modulated
The ultradian process is _________ by circadian and homeostatic processes
1 day
The circadian rhythm lasts how long?
living
The circadian rhythm is the rhythm of _________ organisms
stability, environment
The circadian rhythm is a dynamic balance between ________ of the system and adaptability to demands of the ________
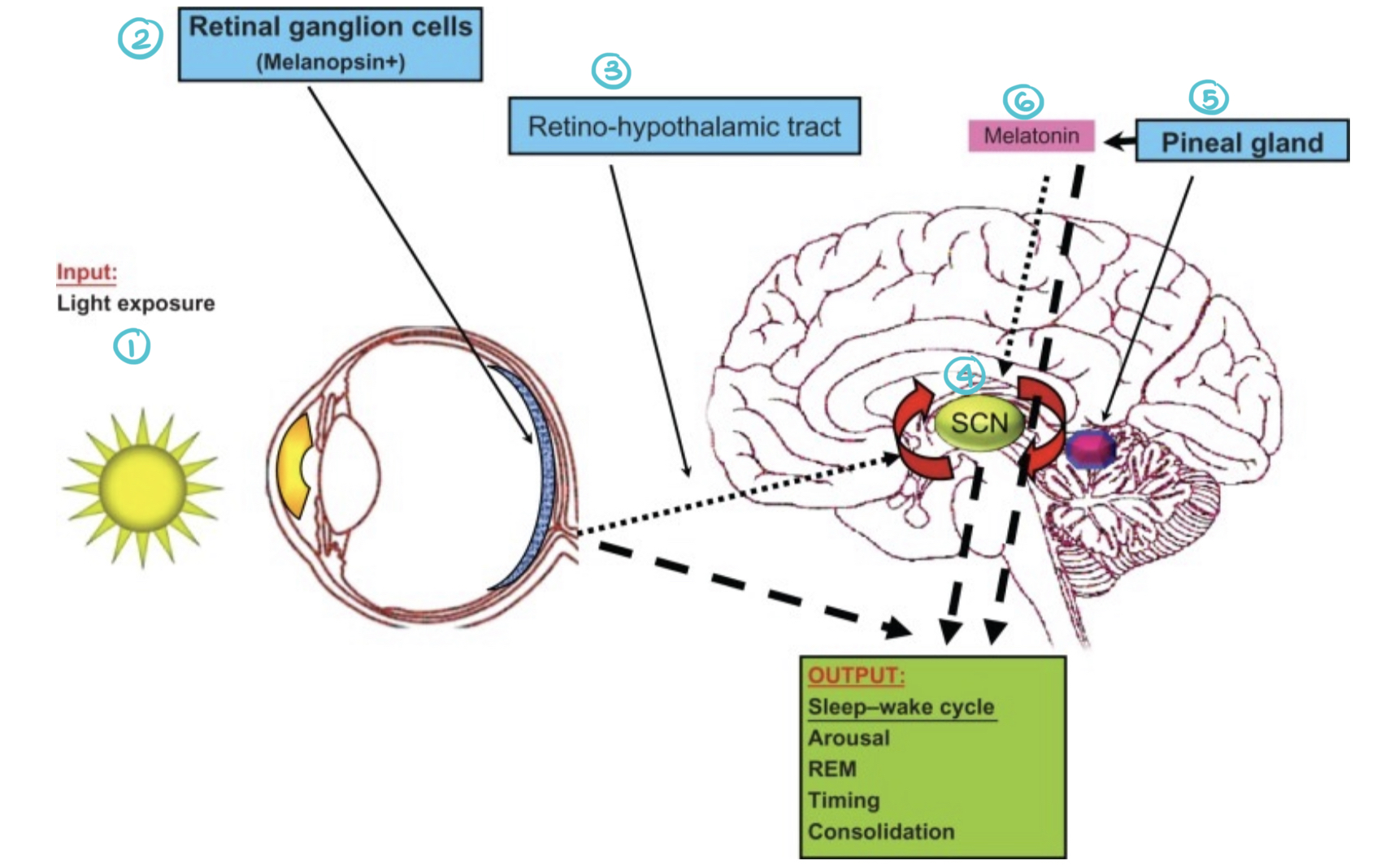
Explain this diagram

It is the main oscillator, the circadian master clock
What function does the SCN serves?
Zeitgebers
The SCN is synchronized by what?
desynchronized
death
If the SCN is lesioned, the body’s oscillators become ________
We can get very thirsty or hungry during the night and it leads to _______ in animals
hypothalamus
Transplanting SCN into the ________ restores rhythms to donor’s circadian phase
light
dilation
melatonin
Projects
Characteristics of retinal ganglion cells:
Contain melanopsin: a ________-sensitive protein
Control pupil _______
Produces ________
________ to SCN and VLPO
higher
firing
Retino-hypothalamic tract:
Need ________ intensity light than cones
After the light is off, it keeps _______ for some time
light
environment
IPRGC:
Slow and progressive response to _______
Why? Because we go from light to darkness all the time in our ________
melatonin
Blue light: stimulates retinal ganglion cells → SCN → pineal gland → supresses _______
Light Source | Melatonin Suppression |
|---|---|
LED bulb | 80% |
Incandescent bulb | 40% |
Candle | 2% |
Candle-light-style OLED | < 2% |
Light sources and melatonin suppression
Light Source | Melatonin Suppression |
|---|---|
LED bulb | |
Incandescent bulb | |
Candle | |
Candle-light-style OLED |
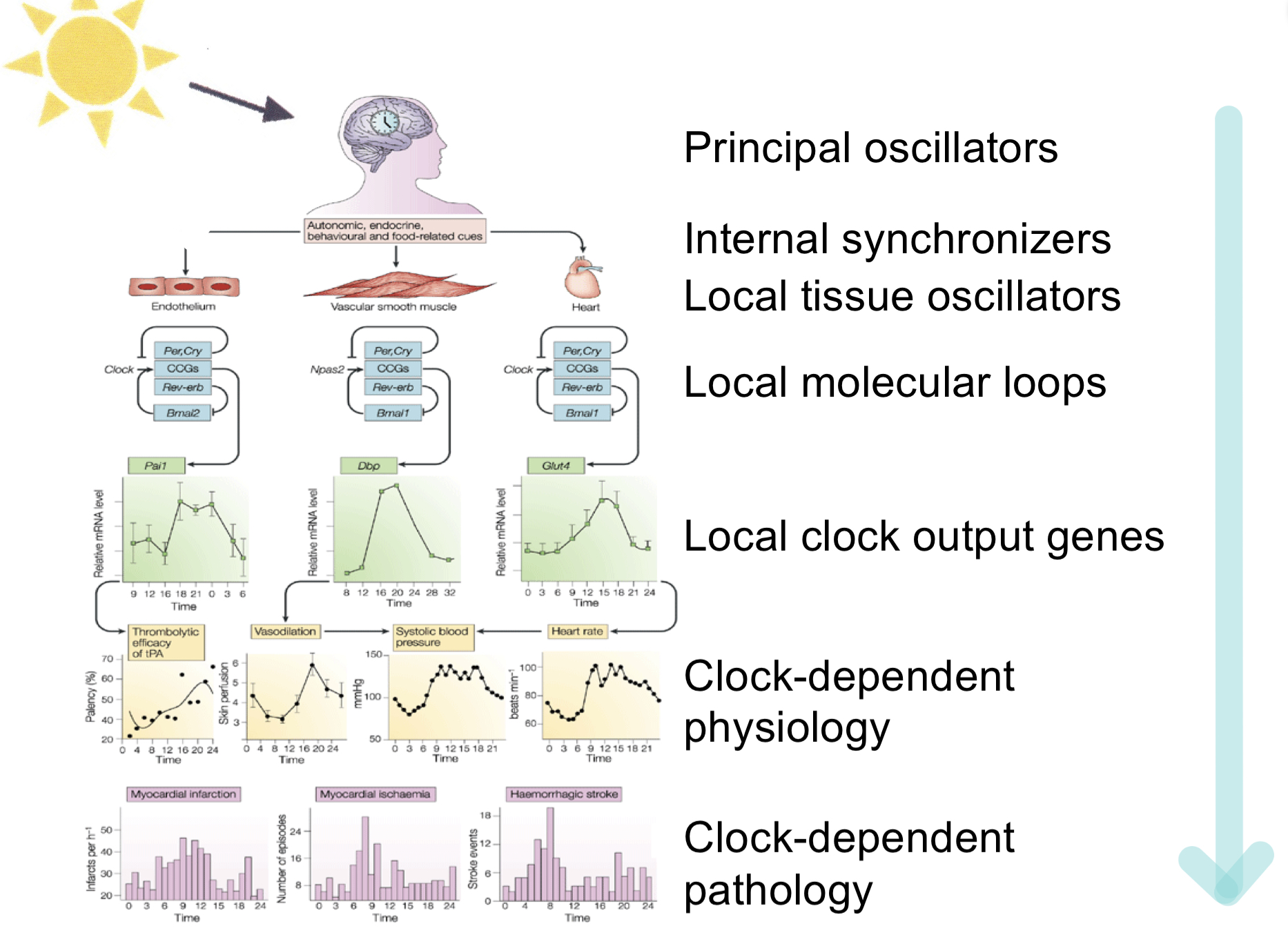
Hierarchical organization:

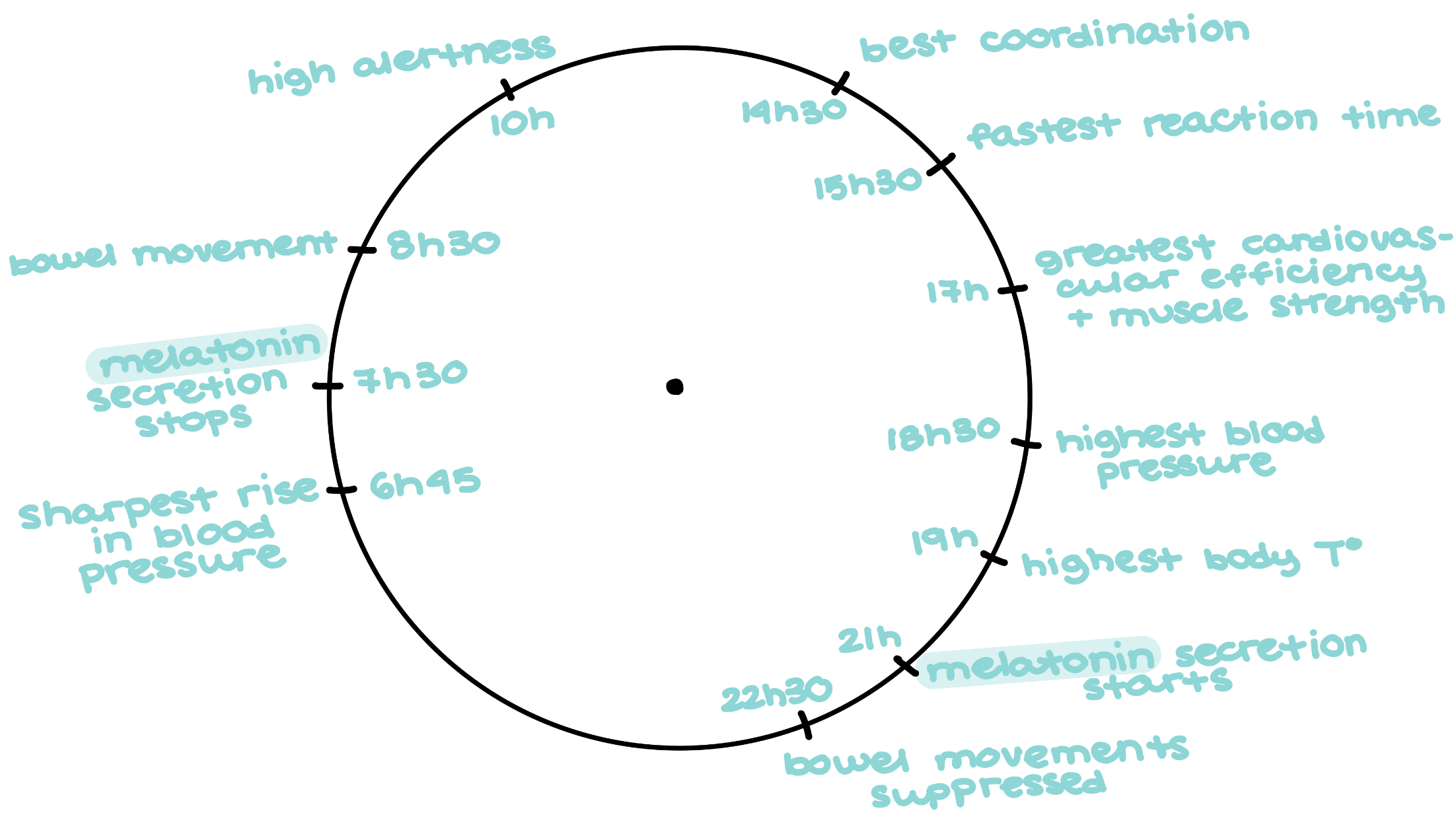
Hours associated with physiological responses in humans

Time giver
What does Zeitgeber means?
entrainment
phase
Zeitgebers:
Participate in circadian _______
Their effect depends on the circadian _______ of the organism
Light
Food
Activity-rest patterns
Social cues (ex: everyone going to sleep)
What are the principal Zeitgebers ranked from most important to less important?
pineal
SCN
darkness, light
opposing
Characteristics of melatonin:
Hormone secreted by the _________ gland
Acts on the _______
Stimulated by _______ and suppressed by _______
Has an _________ action with cortisol
Correlated with body temperature, blood pressure, and growth hormone
less
more
Melatonin has different seasonal patterns:
Summer = _______ melatonin produced
Winter = ______ melatonin produced
breeding
immune
The functions of melatonin:
Regulates ________ patterns in animals
Involved in _______ function
Winter
In which season do we sleep more in Canada?
planetary
Our biological rhythms are adapted to our ________ movement (day/night)
Because our circadian rhythm tells us to sleep but our homeostatic pressure is low
If we go to sleep at 5 A.M., we will have a hard time going to sleep in the evening. Why?
own, SCN
Many organs and peripheral tissues have their _______ circadian clocks but they are subordinate to the ________
lot
At 6 A.M., we have a _______ of cortisol and melatonin so that we can be able to wake up eventually
nightmares
Cortisol increases in the morning could be an explanation for ________
placebo
Sleep is really susceptible to the _______ effect
adaptation
When the circadian phase is shifted by an advance or delay in light exposure, there is a gradual _______ over a few days