SET 4 - History of Art: ID-2241 Exam 4
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Humanism
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms

Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
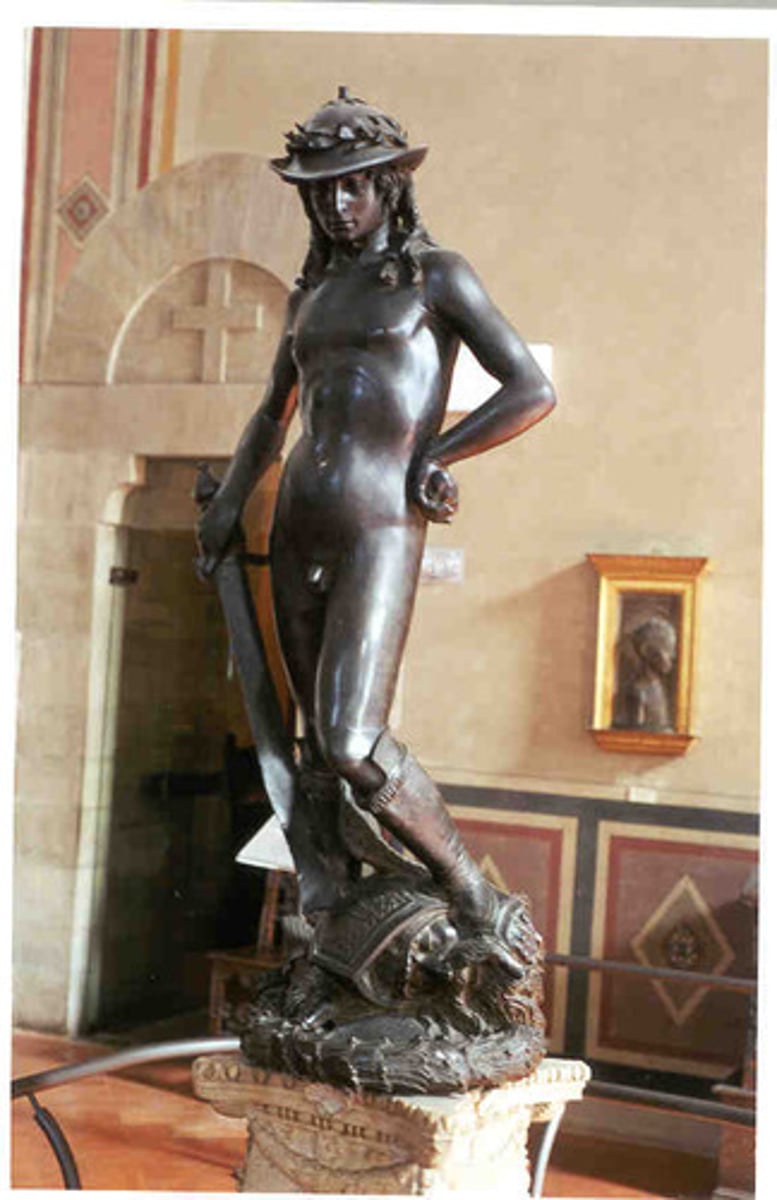
David
1432
Humanism Art
Giottesque becomes Humanism
sculpted by Donatello, (Quattrocento)
story of David and Goliath
subject matter
after the defeat of Goliath hero as triumphant transtion
from youth to maturity
focus on human hero (not mythological character, mortal) intellect over might (without armor, not using body to resolve issue), beauty of human body as representing the "perfection of the soul"
lost wax process of bronze casting
open form, free standing
contrapposto stance ("ponderation", first of its kind in a long time)
first nude figure since ancient Greek/Roman period (nude images were banned by Church)
first successful use of contrapposto stance since the ancient Greek period
first free-standing sculptural figure since the Greek-Roman period

Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
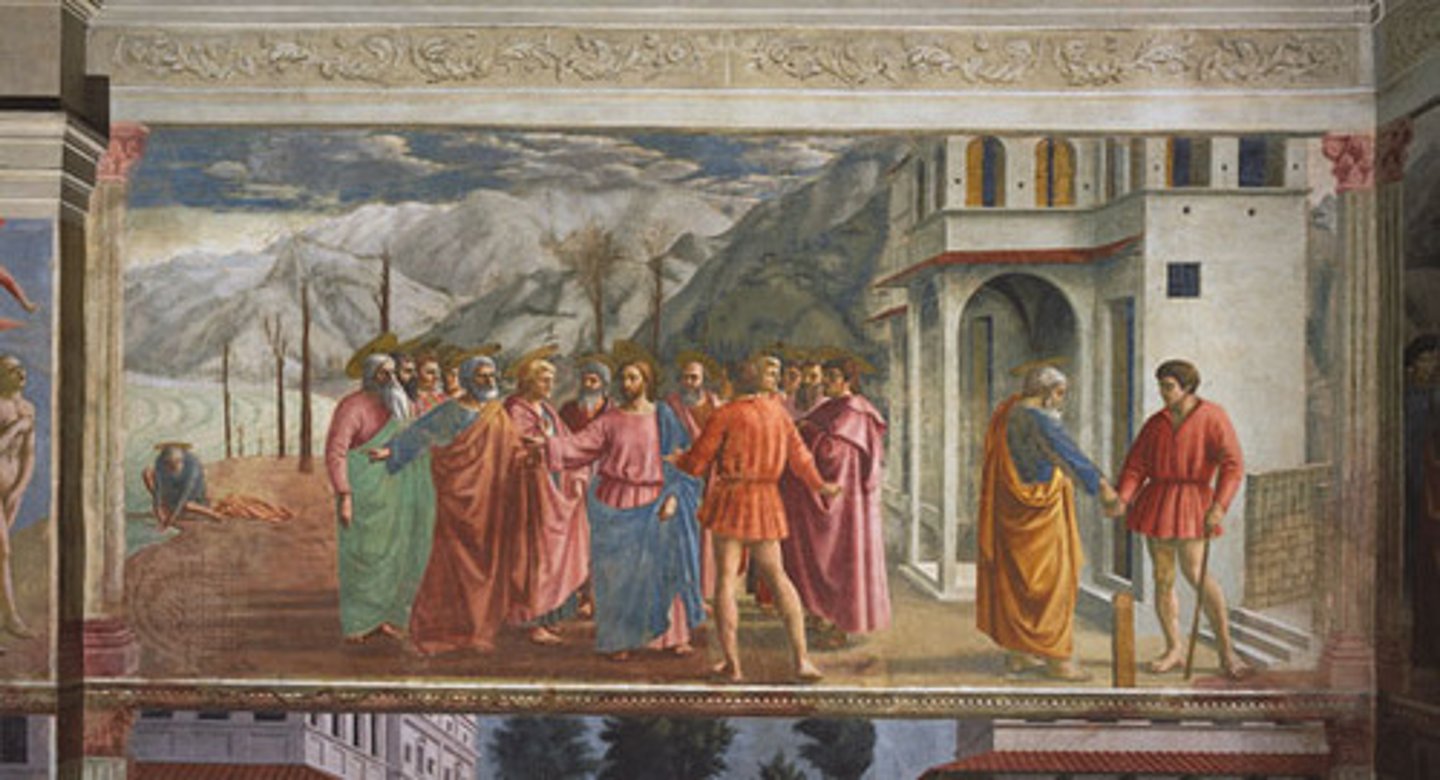
Tribute Money, Brancacci Chapel, Florence
1427
Humanism Art
tax tribute being paid to the Romans
painted by Masaccio, in the Brancacci Chapel in Florence, (Quattrocento)
continuous narration (showing the story of Peter paying taxes)
Giottesque
3D earthly space/3D earthly humans, perspective systems (planimetric separation, overlapping, linear perspective with orthogonals)
Sfumato (further away become sky becomes distorted to imply that it is very deep)
modeling (convexity of human forms)
dramatic (human) moment

Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
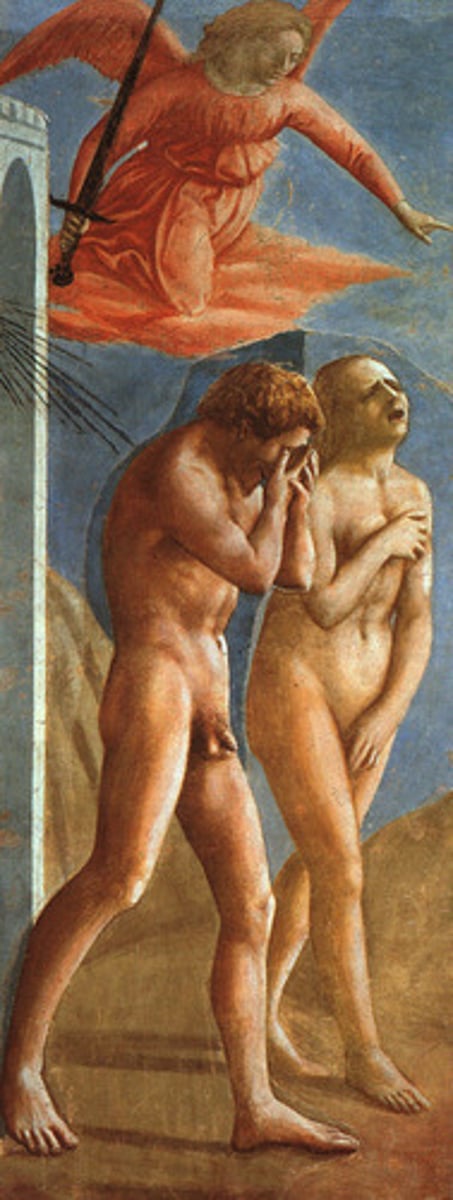
Expulsion of Adam and Eve, Brancacci Chapel, Florence
1425
Humanism Art
painted by Massacio in the Brancacci Chapel in Florence (Quattrocento)
earthly-human space beyond depicted arch
shown as nude to emphasize their human state, casting shadows
focus on human dilemma, - moving through space, time
emotion (suffering) - Eve: birthpains, Adam: toil
anatomy (navel) - earthly born, having to birth children, amblical cord

Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
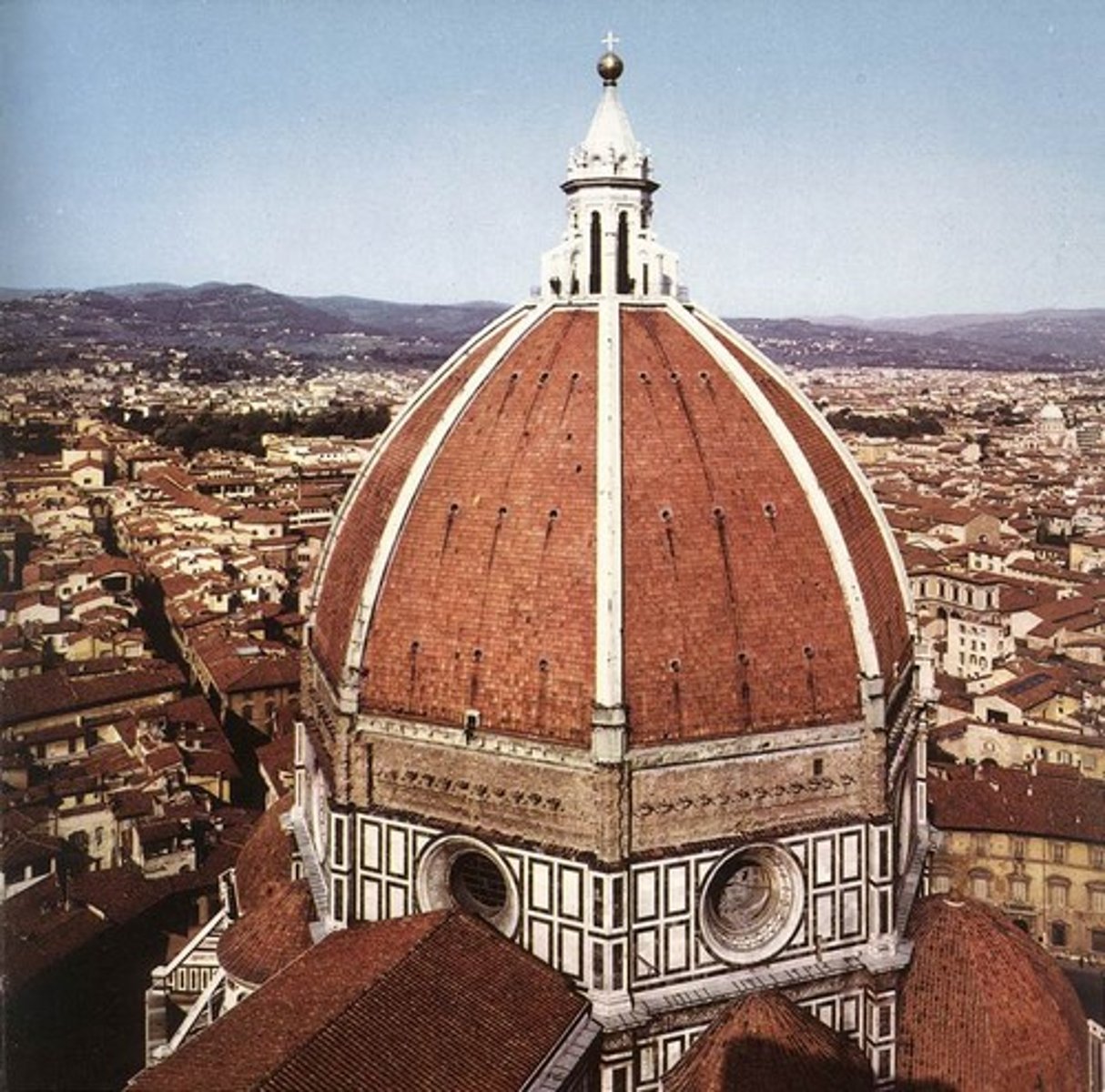
Dome of Florence Cathedral
Humanism Art
1436
designed by Filippo Brunelleschi
studied human ribcage
double shell (8 exterior ribs, 24 interior ribs, based on human anatomy, transfer weight downwards)
lantern on top of dome , small tower placed on top of dome
starts transfer of weight,
latern necessary to stabilize dome shape

Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
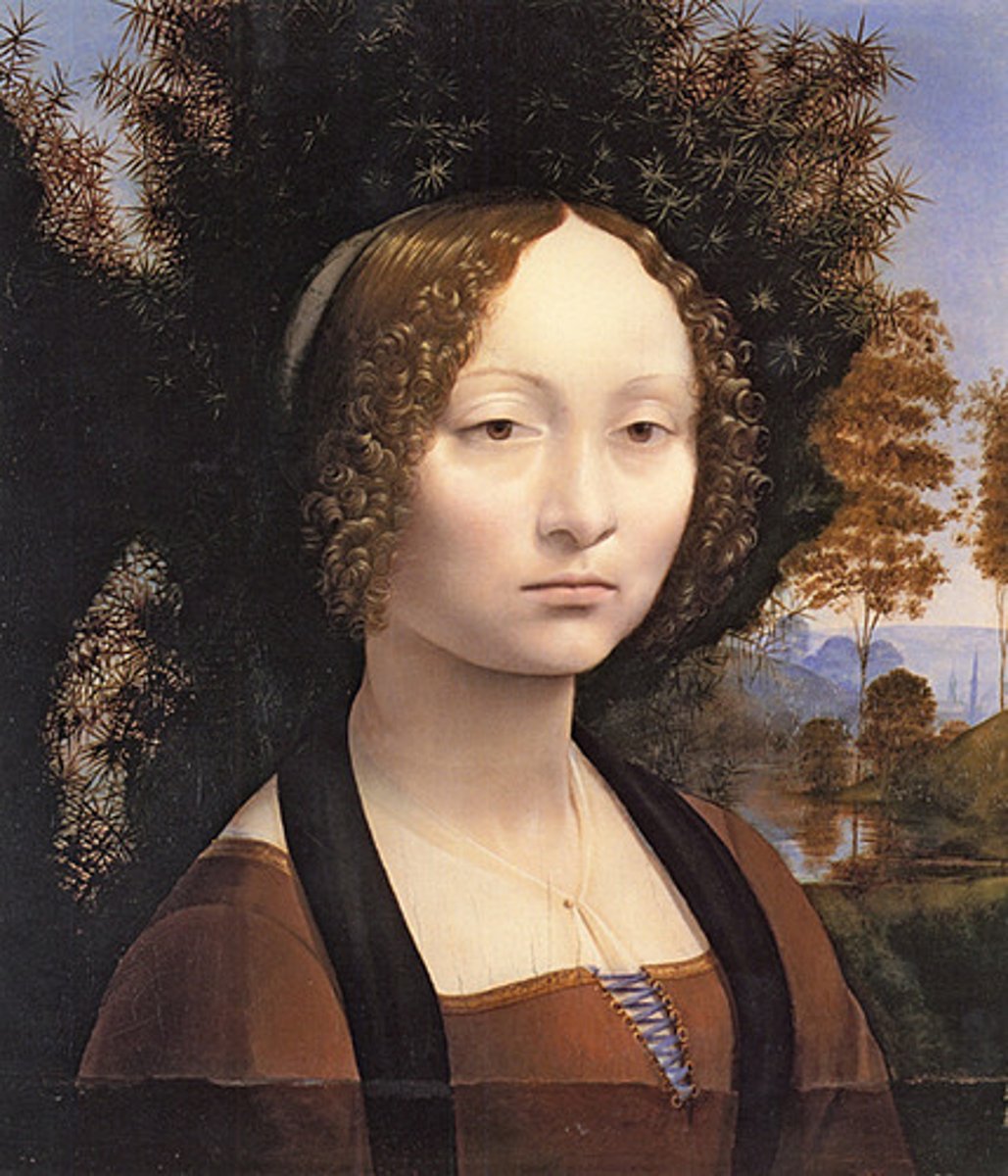
Genevra di Benci
1480
Humanism Art
painted by Leonardo da Vinci
smaller than lifesize
concave space (earthly human space)
perspective systems (planimetric separation)
vanishing point - where it all disappears, complete distance
convex forms (human forms in earthly space, conforming to gravity and 3-dimensionality)
3/4 pose (one shoulder in foreground, other in middle ground, mediation)
chiaroscuro - mapping of convex, concave surface with shadows
Genevra = Juniper tree, her name (tree is located in the painting, behind her head)

Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
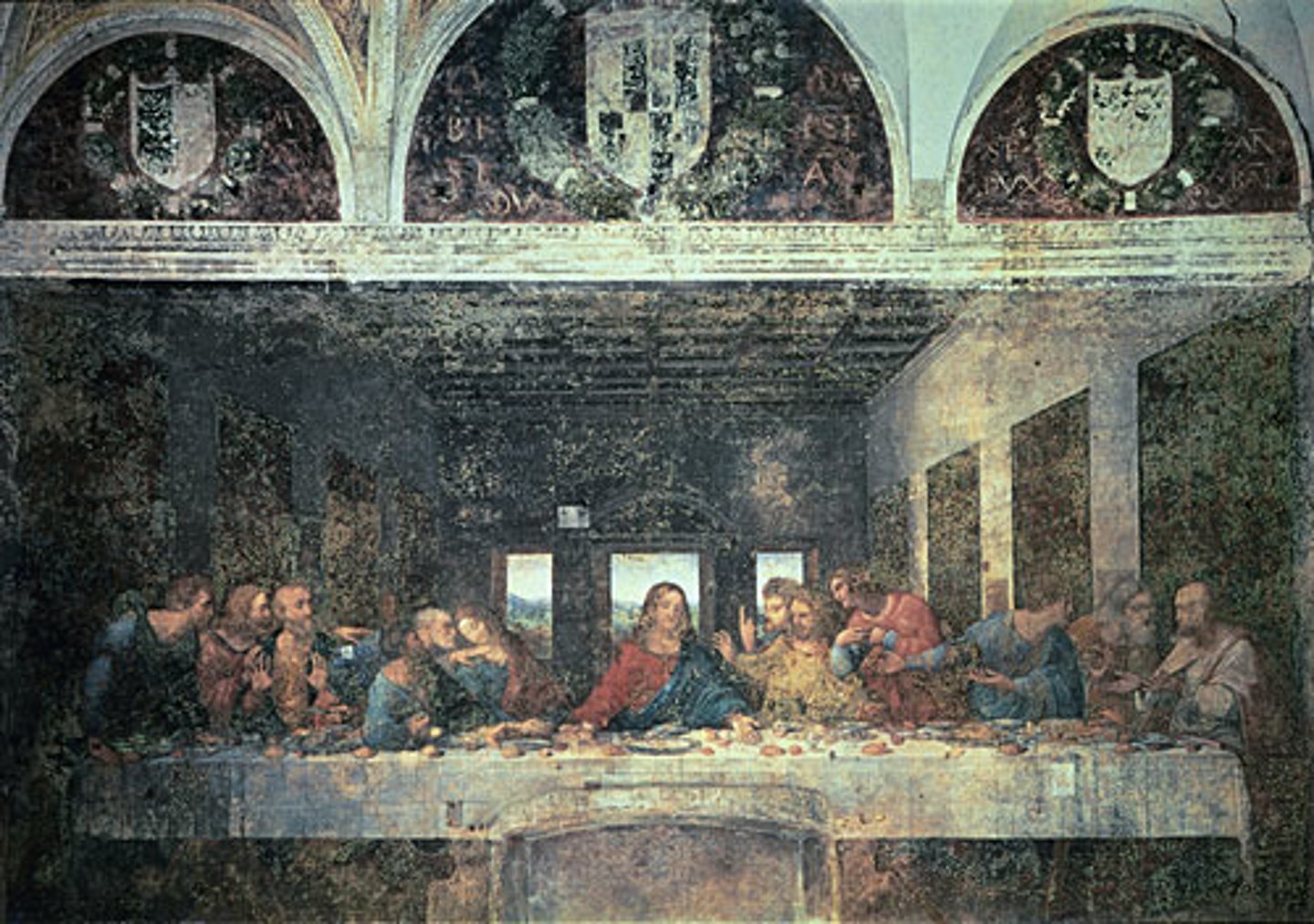
The Last Supper, the refectory of Santa Maria delle Grazie, Milan
1498
Humanism Art
Painted by Leonardo da Vinci in the refectory of Santa Maria delle Grazie
waxing pigment would come of wall before restoration
door cut into wall that removed the feet of Christ
Eucharist
Streatched out that makes up a triangle
Three windows
Disciples in groups of three making up in a triangle
vanishing point (distant point at which infinity is implied)
realistic earthly halo - light refelcting from windows on back of head becomes halo
viewer vantage point from other communion table
orthogonals from painting "in the architecture" to match actual room
implied lines (eye beams)
multiple moments, represents humanity of Christ in earthly setting
gesturing away, like everyone is reacting to something, Christ announces someone will betray him
Judas
head is the lowest, tells his story
Thomas
touches the resurrection of Christ
Peter
holds a knife to represent that he will cut off someone’s ear later

Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
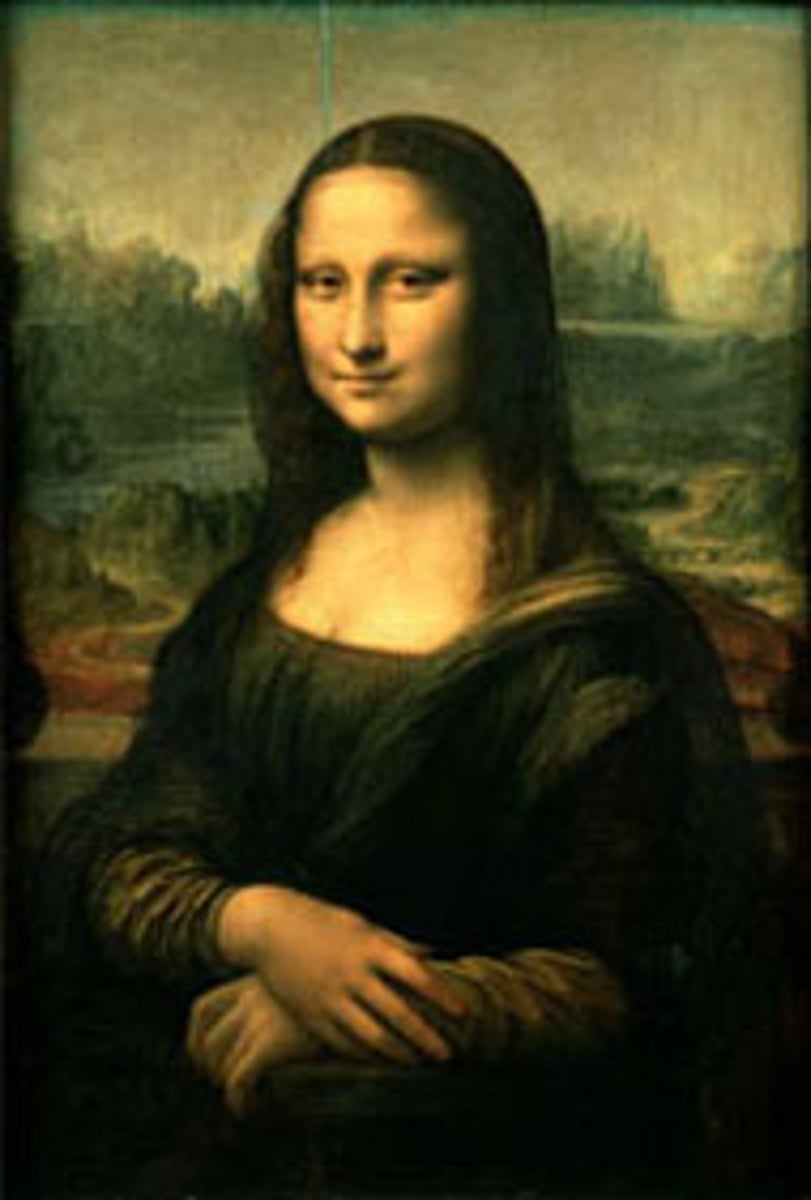
Mona Lisa
1505
Humanism
painted by Leonardo da Vinci
concave space (planimetric separation, vanishing point)
convex form (3/4 pose, , )
chiaroscuro
modeling
30 layers of paint (building space, layering, creating forms)
from inner to outer
strcuture
skin
clothing/hair
light/shadows
divides lanscape after head and after body
different landscape behind head (divine creation by God) and behind body (creation by humans, bridges, roads)
implied lines (motion, eye glance)

Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
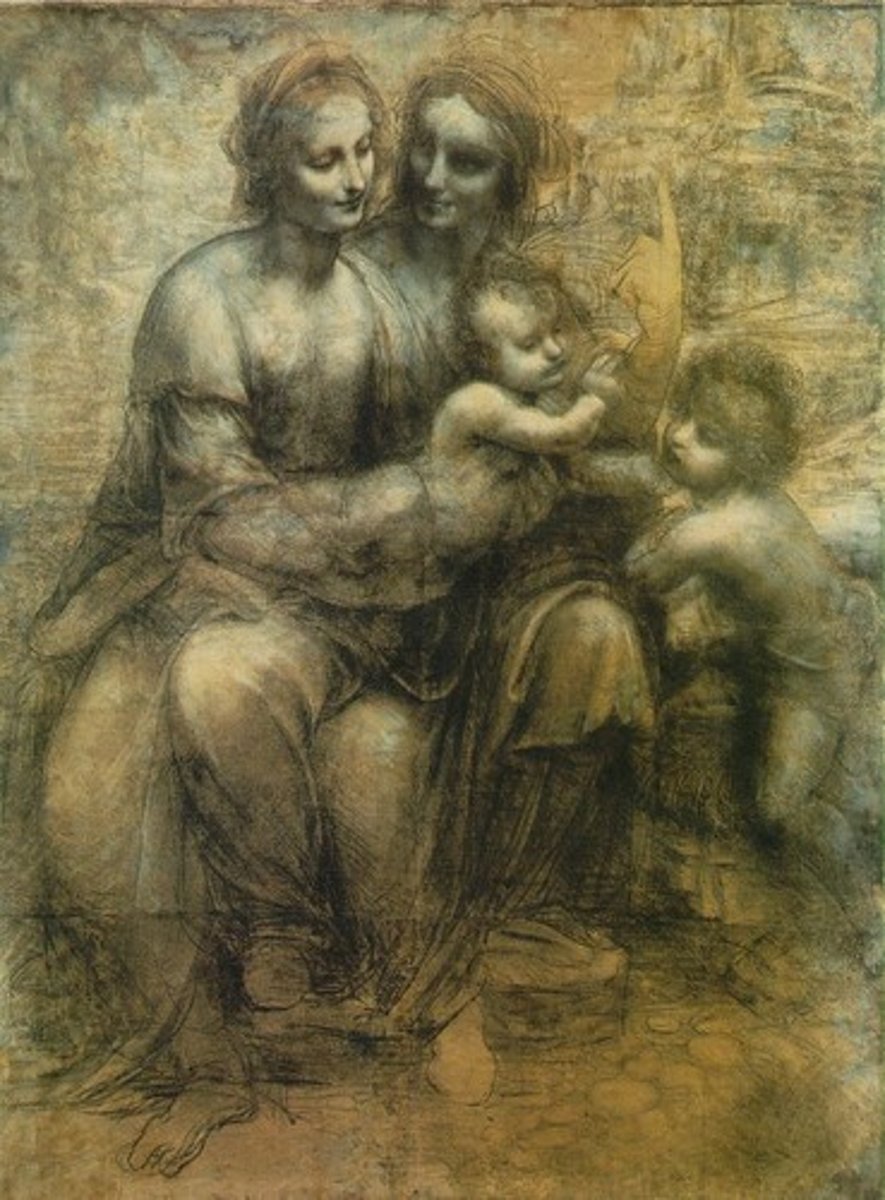
Cartoon for Leonardo, Virgin and Child with St. Anne
1498
Humanism
Drawn by Leonardo da Vinci
cartoon (life-sized preparatory study)
Anne (mother of Mary), Mary, infant Jesus, John the Baptist
eye glance (depicts family lineage, maternal family tree)
pointing gesture to God the Father, bleassing hand up to Godblessing

Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
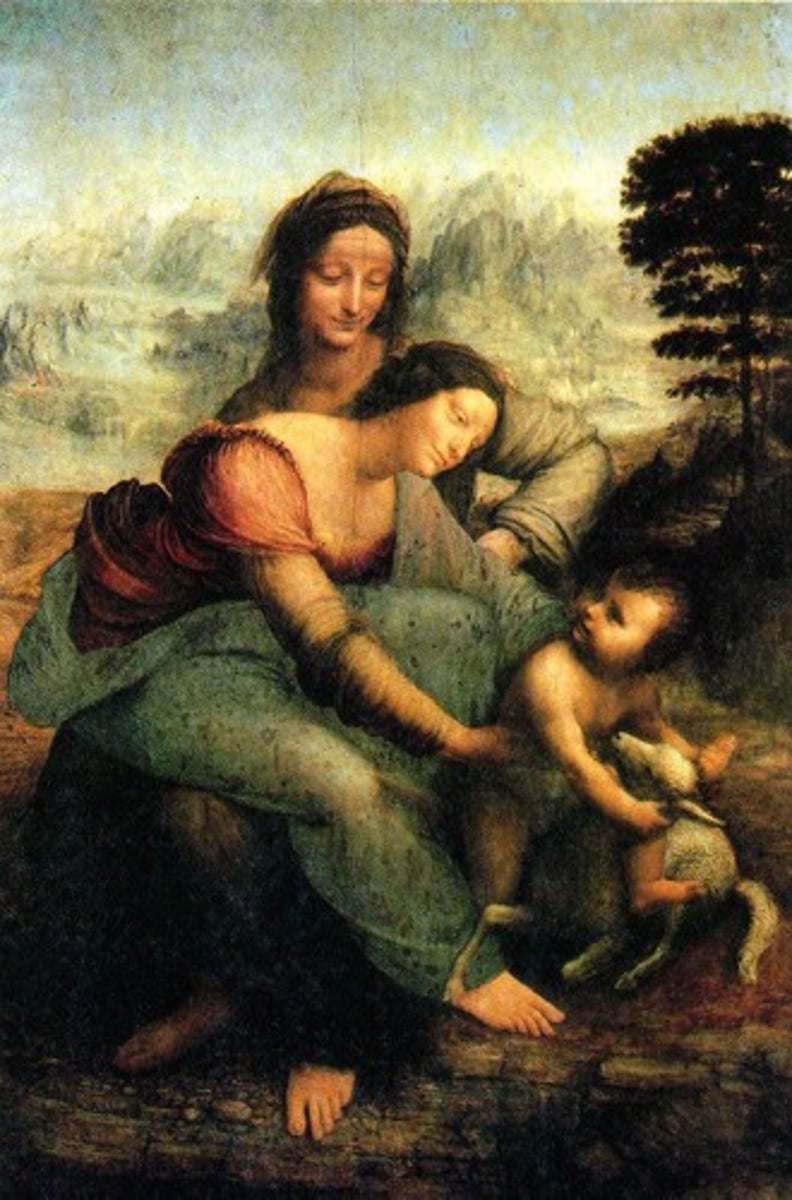
Oil Painting of Virgin and Child with St. Anne
1513
Humanism
Painted by Leonardo da Vinci
Removes John the Baptist and is replaced with a lamb, represnting that Christ is the sacrifce
Anne: foundation, feet on ground, most earthly
Virgin Mary: floating, in between earthly and divine
upper background back of human heads(divine creation) and lower background behind bodies (earthly/human)
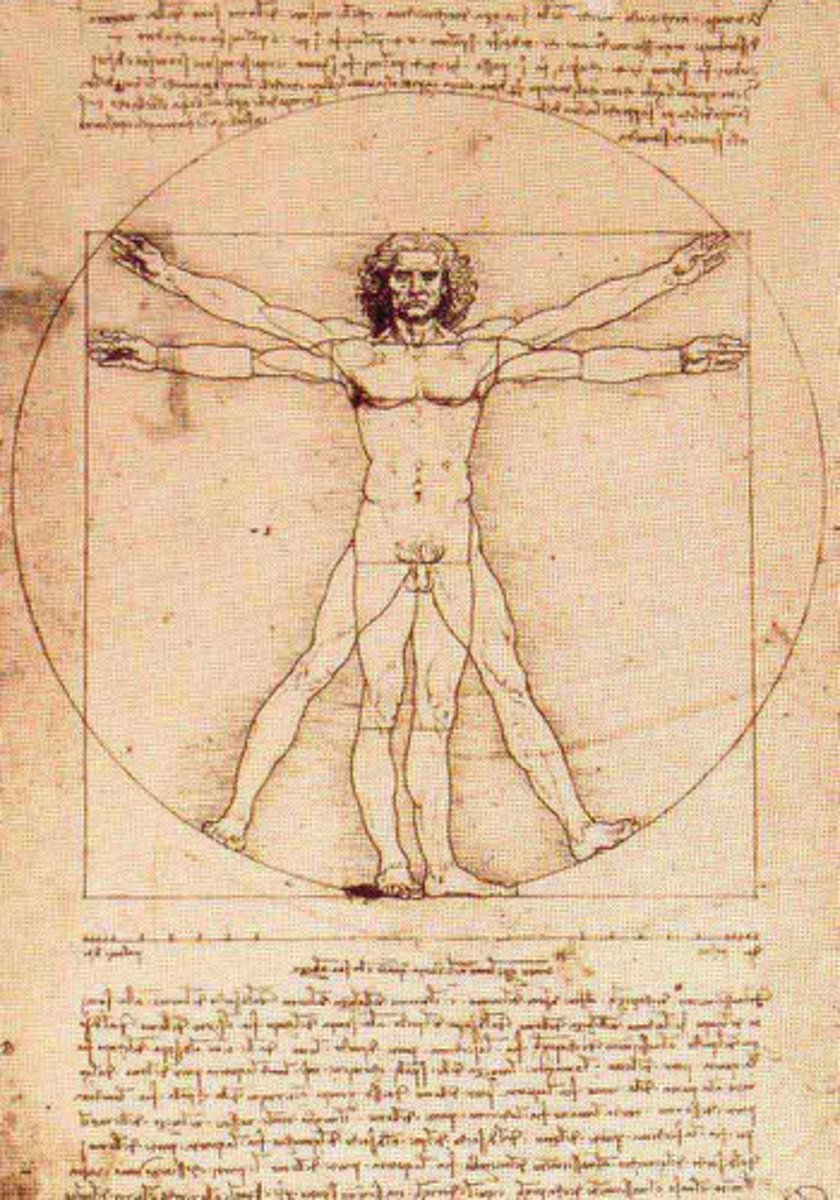
Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
Vitruvian Man
Humanism
notebook page written by Leonardo da Vinci
Vitruvius (1st c. BC Roman architect)
human as center of the world
navel
self-portrait
geometrically perfect
square reconciled with circle

Name?
Date?
Period?
Facts?
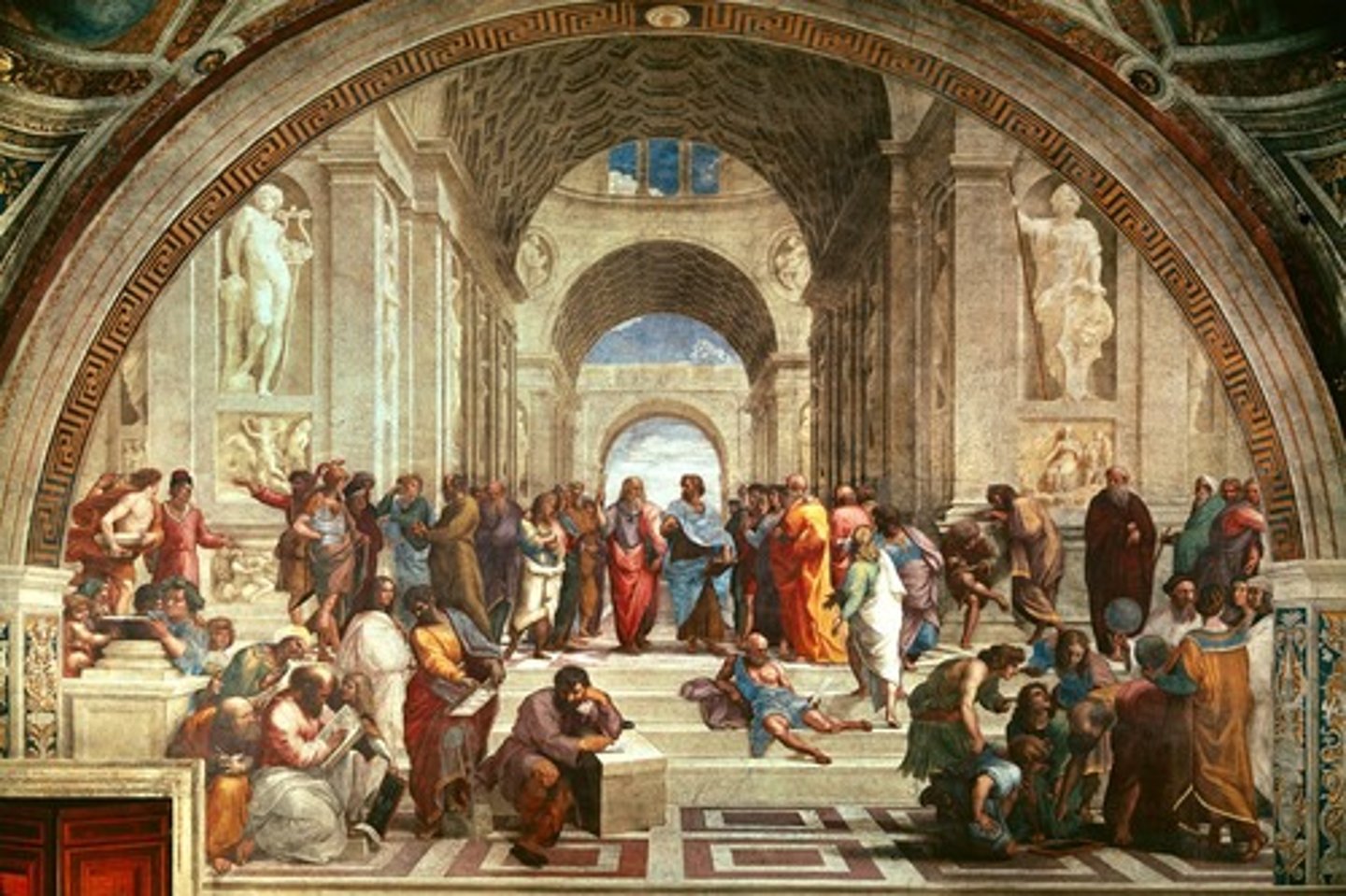
School of Athens, Raphael in the Vatican
1509-1511
Humanism
painted by Raphael in the Vatican
references to Ancient Greco-Roman world
representation of Earthl/human
concave space
human made architecture
planimetric separation
foreground: the Renaissance world/artists - architecure, Brunelleschi
middle ground the ancient Greco-Roman world: Plato, Aristotle
vanishing point
linear perspective, orthogonals
convex forms
modeling
chiaroscuro
Plato (ancient Greek philosophy) and Aristotle (ancient Science)
references to Renaissance artists in foreground
connects Renaissance "renewal" with knowledge from the past
Humanism characteristics
Quattrocentric Art: Humanism
Bubonic plague so a gap in history
referring to the Ducciesque and Giottesque styles
Giotesque becomes Humanism
focus on human form
focus on human stories
accurate human anatomy: contrapposto (ancient Greek sculpture)
Nudity - human body as the refelction of the perfection of the soul, perfect engineering (Ancient Greco-Roman philosophy)
Stories of human heriosm (not mythological stories)
representation of human emotion, psychology
ponderation
perfection of the contrapasso
continuous narration
multiple moments in a story that is presented in the same space
Sfumato
"mistiness", atmospheric perspective, concave space
vanishing point
background space so distant that it disappears = infinity
chiaroscuro
clear/obscure, manipulation of lines to indicate depth of shadows, technique to produce 3D effect, lines to indicate shadows
cartoon
life-sized preparatory study