Chapter 6 (lecture 4+5): Enzyme Action Basics
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Enzymes influence, often dramatically, the rate of chemical reactions by:
Stabilizing the transition state
Enzymes are the principle _______ catalysts.
biological
Enzymes can be ______.
regulated
Enzymes display _______ for a single substrate or closely related groups of substrates and catalyze only the intended reaction with no unintended by-products
specificity
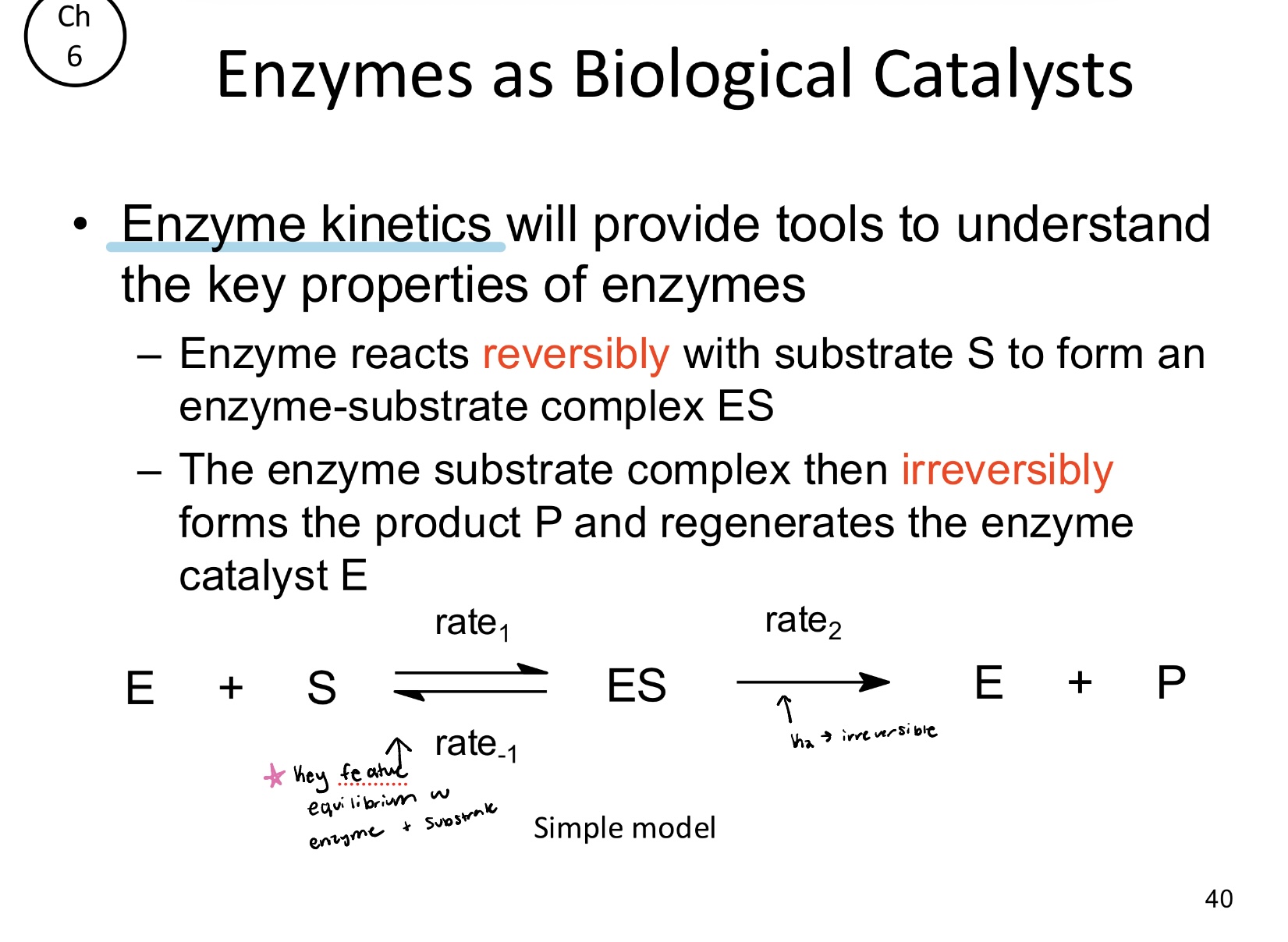
Enzymes reacts _____ with substrate S to form an enzyme-substrate complex (ES)
The enzyme substrate complex (ES) will irreversibly form the product (P) which will also regenerate?
Regenerate the enzyme catalyst E
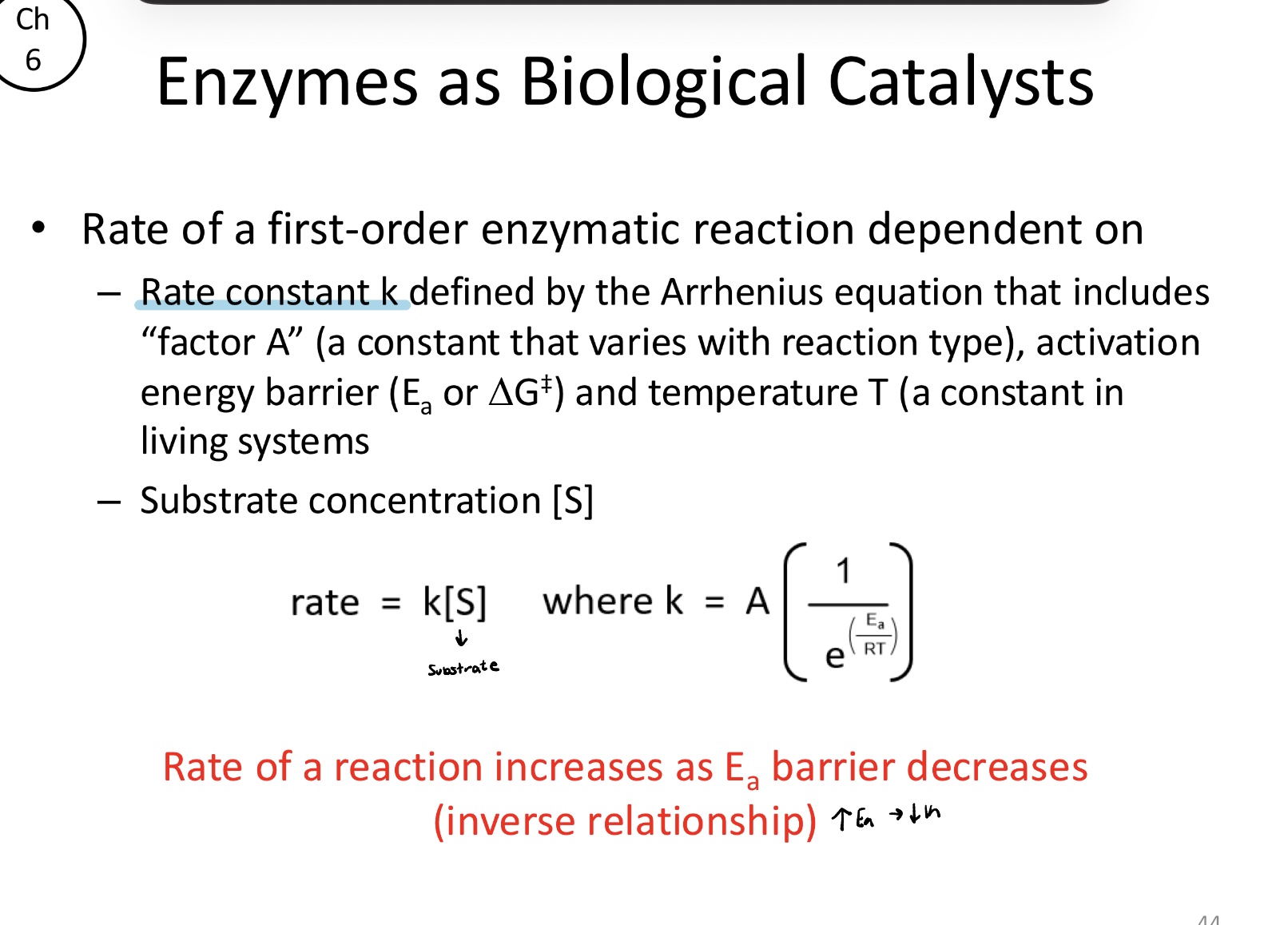
Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by ______ the activation energy barrier (Ea or Gibbs E)
Decrease
Enzymes function as catalysts by ______ the transition state
Stabilizing
Do enzymes alter the difference in energy (deltaG) between substrates and products?
They do not alter the difference in energy, as in the equilibrium constant K unchanged
Rate of a reaction _______ as Ea barrier ______. (Inverse relationship)
Increases; decreases
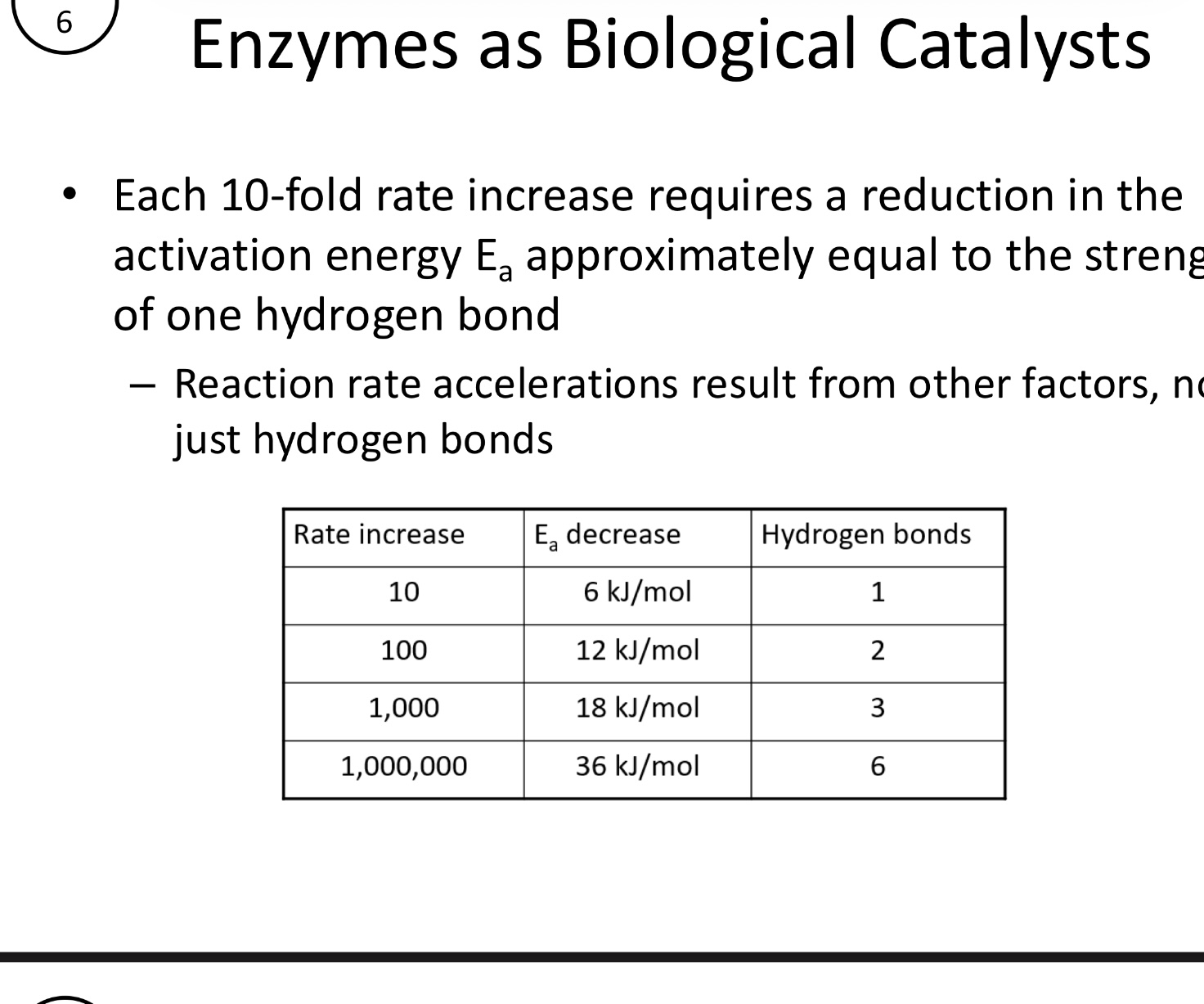
Each 10-fold rate increase requires a reduction in the Ea, approximately equal to the strength of?
One hydrogen bond
Reaction rate accelerations result from other factors, not just H-Bonds
An enzyme stabilizes the transition state of the enzyme-substrate complex (ES) NOT the…..
EnzymeSubstrate complex ES itself
Reaction rate accelerations results from ______ in activation energy.
Reductions
An enzyme achieves stabilization and the dramatic rate acceleration through an array of what type of interactions?
Non-bonding interactions and sometimes bonding interactions
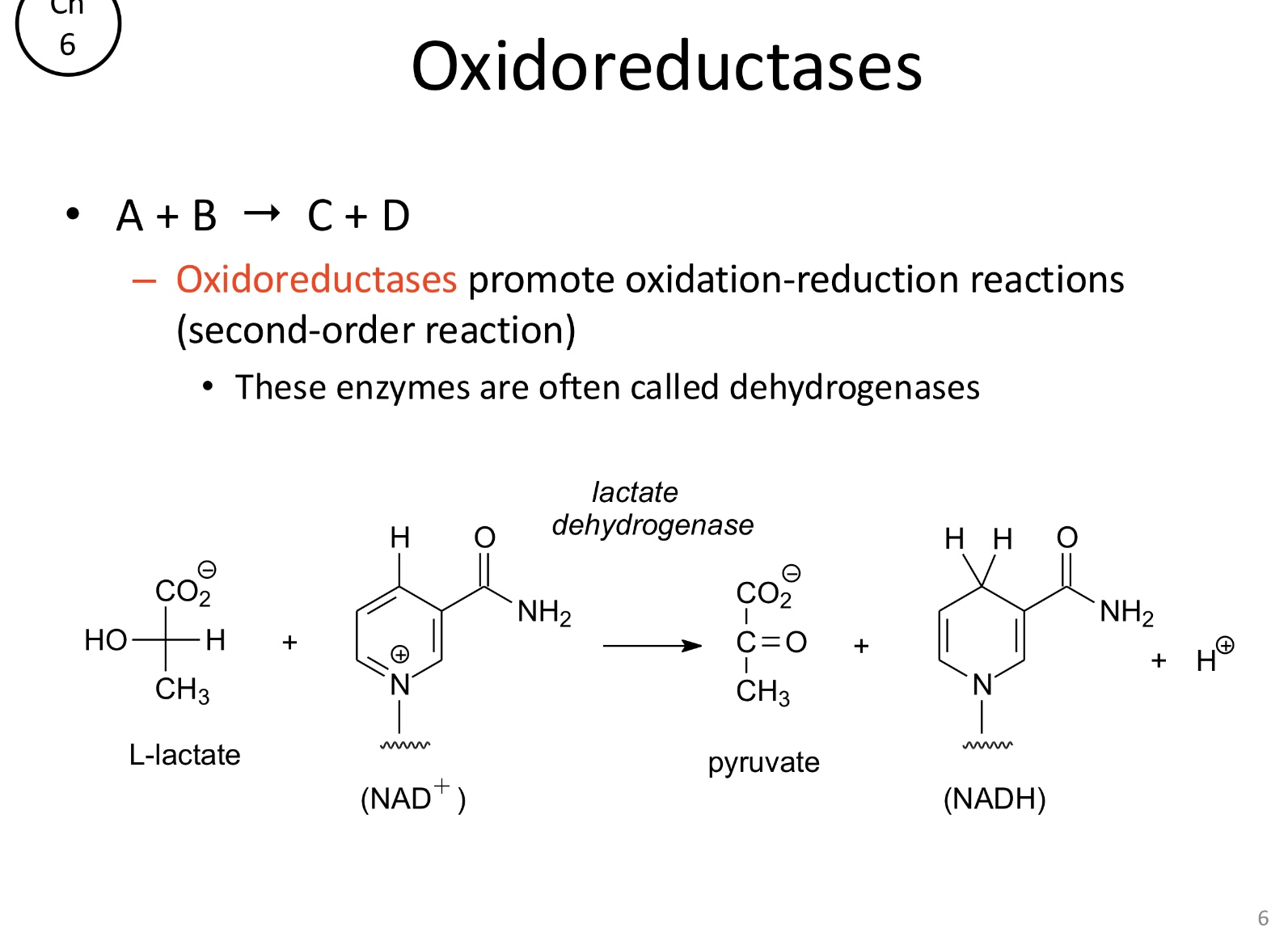
What is the function of oxidoreductases?
Catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions (dehydrogenases)
A+B→C+D (second-order)
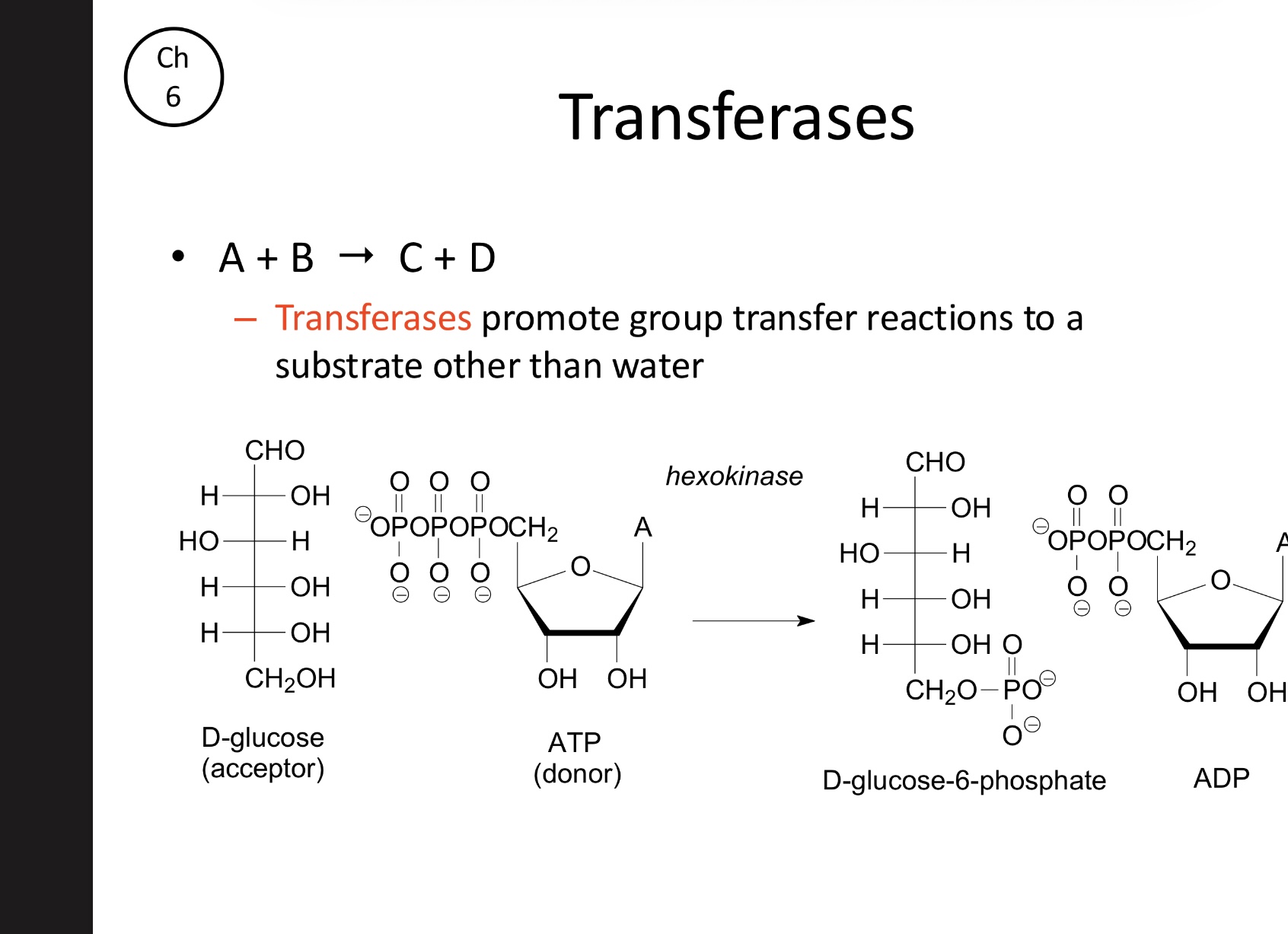
What is the function of Transferases?
Promote the transfer of functional groups from a donor to a substrate (acceptor) other than water. (Hexokinase)
A+B→C+D
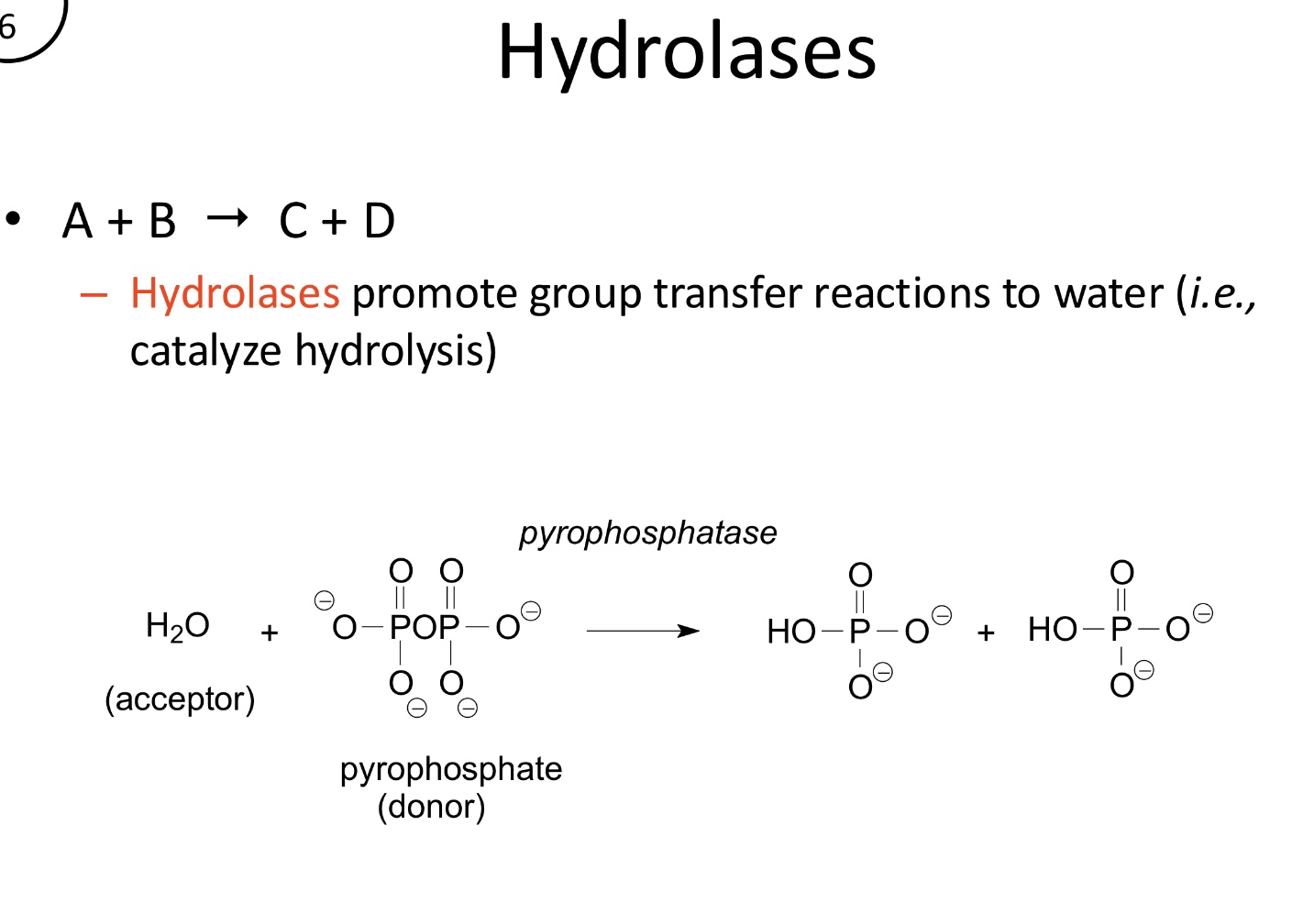
What is the function of Hydrolases?
Catalyze the transfer of functional groups to water, effectively promoting hydrolysis
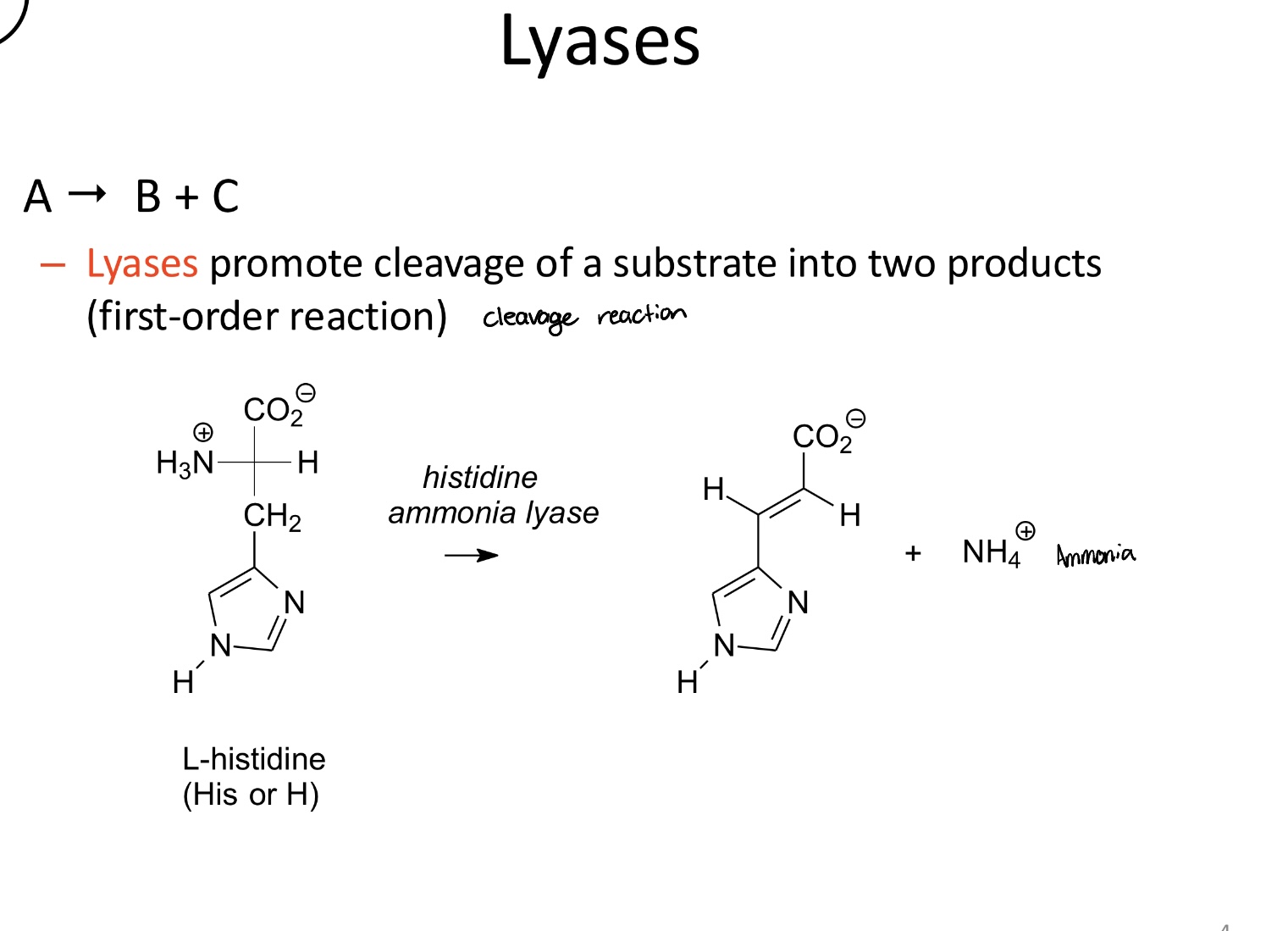
What is the function of lyases?
Facilitate the cleavage of a substrate into two products without the addition of water or redox change
A→ B+C (first-order)
What is the function of isomerases (mutases)?
Catalyze structural changes within a single molecule
A→ B (first-order)
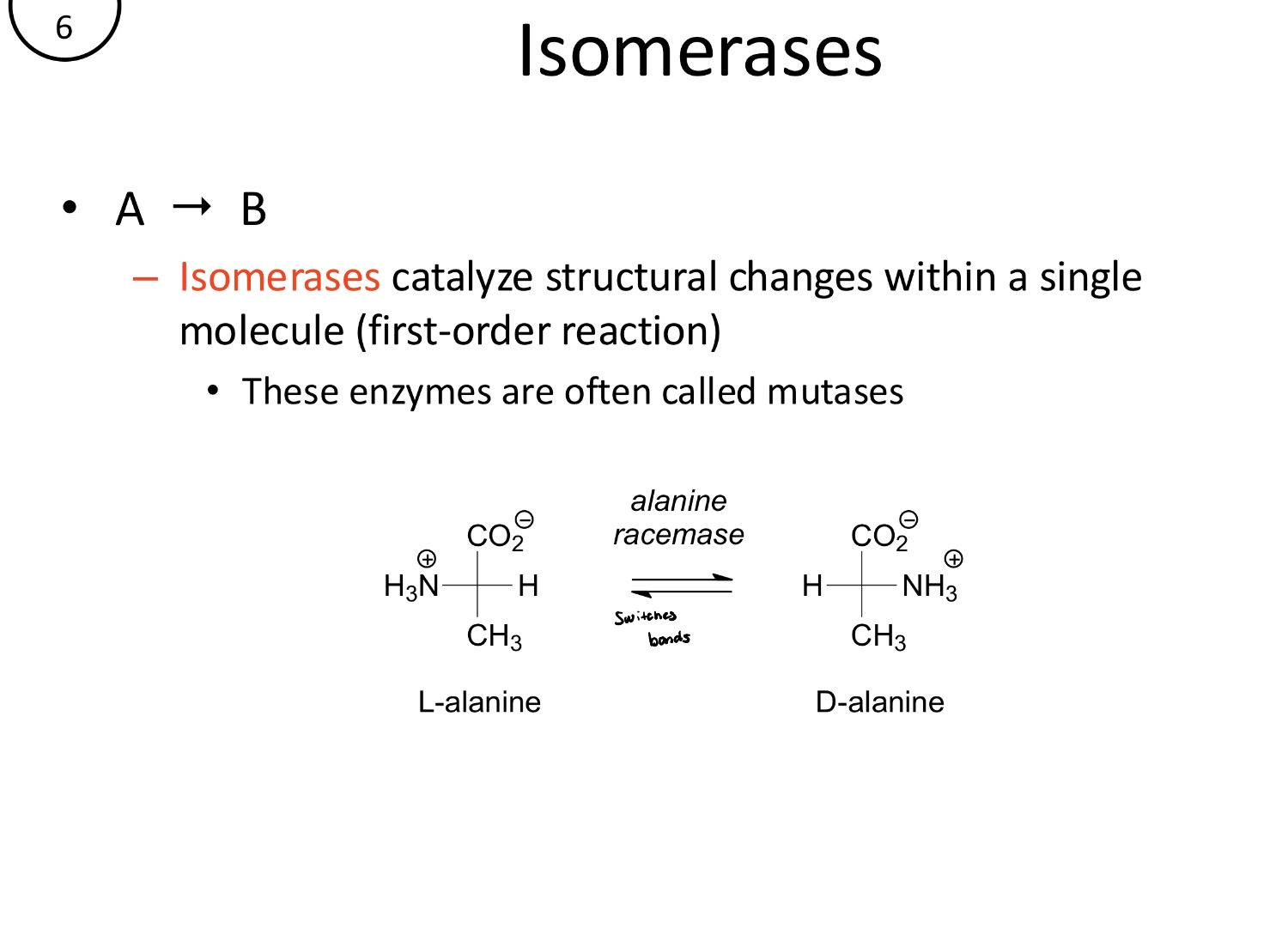
What is the function of ligases?
Promote the joining of two substrates, often coupled with ATP hydrolysis. These are also known as synthases or synthetases
A+B→C (second-order)
Many enzymes require additional non-protein components to function. A holoenzyme consists of?
Holoenzyme = apoenzyme (protein portion) + cofactor (inorganic)
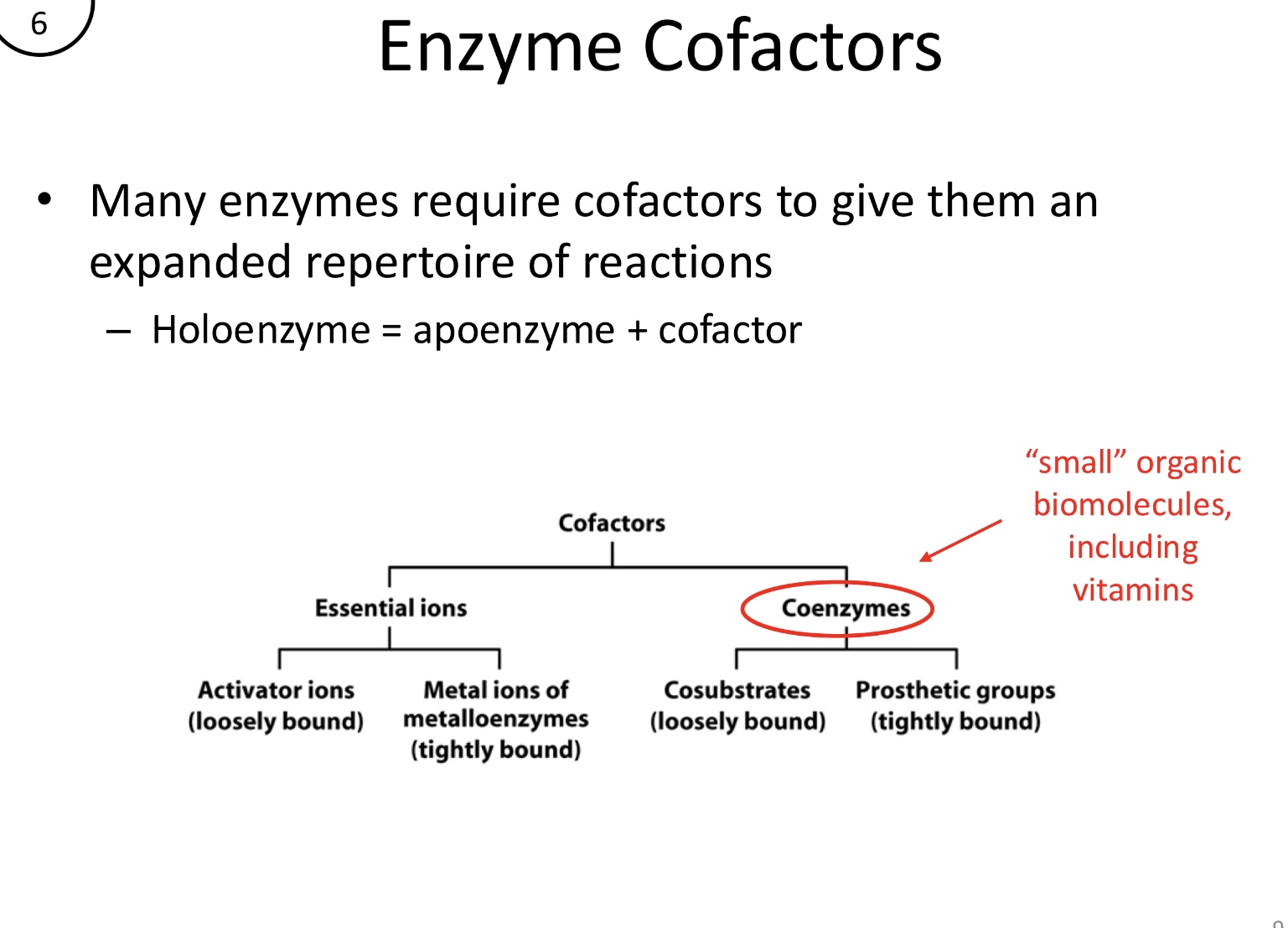
What are coenzymes?
Small organic biomolecules, often derived from vitamins. They are divided into cosubstrates (loosely bound) and prosthetic groups (tightly bound)
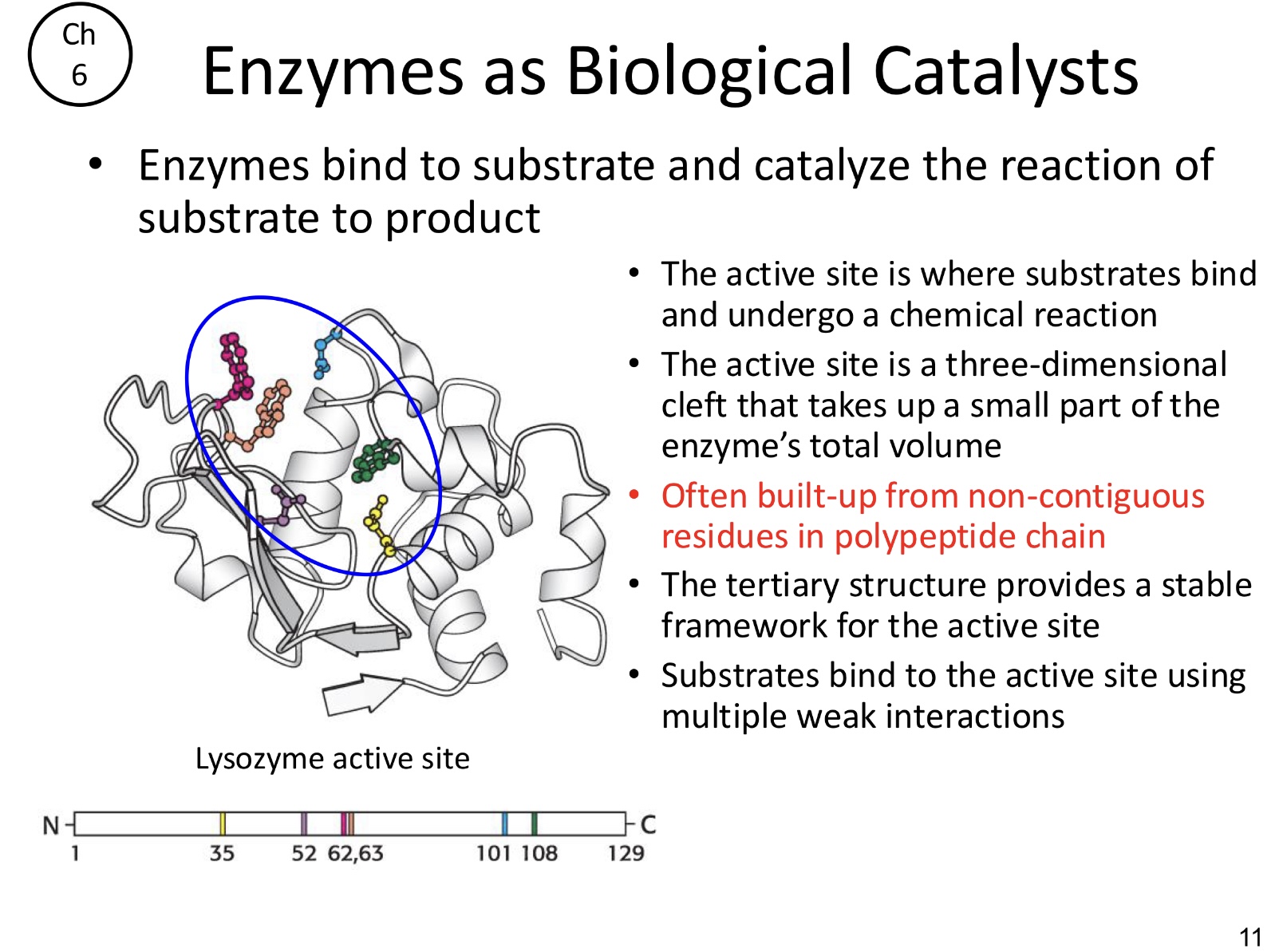
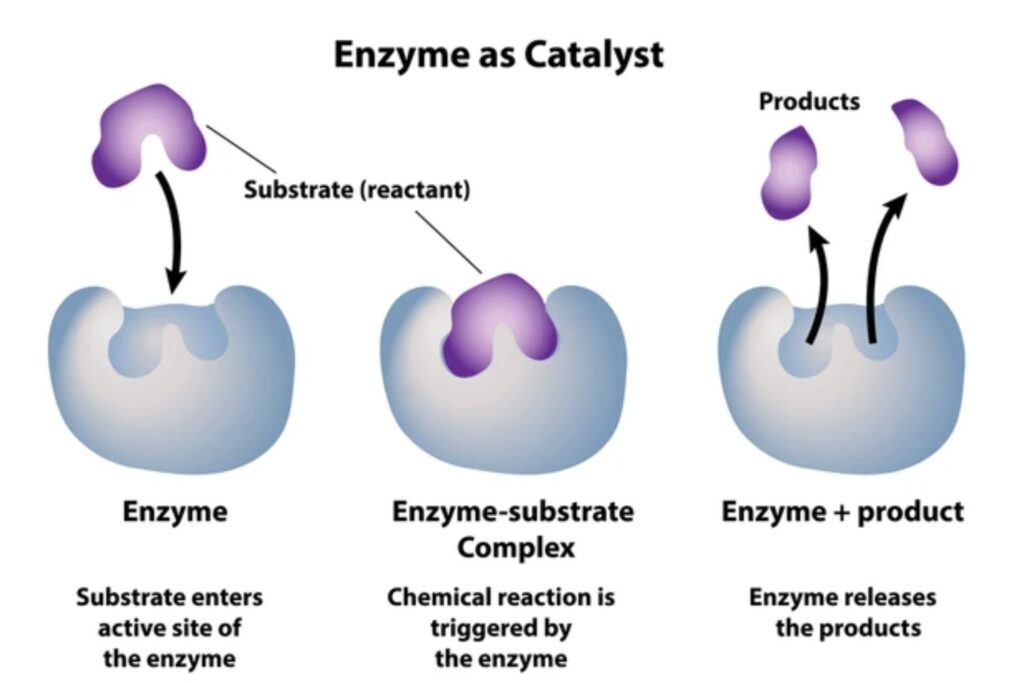
Where is the active site?
The active site is where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction
What is the active site?
A 3-D cleft that takes up a small part of the enzymes total volume. Often built-up from on-contiguous residues in polypeptide chain
Substrates bind to the active site using multiple _____ interactions.
weak
What is the induced-fit model within an active site?
Binding of substrate triggers conformational changes in the enzyme. This leads to an “imperfect” fit in the enzyme-substrate (ES) complex that maximizes non-bonding interactions to drive the reaction forward
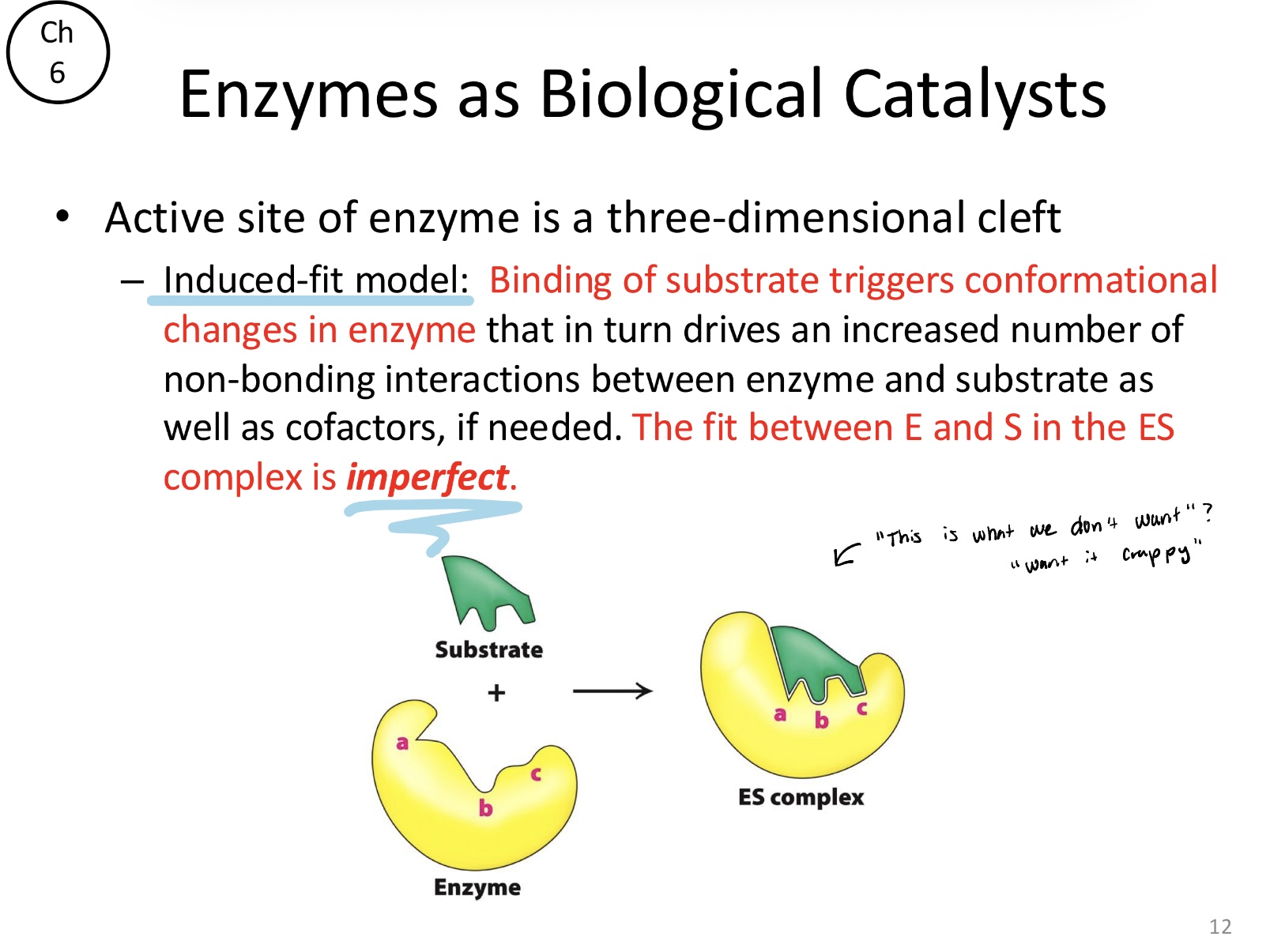
Why is the fit between E and S in the ES complex imperfect?
To facilitate catalysis rather than just binding through an “induced-fit” mechanism. An imperfect, flexible fit allows the enzyme to strain the substrate, reduce activation energy, and stabilize the transition state, which would be impossible with a rigid “lock and key” fit
Active sites matches the _____ of the transition state leading to the product
shape
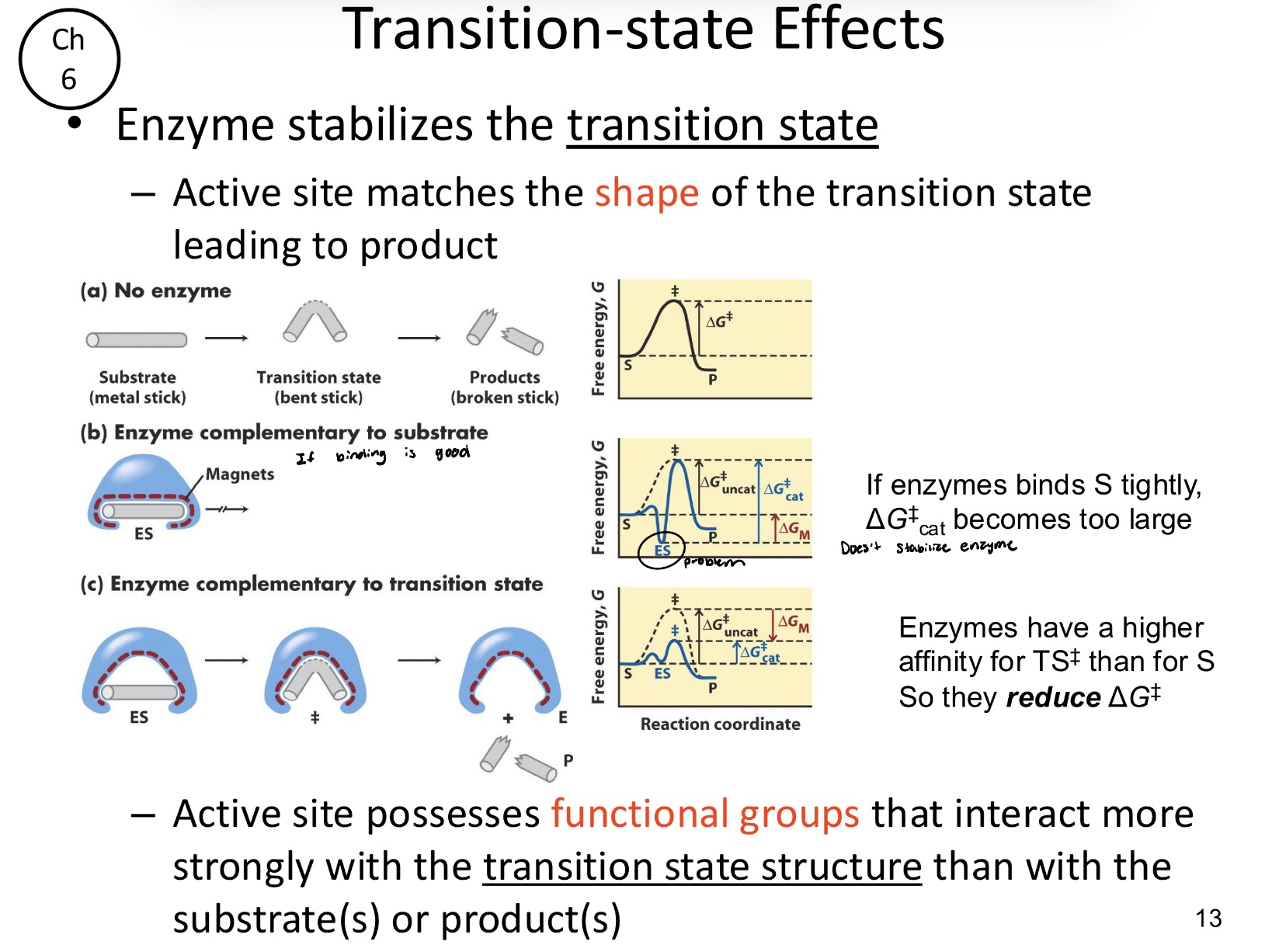
Enzymes do not bind the substrate tightly, rather, they have a higher affinity for the transition state (TS). By matching the shape and charge distribution of the transition state, what does this do?
The enzyme will stabilize it more than the substrate or product, thereby reducing the activation energy
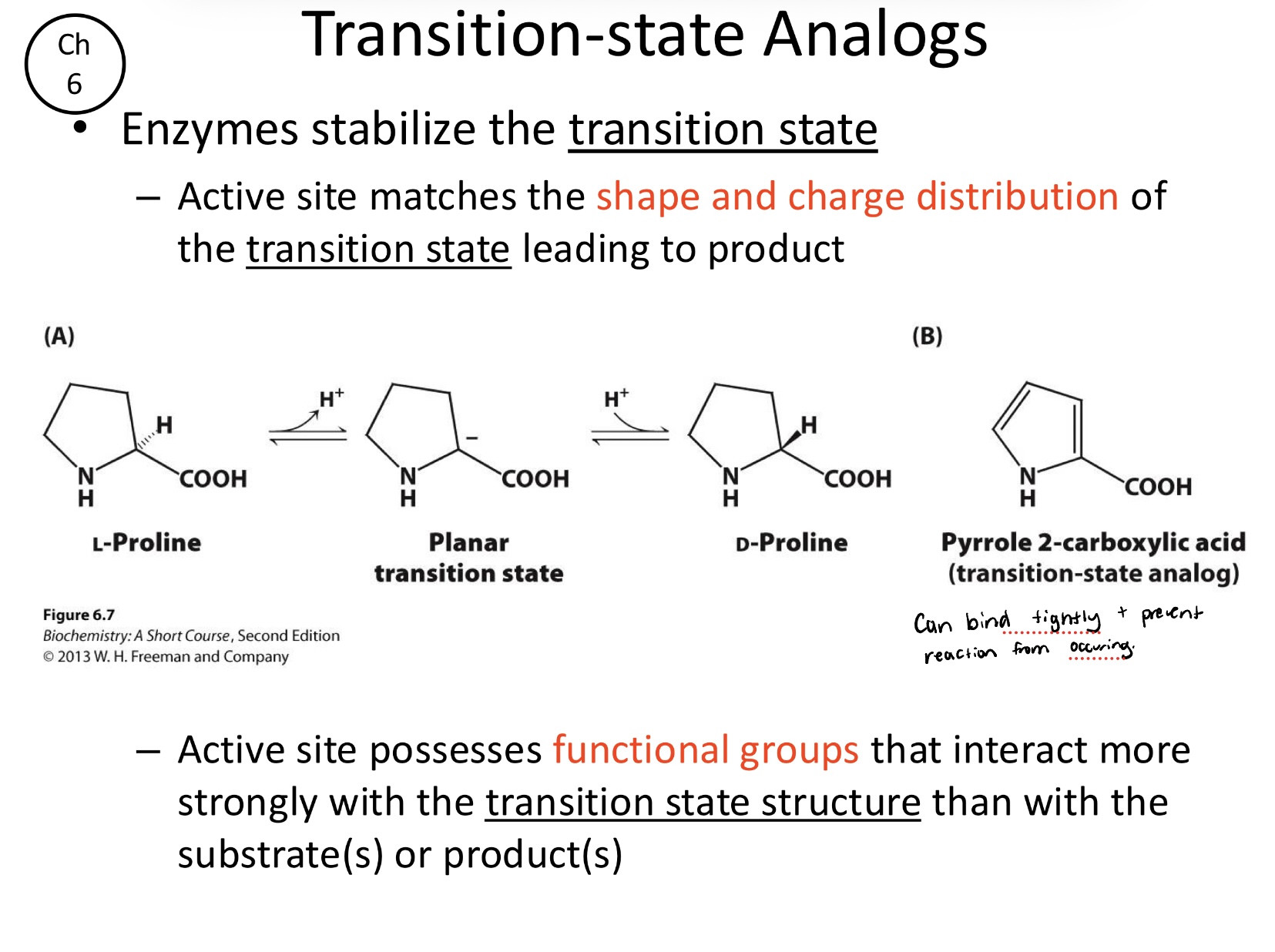
Describe the transition-state analogs:
These molecules resemble the transition state and can bind very tightly to the enzyme, acting as potent inhibitors by preventing the actual reaction from occurring
Catalysis is facilitated by properly _______ functional groups.
positioned
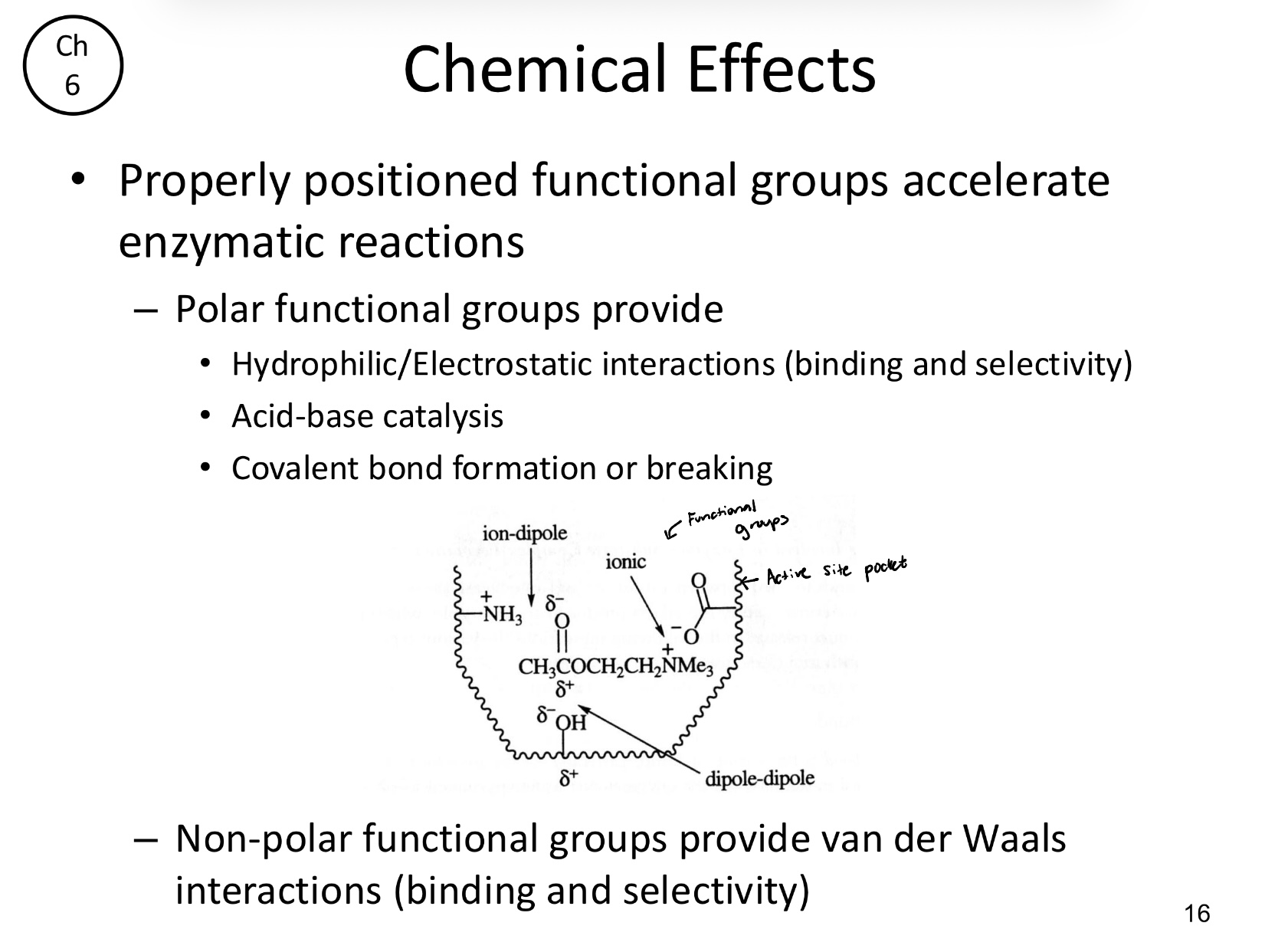
How do polar functional groups facilitate catalysis?
Polar functional groups provide hydrophilic/electrostatic interactions (binding/selectivity), acid-base catalysis, and bond formation
How do non-polar functional groups facilitate catalysis?
Non-polar functional groups provide van der Waals interactions for binding and selectivity
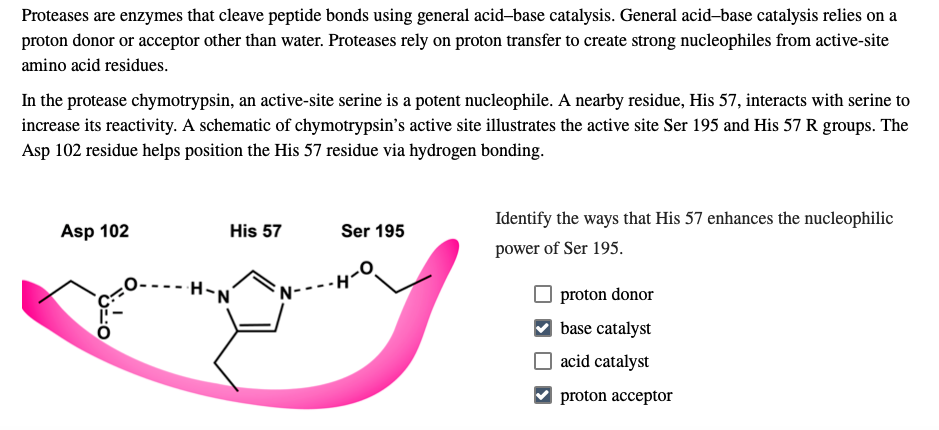
Which enzymes are the most frequent catalytic residues within an active site?
Histidine (18%) and Aspartate (15%) are the most common catalytic residues due to their versatile reactive groups (Imidazole and Carboxylate) which assist in proton transfer and cation binding
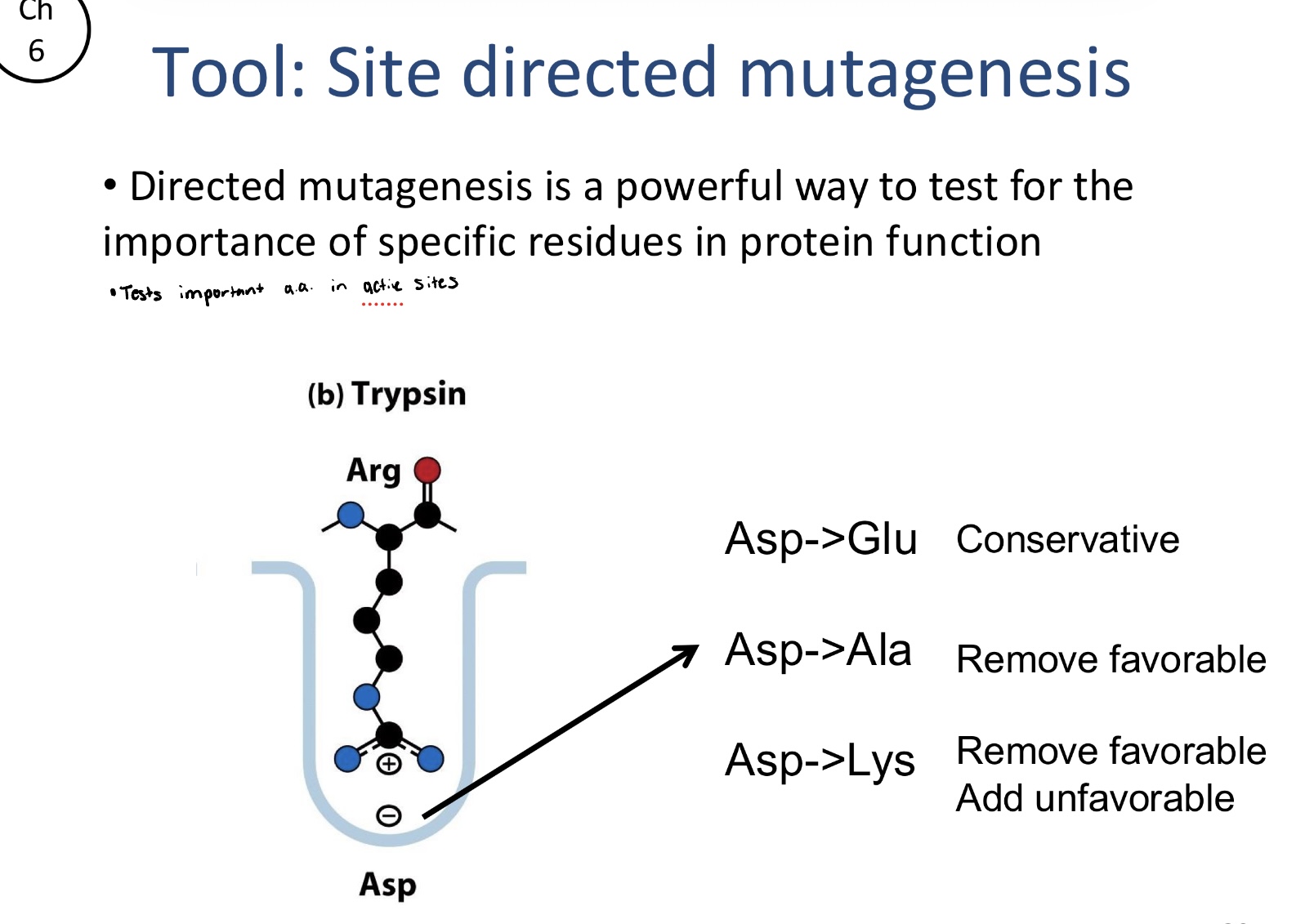
What is directed mutagenesis?
A biochemical tool used to test the importance of specific amino acid residues in protein function. By initially changing one amino acid into another, one can observe how the modification affects the proteins activity.
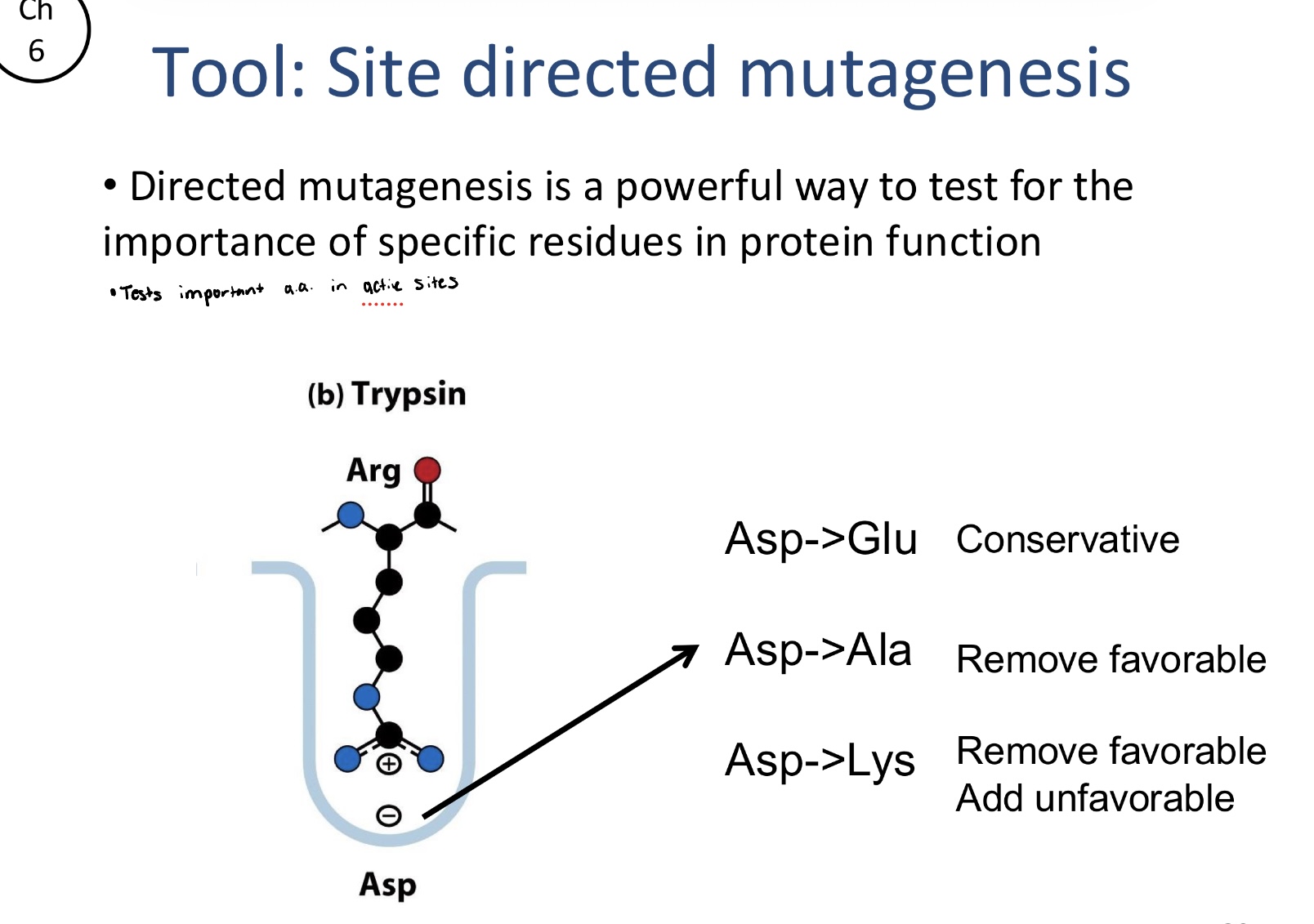
What are the common types of changes in directed mutagenesis?
Conservative changes: swapping Asp for Glu to see if a similar but slightly different residue maintains function
Removing favorable interactions: Swapping Asp to Ala to remove a functional groups that may be critical for catalysis or binding
Adding unfavorable interactions: Swapping Asp to Lys to replace a negatively charged residue with a positive one, which can actively disrupt the proteins native environment