GMetrix Networking Unit 2 - Network Infrastructures
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Learn about types of networks, which standards certain networks use, and which topologies are being used.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
Topologies are…
both physical and logical, and you can have differing topologies in a network
LANs - Local area networks (type of network)
Networks that are generally confined to a single building or even a single area of a building
LANs share…
common resources, such as servers, printers, and to an extent, workstations
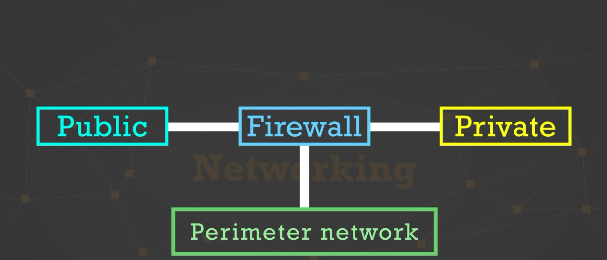
DMZ
This is a perimeter network and one type of LAN
Perimeter networks like DMZ…
hold devices that need to be seen by both the public and private security zones of a network
Perimeter networks tend to include…
web servers, email servers, and proxy servers
Back-to-back configuration
When a firewall is on both sides of a perimeter network
Example of possible configuration for perimeter network
Three-leg perimeter configuration: A single firewall with all 3 connections to security zones, each leg is connected to a single firewall
LANs will have…
private IP addresses, which are reserved address ranges for local use
If an IP address starts with 10 (10.0.2.46)…
then it is a private IP address, meaning that it is not routable over a public network, like the internet
Another range of private IP addresses includes…
if an IP address starts with 192.168.__.___
IP addresses that start with the numbers 172.16 through 172.31 is also…
another range of private IP address
You can often see the same IP addresses being used…
on different LANS. This is the whole purpose of private IP addressing. These addresses can be reused, and prevents public IP address from having to be used on every device.
Any IP address starting with 127 is…
a private IP address. 127.0.0.1 between 127.255.255.254 are the private loopback addresses are used to refer to one’s own computer (internal use, not connecting to external networks)
When using the command prompt tool and you ping 127.0.0.1
You can ping your own network card to see if it’s working. A response means that the network card is working, so any network connectivity issues are not a result of a bad network card.
APIPA
Automatic Private IP Addressing. The address range is 169.254.
APIPA is used when…
a device cannot obtain an IP address through a DHCP server, which is a server that gives out IP addresses to devices
If an IP address is in the range 169.254
the device cannot obtain an IP address from a DHCP server, so it can’t connect to any devices except those in the same 169.254 address range.
Floor plan example for VLANs
This is a common situation, in that you need to have multiple physical areas to be on the same network
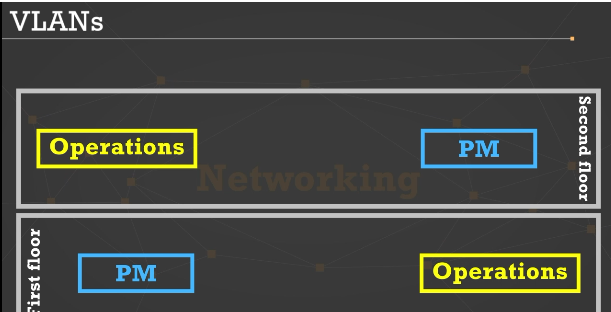
VLAN (Virtual LAN)
Logical networks that can help connect all of the operations people to each other and all the project management people to each other (if there aren’t that many total users)
Connect the VLANs by…
allocating some of the switch ports to operations and then the rest to project managers. This creates two logical networks in one physical area.
If you want to add more physical switches as needed, use trunk ports between switches…
to logically segment the network
To allow communication between VLANs…
use a router or a switch with router capabilities (known as a multiplayer switch)
When building a local area network, there are 2 main types of LANs
Wired LAN and wireless LAN
Wired LAN
Computers and other devices mainly use Ethernet cables to connect to switches and the switches connect, through Ethernet cables, to one or more routers, which connect a network to other networks, like the internet
Wireless LANs are common to
to homes and small offices
Devices on wireless LANs connect…
to each other or the internet, through a wireless access point, often called a wireless router
Wireless LANs offer more…
flexibility than wired LANs because the devices can connect to the LAN from different places within the building
Wireless LANs tend to be…
slower than wired LANs, a little more susceptible to signal interference, and a little less reliable for consistency in speed and performance
WANs (Wide area networks)
Networks that cover multiple geographic areas and are usually a collection of local area networks (LANs)
An example of a WAN
A company has its corporate headquarters in one location and has satellite offices in multiple locations, each with its own LAN
To connect WAN networks…
leased lines are often used
Leased line
a dedicated connection from one location to another
Dial-up line
These are NOT a type of leased line. While pretty rare, dial-up is still the only means of getting to the outside world for some users.
To use a dial-up connection…
a phone line and a server which accepts dial-up connections is needed
Dial-up connections are…
highly slow by today’s standards
Top advertised speed
56 Kbps (Kilobits per second)
The top speed of a dial-up connection is
about 38 Kbps
One of the first advancements from dial-up is…
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)
Types of ISDN connections (Integrated Services Digital Network)
BRI and PRI
BRI (Basic Rate Interface)
Uses two 64 Kbps channels for a total speed of 128 Kbps, which is more than double that of a dial-up connection
PRI (Primary Rate Interface)
Uses twenty-three 64 Kbps channels for a total speed of 1.536 Mbps.
PRI runs on a…
TI circuit line
Many VPN connections use…
Internet Protocol security (IPsec)
IPsec
A suite of protocols that authenticates and encrypts data packets over a VPN connection
IPsec helps to provide…
both confidentiality and integrity of data, which is important for ensuring that data over a VPN connection remains private
3 IPsec protocols
SA, AH, ESP
SA (Security Association)
generates the authentications and encryption keys used in IPsec
AH (Authentication Header)
provides authentication and integrity of data but not data encryption
ESP (Encapsulating Security Protocol)
provides authentication, integrity, and encryption of data
Dedicated lines a customer can obtain for high-speed connections are…
leased lines
T1 Line (type of leased line)
Full T1 line uses twenty-four 64 Kbps channels of data, plus another 8 Kbps for overhead, for a grand total of 1.544 Mbps (not fast by today’s standards)
When someone leases a dedicated leased line…
they have the full, consistent bandwidth of that line
Customers can lease a partial T1 line…
so the customer doesn’t pay for a full T1 line and does not lease the full allotment of 24 channels
T3 Line (type of leased line)
Runs at 44.736 Mbps, equivalent to 28 T1 lines, use 672 64-Kbps channels
Just like with a T1 line
a customer can also lease a partial T3 line and pay less than a full T3 line
The European equivalent of the T1 and T3 lines are…
E1 and E3 lines
The concepts of the E1 and E3 lines are the same as T1 and T3…
but the number of channels each line uses is different, so the line speeds are different
E1 Line (type of leased line)
uses 32 64-Kbps channels, runs at 2.048 Mbps
E3 line (type of leased line)
Uses 16 E1 lines, runs at 34.368 Mbps, which is slower than a T3 line
For leased lines, the speeds from slowest to fastest are…
T1, E1, E3, T3
Common means of high speed internet connection for both residential and business customers is
Digital subscriber line (DSL)
DSL (Digital subscriber line)
a customer has a dedicated phone line from the origin to a telco office
For DSL, the closer a customer is to the Telco office…
the faster the connection
If people are not close enough to a Telco office
they cannot get DSL
SDSL (Synchronous DSL)
Upload and download speeds are the same, usually used in businesses that need fast uploads, and more expensive than ADSL
ADSL (Asynchronous DSL)
Most common form of DSL used in homes and businesses
ADSL has different…
upload and download speeds, with download speeds being much higher than upload speeds
Another common means of high-speed connection for a resident of business is…
Cable modem
Cable modem
Uses a cable TV provider for internet connection rather than a phone company for DSL
For using a Cable modem connection, Cable Internet…
tends to run over shared bandwidth, meaning that customers in a concentrated area are sharing the same bandwidth pipeline
For Cable modem, speeds tend to be…
slower during peak usage hours, which is usually early-to-mid-evening, because Cable Internet runs over shared bandwidth
Overall, cable modem speeds tend to be…
faster than that of DSL
DSL connections are on dedicated lines while…
cable modem connections are NOT on dedicated lines
Cellular Network
type of wireless network which most mobile devices run on
Highest speed cellular network is
5G, but this network is not available in every area nor every mobile device at this time
Most mobile devices have access to…
4G or 4G LTE (Long-Term Evolution networks), a faster version of 4G networks
Some mobile devices only have access to…
3G or 2G networks
Remember that on mobile devices, speeds…
vary greatly based on the proximity of a mobile device to a tower
Depending on one’s cellular service plan…
one’s speeds could be hindered during peak hours, or if a cellular customer exceeds a certain amount of used bandwidth per billing period
Satellite Network
Type of internet connection that is prominent in areas to where there is no cable or DSL internet availability and cell service is not consistent
Satellite Internet is generally…
faster than dial-up internet
The biggest issue with satellite networks is that…
latency, the delay from a source to a destination, since a signal needs to travel up to 20,000 miles above the Earth and back down to a destination
Satellite Internet is not optimal for…
real-time activity, like video conferencing and gaming
Wireless networks operate on the…
IEEE 802.11 standard
Wireless networks run on…
the 2.4 GHz frequency or the 5 GHz frequency
Generally 5 GHz are faster, but have shorter range…
and do not carry signals nearly as well as that of the 2.4 GHz frequency signals
The 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies are NOT…
compatible on the same wireless network (a device with a wireless network card that runs on the 2.4 GHz frequency cannot connect to a wireless router that only runs on the 5 GHz frequency)
Most wireless access points
run both the 2.4 Ghz and 5GHz frequencies
One standard, the 802.11 standard supports…
both frequencies
802.11a Standard
Frequency: 5 GHz
Speed: 54 Mbps
Indoor Range: 30 meters/100 ft
802.11b Standard
Frequency: 2.4 GHz
Speed: 11 Mbps
Indoor Range: 35 meters/115 ft
802.11g
Frequency: 2.4 GHz
Speed: 54 Mbps
Indoor Range: 38 meters/125 f
802.11n Standard
Frequency: 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz
Speed: 300 Mbps up to 600 Mbps on dual link
Indoor Range: 70 meters/230 ft
802.11ac Standard
Frequency: 5 GHz
Speed: Up to 1300 Mbps
Indoor Range: 27 meters/90 ft
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
This form of encryption is considered weak, as it has been cracked. Do not use this if you don’t need to.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
This is stronger than WEP and possibly the strongest form of encryption available, especially if the wireless access point you are configuring is old
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2)
Currently the strongest form of encryption and this should be used whenever possible.
Another option for securing wireless networks is to use the 802.11x option
also known as port-based network access control (PNAC).
PNAC can be used…
for both wired and wireless LANs