Transportation Lesson 1
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Transportation Engineering
It is the application of technology and scientific principles to the planning, functional design, operation and management of facilities for any mode of transportation.
Transportation Engineering is an application of technology and scientific principles that provides
➢ Safe
➢ Efficient
➢ Rapid
➢ Comfortable
➢ Convenient
➢ Economical
➢ Environmentally compatible movement of people and goods
Transportation Engineering
It is a branch of civil engineering profession that is involved in the planning, design, operation, and maintenance of safe and efficient transportation system.
Port and Harbor Engineering
It is the design, construction, and operation of ports, harbor, canal, and other maritime facilities
Airport Engineering
It is the design and construct of airports
Roadway/Highway
_______ are the means of transportation on land.
Roadway/Highway
It consists the modern highways as well as city streets, feeder roads and village roads, catering for a big range of vehicles and the pedestrians
Roadway/Highway
is the only mode which is giving maximum service to one and all.
Railway
The steel tracks laid on the ground, over which the trains move is known as __________.
Airways
In the ______, air crafts and helicopters are used
Airways/Air System of Transportation
This system is more costly compared to all other modes of transportation.
Waterways
It is the slowest among the four modes
Transportation Planning
It is the preparation of transportation systems such as highways and traffic facilities.
Roadway/Highway
This is the only mode which is giving maximum service to one and all. It is possible to provide door to door service only by road transport.
Transportation Planning
It is necessary for a civil engineering company to ensure that these hazards and conditions are routinely fixed and are made up to standard in order to guarantee the safety of those on the road.
Railways
Have been used for long as well as for short distances and also for urban travels.
Airway/Air system of transportation
One of the fastest transportation system
Waterways
Human beings and materials are used to transport from one place to another with the help of ships and boats etc.
Waterways
Transportation by this system is possible between the ports on the sea routes or along the rivers or canals where inland transportation facilities are available.
Transportation Planning
It is the first move before things are decided and needed to be done to ensure things are on the right path along the way to succeed.
Identifying multiple options, problem, and solutions to a transportation system.
Optimization of existing transportation system and structural design.
To guarantee the safety and delivery of person, goods, and services.
To address current and future transportation, land use, economic development, traffic demand, public safety, health, & social needs.
Purpose of Planning
Traffic congestion reductions
Parking cost savings
Consumer savings and affordability (savings to lower-income households)
Improved mobility for non-drivers
Improved safety
Energy conservation
Air, noise and water pollution reductions
Habitat protection
Support for local economic development
Improved public fitness and health (from increased walking and cycling)
Objectives of Planning
Transportation survey, data collection, and analysis
Use of transportation model
Future land use forecasts and alternative policy strategies
Policy evaluation.
4 Main stages of Transportation Planning
Survey and Data Collection
This includes all the different types of available data gathered for transportation such as journey behavior patterns, nature and intensity of traffic, freight structure, costs and benefits like income and employment estimates, etc.
The comprehensive knowledge of traffic flows and patterns within the area is essential.
Aside from traffic data, planners also require the land use and population data for study area.
Travel patterns should be divided into zones so that origins and destinations are can be geographically monitored
▪ Day and date of journey
▪ Vehicle type and occupancy
▪ Origin and destination journey
▪ Origin starting time
▪ Goods carried and their weight(commercial vehicle)
Types of Road-side Interview
▪ Day and date of journey
▪ Origin address and time
▪ Destination address and time
▪ Journey purpose
▪ Mode of travel
▪ Ticket or parking cost
Types of Home-interview
Transportation Model
is a process of data analysis where it is a key to predict future travel demands and network needs, and is derived in four recognized stages such as: TRIP GENERATION, TRIP DISTRIBUTION, MOBILE SPLIT, TRAFFIC ASSIGNMENT
TRIP GENERATION
number of trips within a zone
TRIP DISTRIBUTION
number of trips from one zone to another
MOBILE SPLIT
number of trips in different modes of transport
TRAFFIC ASSIGNMENT
estimates the volume of traffic of every route in network
Future Land Use
It is ideally based on existing and future land developments. This essential on transportation planning since travel demands are variable to the type of area, population, commercial demands, etc., especially for urban planning development. Trips are made due to necessities of an individual according to his purpose. Planning is made in long term either 10 to 30 years prediction.
Travel Demand Forecast
It is necessary to predict the volumes of traffic in every network as the population grows and provide solutions or policy to manage the traffic when congestion is inevitable in the future.
▪ Population – its size, age structure and distribution
▪ Employment – as the journey to work is the
greatest travel demand
▪ Personal income and expenditure
Most Important Variables in Forecasting (Transportation Planning)
Transportation Safety
It is a required factor in the planning process and transportation planners are key partners ensuring that safety is an integral component of all planning processes. With knowledge and understanding of safety and safety planning, transportation planners can enhance collaboration, communication, and coordination with their safety specialist partners to achieve the goal of reducing serious injuries and fatalities.
Engineering
Enforcement
Emergency Medical Services
Education
4E’s of Safety
Education
Highway users are not always aware of the risks associated with their behaviors so proper knowledge and education of the use of highway and safety along the way is highly recommended for all.
Engineering
Engineers play a critical role in identifying and recommending solutions to address safety performance of the transportation infrastructure.
Enforcement
Law enforcement personnel generally are responsible for collecting crash data, traffic law enforcement, behavioral safety campaigns, and sharing information with transportation professionals.
Emergency Medical Services
This group includes first responders and paramedics, fire and rescue personnel, law enforcement, Department of Transportation(DOT) personnel, and tow truck operators.
Policy and Evaluation
It is one of evaluating the alternative policies, which have been suggested. The evaluation stage is probably the most important of all since here lies the economic impacts of the said planning.
Economic evaluation of transport proposals
Necessary because vehicle-km and road space are commodities, which are not directly bought and sold.
Estimates
On the cost side of the calculation, _______ are made for capital outlay, land purchase and maintenance.
Transportation Engineering
The phase of transportation engineering that deals with the planning, geometric design and traffic operations of roads, streets, and highways, their networks, terminals, abutting lands and relationship with other modes of transportation
1. Traffic Studies and Characteristics
2. Performance Evaluation
3. Facility Design
4. Traffic Control
5. Traffic Operations
6. Transportation System Management
7. Intelligent Transportation Systems
ELEMENTS OF TRAFFIC ENGINEERING
70s - Capital Investment
80s - TSM, TDM
90s - Intelligent Control Capital Investment
00s - Communication & Information
General History of Traffic Engineering
Transportation Engineering Diagram
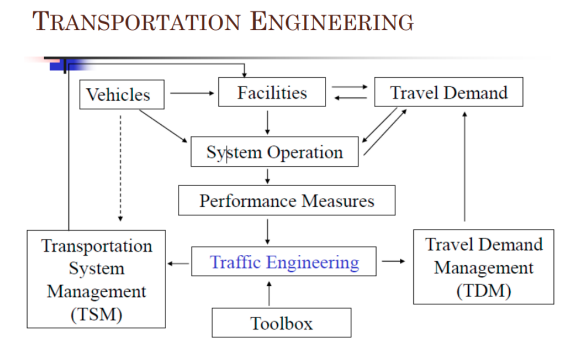
1. Drivers
2. Vehicles
3. Roadway
Basic Elements of the characteristics of Traffic Flow on the Highway System
1. Perception
2. Identification Emotion
3. Reaction or volition
Distinct Actions encountered by the driver of a vehicle during reaction to cues and stimuli:
Comprehensive planning process
It is the traditional transportation planning process.
Transportation planning process
it is an ongoing process which seeks to assess the short and long range transportation problems of a region and to develop, evaluate, select and implement plans and strategies for solving these problems. This is based on the interaction between two basic systems, the transportation system (origins, destinations, volume of people and goods) and the activity system (land uses, population, social and economic activities) within which transportation system operates.
Travel demand modeling
it describes the relationships between trip-making and the regions pattern of population, land use and economic activities which creates that demand.
1. Trip generation
2. Trip distribution
3. Mode choice
4. Traffic assignment
4 Basic Phases of the Traditional Approach to Travel Demand Modeling:
Traffic assignment
is the allocation of traffic flows among routes available.
Traffic volume
the number of vehicles that pass a point on a highway during a specified time interval.
Perception and reaction time
the period of time from when the driver recognizes an object or a hazard on the roadway to the time the driver actually applies the brakes.
Detection and recognition time
the amount of time required for a driver to detect and recognize that an object or hazard is being approached.
Decision and response initiation time
the amount of time for the driver to decide on the proper maneuver to be taken and to initiate the required action.
Maneuver time
the time required to accomplish a vehicle maneuver
Sight distance
the distance at which a driver can see an object lying in the roadway ahead. It should equal or exceed the stopping sight distance.
Decision sight distance
distance required for a driver to detect an unexpected object, information source (traffic signal) or hazard in the roadway and to recognize the hazard, select an appropriate speed and path, and initiate and complete the required safety maneuver.
Breaking sight distance
the distance needed to bring the vehicles to complete stop after the brake have been applied.
Passing sight distance
the shortest distance sufficient for a vehicle to turn out of a traffic lane, pass another vehicle, and then turn back to the same lane safely and comfortably without interfering with the overtaken vehicle or an incoming vehicle traveling at the design speed should it come into view after the passing maneuver is started.
Stopping sight distance
the sum of the braking distance and the perception and reaction distance.
Non-passing sight distance
the length between vehicles as it enters a crest curve (vertical parabolic) and the farthest distance visible to the driver to the top of the object. It is typically assumed that the height of eye is at 3.75 feet above the roadway surface and the farthest distance visible is at an elevation of 6 inches above the roadway.
1.Assess Existing Conditions
2.Evaluate Alternative Improvements
3.Quantify Associate Costs and Benefits
PERFORMANCE MEASURE (Purpose)
Reducing Demand
•Telecommuting
• Trip Chaining
•Shorter Work Week
•Residential Relocation
•Alternative Land Use Pattern (Company Town?)
Shifting Demand
•Flexible Working Hours
•Staggered Working Hours
•Business Operating Hours
Repacking Demand
•Car Pooling and Van Pooling
•Transit
TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT (TDM)
Facility Design
•Add Lanes
•Remove Bottlenecks (Bridges, Tunnel,...)
•Revise Geometrics to Increase Speed •Vehicle Improvement to Reduce Headways
Traffic Control
•Ramp metering
•Signal Coordination
•Signal Phase
Sequence
•Left Turn Treatments
•Parking Restrictions
TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM MANAGEMENT (TSM)
Intelligent Transportation System (ITS)
Collect, store, process and distribute information relating to the movement of people and goods. Examples include systems for traffic management, public transportation management, emergency management, traveler information, advanced vehicle control and safety, commercial vehicle operations, electronic payment and railroad grade crossing safety.”
ITS
involves the application of advanced technology to enhance safety, provide services to travelers, and assist transportation system operators in implementing suitable traffic management strategies.
Transportation Management
•Traffic Operations Centers
•Communications
•Incident Management
•Public Transportation
•Traveler Information
•Enhanced Safety
ITS SOLUTIONS INCLUDE
Regulatory or Mandatory signs
Warning or Cautionary signs
Informatory and Guiding signs
ROAD AND TRAFFIC SIGNS
REGULATORY OR MANDATORY SIGNS
These are traffic signs which are used to inform road users on certain rules and regulations which have to be observed for safe and free flow of traffic.
Warning or Cautionary signs
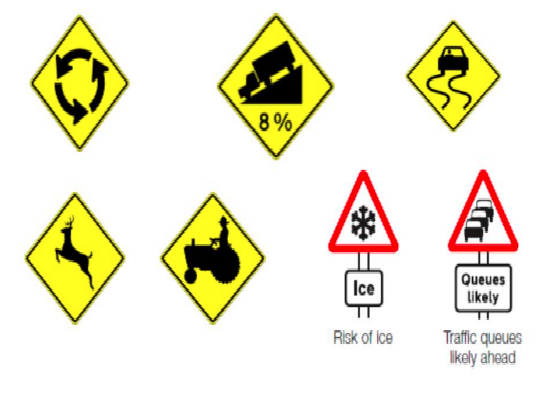
Informatory and Guiding signs

Orange
used as a background color for construction and maintenance signs
Red
used as background color for stop, do not enter, and wrong way signs, as a legend color for parking prohibitions signs, route markers, the circular outline, ant the diagonal bar for prohibitory symbols.
Yellow
Background color for school signs and warning signs (except when orange is specified)
Green
Background color for milepost and guide signs (other than those using brown or white) and as a legend color on white background for certain directional signs and permissible parking regulations
Blue
Background color for information signs related to motorists services, rest areas, and evacuation route markers.
Brown
Background color for guide and information signs related to points of recreational, service or cultural interest.
Black
Background color for certain one way and weigh station signs, as well as for specific night speed limit signs, and as the legend color for white, yellow, and orange signs
White
Background Color for route markers, guide signs, and regulatory sings except for the stop sign, for the legend on the brown, green, blue, black, and red signs
Fixed Time Signals
Type of road signals which are set to repeat a cycle at regular time intervals. These signals are design for peak time traffic requirements. However, they cause delay during off-peak hours
Traffic Actuated Signals
Type of road signals which are designed so that the phase and cycle can be changed acording to traffic demand. A policeman observes these signals suitably. These signals are very expensive.
Flashing Signals
Type of road signals which are installed on main roads and cross roads. A red signal is to be provided on the cross road to warn the driver to stop and proceed. A yellow signal installed on the main road warns the driver to slow down.