Bonding
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
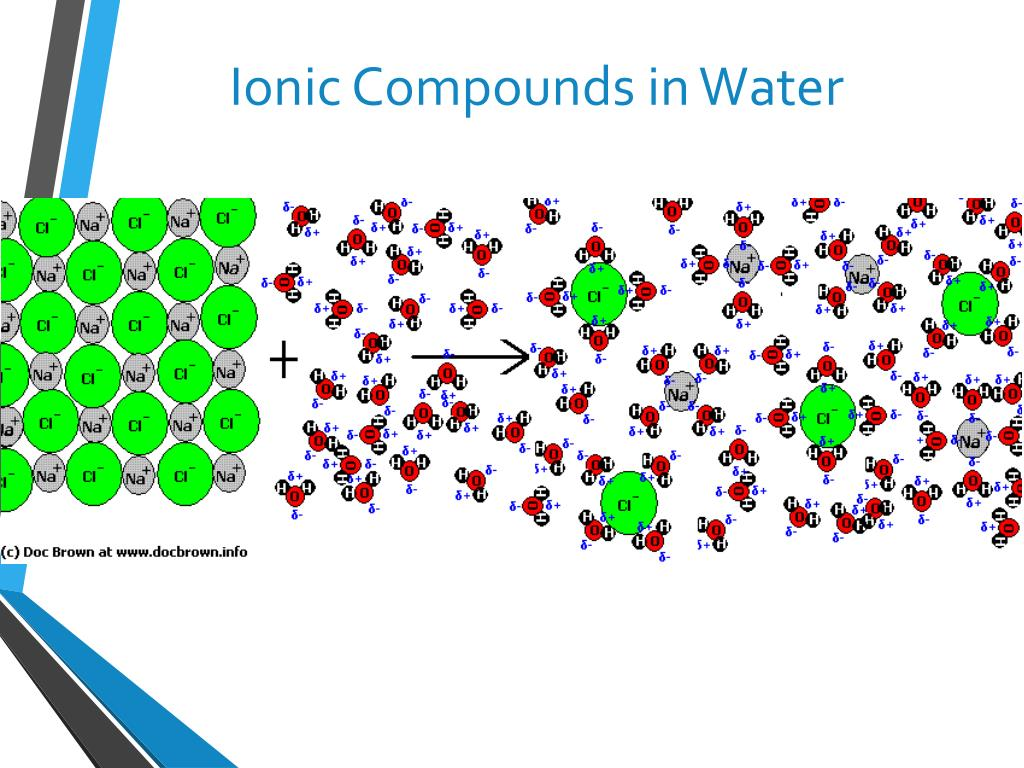
Ionic bonding
Metal loses an electron
Non- metal gains an electron and becomes a negative ion
These two ions are attracted to each other by an electrostatic force of attraction
Ionic compounds form a lattice structure
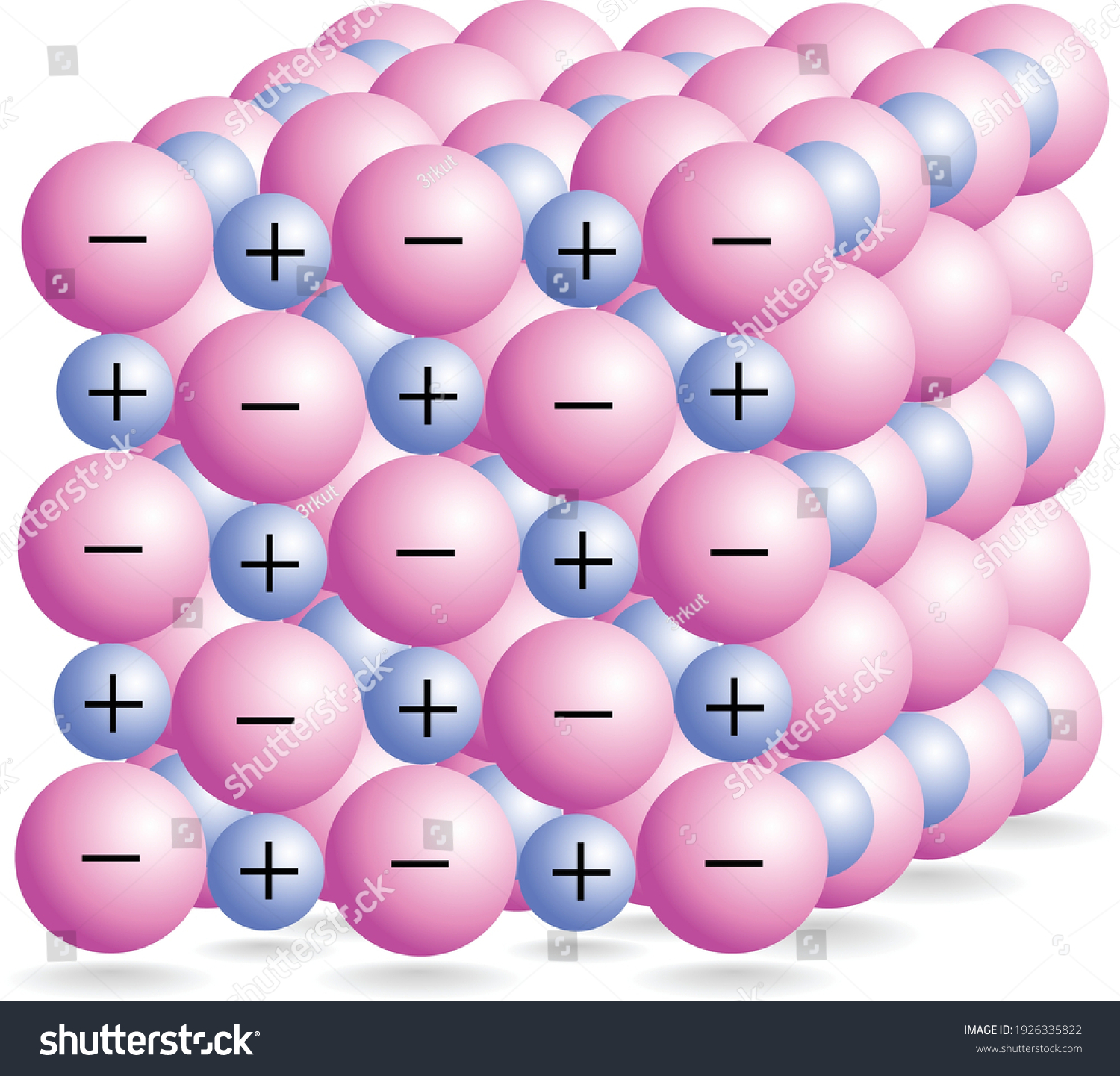

Properties of ionic compounds
High MP/BP-Lots of energy is required to overcome the strong electrostatic force of attraction
Soluble in polar solvents- Water molecules surround the ionic compounds because they have a partial positive and negative charge. Overcoming the electrostatic force of attraction between the positive and negative ions
Don’t conduct electricity when solid-as ions are not free to move so thus unable to carry charge. Only conduct electricity when molten or dissolve.
Brittle
Why are ionic compounds brittle?
In an ionic lattice, positive and negative ions are arranged in a repeating pattern to minimise repulsion
When a force is applied, the layers of ions shift causing like charged ions to align
This causes repulsion and the crystal breaks
Covalent bonding
Non metals share electrons
A single covalent bonds contains a pair of electrons
The shared electrons are attracted to the two nuclei of the atoms forming the bond.
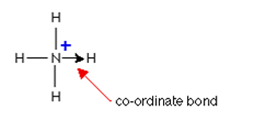
What is a dative/coordinate bond?
A dative covalent bond contains a shared pair of electrons, with both electrons supplied by one atom
Dative bond is shown by an arrow
Example of a dative bond
NH4+
NH3 has a lone pair of electrons which bond to a hydrogen ion
Metallic bonding
Involves attraction between delocalised electrons and positive ions arranged in a lattice
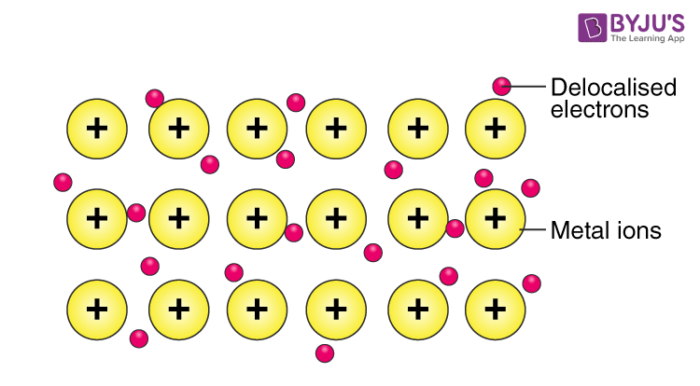
Properties of metallic bonding
High conductivity- Free electrons move easily and can carry charge
Malleable-Layers of metal atoms can slide over each other
Sonorous
What factors affect the strength of a metallic bond?
Number of protons/strength of nuclear charge- More protons, stronger the bond
Number of delocalised electrons- more electrons, stronger the bond
Size of the ion- smaller the stronger the bond. Smaller ions have higher charge density because the charge is more concentrated and less spread out in a smaller ion.
4 types of crystal structure
Ionic
Metallic
Macromolecular (giant covalent)
Molecular (simple covalent)
Why do simple molecular substance have a low MP/BP
weak intermolecular forces that require little energy to break
What happens to all simple molecular substances if you cool them below their melting point?
Becomes solid
Forming a simple molecular lattice
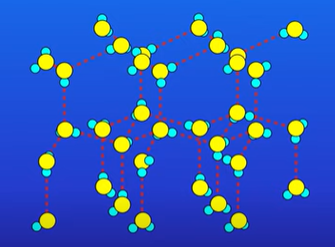
Why does H2O have a high MP/BP (despite being a simple molecular substance)
In ice H2O molecules are held together by intermolecular forces
But one of the IM forces is hydrogen bonding which require lots of energy to break
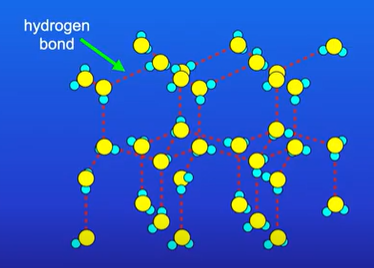
What does the solubility of a simple molecular substance depend on?
Whether or not the substance is polar or non polar
Non polar substance dissolve well in non polar solvents
Polar substances dissolve in polar solvents
Why do simple molecular substances not conduct electricity?
They don’t carry mobile charged particles that are able to carry charge
Define electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract the pair of electrons in a covalent bond
What does electronegativity depend on?
The size of the positive charge on the nucleus
Atomic radius- Smaller the atom the more electronegative
Shielding- Less shells more electronegative
What is a pure covalent?
Pair of electrons is midway between both nuclei of the atoms
Occurs when both atoms have the same electronegativity e.g. cl-cl (cl2)
What is a dipole ?
Separation of charge
What is the electron pair repulsion theory?
Shape of a molecule is determined by the electron pairs surrounding the central atom
The electron pairs will move away from each other as far as possible
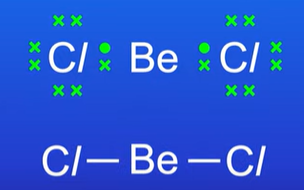
Linear (shape of molecules)
2 bonding pairs (surrounding the central atom)
Bond angles is 180 degrees
If the central atom has 2 bonding pairs its linear but this is not the case if central atom has lone pair of electrons
Trigonal planar
Central atom has 3 bonding pairs
Bond angle 120 degrees

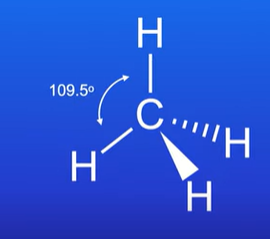
Tetrahedral
Central atom has 4 bonding pairs
Bond angle is 109.5 degrees
Trigonal bipyramidal
5 bonding pairs
Bond angles 90 and 120 degrees
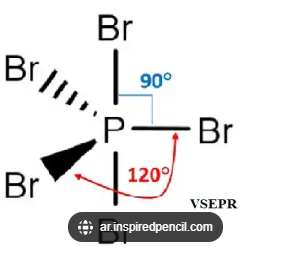
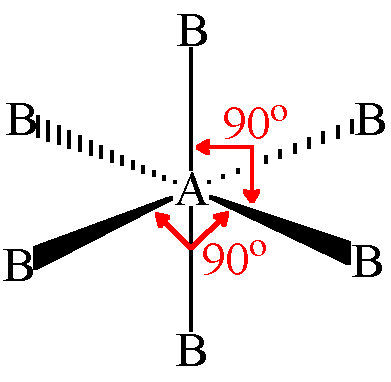
octahedral
6 bonding pairs
Bond angle 90 degrees
What does the dashed and solid wedge mean?
Dashed= atom is projecting behind the plane
Solid= atom projecting outwards
What does it mean if atoms are lying on the same plane?
They all lie flat rather than being above or below each other
How do lone pairs effect bond shape of molecule
Lone pairs repel more strongly than bonding pairs.
(There’s extra repulsion)
What does the extra repulsion do to bond angles
Decreases bond angles by 2.5 degrees
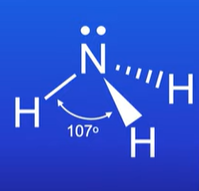
Describe the trigonal pyramidal shape
Has 3 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair of electrons on the central atom
BA = 107
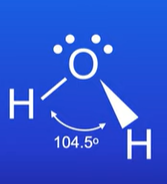
Describe the bent shape
Has 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs of electrons on the central atom
BA is 104.5 degrees
What is a polar molecule?
A molecule with an uneven distribution of electrons which results in a permanent dipole
Why may a polar bond not have a dipole?
A molecule may contain polar bonds, but not be a polar molecule if the shape of the molecule is symmetrical (if the arrows towards the more electronegative elements face away from each other)
This causes the dipoles to cancel each other out
What can break a covalent bond?
Covalent bonds are extremely strong and can only be broken via a chemical reaction
Physical changes like boiling only overcomes IM forces between molecules NOT covalent bonds
Explain Vander Waals forces
Random movement of electrons shifts all electrons in atom 1.
This repels electrons in atom 2 causing an induced dipole
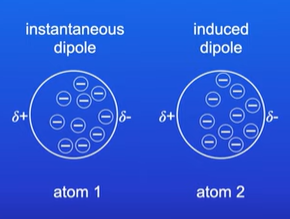
What does the strength of Vander Waals forces depend on ?
The number of electrons
More electrons= High strength
Explain permanent dipole dipole forces
This force occurs between polar bonds that contain a permanent dipole

Explain hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen interacts with a significantly more electronegative atom F,O,N
The F,O,N atoms must have an available lone pair of electrons
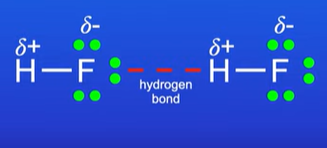
Why is ice less dense than liquid water ?
In liquid, the h2o molecules are moving randomly, forming and breaking hydrogen bonds
When you freeze water, the H2o molecules arrange themselves in an ordered structure, stabilised by hydrogen bonding.
Therefore the H2o molecules are further apart in ice than liquid