Control of communicable diseases
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What are communicable diseases?
Bacterial, viral, fungal and parasitic infections that can be passed from human to huma
What do communicable diseases cause and in what countries
significant morbidity (ill health) and mortality
particularly in low- and middle-income countries
pandemic infections - economic, social and security impacts
Name 3 control measures to control communicable diseases
social distancing
mask wearing
isolation period
What are reservoirs in the chain of infection and name them
where infectious agent lives
animals, humans, environment
Draw the chain of infection
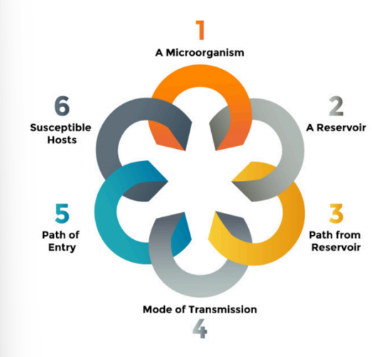
What are the 3 paths from reservoir to human being infected in chain of infection
direct (faecal-oral and direct contact)
indirect (vector-borne and vehicle-borne)
airborne (respiratory infection)
Most important part of chain of infection
susceptibility to infection
4 factors that affect susceptibility to communicable disease
susceptible host (immunosuppression, extremes of age, medical treatment)
genetics
lifestyle factors
socio-economic factors (pop density, sanitation, vaccination coverage, deprivation, access to healthcare and travel)
4 definitions of outbreak (of infectious disease)
2+ people experiencing a similar illness are linked in time or place
greater than expected rate of infection compared with usual background rate for place and time where outbreak has occurred
single case of certain rare diseases (polio, rabies)
suspected, anticipated or actual event involving microbial or chemical contamination of food or water
4 outbreak identifications
lab reports (whole genome sequening, microbiolgoy)
clinical notifications (NOIDs)
public concerns
demand for related products/ services (NHS111 data for given sxs)
define surveillance
collecting data to identify or monitor trends in communicable disease incidence or distribution
what can surveillance provide information on
incidence of disease
geographical distribution
seasonal distribution
age and sec distribution
(provide early warning signals and help detect outbreaks)
Name 4 types of surveillance
passive
active
sentinel
enhanced
syndromic
describe passive surveillance
routinely collected data (lab reports/ clinician notifications)
describe active surveillance
specifically collected data
aims for completeness - usually reserved for rare/ highly contagious infections
describe sentinel surveillance
provides rough estimate of disease incidence and uses a sample of reporting units (e.g. GP practices)
descrive enhanced surveillance
a form of active surveillance
usually limited to particular time/ place/purpose (monitoring vaccine effectiveness)
5 most common HAIs (Hospital acquired infections)
clostridium difficile
MRSA
CPE
Legionella pneumophila
norovirus
Why are HAIs common in pts, staff and visitors
high density setting
immunosuppression
illness (diabetes)
invasive procedures (IV lines, catheters)
5 ways to prevent HAIs
education
sreening
isolation/ cohorting
environmental cleaning
learning from previous events (root causes analyses (RCA), audits)
3 (groups of) people that manage HAIs
infection prevention and control team
director of infection prevention and control - board level representation
public health england - health protection team/ field epidemiology team
staff - responsibility to prevent infections
visitors
local authority - responsible for community IPC
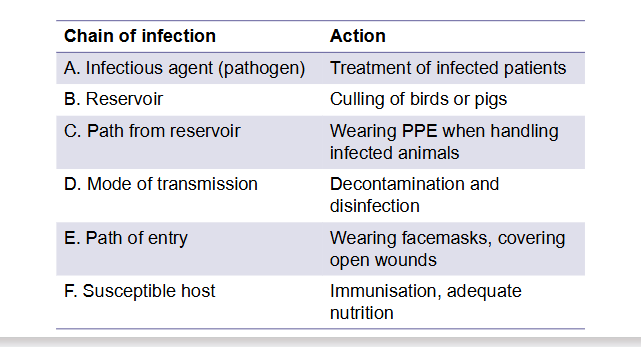
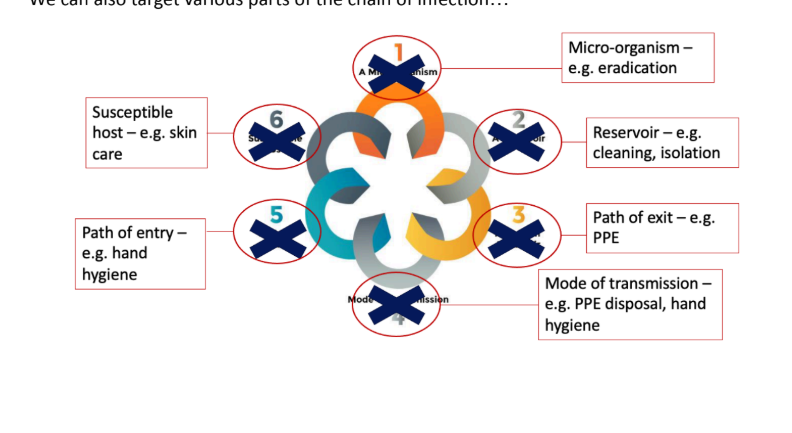
Draw the chain of infection and label how it can be targeted to prevent HAIs
name 3 bacterial communicable diseases
pneumococcal infection
Legionnaire’s disease
Meningococcal disease
name 3 viral communicable diseases
influenza
Measles
HIV
name 3 fungal communicable diseases
candidiasis
ringworm
aspergillosis
name 3 parasitic communicable diseases
malaria
giardiasis
tapeworm
define pandemics
outbreak of disease that spread across the world
Name a (indirect) vector-borne pathogen
malaria
Name an (indirect) vehicle-borne pathogen
Hepatitis B
Name 2 airborne respiratory pathogens
TB
legionella
Name a (direct) faeco-oral pathogen
viral GE
name 2 (direct) direct contact pathogens
STIs
scabies
What are vehicle-borne diseases transmitted through
through objects (e.g. needles)
describe syndromic surveillance
based on sxs of pts in GP practices, A+E rather than definite diagnosis
can serve as an early warning system
Most important HAIs pathogens in terms of outbreak potential
C.difficile
MRSA
CPE
Define R number
average number of new individuals who will contract an infectious disease from a single infected person
R0
R number in a pop that is highly susceptible to infection (no immunity)
Re
R number in pop with some level of immunity (vaccinated or where measures to limit spread have been taken e.g. self isolation)
What causes the R number to differ for different pathogens
innate infectiousness of pathogen
measures to limit transmission
List the steps of an outbreak management

Which members of MDTs manage outbreaks
outbreak control teams (OCTs)
incident management teams (IMTs)