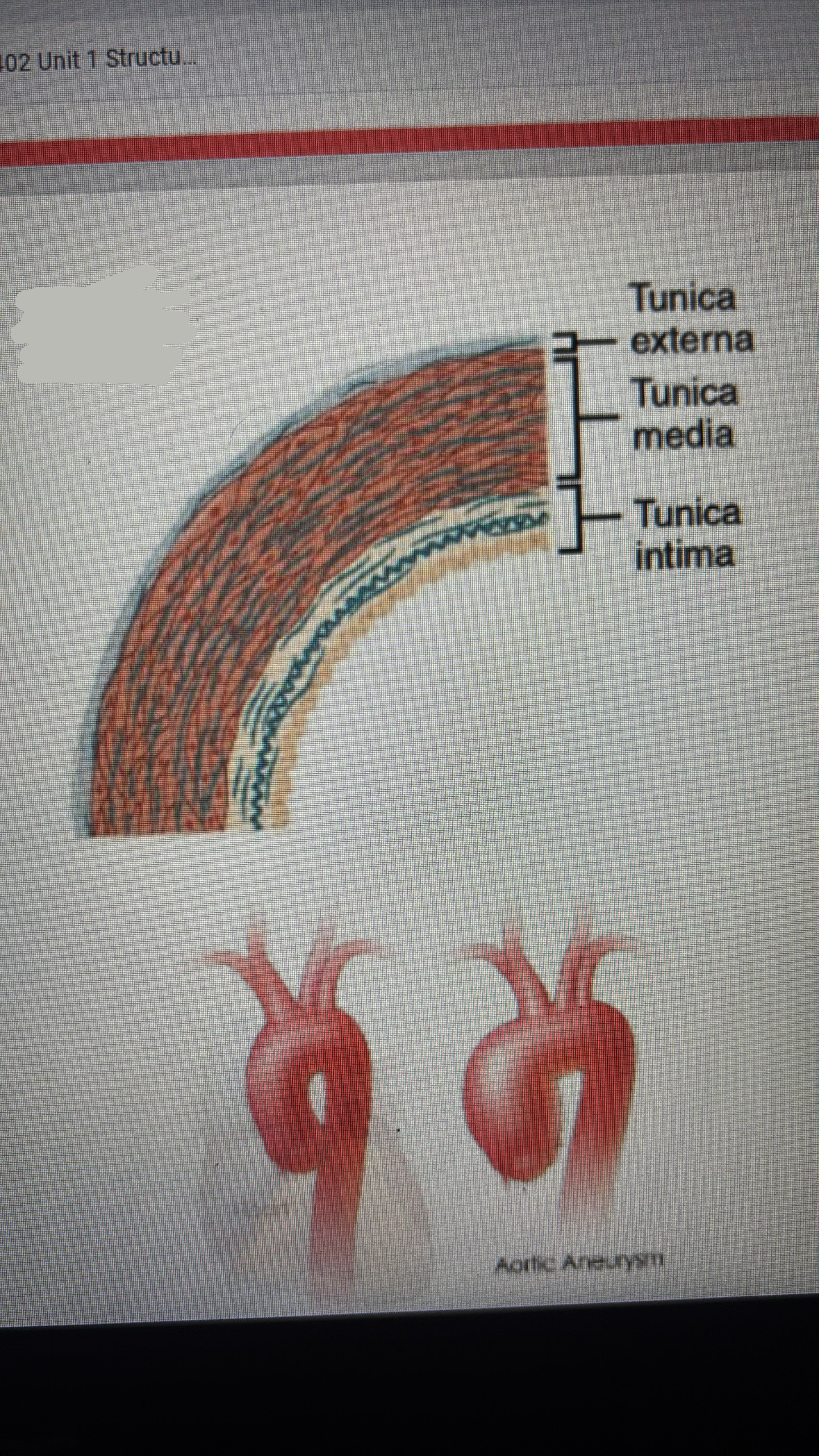
classes of arteries
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
elastic arteries
closest arteries closest to the heart
tunica media consist of many (40-70) sheets of elastic fibers
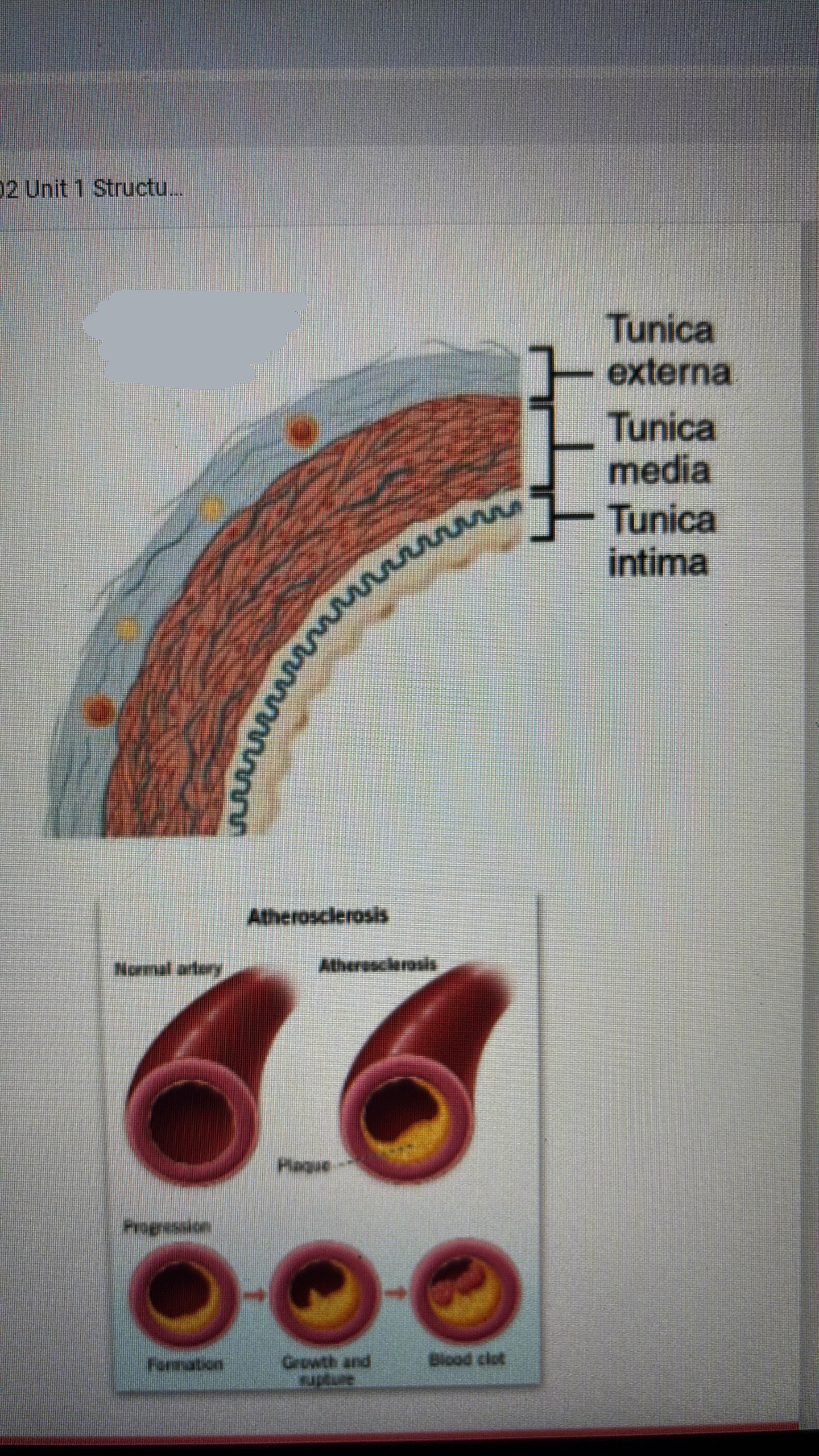
muscular arteries
intermediate diameter
includes arteries that simply organs
tunica media is mostly smooth muscle
allows for nervous and endocrine control of blood flow (vasoconstriction vasodilation)
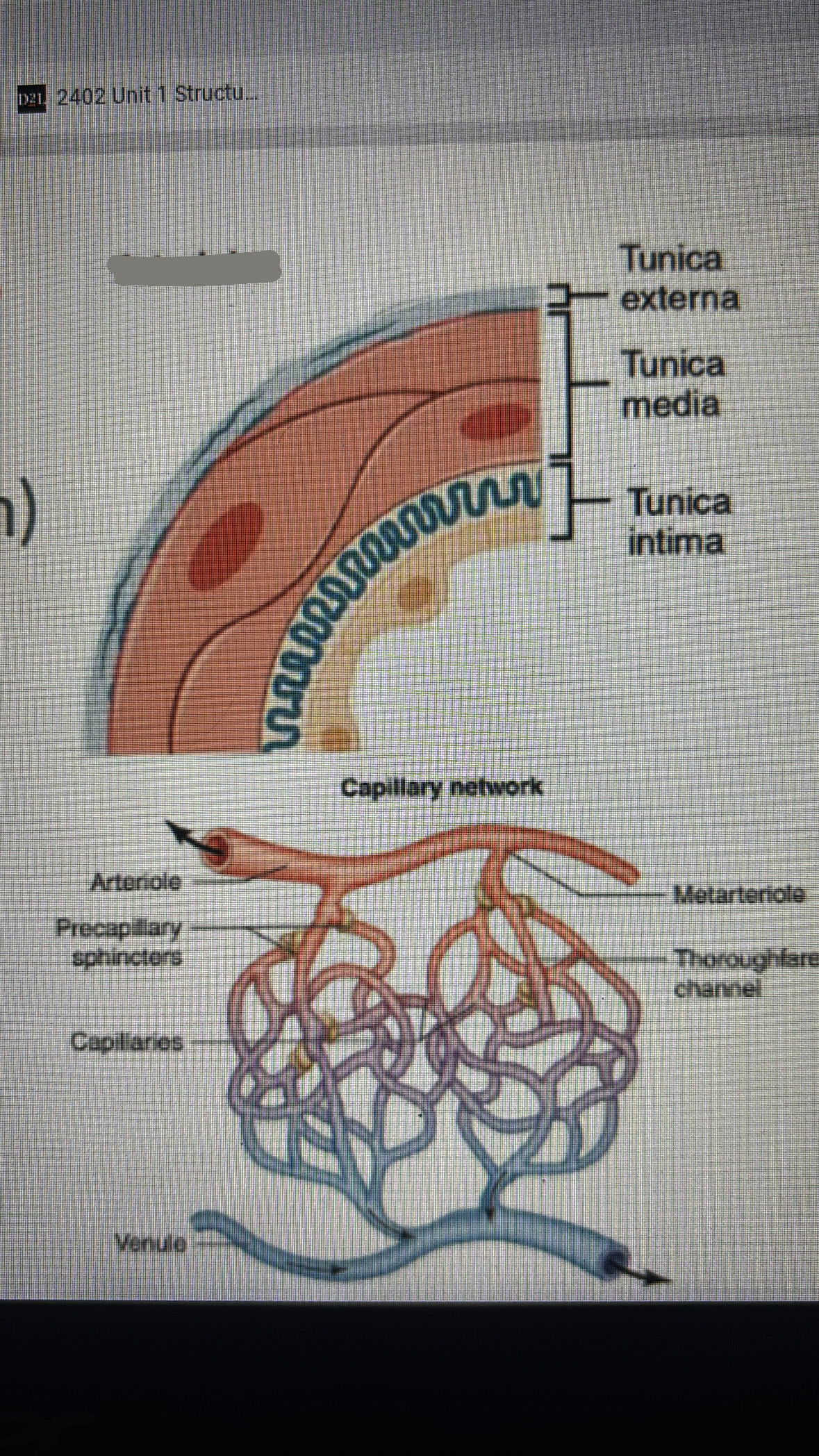
arterioles
smallest arteries
all 3 tunics are present but very thin
vasoconstriction and vasodilation have major effects on blood flow to capillary beds in tissues
( blood flow can be completely cut off)
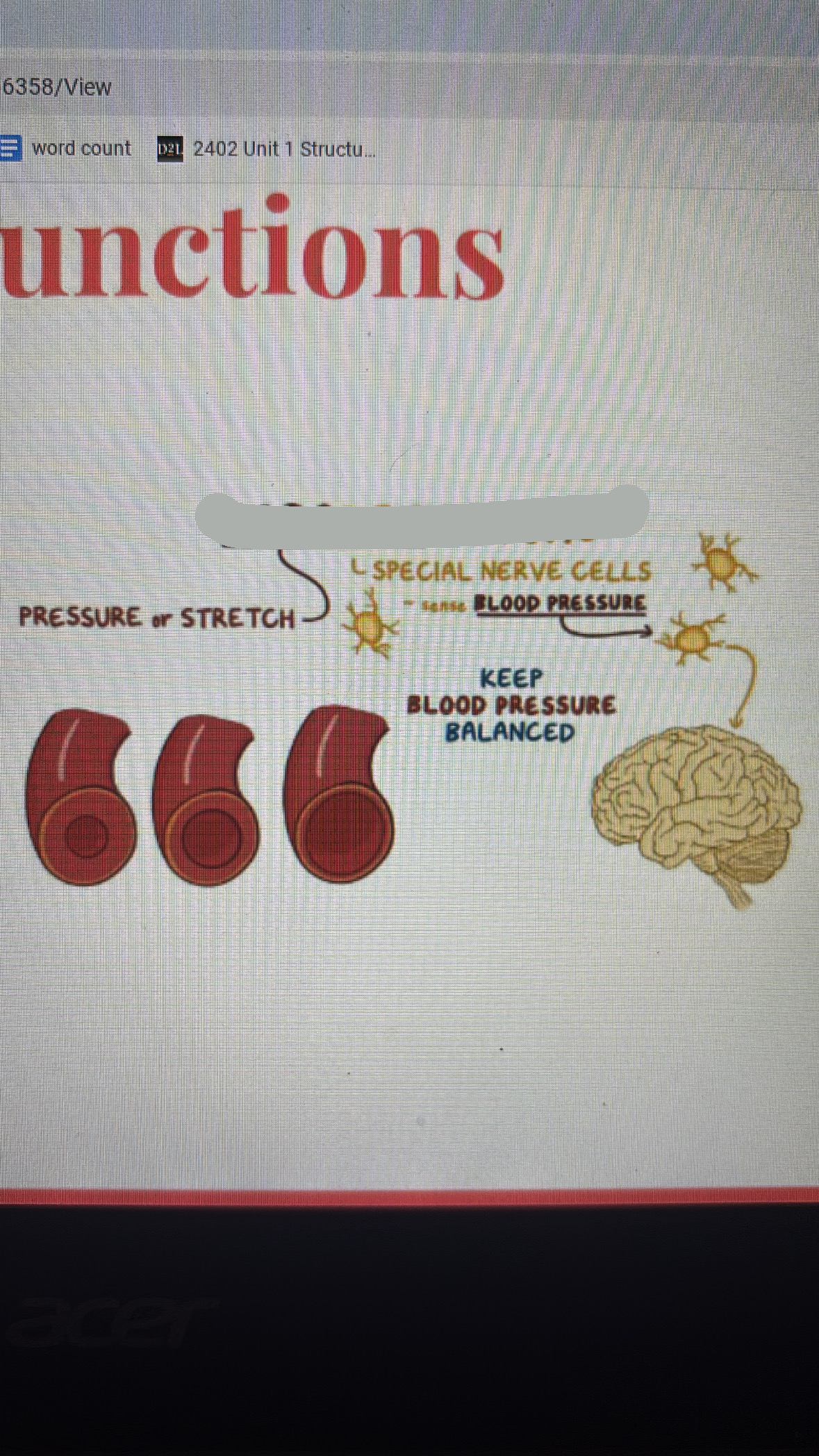
baroreceptors
detect blood pressure in aorta and carotid artery
chemoreceptors
detects O2, CO2, and pH within the aorta and carotid artery
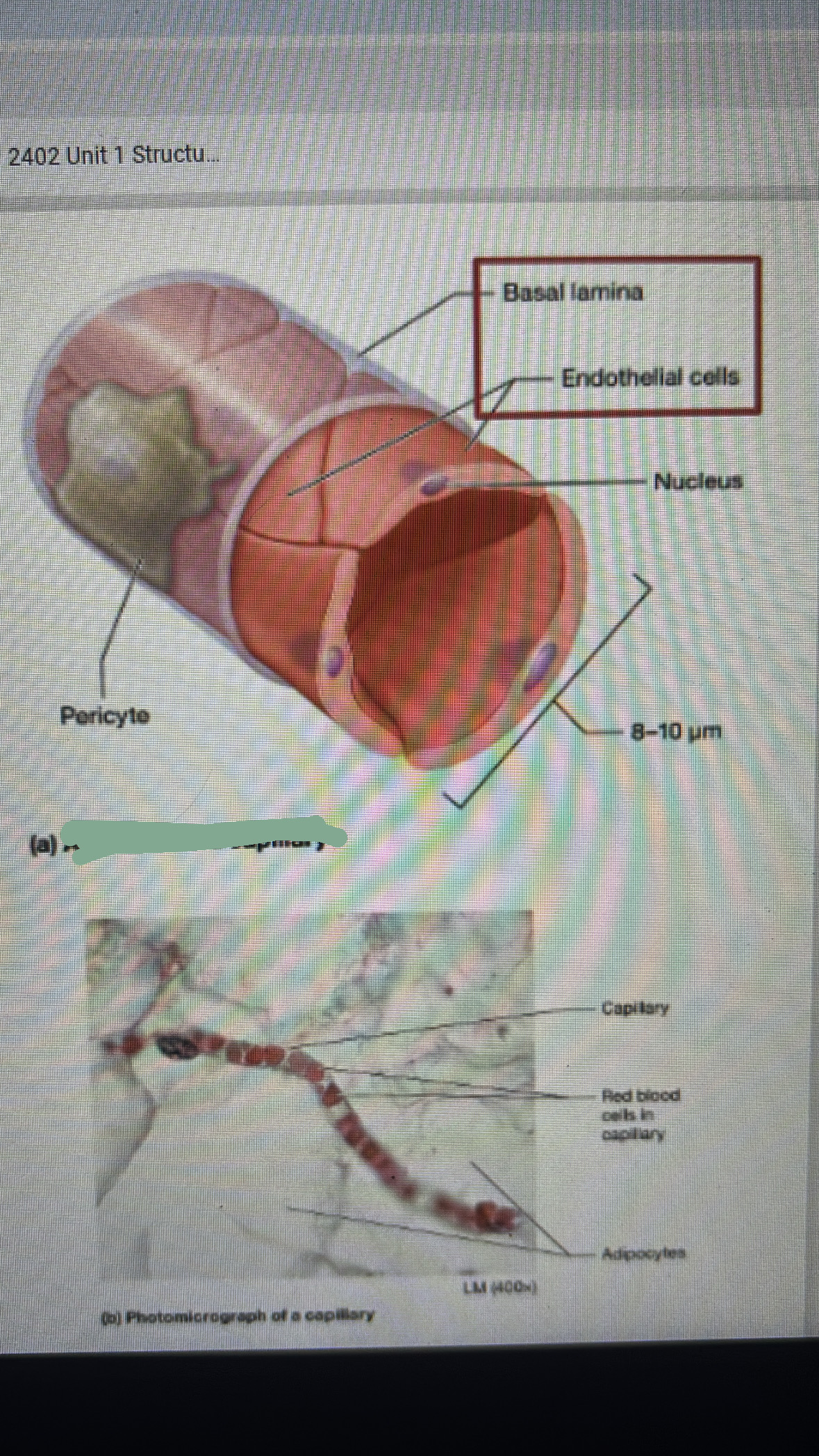
capillaries
extremely thin-walled vessels
Endothelium (1-3 cells) rolled around a tube surrounded by little basal lamina (connected by tight junctions
diameter 8-10 um
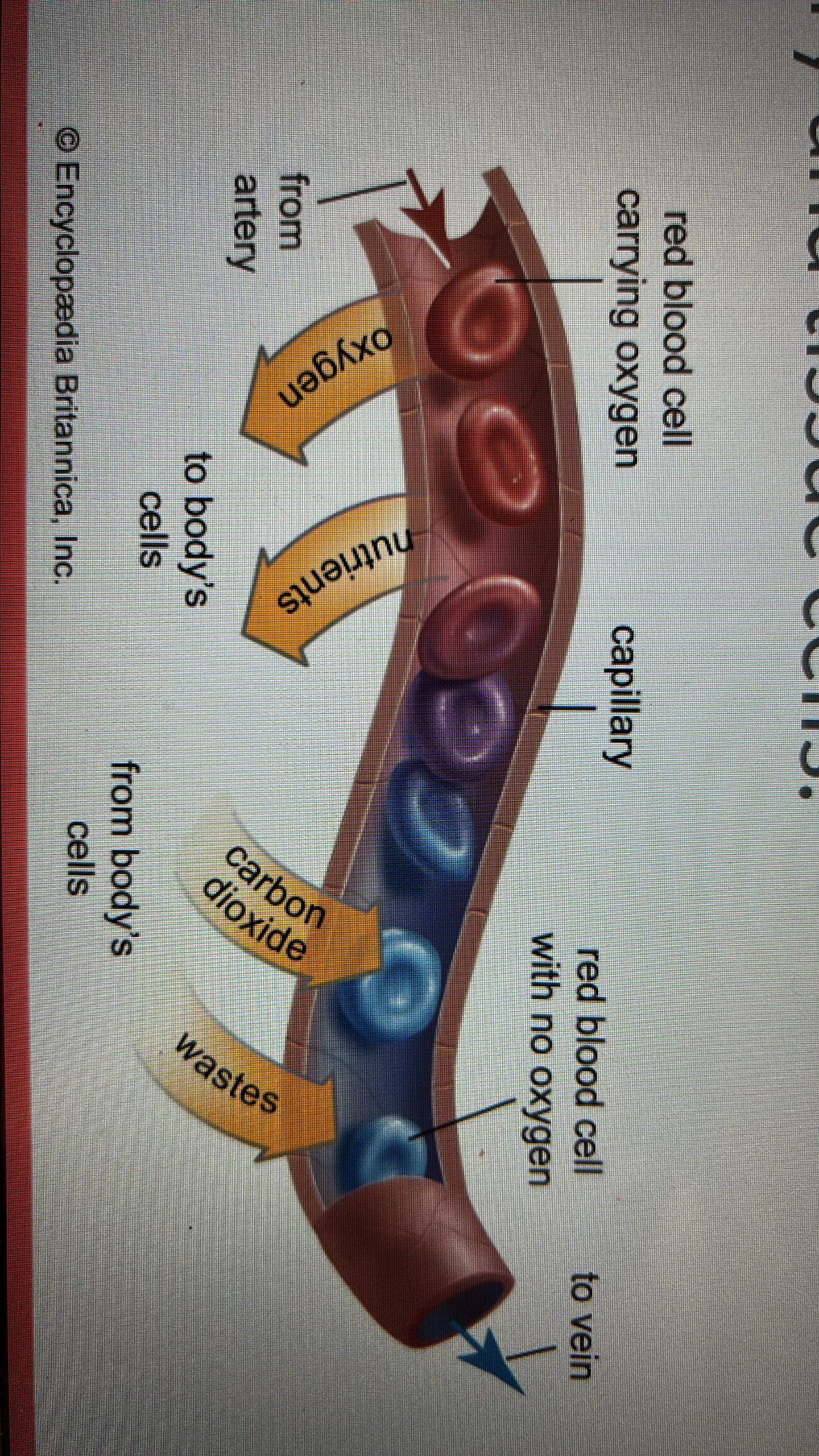
capillary exchange
the movement of nutrients, gases, ions, and wastes between blood in the capillary and tissue cells
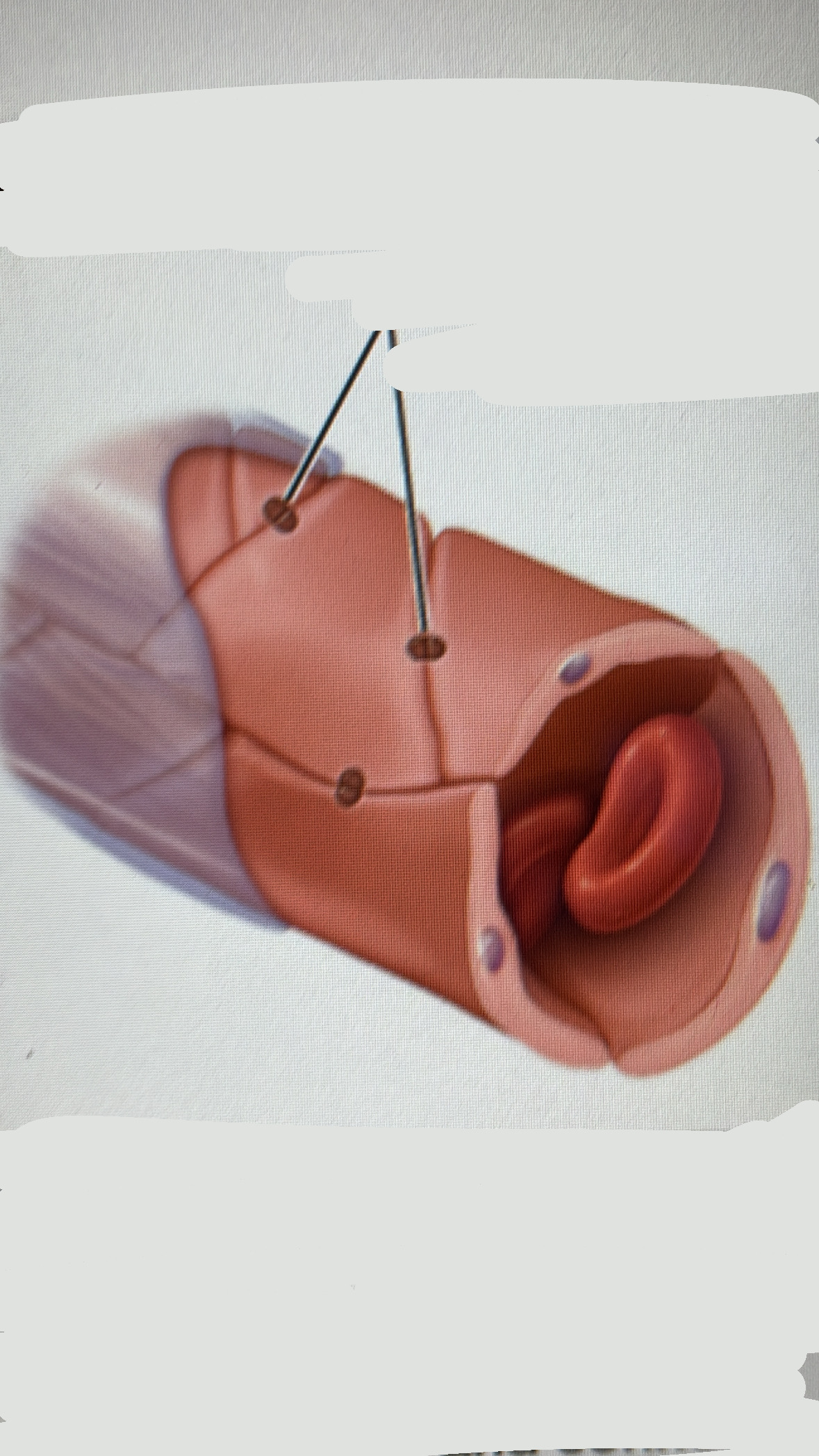
continuous capillaries
endothelial cells joined by tight junctions
LOCATION skin , most nervous/connective tissue , muscle tissue
least “leaky”- permit a narrow range of substances to cross walls
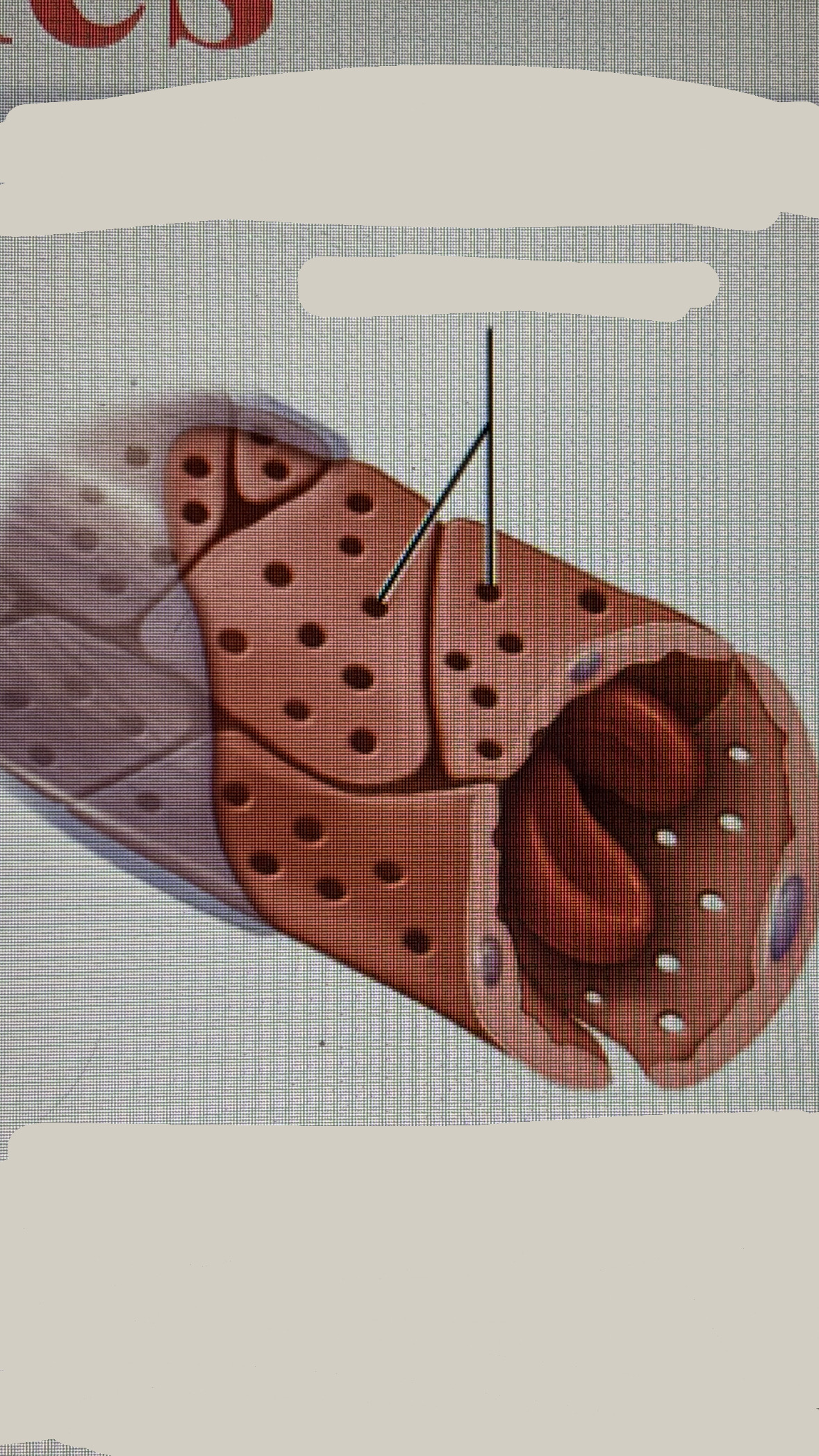
fenestrated capillaries
contains fenestrations in the endothelial cells
LOCATION
Kidneys, endocrine glands, small intestine
moderately leaky- allow large volumes of fluid and larger substances to cross capillary walls
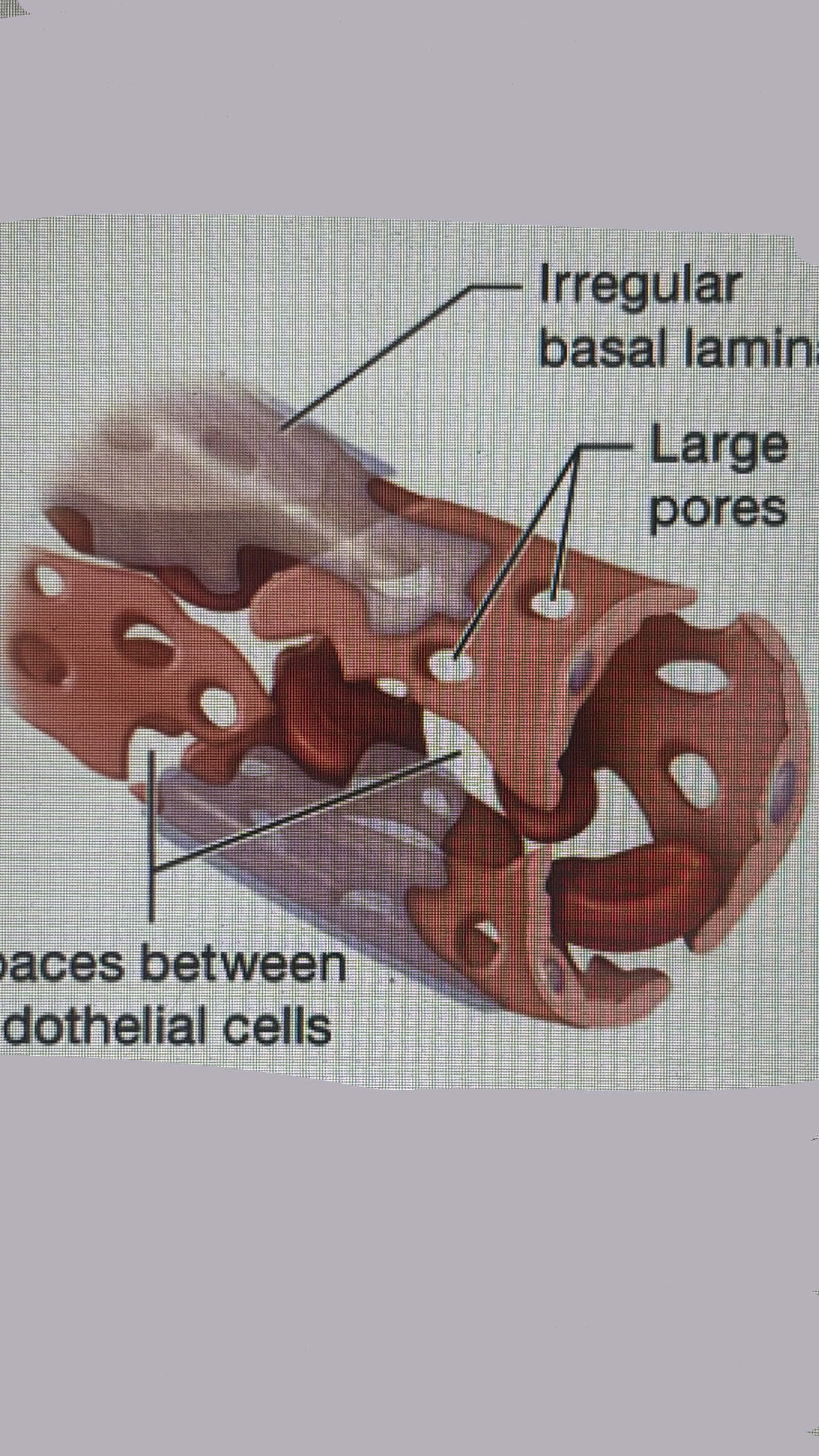
sinusoidal capillaries
discontinuous sheet of endothelium, irregular basal lamina, very large pores
LOCATION
liver, lymphoid organs, bone marrow, spleen
leakiest— allow large substances such as cells to cross the capillary walls
tissue perfusion
blood flow to tissue thru capillary bed, its tightly controlled
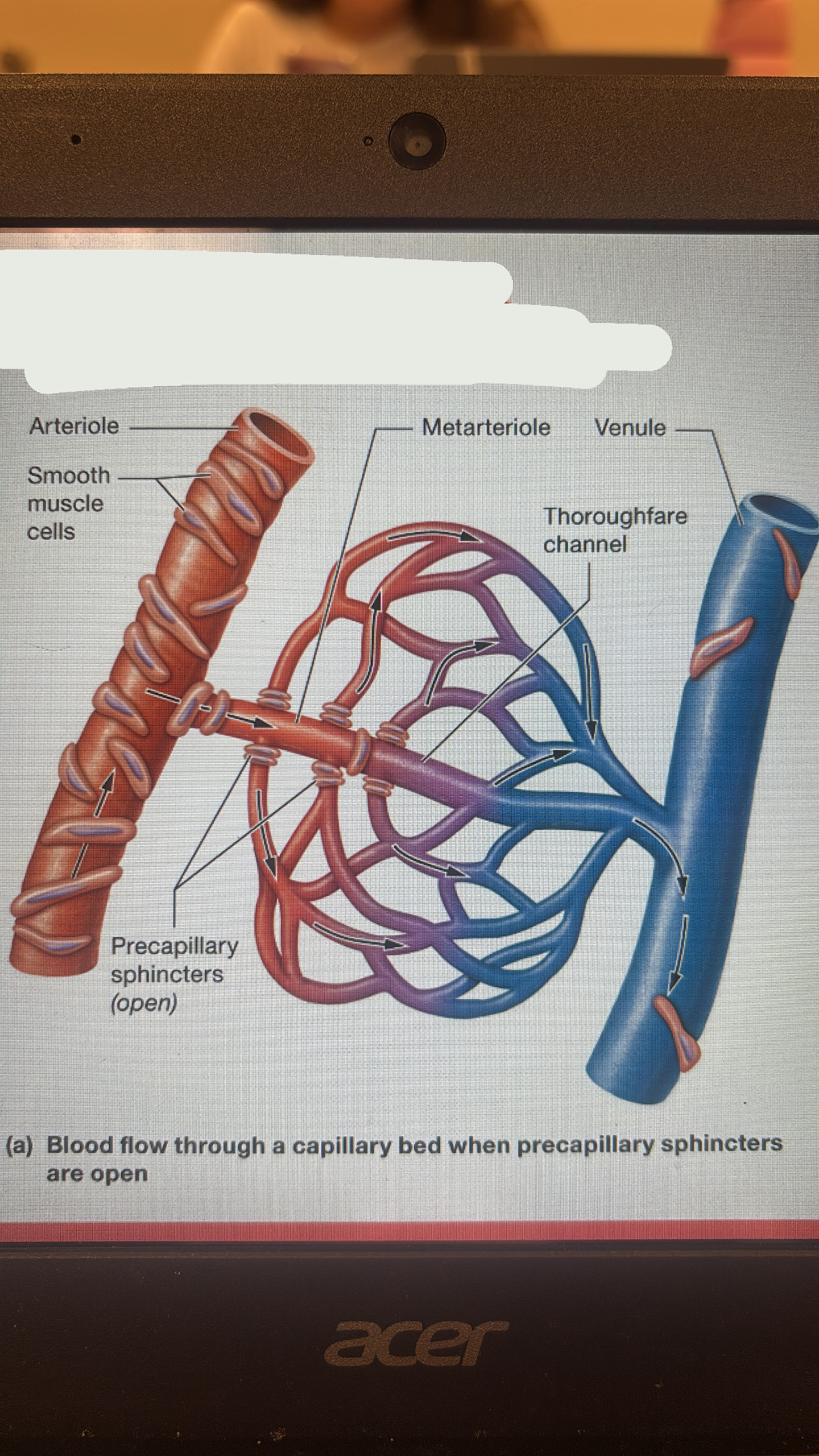
capillary beds
networks of capillaries that pass between the cells of most tissues
hemodynamics
physiology of blood flow within the cardiovascular system
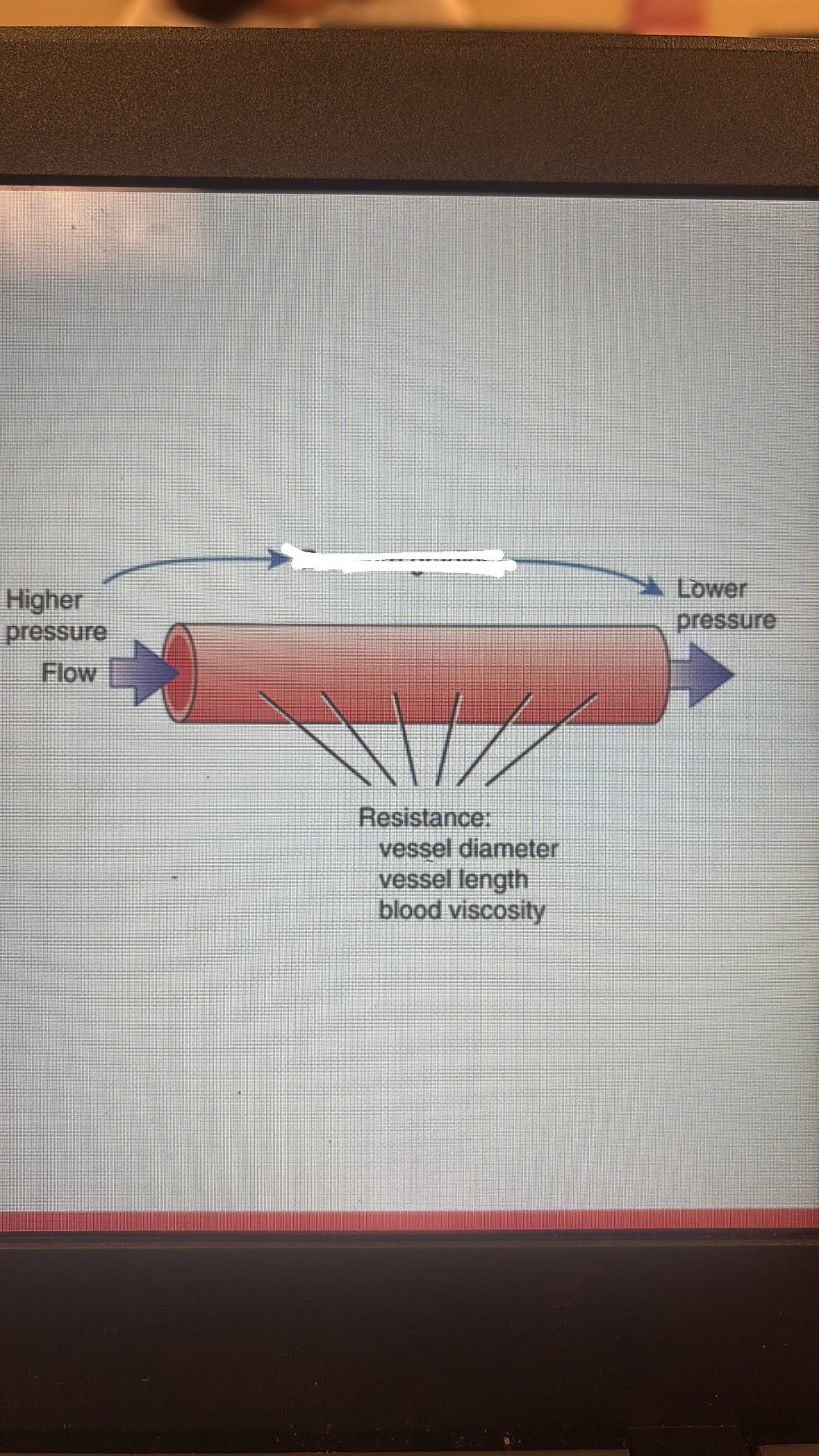
pressure gradient
as ventricles of the heart contract, they push blood thru the blood vessels
blood flows from high pressure areas- to low pressure areas
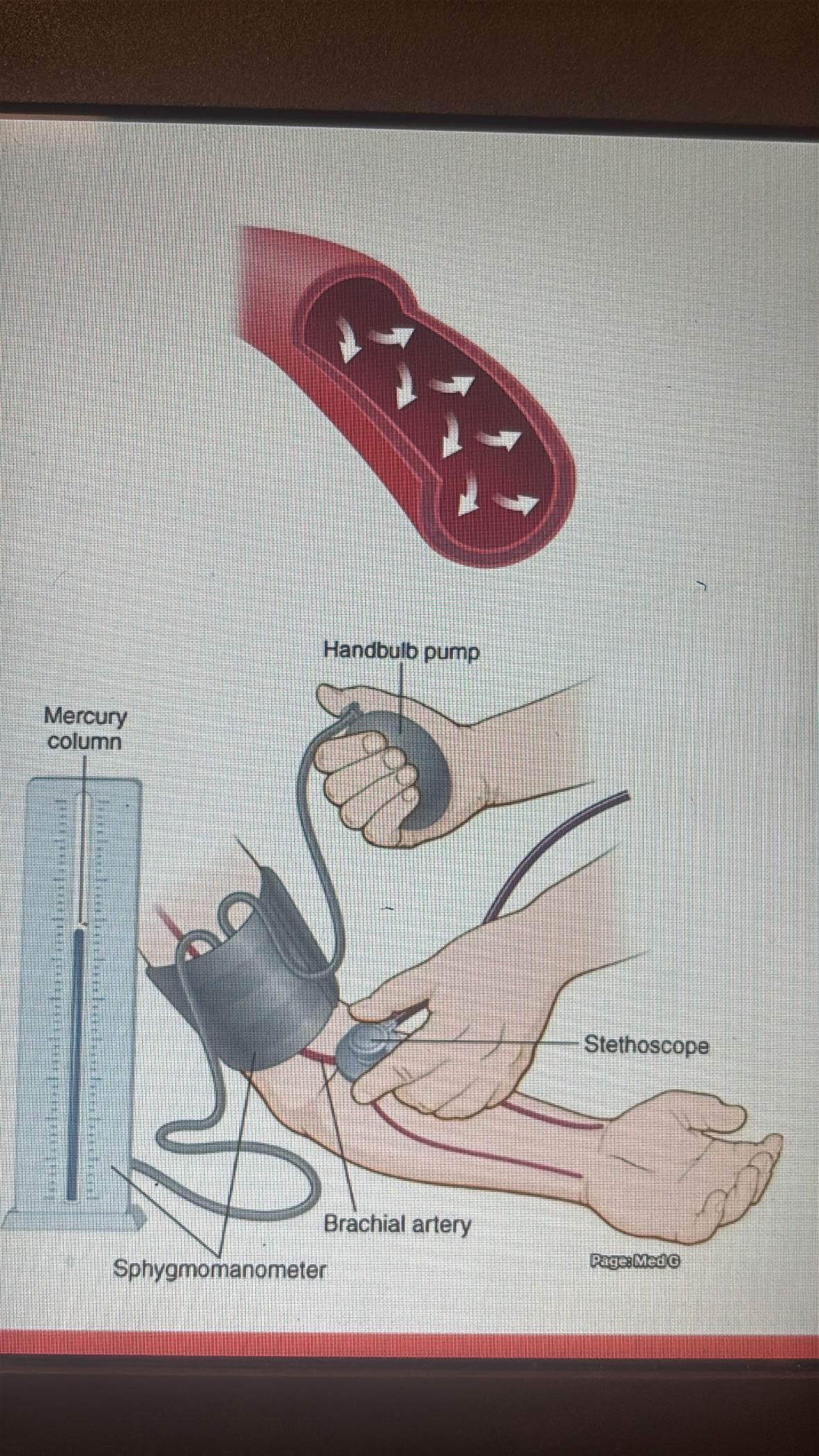
blood pressure
the outwards force the blood exerts on the walls of blood vessels
blood flow
the volume of blood that flows thru vessel during a period of time
measured in liters per minute (L/m) usually ~5-6 L/m
affected by
magnitude of the blood pressure gradient and resistance
peripheral resistance
anything that hinders blood flow thru vessels away from the heart
when this is 👆 so is the blood pressure 👆
DETERMINED BY
blood vessel radius
blood viscosity
blood vessel length
obstructions
cardiac output
will increase along with increases in either stroke volume or heart rate
blood volume
increases as the amount of water in blood increases