Unit 2 - The Living World Biodiversity
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
biodiversity
The diversity of life forms in an environment.
genetic diversity
A measure of the genetic variation among individuals in a population.
species diversity
The number of species in a region or in a particular type of ecosystem.
ecosystem/habitat diversity
The variety of ecosystems within a region.
bottleneck effect
A reduction in the genetic diversity of a population caused by a reduction in its size (usually due to a catastrophe, such as a fire or hurricane).
species
A group of organisms that is distinct from other groups in its morphology (body form and structure), behavior, or biochemical properties. It is a group of individuals that are able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
speciation
The evolution of new species.
background extinction rate
The average rate at which species become extinct over the long term – about 2 species per year worldwide.
species richness
The number of species in a given area – a measure of species diversity.
factors that influence species richness
Latitude (highest towards the equator/where there is more sun available), Time (the longer a habitat exists, the more colonization, speciation and extinction can occur), Habitat size (can support more species), and Distance from other communities (may have fewer species due to distance).
species evenness
The relative proportion of individuals within the different species within a given area. An ecosystem has high species evenness if its species are all represented by similar number of individuals.
habitat
The place where an organism lives (its address) – the place where an organism finds food, shelter, protection, etc..
specialist species (with examples)
Species with a narrow ecological niche. They may be able to live in only one habitat and can only tolerate a narrow range of conditions. Examples include Koalas and pandas.
generalist species (with examples)
Species with a broad ecological niche. They can live in many different places, eat a variety of food, and tolerate a wide range of environmental conditions. Examples include Humans, rats, mice, cockroaches and flies.
simpsons diversity index (what it is)
A calculation that is a measure of diversity that takes into account both richness and evenness. Values near 1 indicate a highly diverse ecosystem, and values near 0 indicate a less diverse ecosystem.
shannon wiener index of diversity (what it is)
A calculation that is a measure of diversity that takes into account both richness and evenness. Values near 7 indicate a highly diverse ecosystem, and values near 0 indicate a less diverse ecosystem.
ecosystem services
The processes by which life-supporting resources such as clean water, timber, fisheries, and agricultural crops are produced.
provisioning services
The “products” obtained from ecosystems.
Food
Fibers
Ornamentals
MedicinesBiofuels
Fresh water
Genetic resources
regulating services
Benefits obtained from the regulation of ecosystem
Climate regulation
Flood prevention
Erosion control
Pest control
Pollination
Seed dispersal
Disease regulation
cultural services
Nonmaterial benefits obtained from ecosystems
Educational
Recreational
Sense of place
Spiritual
Cognitive development
Stress relief
Gardening
Tourism
supporting services
services necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services
Biodiversity
Nutrient recycling
Primary productivity
island biogeography (including distance, evolution, and biogeography)
A theory that demonstrates the dual importance of habitat size and distance in determining species richness. Distance from the mainland influences species richness because fewer species can disperse longer distances. Evolution is also affected, as some species have evolved to be specialists due to limited resources on an island. The theory may also refer to protected habitats (like national parks) surrounded by less hospitable areas (a form of biogeography).
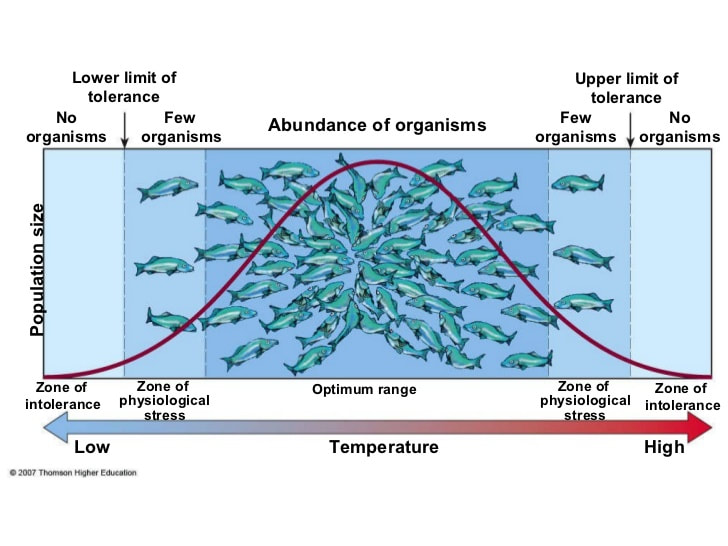
ecological tolerance
The limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate before injury or death results (also called range of tolerance). Every species has an optimal environment in which it performs well.
tolerance curve
Illustrates the range of survival for a species or population
survive, grow, and reproduce → survive and grow → survive
fundamental niche
The set of abiotic conditions under which a species can survive, grow, and reproduce.
realized niche
The range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species actually lives
anthropogenic activities
(chiefly of pollution or environmental change) originating in human activity
Deforestation
Overpopulation
Pollution
K-T extinctions
more than ¾ of all plant and animal species became extinct
local extinctions
local natural species go extinct in their original habitats
background extinctions
the loss of species at a low rate of extinction (1 to 5 species for each million species on Earth)
mass extinctions
a significant rise in extinction rate (25%-75%)
usually due to some catastrophic event
episodic
groups of events that happen occasionally
El Nino
Hurricane Season
Pollen Release
microevolution
evolution below the species level
small genetic changes
macroevolution
evolution that gives rise to new species
genera, families, classes, or phyla
large scale, long term evolutionary changes
artificial selection
the process in which humans determine which individuals breed
dog breeding
herbicide resistance
the process by which farmers' repeated use of the same herbicide creates a selective pressure on weed populations, causing them to evolve resistance over time
natural selection
the process in which the environment determines which individuals survive and reproduce
survival of the fittest & adaptation
mutations
a random change in the genetic code produced by a mistake in the copying process
as the number of mutations accumulates, evolution occurs
gene flow
the process by which individuals move from one population to another and thereby alter the genetic composition
genetic drift
a change in the genetic composition of a population over time as a result of random mating
founder effect
a change in the genetic composition of a population as a result of descending from a small number of colonizing individuals
speciation
the evolution of a new species
new species evolve through two processes
allopatric speciation
the process of speciation that occurs with geographic isolation
sympatric speciation
the evolution of one species into two, without geographic isolation
ecological succession
the predictable replacement of one group of species by another group of species over time
primary vs secondary succession
primary occurs on surfaces initially devoid of soil
secondary succession occurs in areas that have been disturbed but not lost their soil
primary succession
pioneer species → help create soil → mid successional species → grow and help form more soil → late successional plant (mostly trees) → climax community
pioneer species
a species that can colonize new areas rapidly and grow well in full sunshine
they break down the rock chemically and physically
these processes along with the organic matter of dying pioneer species create soil
keystone species
a species that is not very abundant but has large effects on an ecological community
indicator species
a plant or animal species that, by its presence, abundance, scarcity, or chemical composition reflect the conditions of the ecosystem around it