Organic Chemistry 1- mechanisms and factoids
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
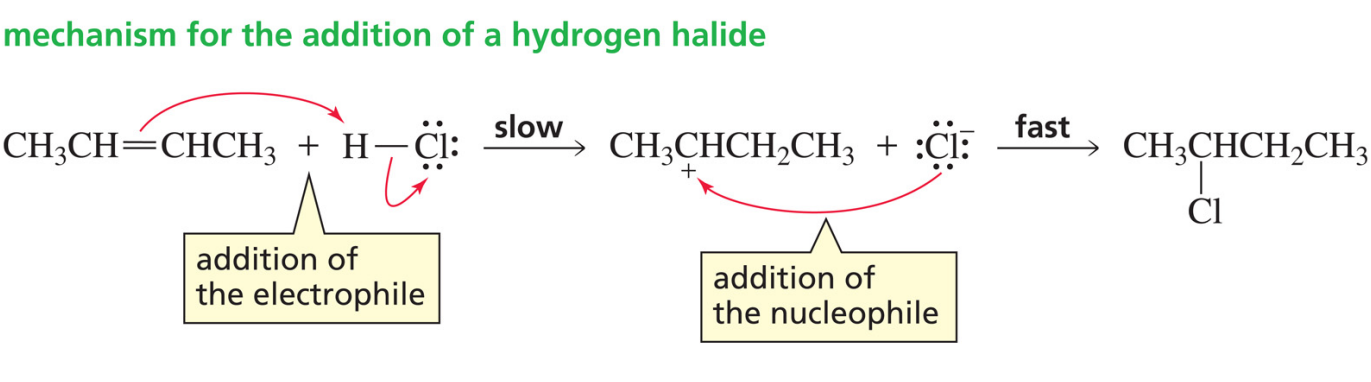
Alkene with hydrogen halide
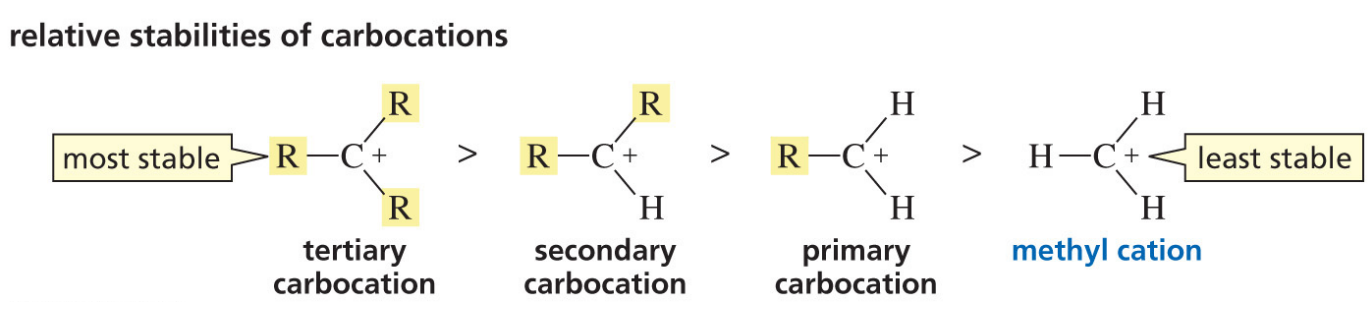
What dictates the stability of a carbocation?
The amount of substituents attached
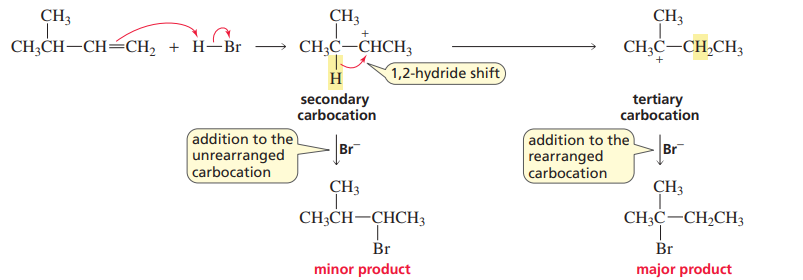
1,2-Hydride shift
The prefered carbocation rearrangement
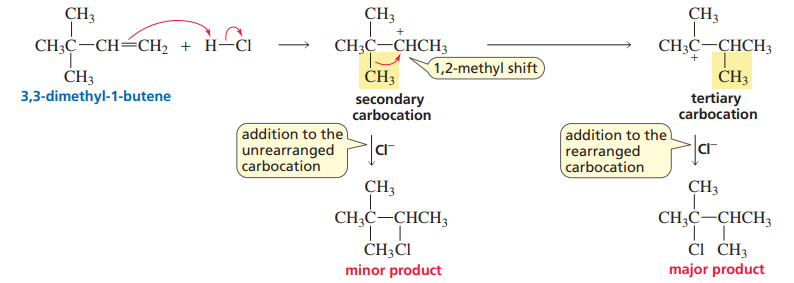
1,2-methyl shift
Whenever a carbocation is formed, check to see if rearrangement occurs
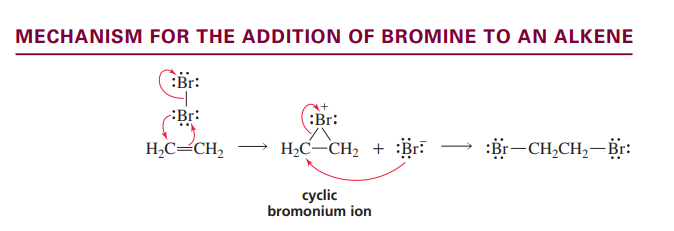
Bromine to Alkene mechanism
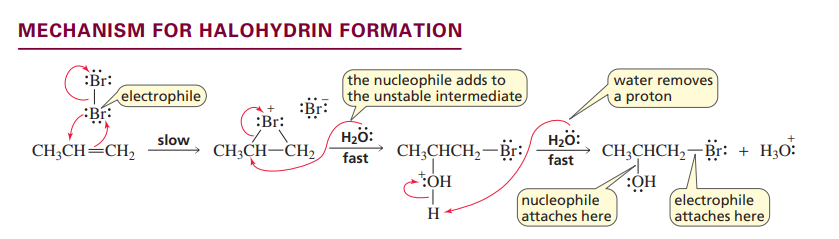
Halohydrin formation
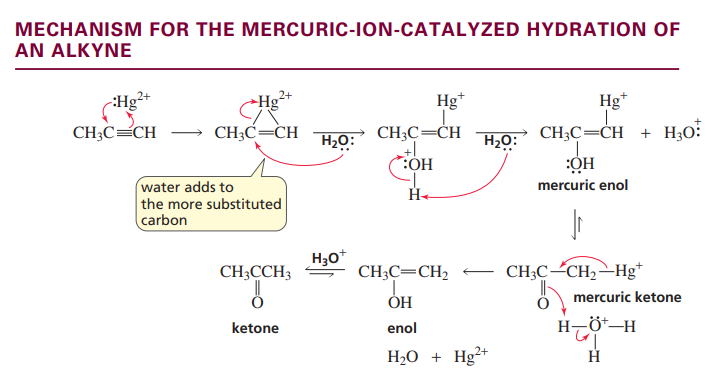
Hydration of a terminal alkyne
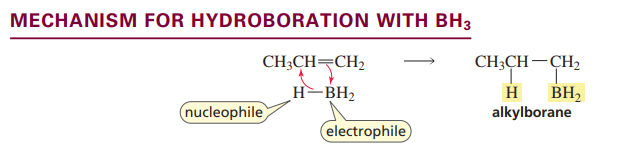
Hydroboration of an alkene
BH3 adds to the least substituted carbon
Oxidation step hydroboration alkene
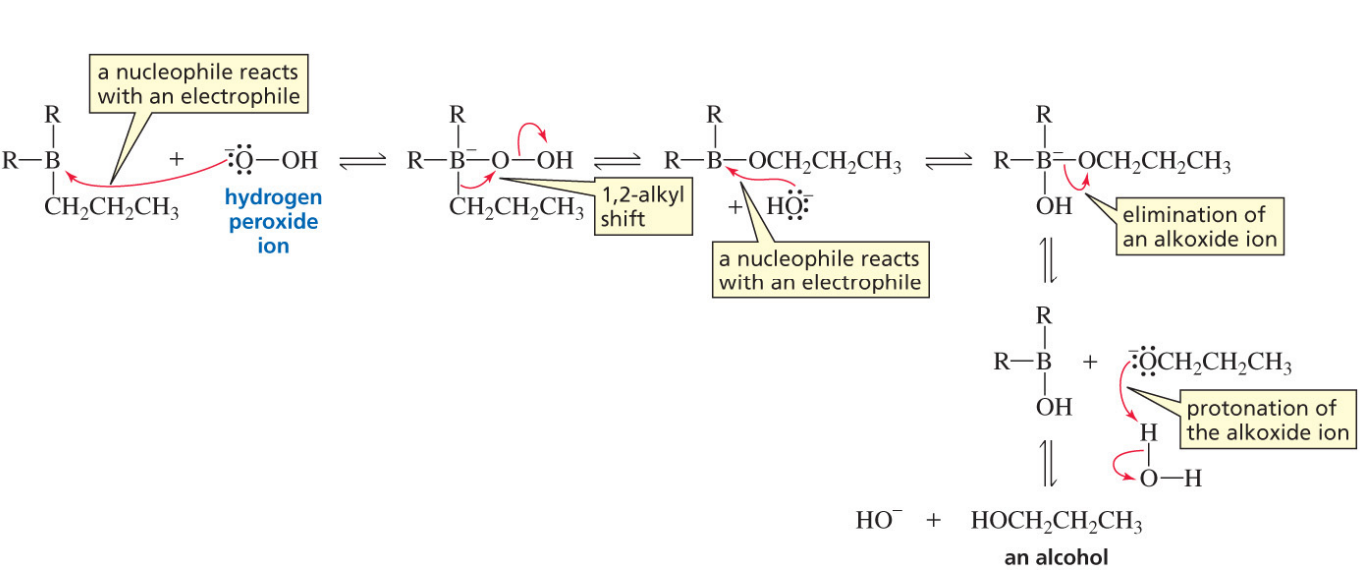
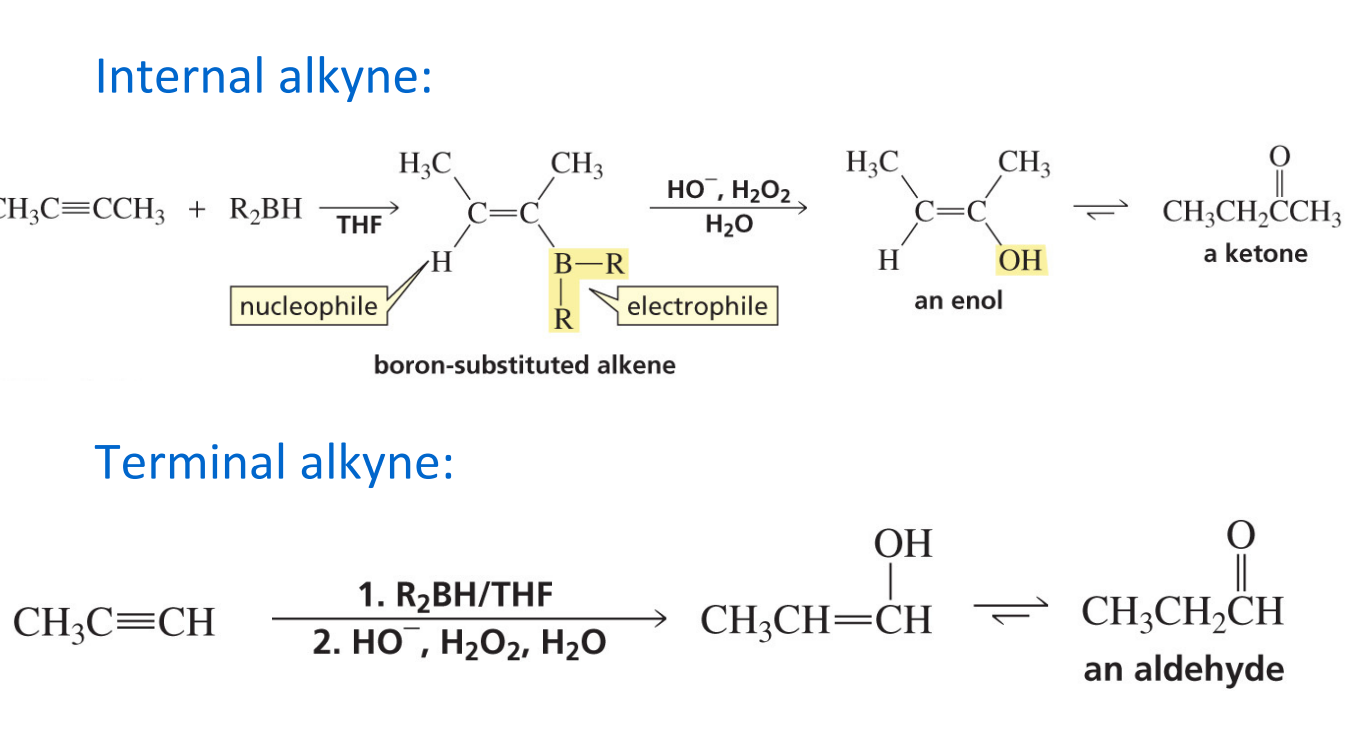
Hydroboration-oxidation product for an alkyne
Hydrogenation of an alkane
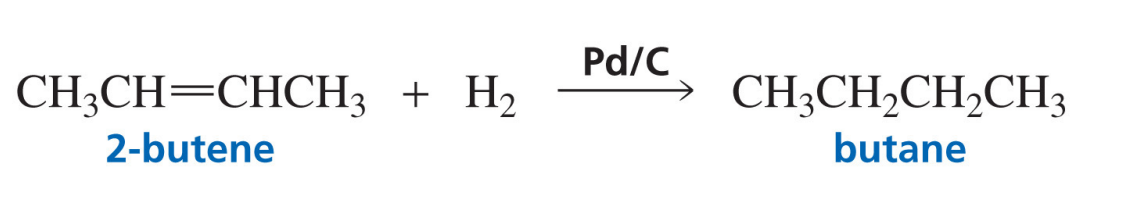
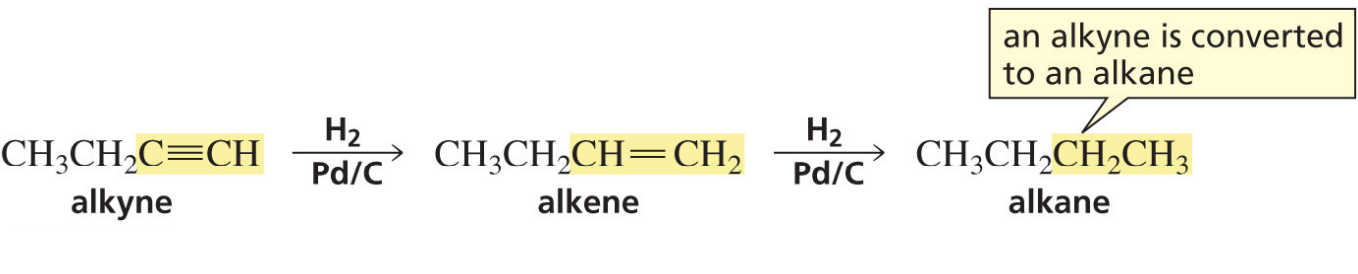
Hydrogenation of alkynes (Pd/c)
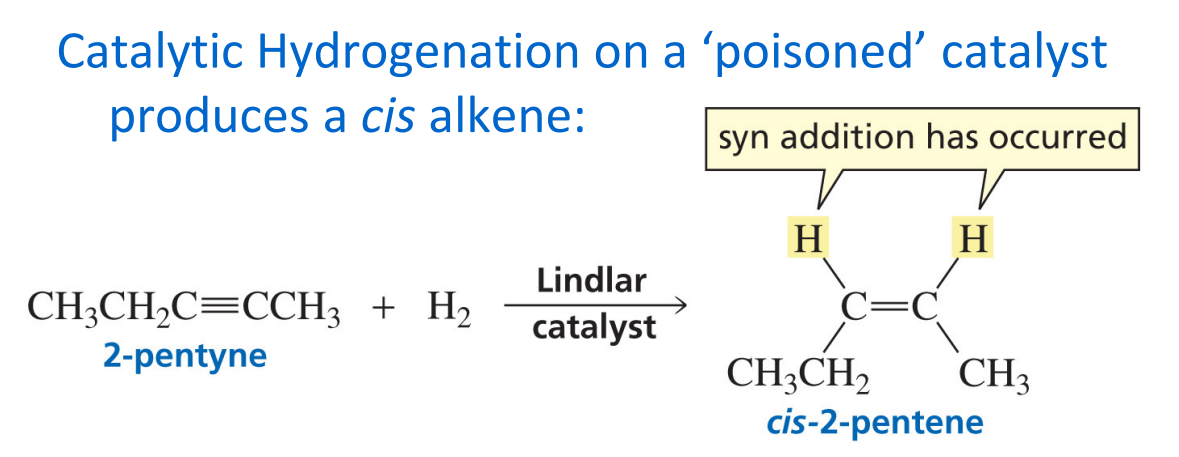
Hydrogenation of alkyne (lindlar catalyst)
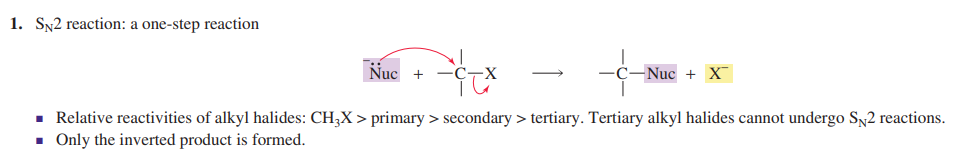
Sn2 reaction
Back attack
Inversion
Needs space
Strong nucleophile needed
Polar aprotic solvent
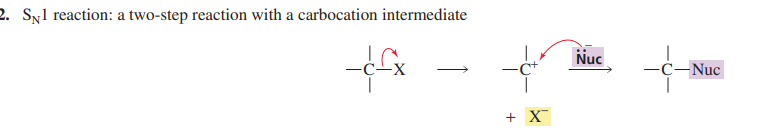
Sn1 reaction
Carbocation intermediate formed
Two step reaction
Weak nucleophile needed
Polar solvent needed
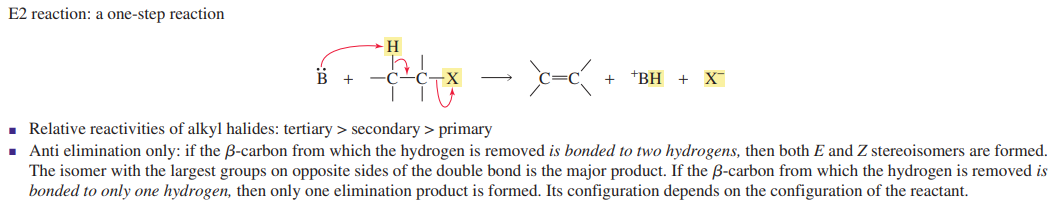
E2 reaction
One step
E1 reaction
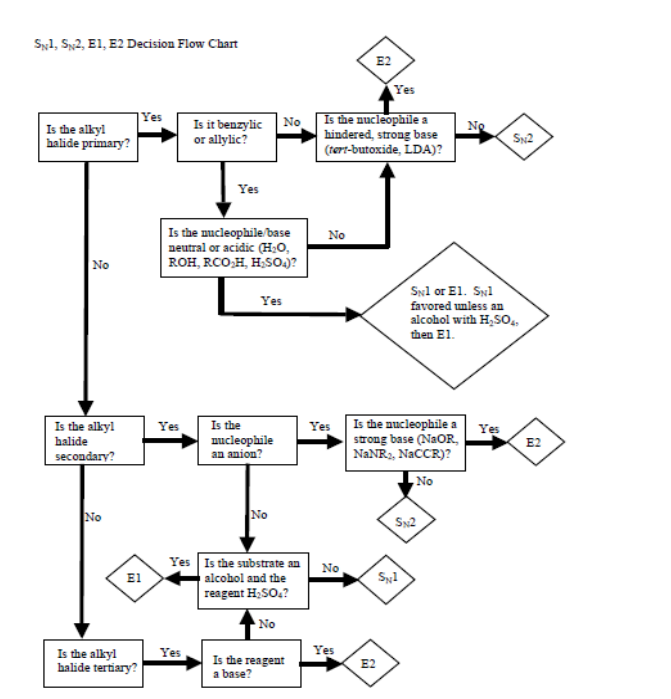
Sn1/Sn2/E2/E1 decision flowchart
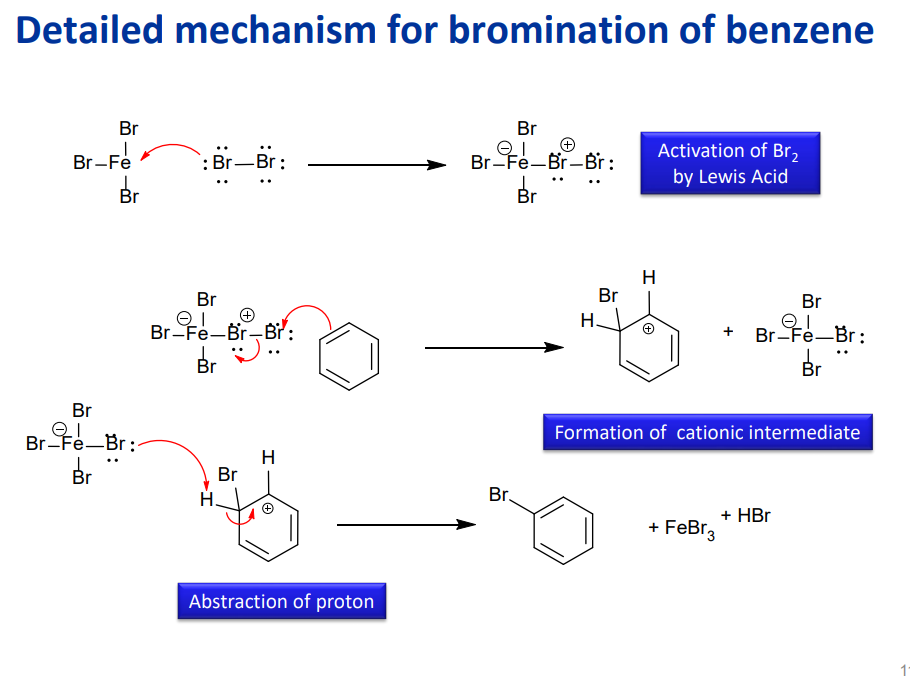
Bromination
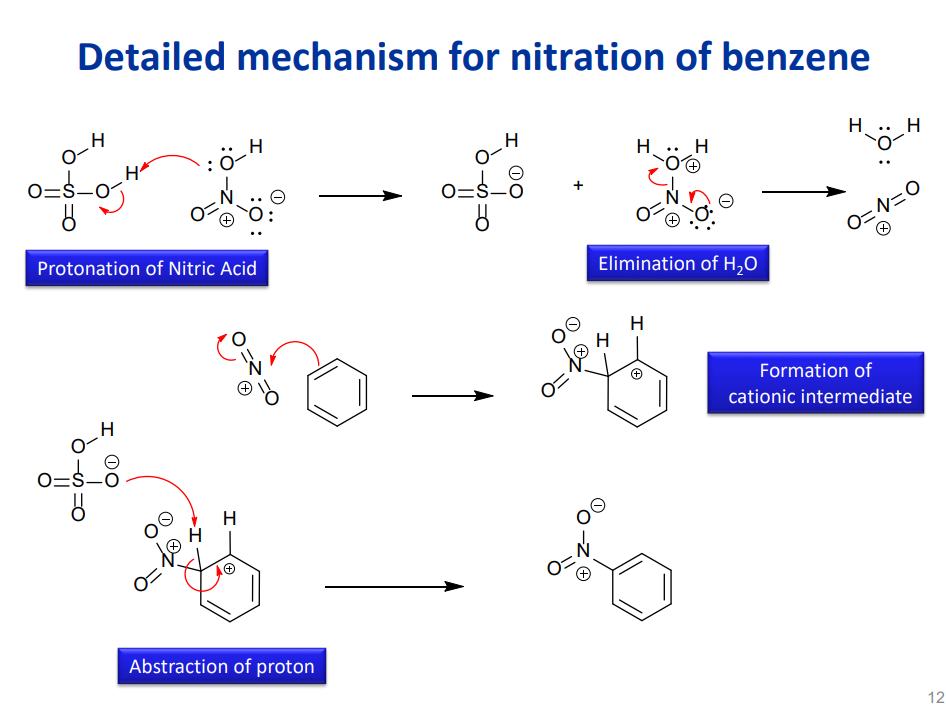
Nitration
Chlorination
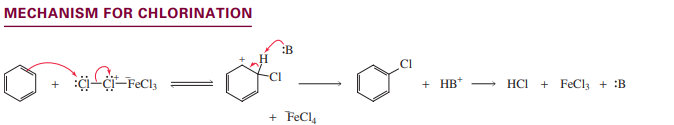
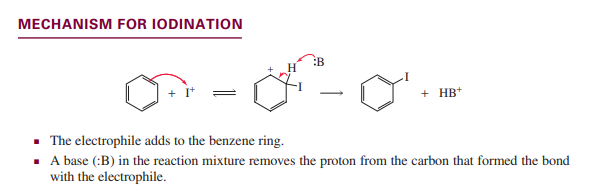
Iodination
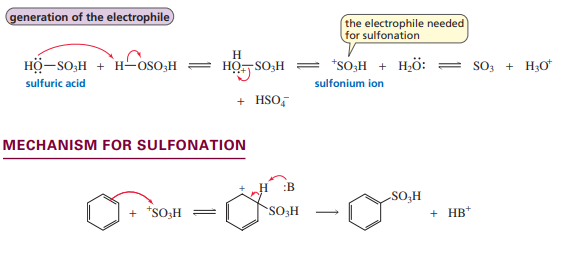
Sulfonation
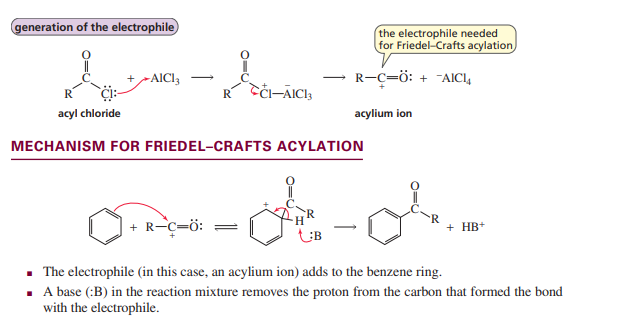
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
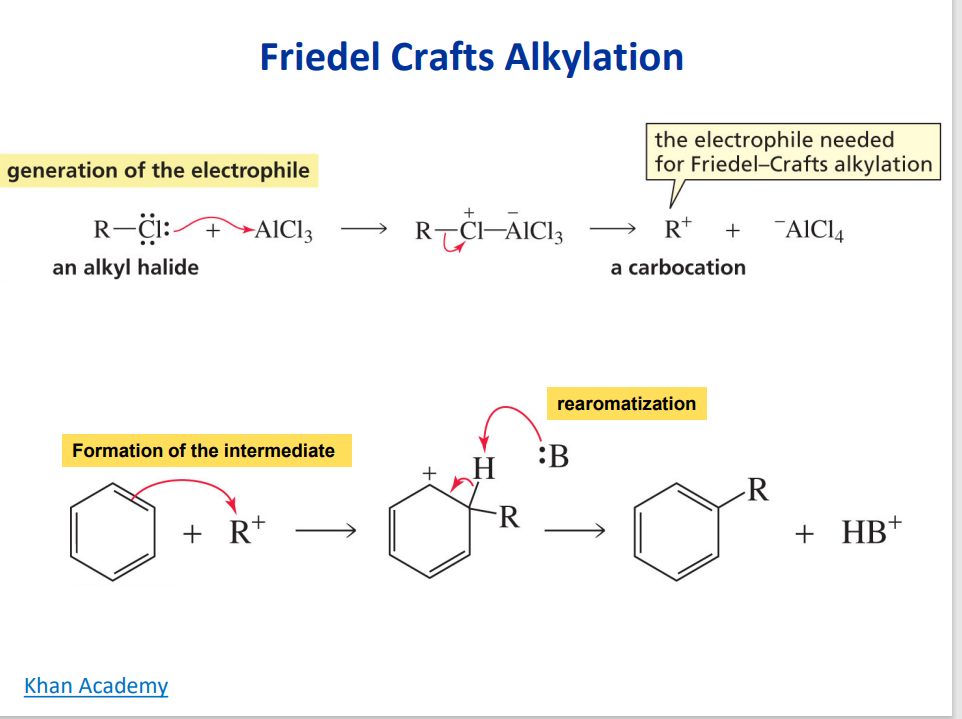
Alkylation of benzene by acylation reduction
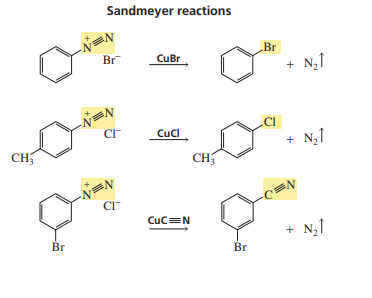
Sandmeyer reactions
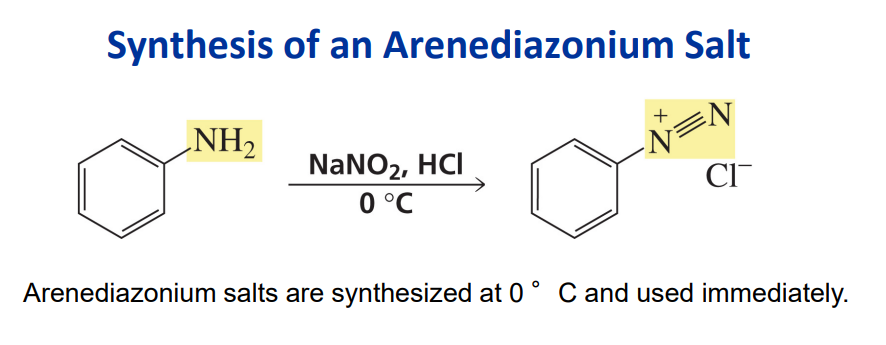
Synthesis of a diazonium salt
What is a electron withdrawing group and how does it effect benzene reactivity?
EWGs can withdraw electron density from the benzene ring via inductive or resonance effects. They deactivate benzene and are meta directors.
Examples: -NO2
- COO
-CN
-SO2R
What is a Electron Donating Group and how does it effect benzene reactivity?
EDGs donate electron density to the benzene ring via inductive or resonance effects. They activate benzene and are ortho/para directors.
Examples:
-OH
-NH2
-CH3
Which group is deactivating but ortho/para directors?
Halogens
What is the general rule to identify activating vs deactivating groups?
Lone pairs = Activating EDGs
Pi bond to electronegative atom = Deactivating EWGs