Photosynthesis
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
biological process performed by photoautotrophs (plants, some bacteria and protists); captures energy from sunlight and converts it to chemical energy stored in the form of glucose.
Where does photosynthesis take place?
in the chloroplasts
What is the overall reaction of photosynthesis?
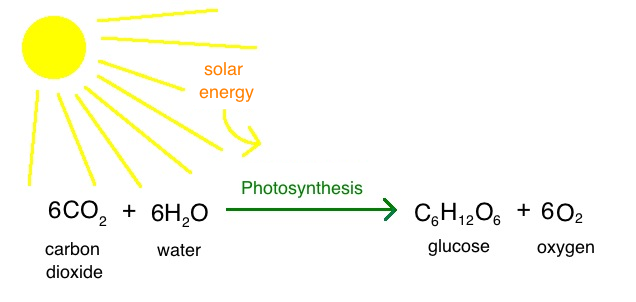
What is the organelle called? Only found in eukaryotic photoautotrophs; contains chlorophyll.
Chloroplast
What is chlorophyll?
It’s a light-absorbing pigment with a porphyrin ring (contains central Mg atom); similar structure to hemoglobin.
Acts as the cytoplasm of the chloroplast?
The stroma
What are the two reactions of photosynthesis?
Light Dependent (Light reation) →products ATP,NADPH,O2
Light Independent (Dark reaction/ Calvin Cycle) → converts CO2 to glucose
Light dependent reaction includes __ and _ using photosystems
Cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation
What are photosystems?
A large chlorophyll containing proteins found in the thylakoid membrane
What is the first step of noncyclic photophosphorylation?
Photons from sunlight excite electrons in PS II to a higher energy level
Noncyclic photophosphorylation occurs in the?
Thylakoid membrane
What is photolysis? It is split into?
The splitting of water by light that occurs in PS II
It is split into H+ , electrons, and oxygen
Cyclic occurs in the? and only involves?
stroma lamella and only involves PS I
Dark reaction, also known as calvin cycle, occurs in the ?
Stroma
What is the primary function of the dark reaction/Calvin cycle?
Use products from the light reaction and fix CO2 to eventually make sugar
What are the three phases of the Calvin cycle? and what is their purpose
Carbon Fixation: Inorganic carbon is converted into organic compounds (glucose)
Reduction: Steps that use ATP and NADPH from the light reaction
Regeneration: Intermediates are regenerated so the cycle can continue
In C4 photosynthesis, malate is produced in the _ and transferred to _
The mesophyll cells into the bundle-sheath cells
In what type of plants can C4 occur?
In corn and sugarcane
Other than CO2 combining with RuBisCo, what else can bind to it (acts as a competitive inhibitor)?
O2: Photorespiration, which is bad because it creates a useless byproduct/ reduces efficiency. of the Calvin cycle
The ATP made in photosystem 2 is exclusively used for?
photosynthesis
The reduction phase of the Calvin cycle directly require?
ATP & NADPH
The stomata are open during?
The night in CAM to allow CO2 in
What connects the thylakoid togehter?
Stroma lamellae
what is C2 and C3?
C2: photorespiration
C3: normal photosynthesis
What is the advantage of C4 photosynthesis?
It prevents photorespiration. It’s done by separating the light-dependent reaction and the Calvin cycle
What plants undergo CAM?
Cactus and pineapple
Where are chlorophyll contained during ight-dependent reaction
Photosystems 2&1
Where does the Calvin cycle and RuBisCo take place in C4?
In the bundle-sheath cell
Where is e.t.c embedded in non-cyclic photophosphorylation: photosystem 2?
In the thylakoid membrane
Which photosystem captures electrons and produces high levels of NADPH?
Photosystem 1
Which photosystem is p680?
2
Which photosystem is p700?
1