H Bio CAP
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Characteristics of life
potential to Reproduce
React to stimuli
made of 1 or more cells
Adapt and evolve
Grow and/or develop
Gas exchange
Requires energy source
contains genetic info
testable Hypothesis/question
(Do) plants get energy from the sun (?)
Non-testable question/hypothesis
(does) the sun has layers (?)
control group
a group that ensures accurate results and is used to be able to see the effect of the independent variable in comparison to the experimental group. All factors remain the same in this group except for the independent variable.
experimental group
Factors remain the same as well except for the independent variable: but this variable is applied to the group
independent variable
the variable that is changed in order to experiment; (ex. amount of water, color of lighting, change in diet, temperature.)
What to avoid when referring to independent variable?
don't say a specific change that only applies to one group when referring to this variable, (ex. 72 degrees temp, vegetarian diet, nor watering with gatorade) JUST SAY WHAT IS BEING CHANGED BETWEEN BOTH IN GENERAL AND NOT ON ONE.
dependent variable
The variable that shows the outcome; the results of the independent variable on the experiment; Any changed feature as result of what was changed.(ex. Growth as result of the change of fertilizer; the vitality of a plant as result of the lighting)
controlled variable
a factor in an experiment that remains constant
(i.e: in an experiment measuring the effect of light on plants, the ph of the soil and the species of the plant are controlled variables.)
Quantitative Data
numerical data; data made up of measurements or possible to make counts
qualitative data
non-numerical descriptive data
Correlation
relationship between two variables that may indirectly change together over time.
casuation
Cause and effect; when one change in variable causes the other to change. (ex. a increase of a plant's temperature will casuate the growth and life span of the plan
Hypothesis
A prediction or proposed explanation to what will happen, especially to answer a question in the scientific method.
theory
A group of proven propositions made to explain facts or phenomena in the natural world; has to do with trying to answer why and something happens
law
Statements that currently describe and predict a range of phenomena; describes what will happen.
Eyepiece
Contains the ocular lens (10x)
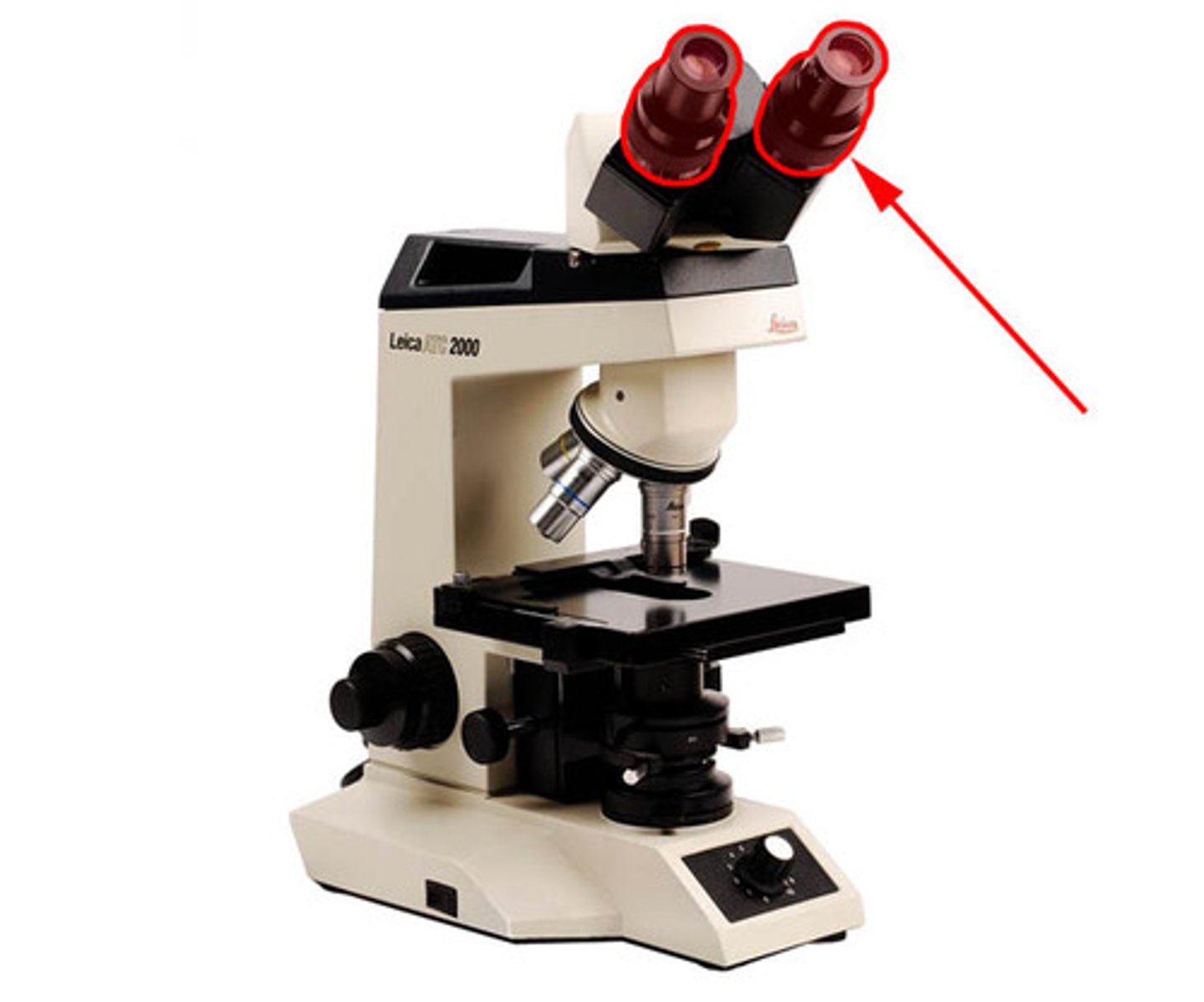
ocular lens
10x
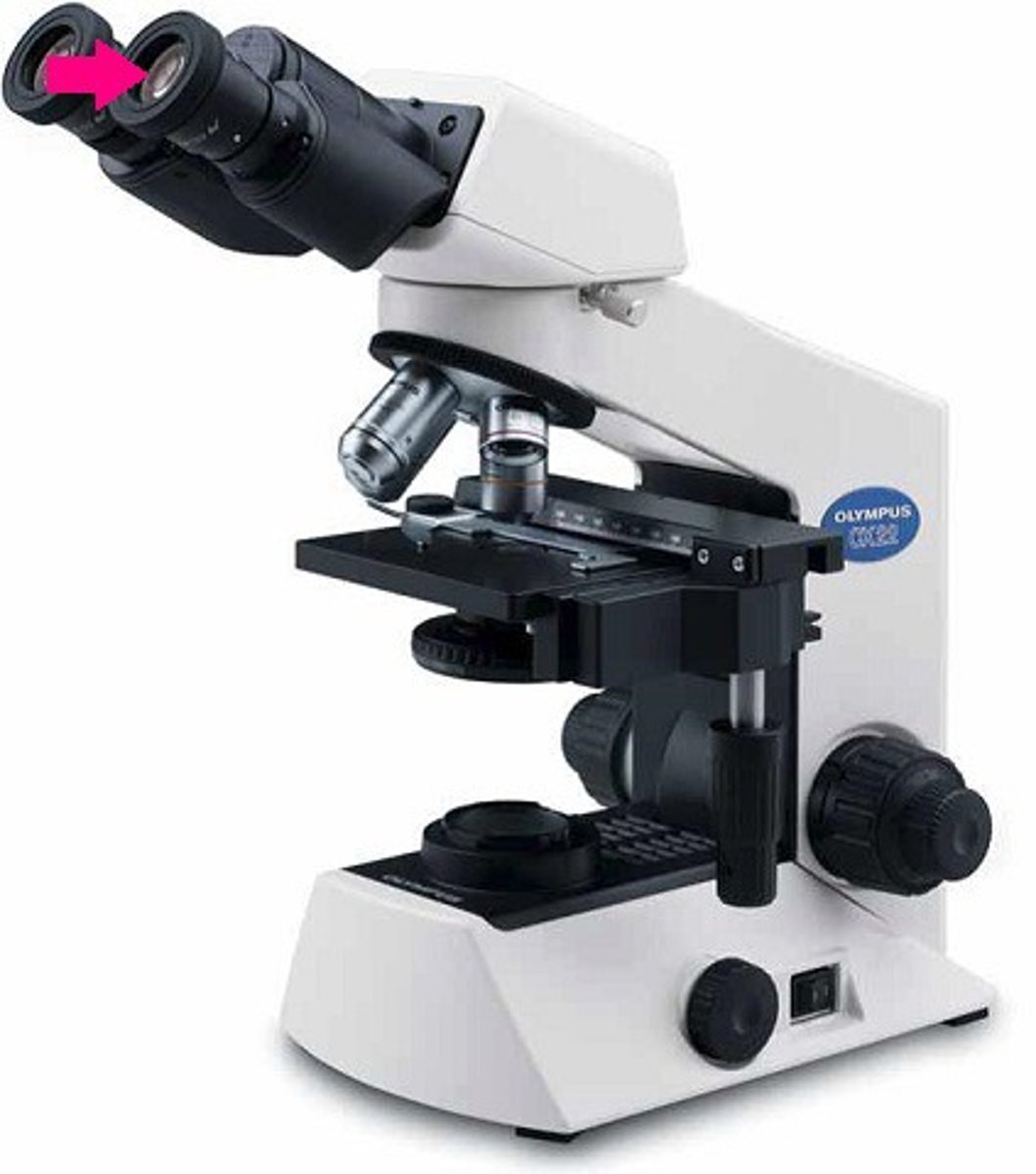

nosepiece
Holds the objectives and can be rotated to change the magnification
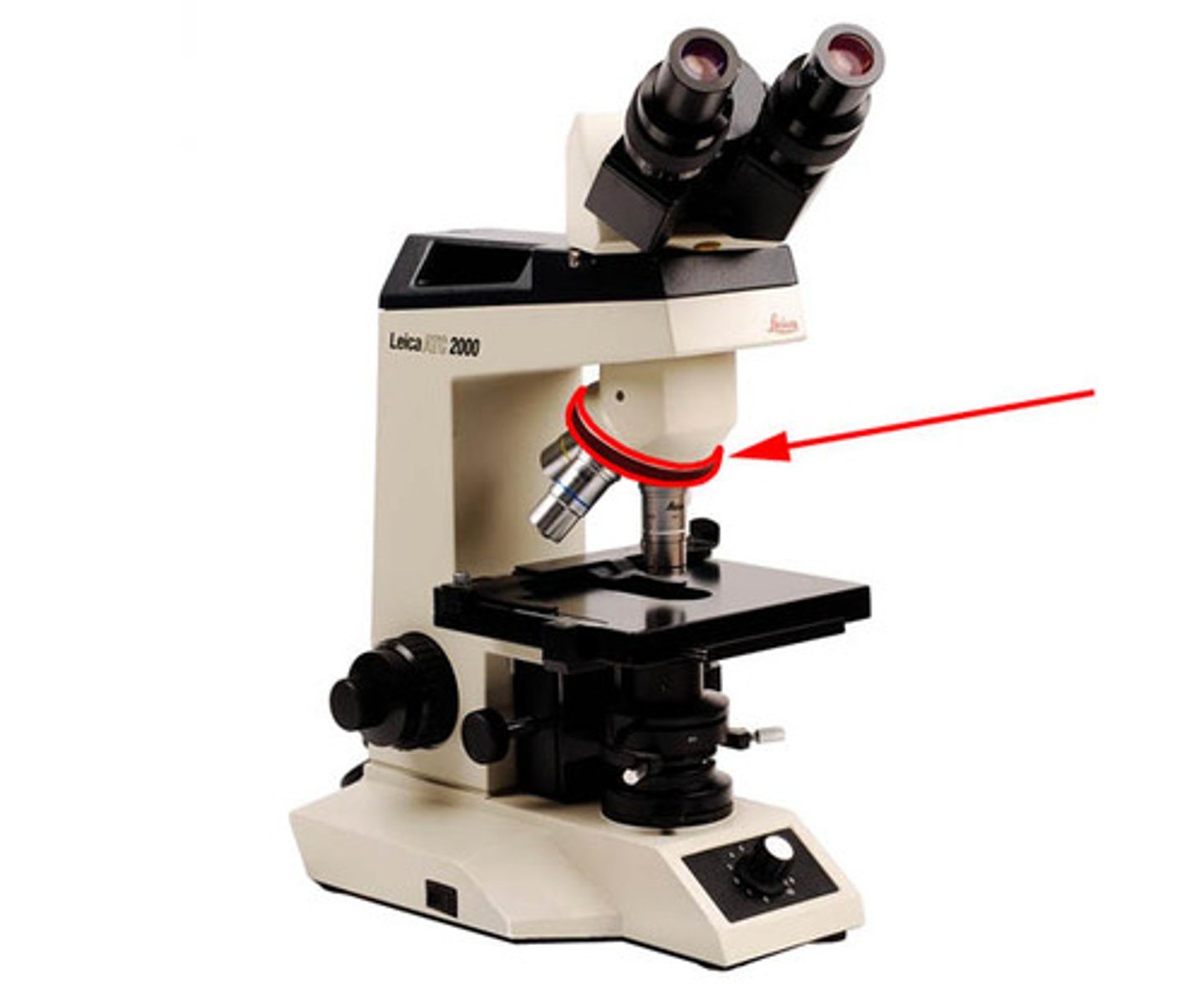
objective lenses
4x, 10x, 40x
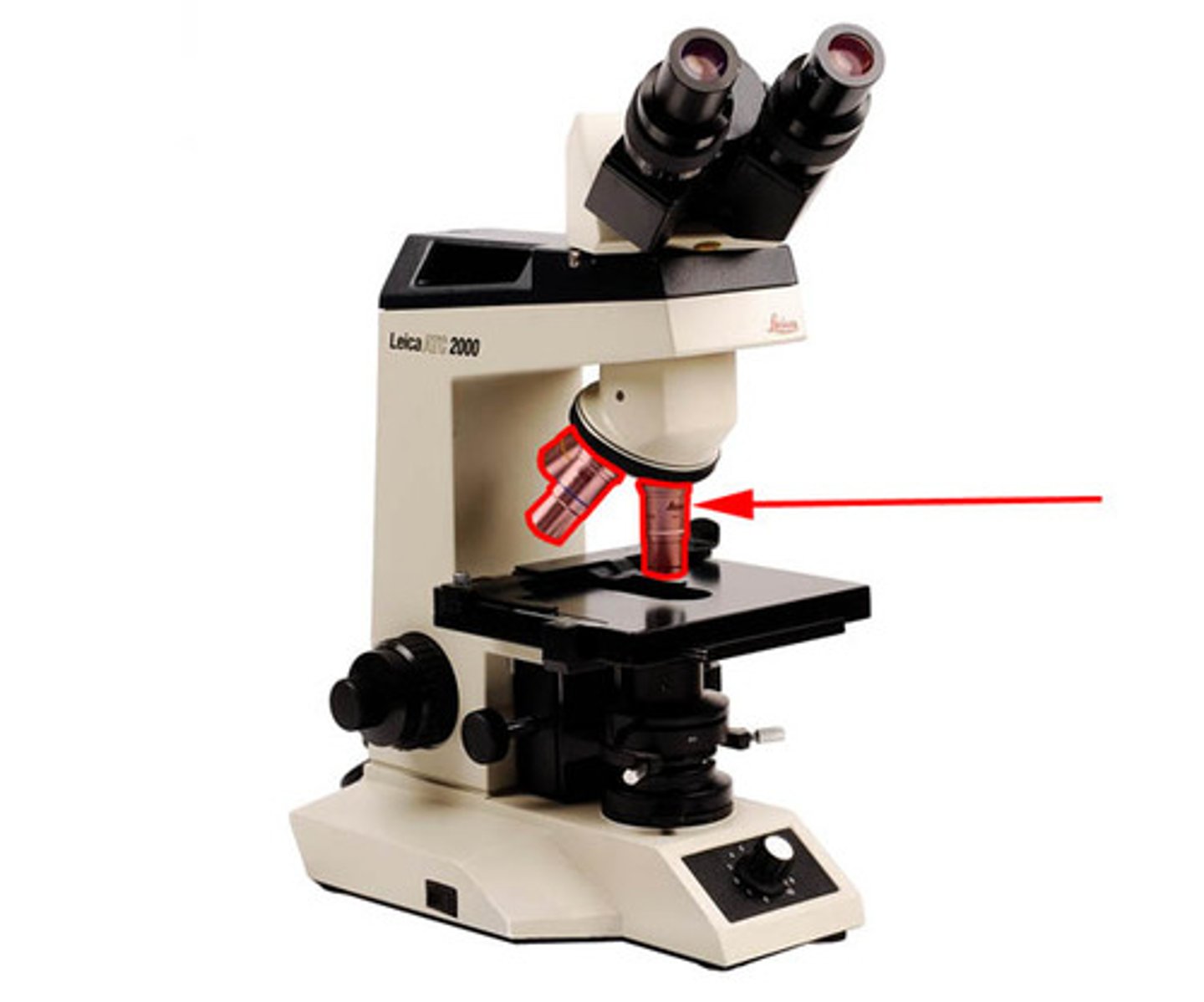
stage
Supports the slide being viewed
stage clips
Holds the slide in place
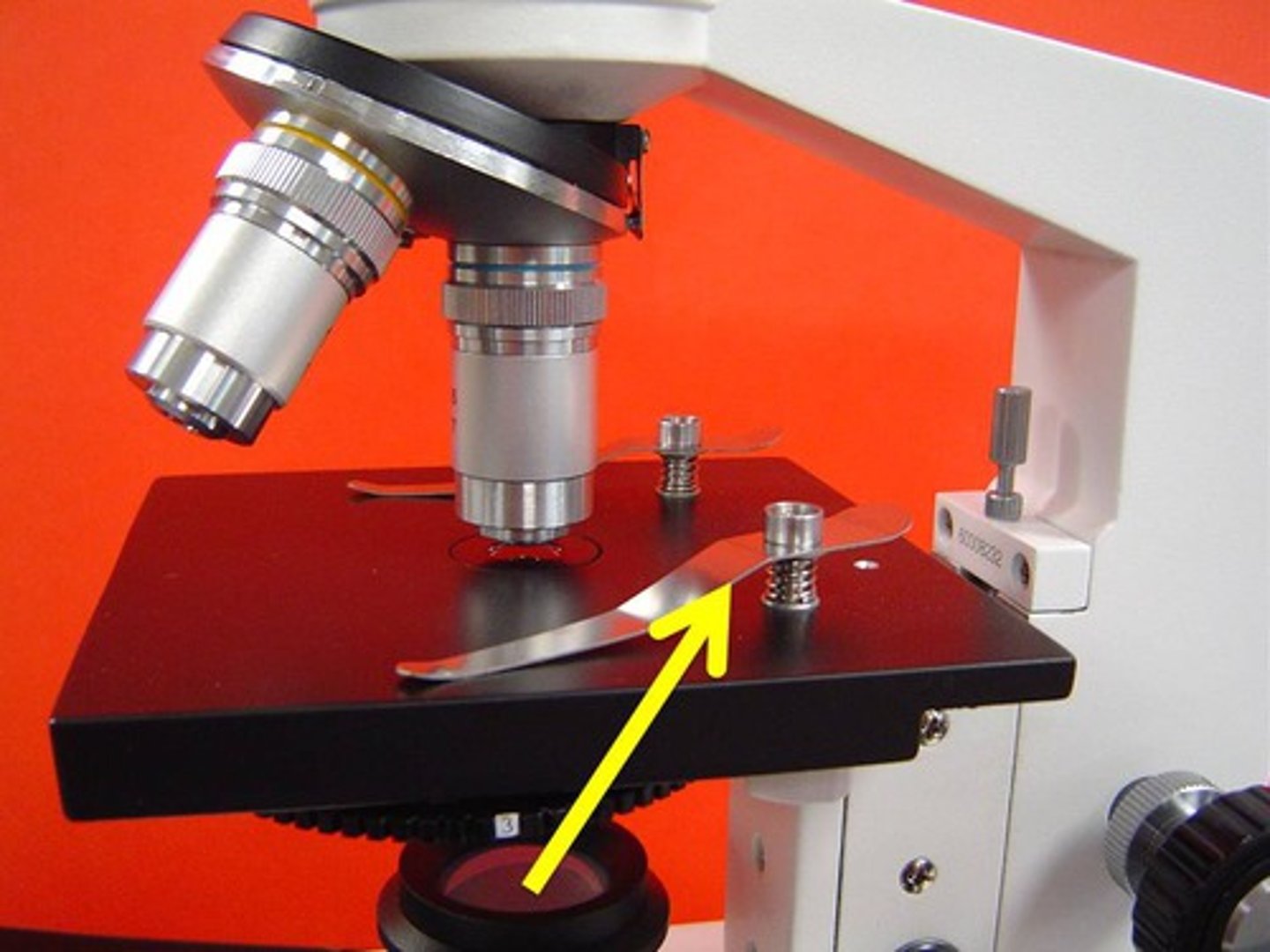

coarse focus
Knob that allows you to make major focusing adjustments. (large knob)
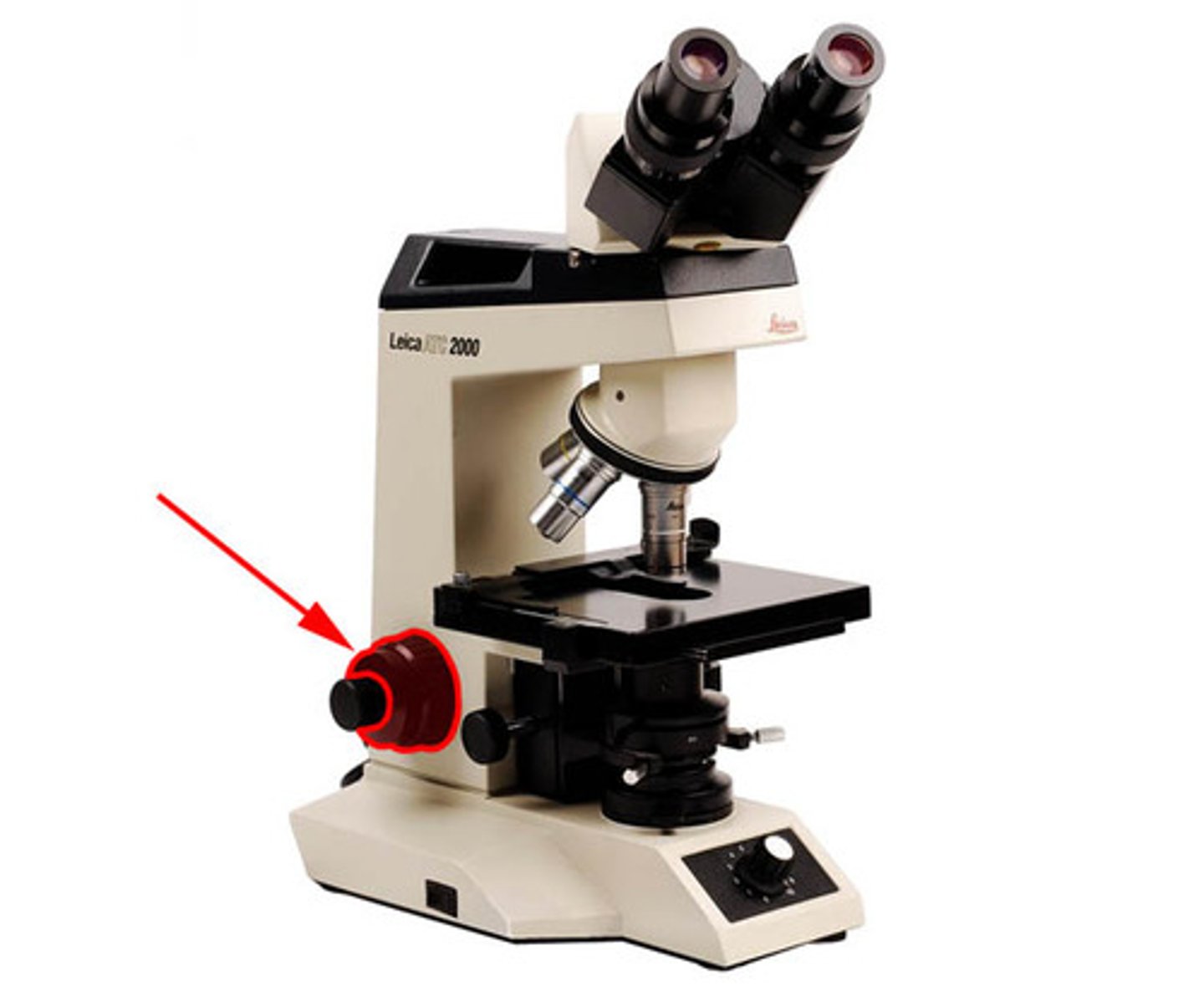
fine focus
Knob that allows you to make fine focusing adjustments. (small knob)
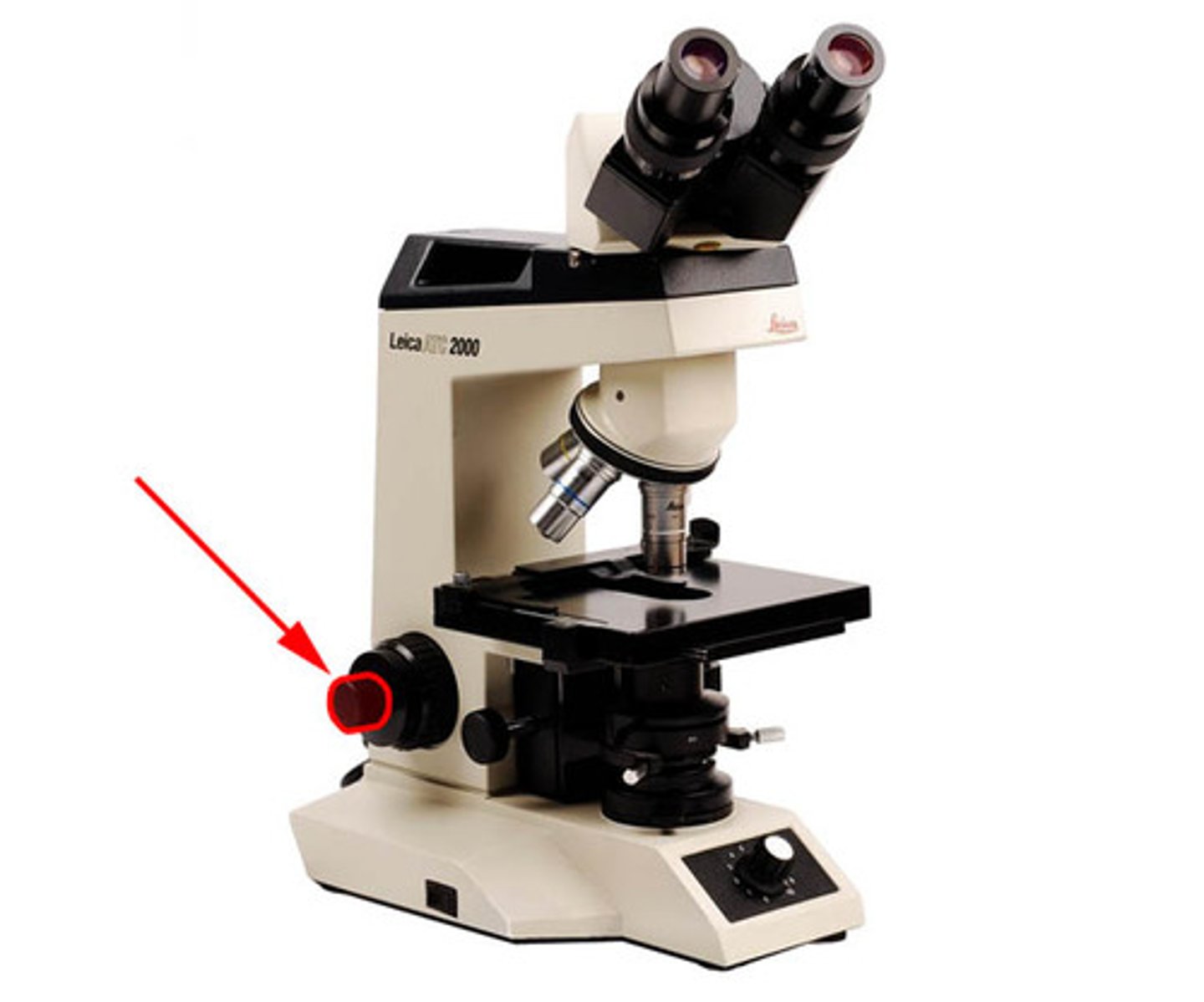
why is quantitive data more important?
More precise data adds credibility to the experiment
Difference of Eukaryotic over prokaryotic cells
larger, complex structure, membrane bound organelles, able to be motile, can be multicellular, more chromosomes.
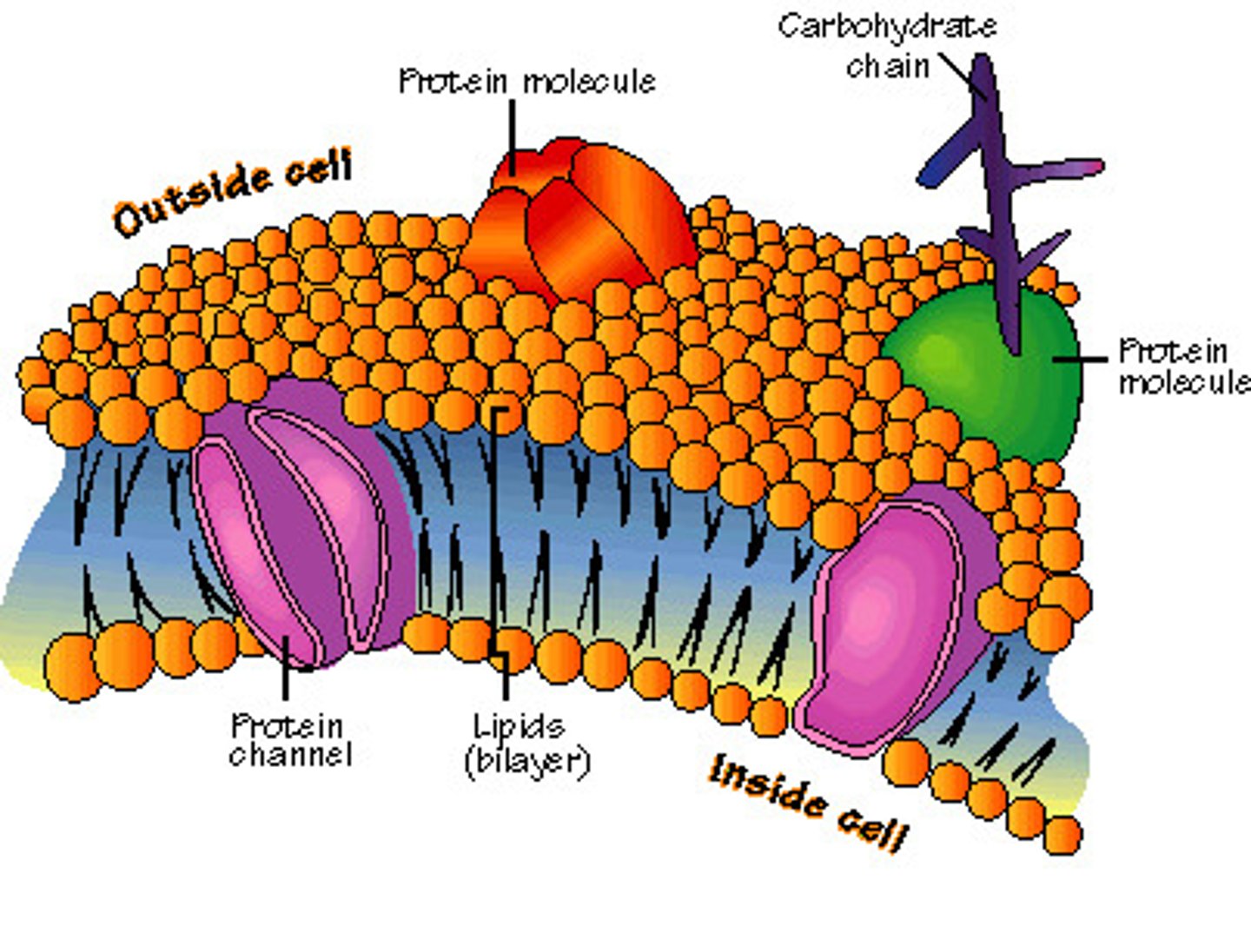
plasma membrane
semi-permeable phospholipid bilayer; each phospholipid consists of one hydrophilic phosphate head and 2 fatty acid lipid hydrophobic tails inside; also contains carrier and channel proteins for facilitated diffusion and to move larger particles.
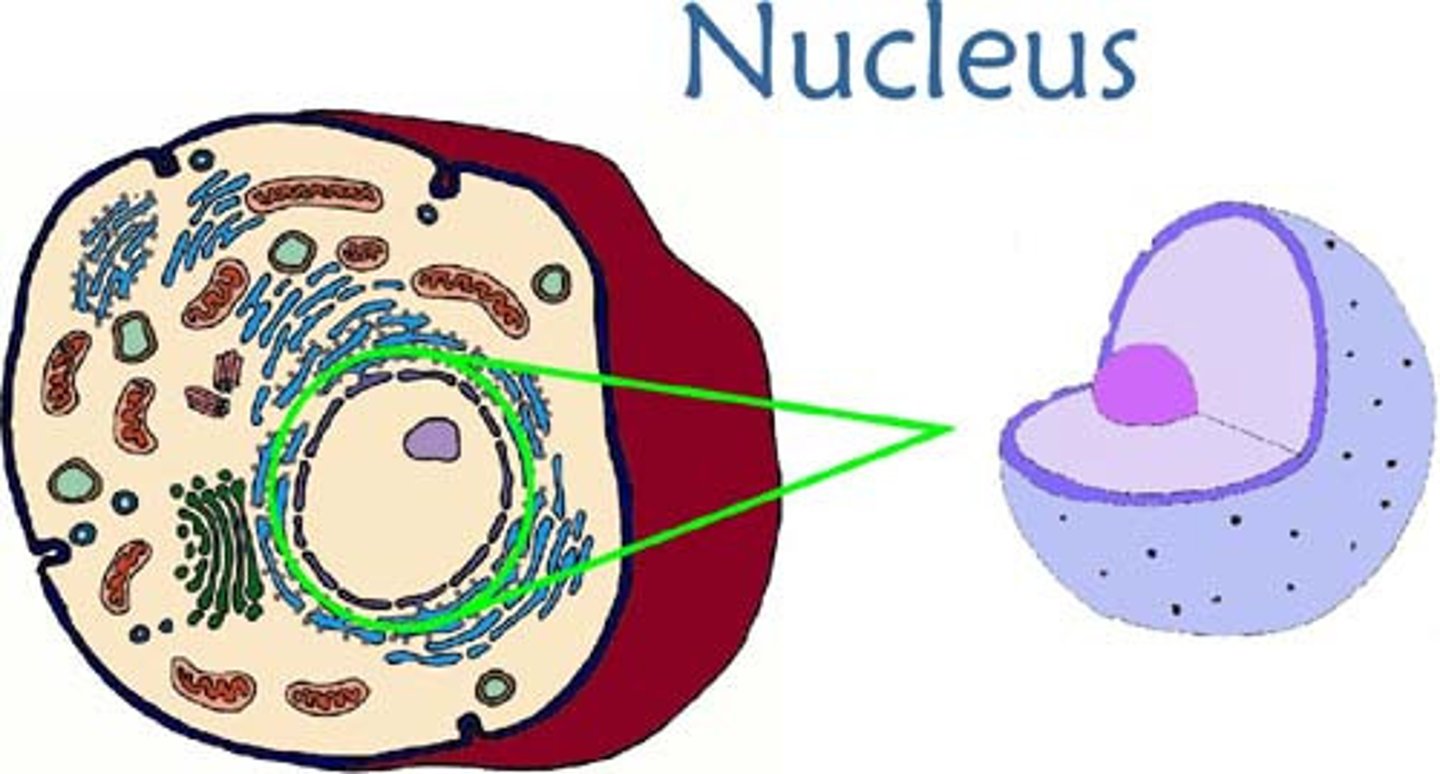
Nucleus
brain of cell, contains DNA which codes the proteins.
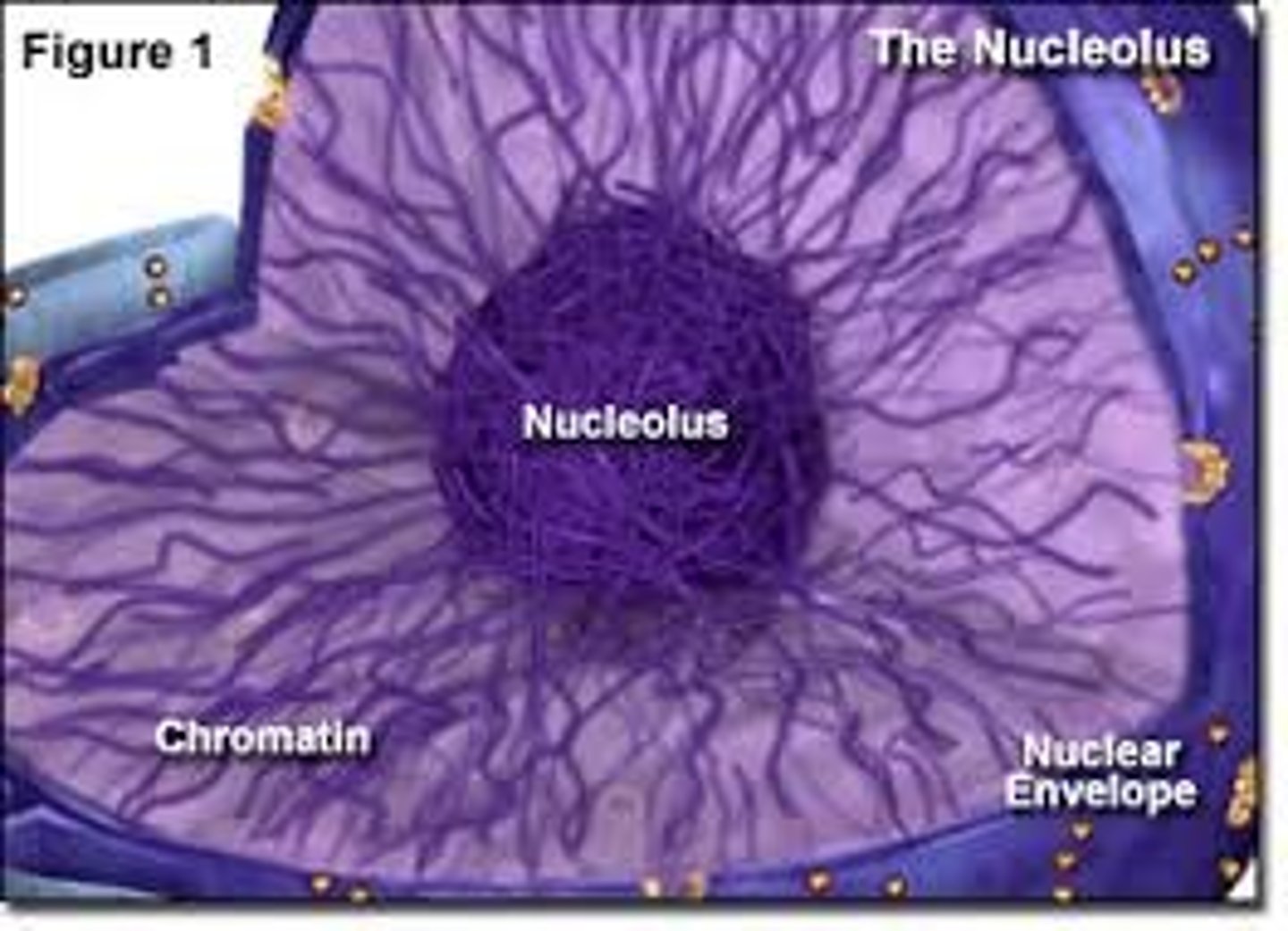
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
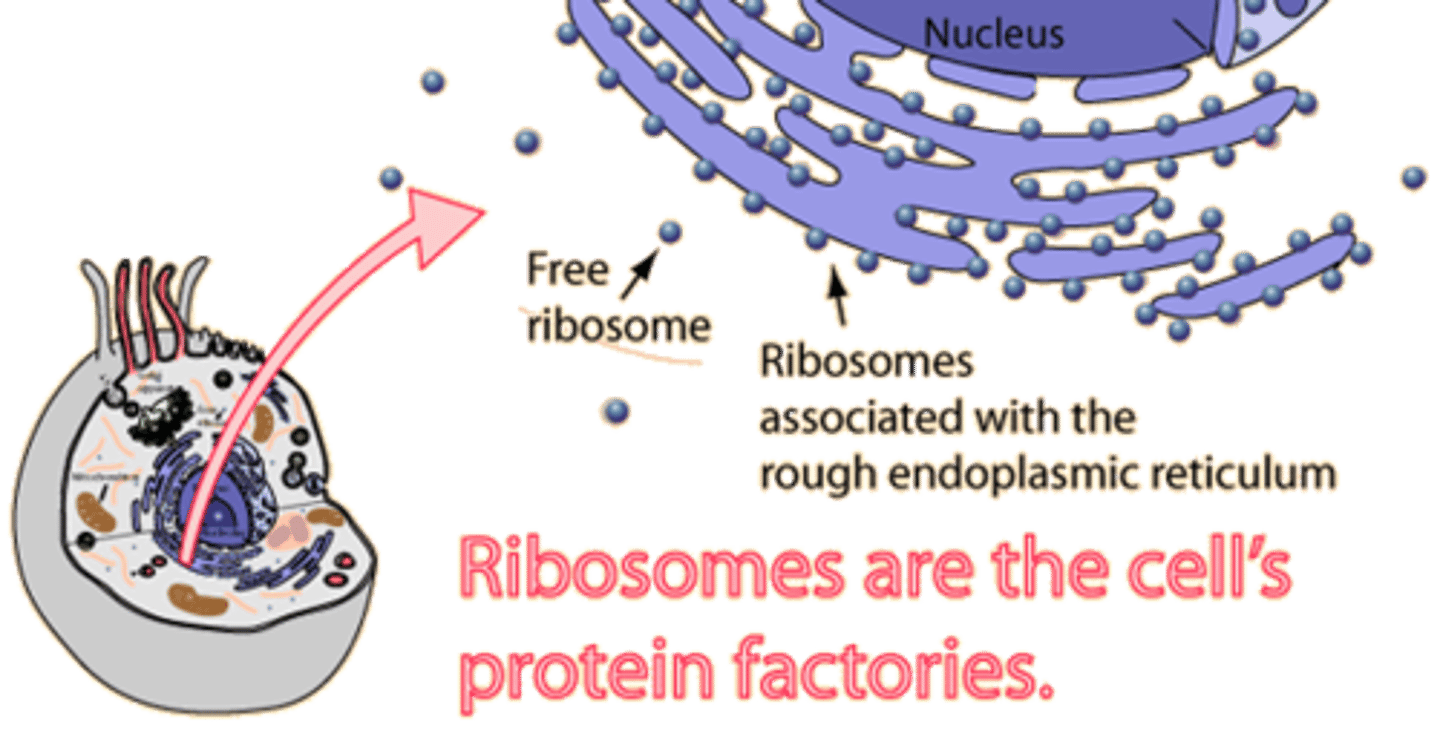
Ribosomes
protein synthesis; can be free or bound to ER; uses RNA to assemble protein.
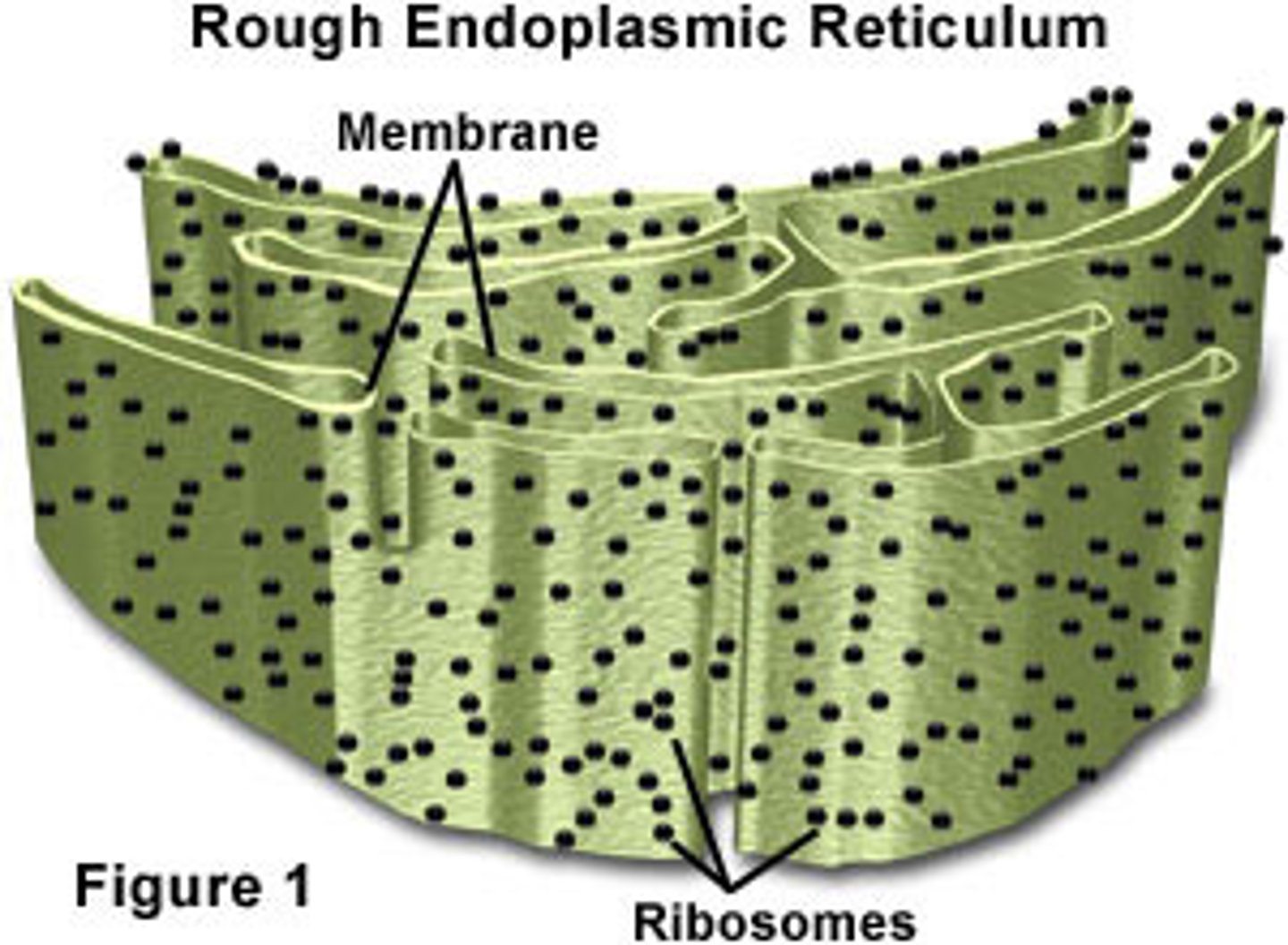
Rough ER
part of Endoplasmic Reticulum with Ribosomes attached which makes its use for protein synthesis, transports "domestically" within the cell.
Smooth ER
Part of Endoplasmic Reticulum without Ribosomes attached, making its use for lipid synthesis and storage; transports "domestically" within the cell.
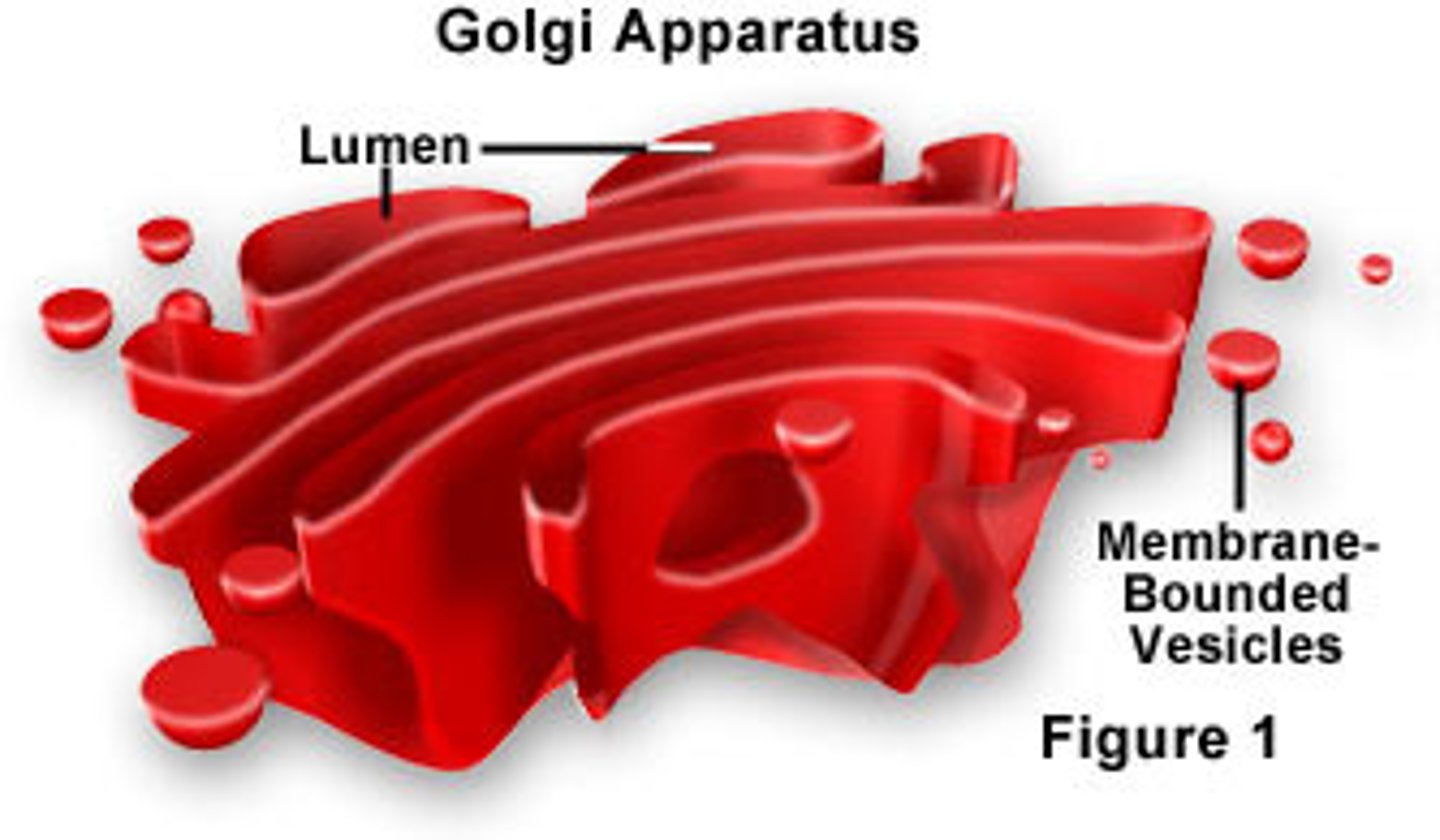
Golgi apparatus
flattened sacs; packages, transports, and temporarily stores proteins inside and out of the cell not domestically; transports cells by pinching and fusing vesicles to and from the golgi and sometimes to the ER as well.
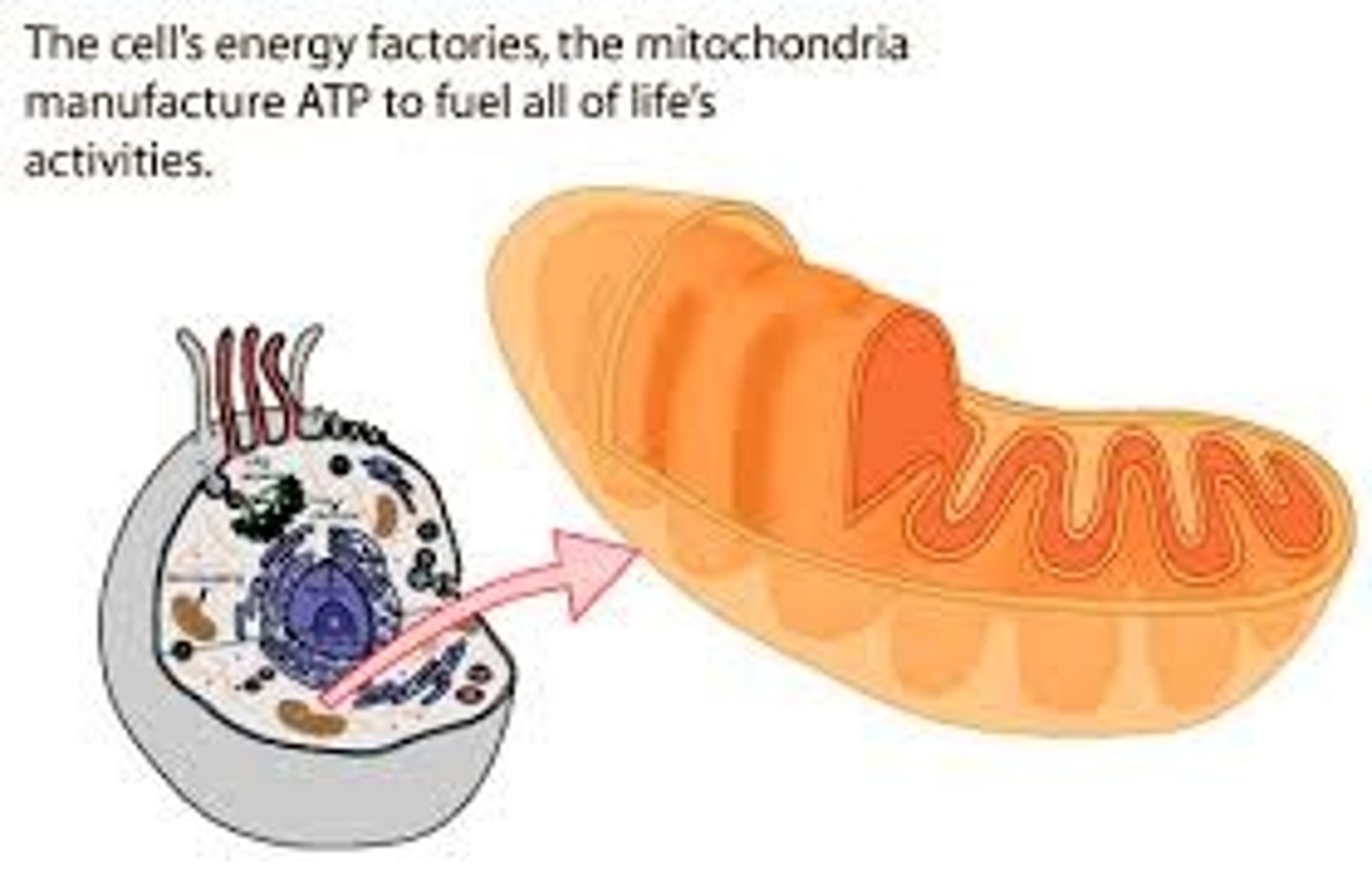
Mithochondrion
membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells where cellular respiration takes place
Powerhouse of the cell as it produces ATP; double membrane with a folded inner one called cristae; has own DNA and ribosomes.
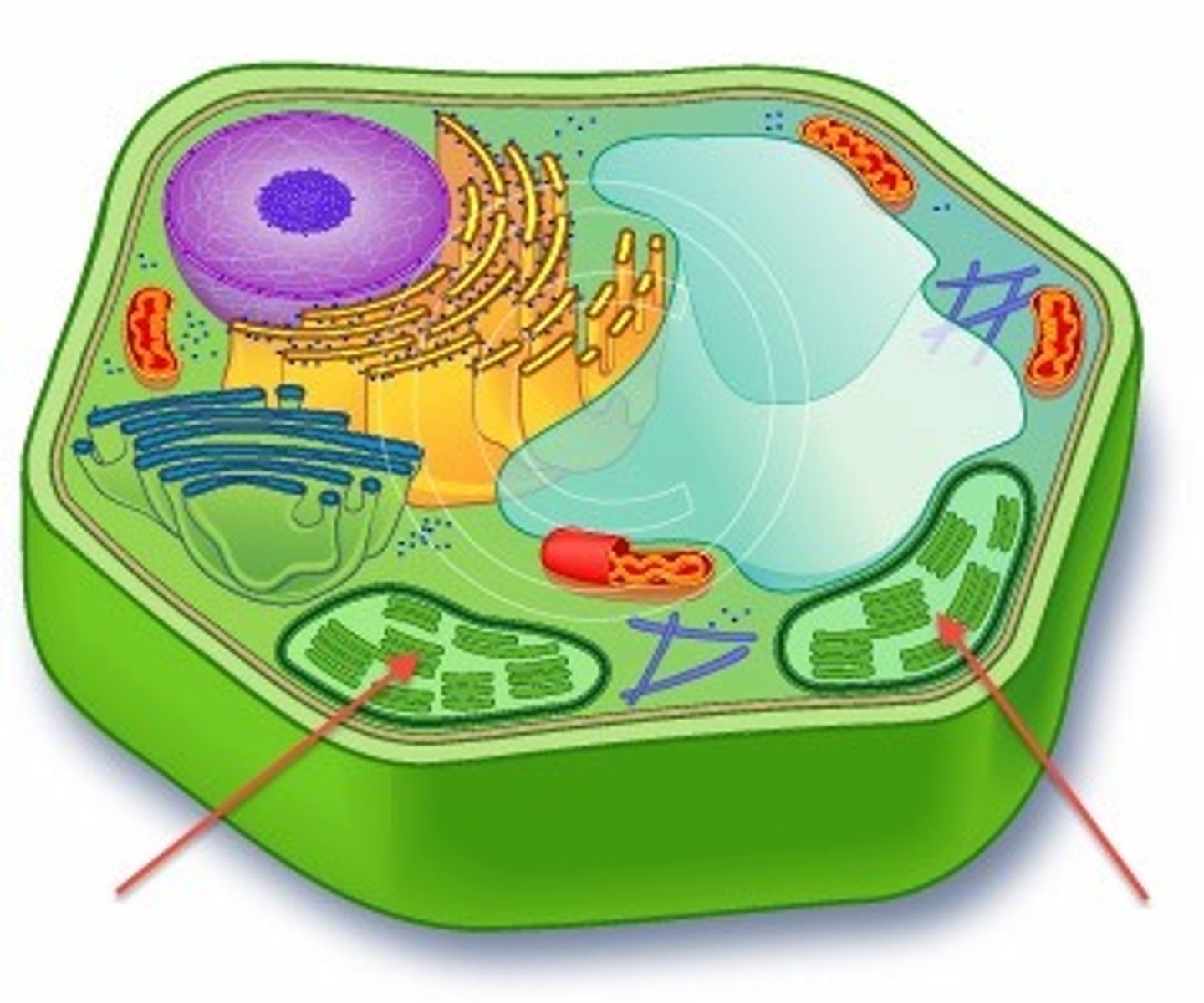
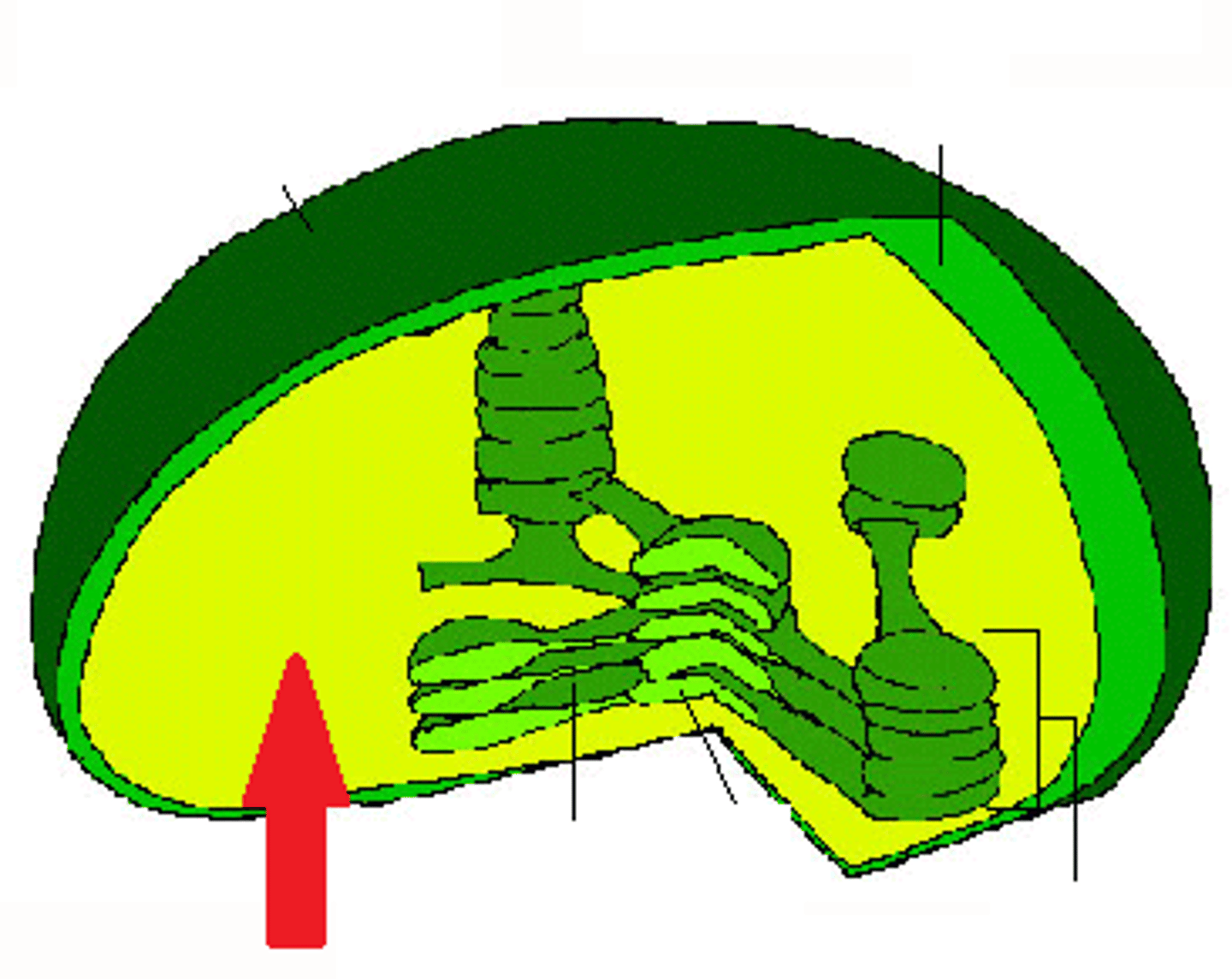
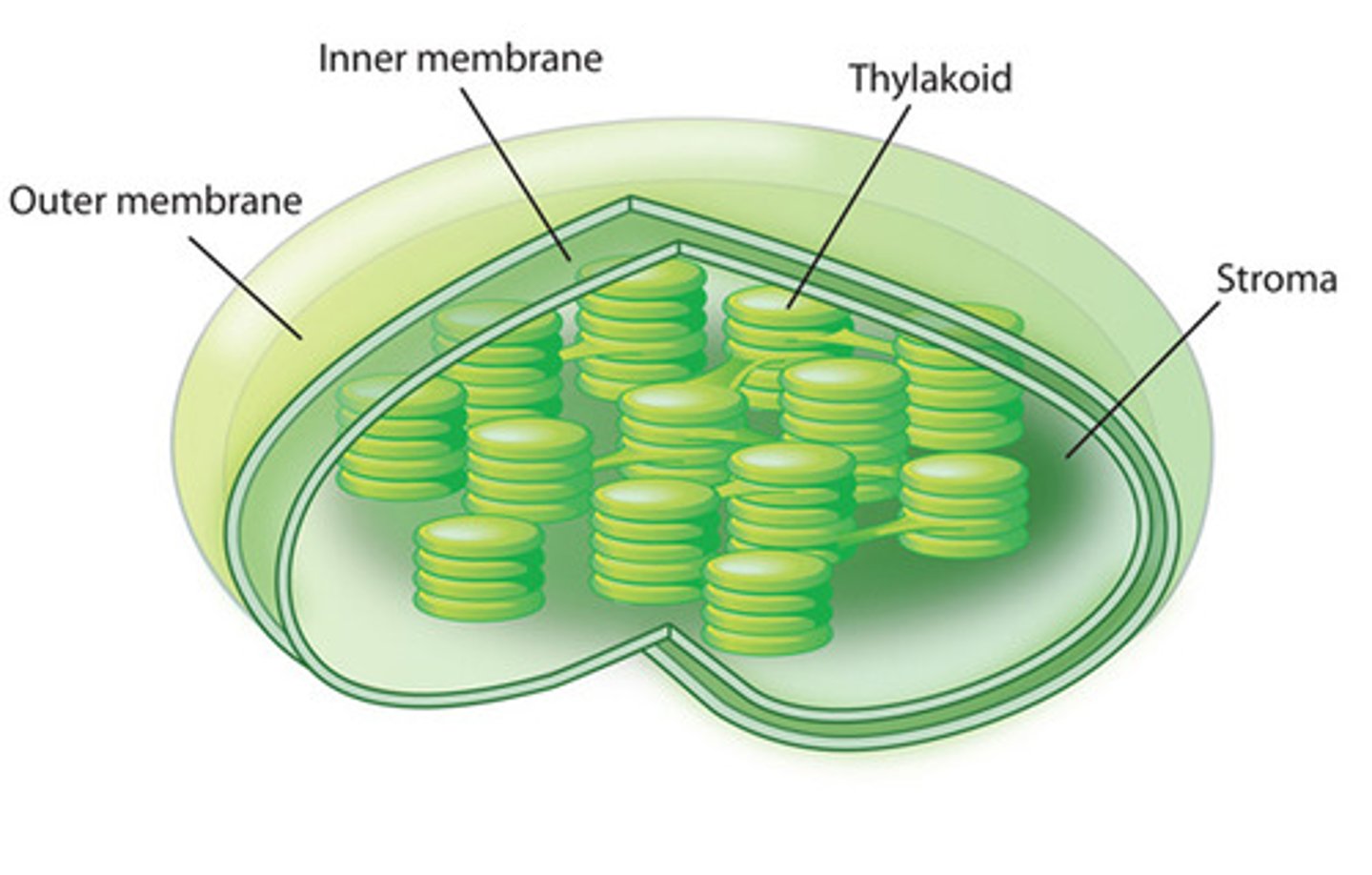
Chloroplast
Only found in plant cells; membrane bound with own DNA and ribosomes; contains inner membranous sacs called thylakoids; when stacked stoma; responsible for generating sugars through photosynthesis; contains chlorophyll.
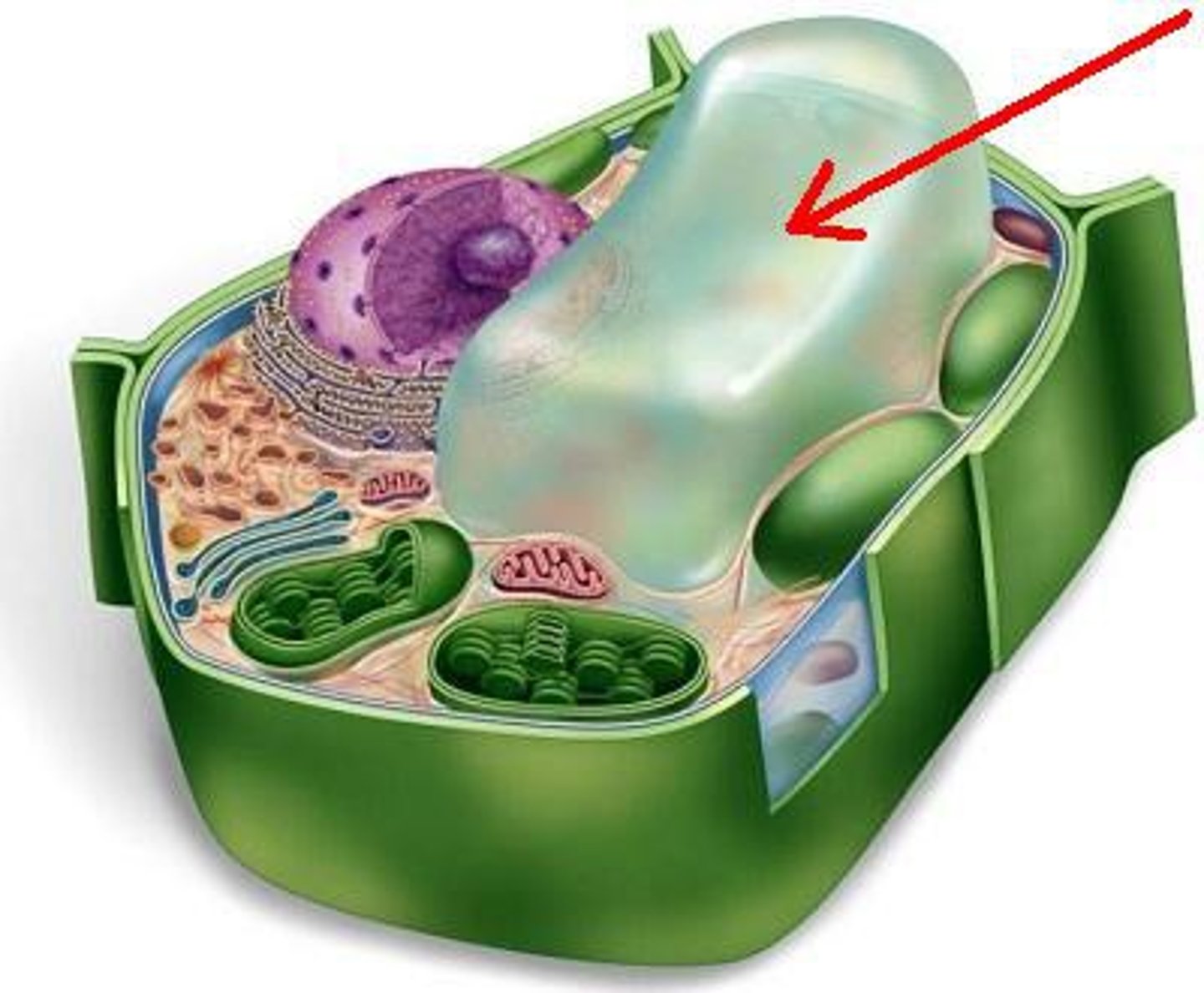
Vacoule
membranous sacs for storage of nutrients, water, and sometimes waste; tend to be larger in plants.
Vesicle
membranous sacs for transporting cellular products and wastes; fuses and pinches off ER and golgi apparatus; motor proteins move them throughout the cytoskeleton.
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement and transport; made of 3 parts: microtubules, intermediate filaments; and microfilaments.
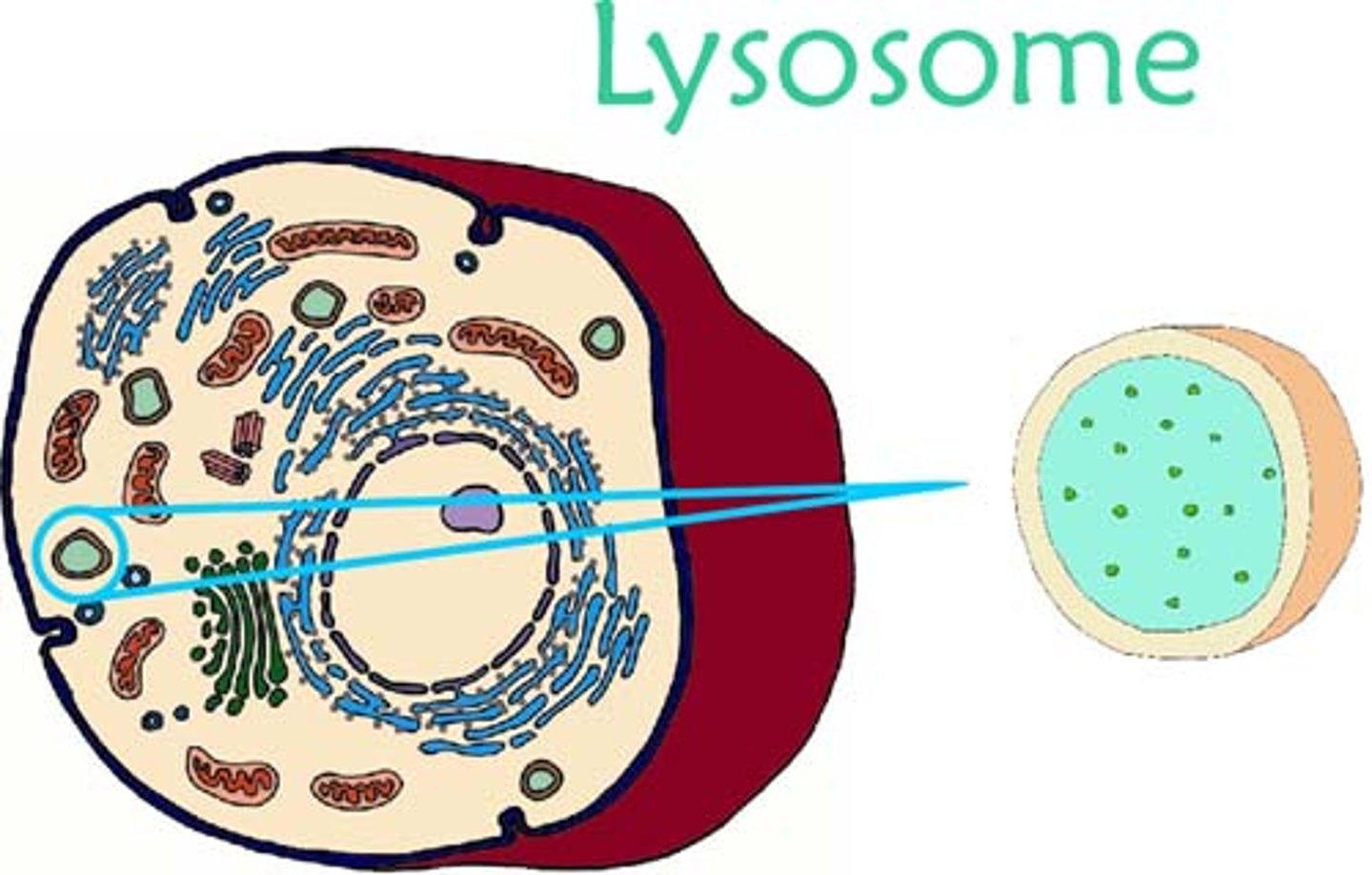
Lysosomes
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell; contains digestive enzymes.
Peroxisomes
similar to lysosomes but digest toxins by stripping hydrogen ions off them and holding onto the removed hydrogen peroxide product until it can be disposed
cilium
short, numerous projections that look like hairs made of microtubules; move back and forth to move the cell or "sweep" substances out of the cell.
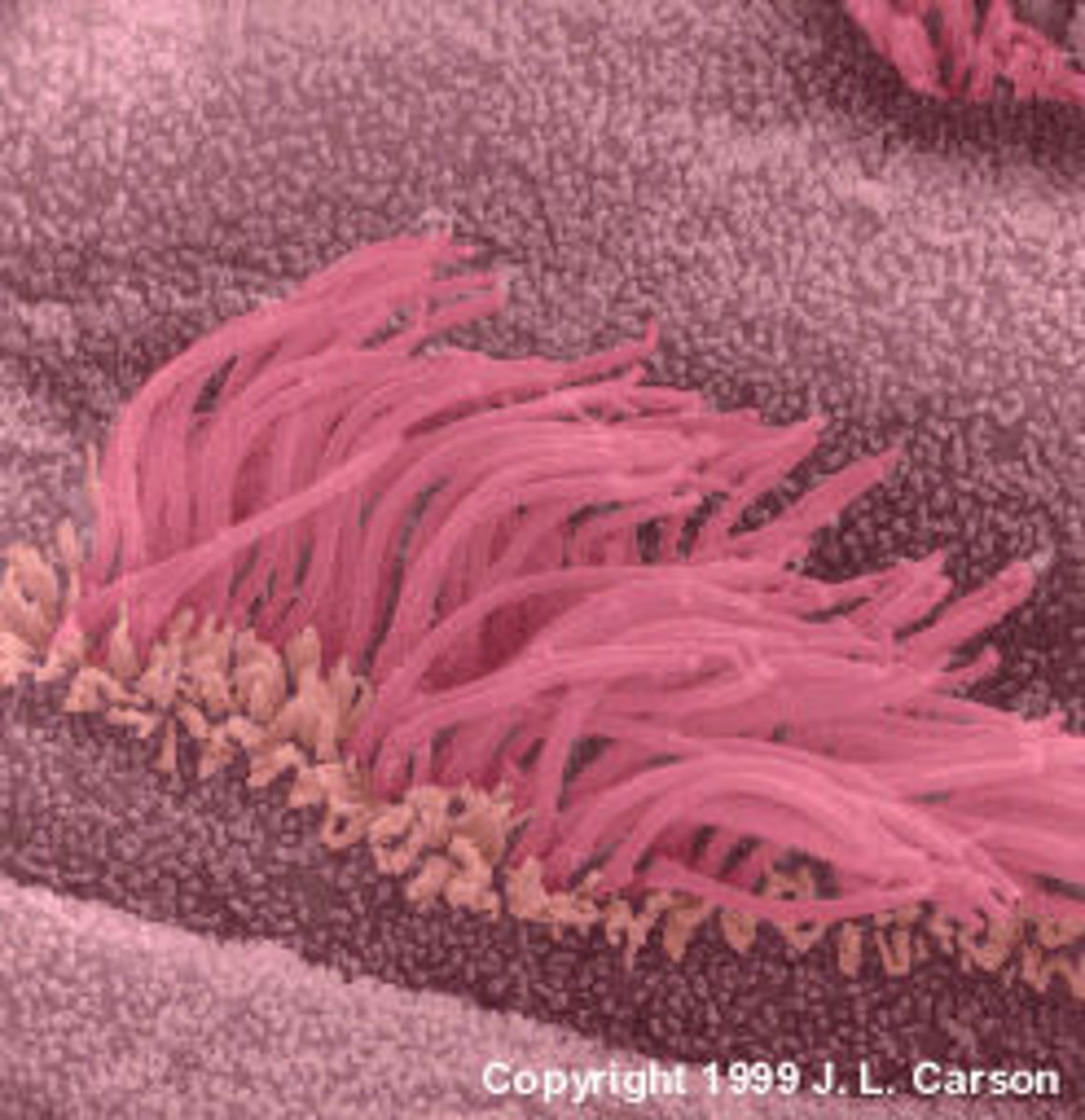
flagellum
A long, whiplike structure(s) that helps a cell to move
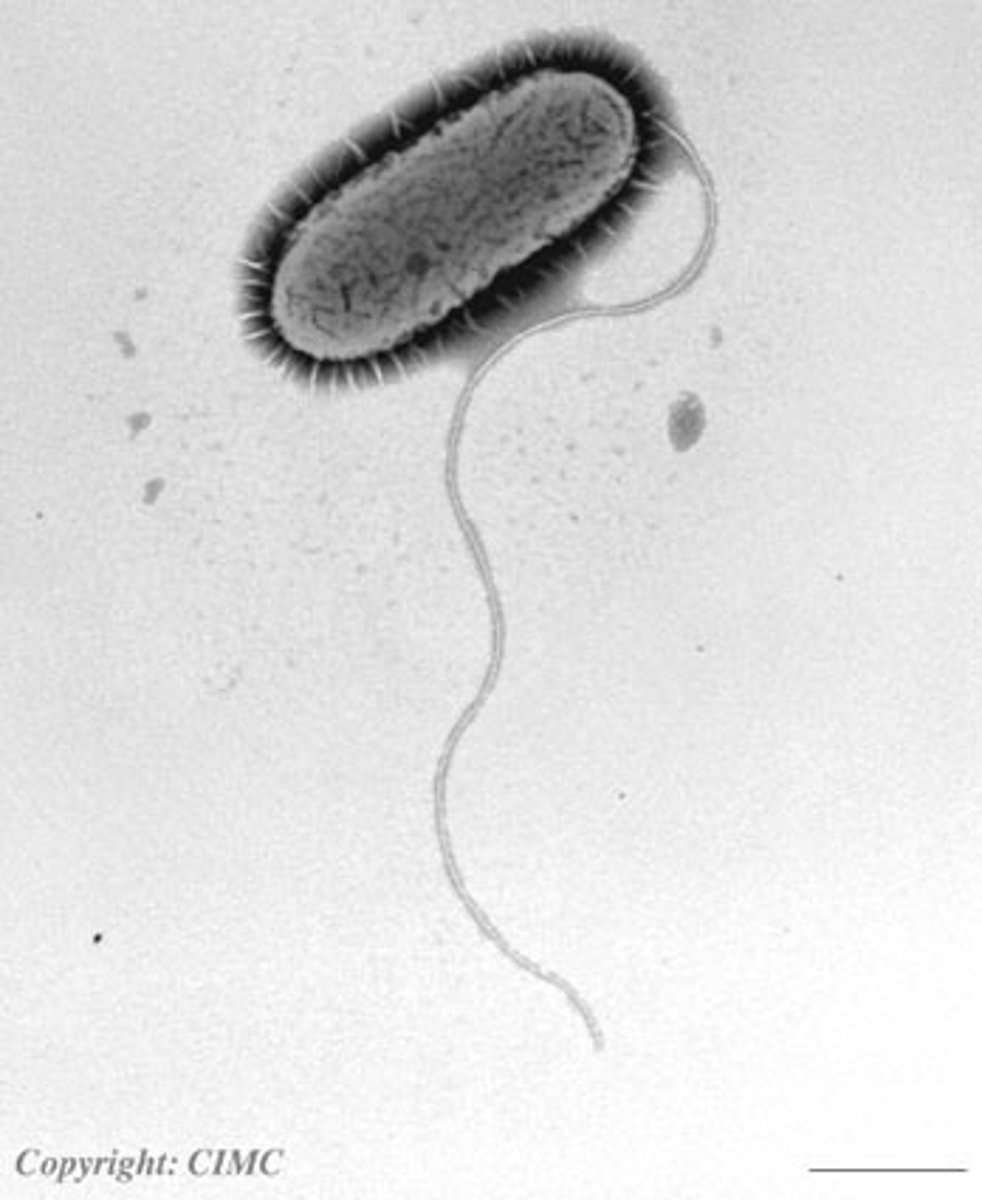
Cell wall
not in animals; outside of the plasma membrane and provides extra protection and rigidity; plants made of cellulose with plasmodesmata..
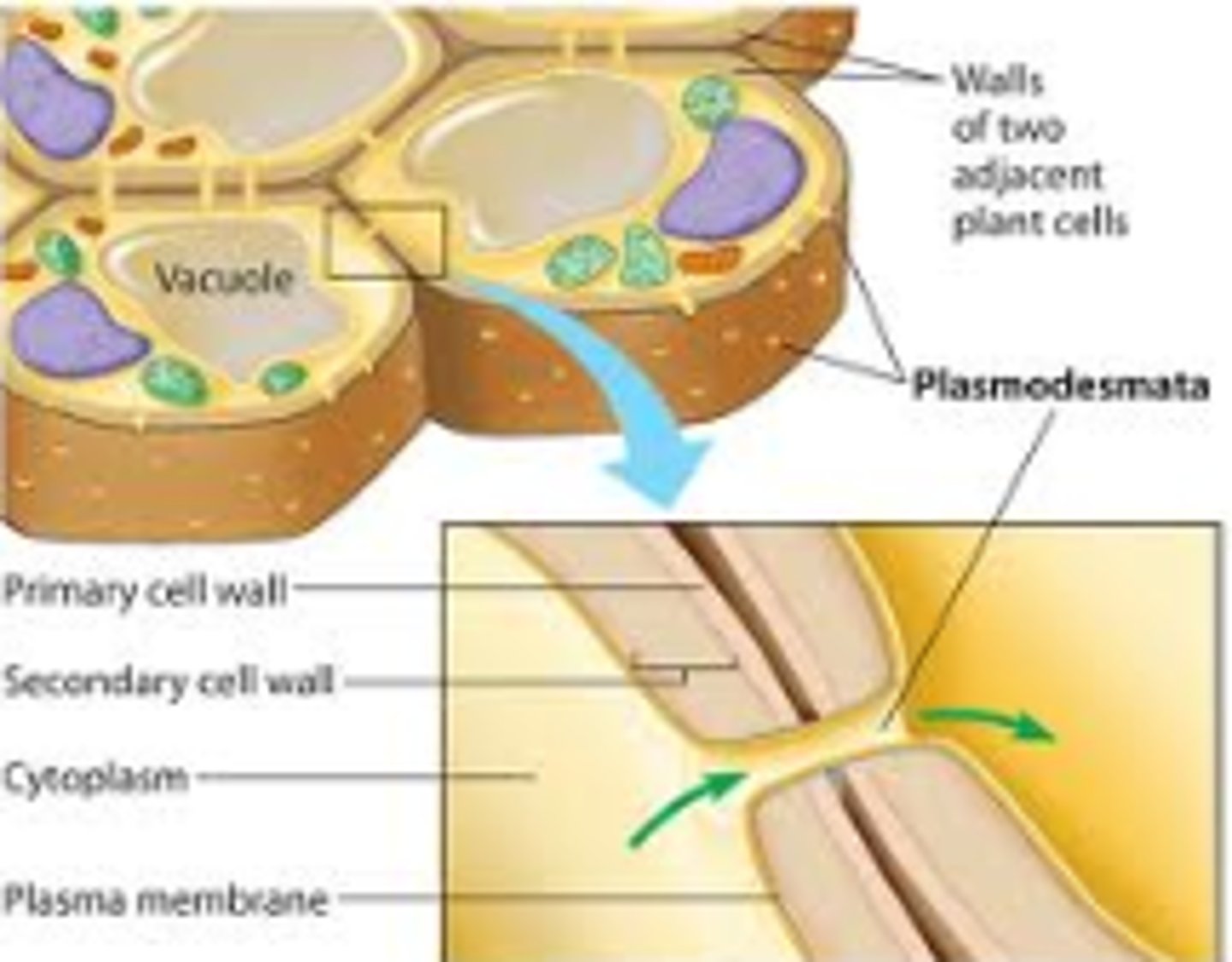
Differences in plant and animal cells
plants have cell wall, large central vacuole, chloroplasts; animal cells have centrioles
how does the plasma membrane help transport?
Semi-permeable, has proteins which help inpassing larger materials, and uses facilitated diffusion.
passive transport
Requires NO energy, Movement of molecules from high to low concentration, Moves with the concentration gradient.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration; type of passive transportation.
Simple diffsuion
Diffusion that doesn't involve a assistance by carrier proteins; passing through the bilayer.
facilitated diffusion
the transport of substances through a cell membrane along a concentration gradient with the aid of carrier proteins
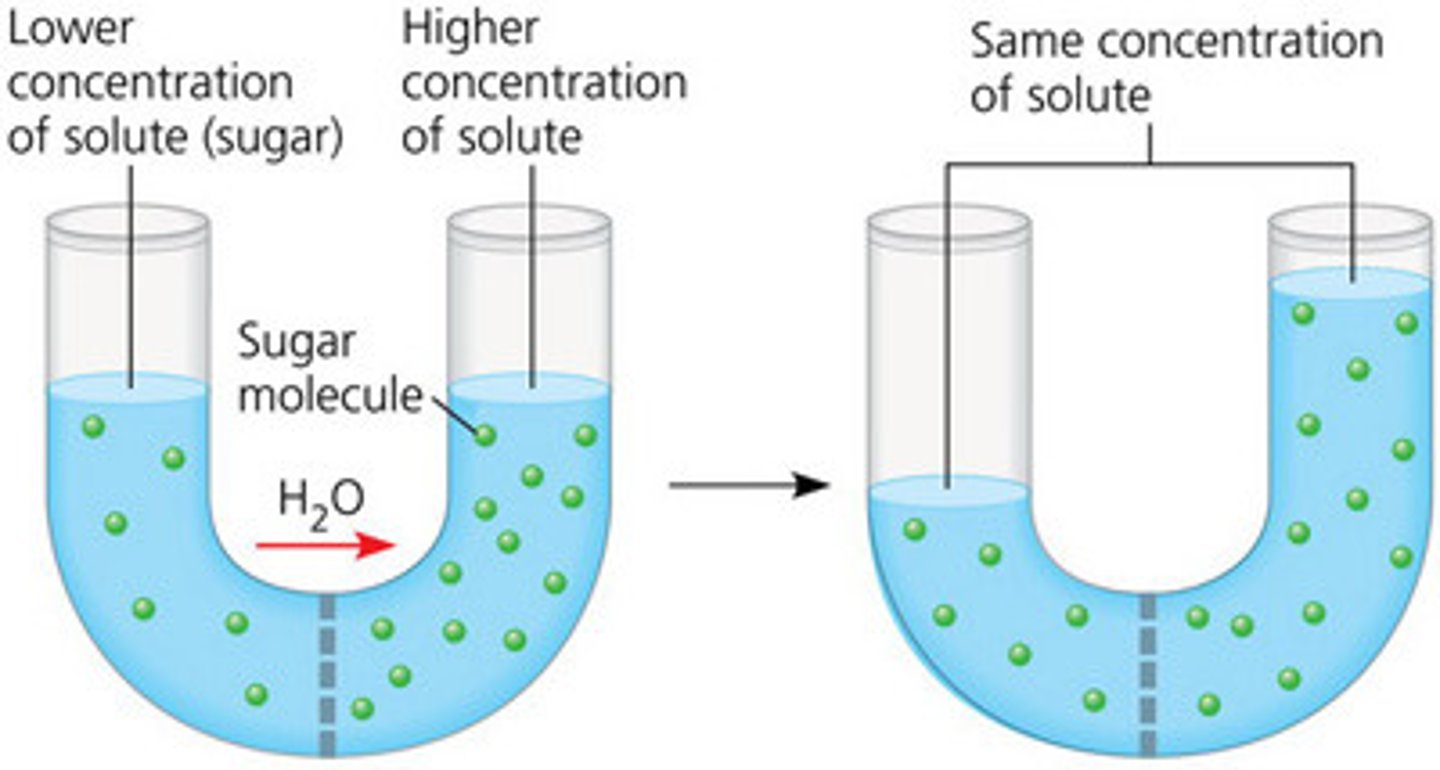
Osmosis
diffusion of water; movement of water to where there is less water by concentration
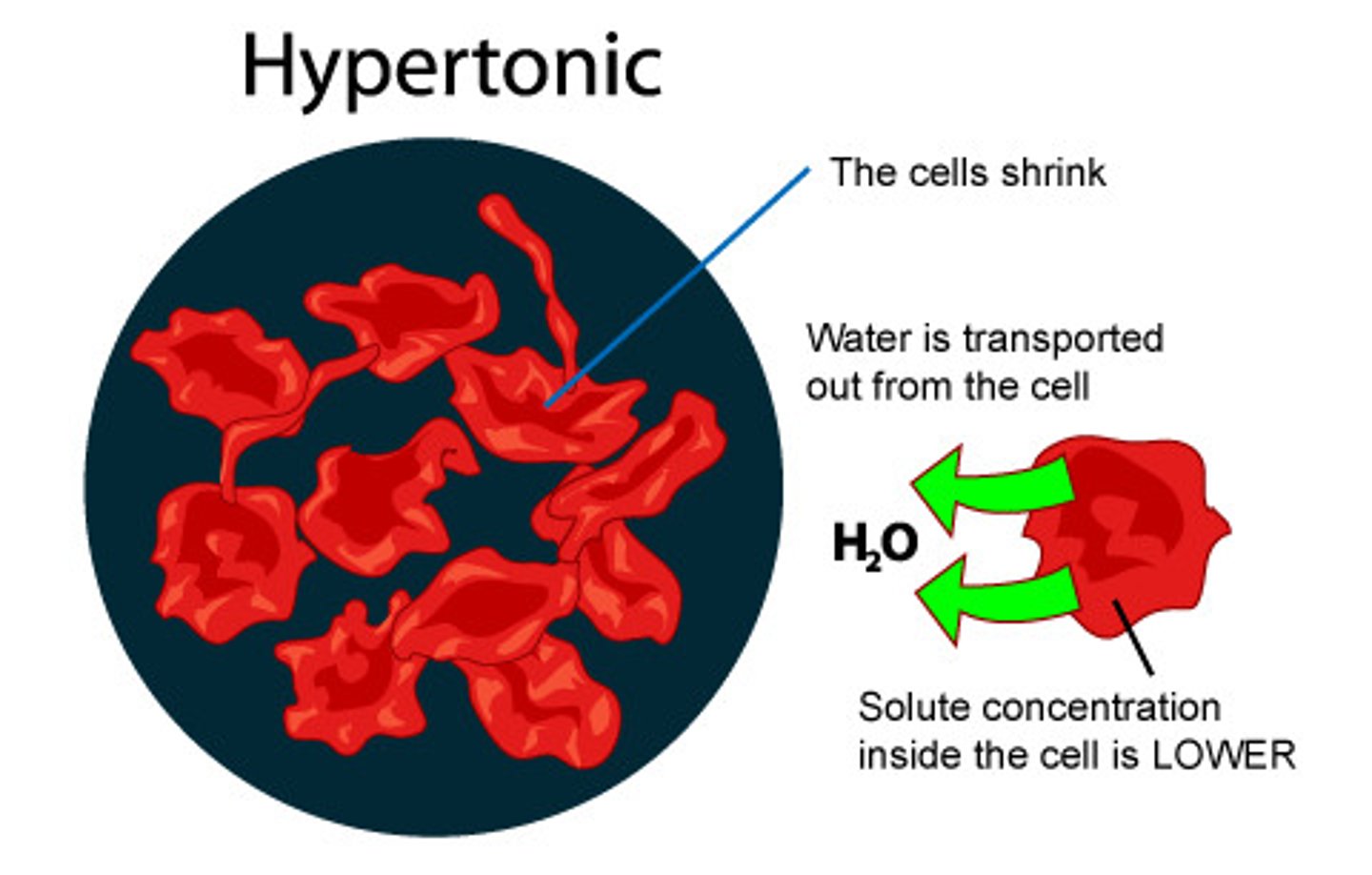
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute (not water things) than another solution.
lower concentration of water outside of cell, water moves out, cell shrinks.
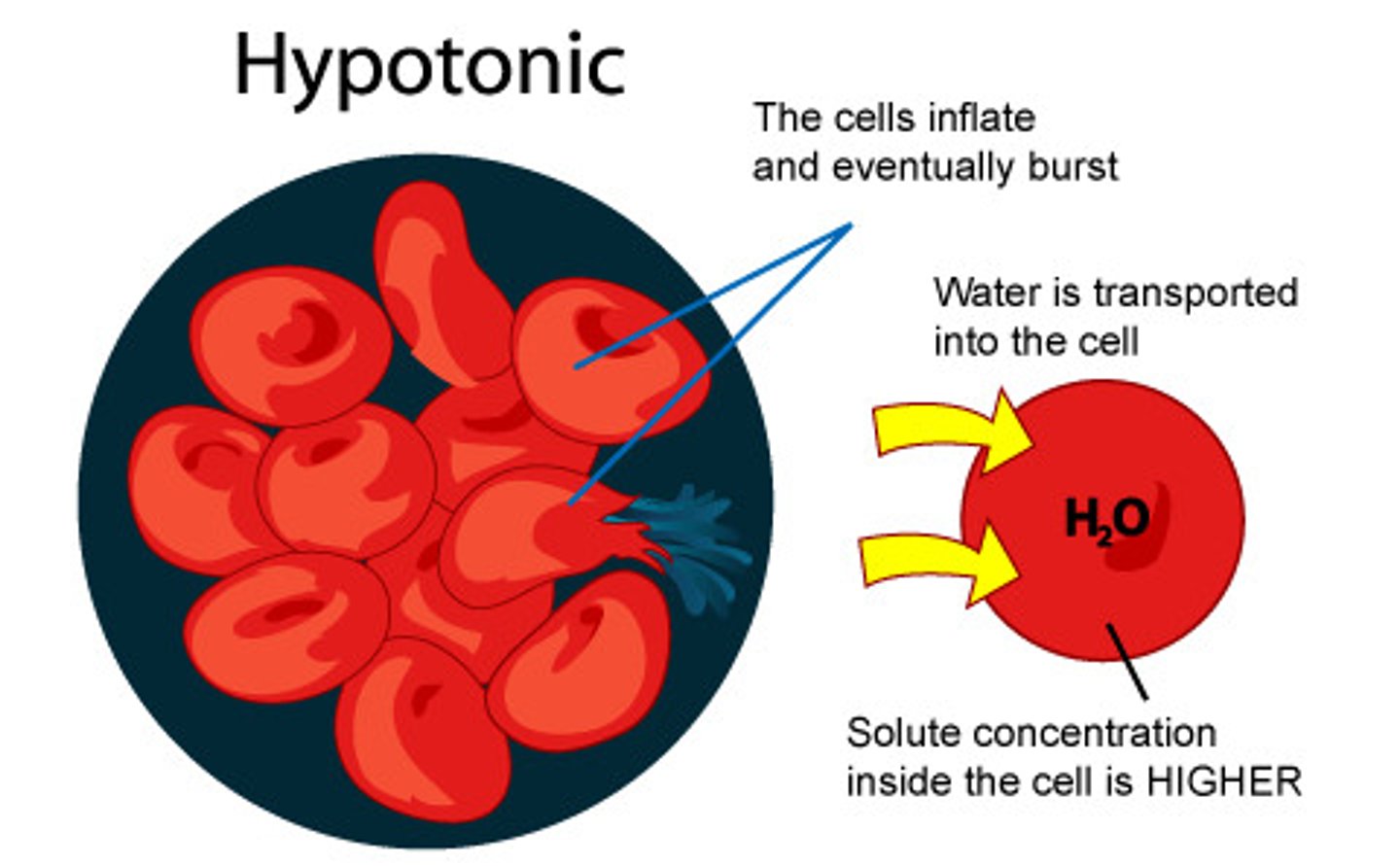
Hypotonic
Outside Having more water than the cell, causes water to move inward causing cell to swell.
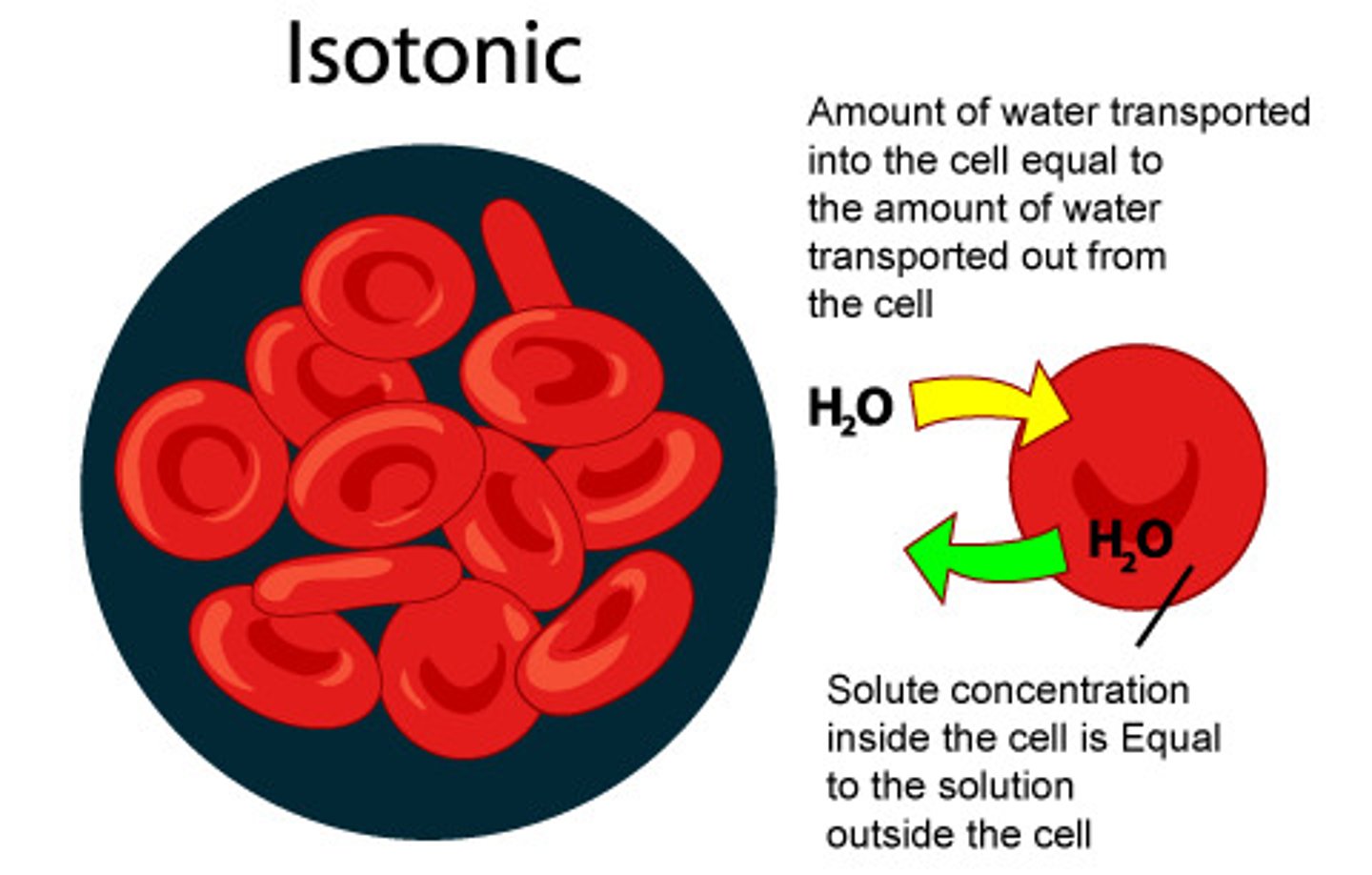
Isotonic
Having the same solute concentration (water) as another solution.
net water movement
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
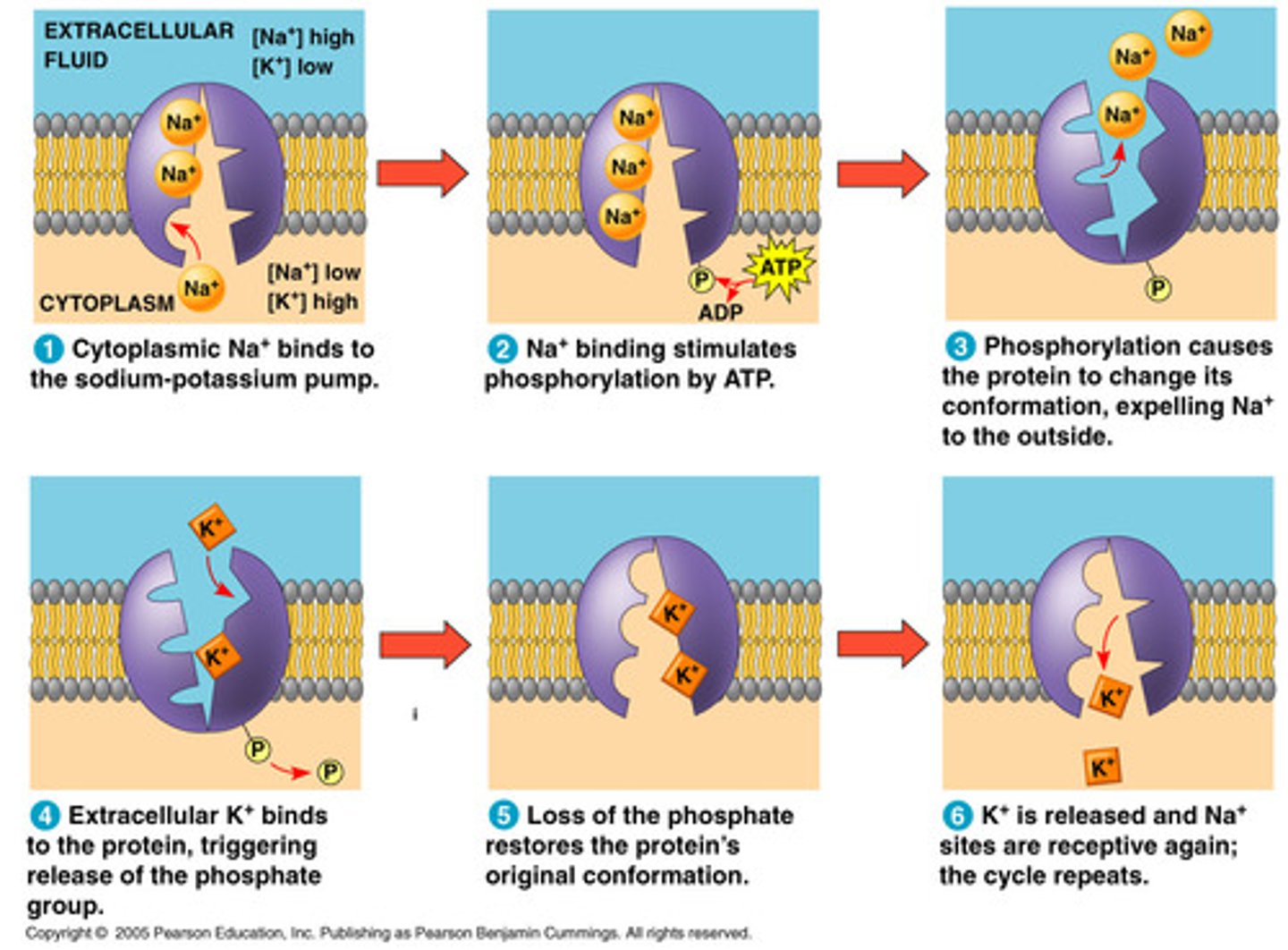
Na+/K+ pump
Active transporter that moves three Na+ out of a cell and two K+ into the cell against their respective concentration gradients. uses ATP
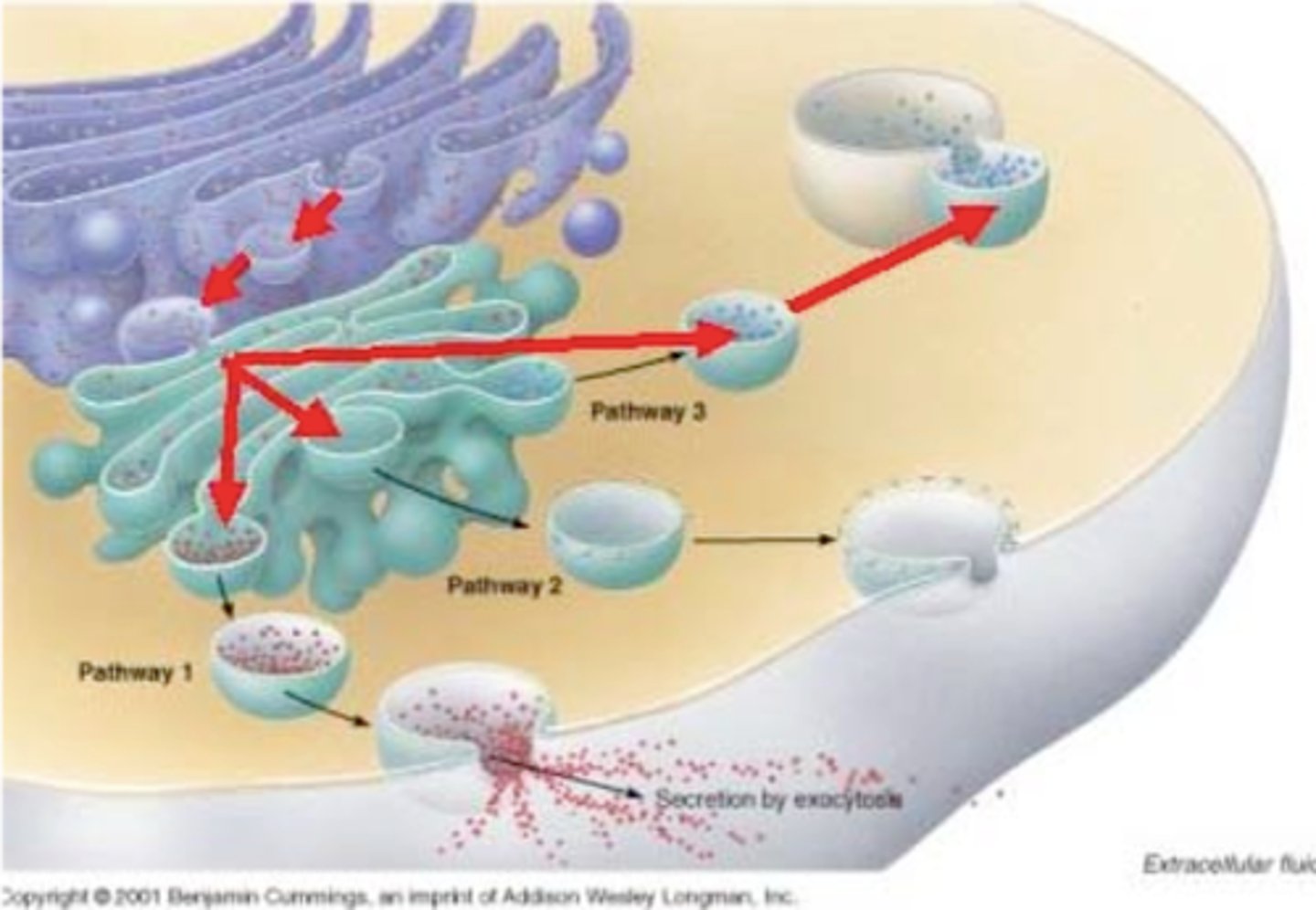
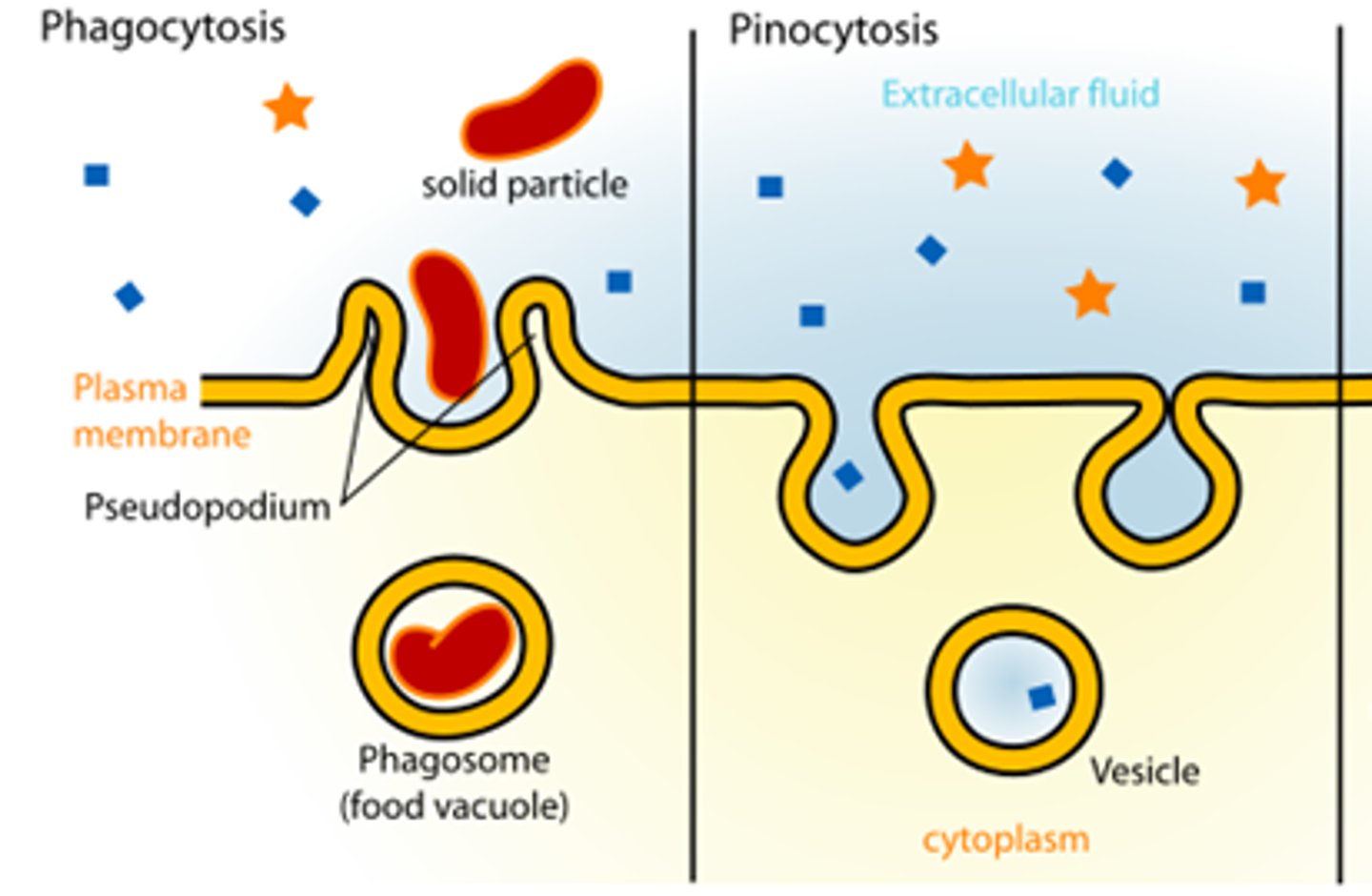
Endocytosis
when a particle is taken into the cell by the plasma membrane by making it a membrane around it in the form of a vesicle.
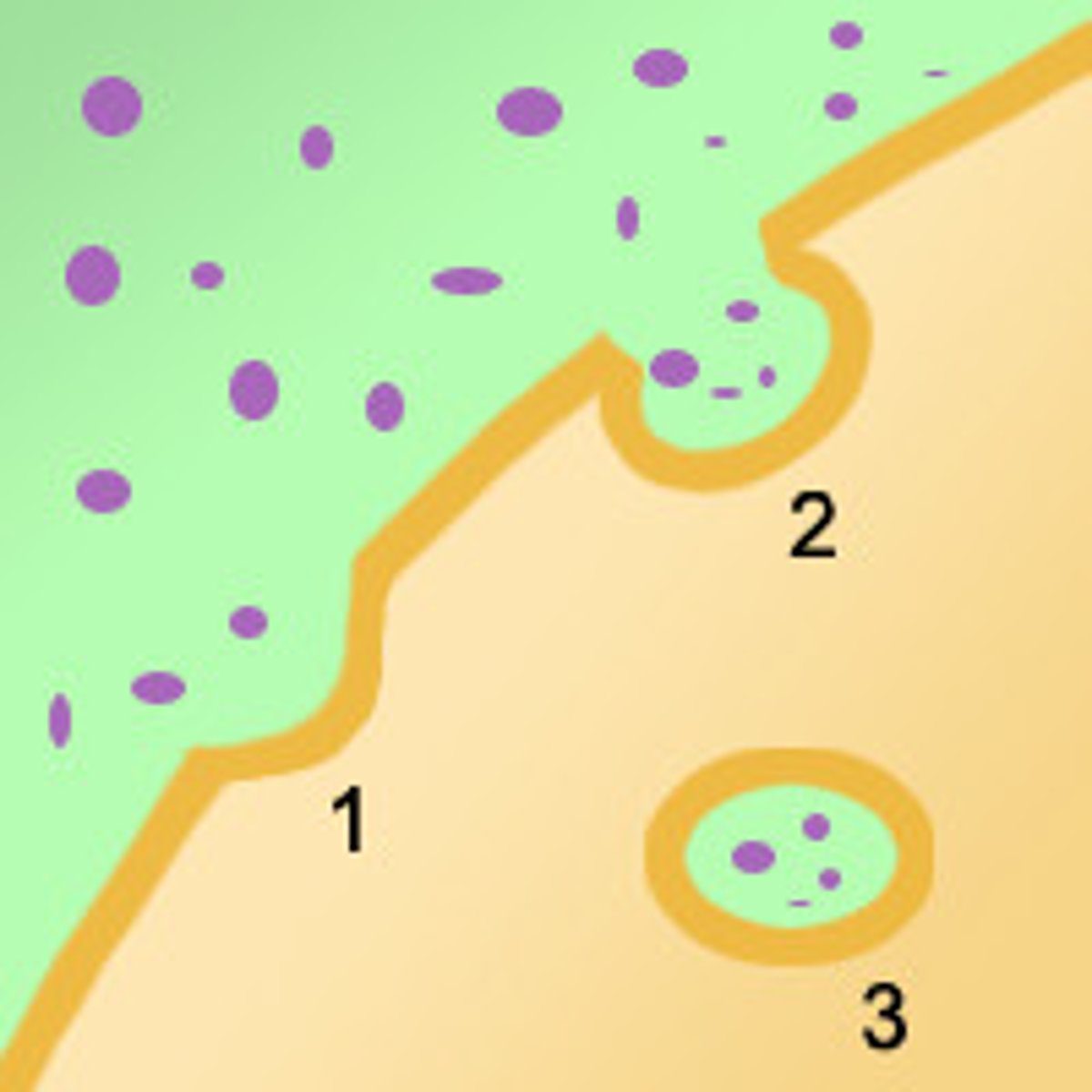
phagocytosis and pinocytosis
two types of endocytosis
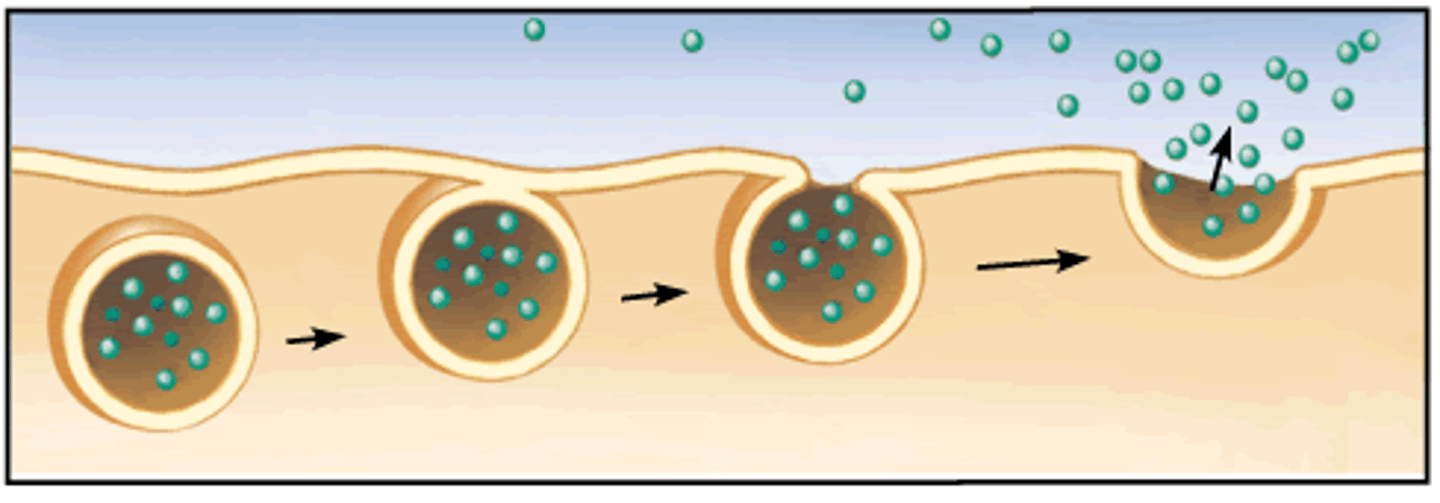
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O --> light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
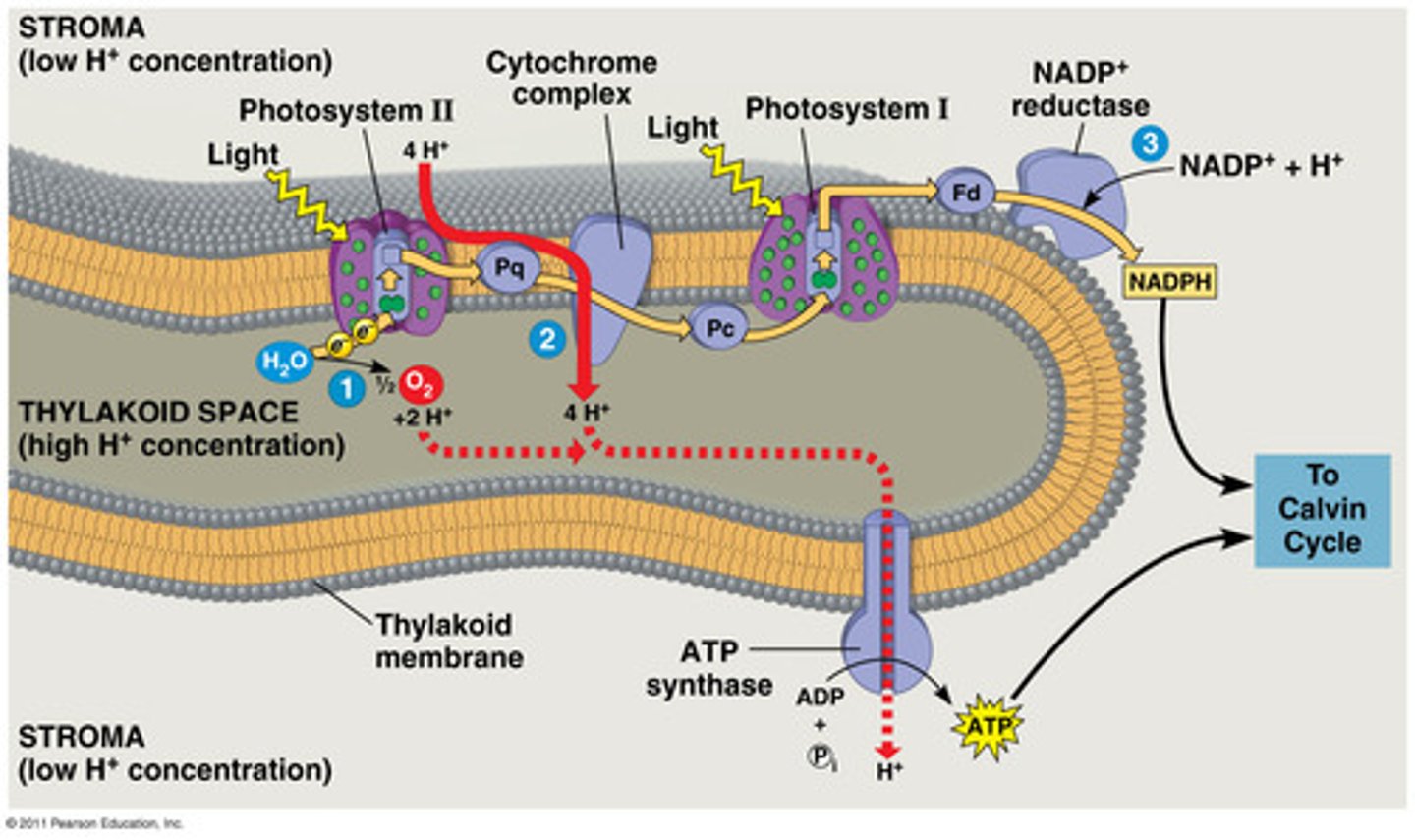
Where do the light-dependent reactions take place?
within the thylakoid membranes
Where do the dark reactions take place?
stroma of the chloroplast
what molecule is mainly responsible for a plant's mass increase over time?
CO2
photosystems
light-collecting units of the chloroplast; protein+chlorophyll
photosystem II
First; makes ATP
photosystem I
First; makes ATP
light-dependent reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light and water to produce ATP and NADPH
-happens in the thylakoid membrane
1.) Light enters through photosystem II and then I by photon being absorbed by chloroplasts within.
2.) Light excites H2O particles which makes them split into in electrons and Hydrogen protons ;O in H2O leaves. (Only happens in photosystem II)
3.) Light also excited these electrons, and causes them to leave and pass through integral proteins; Electrons from H2O replenish this.
4.) Photosystem I receives these electrons and also uses P2 generated supply, and sunlight causes it to work with NADP+ reductase to make NADPH.
5.) Hydrogen protons also split by P1 and light flow to ATP synthase to generate ATP.
Creates Energy- "photo"; products: ATP, NADPH, and oxygen
light-independent (dark) reactions
Calvin-Benson cycle; takes place in stroma
1.) Carbon Fixation: 6 CO2 (◉ each)combine with 6 RuBP (◉◉◉◉◉) with RuBisCo to make 12 PGA (◉◉◉)
2.) Reduction: 12 ATP (2 per CO2 invested) and 12 NADPH turn into 12 ADP and 12 NAD+; this powers the 12 PGA (◉◉◉) to turn into 12 G3P (◉◉◉)
3) Regeneration: of 12 G3P (◉◉◉), 2 G3Ps (has 6 C total) are used to make 1 glucose; other 10 G3P (30 C total) use half of previous ATP (6 in this case) to regenerate 6 RuBP to start cycle again. (◉◉◉◉◉)
synthesis part; uses energy from light reaction plus CO2 to make glucose.
Chloroplast (Parts and Functions)
combustion reaction equation
Fuel+O2--->CO2+H2O
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O2 + 6O2 ------> 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy (ATP)
carbs and oil can be fuel because
they are made of hydrocarbons
cellular respiration
the process by which cells use oxygen to produce energy from food (aerobic and anaerobic)
aerobic respiration
3-4 steps: glycolysis*, link reaction, krebs cycle, ETC
small energy inversion+glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + more energy
Anaerobic vs. Aerobic
small energy inversion+glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + more energy