S296 Cell and Molecular Biology
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
List properties that are characteristic of life of living cells
Growth
Reproduction
Response to stimuli
Metabolism
Organisation
Excretion
Movement
Evolution
Homeostasis
What two main categories can organisms be divided into based on the morphology of their cells
Prokaryotes & eukaryotes
What are prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. They are characterized by their simple cell structure and include bacteria and archaea.
What are eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes are organisms composed of one or more cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. They include plants, animals, fungi, and protists, showcasing a more complex cell structure compared to prokaryotes.
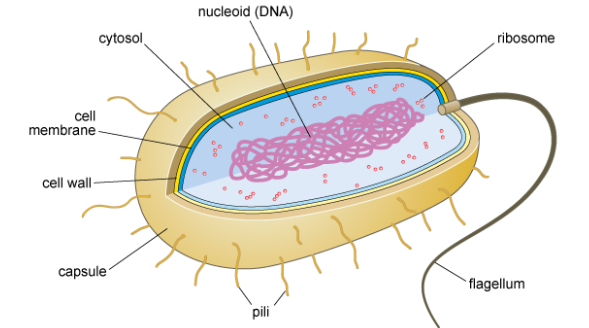
Bacterium
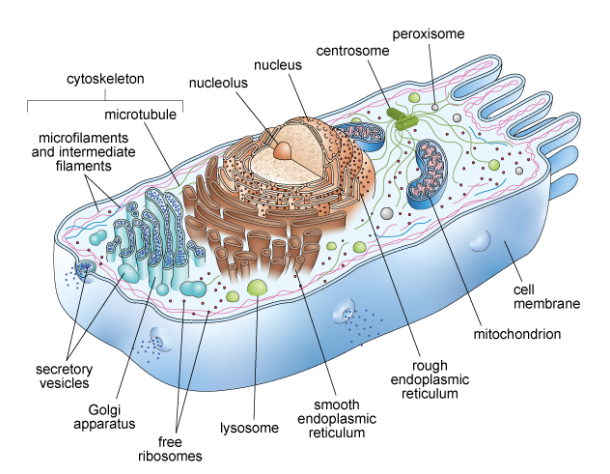
Animal cell
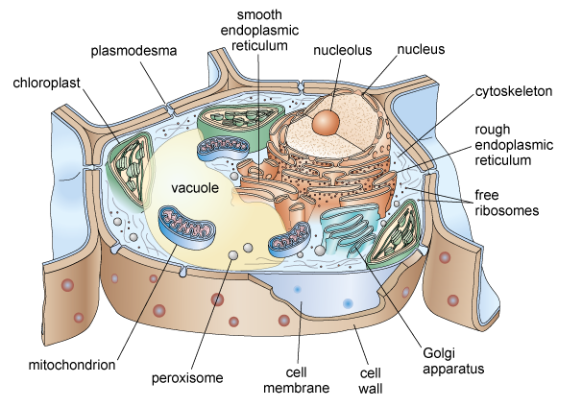
Plant cell
Typical cell diameter of a bacterium
0.1 - 1μm
Typical cell diameter of an animal cell
10 - 50μmTy
Typical diameter of a plant cell
50 - 100μm
Does bacteria have a nucelus?
No, the genetic material is in an area of the cytoplasm called the nuceloid
Do animal cells have a nucleus?
Yes, a membrane-bound nucleus encloses the genetic material.
Do plant cells have a nucleus?
Yes, a membrane-bound nucleus encloses the genetic material.
Do bacteria have membrane-bound organelles?
No membrane bound organelles.
Do animal cells have membrane-bound organelles?
Yes, membrane-bound organelles include the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
Do plant cells have membrane-bound organelles?
Yes, membrane-bound organelles include the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplasts and, usually, a large central vacuole
Do bacteria have a cell wall?
Yes, a cell wall, and, in some cases, a slimy outer capsule and surface appendages (pili and flagella).
Do animal cells have a cell wall?
No cell wall.
Do plant cells have a cell wall?
Yes, a cell wall wit pores called plasmodesmata connecting neighbouring cells.
What is the key difference between the structure of a prokaryotic bacterium and that of eukaryotic animal/plant cells?
The bacterium does not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles (like mitochondria or an endoplasmic reticulum)
What two membrane-bound organelles are common to all three cell types (bacteria, plant, animal)?
A cell membrane and ribosomesWh
What is the function of ribosomes?
They are structures which decode the information in a cell’s genetic material and synthesise protein molecules.
Which molecule constitutes the heritable genetic material in all cells?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
What did Darwin comment on how the original spark of life probably began?
in some warm little pond with all sorts of ammonia and phosphoric salts, light, heat, electricity etc. present, [so] that a protein compound was chemically formed, ready to undergo still more complex changes.
When the did the formation of the Earth occur?
4.5 billion years ago
How did the formation of the Earth occur?
The Earth formed as gravity pulled in dust and gases to form a solid core and crust of lighter material. Most of the surface was probably molten and subject to frequent collisions with other bodies.
When did Earth’s earliest oceans form?
4.4 billion years ago
How did Earth’s earliest oceans form?
The Earth’s crust eventually cooled and solidified, allowing liquid water to form on the surface. The atmosphere was probably mainly nitrogen (N2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) with small amounts of other gases including water, methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2).
When is the earliest evidence of prokaryotes from?
3.4 billion years ago?
What was the earliest evidence of prokaryotes?
What appear to be fossilised stromatolites (meaning layered rocks) have been found in 3.4 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia. Stromatolites are known to form when photosynthetic cyanobacteria grow in biofilms that glue together rocky materials to form mat-like layers.
When was the Great Oxygenation Event?
2.0 to 2.4 billion years ago
What was the Great Oxygenation Event?
At first, the oxygen released by the photosynthetic ancestors of cyanobacteria was absorbed by the oxidation of minerals, such as iron ores. Oxygen only started to accumulate in the atmosphere about 2.0 to 2.4 million years ago, causing the extinction of many anaerobic species. Once oxygen levels were high enough, the formation of an ozone layer would have filtered out some of the sun’s radiation, allowing organisms to start colonising land.
When was the earliest evidence of eukaryotic cells from?
2.1 to 1.7 billion years ago
What was the earliest evidence of eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotes have many features that differ from prokaryotes, including membrane-bound organelles (the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and chloroplasts) as well as distinctive biochemical pathways and proteins (e.g. cytoskeletal proteins). Numerous hypotheses have been proposed for when and how these components arose. The presence of early eukaryotic cells has been inferred by detecting ‘molecular fossils’, traces of eukaryotic biochemicals in oil trapped in ancient rocks. An approximately 2.1 billion-year-old fossil of a thread-like organism called Grypania spiralis is generally accepted to be a eukaryote, although it may have been a giant bacterium.
When were the earliest large multicellular organisms from?
600 million years ago
How were the earliest large multicellular organisms formed?
Cyanobacteria probably started working together as groups of cells as long ago as 3.4 billion years, but the earliest evidence for large multicellular organisms are fossilised sponges dating to around 600 million years ago. Multicellularity in eukaryotes is thought to have evolved about 25 times, but complex multicellularity has only developed in animals, fungi, land plants and algae.
When were the earliest land plants formed?
470 million years ago
What were the earliest land plants?
The earliest land plants were small, low-growing, non-vascular plants (lacking channels for transporting water and nutrients) like mosses and liverworts. Vascular plants with a root and stem transport system, and in some cases leaves, started to evolve about 425 million years ago. The first flowering plants appeared around 130 million years ago.
When were the earliest land vertebrates from?
360 million years ago
What were the earliest land vertebrates?
The earliest land vertebrates evolved from fish-like animals about 360 million years ago. Amniotes (organisms that lay their eggs on land, or develop them inside the body) including dinosaurs, birds and mammals evolved from about 330 million years ago. Dinosaurs dominated the land for 150 million years, perishing in a major extinction event about 65 million years ago. Mammals subsequently increased in size and diversity very rapidly.
When were the earliest apes from?
15 to 20 million years ago
What were the earliest apes?
The Hominidae (great apes) diverged from other primates about 15 to 20 million years ago and the Hominini (humans) diverged from chimpanzees 4 to 7 million years ago. Anatomically modern humans appeared in Africa about 300 000 years ago.
What was the Oparin-Haldane hypothesis?
Biological molecules could have arisen from inorganic substances. At the time, it was believed that the Earth’s early atmosphere contained large amounts of water vapour and the gases ammonia (NH₃) and methane (CH₄) created by volcanic eruptions, but no oxygen. The Oparin–Haldane hypothesis proposed that these harsh, chemically reducing conditions could have promoted chemical reactions that formed small carbon-containing organic molecules, such as amino acids. A ‘primordial soup’ of these small organic molecules dissolved in the warm oceans could have given rise to increasingly complex polymers and, eventually, life forms that were capable of synthesising molecules such as proteins, lipids and nucleic acids.
What is a hypothesis?
An investigator’s proposal for the most likely explanation for an observed phenomenon
What is a theory?
An interpretation of a group of observations or experiments that is widely accepted among the scientific community.
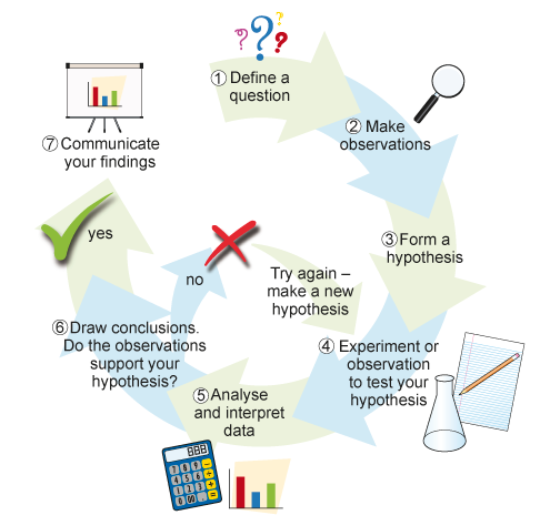
Flowchart of formulating a testable hypothesis (the scientific method)
What experiment was carried out to test the Oparin-Haldane hypothesis?
The Miller-Urey Experiment (1950s)
/what was the Miller-Urey experiment?
Subjected a mixture of water vapour, methane, ammonia and hydrogen gases to high temperatures and electrical discharges (to mimic lightning, a source of energy). Several different organic compounds, including amino acids, were detected at the end of the experiment (Figure 1.3).
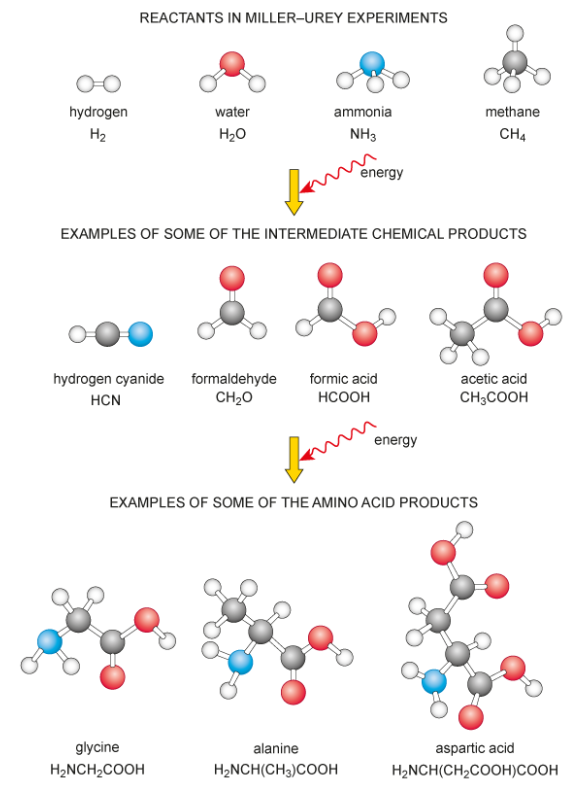
Does the Miller-Urey experiment prove that this is how organic molecules first arose on Earth?
No. It supports the Oparin–Haldane hypothesis that organic molecules could form under the conditions specified, but it does not offer any proof that those were the conditions that existed at the time.
What is now believed about the Earth as opposed to the Oparin-Haldane Hypothesis?
The Earth’s early atmosphere was much less harsh than proposed in the hypothesis, with high concentrations of nitrogen and carbon dioxide but only small amounts of methane and ammonia. However, more recent experiments (Cleaves et al., 2008) have demonstrated that amino acids, sugars and the building blocks of RNA and DNA can form even under these milder conditions. Traces of organic molecules, including amino acids, have also been found in fragments of meteorites that have reached Earth, suggesting that the basic building blocks of life may exist elsewhere in the universe – although the examples identified so far all originate from within our own solar system. Some scientists have suggested that the frequent bombardment of the early Earth with asteroid fragments containing organic molecules may have helped to accelerate chemical reactions that started the process of life.
How is DNA copied (replicated)?
A cell divides and one copy is inherited by each of the two new ‘daughter’ cells.
How is the information for a protein encoded in a DNA sequence?
The amino acid sequence of a protein is specified by the order in which the four types of nucleotide (A, G, C and T) occur along the DNA strand. Each set of three nucleotides (known as a codon) encodes one amino acid in the protein.
Define transcription
The process of making an RNA copy of genetic information stored in DNA. Using one DNA strand as a template, RNA polymerase adds ribonucleotides to the RNA chain according to the rules of complementary base pairing.
Define translation
The process of protein synthesis that occurs at the ribosome; the information in an mRNA is used to specify the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
What is MRNA?
A type of RNA that acts as an intermediary in transferring the genetic information from DNA during protein synthesis; mRNA is translated at the ribosome to specify the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
What is mRNA composed of?
Ribonucleic Acid
What is ribonucleic acid?
A long polymer molecule composed of nucleotides. It is similar to DNA, except that it is mainly single-stranded rather than double-stranded and the individual RNA nucleotides contain ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose sugar, and uracil instead of thymine. Ribonucleic acid is also known as RNA.
Define metabolism
The sum of the chemical reactions that take place within each cell of a living organism and that provide energy for vital processes and for synthesizing new organic material.