Malignant Leukocyte Disorders
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
A disease, usually of leukocytes, involving the blood and bone marrow
It is characterized by the overproduction of various types of immature or mature leukocytes in the bone marrow and/or peripheral blood
Leukemia
A general term for malignancies that start in the lymphatic system, mainly the lymph nodes
Lymphoma
Two main types of Lymphoma
Hodgkin Lymphoma - characterized by presence of Reed-Sternberg cells
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
A form of cancer of the plasma cells
Abnormal plasma cells overgrow and form a mass/tumor that is located in the bone marrow
Myeloma
Characterized by abnormal and uncontrolled proliferation and accumulation of one or more hematopoietic cell lines
Leukemia
Leukemia comes from the Greek word _ (white), and _ (blood)
leukos - white
haima - blood
Leukemia
Generalization (4):
More blasts: shorter, more fatal course of disease
High WBC count with shift to the left
M:E ratio of 10:1
Normocytic, normochromic
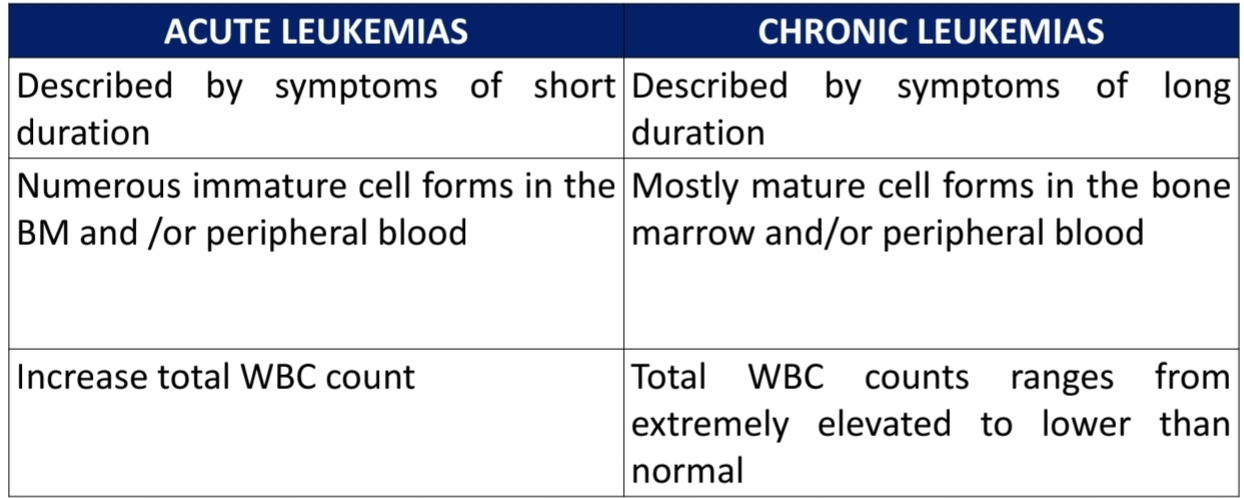
Differences between Acute and Chronic Leukemia
FAB Classification of Leukemia
Based on (2)
Based on morphology of cells in Romanowsky-stained smear
Based on cytologic and histochemical characteristics of cells involved
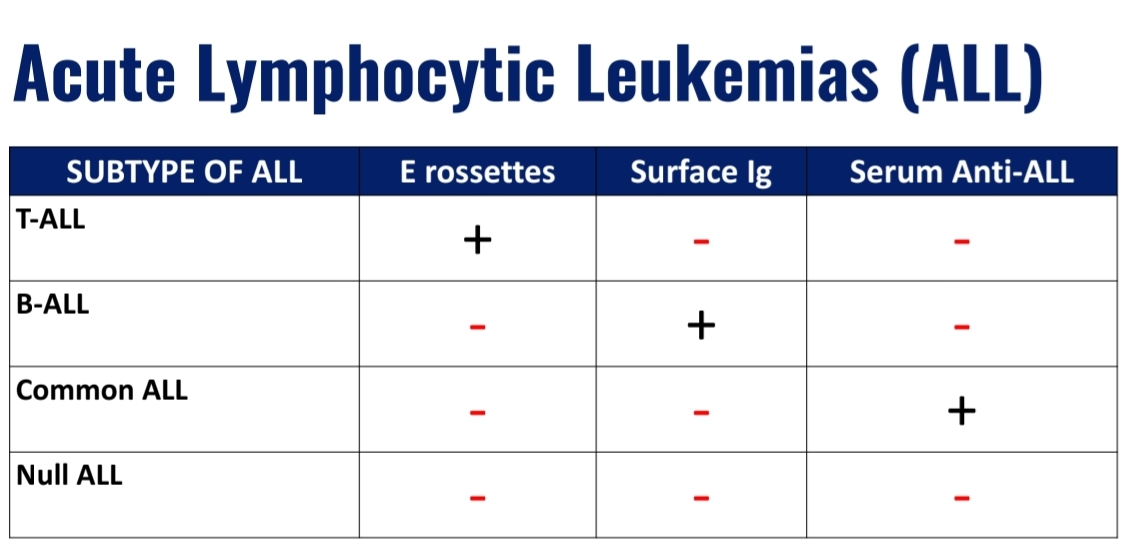
Lymphocytic Leukemia
General Cytochemical Characteristics (2)
Myeloperoxidase (MPO): NEGATIVE
Sudan Black B (SBB): NEGATIVE
Most common form of childhood leukemia
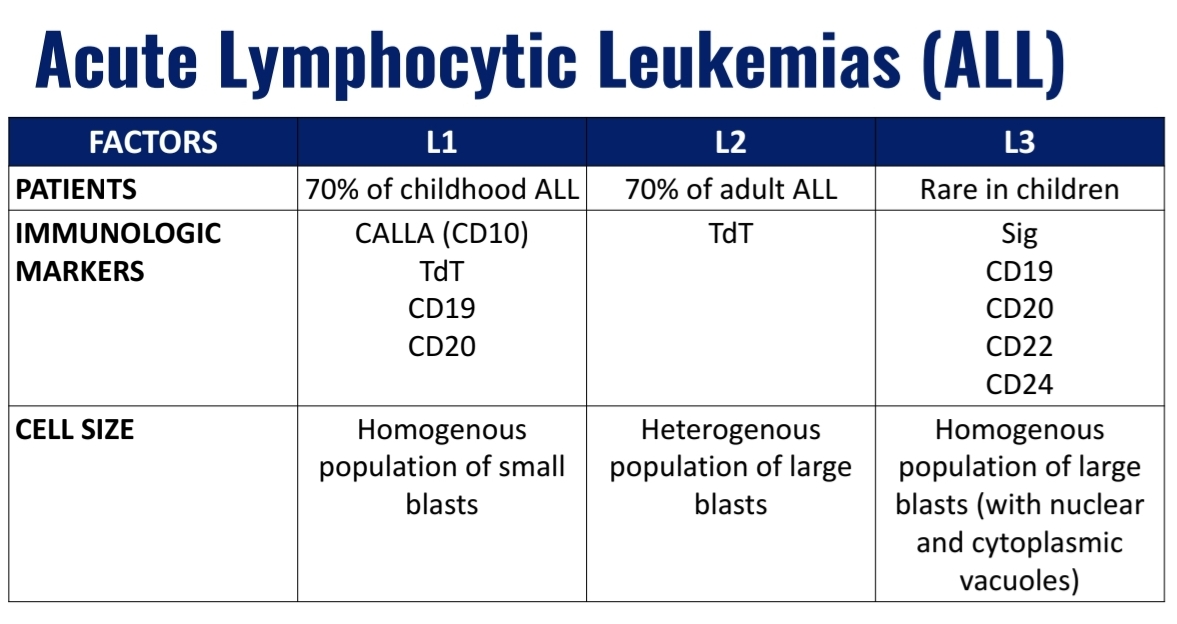
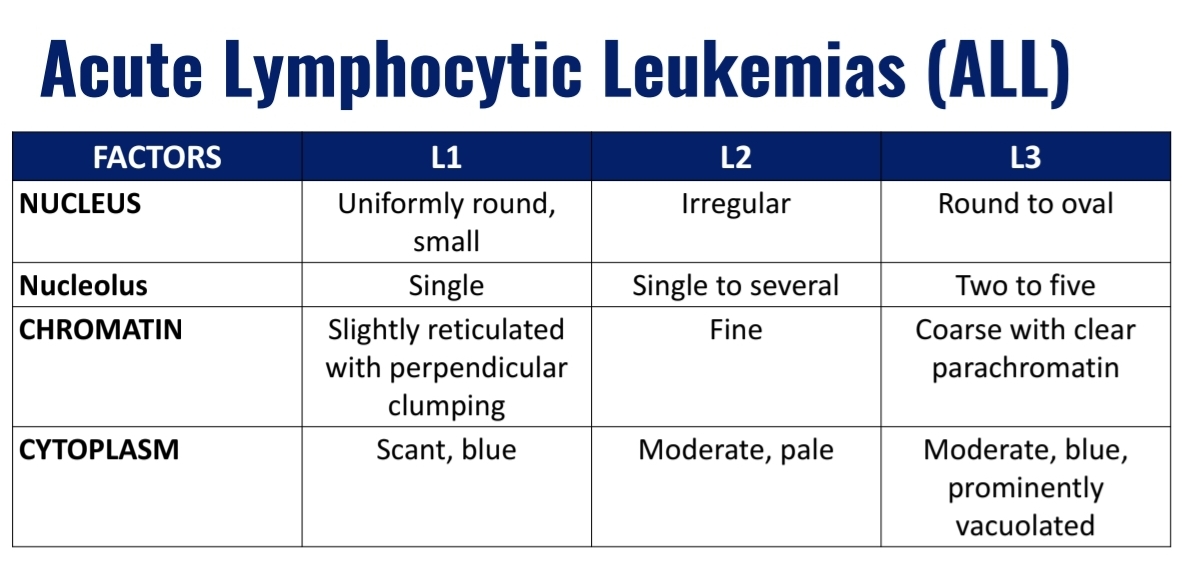
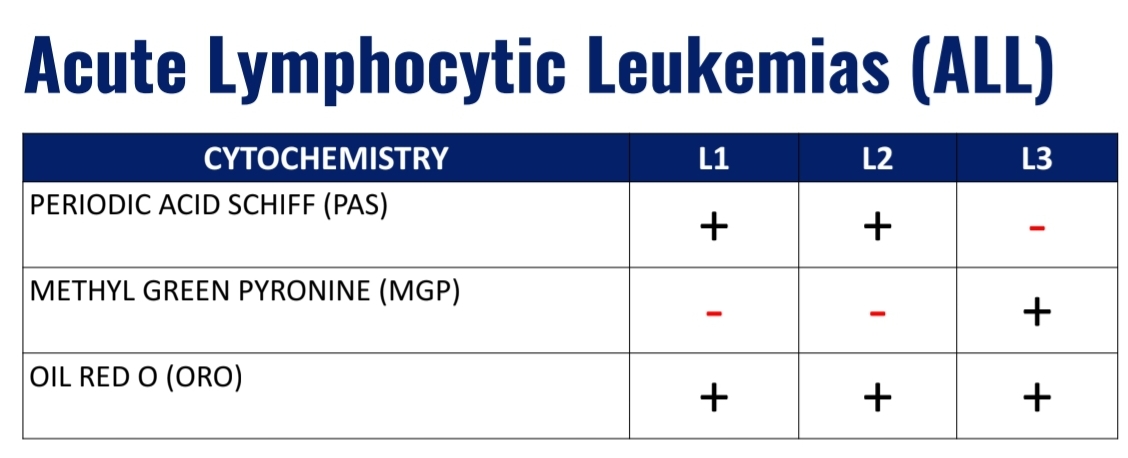
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)
FAB subtypes include:
L1
L2
L3
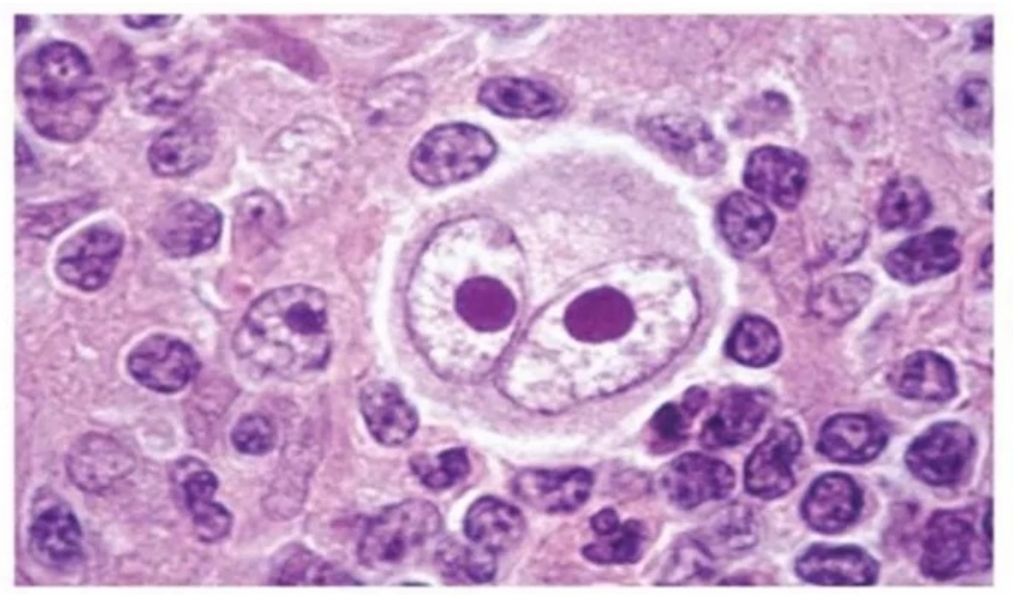
Most common type of leukemia in elderly
Characterized by persistent lymphocytosis
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
Common Findings: (2)
Smudge cells
Rieder cells
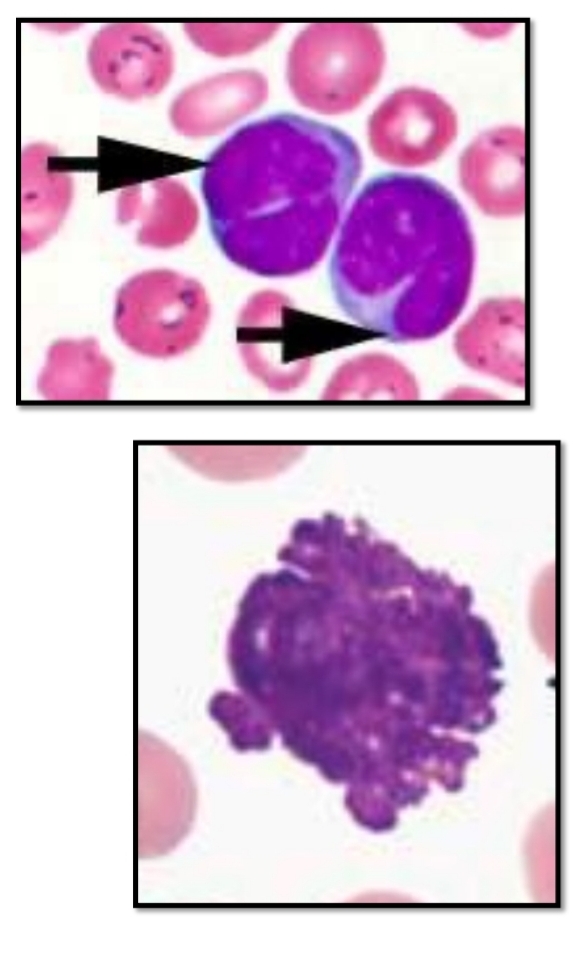
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
Example of clinical variations:
Hairy-cell leukemia (TRAp+)
Lymphosarcoma cell leukemia
Prolymphocytic leukemia
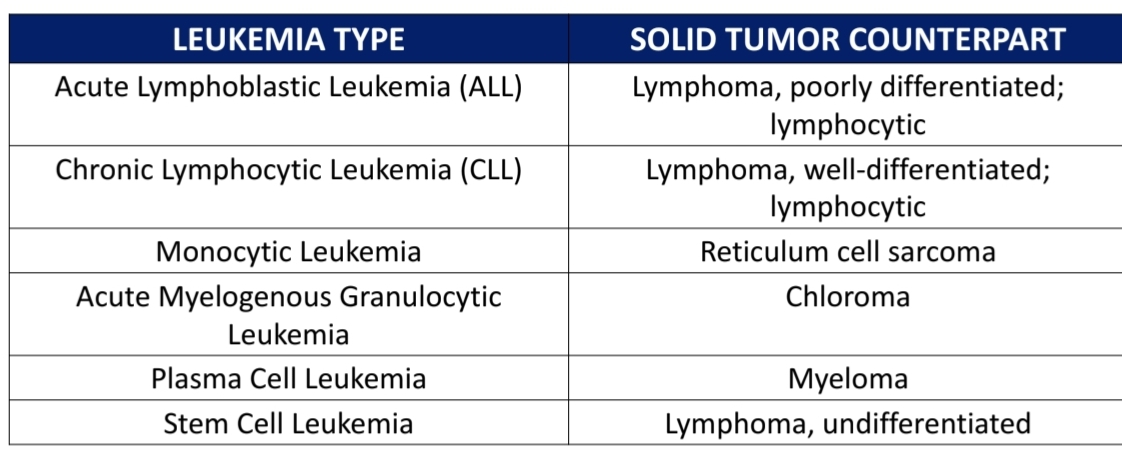
Solid Tumor Counterparts of Leukemia Types
Non-lymphocytic Leukemia / Myelogenous Leukemia
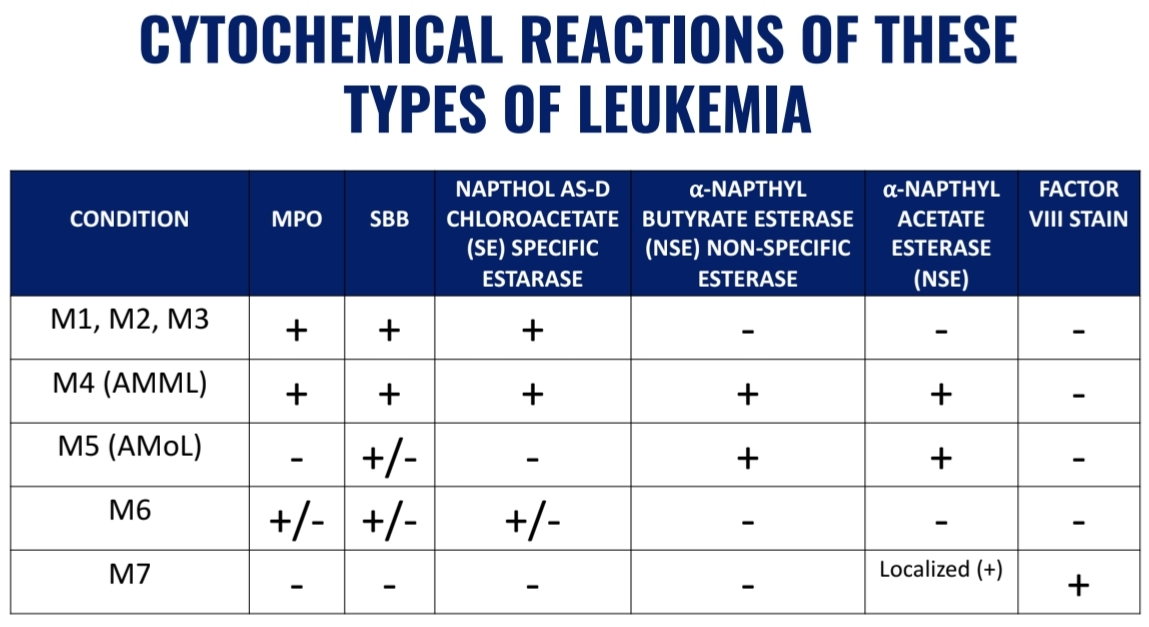
General Cytochemical Characteristics: (2)
Myeloperoxidase (MPO): POSITIVE
Sudan Black B (SBB): POSITIVE
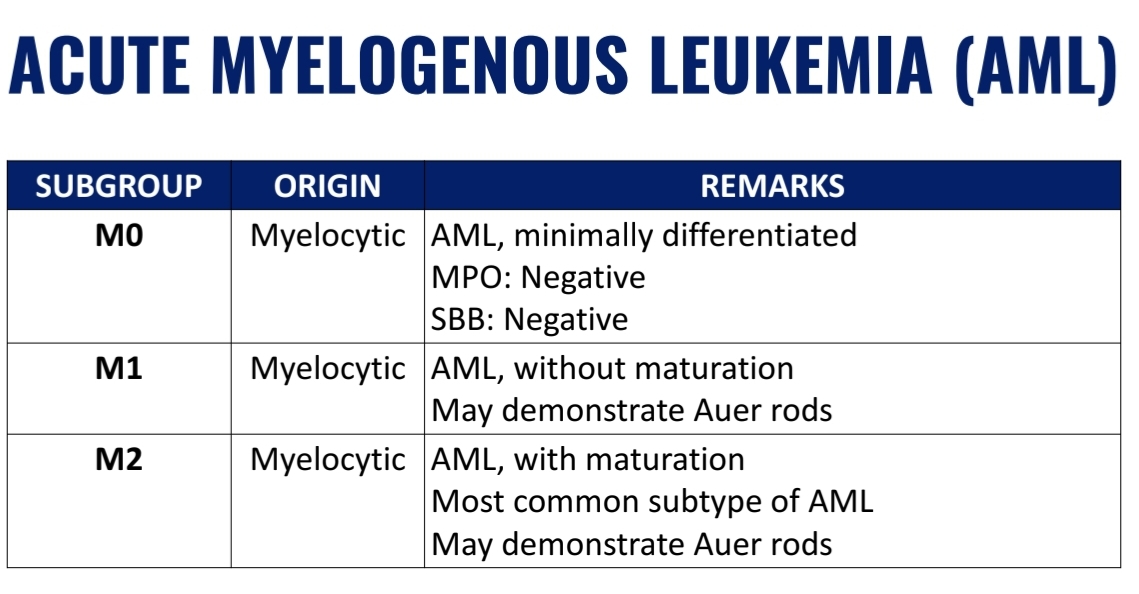
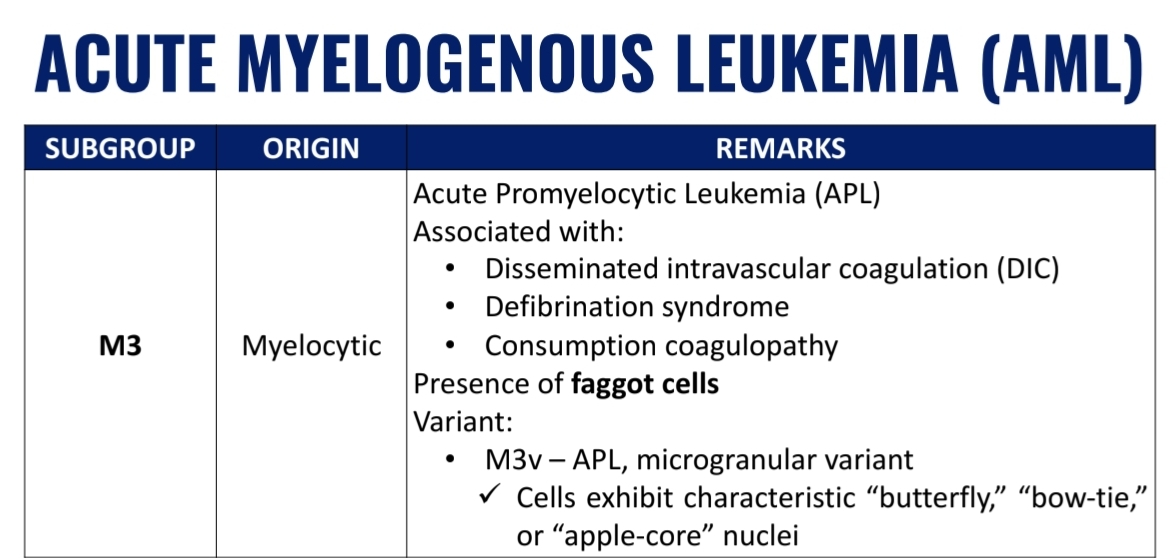
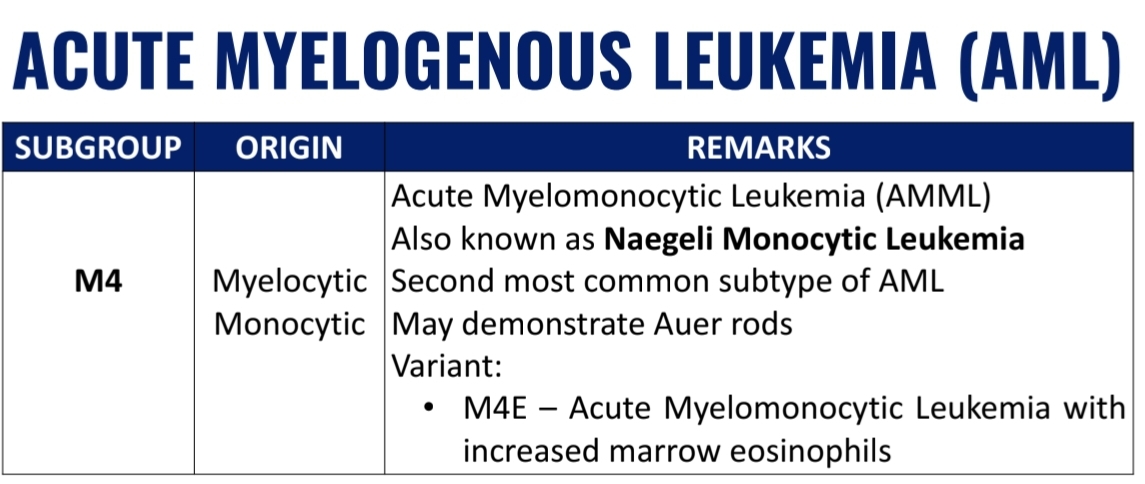
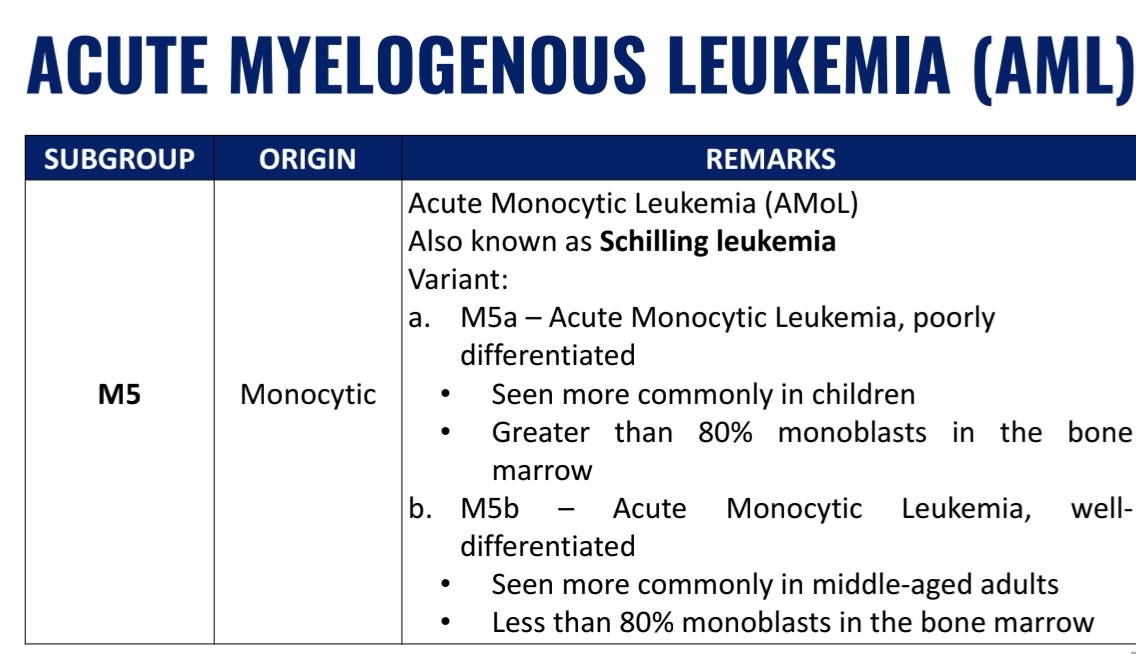
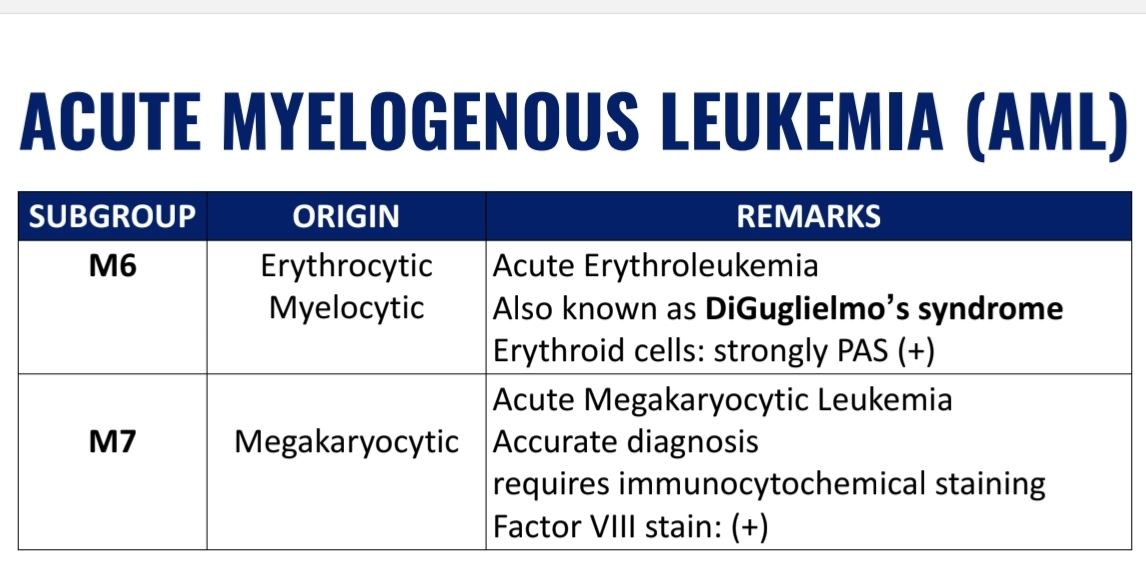
WHO Classification of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) (7)
AML with certain genetic abnormalities
AML with myelodysplasia-related changes
AML related to previous chemotheraphy or radiation
AML, NOS (not otherwise specified)
Myeloid sarcoma
Myeloid proliferation related to Down syndrome
Undifferentiated and biphenotypic acute leukemia
AML with certain genetic abnormalities:
AML with translocation between chromosomes 8 and 21 [t(8;21)]
AML with PML-RARA fusion gene (t(15;17))
AML with mutated NPM1 gene
Similar to FAB but with
Acute Basophilic Leukemia
Acute Panmyelosis with fibrosis
AML, NOS
Example of Myeloid sarcoma
Granulocytic sarcoma
Chloroma
Undifferentiated and biphenotypic acute leukemia
Not strictly _
Leukemias that have both _ and _ features
Aka _
Not strictly AML
Leukemias that have both lymphocytic and myeloid features
Aka Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias (MPALs)
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
Aka _
Chronic Granulocytic Leukemia
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
Characterized by: (3)
Presence of Philadelphia chromosome (Ph1) in approximately 90% of patients
A reciprocal translocation involving the long arms of chromosome 9 and 22
Formation of BCR-ABL1 fusion gene
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
3 Clinical Phases
Chronic phase
Accelerated phase
Blast crisis
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
Must be differentiated from _
Leukemoid Reaction (LR)
Generally used to distinguish LR from CML
Leukocyte (Neutrophil) Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP/NAP) Test
Leukocyte (Neutrophil) Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP/NAP) Test
Principle:
High LAP activity can be observed in neutrophils that have undergone normal growth
Leukocyte (Neutrophil) Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP/NAP) Test
KAPLOW'S METHOD
→Principle:
Hydrolysis of sodium alpha naphthyl phosphate by alkaline phosphatase produces a colored precipitate with a diazotized amine
Leukocyte (Neutrophil) Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP/NAP) Test
KAPLOW'S METHOD
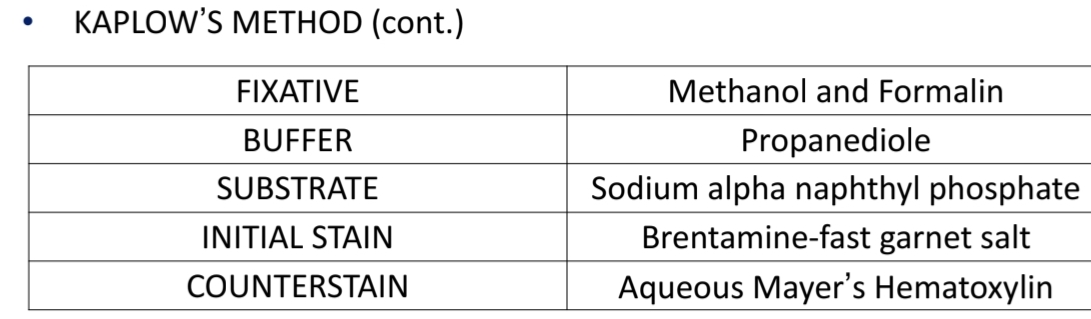
Leukocyte (Neutrophil) Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP/NAP) Test
KAPLOW'S METHOD
→PROCEDURE
Immerse dry blood smear in fixative for 30 seconds
Pour onto smear the working substrate (made of buffer, substrate, and initial stain) and allow to stand for at least 10 minutes
Rinse with distilled water and dry
Counterstain for 10 to 15 minutes
Rinse with distilled water and mount in mounting solution like glycerol
Examine immediately under microscope and look for the presence of reddish brown to black precipitate of alkaline phosphatase activity in cytoplasm of neutrophils
Count 100 segmented neutrophils and bands, and score each cells
Leukocyte (Neutrophil) Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP/NAP) Test
KAPLOW'S METHOD
→SCORES

Leukocyte (Neutrophil) Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP/NAP) Test
KAPLOW'S METHOD
→Normal Kaplow's Score
20 to 100
High LAP score = LR
Low LAP score = CML
Disorders with INCREASED Kaplow's (LAP) Score
3rd Trimester of pregnancy
Polycythemia vera (PCV)
Infections
Intoxications
Disorders with DECREASED Kaplow's (LAP) Score
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
Sideroblastic anemia
Myelodysplastic syndrome