Intro to digital marketing - Chapter 6: Paid search marketing
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Paid search marketing
When a search engine charges a webmaster after someone clicks on their link
Why do firm’s do paid search marketing?
Search engine advertising drives more NEW website traffic than any other online advertising method
No other advertising method enables a more precise targeting of potential customers.
The site owner can measure the effectiveness of search engine advertising more reliably using DATA
Google Ads (advertisers bid to get ads shown on SERP)
How are Google ads shown?
Google search
Complete ad list with all bidders
Auction where bids and quality’s evaluated
Results where winning ads are ranked and displayed
What factors do advertisers select when it comes to showing their ad?
The entered search phrase
Other traits of the search (e.g. the searcher’s location, device used, etc)
What sort of people do companies want to advertise to?
People who show an interest that lines up with the offering provided by the company
Exact match
A search-up phrase that’ll match an exact keyword and close variants such as misspellings, synonyms, abbreviations, etc that’ll waste little money advertising to uninterested searchers
How to use exact match
Place brackets around [a keyword]
Broad match
Listing a keyword with no modifying characters, which leads to the ad showing up for any relevant searches to their products
Phrase match
Tells Google to show ads on searches that have the include the keyword, close variants, or other terms with a similar meaning
How to use a phase match
Put quotation marks around “a keyword”
Negative keyword
Ensuring an ad won’t be displayed is a certain word is used, regardless of what’s searched up
e.g. If a firm doesn’t sell men’s dress shoes, then dress will be entered as a negative keyword to make sure the ad won’t show up if dress is used
Other selection factors
Geography
Device type
Timing
Language
Search intent
The why behind a search
e.g. to learn something, make a purchase, looking for a site
Searcher’s flow
Search box
Search page
Landing page
Conversion
How to search for yourself
Take on the role of a customer, sit at a computer, and think about what you’d search and what keywords you’d put in
Google Keyword Planner
Provides suggestions on relevant keywords as well as their searches, competition, top of page bids, etc
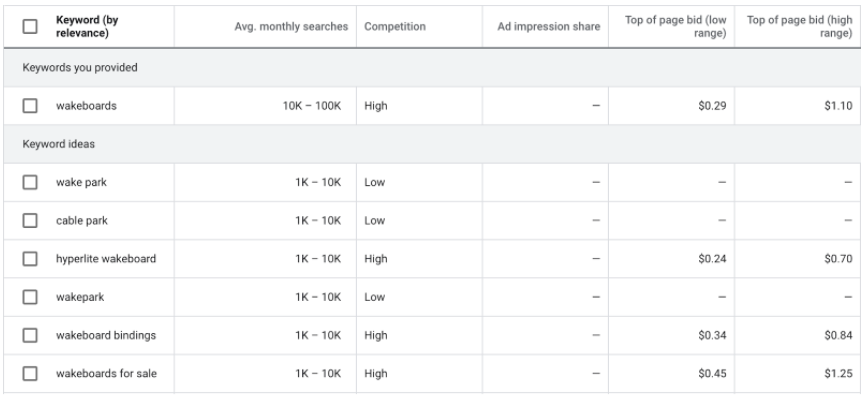
The 4 things to consider when choosing keywords to use in search advertising
Searcher intent
Search volume
Level of competition
Suggested bid
Branded keywords
When a firm includes its name on a search query
e.g. Best Buy Tv
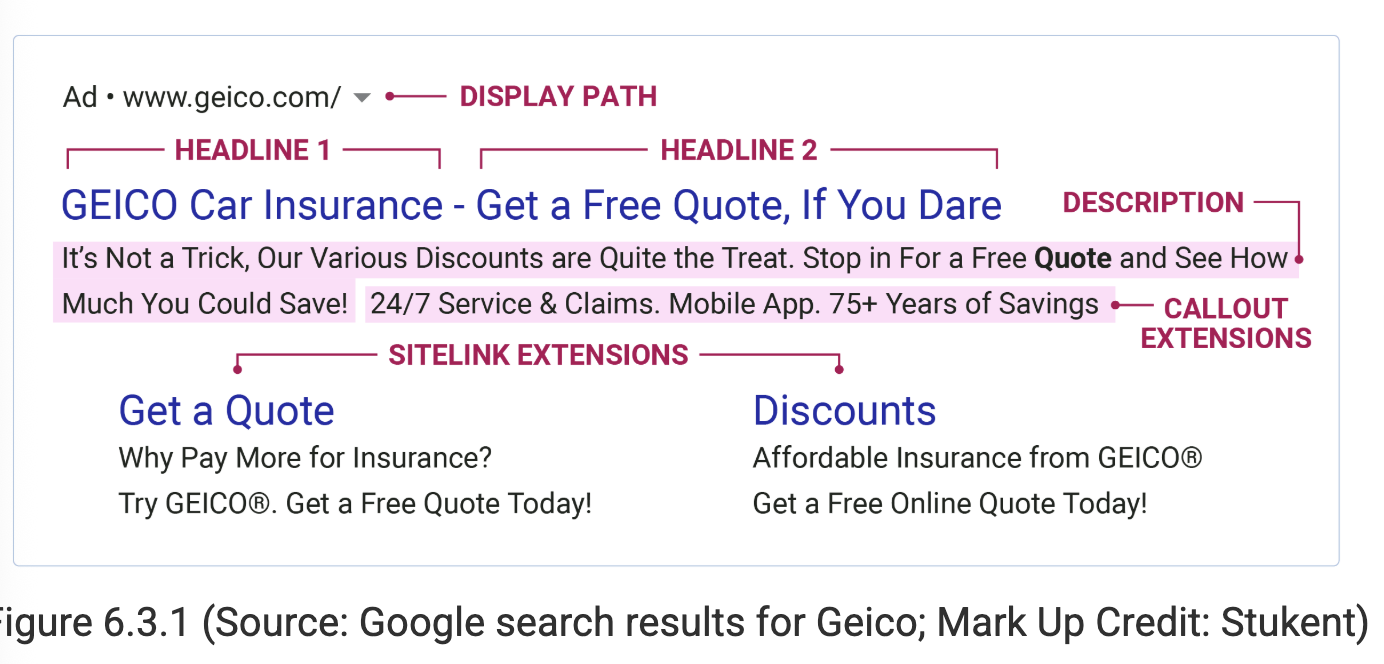
The 5 key elements of ads in search results
Final URL
Headlines
Display path
Descriptions
Ad extensions
How does Google evaluate ad quality (1-10)?
Expected CTR (effective ad copy)
Ad Relevance (use of key words being searched for)
Landing Page Experience (fulfills expectations)
Higher quality yields a higher ranking
How does Google determine what you pay?
Ad rank of the person below you divided by quality score + $0.01
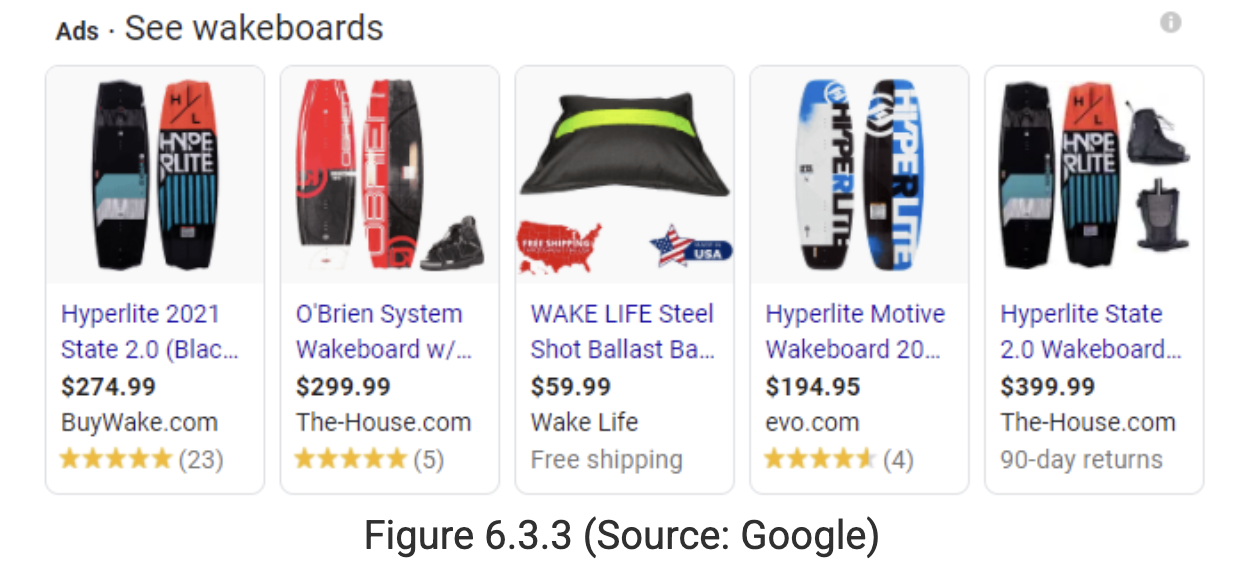
Shopping ads
Ads that display product images and prices as opposed to text. They can show up on different areas of the webpage
Google maps ads
Text ads that can be displayed when someone is searching on Google Maps, and can be set up by connecting a business’s local listing on My Business with its Google Ads account
Call only ads
Makes the number of the business the main content of the ad
Call extension
An additional line attached to a usual search ad that allows users to click to make a call
Dynamic search ads
Lets advertisers turn over some control of their search ads to Google for it to pull info about the advertiser’s products to show on relevant search results
Keywords for relevance
When keyword usage and bolding improve click rate(s)
What can an effective headline and description with good grammar do?
Make a good impression to visitors
Unique value proposition (UVP)
Something that sets a site apart from other sites
e.g. Geico offering 24/7 service, State Farm having fast and free quotes
Call to Action (CTA)
The last push to get the consumer to click on an ad
e.g. “Get a free quote”, “Switch and save”, etc
Ad rank
The ad locations for searches on any given keyword; is determined by bids on a keyword
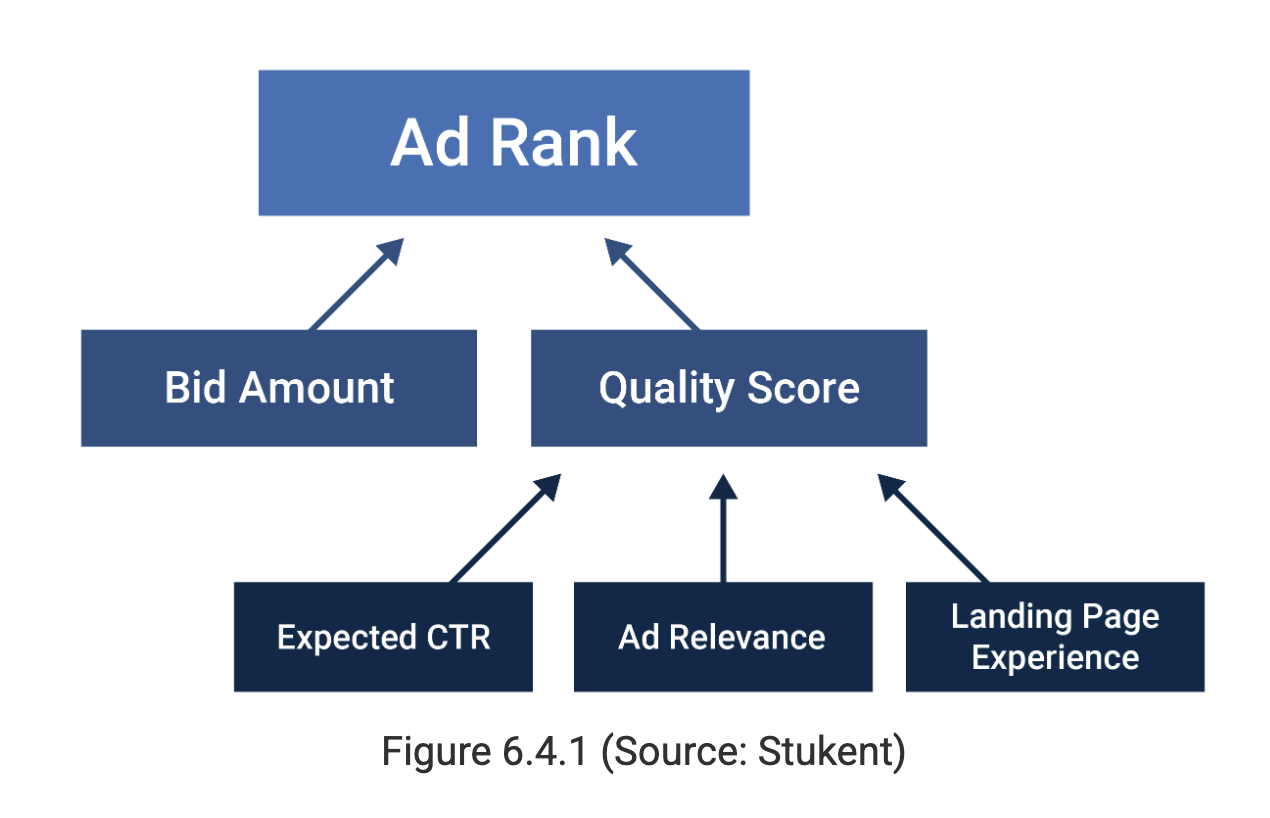
Quality scores
A measurement of how relevant the ads, keywords, and landing pages are; higher quality scores can lead to lower prices and better ad positions
The criteria that affects quality score
Expected CTR
Ad relevance
Landing page experience
Cost per action
The amount an advertiser is willing to pay per conversion
e.g. An advertiser with 4% conversion rate who bids $20 cpa would essentially be submitting a cost per conversion bid $0.80 ($20×0.04)
Benefits of automated bidding
Google’s knowledge of keyword performance traits will be applied to campaigns
Performance will constantly improve as Google learns which keywords and traits lead to higher conversion(s)
Prevents common errors caused during manual bidding
Drawbacks of automated bidding
Hinders learning about the search market
Campaigns will grow unfavourably if the wrong bid strategy is chosen
Large amounts of data are needed in order for improvements to occur
Impressions
Every appearance of an ad on the search results page
Click
Each time someone clicks on an ad in the results page
Click-through rate (CTR)
The percentage of impressions that get a click
e.g. 60,367 impressions got 2,101 clicks for a CTR of 3.48%
What does Cost per click (CPC) determine?
Determines whether the search ads are profitable
Cost
The cost per click times the number of clicks
e.g. $0.83 per click times 2101 clicks equals a cost of $1742 for a keyword
Conversions and profit
Multiply the profit per sale by the number of conversions
e.g. If one generated 140 conversions with $20 in profit each, they would’ve gained $2800 in profit from a $1742 cost, thus making a profit
Conversion rate
The percentage of visitors who convert
e.g. 140 of 2101 visitors converted, leading to a conversion rate of 6.66%
What should an advertiser do if they suspect a lower than average conversion rate?
Make sure the ad and landing page are relevant to the searched keyword
Make sure the ad and landing have compelling and competitive offers
Ensure broad match keywords aren’t attracting traffic from irrelevant sources
Stop use of the keyword if all else fails
Return on Advertising Spend (ROAS)
(Total Profit/Total Adspend) x 100
What’s the typical click through rate for ads across multiple industries?
Between 1% and 4%
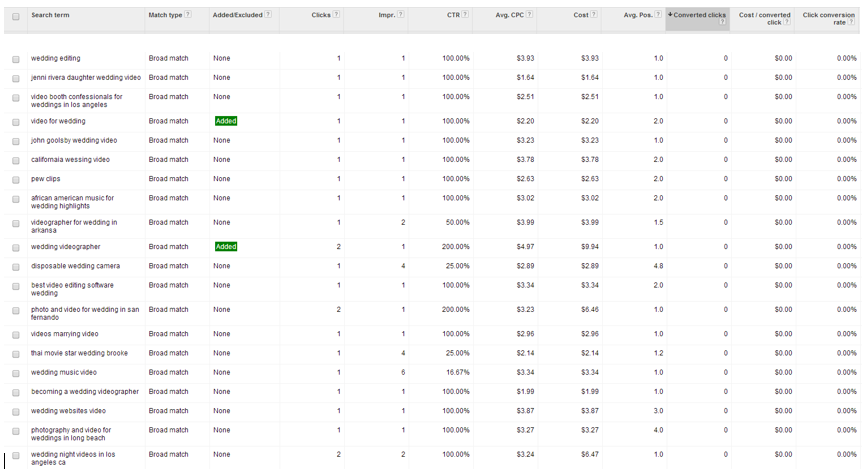
Search query reports
Shows the searches that resulted in a click; it’s valuable as it shows where Google chooses to display an ad
Poor mobile optimization
When sites not optimized for mobile usage lead to lower conversion rates from mobile users
Low purchase intent
When users research a product or look for basic info, thus makes more sense to adjust mobile bids to be lower to save money on searches with unlikely conversions
Alternate mobile conversion
When a user researches a product they like on their phone, but takes the process to their computer to convert from there
Google Ads Account structure
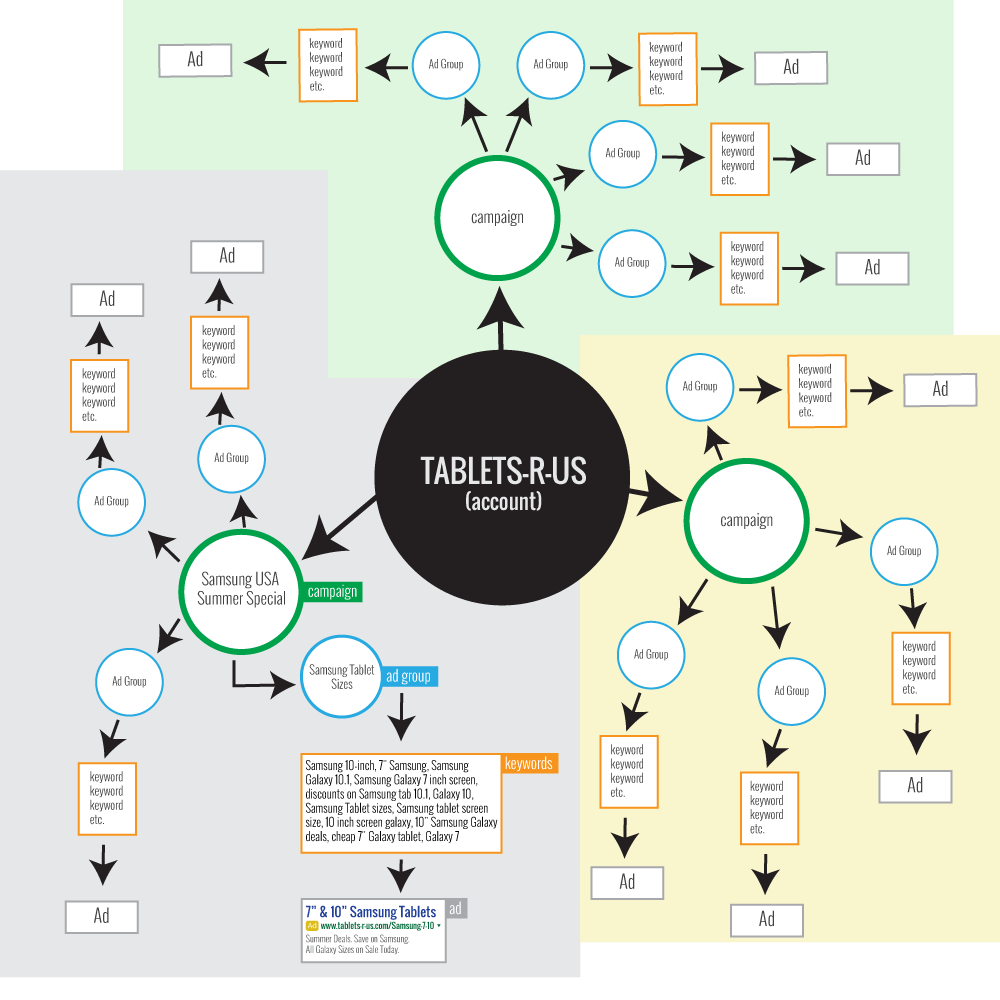
Account
Advertisers who add their credit card info to pay for the clicks
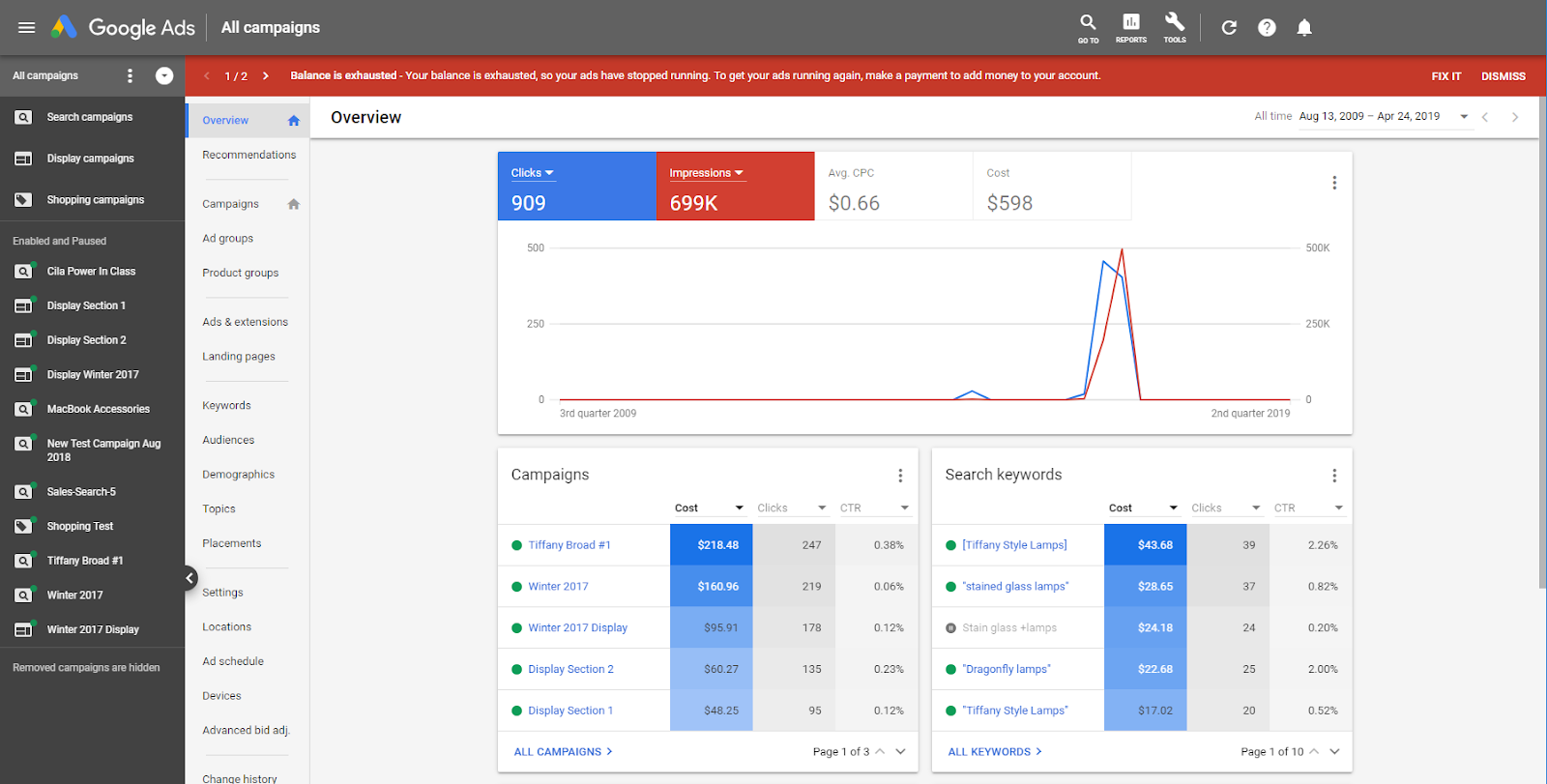
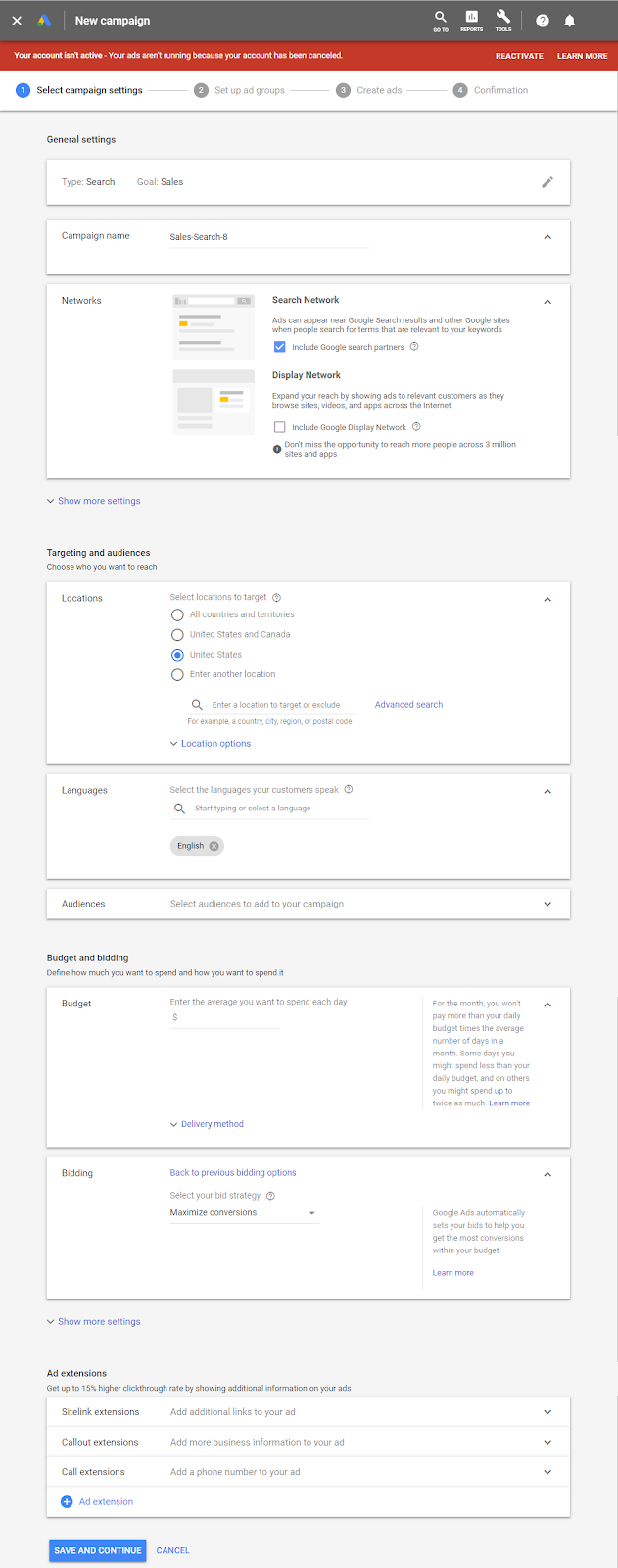
Campaign
An easy-to-remember name, as well as the type of campaign, which allows advertisers to pick which advertising network they’re trying to reach
Display network only
A campaign type for running text and banner ads across Google’s ad network and its huge list of sites that run Google’s ads on their site
Search network with display select
Allows text ads to display on keywords a company chooses in Google SERP
Shopping
A campaign type that allows an advertiser to separately manage its Google Shopping ads
Ad extensions
Ad extensions and other adjustments which are made at the campaign level; the structure of successful campaigns can be copied and reused, but not whole ads and keywords
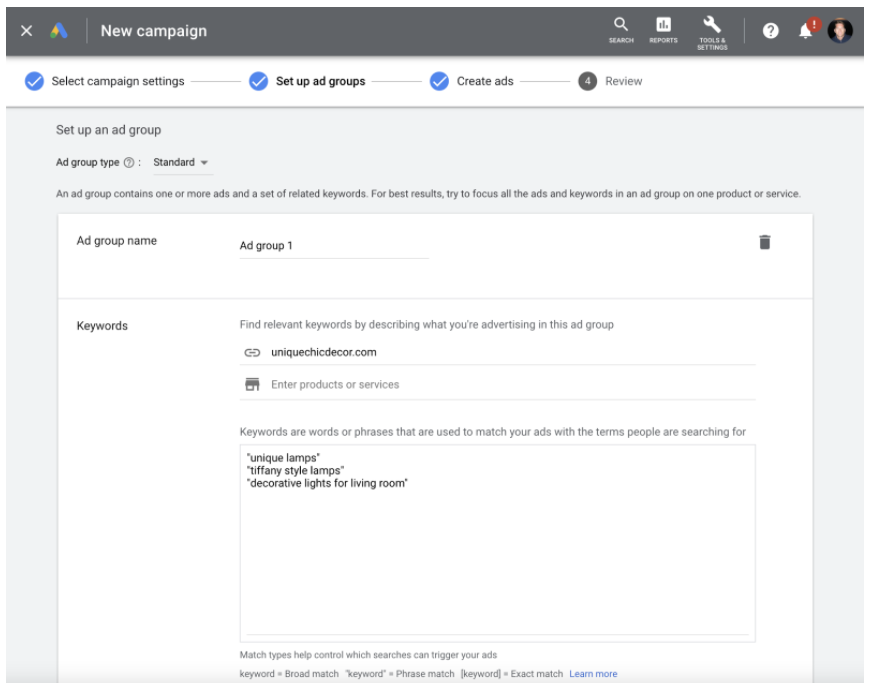
Ad group
The user picks keywords at the Ad group level and can specify the bid amounts for manual CPC strategies only
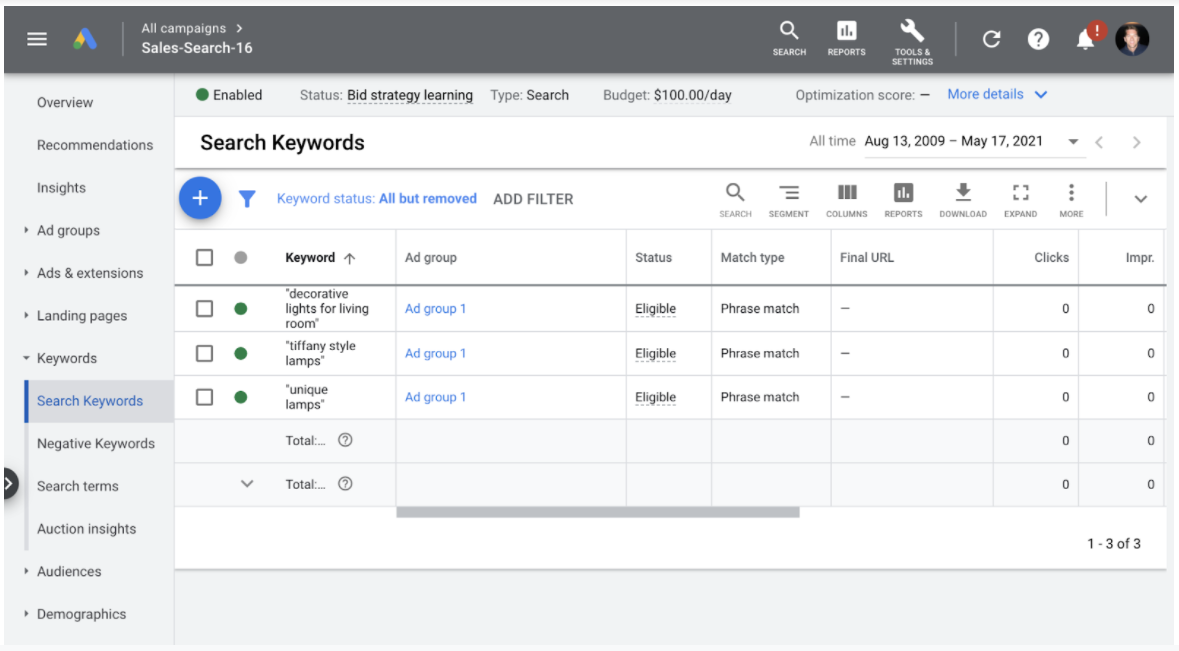
Keywords
Keyword bids, match types, and data can only be managed at the campaign and ad group levels
P.P.C
Pay Per Click