Assessment of Head, Eyes, Ears, Nose, and Throat
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Tension headache
Caused by stress, poor posture, sleep.
Migraine
Triggered by hormonal changes, foods, stress.
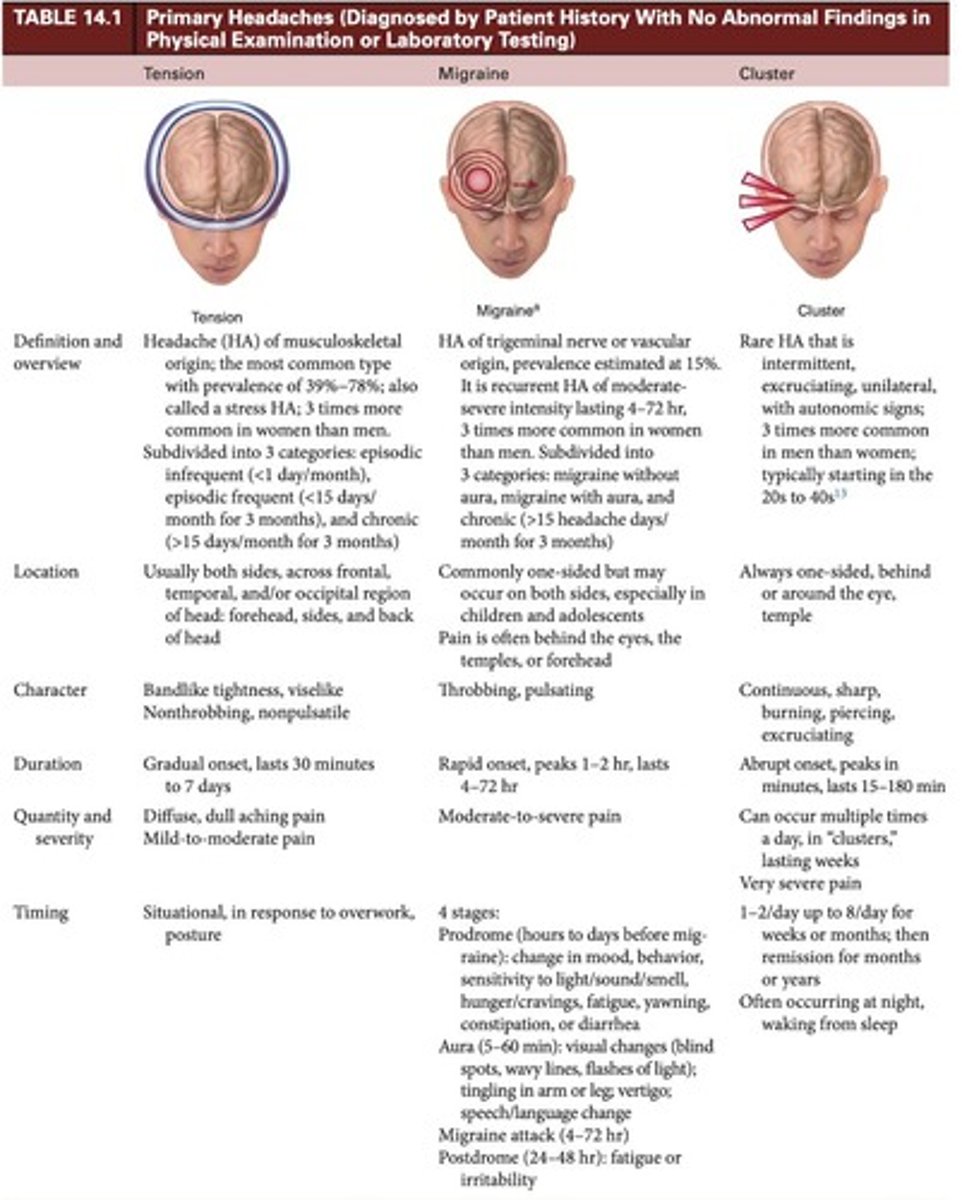
Cluster headache
Awakens from sleep; linked to alcohol, nitroglycerin.
Thunderclap headache
Worst headache; indicates potential brain aneurysm.
Brain aneurysm
Weak spot on artery; bulges like bubble.
Concussion
Head injury; assess loss of consciousness.
Meningitis
Neck pain with stiffness, headache, fever.
Normocephalic
Round, symmetric skull; normal head shape.
Microcephaly
Abnormally small head size.
Macrocephaly
Abnormally large head size.
Bell's palsy
Cranial nerve 7 damage; caused by herpes.
Nystagmus
Oscillating eye movement; indicates inner ear issues.
Vertigo
Sensation of spinning; often related to inner ear.
Exophthalmos
Protruding eyes; associated with Grave's disease.
Goiter
Enlarged thyroid; caused by low iodine.
PERRLA
Pupils Equal, Round, Reactive to Light and Accommodation.
Decreased tear production
Related to lacrimal gland involution in older adults.
Ectropion
Lower lid eversion; loss of elasticity.
Cataracts
Thickened, yellowed lens fibers; causes vision issues.
Accessory muscles
Muscles used for neck movement assessment.
Lymph nodes
Palpate for size, shape, mobility, tenderness.
Normal lymph nodes
Movable, discrete, soft, and nontender.
Pupillary constriction
Both pupils constrict in response to light.
Cranial nerve 3
Responsible for controlling pupillary constriction.
Accommodation
Convergence of eyes when focusing on near objects.
Snellen eye chart
Chart used to assess visual acuity with letters.
Visual acuity measurement
Top number is distance; bottom is normal vision distance.
Age-appropriate screening
Tools tailored to the patient's age for eye exams.
Fundus variation
Fundus color varies with individual's skin color.
Glaucoma screening
Health promotion recommendation for early detection.
Subjective data
Patient-reported symptoms regarding vision issues.
Strabismus
Deviation in the parallel alignment of eyes.
Diplopia
Seeing two images of a single object.
Red eye emergencies
Conditions causing sudden vision loss or trauma.
Intraocular pressure
Increased pressure associated with glaucoma.
Patient-centered care
Focus on individual patient's eye health needs.
Snellen chart procedure
Position patient 20 feet away for vision testing.
Opaque card use
Shield one eye during Snellen chart testing.
Reading glasses removal
Remove only reading glasses for vision testing.
Smallest line reading
Patient reads the smallest line on the chart.
Numeric fraction recording
Record vision result as a fraction (e.g., 20/20).
Conjunctiva and sclera inspection
Assess eye surface for color and clarity.
Pallor
Color change indicating possible anemia.
Glaucoma
Increased intraocular pressure damages peripheral vision.
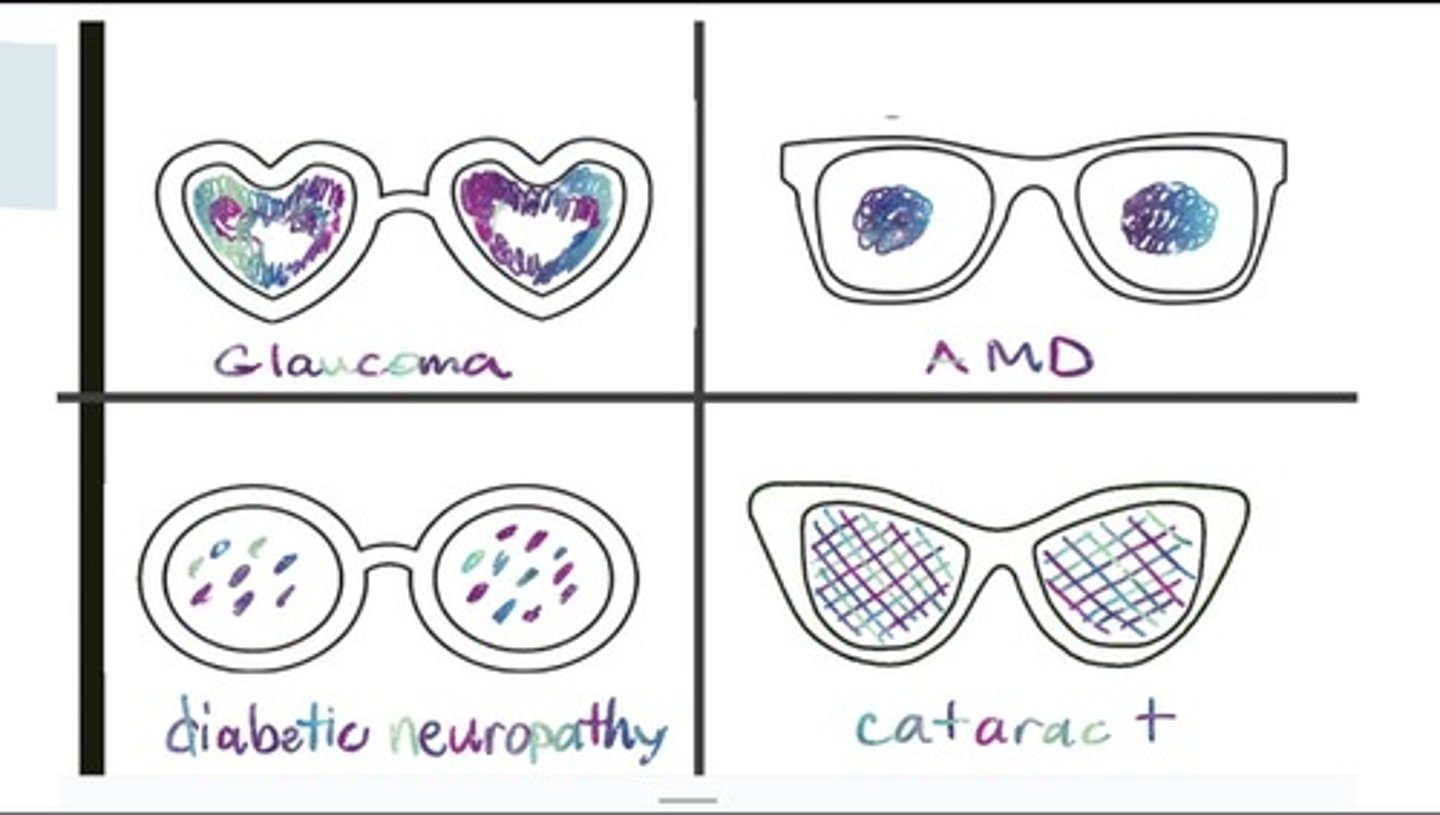
Intraocular pressure
Pressure from aqueous humor in the eye.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
Loss of central vision; peripheral vision intact.
Risk factors for AMD
Age >50, smoking, family history, UV exposure.
Diabetic retinopathy
Shade patches in the lens due to diabetes.
Cataracts
Clouding of lens, leading to vision impairment.
Preventable cataracts
80% preventable with surgery and lifestyle changes.
Conductive hearing loss
Mechanical dysfunction in external/middle ear.
Sensorineural hearing loss
Pathology of the inner ear; nerve degeneration.
Mixed hearing loss
Combination of conductive and sensorineural loss.
Normal hearing changes with aging
Gradual loss; cerumen becomes drier and harder.
Cerumen
Earwax that protects and lubricates the ear.
Tympanic membrane inspection
Should be pearly gray and translucent.
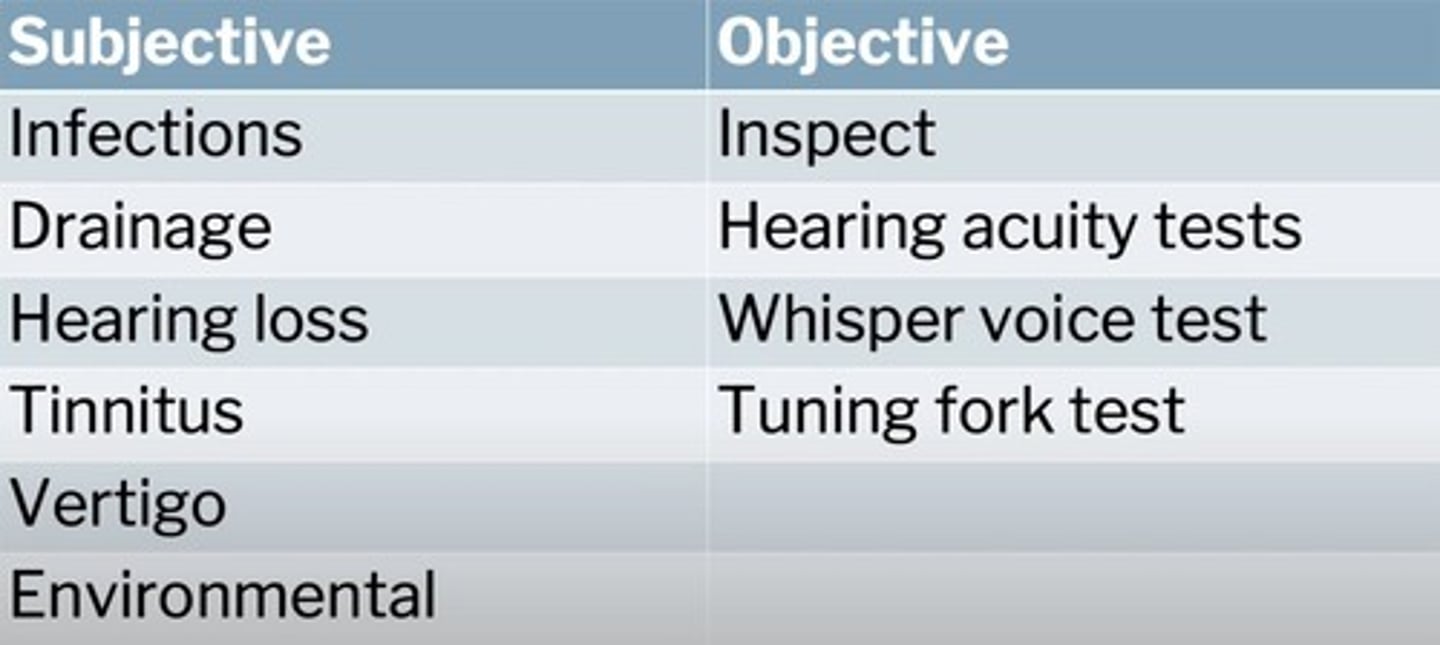
Hearing acuity tests
Assess hearing ability using various methods.
Audio meter
Device to test hearing by sound detection.
Whispered voice test
Test for hearing using whispered speech.
Tuning fork test
Tests air and bone conduction of sound.
Risk factors for cataracts
Age, smoking, obesity, diabetes, UV exposure.
Symptoms of cataracts
Blurry vision, glare, halos, poor night vision.
Monitoring glaucoma
Regular eye exams to check for pressure.
Corticosteroids and cataracts
Long-term use can increase cataract risk.
Nasal Polyps
Noncancerous growths in the nasal cavity.
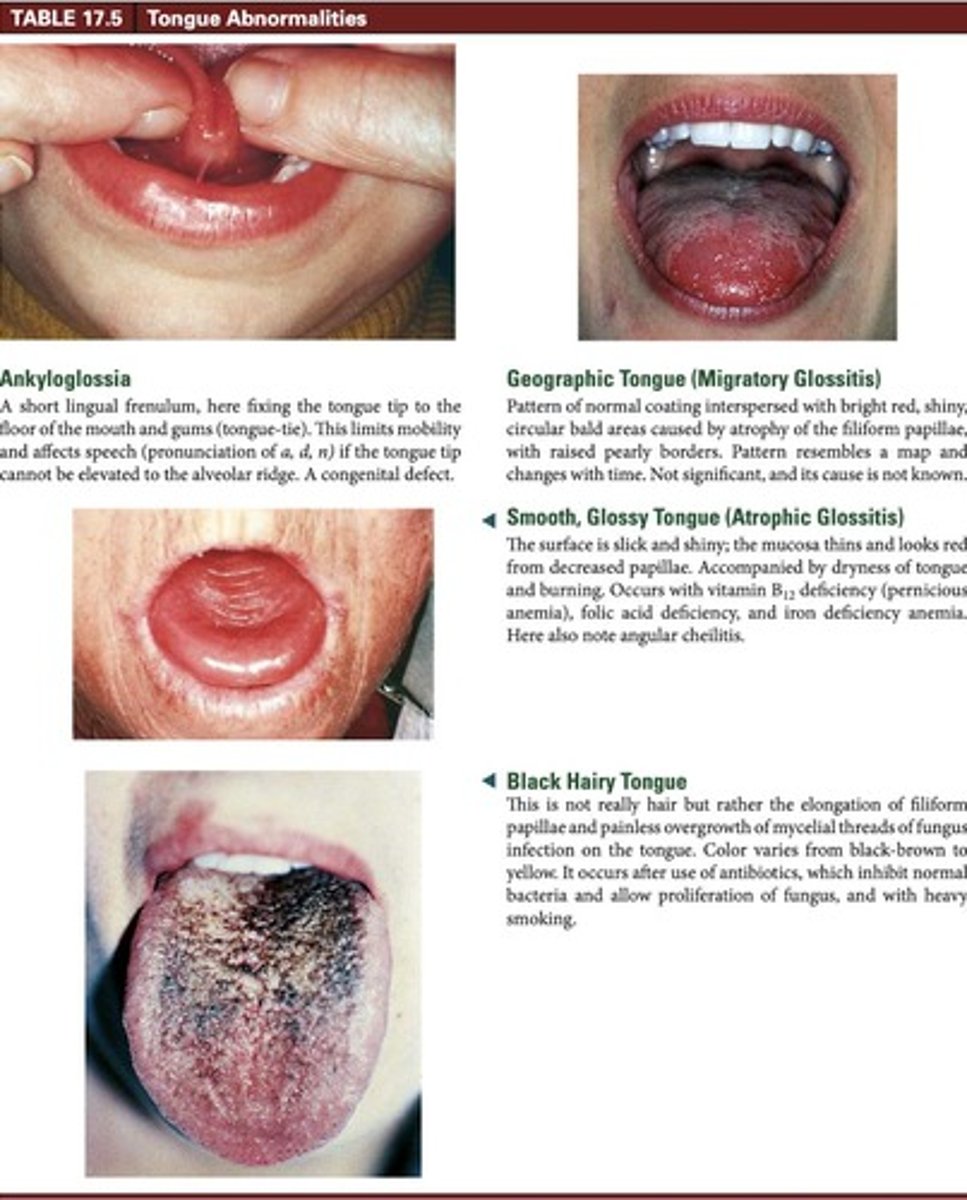
Tongue Appearance
Pink, rough surface; may have white coating.
Older Adult Nose Changes
More prominent due to subcutaneous fat loss.
Taste and Smell Decline
Decreased olfactory nerve fibers and taste buds.
Candidiasis Infection
Fungal infection, increased risk in older adults.
Antibiotic Effects
Can cause black hairy tongue and Candidiasis.
Papillary Atrophy
Smoother tongue surface due to loss of papillae.
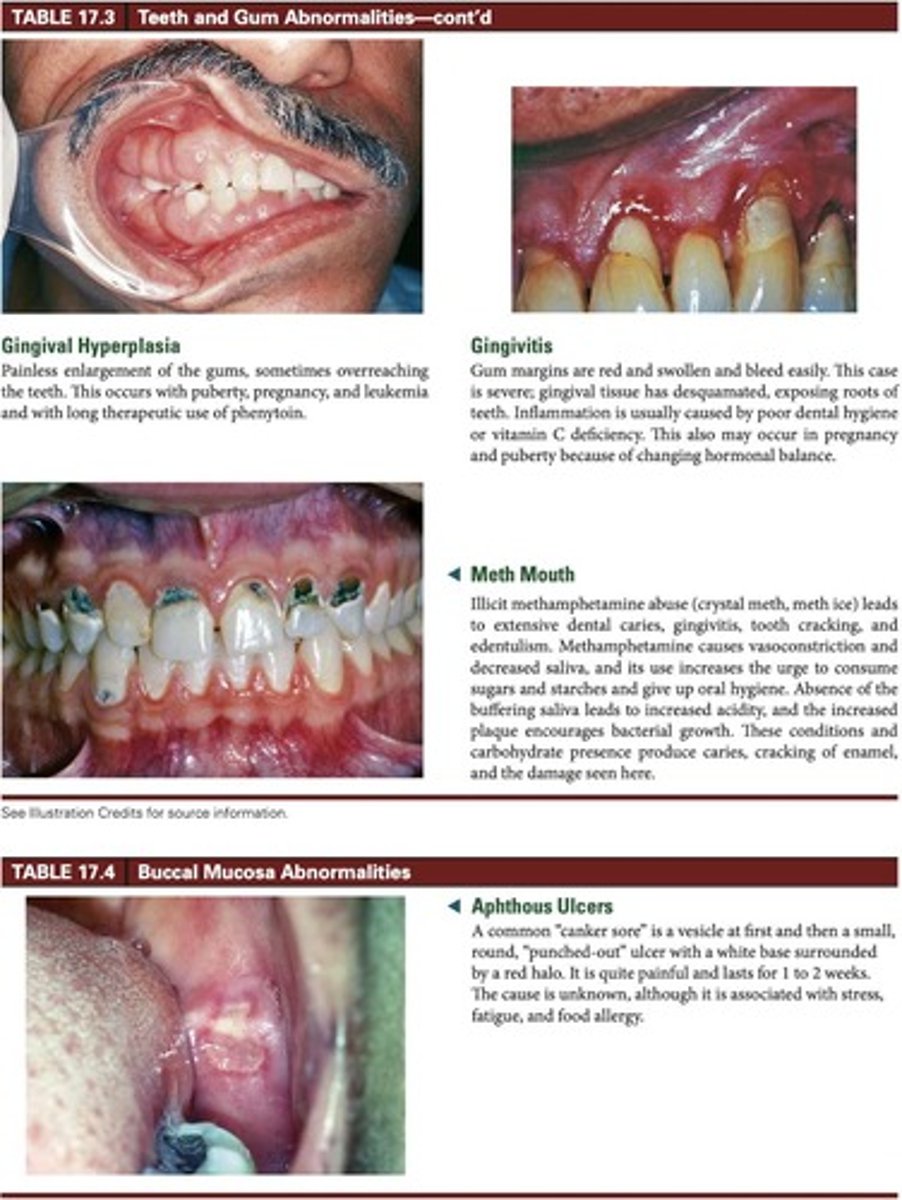
Gingivitis
Inflammation of gums, can relate to various factors.
Dysphagia
Difficulty swallowing, assess for coughing or choking.
Leukoplakia
White patches on the tongue, potential concern.
Cranial Nerve 10 Test
'Ah' test to assess throat function.
Cranial Nerve 12 Test
Sticking out tongue to assess motor function.
Cranial Nerve 9 and 10 Test
Gag reflex test for throat sensation.
Breast Symmetry
Normal breasts may have slight size differences.
Breast Skin Condition
Should be smooth and even in color.
Nipple Alignment
Nipples should be on the same plane.
Gynecomastia
Enlargement of male breast tissue, medication side effect.
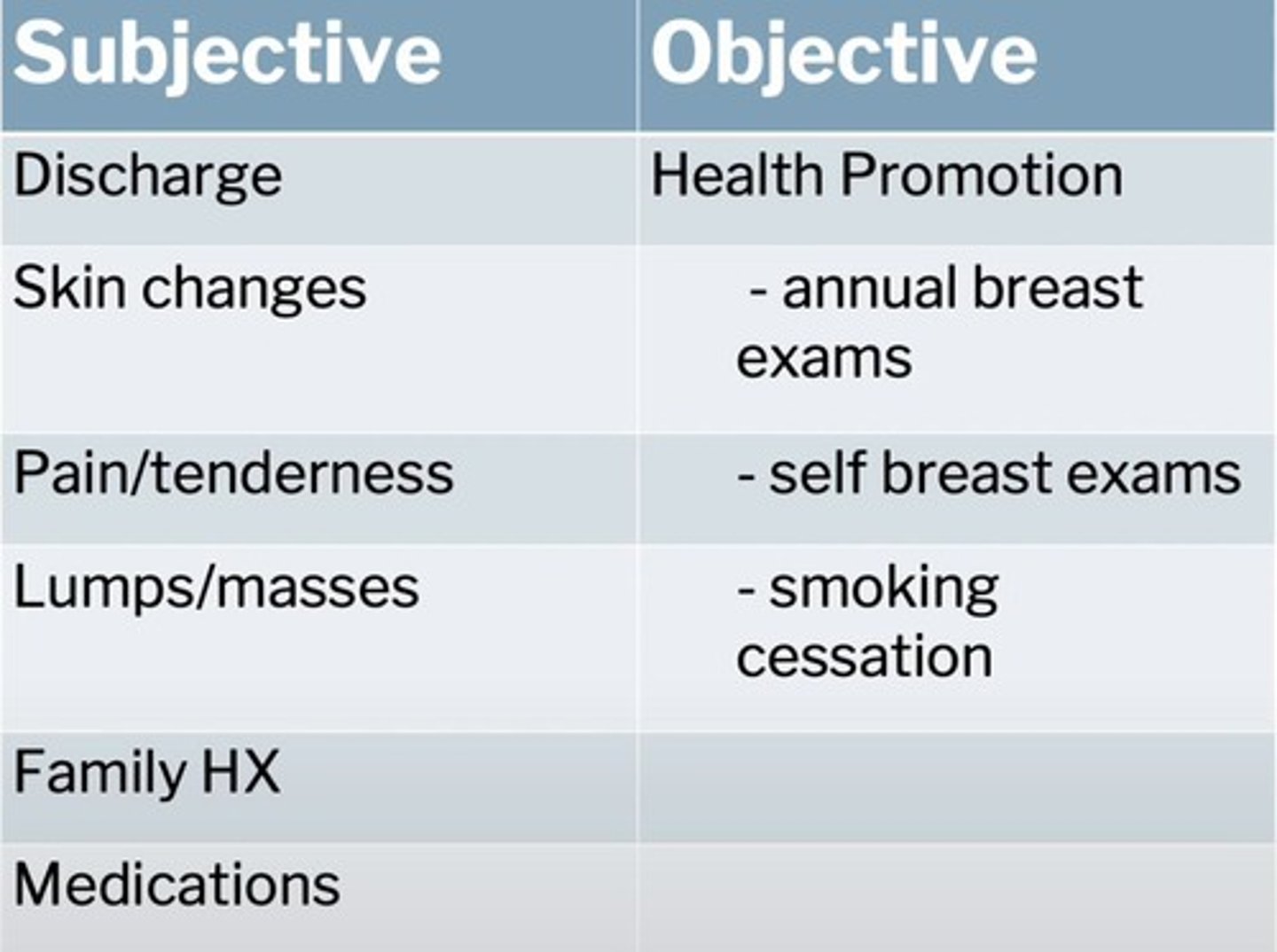
Breast Cancer Risk Factors
Family history increases risk of breast cancer.
Inframammary Ridge Thickening
Normal change in lower breast with age.
Postmenopausal Breast Changes
Loss of glandular tissue leads to size decrease.