Physics
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Electrical Power =
current x voltage
Voltage =
current x resistance
Charge =
current x time
Average Speed =
distance / time
Acceleration =
Change in Velocity / Time Taken
Force =
Mass x Acceleration
Pressure Difference =
Height x Density x Gravity
Moment =
Force x Perpendicular Distance from Pivot
Pressure =
Force / Area
Wave Speed =
Frequency x Wavelength
Refractive Index =
Sin (I) / Sin (R)
Sin (Critical angle) =
1 / Refractive Index
Energy Transfer =
Work Done
Work Done =
Force x Distance Moved
Efficiency =
Useful Energy Output / Total Energy Input
Weight =
Mass x Gravity
GPE Potential Energy =
Mass x Gravity x Height
Kinetic Energy =
1/2 x Mass x V^2
Density =
Mass / Volume
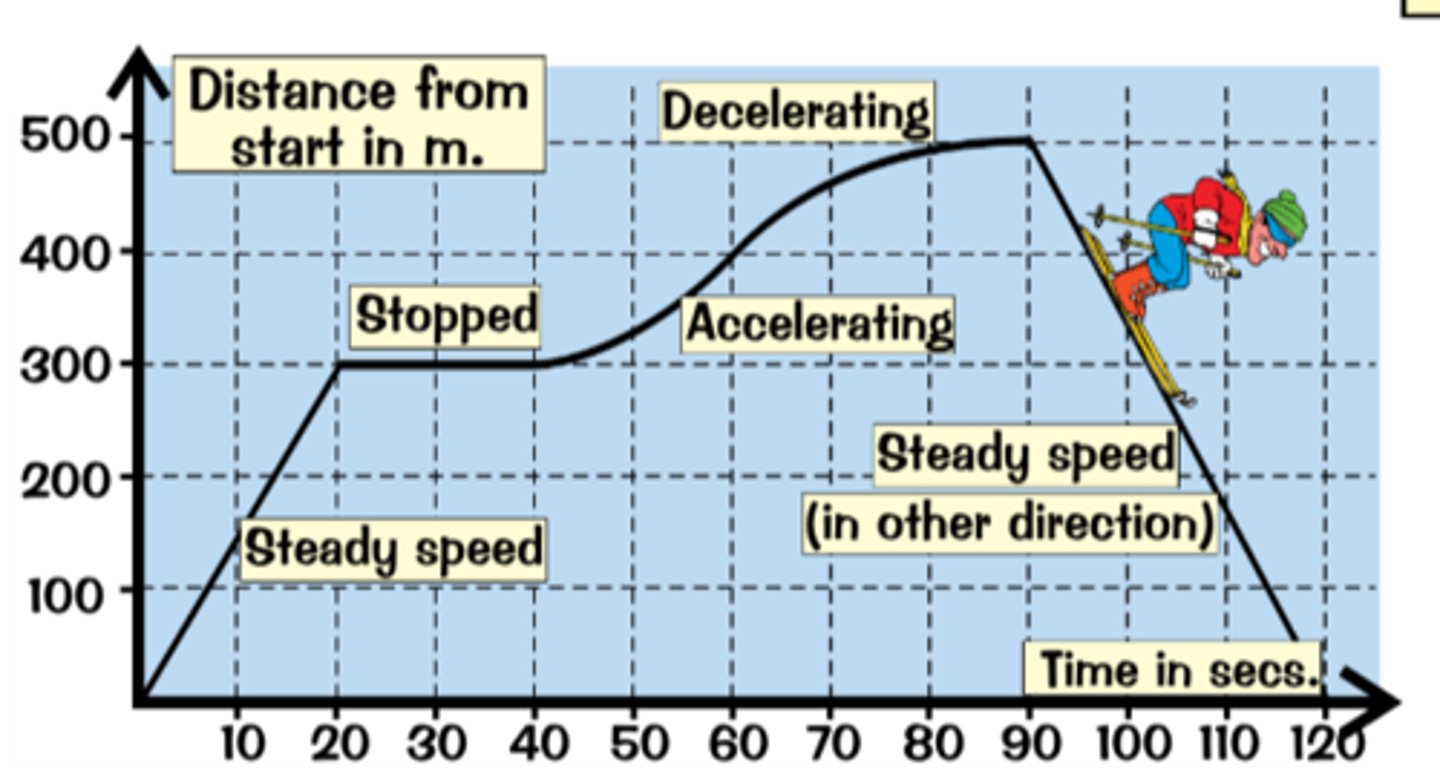
Distance Time Graphs
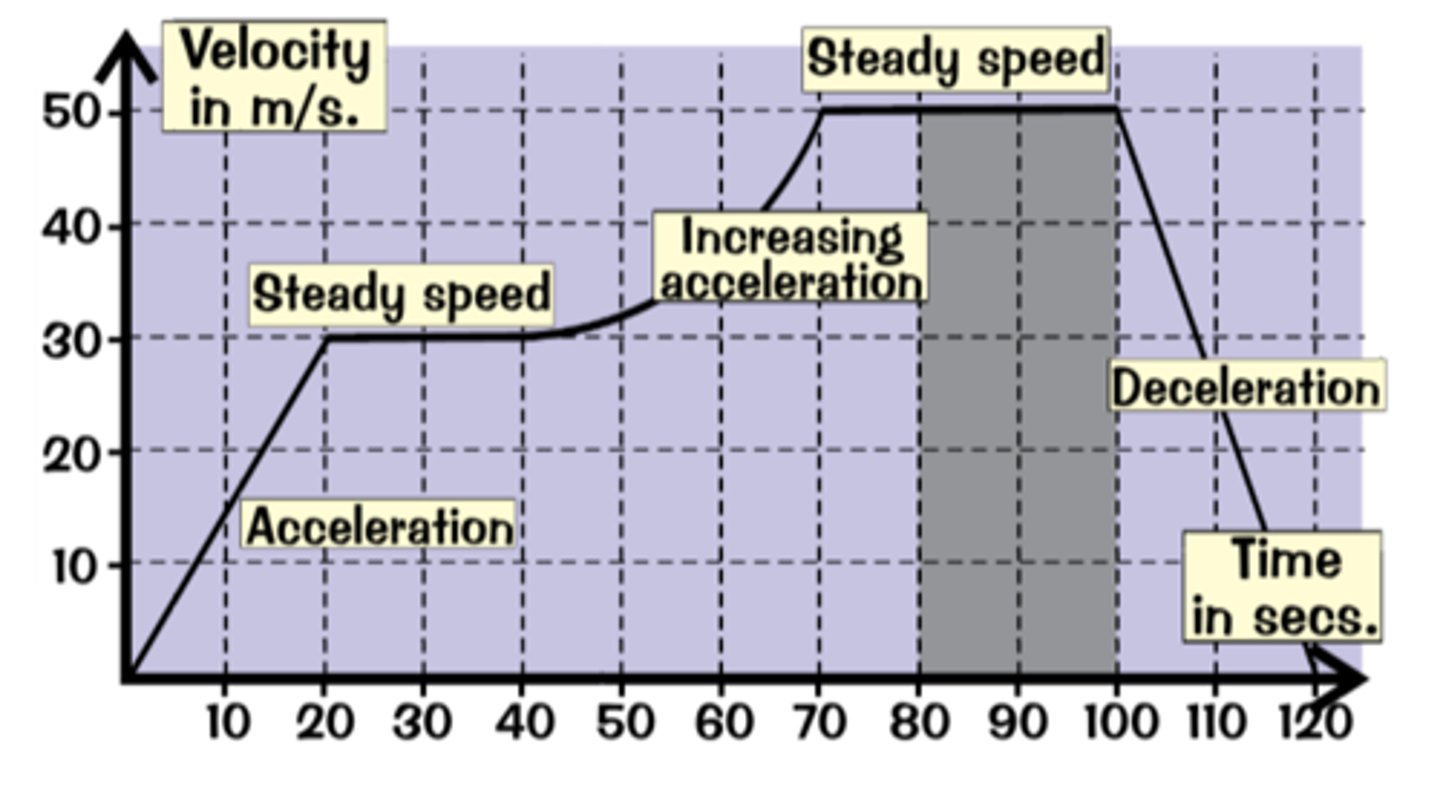
Velocity Time Graphs
Gravity
Force of attraction between all masses
Hookes Law
Extension is directly proportional to force until the spring reaches it's elastic limit
Solar Systems
Galaxy = large collection of stars
Sun = one of many stars
Effects of gravity on planets
Closer you get to a star or a planet the stronger the force of attraction is, so they move quicker in orbit
Types of orbit
Moons and planets have slightly elliptical orbits
Comets orbit the sun, they have very elliptical orbits
Artificial Earth Satellites
Have orbital period of 1 day = geostationary satellites, used for communications
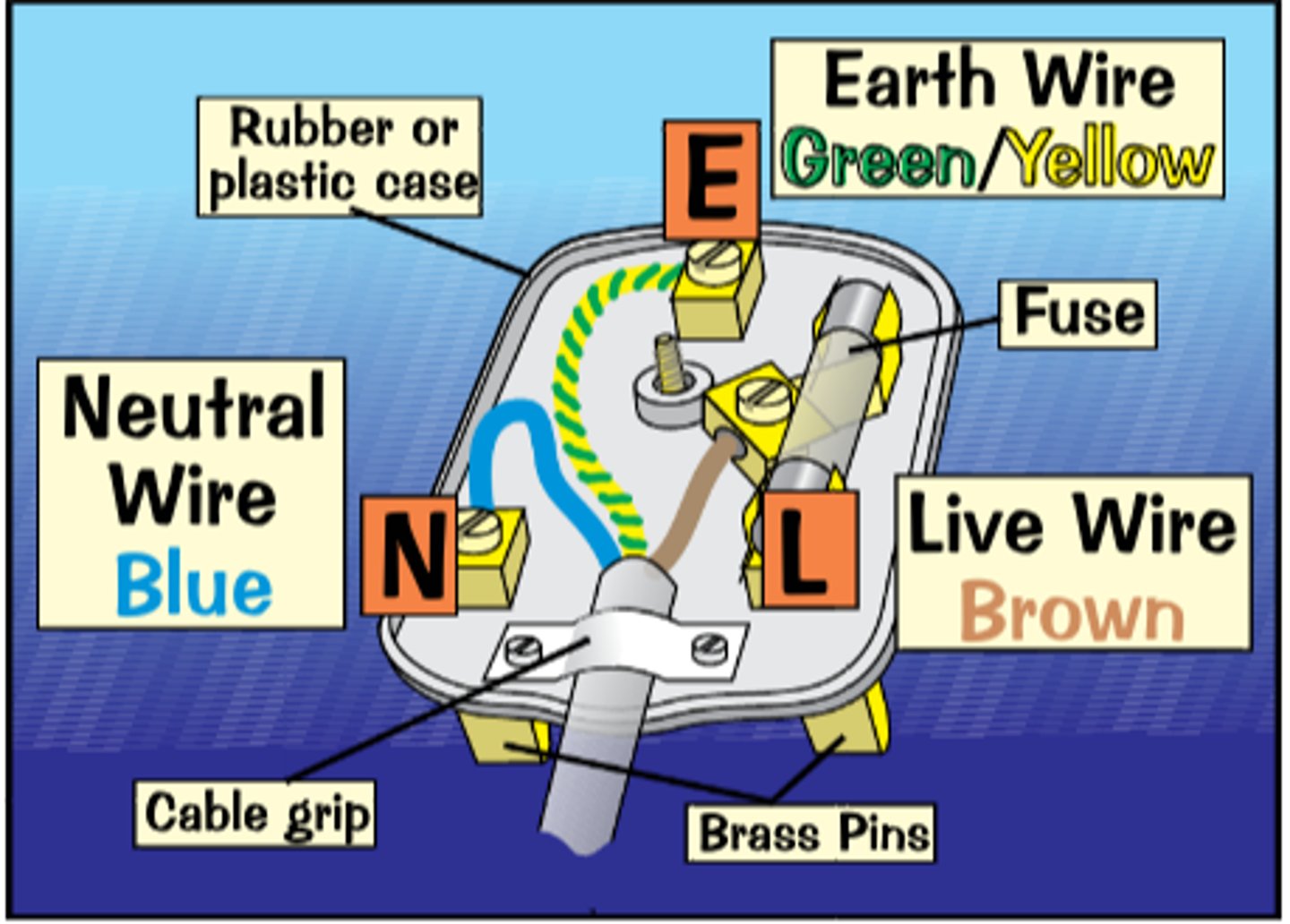
Safety features of Plugs
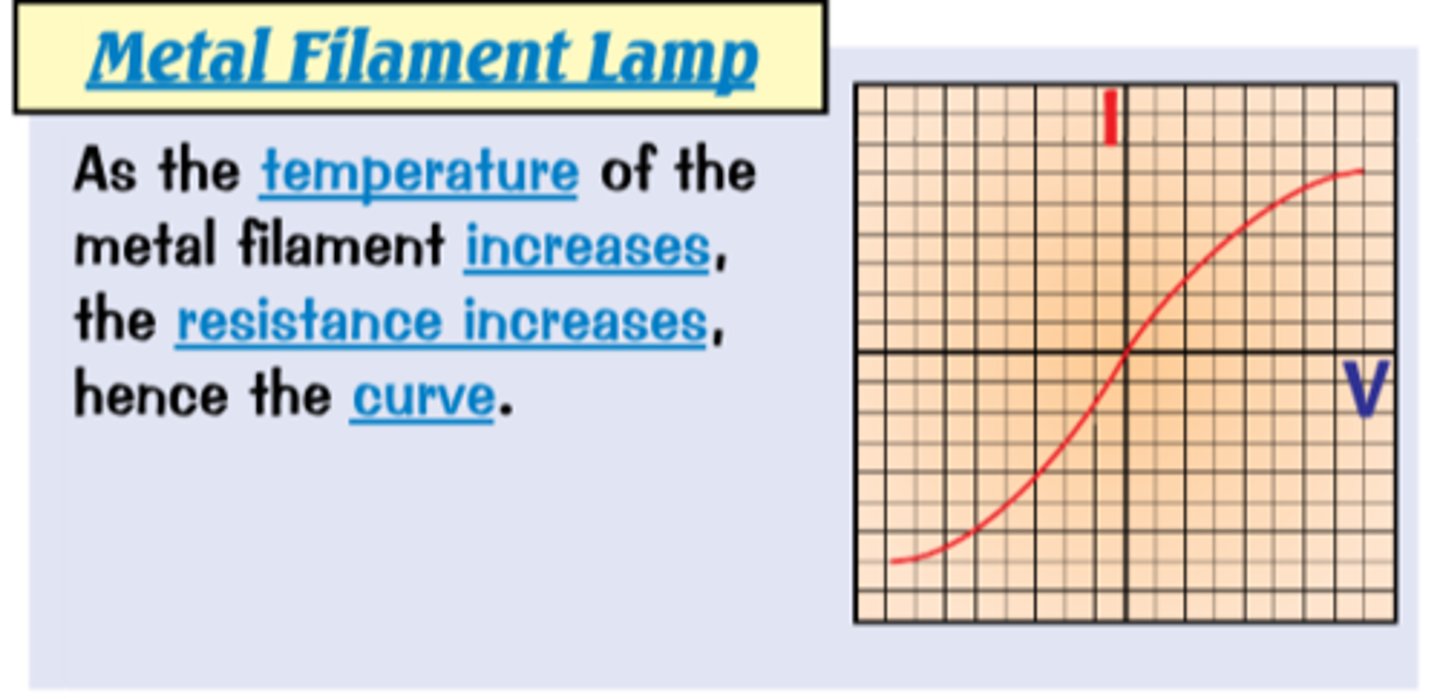
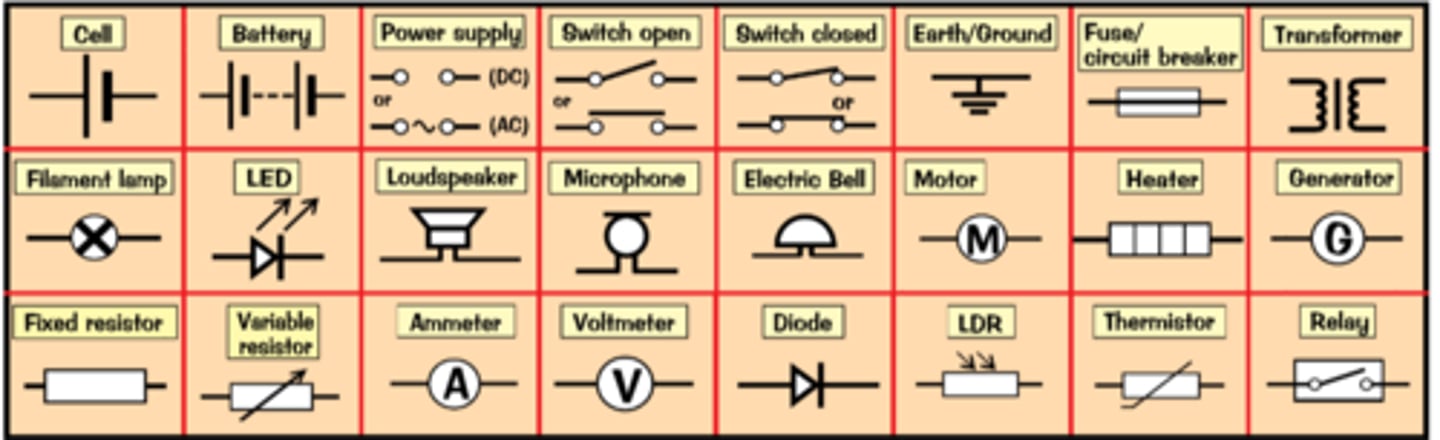
Filament Lamp
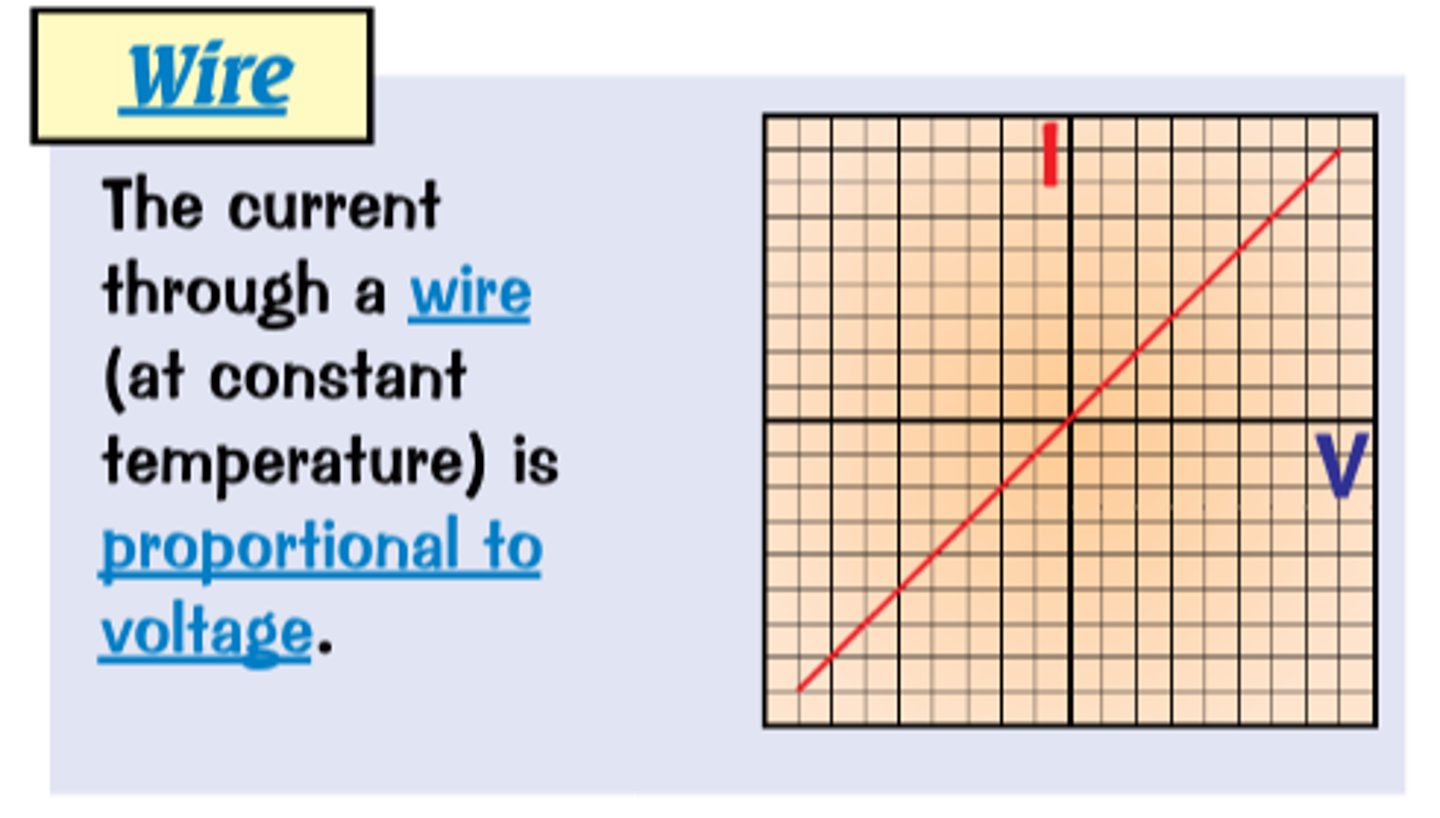
Wire
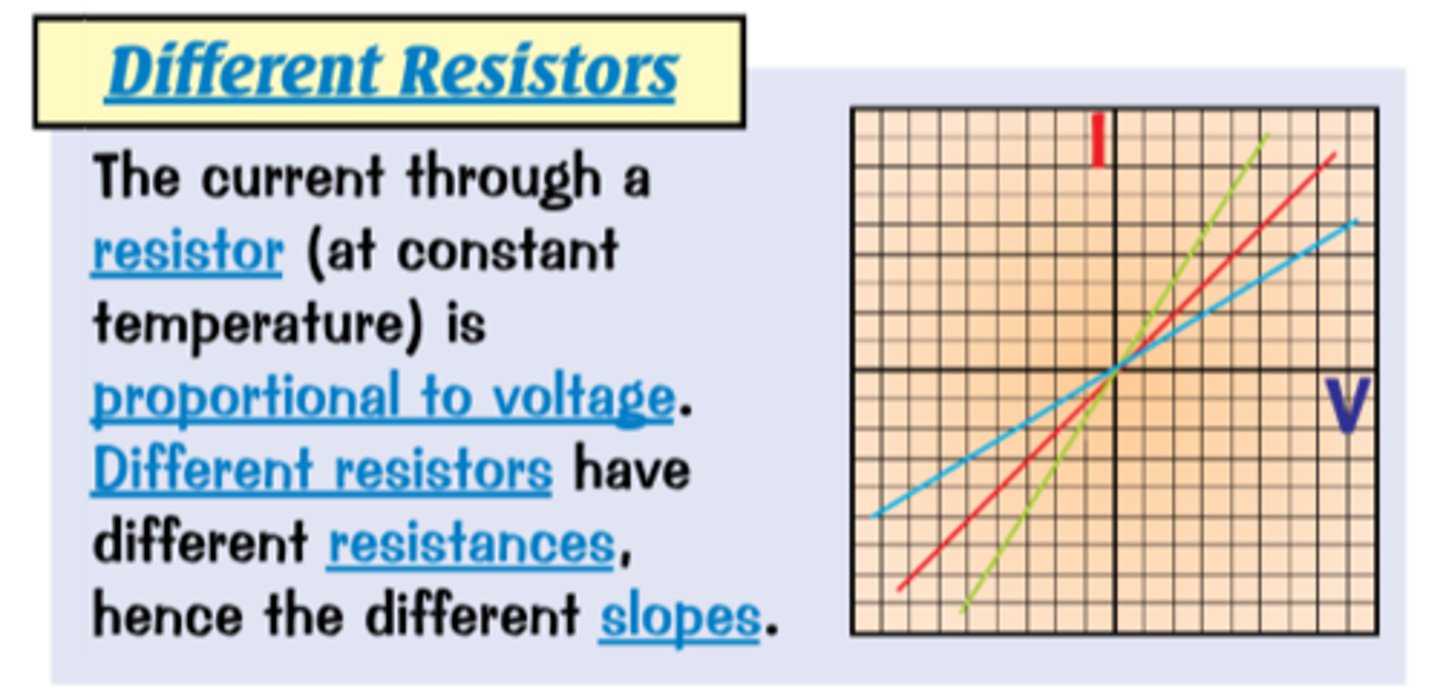
Resistors
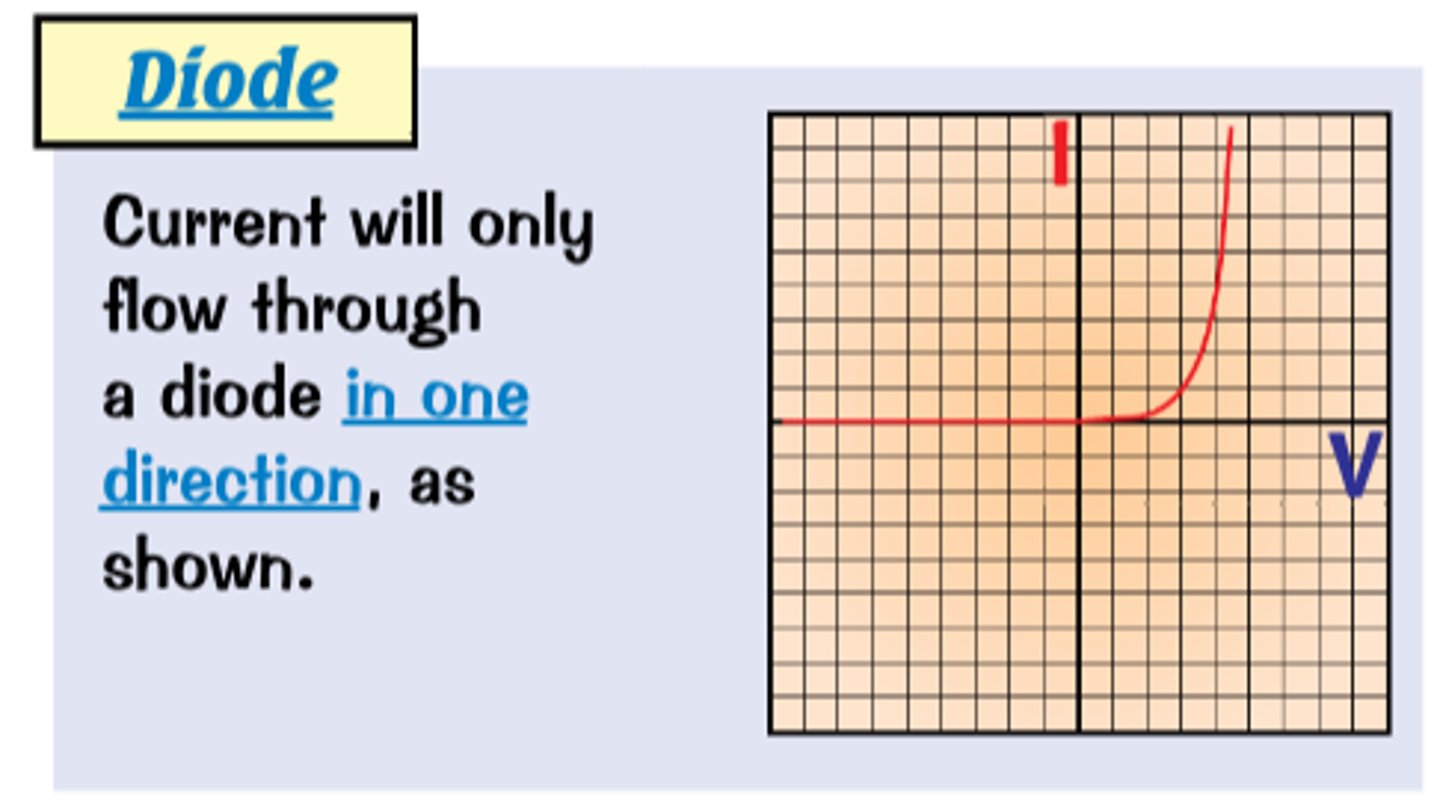
Diodes
Electric Circuit Symbols
Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) Diagram
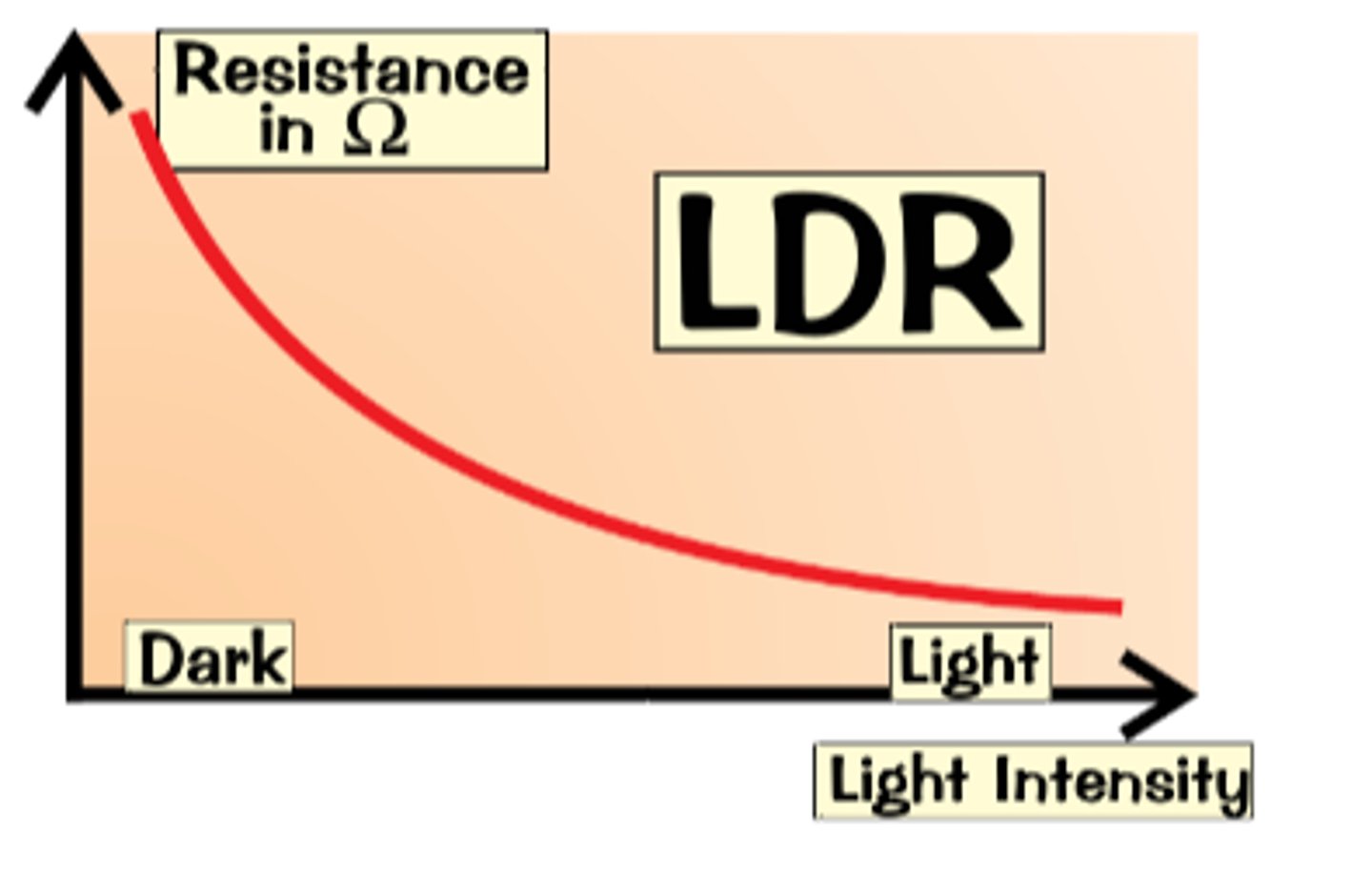
LDR Explanation
Changes it resistance depending on the amount of light
In bright light the resistance decreases
In dark light the resistance increases
Acts as a light sensor
Thermistor Diagram
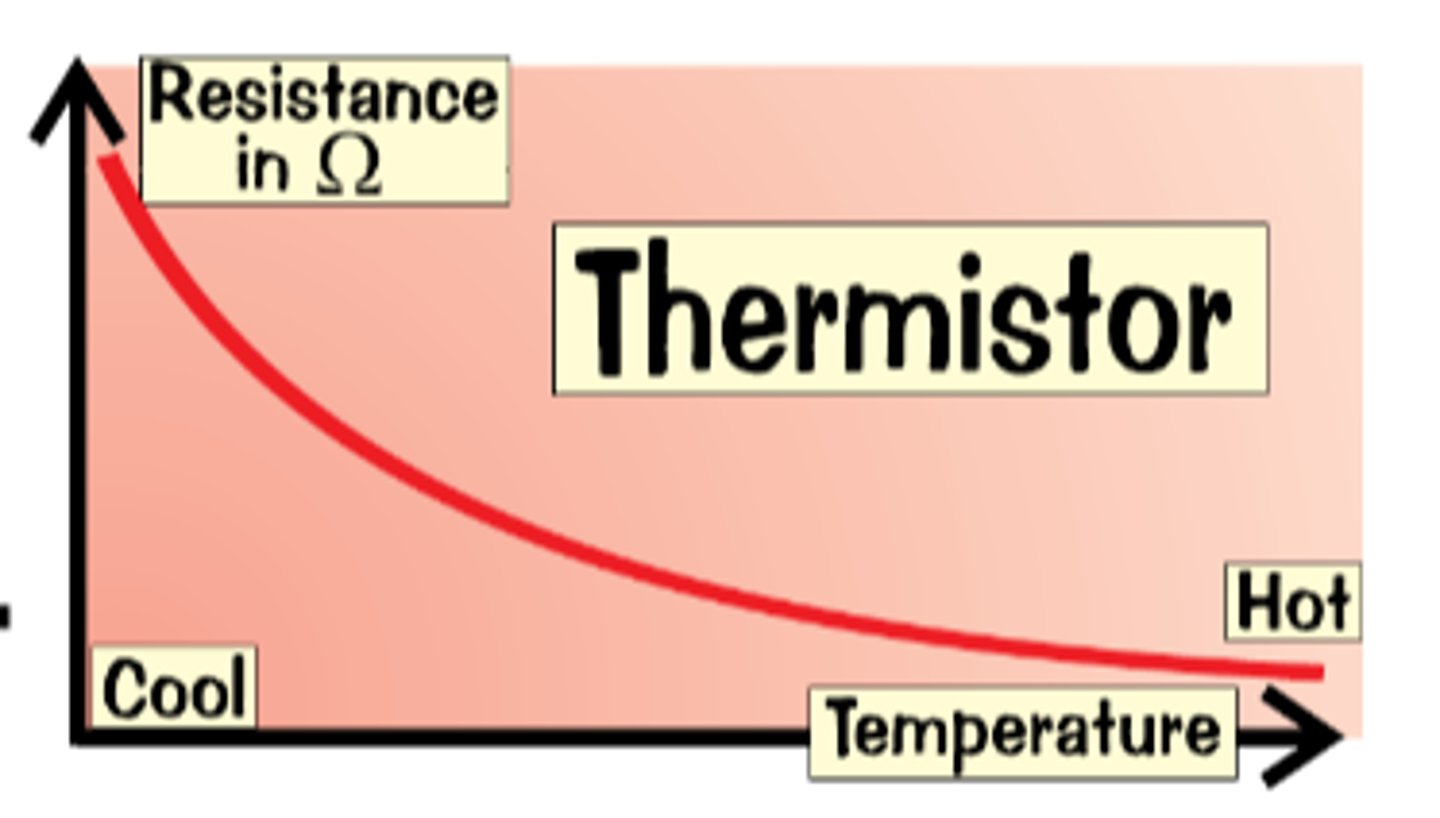
Thermistor Explanation
Changes in resistance as temperature changes
In hot condition the resistance decreases
In cool conditions the resistance increases
Acts as temperature detectors
Current
Rate of flow of Charge
Voltage
Driving force which pushes current (Electrical Power)
Resistance
Something which slows down the flow
Circuit Rules
Increase voltage = more current will flow
Increase resistance = less current will flow
Series Circuit
Current the same
Voltage = Voltage of all components
Parallel Circuit
Current = Current of all components
Voltage the same
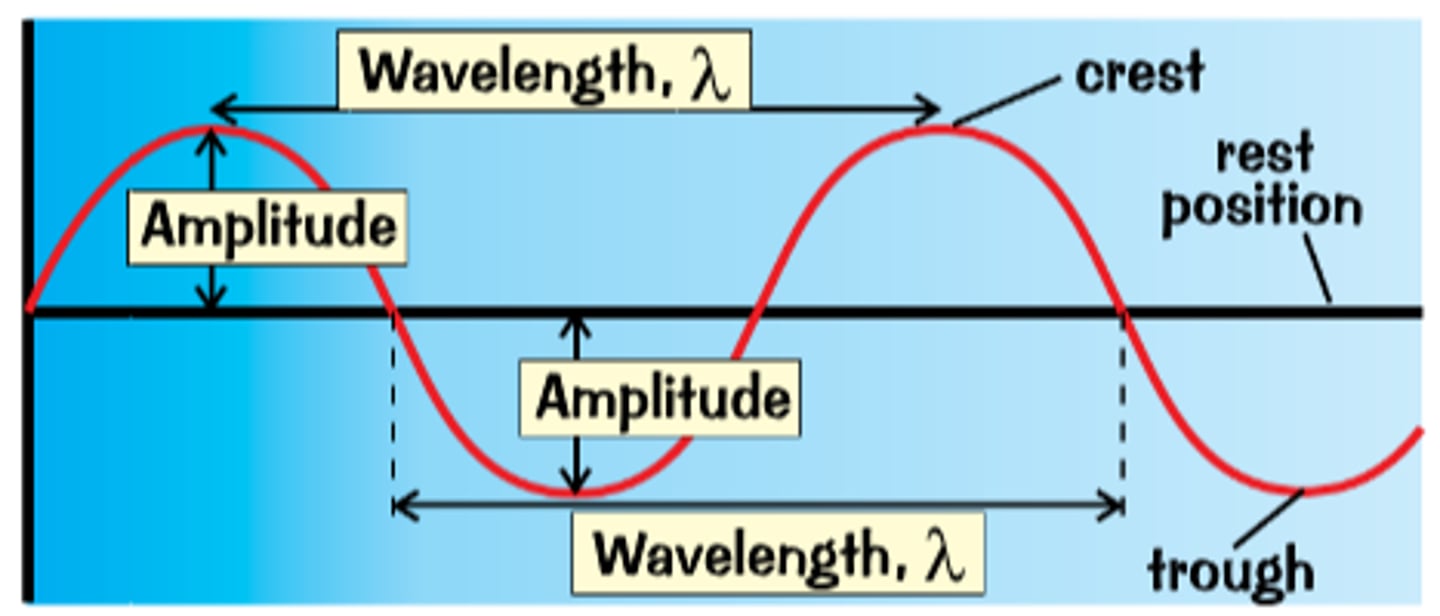
Transverse Wave Diagram
Longitudinal Wave Diagram
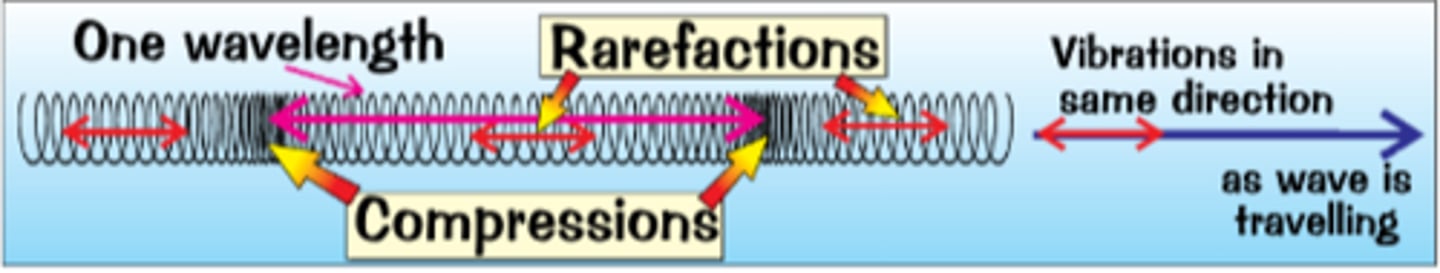
Examples of Transverse Waves
Electromagnetic Waves
Ripple in Water
Examples of Longitudinal Waves
Sound + Ultrasound
Shock Waves
Transverse Wave
Vibrations are at 90° to the direction energy is transferred
Longitudinal Waves
Vibrations are parallel to the direction the wave transfers energy
Wave Info
All waves transfer energy and information without transferring matter
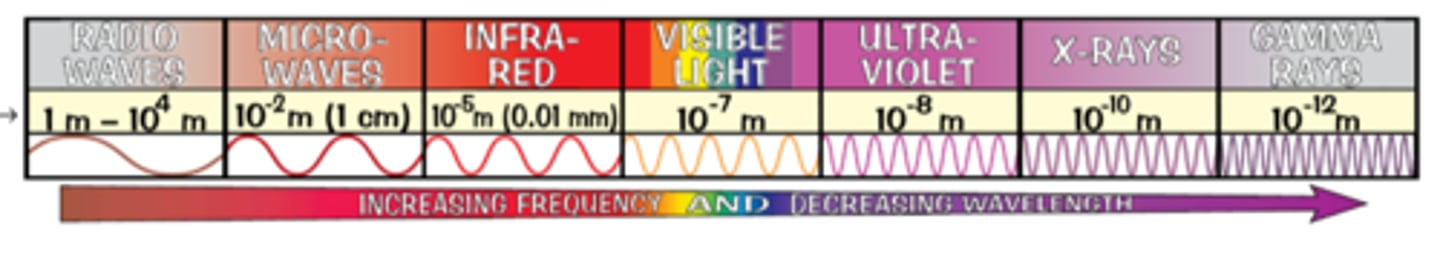
Electromagnetic Waves
Waves have different wavelengths - continuous spectrum
All transverse - Travel at same speed through a vacuum
Diagram of Electromagnetic Waves
Uses of Waves
Radio Waves: Communication
Microwaves: Satellite Communication
Infra-Red Radiation: Heating and monitor temperature
Visible Light: Travel though optical fibres + Photography
Ultraviolet Light: Fluorescent Lamps
X-Rays: See inside things
Gamma Rays: Sterilising medical equipment
Conduction
Process where vibrating particles pass on their kinetic energy
Convection
Particles from their hotter region to the cooler region and take their heat energy with them
Dangers of Microwaves
Yeah human body tissue internally
Dangers of Infra-Red
Skin Burns - Heating effect
Dangers of Ultraviolet
Damage surface cells and causes blindness
Dangers of Gamma
Cell mutation and Tissue damage - can cause cancer
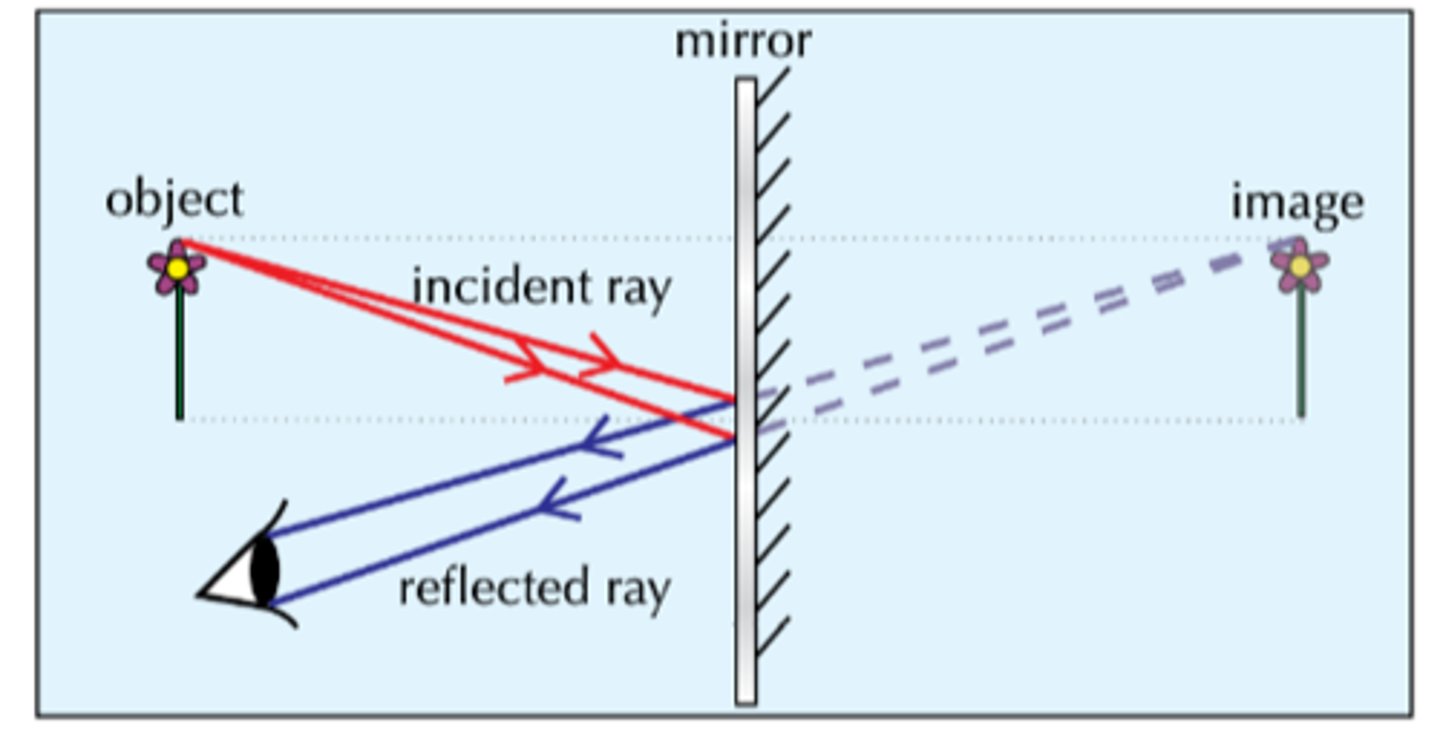
Virtual Image
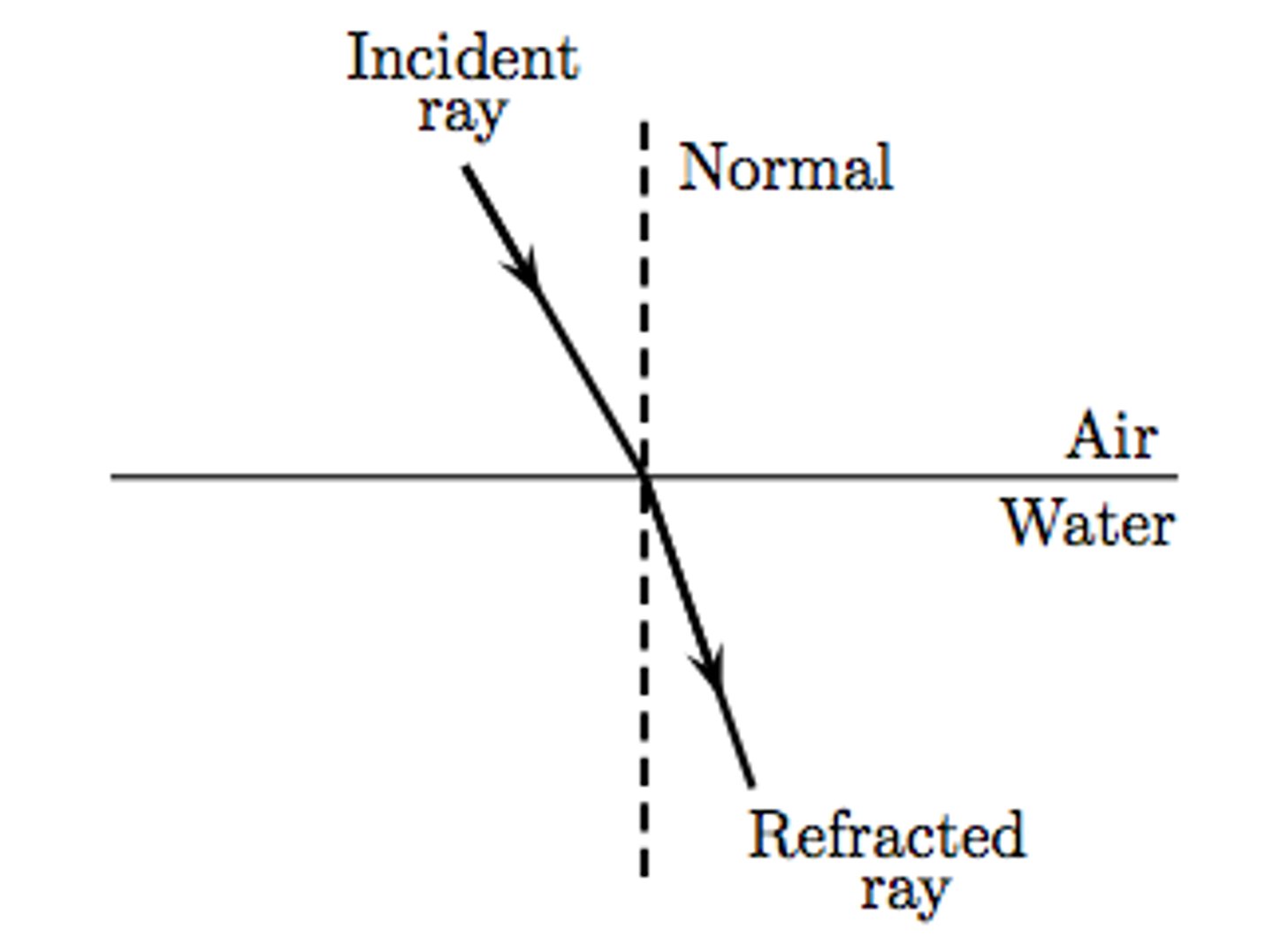
Light Refraction
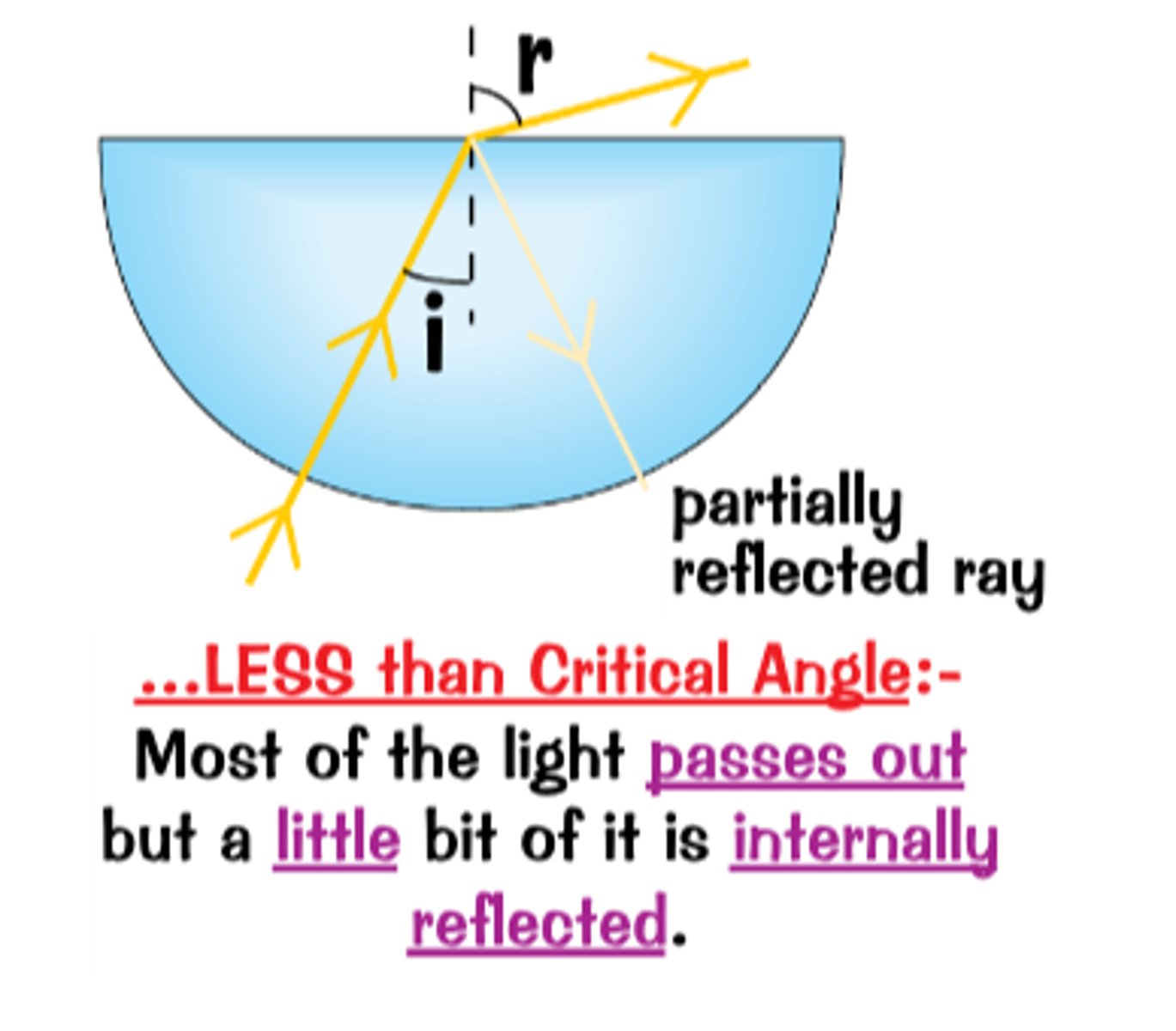
Angle of Incidence is less than critical angle
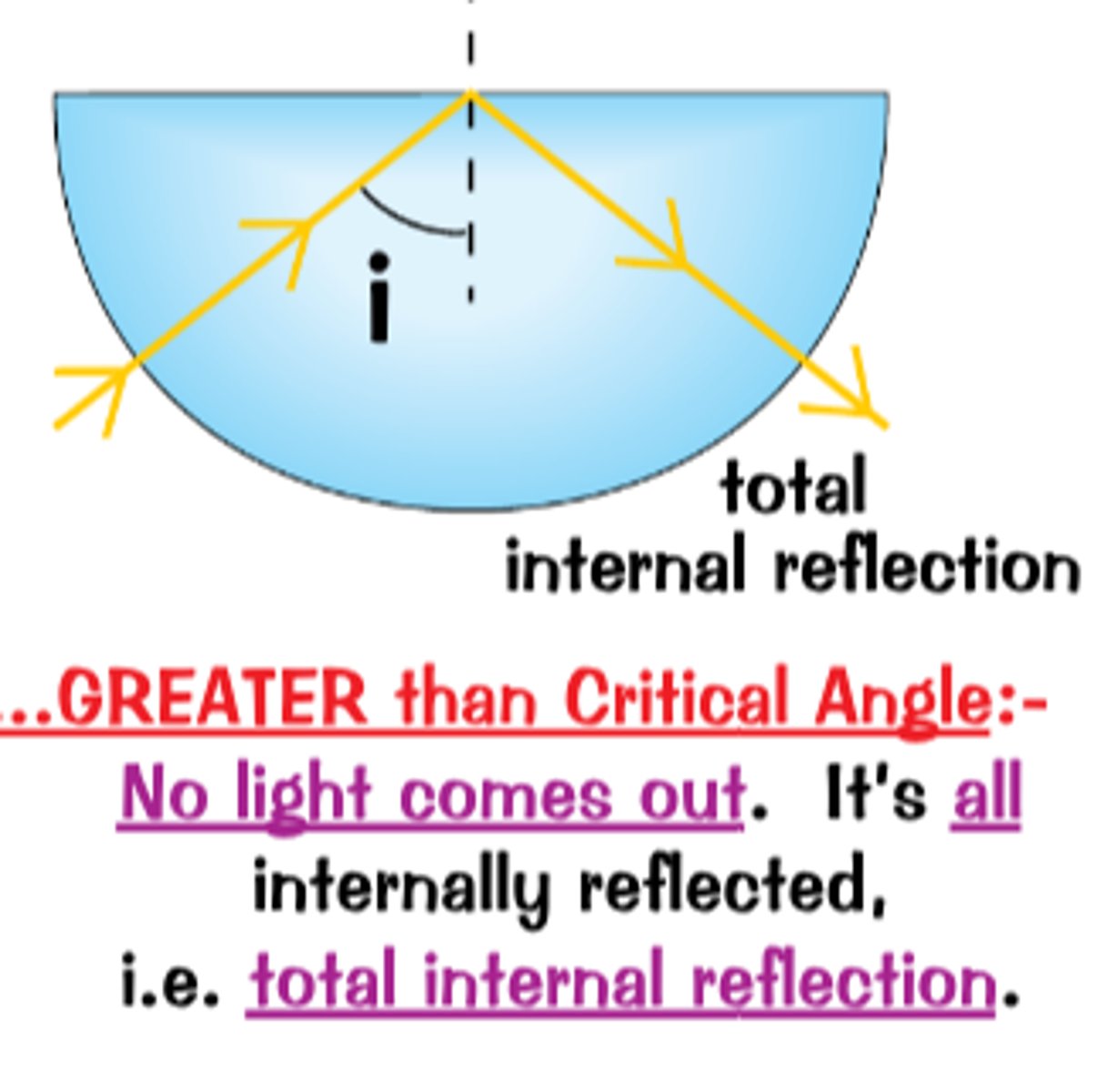
Angle of Incidence is more than critical angle
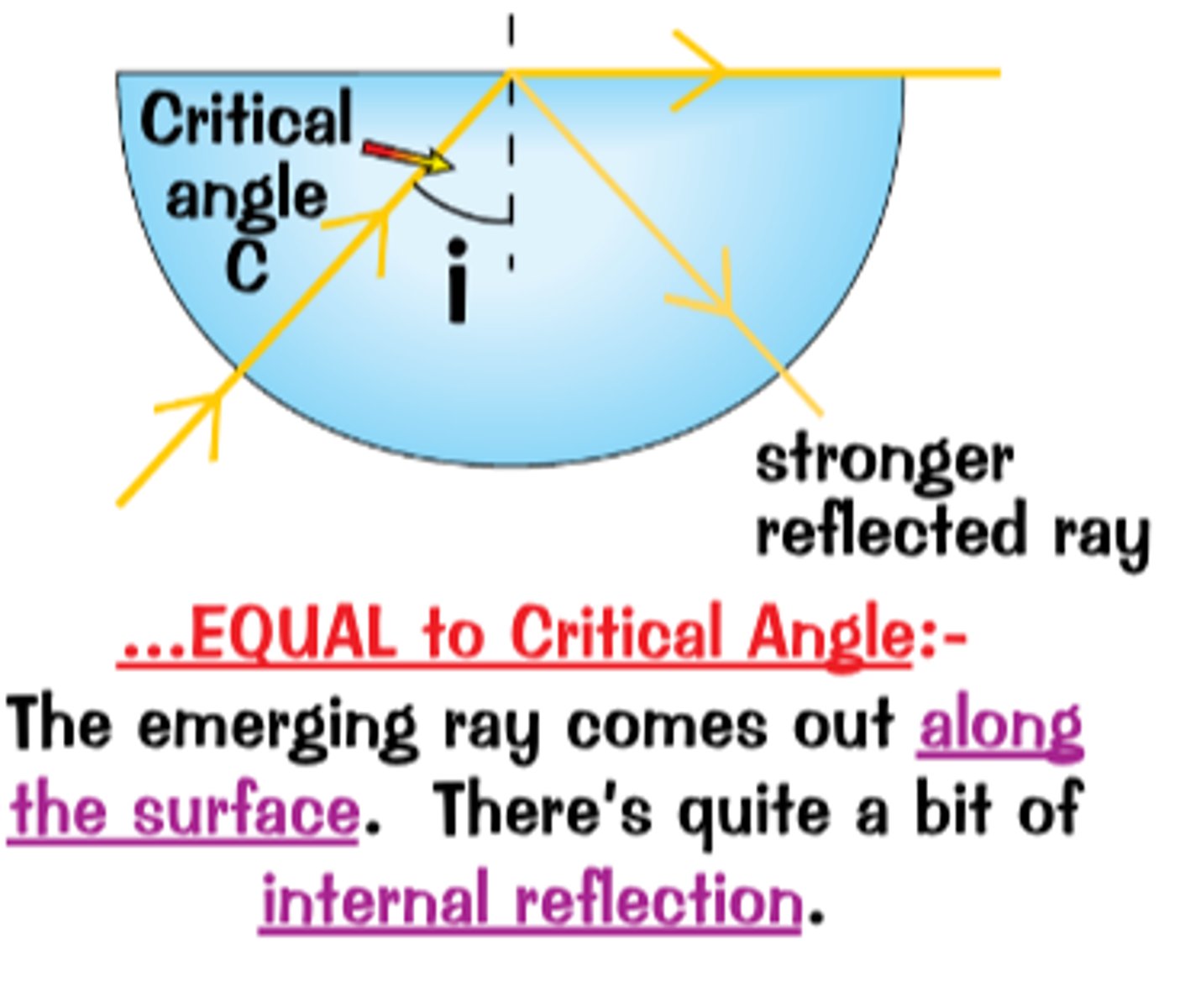
Angle of Incidence is equal to critical angle
Total internal reflection - Optical fibres
Angle of Incident is always higher than critical angle, light always totally internally reflected - only stops if fibre is to sharp
Sankey Diagram
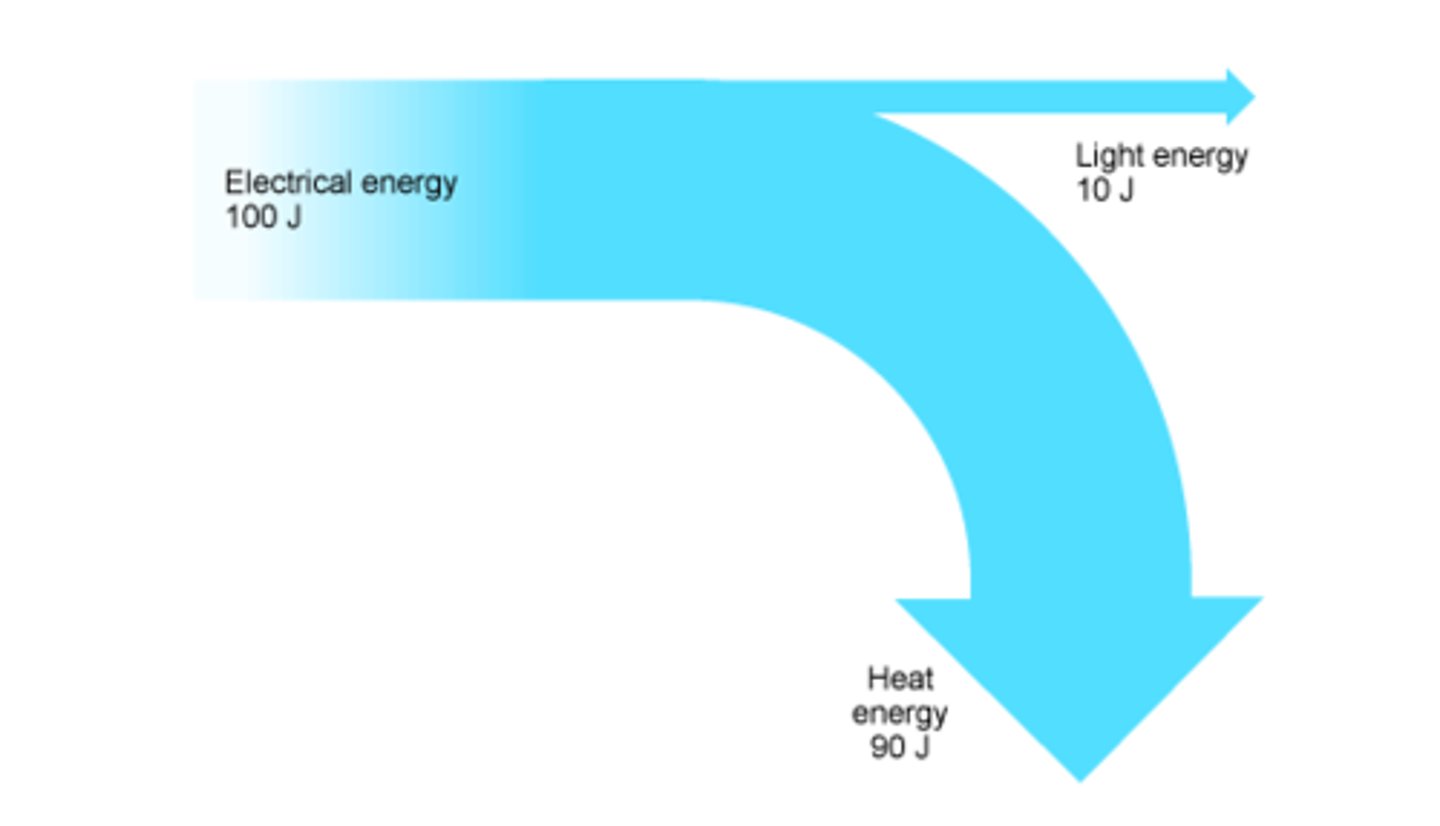
Power
One Watt = 1 joule of energy transferred per second
Human Hearing Range
20 - 20,000 Hz
Renewable Energy
Wind Farms
Geothermal Energy
Solar Energy
Hydroelectric Power
Brownian Motion
Small particles have a constant, rapid and random movement - small particles can move larger particles - causes pressure
This discovery was proved with the use of pollen grains
Absolute 0 - Kelvin Scale
Absolute 0 - atoms have as little kinetic energy as possible
Absolute 0 = -273°C
50 Kelvin = -223°C
15°C = 288 Kelvin
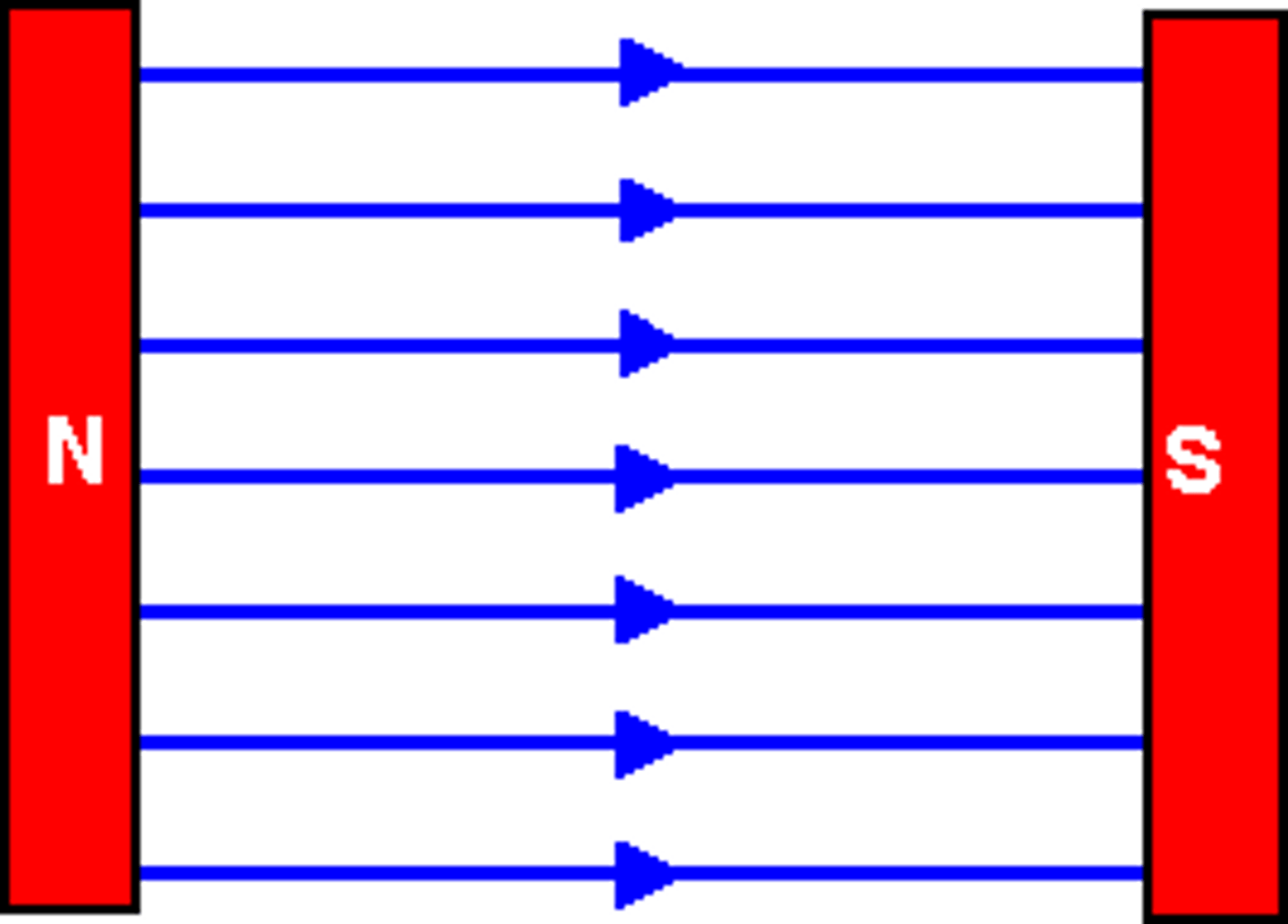
Uniform Magnetic Field
Loudspeaker
A.C electrical signals - from amplifier - to coil of wire - wrapped around cone
Cone surrounded - permanent magnet - cause a force forwards + backwards
Movements = cone vibrate = sound
Resistance of LDRs and Thermistors Experiments
Measure current at any know/fixed temp
Measure voltage at any known/fixed temp
Vary temp and take new readings
Calculate and draw voltage - current graph
Repete and average
Refraction of light experiment
Place block on sheet of paper
Draw around the block
Turn ray box on and shine beam of light into block
use pencil to mark path of light into and out of block
Remove the block, measure the angle of refraction
Repeat
Measuring speed of sound
Person at one end with a pistol
Other person at a distance a way from the pistol (e.g 500 metres)
Person fires gun
People with stopwatches start time when see the smoke from gun and stop when they hear the bang
Average the time
How temperature effects Gas experiment
Use water bath to vary the temperature
Calculate the volume of air in test tube before heating
Measure volume of air after heating
Use a narrow glass tube with liquid above the air so you can clearly see how it has expanded
Investigating the magnetic field experiment
Place sheet of paper on wooded bench (avoid interaction with other magnets)
Place magnet on sheet of paper
Place plotting compass against the magnet
Mark position of compass needle on the paper with a dot
Move plotting compass so that the tail of the arrow sits where the tip of the arrow was
Repeat process
Join dots
Marsden experiment Diagram
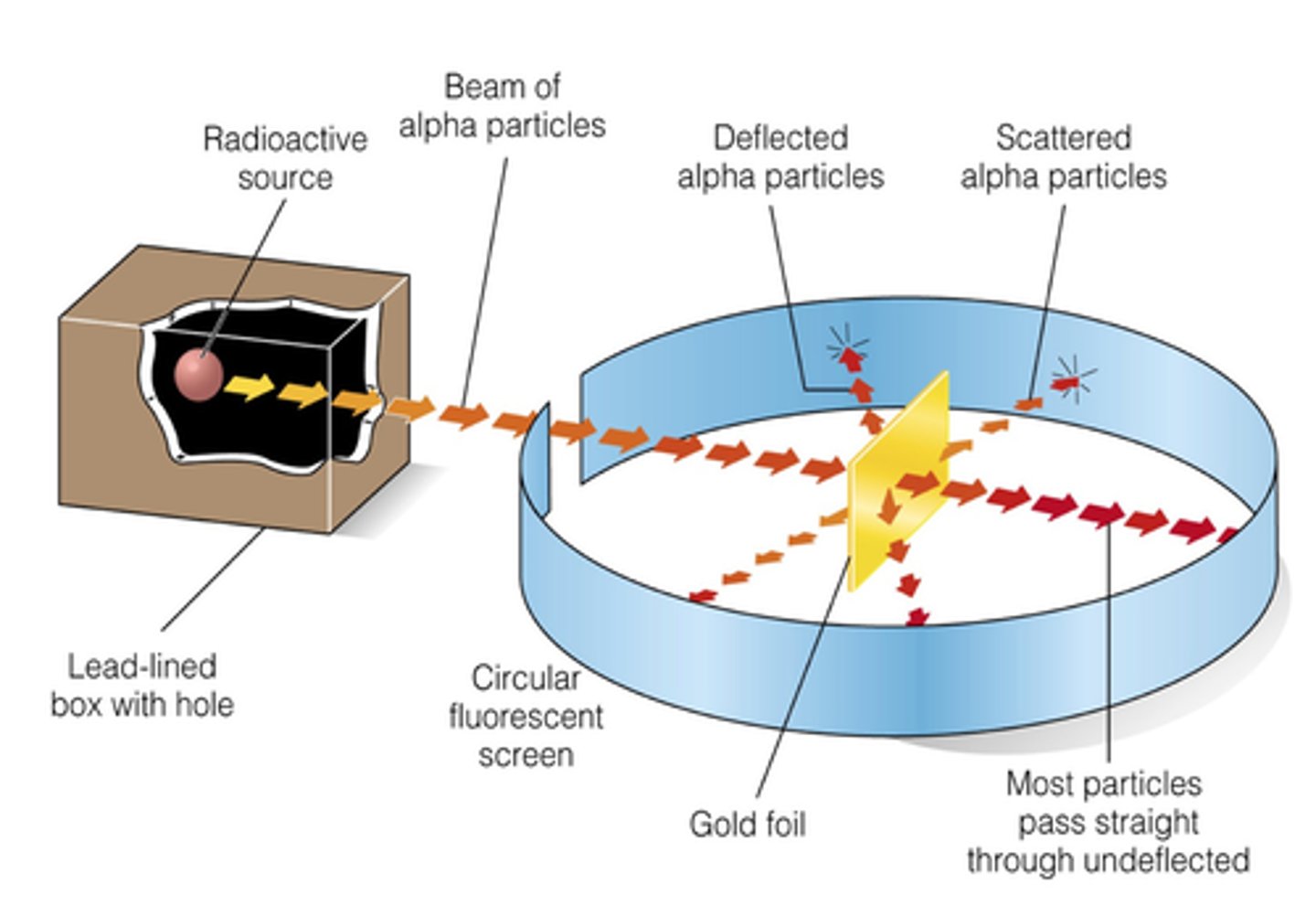
Marsden experiment
Alpha particles were detected as tiny flashes of light on screen
Most alpha particles went straight thought gold foil
A small number deviated as they were repelled
Very few alpha particles bounced back because of the dense nucleus
Conclusion of Marsdens experiment
Most of atom is empty space
Nucleus is small
Nucleus is dense
Nucleus is positive
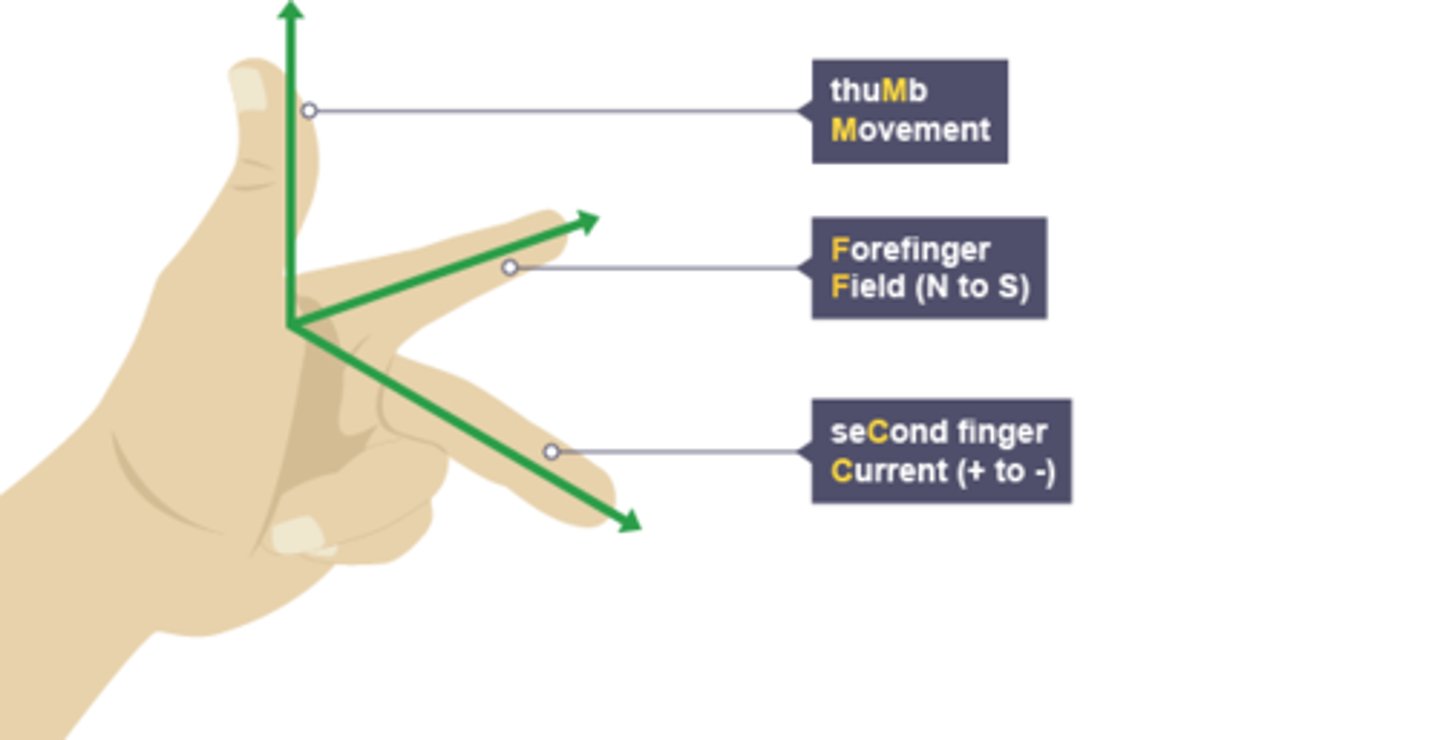
Flemmings Left hand rule