Mushroom Toxins
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
true or false. it is easy to safely identify edible mushrooms
false
the stipe of the mushroom is also known as what?
stalk
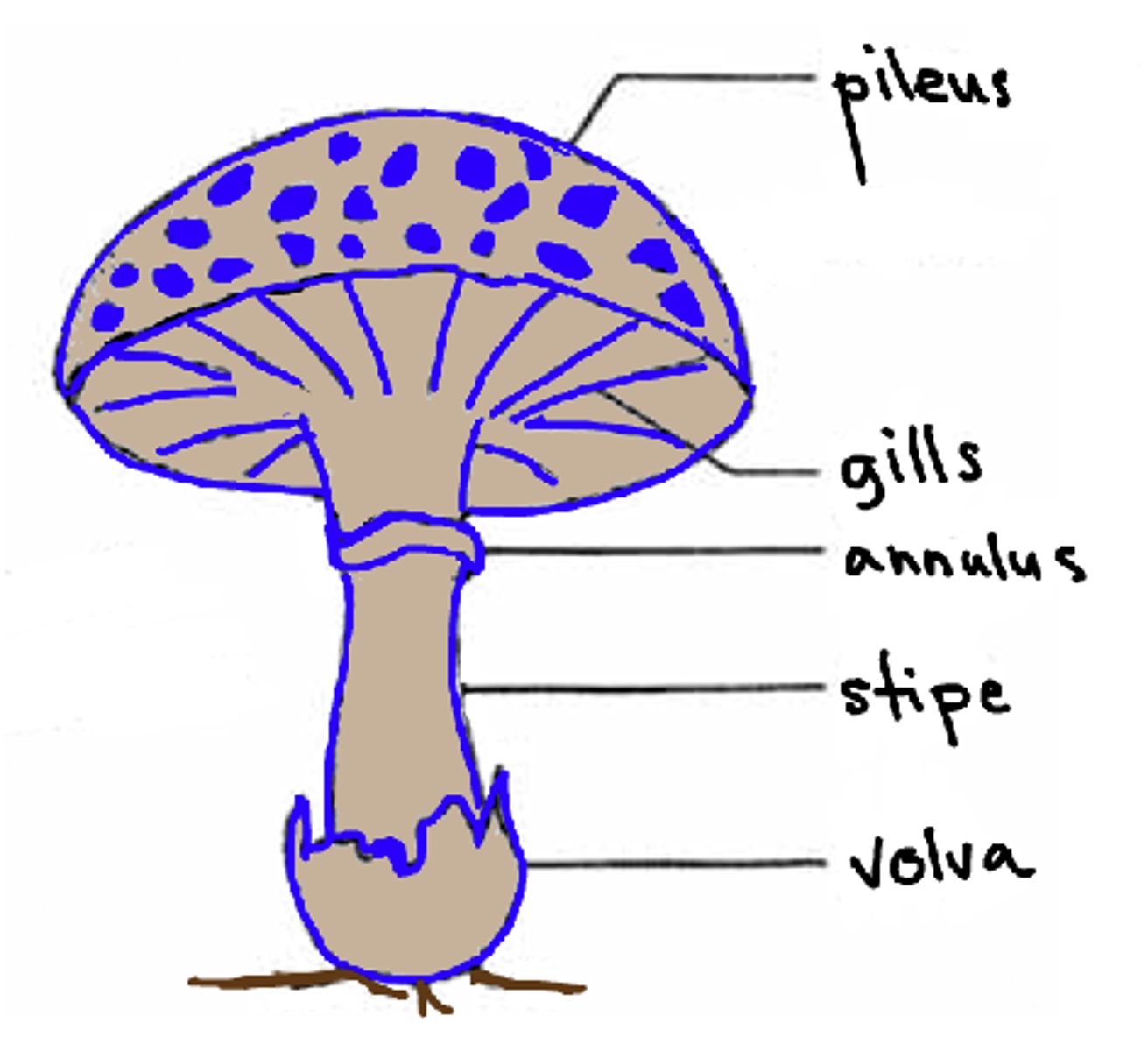
the pileus of the mushroom is also known as what
cap
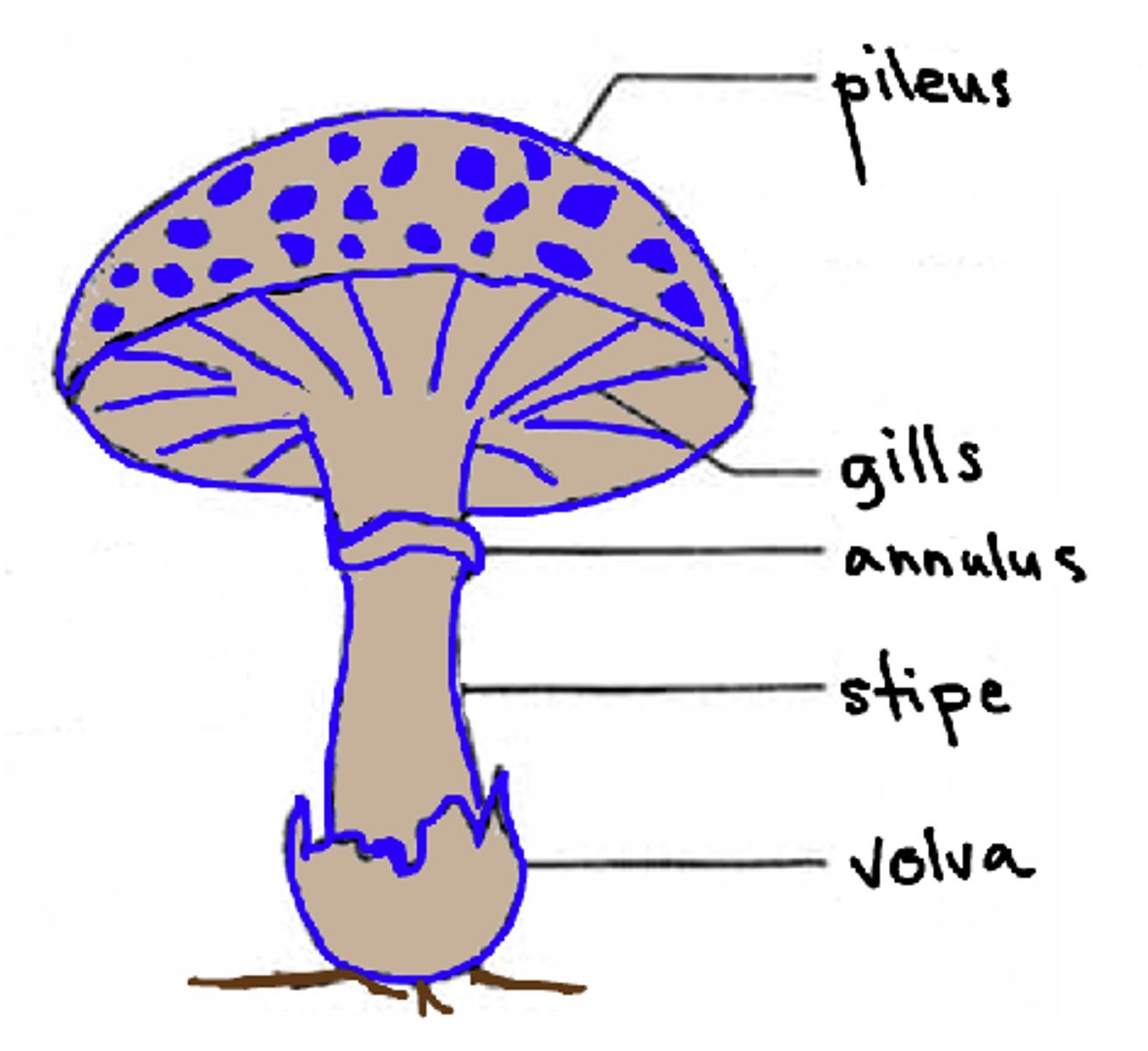
the lamellae of the mushroom is also known as what?
gills
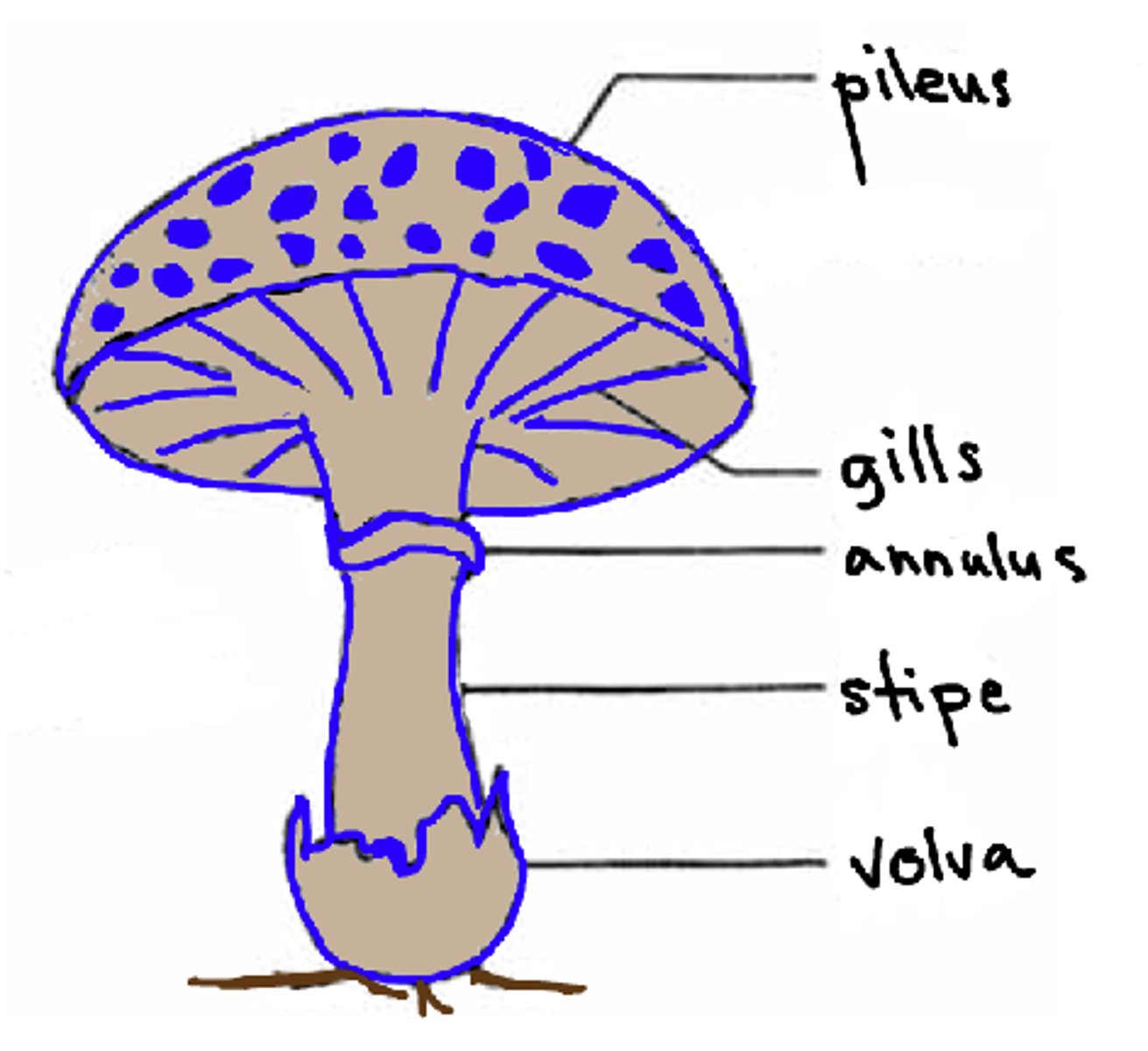
the annulus of the mushroom is also known as what?
ring
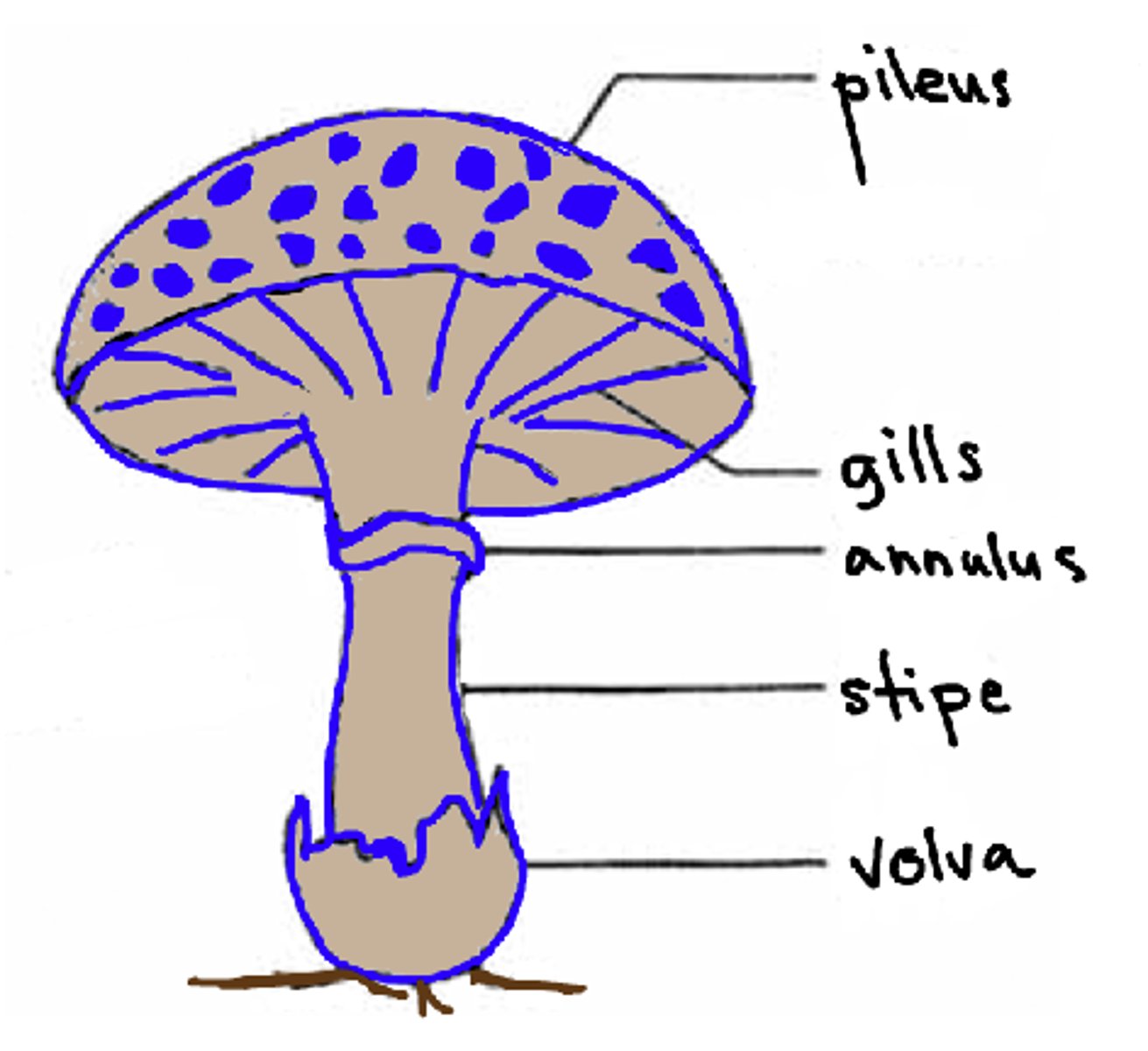
the volva of the mushroom is also known as what?
cup
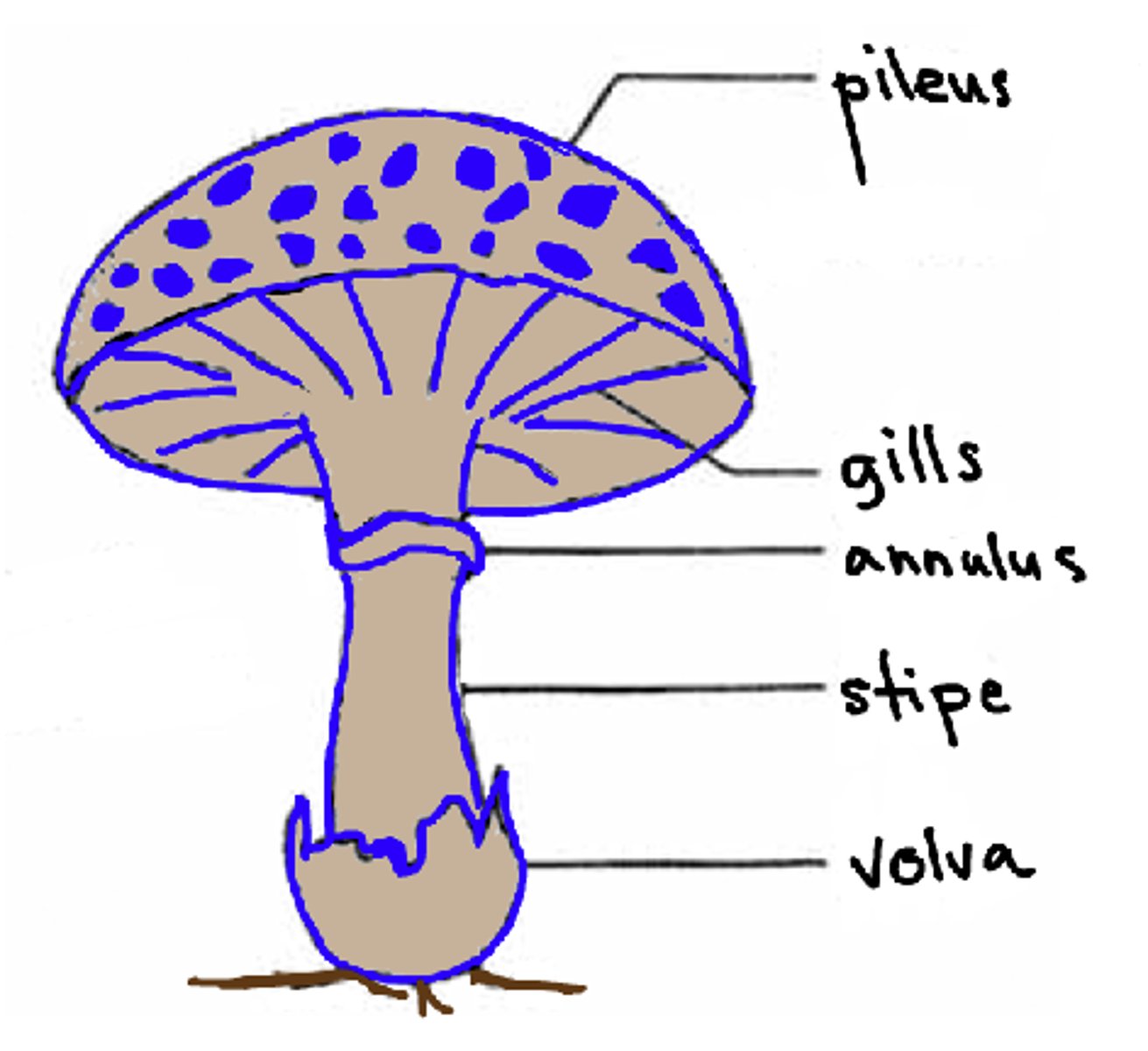
what are the scales on a mushroom?
remnants of the universal veil
what part of the mushroom contains spores?
gills
what is the name of a mushroom at the beginning of development?
button

what is confused with the button phase of mushrooms and are accidentally eaten?
puff balls
what technique is most commonly used to identify mushrooms? what does it tell us?
spore prints; spore color
apart from spore color, what are other identification features of mushrooms?
type of hymenium, features of gill trama, features of cystidia
what is the hymenium?
spore containing tissue found on the underside of mushroom cap
what is are gill trama?
spongy tissue within the gills
what are cystidia?
non-spore producing cells found on the surface of mushrooms
which types of mushroom toxins affect the autonomic nervous system?
coprine and muscarine
how quick is the onset of symptoms in coprine and muscarine toxins?
2 minutes-2 hours
what is the mechanism of action of muscarine?
agonist to muscarinic receptors
what mushroom genus produces coprine?
coprinus
what toxin does clitocybe clavipes produce?
coprine
which mushrooms are known as "inky cap" mushrooms? why are they given this name?
coprinus; as tissue at the end of the cap degrades, an ink-like substance is released allowing spores to be dispersed
what is the mechanism of action of coprine?
inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase
why is it dangerous to combine alcohol with coprine?
coprine prevents the metabolism of alchohol causing an alcohol flush reaction
what symptoms are caused by coprine + alcohol exposure (coprinus syndrome)?
facial flushing, headache, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia
true or false. coprine is heat stable so it can't be destroyed through cooking
true
the symptoms of coprinus syndrome are similar to what?
alcohol withdrawing drug, disulfiram
which mushroom genus produce muscarine?
clitocybe and inocybe
what was muscarine first isolated from?
Amanita muscaria
structure of muscarine
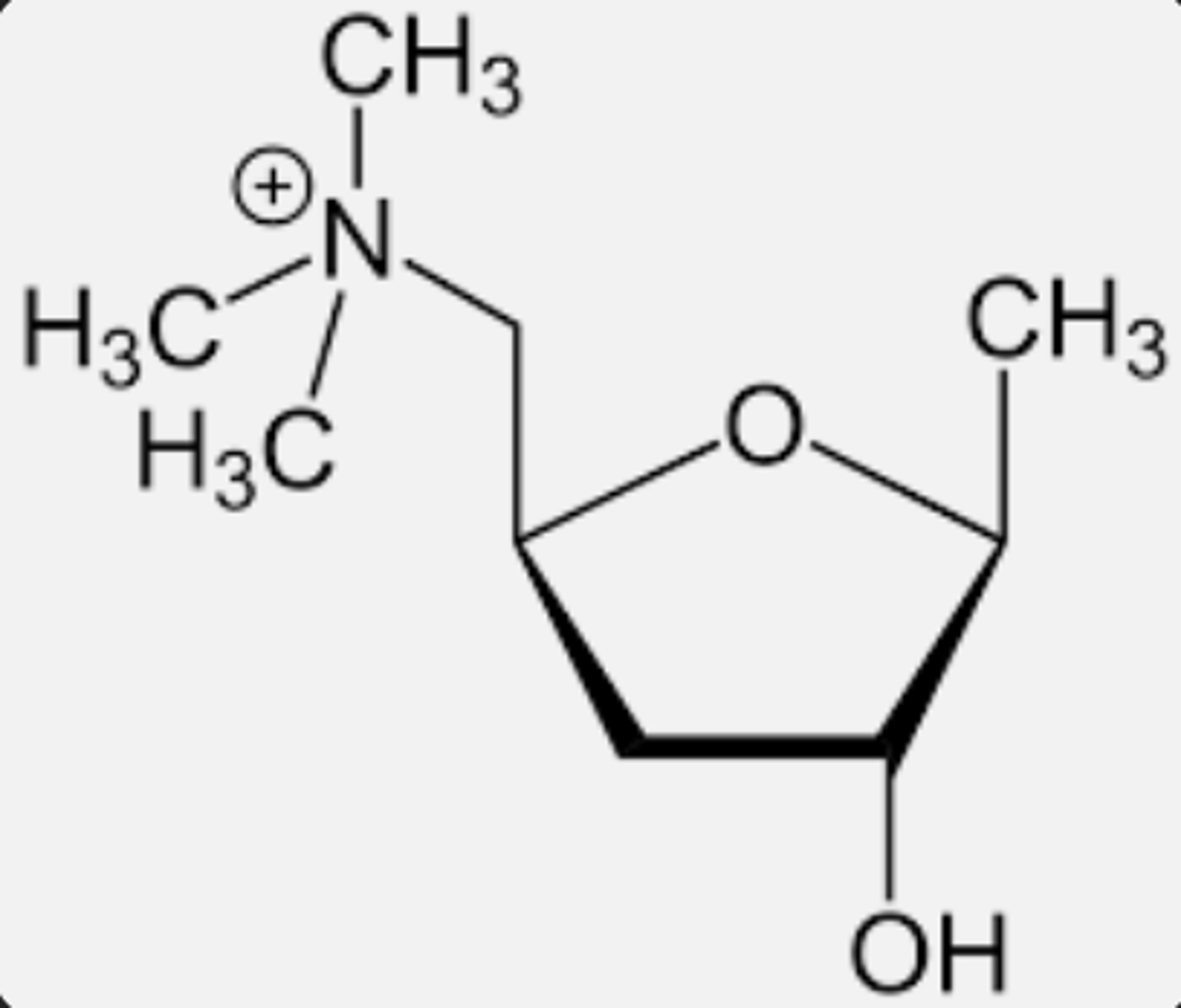
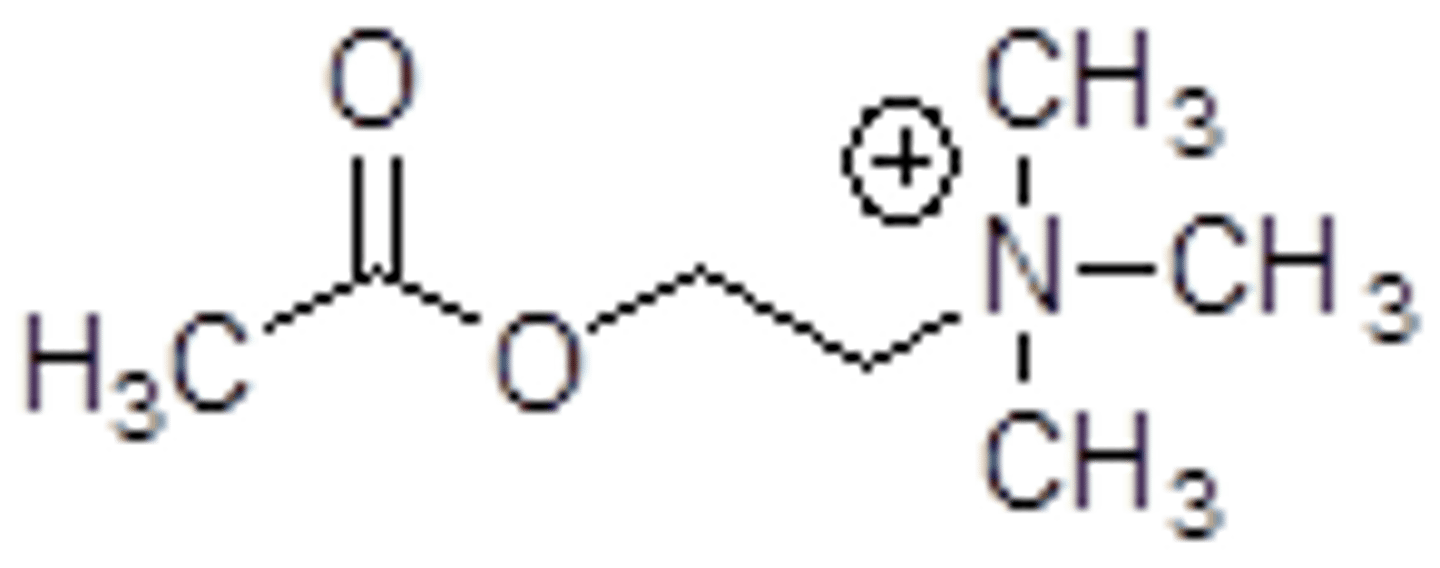
structure of acetylcholine
what part of the autonomic nervous system does muscarine effect?
peripheral parasympathetic nervous system
why is muscarine a good agonist of muscarinic receptors?
similar structure to acetylcholine
why is muscarine poorly absorbed by the GI tract?
it is a quarternary ammonium salt
true or false. muscarine does not cross the blood-brain barrier
true
true or false. muscarinic receptors in the brain are affected by muscarine
false
which toxins affect the central nervous system?
ibotenic acid and muscimol
how quick is the onset of symptoms of ibotenic acid and muscimol?
20 minutes-2 hours
what mushroom genus produces ibotenic acid and muscimol?
amanita, panaeolus, conocybem, gymnopilus
which mushroom is known to produce psychedelic effects?
amanita muscarina
mechanism of action of ibotenic acid
weak agonist of glutamate receptors
true or false. even a minimal dose of ibotenic acid is dangerous
false
what is the precursor to muscimol?
ibotenic acid
what is more dangerous ibotenic acid or muscimol?
muscimol
mechanism of action of muscimol?
agonist for GABAA receptors
what symptoms result from an exposure to muscimol?
sedative, hypnotic, depressant, and hallucinogenic psychoactivity
what color is ibotenic acid?
bright red
what color is muscimol?
colorless or white
apart from muscimol what other toxin is known to have psychoactive effects?
psilocin
what mushroom genus produces psilosybin?
conocybe, gymnopilus, panaeolus, psilocybe
what is the precursor to psilocin
psilocybin
structure of psilocybin and psilocin
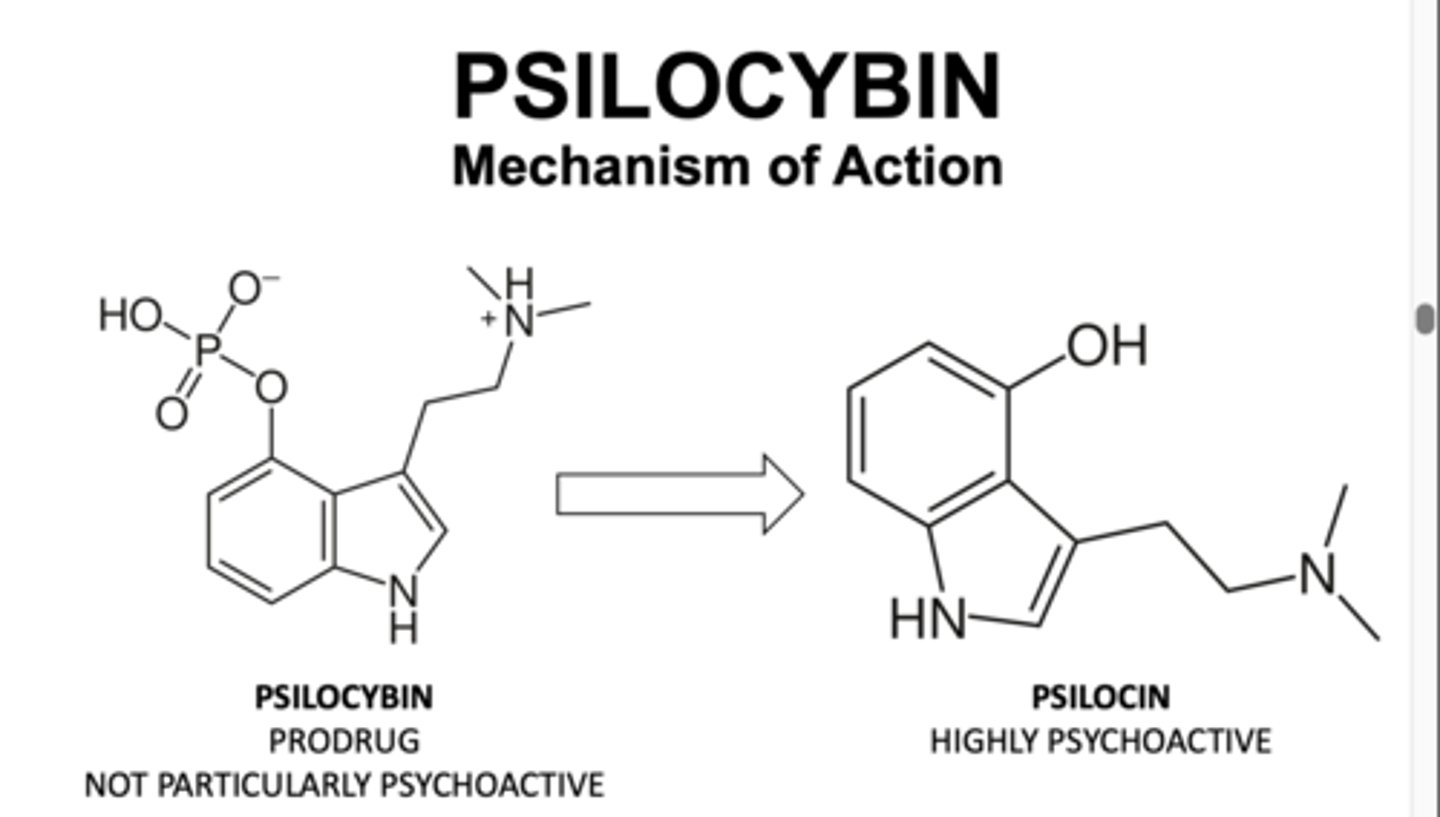
what is unique about psilocybin's structure that causes some of its effect
it has a similar structure to serotonin
what symptoms are a result of psilocin exposure?
euphoria, hallucinations, altered perception, distorted sense of time, spiritual experiences, nausea, panic attacks
which toxin produces similar effects to LSD, mescaline, and DMT?
psilocin
what has psilocybin been used to treat?
depression
which mushroom toxins can cause cellular destruction, liver and kidney damage, and death?
amanitins (cyclopeptides), gyromitrin, orellanine
how quick is the onset of symptoms for amanitins and gyromitrin?
6-10 hours
90% of deaths from mushrooms are caused by which mushroom toxin
amanitin
what mushroom genus produce amanitin?
amanita, galerina, lepiota, and conocybe
what is the mechanism of toxicity of amanitins?
it inhibits DNA transcription carried out my RNA polymerase II by inhibiting the production of mRNA which prevents the production of proteins necessary for cellular function
what mushroom genus produces gyromitrin?
gyromitra, helvella, sarcosphaera
gyromitrin gets converted into what?
monomethyl hydrazine
what led to the discovery of gyromitrin toxicity?
space travel
what does gyromitirin/monomethyl hydrazine (MMH) do in cells?
acts as a hemolytic, depletes vitamin B6, reduces GABA synthesis
how long might it take for symptoms to show in orellanine toxicity?
8 days
what mushroom genus produce orellanine?
cortinarius
what is the result of orellanine exposure?
kidney failure