ZOOL 250 LAB
1/243
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
244 Terms
Autogenic Test
Armor made by protist
Allogenic
Armor made by external material.
Contractile Vacuole
Stores/excretes water
Chloroplast
Energy production
Gelatinous Matrix
Holds flagellated cells together
Kinetoplast
Contains genetic material.
smaller ‘nucleus’
Food Vacuole
Stores/digests food
Phylum Euglenida
Euglena
Closer to plants because of the way they produce energy.
Common in freshwater.
Phylum Chlorophyta
Volvox
Colonial protists
Phylum Dinoflagellata
Autogenic armor of cellulose.
Multiple flagella
Thecal plates
Annulus
Annulus
Separates thecal plates
Feeding/excretion, flagella attachment.
Phylum Diplomonadida
Giardia
Most primitive of living things (lack mitochondria)
Adhesive discs
2 nuclei
Phylum Kinetoplastida
Trypanosoma (sleeping sickness)
Lives inside cells.
Undulating membrane
Undulating membrane
Movement
Like a fin, elongated flagellum
Sarcodines
Amoebozoa & Granuloreticulosa
Pseudopodia for locomotion and feeding
Foraminiferans
Pseudopodia
Outgrowths of main cell, grows in direction of movement (does not extend)
Foraminiferans
Marine, good fossil record.
Autogenic tests
Shell pores
Shell pores
Holes for pseudopodia to extend through/for food
Phylum CIliophora
Paramecium (2 different nuclei).
Macronucleus
Micronucleus
Oral groove
Stentor (concentrated cilia)
Macronucleus
DNA used for growth, maintenance
Micronucleus
Creates new macronucleus
Oral groove
Slit with cilia for feeding
Sponges
No well defined tissues or organs
Calcarea
Hexancitellida
Demospongiae
Mesohyl
Skeletal support systems
Spicules, sometimes spongin
Asconoid
Calcarea
Ancestral
Entire inside is hollow, lined with flagellated cells.
Syconoid
Calcarea
Wrinkly & knobby insides, creates pockets of choanocytes (more SA)
Leuconoid
All sponge classes
No choanocytes in spongocoel
Flagellated chambers lining ostia instead.
Ostia
Small incurrent openings
Oscula
Large excurrent opening
Pinacoderm
Layer formed by pinacocytes, for protection
Spicules
Mineral shard connected to form structure
Spongocoel
Inside of sponges body
Choanocytes
Flagellated cells that draw in water
Spongin
Structure, flexibility
Gemmules
Asexual spores
Class Calcarea
Calcareous sponges
Spicules of calcium carbonate, lack spongin
Class Demospongiae
Spongin, siliceous spicules
Class Hexactinellida
No spongin, siliceous spicules
Modified leuconoid
Cnidarian bodies
Diploblastic
Radial symmetry
Nematocysts
Hydrostatic skeletons
Hypostome
Tentacles
Basal disk
Epithelial muscular cells
Gastrodermis
Cnidocytes
Velum
Manubrium
Radial canals
Mesoglea
Gastrovascular cavity
Diploblastic
Epidermis & gastrodermis (both have basal lamina)
Sometimes have mesoglea (non-living middle layer)
Mesoglea
Support.
In medusae form
Nematocysts
Stinging cells in cnidocytes
Concentrated in epidermis of tentacles
Sometimes in gut lining in Scyphozoa & Anthozoa
Planula larva
Development
Resemble ancestral form
Only product from sexual reproduction
Hypostome
Holds mouth, same idea as manubrium
Tentacles
Hold stingin cells, feeding and defense.
Epithelial muscular cells
Single cells that serve as basic ‘muscles’
Gastrodermis
Makes up inside of body cavity, for digestion
Cnidocytes
Stinging cells on tentacles, hold nematocysts
Velum
Thin membrane to keep water in
Manubrium
Holds mouth
Radial Canals
Provide structure, excrete waste
Gastrovascular Cavity
Digestive cavity
Anthozoa
No medusa stage
Hexacorallia & Octocorallia
Multiple siphonoglyphs
Septa
Ancontia
Pharynx
Hexacorallia
Stony corals
12 tentacles, 6 pairs of septa
Octocorallia
Gorgonian corals
8 tentacles, 8 pairs of septa
Siphonoglyphs
Covered in cilia to create water current
Septa
Extensions in pharynx for increased SA 4 digestion
Acontia
Stinging cells in gastrovascular cavity
Pharynx
Mouth-gastrovascular cavity
Hydrozoa
Medusa produced by budding
No anus
Gastrozooid & Gonozooid
Hydrozoa life cycle
Adult polyp-planula-bby polyp
Hydra Medusa
Velum, simple bell, simple manubrium no nematocysts
Hydra Polyp
Simple mouth, simple gastrovascular cavity, no nematocysts
Gastrozooid
Houses stinging tentacles
Gonozooid
Produce eggs & sperm
Scyphozoa
Medusa produced by strobilation
Mouth lobe
Gastric pouches
Rhopalia
Scyphistoma
Sphyra
Strobilation
Scyphozoa Medusa
No velum, notched bell, mouth lobes extend from manubrium, nematocysts
Scyphozoa Polyp
Simple mouth, septate in gastrovascular cavity, nematocysts in gastrodermis
Mouth lobe
Extend from manubrium, for prey movement into mouth
Gastric pouches
Surround gonads, serve as digestive chamber
Rhopalia
Light sensory, on rim of swimming bell where segments of the swimming bell join together
How many radial canals does Aurelia have?
Lots
How many radial canals does Gonionemus havve?
4
Scyphistoma
Same thing as polyp, eats and reproduces
Ephyra
Break off from strobila, turn into adult jellies
Strobilation
Body column breaks into ephyra
Anthozoan polyp
Mouth opens into pharynx with ciliate siphonoglyphs, septate in gastrovascular cavity, nematocysts in gastrodermis
Ctenophores
Diploblastic
Mesoglea
Gastrovascular canal system
8 comb rows of cilia for locomotion
2 long branched tentacles with sticky colloblast cells
Biradial symmetry
Sometimes develop anus as adults
Comb rows
Outbranches formed by clumped cilia.
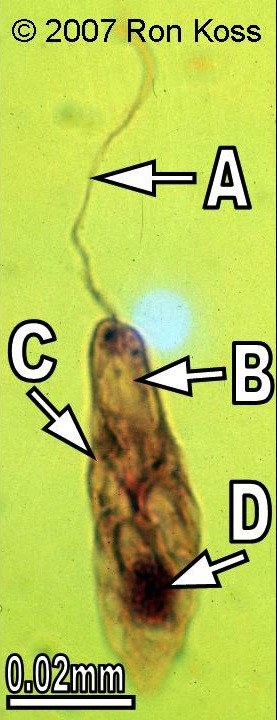
Euglenida
A-Flagella
B-Chloroplast
C-Contractile Vacuole
D-Nucleus
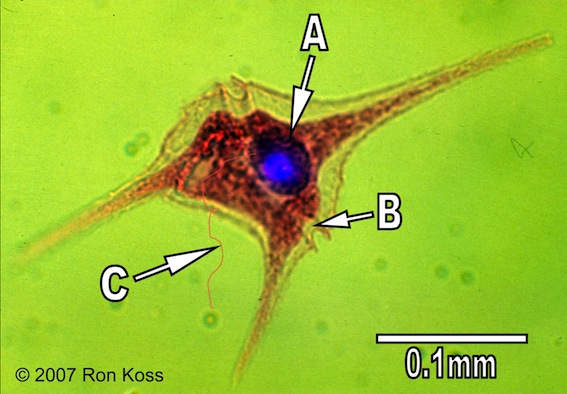
Dinoflagellate
A-Nucleus
B-Annulues
C-Flagellum
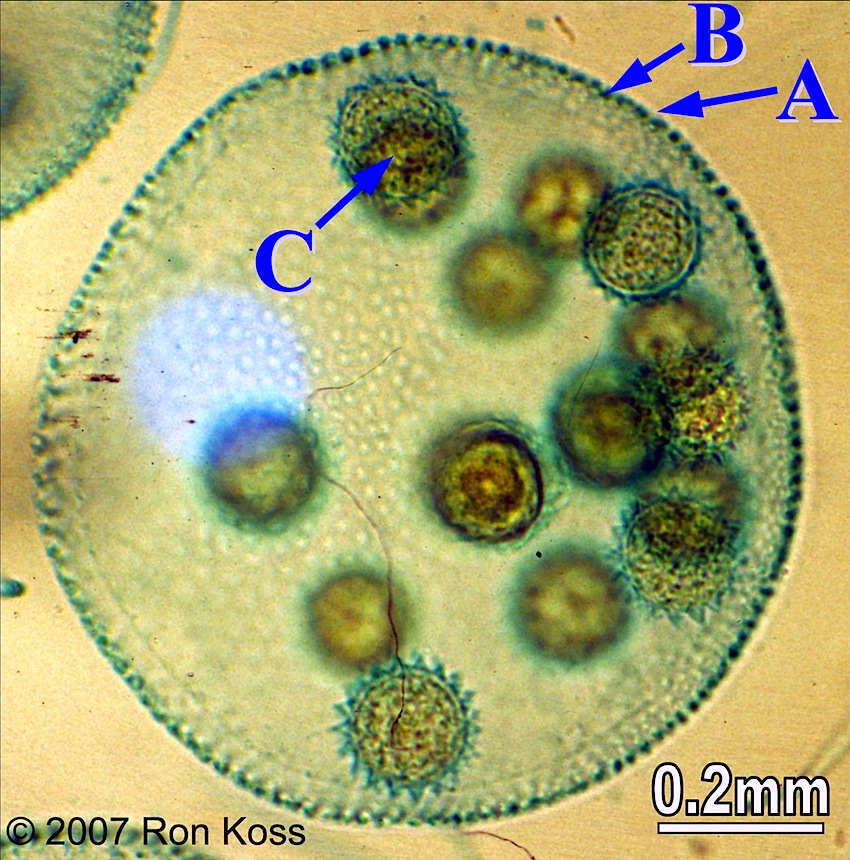
Volvox
A-Gelatinous matrix
B-Flagellate cells
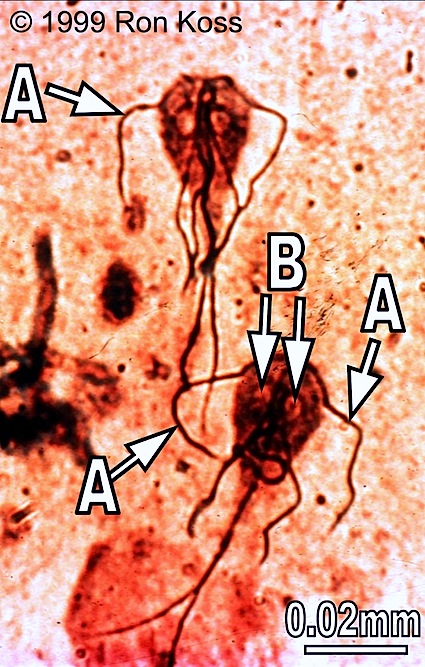
Giardia
A-Flagellum
B-Adhesive disc
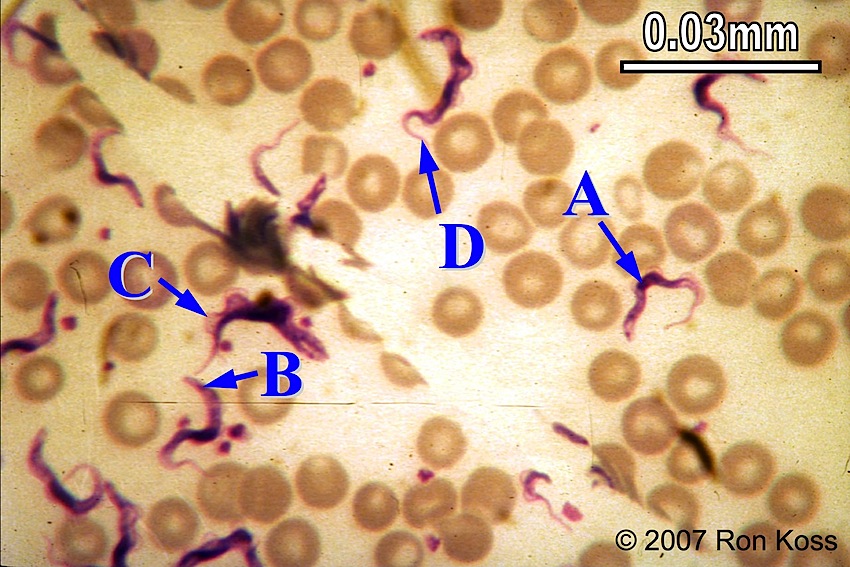
Trypanosoma
A-Nucleus
B-Kinetoplast
C-Undulating membrane
D-Flagellum
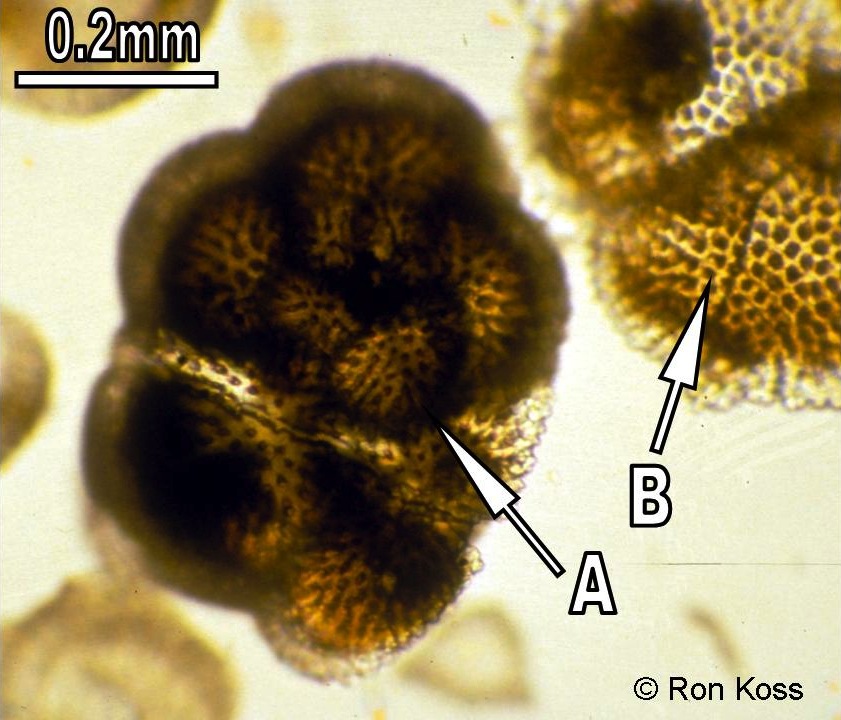

Foraminifera
A-Test
B-Shell pores
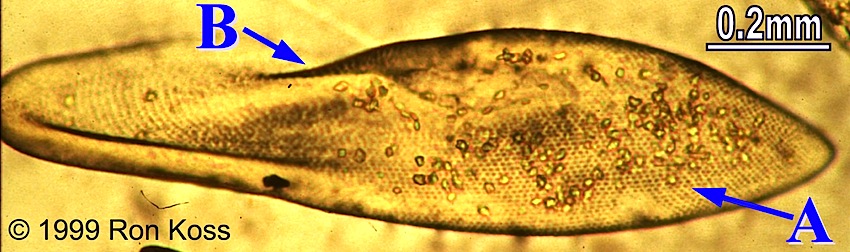
Paramecium
B-Pellicle
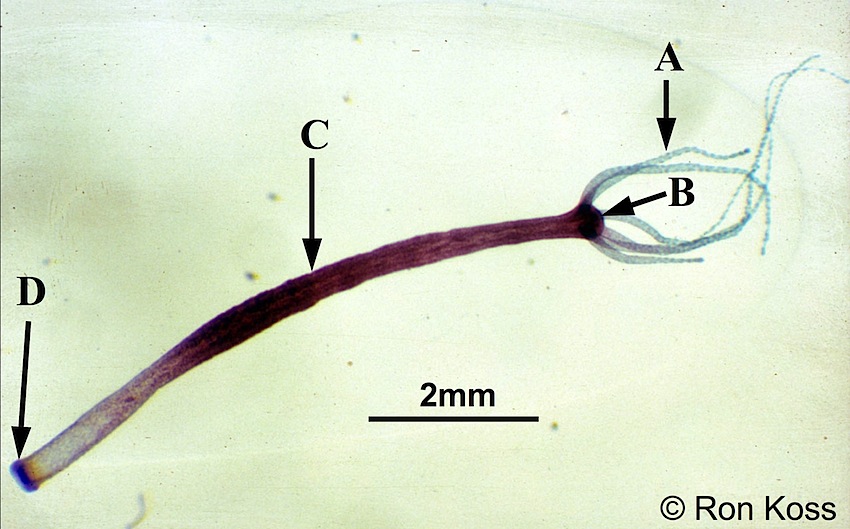
Hydra
A-Tentacle
B-Hypotstome
C-Body Column
D-Basal disc
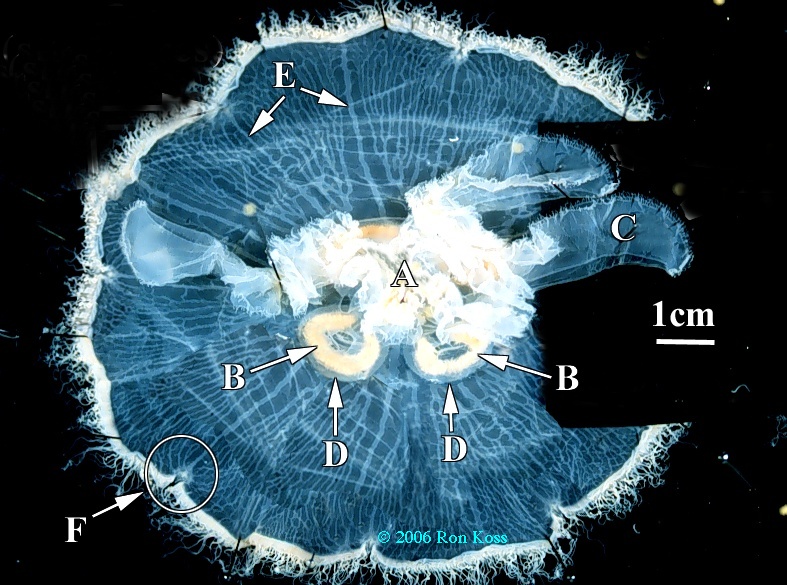
Aurelia
A-Mouth
B-Gonad
C-Oral arm
D-Gastric pouch
E-Radial canals
F-rhopalium
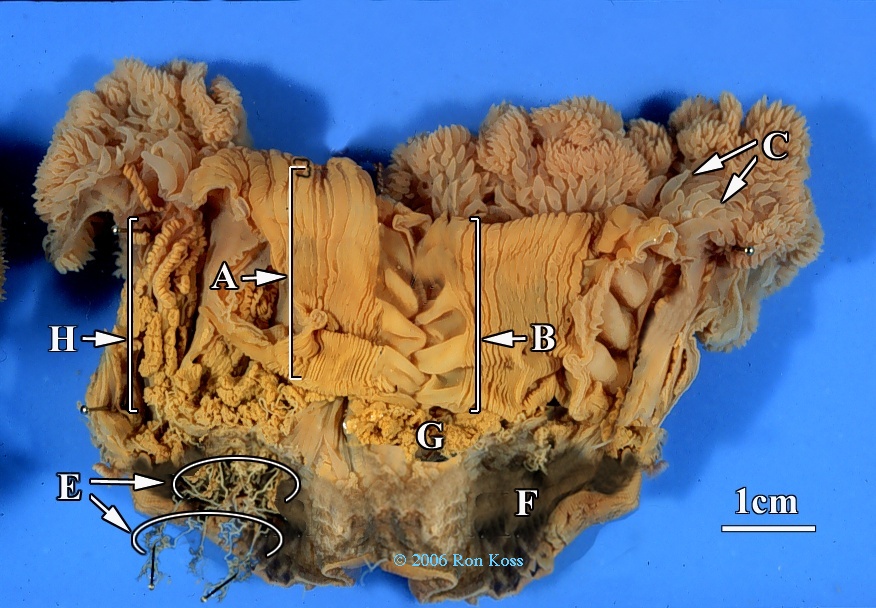
Metridium
A-Pharynx
B-Siphonoglyph
C-Tentacles
E-Acontia
F-Pedal Disc
G-Septa
H-Gonads
Echinodermata
-Water vascular system not present in any other animals.
Crinoidea
Feather stars
Crinoidea Morphology
-Pinnules.
-Cirri
Pinnules
Have cillia that branch off, attached to arms.
For filter feeding/prey.
Cirri
Small ‘arms’ that attach to substrate
Astroidea
Starfish
Astroidea Morphology
Bipinnaria larvae
Dermal papulae.
Pedecellaria
Madreporite
Ambulacral grooves
Tube feet
Stone canal
Ring canal
Polian vessicles
Radial canals
Lateral canals
Ampullae
Peristomial membrane
Dermal papulae
Oxygen exchange, tiny little bumps (solid not split like pedecllaria).
Pedecellaria
Taller than papulae, split into 2 ‘claws’.
Aboral end.
Used for defense to stop things from growing on it.
Madreporite
Looks like little embedded rock between arms.
Water enters, blocks larger particles from entering, start of water vascular system.
Ambulacral grooves
Where tube feet are held.