Mendel and the Laws of Heredity (Part 1)
Gregor Johann Mendel - July 20, 1822 - January 6, 1884
- @@Born in a German@@ speaking family in the Silesian part of the Austrian Empire and gained posthumous recognition as the @@Founder of the Modern Science of Genetics.@@
- Austrian Monk at the Monastery of ==St Thomas in Czech Republic.==
- High School teacher of ==Physics and Natural History.==
- Spent most of his time conducting Biological Experiments.
- Famous on his experiments on ==Crosses of Garden Peas (Pisum sativum) from 1856-1863==
Before Mendel ( Early beliefs about Heredity)
- @@Charles Robert Darwin (1809-1882)@@: English naturalist Darwin introduced the Theory of Natural Selection.
- He expressed his findings and ideas in his famous research publication, =="Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection"== in the year ==1859==, after observing the living communities of Galapagos Islands.
- Charles Darwin thought that the traits from parents were transmitted to their offspring by BLOOD, thus came the ==blood theory of heredity.== This theory gives rise to the expressions “bloodline” “blue blood” and “blood relative”.
- Early concepts about transmission of traits are now considered inaccurate as we now know that both parents contribute hereditary traits to their offspring and that these ==traits are not contained in blood but in sex cells.==
Intro to Genetics
- ==GENETICS== – branch of biology that deals with heredity and variation of organisms.
- ==Chromosomes== carry the hereditary information (genes)
- Arrangement of nucleotides in DNA
- ==DNA > RNA > Proteins==
- Chromosomes (and genes) occur in pairs ==Homologous Chromosomes==
- New combinations of genes occur in sexual reproduction ==Fertilization from two parents==
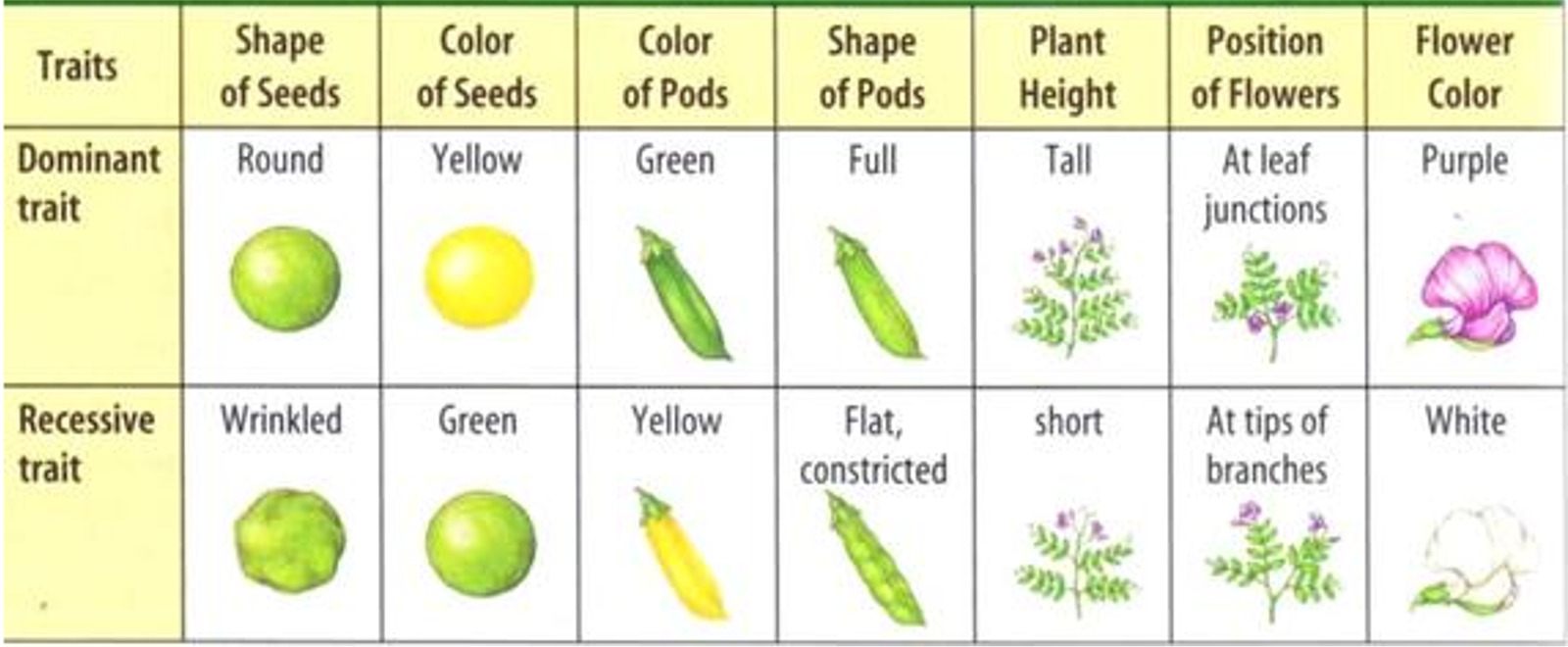
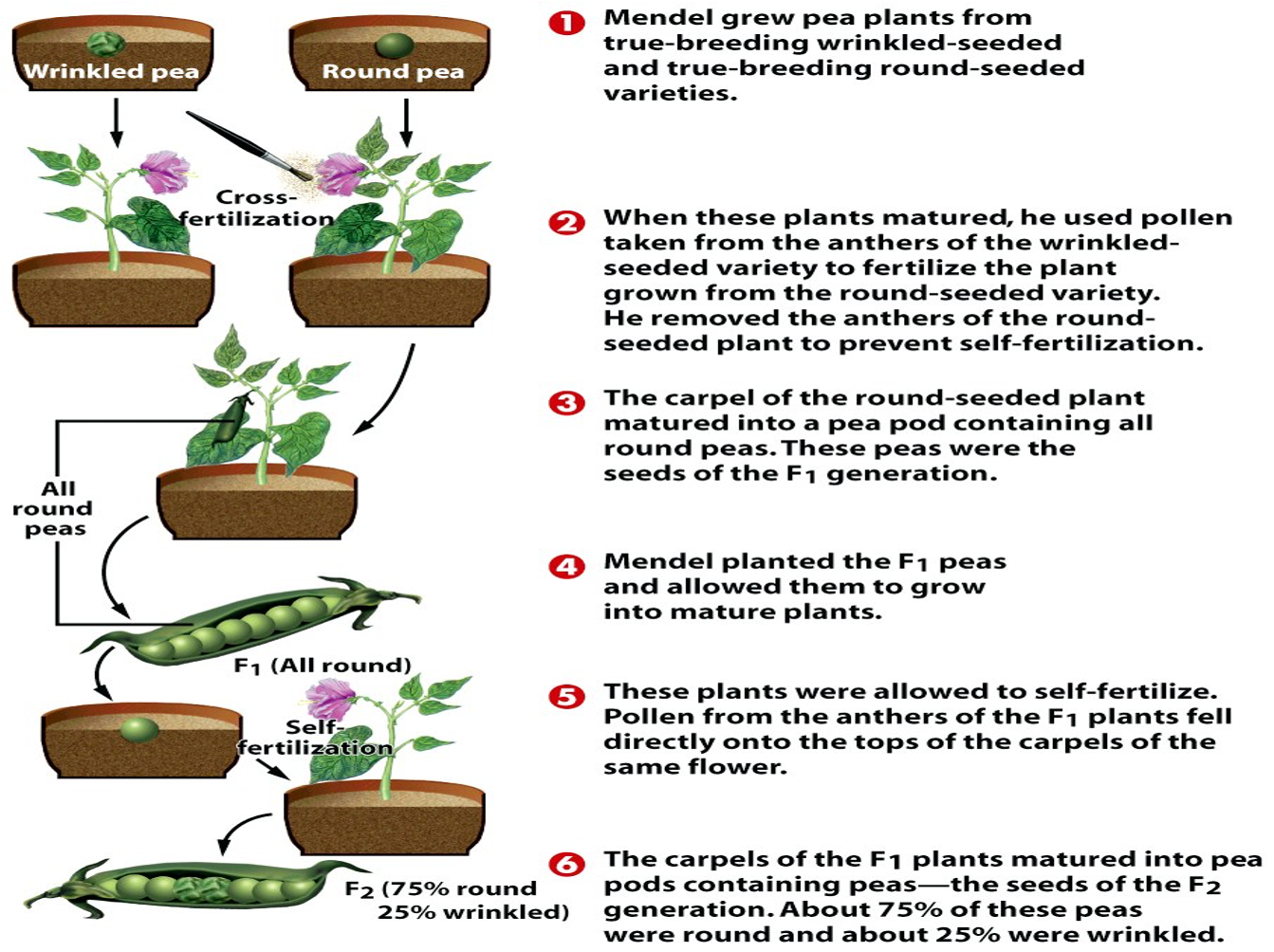
Mendel’s Experiment (why Garden Peas)
Garden Peas have ==several varieties that have observable, contrasting characteristics==
Garden Peas ==reproduce by self-pollination== (they reproduce by themselves)
Seven Contrasting Traits in Garden Peas observed by Mendel.
Mendel’s Experiment Findings…
- Published these findings in its Scientific journal in 1866 after he reported it to a local natural history society.
- His work was not appreciated until 3 scientists rediscovered his work at around 1900 ==Hugo de Vries, Karl Correns and Erich von Tschermak==
- His achievement was only recognized after the turn of the century, many years after his death