Biochem Unit 3 Week 1
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What form are high energy electrons captured in in the CAC cycle?
NADH and FADH2
Where does the CAC occure?
mitochondrial matrix
Where does the ETC occur?
mitochondrial matrix
How many complexes make up the ETC?
5
Which complexes of the ETC are pumps?
1,3,4,5
What is the ultimate acceptor of electrons in the ETC?
O2
What direction does H+ move in the transport pumps in ETC?
For complexes 1,3,4 H+ is moved out of the matrix. For complex 5, H+ is moves into the matrix.
What are the steps of the ETC?
C1, C2, Coenzyme Q, C3, Cytochrome C, C4, c5
The ETC catalyzes the flow of electrons from (high/low) reduction potential carriers to (high/low) reduction potential carriers
low, high
Is the ETC endo or exo? why?
Exo; Energy is released when the high energy electrons are transferred to oxygen.
Summary of Complex 1
E- are transferred from NADH to coenzyme Q
Summary of C2
e- picked up from succinate; passed to FADH2 and then to ubiquinone
Summary of C3
transfer of e- from coenzyme Q to cytochrome C
Cytochrome C purpose
Carries e- to complex 4 of the ETC
Summary of Complex 4
E- carried by cytochrome C are transferred to oxygen
What redox reactions occurs in C1?
NADH>NAD+
What redox reactions occur in C2?
Succinate>Fumarate, FAD+>FADH
What redox reaction occurs in C3?
None
What redox reaction occurs in C4?
O2 to H20
What reaction occurs in C5?
ADP+Pi>ATP
What do electric potentials tell us?
High means that the reaction is favored, low means that the reverse reaction is more favored.
How to calculate cell potential of two half reactions:
E’cell=E’reduction-E’oxidation
What molecule is the ultimate electron receiver in general?
O2 (Forms H20)
Ecell formula
Ecell= E’cell-(RT/nF)lnQ
How to compare the amount of energy transferred in two REDOX reactions?
A higher difference in E’ is representative of higher energy transfer
What is the prosthetic group structure for C1 and C2?
Fe-S (iron covalently bound to sulfurs of Cysteine groups)
What is the prosthetic group for C3?
Heme
What is the prosthetic group for C4?
Heme and Copper
Whats the difference between heme in hemoglobin and complex 3/4?
For complex ¾, iron alternates between a 2+ and 3+ charge
Overall reaction for NADH-Q Oxidoreductase
NADH + Q + 5H+matrix > NAD+ + QH2 + 4H+intermembrane space
What happens in Complex 1?
E- goes from NADH to FeS prostheetic groups to Q. When Q gets the electrons, its negative charge causes a conformational change in the complex. This conformational change changes the pka so that the side chains of the complex accept protons. The protons move from the matrix side, through the water channel, and then get carried out by the intermembrane side chains.
What happens in complex 3?
Electrons from the reduced Q are used to reduce two molecules of cytochrome c
How many electrons can Cytochrome C accept?
Only one at a time. It goes from Fe3+ to Fe2+
What happens in Complex 4?
The electrons from cytochrome C go to the heme group. The reduced Cu and Fe in heme bind to O2 to form a peroxide bridge. The cytochrome C donates more electrons. And now there is an OH bound to Fe and Cu. This repeats and now we have two H20 leaving groups.
What is the name of each complex of the ETC?
NADH Q Oxidoreductase
Succinate-Q Reductase
Q-Cytochrome C Oxidoreductase
Cytochrome C oxidase
ATP synthase
Which carrier in the ETC is a protein?
Cytochrome C (NOT coenzyme Q)
What is the ETC coupled with?
Complex 5, ATP synthase
Where do electrons from the CAC go?
Complex 2 of the ETC, and some to Complex 1
Differentiate which section has greek letters and which one has regular: F1, F0
F0-regular, F1-greek
What subunits makeup the ‘knob’ of the ATP synthase?
3 alpha beta dimers
Where is the catalytic active site in ATP synthase?
The alpha beta dimers
What subunits make up the rotor of ATP synthase?
gamma and epsilon
When the ATP synthase complex spins, which subunits are spinning360 degrees and which are stationary?
The gamma, epsilon, and C subunits spin while the rest are stationary
What subunits make up the peripheral stalk or stator of ATP synthase?
a, b2, delta
What is the purpose of the peripheral stalk of ATP synthase?
Stabilizes the knob so that it does not spin. Also, protons enter the complex through the A sub unit of the peripheral stalk
Describe how the central stalk or axel of ATP synthase spins
It spins 360 degrees in 120 degree jolts as the energy from the c subunit builds up.
What role does ATP synthase have in the structure of the miochondria?
ATP synthases dimerize which causes the folding of the intermembrane of the mitochondria aka the cristae. The cristae and nearby ETC helps create the proton gradient for ATP synthase.
What residues are found on the C subunits?
Acidic aspartate or glutamate residues
What reaction drives the spinning of the C subunit?
HA & h20 > A- & H30+
How do we get NADH into the ETC in muscles?
Glycerol phosphate shuttle
What happens in the glycerol phosphate shuttle?
Electrons from NADH are passed onto dihydroxyacetone phosphate. The product of this is glycerol 3 phosphate. The glycerol 3 phosphate passes the electrons off to E-FAD. E-FADH2 passes the electrons onto Q. Note that NAD+ is regenerated!
Why is NAD+ regenerated in the glycerol phosphate shuttle?
To participate in other reactions like glycolysis
How are NADH molecules transferred to the ETC in the heart and liver?
Malate-aspartate shuttle
Draw the malate-aspartate shuttle
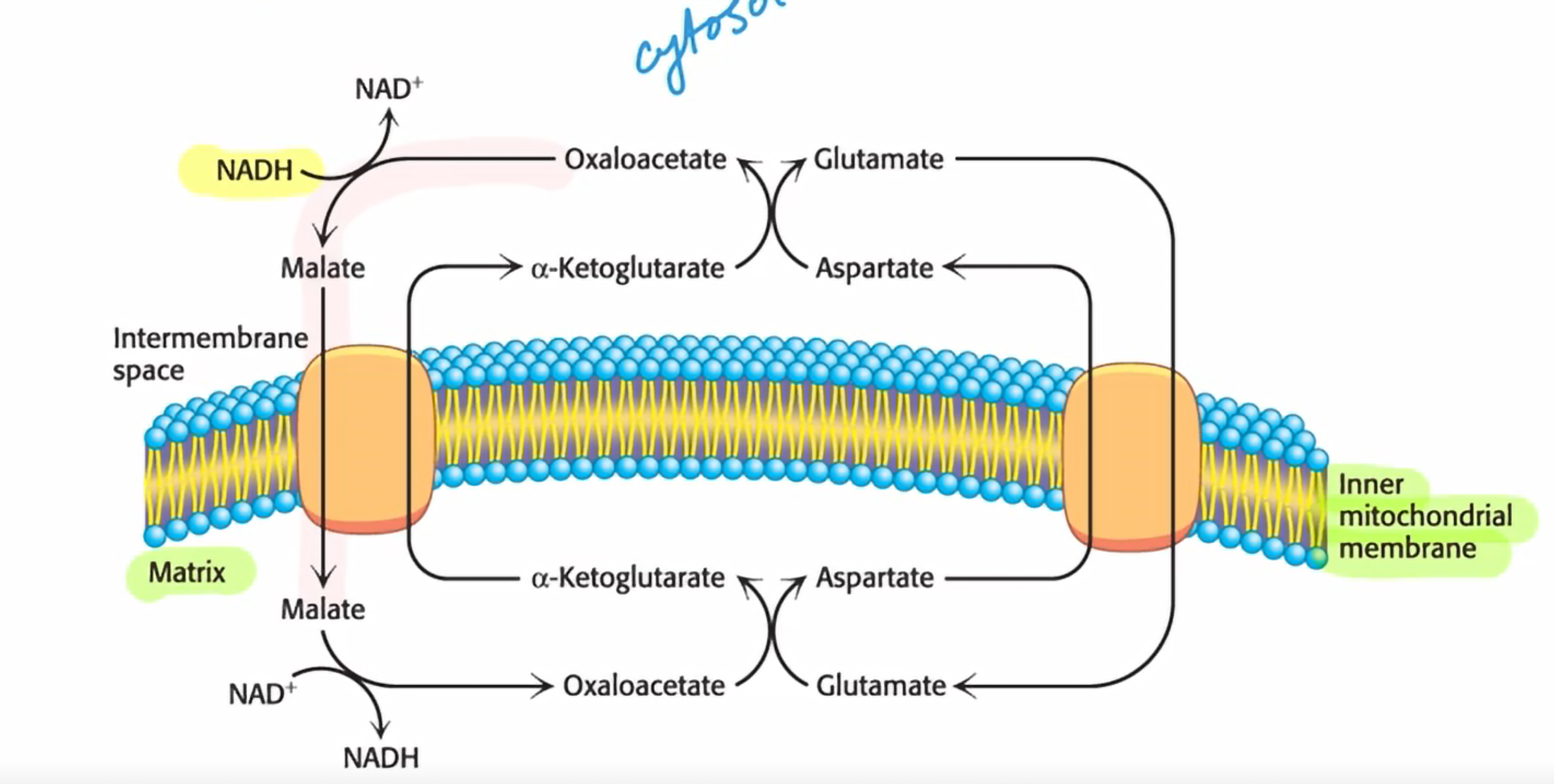
What type of reaction happens in the malate aspartate shuttle?
Antiport reactions and transanimation reactions
How does ADP enter the mitochondrial matric?
It is coupled with the exit of ATP and the reaction is catalyzed by ATP-ADP translocase. It is powered by the proton-motive force
ATP has a more negative charge than ADP. This helps what?
This helps to drive ATP out of the cell and ADP into the cell
What makes up ATP synthosome?
ATP-ADP translocase, the phosphate carrier, ATP synthase
How much ATP is yielded by the complete oxidation of glucose? Where do they come from?
about 30 total; ~26 from oxidative phosphorylation & 4 from glycolysis. BUT if glucose undergoes fermentation only two molecules of ATP are generated per glucose molecule instead of 4 from glycolysis.
What determines the rate of oxidative phosphorylation?
ADP concentration. If there is no ADP, the electrons will not go through the ETC
What is acceptor or respiratory control?
The regulation of oxidative phosphorylation by ADP. It is an example of control of metabolism by energy charge.
What hormones control glycogen breakdown?
Epinephrine and glucagon
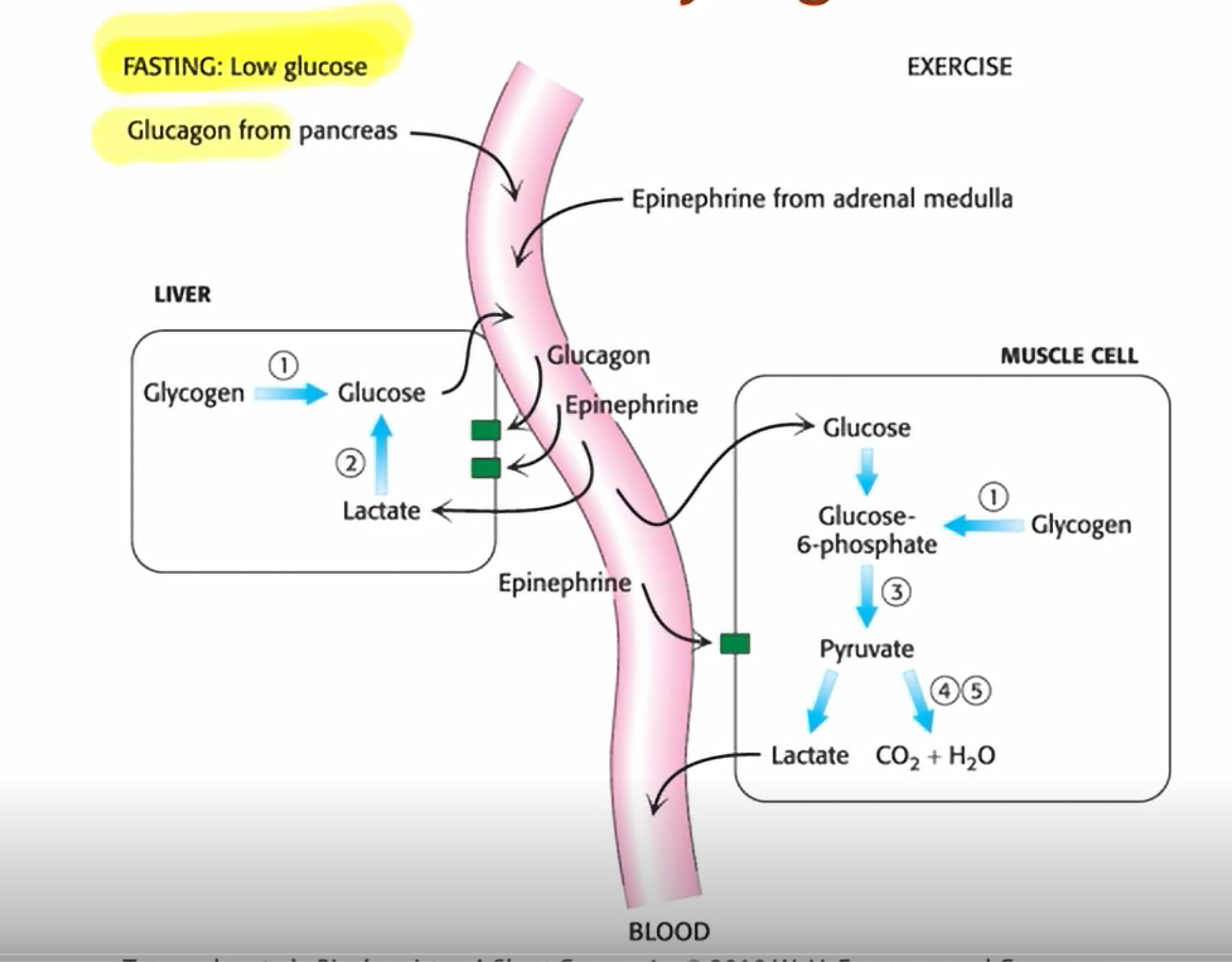
When does the pancreas excreet glucagon?
during fasting
When do the adrenal glands excrete epinephrine?
exercise
What is the regulatory cascade for glycogen breakdown?
7TM receptor receives signal>GDP is activated>GTP binds to adenylate cyclase> ATP is generated> Cyclic AMP is generated> Protein Kinase A is activated> Phosphorylase Kinase is activated> Phosphorylase a is phosphorylated and therefore activated.
What role does Ca2+ have in glycogen degradation?
It partially activates phosphorylase kinase. PKA then fully activates it
Phosphorylase a vs Phosphorylase b
a has phosphates and b does not. The b form is less active than the a form.
R state vs T state of phosphorylase
For a, R is more common. For b, T is more common. R is more active than T.
List the most to least active form of phosphorylase:
R state, a form
T state, a form
R state, b form
T state, b form
Why are there multiple different levels of activity of phosphorylase?
Certain forms have regulatory sites that hinder the active site
Phosphorylase is different in muscle and liver cells. This means that the different versions of phosphorylase are…
isozymes
Which form of phosphorylase is the default in the liver?
a form, R state favored. At really high [glucose], insulin will cause a cascade that dephosphorylates phosphorylase.
What form of phosphorylase is the default in muscles
b, T state is favored. High [AMP] shifts it to R state. High [ATP] or [glucose] shifts to T state
What are the three mechanisms to stop glycogen breakdown?
inherent GTPase activity
Phosphodiesterase converts cAMP into AMP which does not stimulate PKA. Ends the signaling cascade.
Protein Phosphatase 1 removes phosphoryl groups from phosphorylase kinase and glycogen phosphorylase. Based on hormone signals.