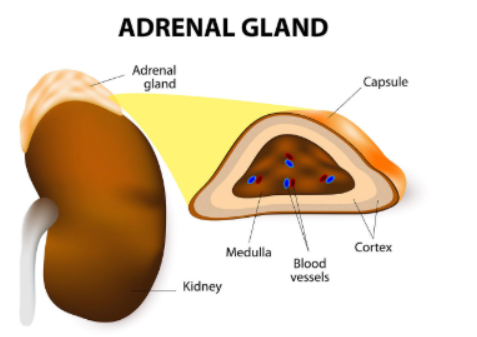
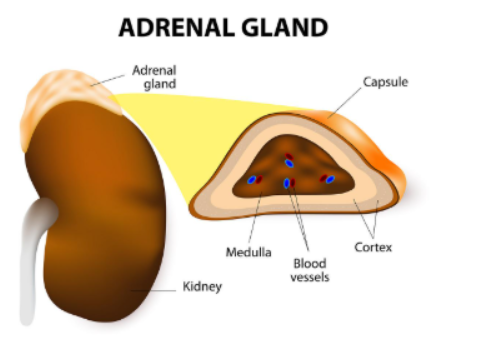
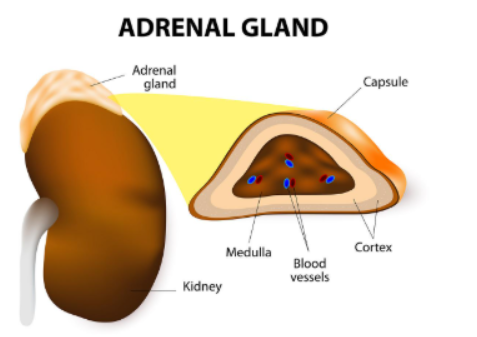
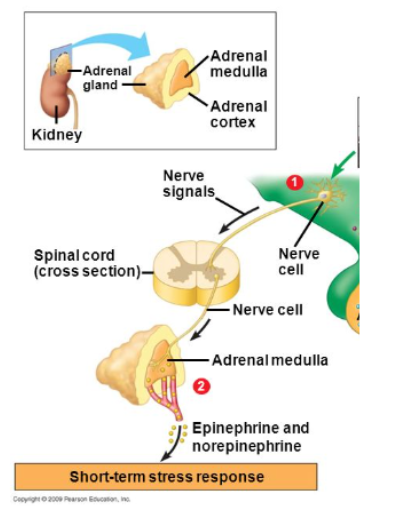
Where are the adrenal glands located?
On top of the kidneys
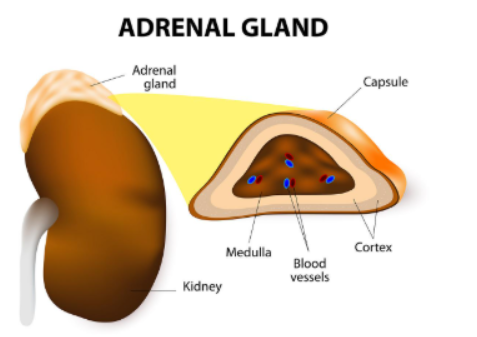
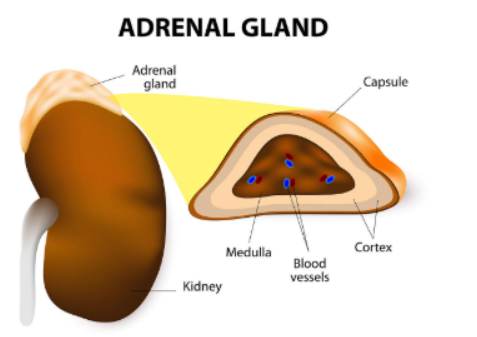
What is the adrenal medulla?
inner layer of the adrenal glands
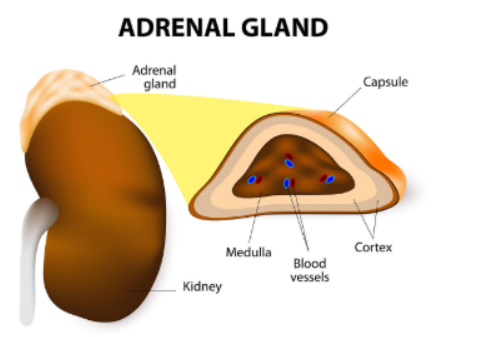
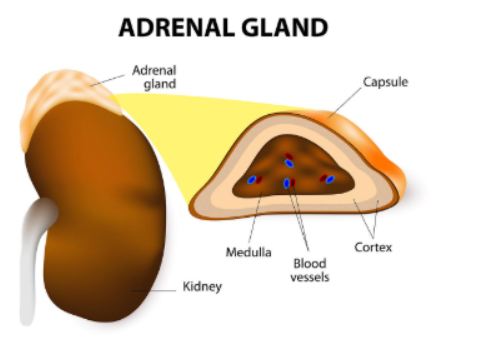
Name of the outer layer of adrenal glands
Name of the outer layer of adrenal glands
Adrenal cortex
What regulates short-term stress responses (Fight or flight)? What hormones are produced
Adrenal Medulla
Epinephrine/adrenaline and norepinephrine/noradrenaline
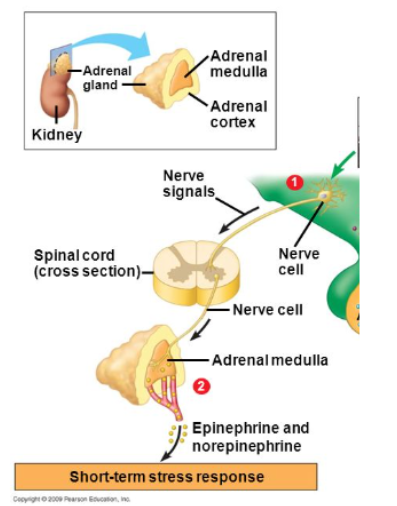
3 steps of Short-term stress response:
Hypothalamus triggered by stressor
Nerve signal is carried from hypothalamus to adrenal medulla
Signal triggers release of epinephrine and norepinephrine, which targets adrenoreceptors
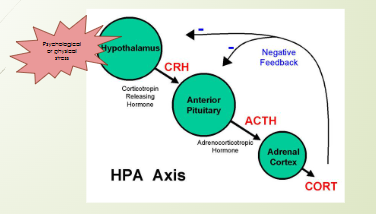
What hormones are produced during long-term stress response? What part of the body regulates its release?
Cortisol
Adrenal cortex
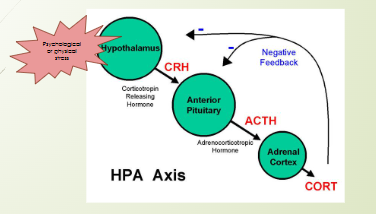
5 Steps of long-term stress response?
Hypothalamus releases CRH(Corticotropin Releasing Hormone)
CRH triggers release of ACTH from anterior pituitary
ACTH triggers release of cortisol from from the adrenal cortex
Release of cortisol triggers an increase in blood glucose levels, breaks down proteins + fats
Immune system is suppressed, inflammation reduced
What hormones help with sperm production? Where are they produced?
Androsterone and testosterone
Produced in the testes
What controls the production of hormones/sperm?
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
What does the hypothalamus secrete at puberty? What is the function of this hormone?
(GnRH) gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Stimulates ant. pituitary gland to produce and store gonadotropic hormones FSH and LH
What does testosterone inhibit? How?
LH production
Deactivates the hypothalamus
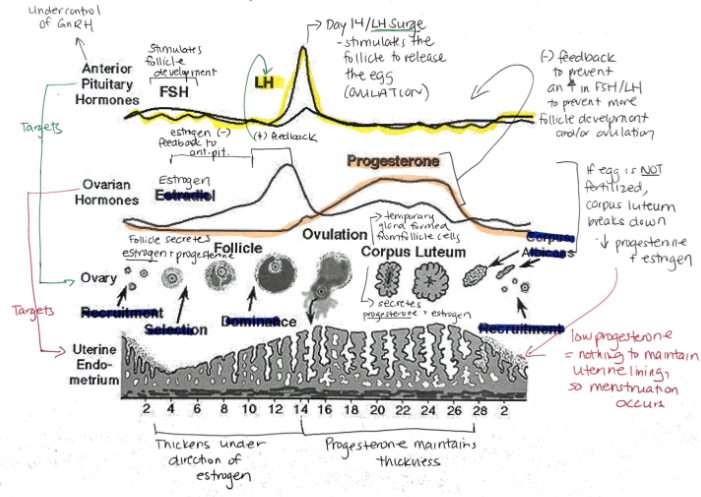
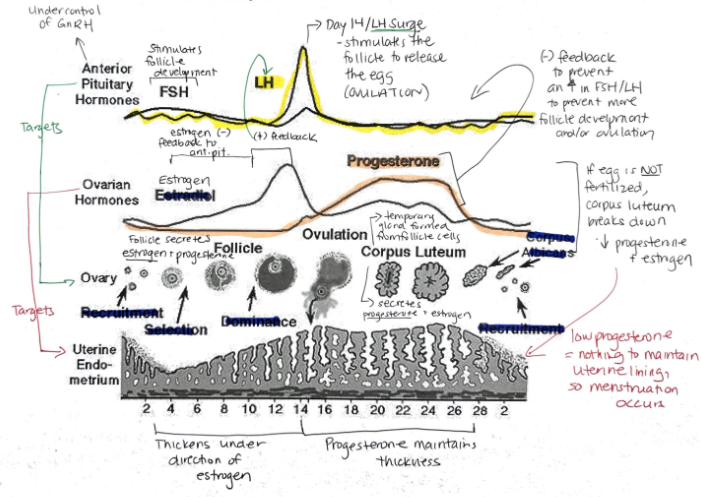
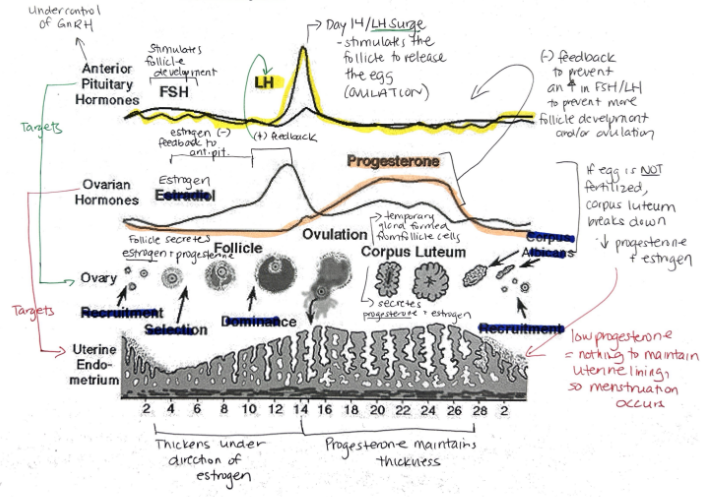
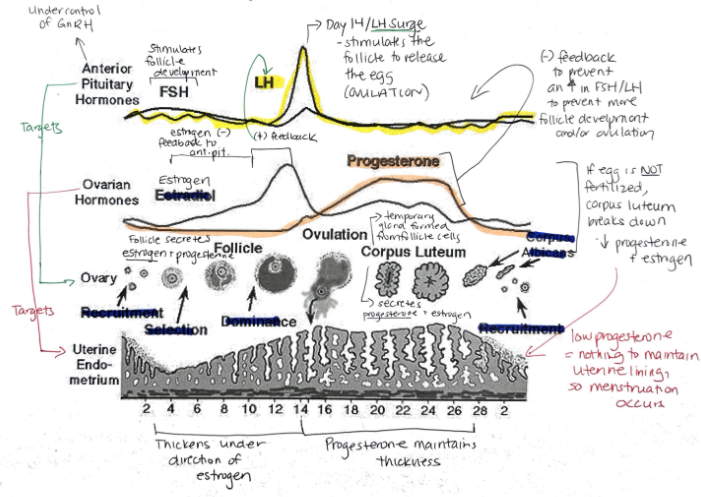
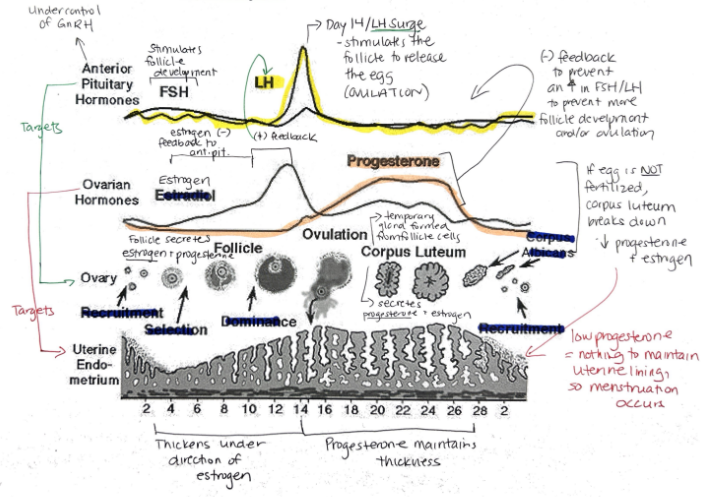
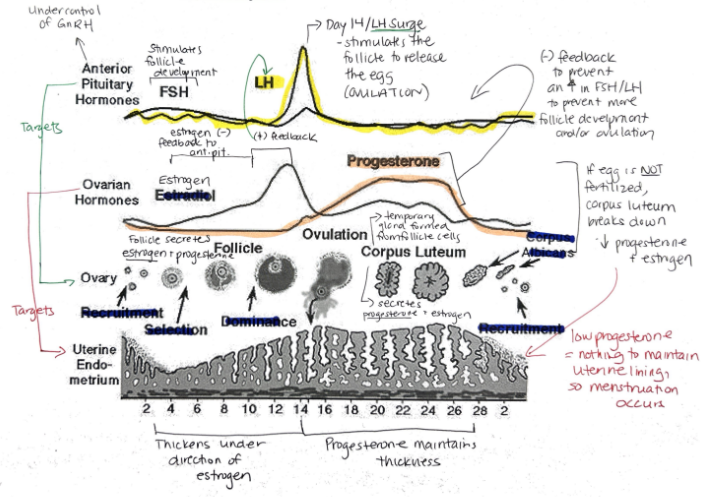
What are the female sex hormones?
Estrogen
Progesterone
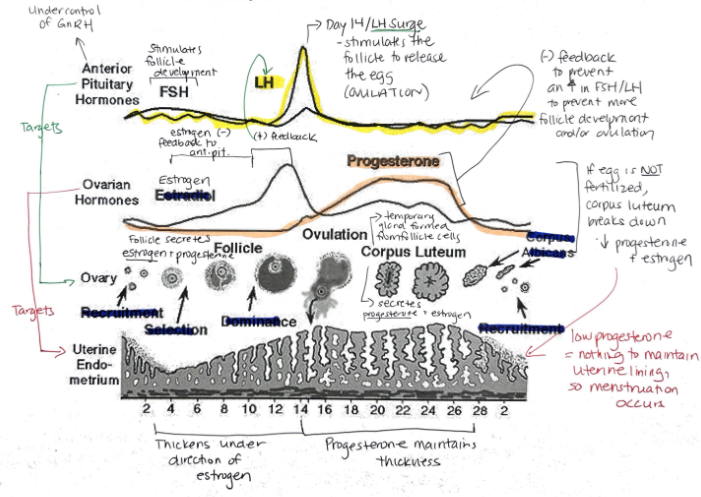
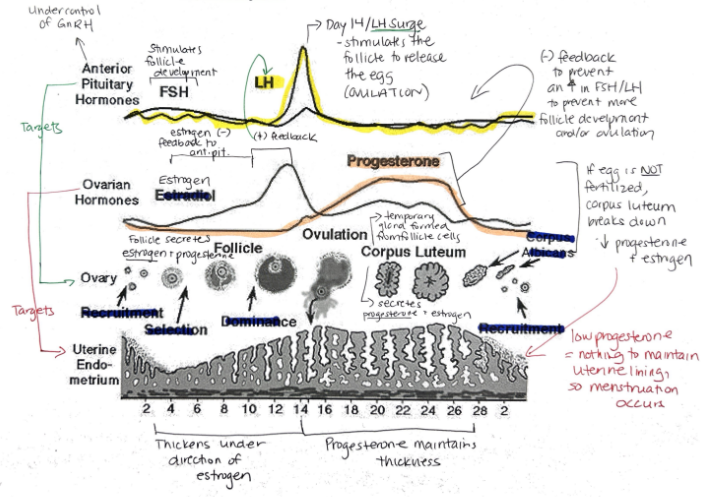
Groups of cells in the ovaries are called?
Follicles
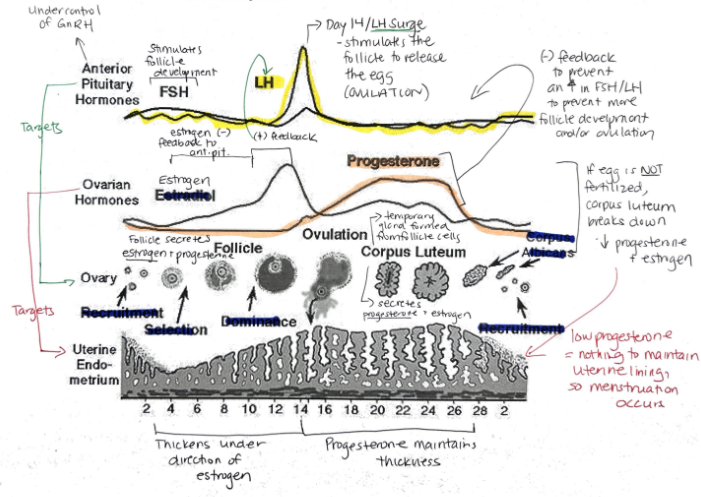
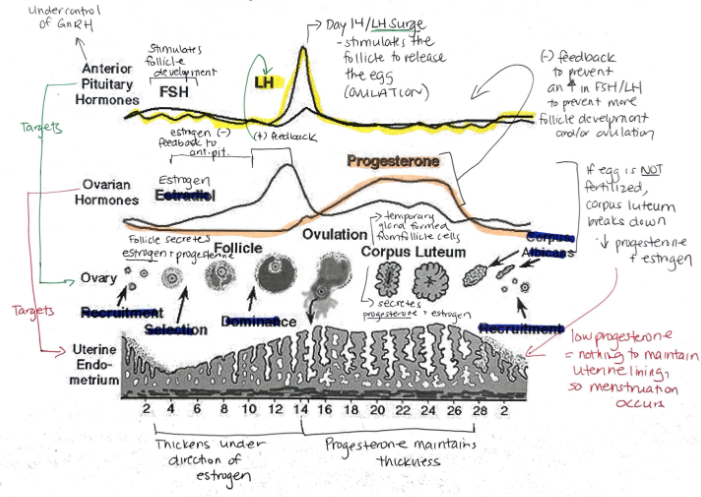
Relationship between FSH + LH and estrogen and progesterone
FSH and LH regulate control of estrogen and progesterone
Estrogen and progesterone control FSH and LH
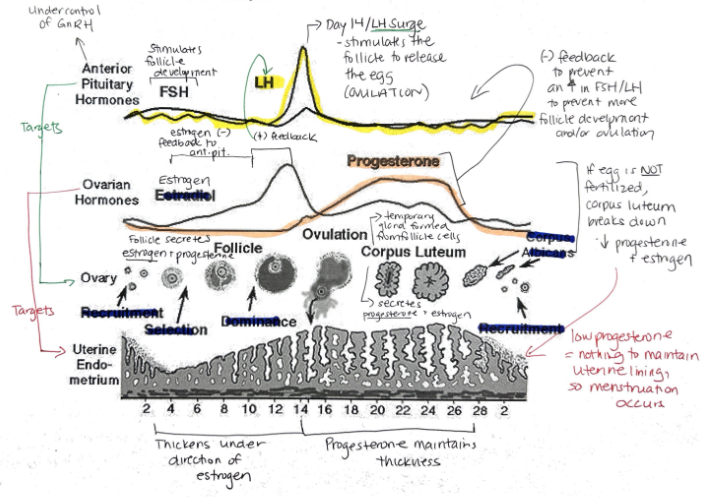
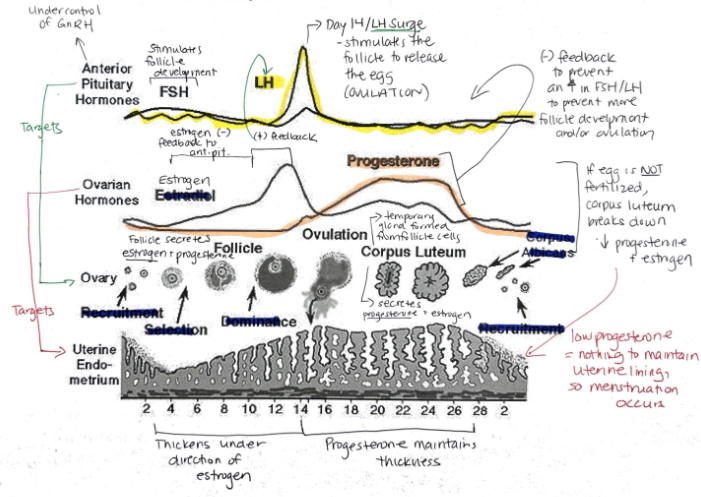
Hormone released when a fertilized egg implants in the uterine lining? What is its function?
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
Maintains endometrial lining because corpus luteum secretes estrogen and progesterone
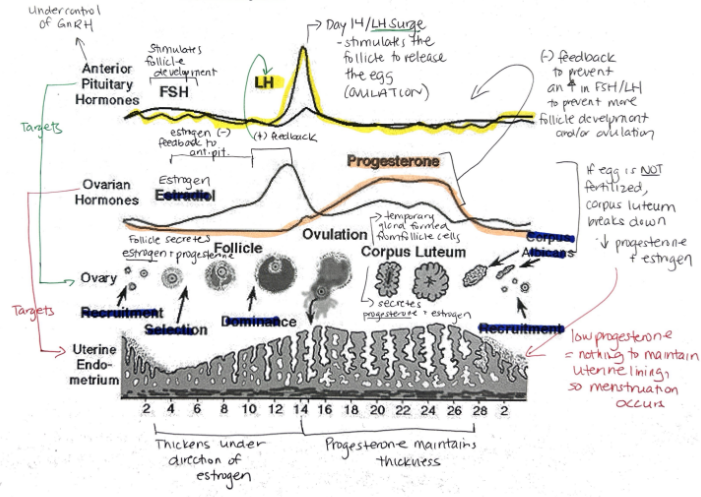
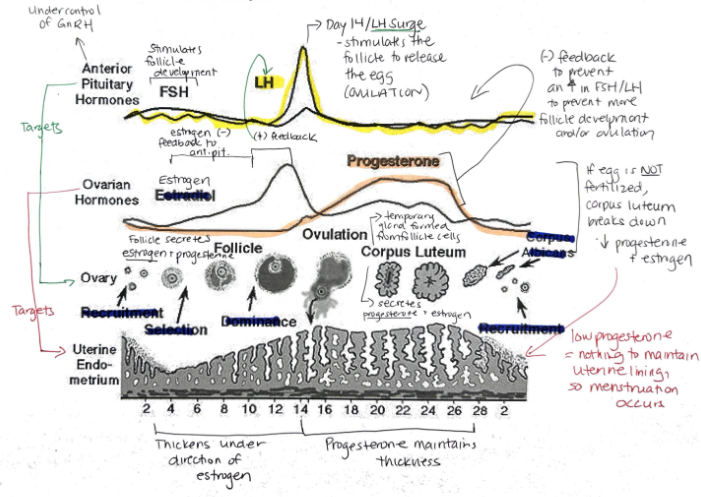
Function of synthetic estrogen and progesterone in the birth control pill?
Suppresses release of FSH, stopping follicle maturation + uterine lining from thickening + LH (preventing ovulation)
(TRH) Thyroid Releasing Hormone: Function, Target, What secretes it?
Stimulates thyroid to produce thyroxine
Thyroid gland
Anterior pituitary
(hGH) Human Growth Hormone: Function, Target, What secretes it?
Whole body
Anterior pituitary
(TSH) Thyroid Stimulating Hormone: Function, Target, What secretes it?
Stimulates thyroid to produce thyroxine
Thyroid gland
Anterior pituitary
Thyroxine/T4: Function, Target, What secretes it?
Increases basic metabolic rate/blood sugar
All body cells
Thyroid
Calcitonin: Function, Target, What secretes it?
Decreases Ca in blood, Adds Ca to bones
Blood/Bones
Thyroid
(PTH) Parathyroid Hormone: Function, Target, What secretes it?
Increases Ca level + Decreases PO4 in blood, removes from bones.
Bones + Kidney tubules
Parathyroid
Insulin: Function, Target, What secretes it?
Causes muscle/liver cells to become permeable to glucose
Muscle, fat, liver
Beta islet cells (Pancreas)
Glucagon: Function, Target, What secretes it?
Catalyses breakdown of glycogen into glucose in liver, which is released into blood.
Cortisol: Function, Target, What secretes it?
Stimulates breakdown of protein, releases amino acids that are converted to glucose by liver, raises blood sugar
Liver, fat, muscle
Adrenal cortex
Progesterone: Function, Target, What secretes it?
Prepares uterine lining for implantation of egg
Prevents menstruation during pregnancy
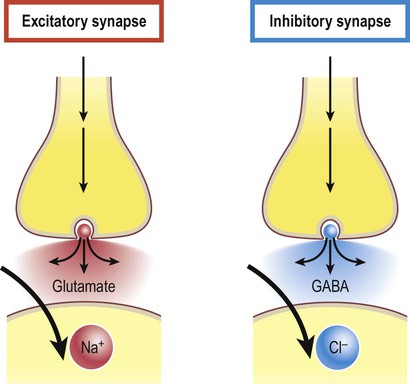
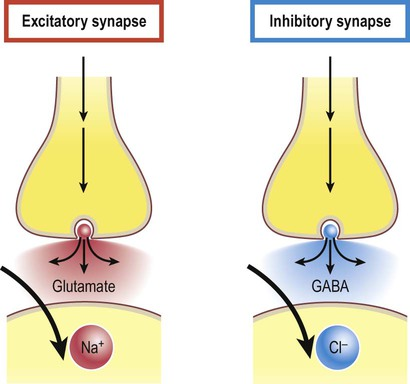
EXCITATORY SYNAPSE
The binding of a neurotransmitter to postsynaptic neuron OPENS Na+ gated channels
Na+ Diffuses INTO postsynaptic neuron
Depolarization occurs, less stimulus required to achieve action potential because of an increase in charge
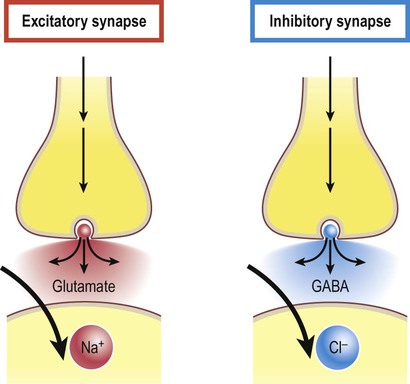
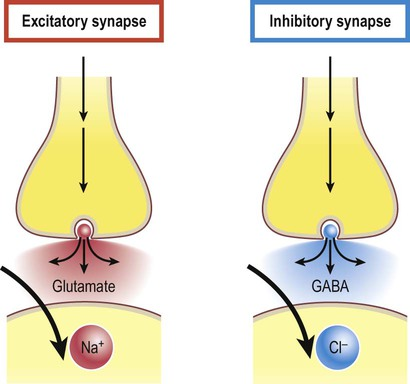
INHIBITORY SYNAPSE
Binding of neurotransitter to postsynaptic neuron opens K+ gated channels
Inside of neuron becomes MORE negative, hypolarizing the membrane and making it difficult to reach action potential
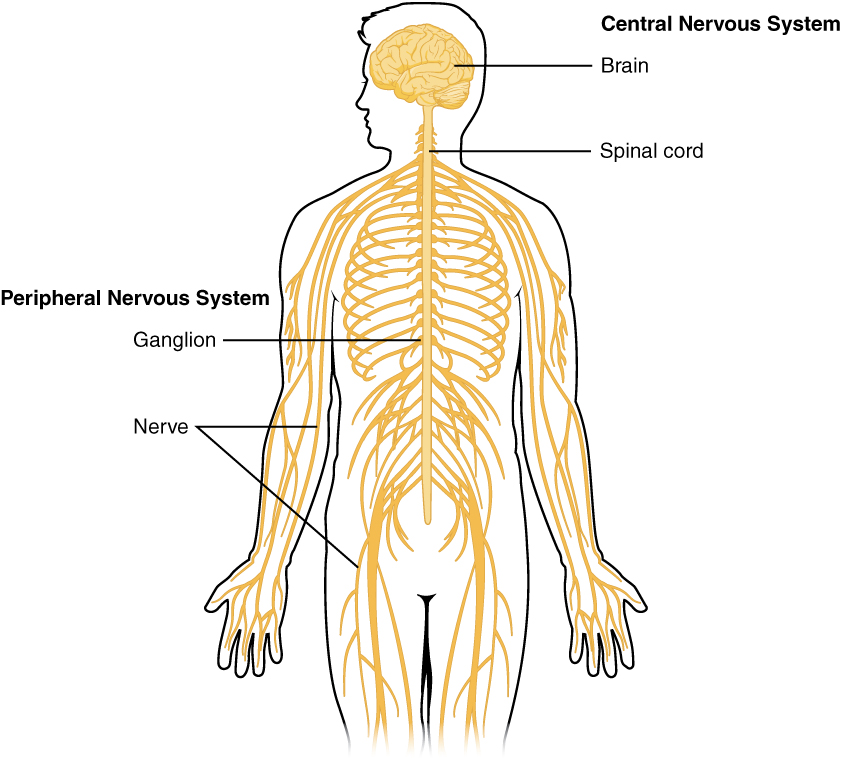
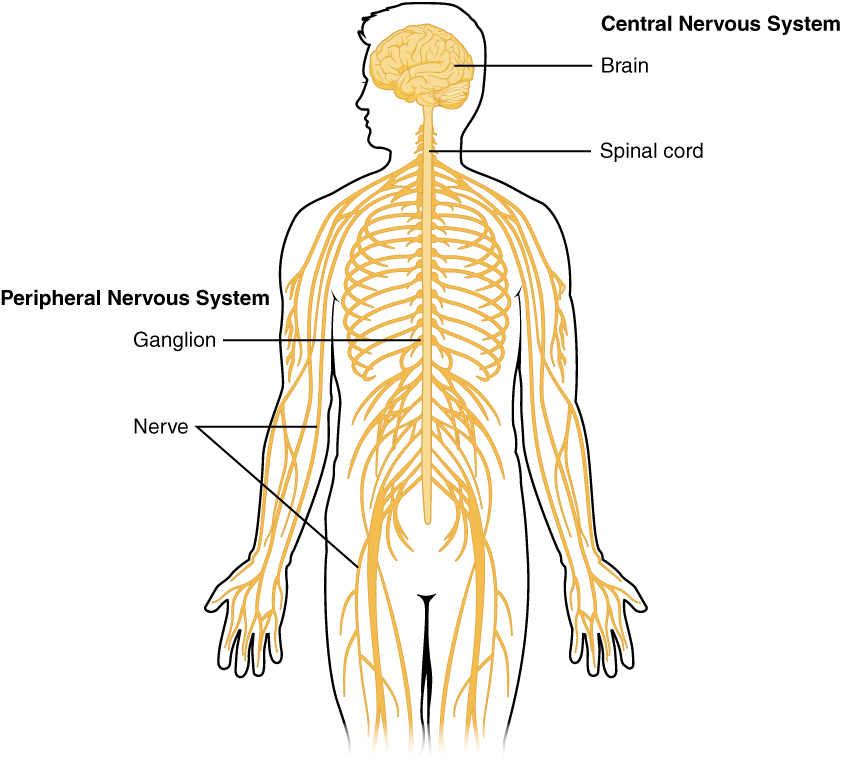
Which nerves comprise the Central Nervous System(CNS)
Nerves of brain
Spinal cord
2 Types of nerves in the Peripheral Nervous System(PNS)
Somatic
Autonomic
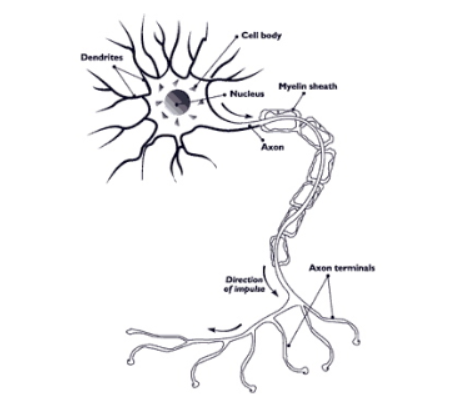
2 Types of cells in Nerve Tissue
Neurons
Glial cells
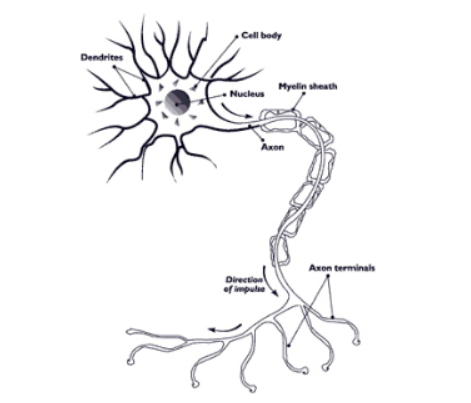
In which direction do neural impulses travel?
Dendrite to axon
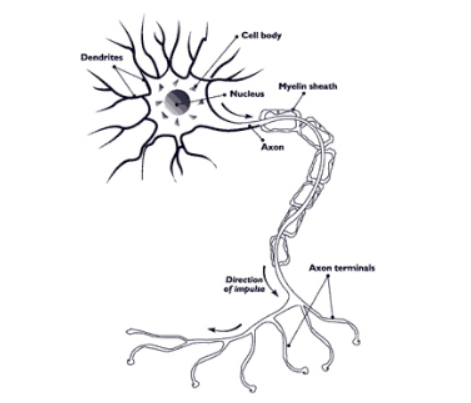
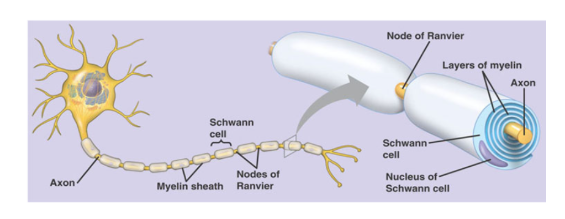
What is a myelin sheath?
Fatty protein that surrounds + insulates SOME axons
Formed by Schwann(Glial) cells
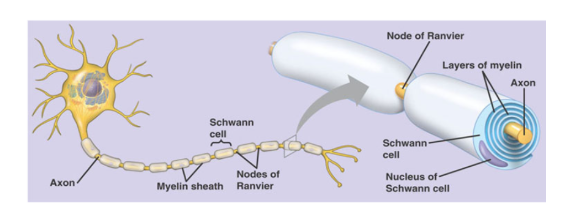
Name for spaces between segments of myelin sheath?
Nodes of Ranvier
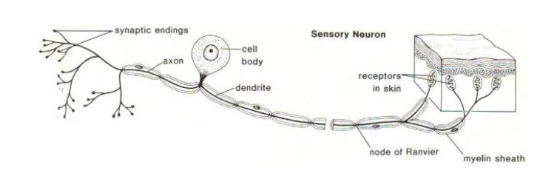
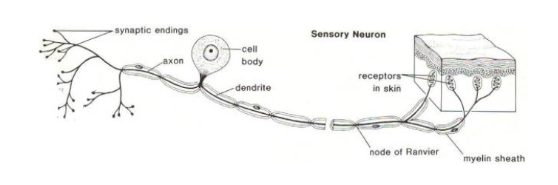
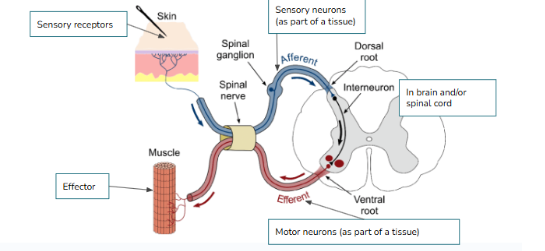
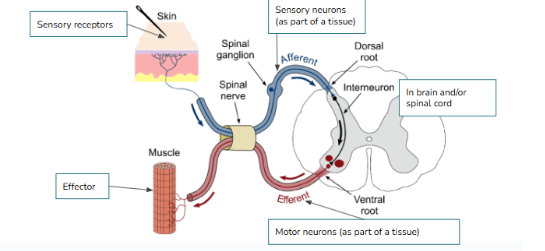
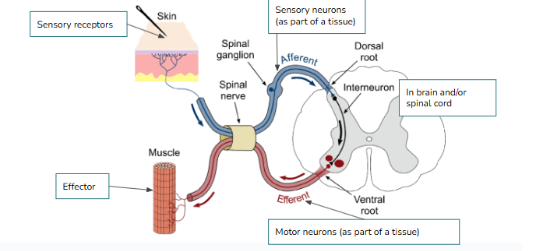
What type of neuron is pictured below? Function? Location?
Sensory/Afferent neurons
Sense + Relay information from environment and organs to CNS
Clusters found outside spinal cord
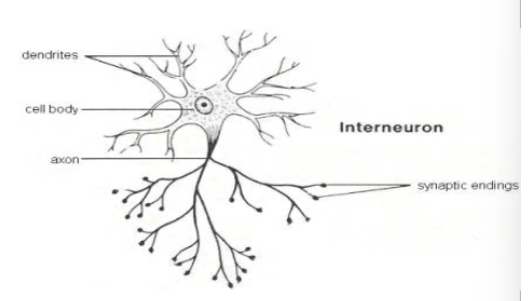
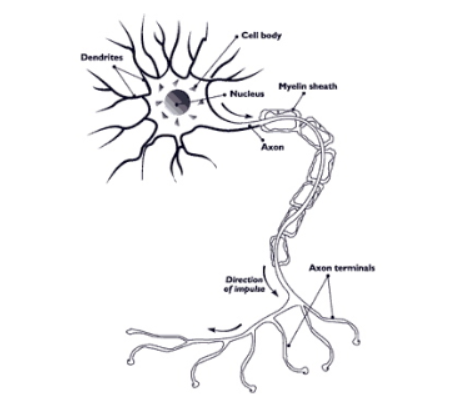
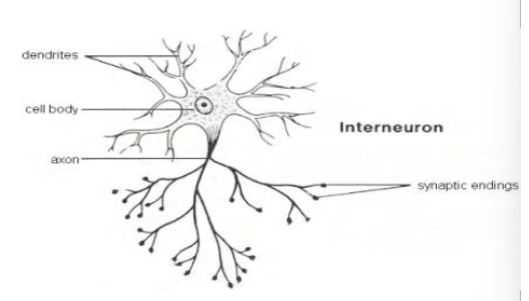
What type of neuron is pictured below? Function? Location?
Interneurons/Association neurons
Interpret stimuli, connect incoming (afferent) to outgoing (efferent) neurons
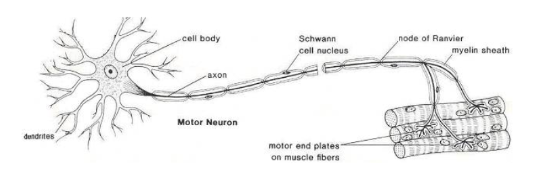
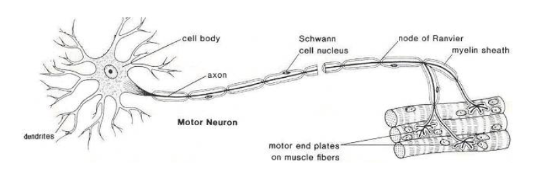
What type of neuron is pictured below? Function?
Motor/Efferent neuron
Relays information to effectors (Muscles, organs, glands)
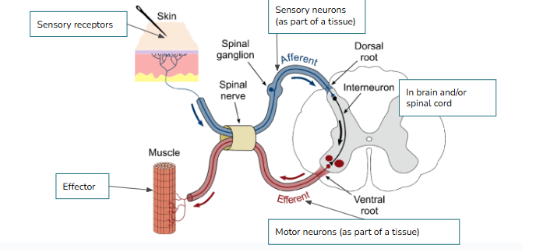
(NEURAL PATHWAY) Put the following in order:
Sensory (afferent) neurons, motor (efferent) neurons, Sensory receptors, Interneurons(brain/spinal cord), effectors(gland, muscle, etc.)
Sensory receptors → Sensory (afferent) neurons → interneurons (brain and/or spinal cord) → motor neurons (efferent) → effector (gland, muscle, etc)

What creates electrochemical messages sent by neurons?
Movement of ions across neural membrane
Under direction of voltage-gated ion channels

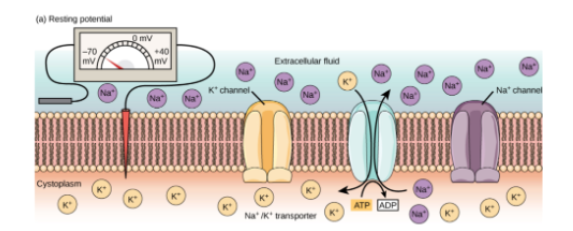
What’s resting potential? Where are high concentrations of K+ and Na+ ions found during resting potential? What's the approximate potential difference of a resting nerve membrane?
(Electrical potential inside neuron) - (outside neuron)
High K+ INSIDE cell
High NA+ OUTSIDE cell
State at which there is no net movement of K+
-70 mV
What is a voltage-gated channel?
A membrane channel that opens and closes depending on the voltage surrounding them
What is the action potential? What is the AP value when a nerve is excited?
Action potential
+40mV
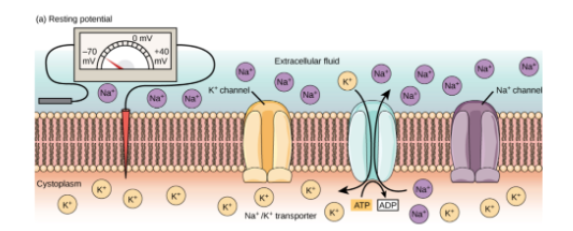
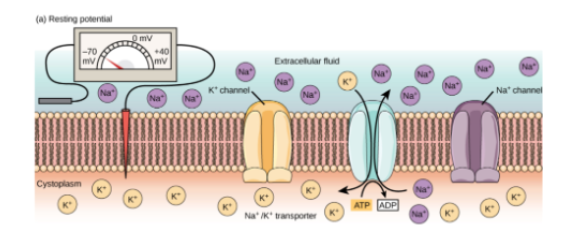
Which gated channels are closed @ resting potential?
Na+ Channels
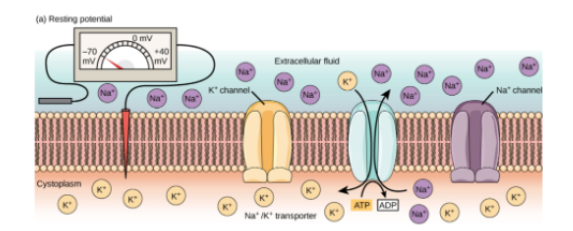
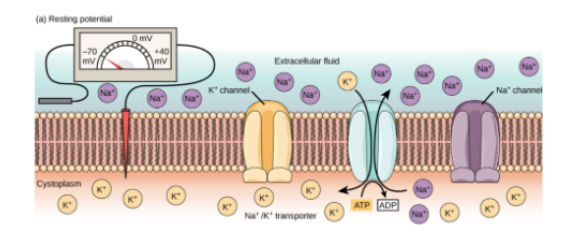
After K+ diffuses outside the cell during resting potential, why are K+ ions attracted back into the cell?
Inside of cell has negative proteins.
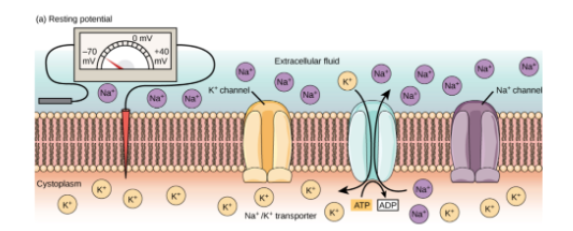
What does it mean when a membrane is POLARIZED?
Uneven distribution of + charged ions inside/outside of nerve cell creates an electrochemical charge
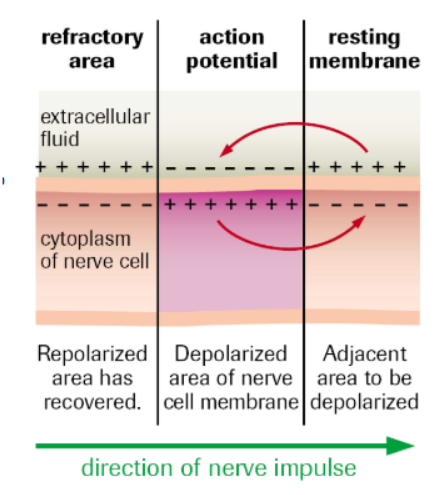
Process of depolarization
Stimulus disturbs plasma membrane on dendrite, Na+ channels OPEN
Na+ diffuses into neuron, more Na+ channels open as concentration of Na+ gets higher (At around -50 mV, the rest of the channels open)
When stimuli is above THRESHOLD level, a response is produced.
Na+ rush into the cell, potential becomes very positive (Peak of action potential)
Neuron is DEPOLARIZED
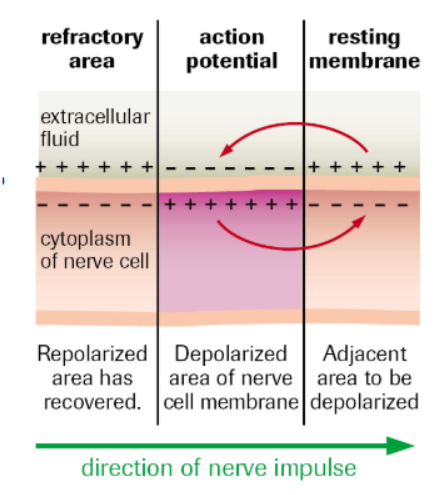
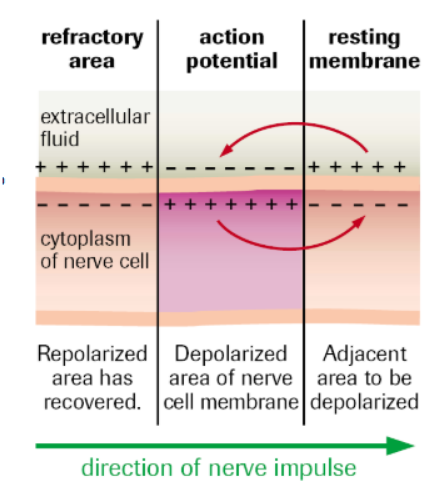
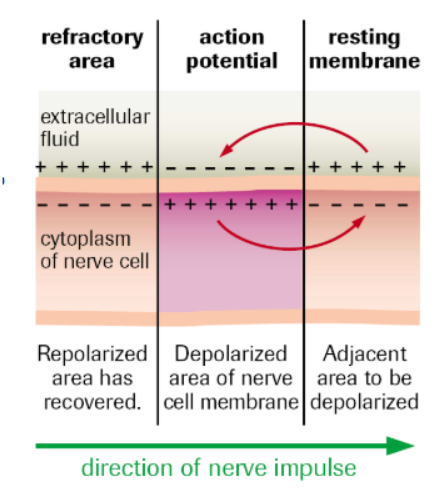
Process of Repolarization
At approx. +40 mV, Na+ channels close, K+ channels open.
K+ ions flow out of cell, inside becomes more negative
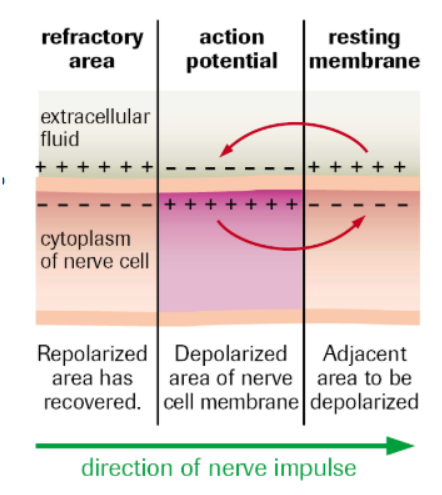
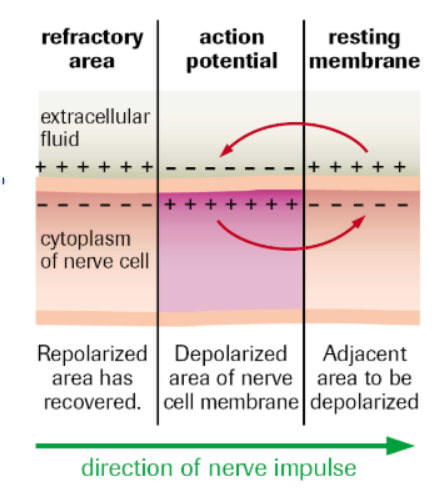
What is the refractory/hyperpolarization period? What restores resting potential? Purpose?
When the rapid release of K+ ions causes membrane potential to dip LOWER than RESTING potential
Sodium-Potassium pump transports 3 Na+ out, 2K+ in
Ensures action potential moves along the neuron membrane in the correct direction (Nerves cannot be activated until resting potential is restored).
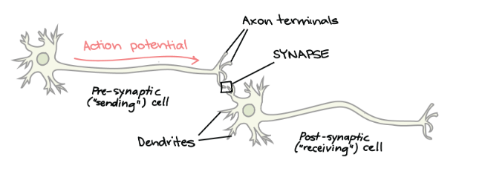
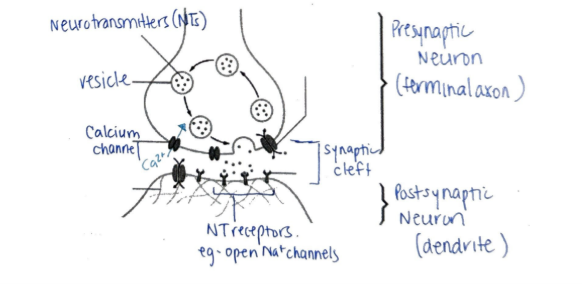
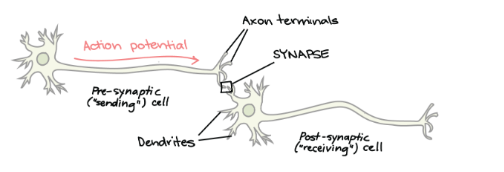
What is a synapse? How does it work?
The point of communication between two neurons/a neuron and effector.
Impulse travels down axon > NTs released from PRESYNAPTIC NEURON > NTs diffuse across SYNAPTIC CLEFT > POSTSYNAPTIC neuron is depolarized.
Sacs that contain neurotransmitters found in the end plates of terminal axons.
Synaptic vesicles
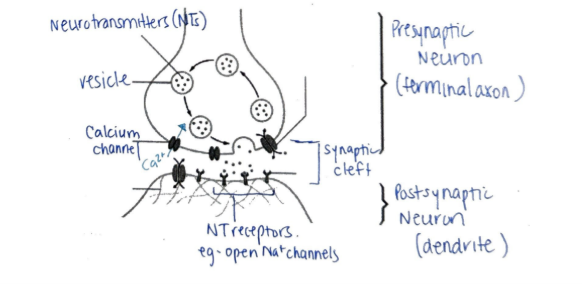
During excitatory synaptic transmission, the action potential arrives at the presynaptic neuron, causing voltage-gated _________ channels to open. __________ ions then diffuse into the cell, causing synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters via ___________. These neurotransmitters cross the _______ cleft through __________ and bind to _________ channels on postsynaptic membrane. Na+ rushes into postsynaptic neuron, depolarizes membrane potential to threshold and action potential fires
Calcium, Calcium, Exocytosis, synaptic cleft, diffusion, sodium