Cells and Membrane Structure Quiz
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Bio Mrs. Bose
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
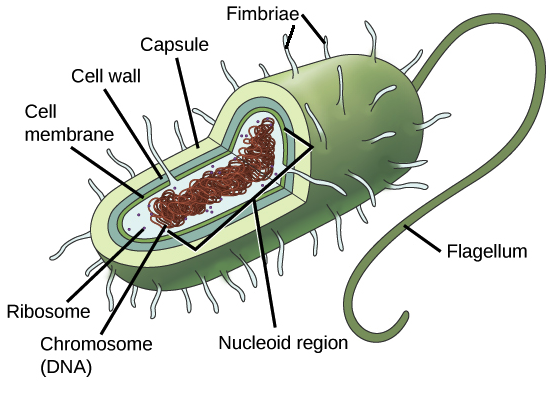
Prokaryotes
Bacteria
No nucleus or membrane bound organelles
Eukaryotes
Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals
Have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Genetic Material of Prokaryotes
Single circular chromosome w/ DNA
Genetic Material of Eukaryotes
Many rod shaped chromosomes w/ DNA
All cells have
A plasma membrane
cytosol
genetic material
ribosomes
Compartmentalization
Organelles create separate areas within the cell, each with a special environment and its own metabolic function
Allows for different reactions that need different conditions to happen separate from each other at the same time
Structure of Cell Membranes
Lipid bilayer, 2 layers of phospholipids w/ proteins embedded
Function of Cell Membranes
Separates cell from the outside
Allows for the exchange of nutrients and waste with environment, selects what goes in and out
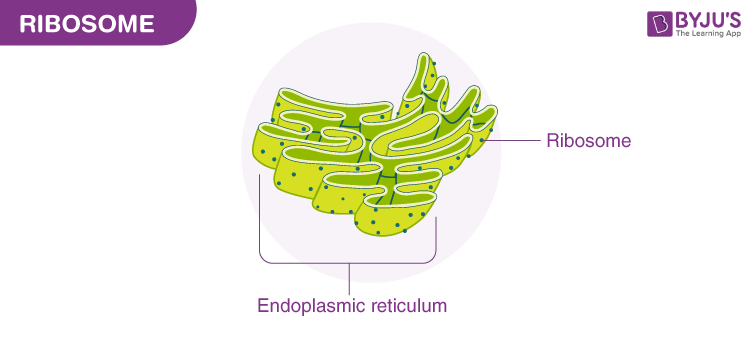
Structure of Ribosomes
Contain rRNA and proteins
Function of Ribosomes
Makes proteins according to mRNA sequence
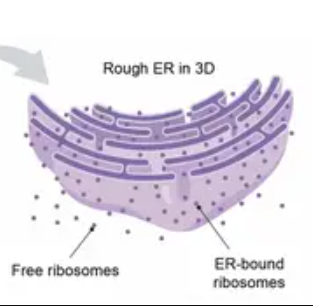
Free Ribosomes
Float in Cytosol, Produce proteins within cell
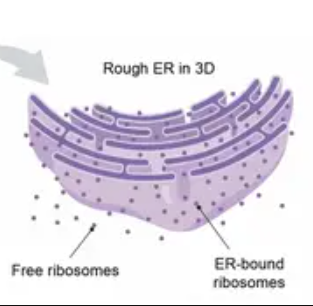
Bound Ribosomes
Attached to ER, make proteins for export from cell
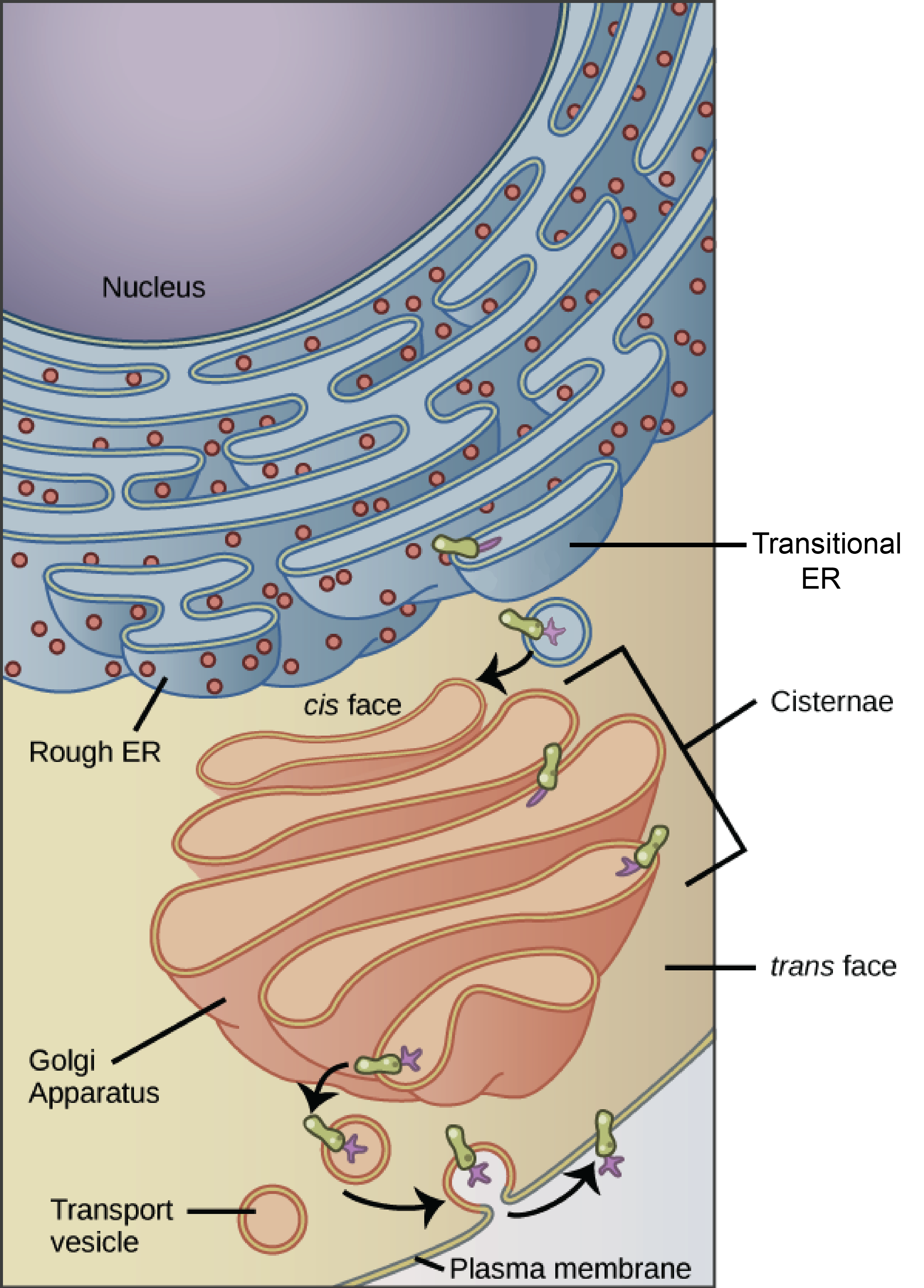
Endomembrane System
Group of organelles that work together to create, modify, and transport lipids and proteins
Includes Nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, ER, and Golgi, which all have the same membrane structure
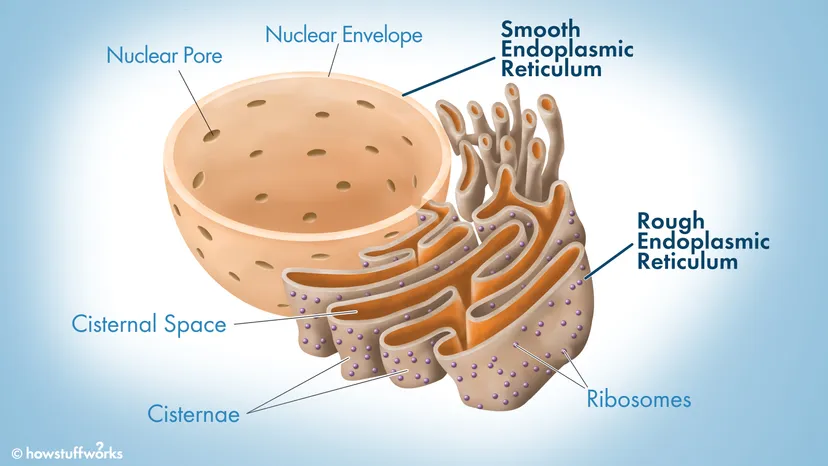
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Structure
System of tunnels/tubes throughout cell
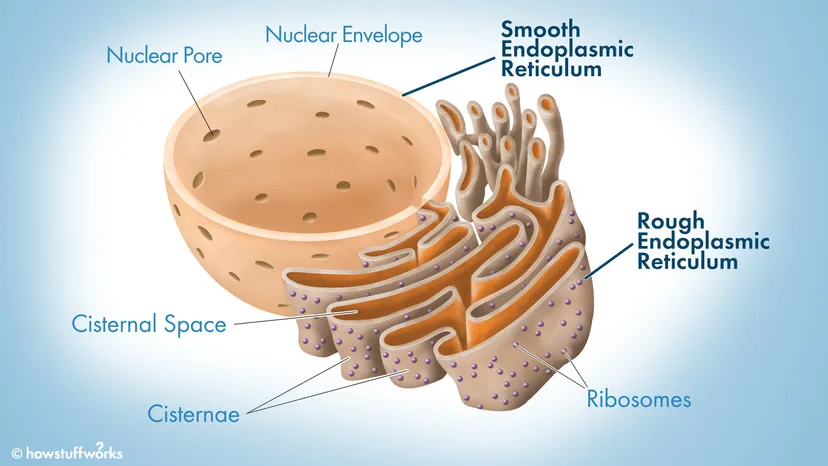
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Function
Intracellular Transport
Smooth ER
No ribosomes
Lipid synthesis, detoxifies drugs and poisons
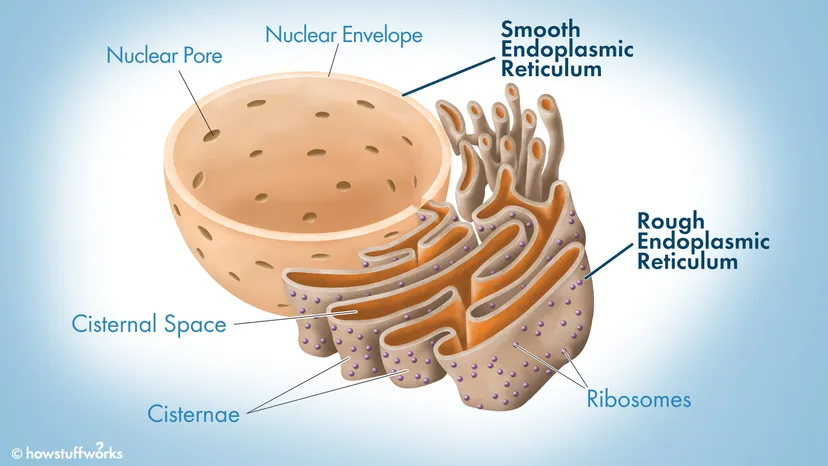
Rough ER
Has ribosomes
Takes protein by ribosomes and folds it into a 3D shape
Golgi Apparatus Structure
Stack of flattened fluid-filled membranes or sacs
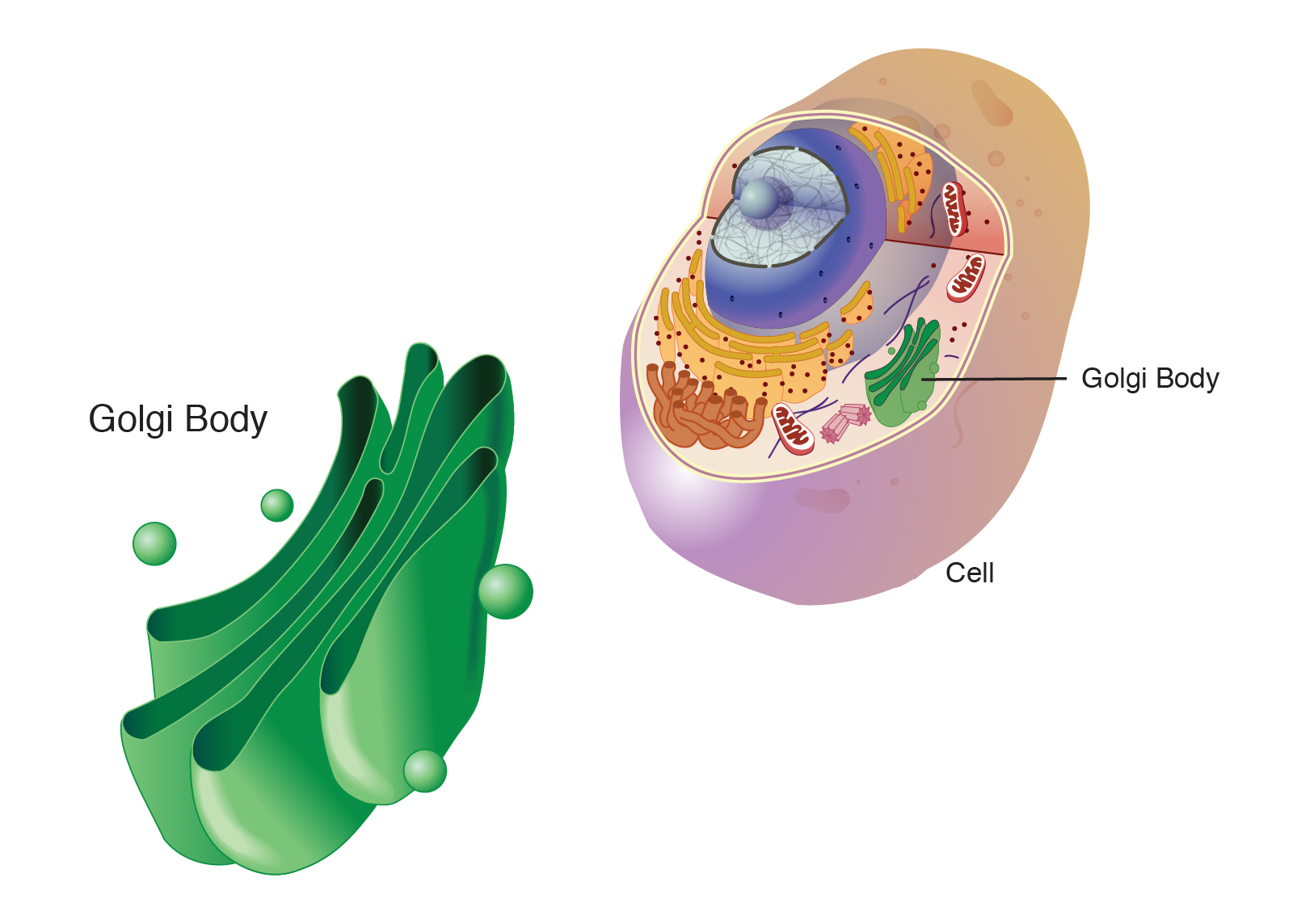
Golgi Apparatus Function
Folding, chemical modification, packaging (into vesicles) and sends out proteins that were made in the cell
Path proteins take
Rough ER - Golgi - Vesicle - Final destination
Lysosome Structure
Membrane bound vesicle (from golgi)
contains hydrolytic enzymes for chemical digestion
Lysosome Function
Its enzymes can digest food (macromolecules), kill bacteria, and break down old cell parts
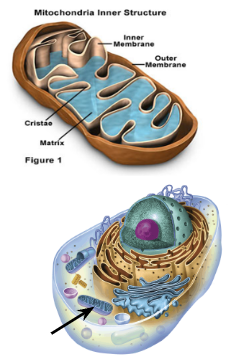
Mitochondria Structure
2 membranes create compartments for different reactions
The membranes (outer is smooth, inner is folded) provide more surface area for electron transport and ATP synthesis

Mitochondria Function
Converts nutrients (glucose) into ATP energy
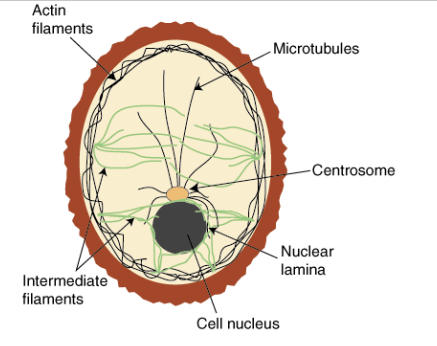
Cytoskeleton Structure
Network of protein fibers and tubes
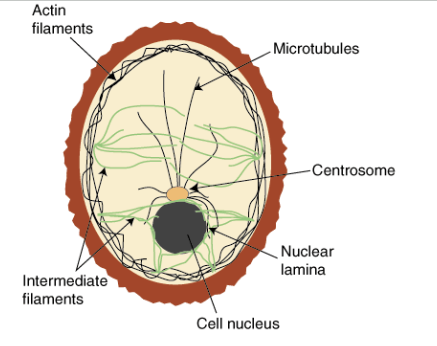
Cytoskeleton Function
Shapes and supports the cell. helps hold and move cellular materials
helps in cell division
Cytosol Structure
Jelly-like material, made of water, protein, salts, and organic molecules
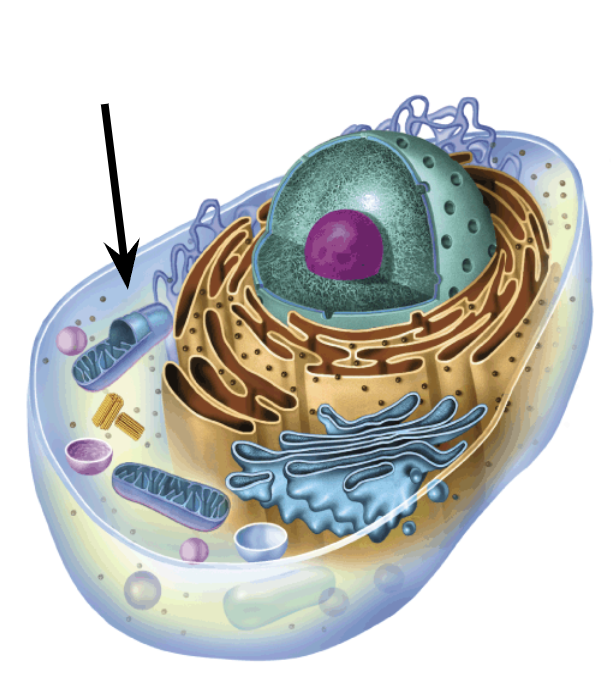
Cytosol Function
Site of many chemical reactions
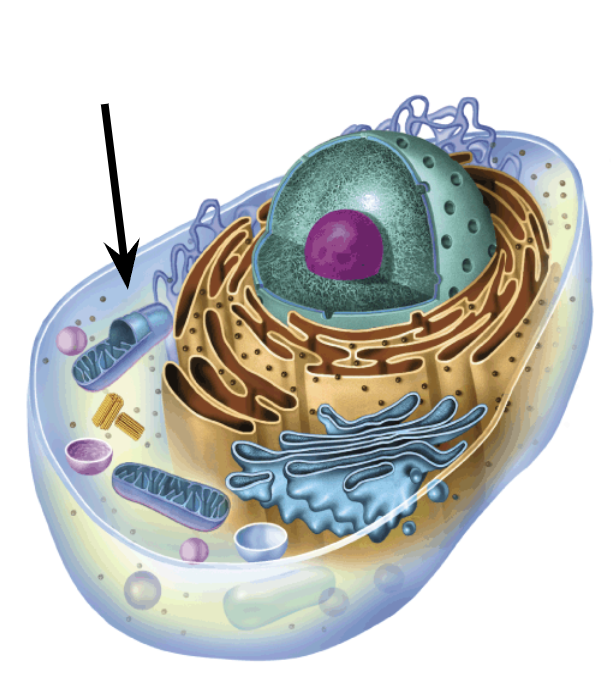
What is the Cytoplasm made of
Cytosol + organelles
Nucleus Structure
Surrounded by Nuclear Envelope
Pores - holes that allow things in and out of nucleus
Has DNA
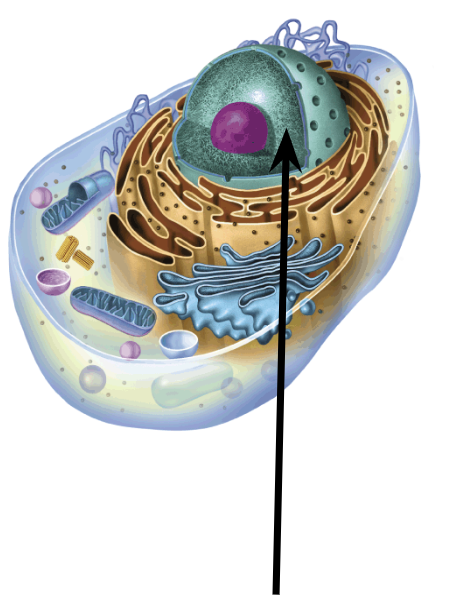
Nucleus Function
Stores Genetic Info, which directs protein synthesis in the cell
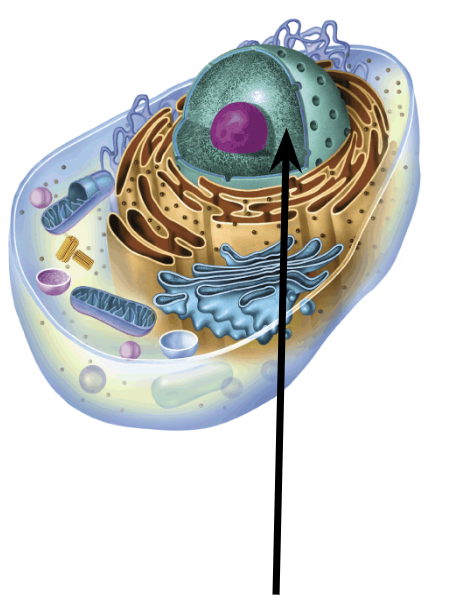
Plant cell specific organelles
Cell Wall
Vacuoles
Chloroplasts
Cell Wall Structure
Made of cellulose in plants + hardening proteins, has pores
Cell Wall Function
Rigid Covering, strengthens and protects plant cells
Vacuole Structure
Large, membrane-bound vesicle
Vacuole Function
Storage of materials such as food, water, ion, and wastes
Chloroplast Structure
Has a double membrane + its own DNA
Thylakoid disks in stacks (grana) - membrane contains chlorophyll
Stroma surrounds thylakoid
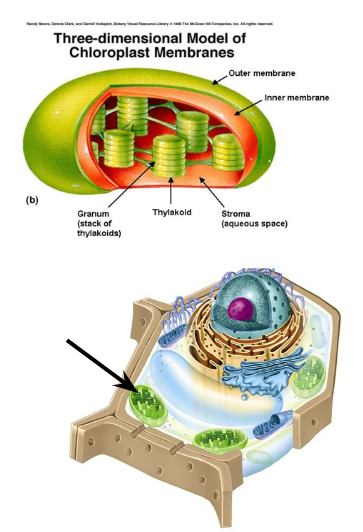
Chloroplast Function
Absorbs sunlight for making sugar - photosynthesis
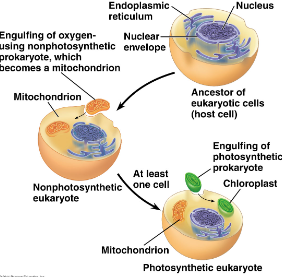
Endosymbiosis Theory
Prokaryotic cells were engulfed by larger prokaryotic cells
The smaller cells lived and reproduced inside the larger cell, eventually becoming one cell
Led to eukaryotic cells with mitochondria/chloroplasts
Evidence of Symbiosis
Mitochondria and chloroplasts
Resemble prokaryotic cells
Replicate similar to prokaryotes
DNA
Ribosomes similar in size to bacteria
Double phospholipid membrane
Similar size as bacteria
Why are cells so small?
Smaller cell means larger SA:V ratio, which leads to a better transport of nutrients (and waste out) which leads to more chemical reactions
SA:Volume ratio importance
The surface area of cell membranes is used to exchange materials
Big cells have more volume, so they need more stuff and make more waste, while having less surface area for transport
With less surface area, the less effective the process of exchanging materials is
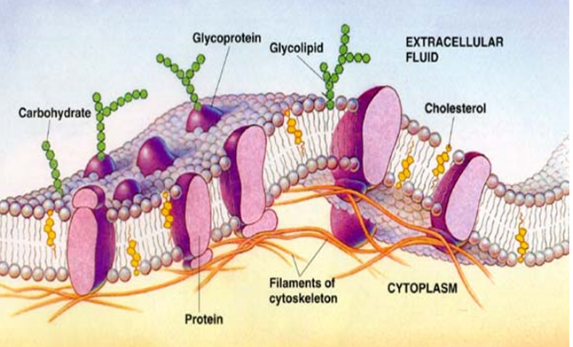
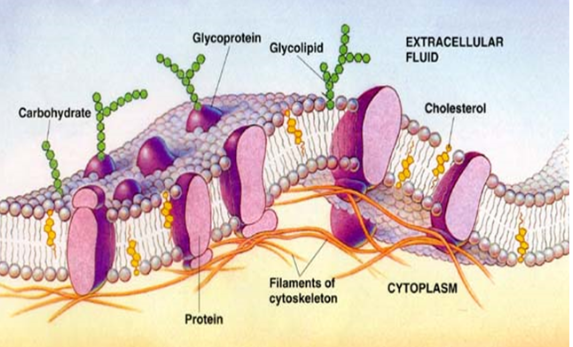
Fluid Mosaic model
Made of mosaic of proteins embedded in fluid phospholipids, has carbs and steroids
Membrane held together by weak hydrophobic interactions
Lipids and some proteins can shift laterally
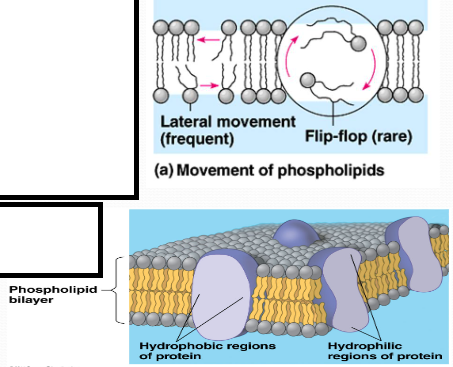
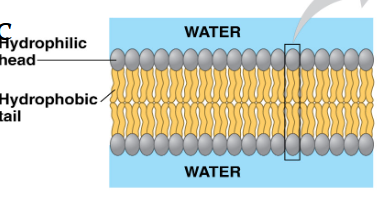
Phospholipid bilayer structure
Forms main fabric of membrane
it is amphipathic - has a hydrophobic head and hydrophobic tails
Membrane is mostly hydrophobic barrier, keeps hydrophilic molecules out
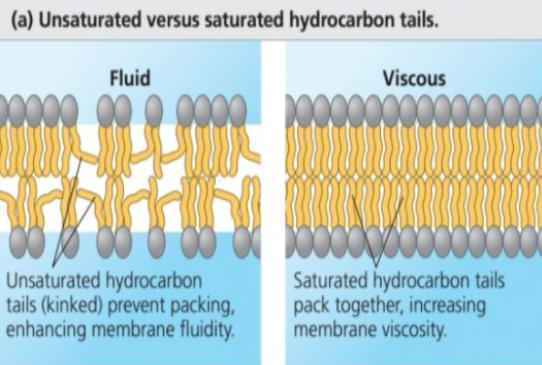
How does phospholipid type keep membrane fluid?
Phospholipids with unsaturated tails good when temperature decreases, it prevents it from being solid
Saturated tails are good when temperature increases, you don’t want it too fluidy
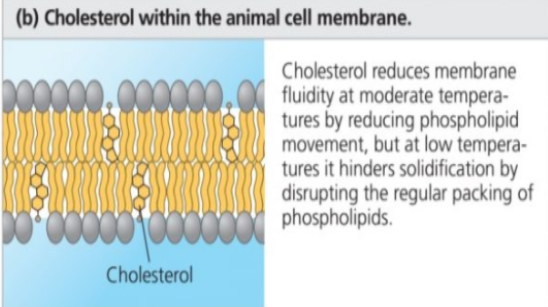
How does cholesterol type keep membrane fluid?
it limits excessive fluidity at high temperatures by slowing phospholipid movement
it hinders close backing of phospholipids at low temperatures
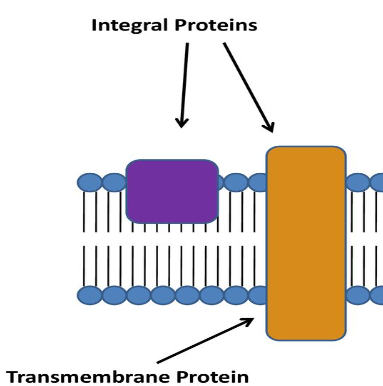
Integral Proteins
Embedded in membrane
Some have helical structure w/ hydrophilic aa’s on outside and hydrophobic aa’s in middle (transmembrane)
Some have hydrophilic channel to allow passing of hydrophilic molecules
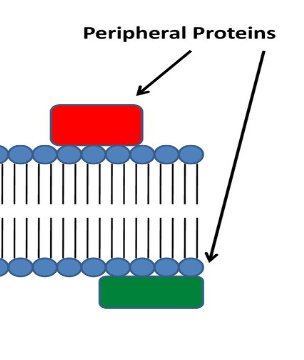
Peripheral Proteins
NOT embedded
Held in place by the cytoskeleton
Hydrophilic
Provides stronger framework for animal cells
Functions of Membrane Proteins
Intercellular joining - cells hook together
Transport
Enzymes
Cell communication
Cell to Cell Recognition
Attachment to cytoskeleton or ECM - helps maintain cell shape
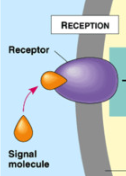
Cell Communication of Membrane Proteins
Receptor proteins have shape specific binding sites for a messenger like a hormone, message is relayed to cell interior
Cell to Cell recognition of Membrane Proteins
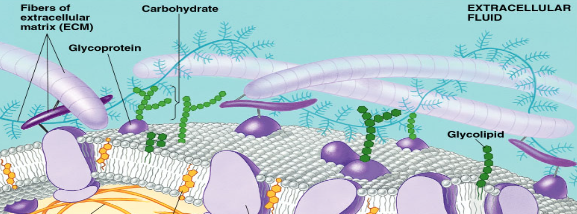
glycoproteins act as ID tags that can be recognized by proteins of other cell membranes
Carbohydrates in Cell Membranes Structure
Short chains, vary
types are glycolipids and glycoproteins
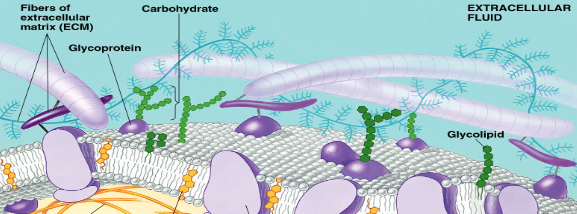
Carbohydrates in Cell Membranes Function
Cell-cell recognition, important in tissue rejection, blood types