MOD2 Bacterial Anatomy
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
what is a tetrad
cocci arrangement group of four
what are sarcinae
cocci arrangement cube of eight
what is a palisade
bacilli arrangement stacks
involution forms
dead, degenerating, or old/dying bacteria
what causes involution forms
poor growth conditions
lack of nutrients
abx treatment
flagella
long filamentous appendages for movement
what is the outer part of a flagellum
hollow core surrounded by strands of protein called flagellin
how are flagella connected to bacteria
anchored to the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane by a basal body
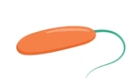
what flagellum arrg is this and what type of movement
monotrichous; rapid and directional movement
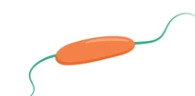
what flagellum arrg is this and what type of movement
amphitrichous; spin/flip end to end/tumbling
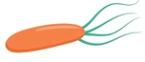
what flagellum arrg is this and what type of movement
lophotrichous'; rapid, directional movement
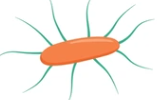
what flagellum arrg is this and what type of movement
peritrichous; slow, non-directional, spinning, circular
which type of bacteria are flagella found
some rods and spirals. NOT cocci
how does flagella work
spinning actions of filaments around each access
requires continuous generation of energy
how can we detect flagella
flagella stains — tar and feather
electron microscope
what movement might be observed with wet preps
brownian motion
drifting/streaming
true motility
what are the advantages of motility
move to areas with better nutrition/atmosphere
colonize another area of host
allows pathogenic bact to spread infection
brownian motion
caused by molecular bombardment by sale against bacteria
appears to vibrate or jiggle
drifting/streaming
everything moves in direction with the flow of the liquid
true motility
movement of bacteria against flow of liquid
slide motility
liquid culture under the microscope, see if the bacteria move
motility media
inoculate a semisolid medium and observe for growth spreading
what growth phase is best for org
log phase
what temperature should plates be incubated in
room temp
what is observed if bacteria is nonmotile using the test tube method
stab line, clear medium
what does a positive motility tube look like
medium is cloudy
what is umbrella motility
cloudy at the top of the tube, stab line and clear medium in the rest
seen w aerobic org — grows with oxygen
what are capsules
organized glycocalyx, firmly attached to cell wall
what is the viscous layer that surrounds cells
glycocalyx
what is glycocalyx +composition
viscous layer excreted by SOME cells
polymer — usually polysaccharide, sometimes polypeptide or combo of both
what are slime layers
unorganized glycocalyx, loosely attached to cell wall
functions of capsules
protection
interferes with phagocytosis
allows bacteria to adhere to host — inc virulence
maintains colonization — forms biofilms
what is a biofilm
community of mono/polymicrobial bac living tgh on surface
what do colonies of capsulated bacteria look like
mucoid and slimy
how are capsules identified on stained slides
clear halo surrounding bacterium
how many genes are in bacterial chsomes
1000-5000
what are plasmids
extrachromosomal elements
nonessential genetic material — can be gained or lost without affecting cell
size: 1-2kilobases to >1megabase
what are the functions of plasmids
encode for Abx resistance
decomp of organics
production of toxins harmful to host
allow bacteria to mate and exchange genetic info
what are fimbriae
non-flagellar, short, hair-like projections — many
on both GP and GN cells
facilitates in adhesion of org to host cell surface
what are pili
longer than fimbriae
only 1 or 2 on cell
aka “sex pili”
exchange of genetic info
ONLY GN
what type of soln is used for bacterial growth and suspensions in the lab
isotonic saline — 85% NaCl
what is in the cytoplasm
80% water
ribosomes
volutin/metachromatic granules —phos. storage
polysaccharide granules —glycogen/starch/food storage
lipids (few bact)
sulfur granules (sulfur bact)
whats a bacterial colony
single bacterium that divides and all daughter bact stay together — forms visible cluster on plates
what is observed when hemolysis occurs on a plate
clearing around colonies
degree of clearing depends on extent of hemolysis
complete RBC lysis = beta-hemolysis
what does the cell wall do
rigid structure outside of plasma membrane
f’n:
cell shape
strength to withstand changes in environmental pressure
protect against mechanical stress
barrier of passage to larger molecules
cell wall composition
peptidoglycan aka murein layer
NAG and NAM sugars = backbone
NAG/NAM polymers cross link to form polypeptide sheets
sheets cross link w each other to form multilayer
whats the difference between the cell walls of GPO and GNO
GPO has thicker peptidoglycan layer (up to 10x)
GNO have outer phospholipid/lipopolysaccharide layer
GPO has teichoic acid
penicillin inhibits cell wall synthesis by binding enzymes in peptidoglycan production, why is it not usually used for GNO
outer lipid layer on GNO protects peptidoglycan layer
abx would be ineffective
GPO doesnt have lipid layer, more exposed peptidoglycan
why do we use gram stains
rapid assessment of level of infection prior to having culture
allows physician to decide what abx to use
what happens if a direct smear is too thick
cellular detail unclear
may interfere with staining
bacteria may be hard to find
what happens if a direct smear is too thin
cellular and bacterial populations not accurately represented
difficult to locate cells
inaccurate staining results
what is the first step of gram staining
fixation
what is fixation —gram staining
process of adhering specimen to glass slide
kills bacteria — NOT spores
fixes morphology of the cells
makes cells more permeable to stain
prevents autolysis
what happens if the specimen is not fixed to the slide
specimen may wash off slide
cells may float in oil under scope
what happens if the specimen is overfixed
poor staining results
odd shapes
pale staining
what four reagents are used in gram staining
primary stain of crystal violet CV
iodine I
decolourizer
counterstain of safranin
crystal violet
first reagent used in gram staining
cationic/basic stain
positively charged stain molecule
bonds with negatively charged proteins in cell
all cells/bact stain DARK BLUE
iodine
mordanting effect — enhances staining effect
forms crystal violet-iodine complex
traps CV dye into cells/bact
mordant
molecule that enhances the staining effect
decolourization
most important step
uses acetone-alcohol
makes peptidoglycan layer more porous
allows CV-I to escape
GPO: thick peptidoglycan layer retains CV-I — still dark blue
GNO: thin layer, CV-I leaves cell — colourless
what happens if a slide is over decolourized
affects cell wall integrity
GPO appear pink instead of blue
excess CV-I taken out
false GN
what happens if a slide is under decolourized
GNO appear blue
not enough CV-I taken out
false GP
safranin
last step
counterstain
colourless GNO take up counterstain
appear pink/red
what objective lens should gram slides be examined under
100x oil immersion lens
what colour should the background of the slide be
pink bcs last stain was pink
factors affecting gram stain
lysozyme in human fluids
rough handling of bact during processing, freezing, drying, heat, ect
cells in death phase/ old
patient alr on abx
*expired reagents*
what bacteria type are spores found in
only gram positive bacilli
when are bacterial spores formed
when nutrients are low/depleted or environmental conditions are poor
survival mechanism
when is the best time to see spores
death phase of bacterial growth
what do spores look like under the scope
resistant to staining
hollow cavity in cell
endospore — middle of cell
terminal spore — end of cell
qualities of spores
heat resistant — autoclave to destroy (121C)
not killed by moderate heat or disinfectants
can survive in environment for years
survival factor, not virulence factor